Corrosion Activity of Carbon Steel B450C and Stainless Steel SS430 Exposed to Extract Solution of a Supersulfated Cement
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Steel Samples and Surface Characterization
2.2. Supersulfated Cement and Extract Solution
2.3. Immersion Test
2.4. Electrochemical Measurements
3. Results
3.1. Change in Time of pH of the SS1 Cement Extract Solution
3.2. Change in Time of the Open Circuit Potential (OCP)
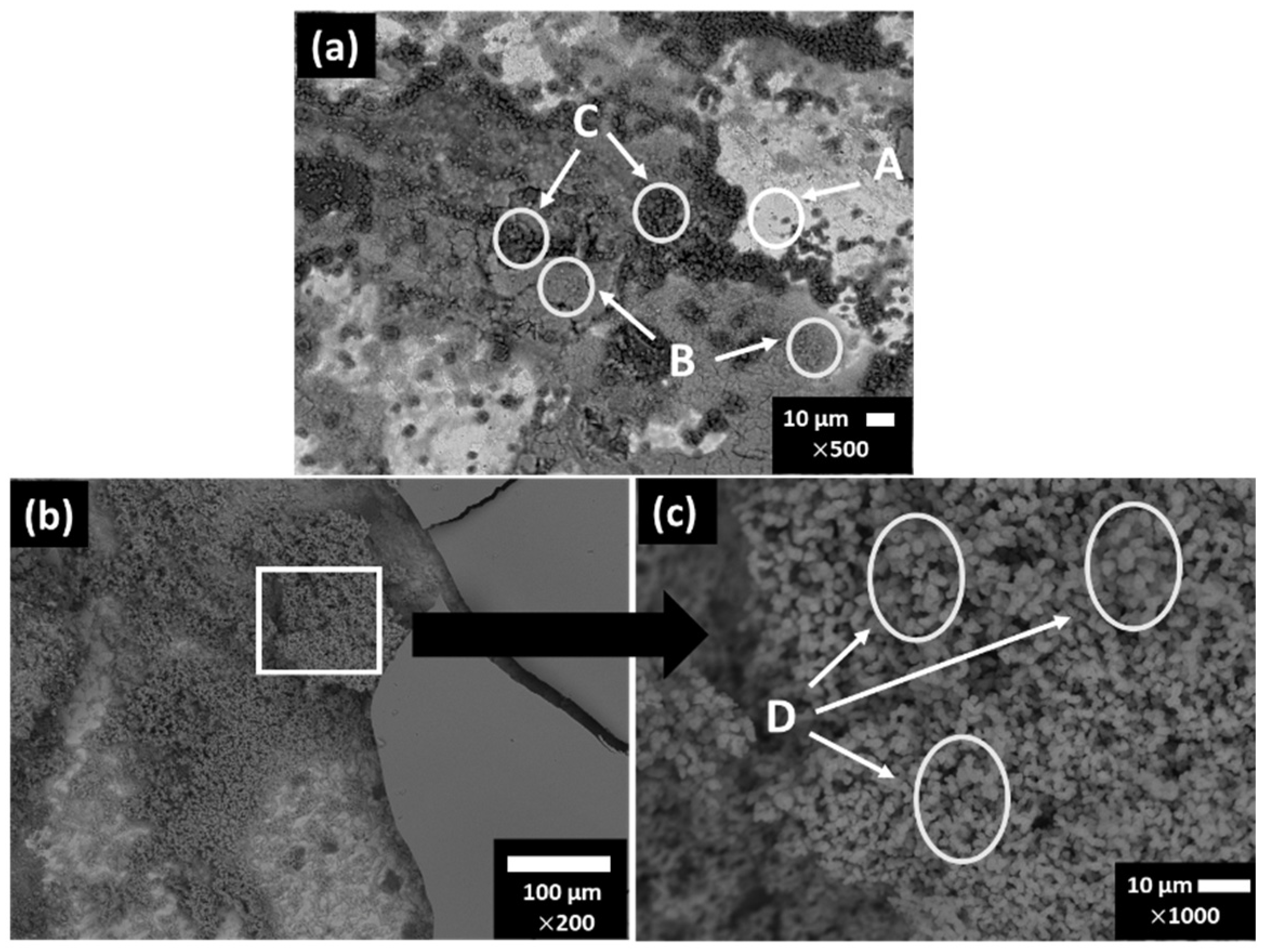
3.3. Carbon Steel B450C Surface Characterization after Exposure to SS1 Cement Extract Solution
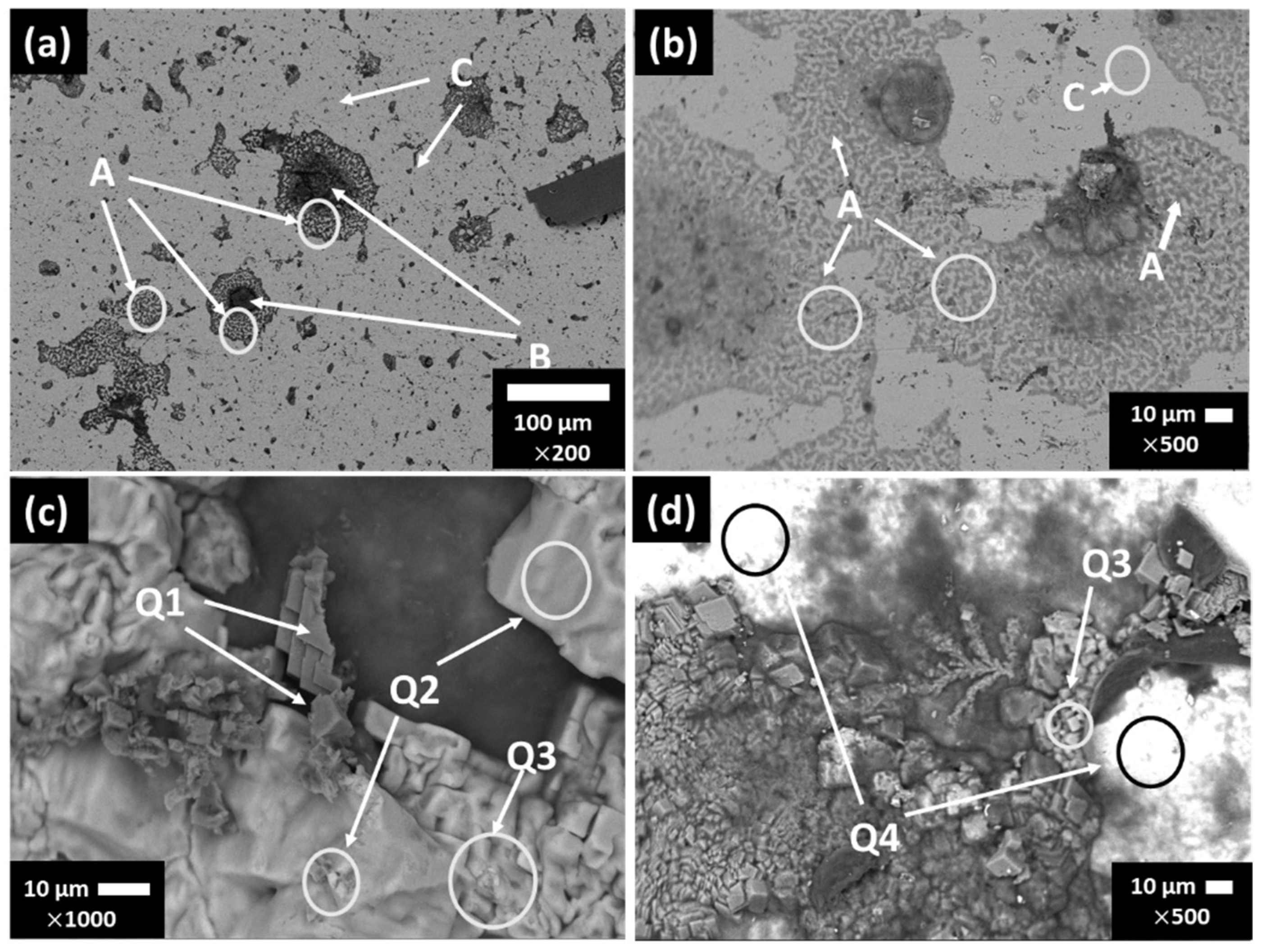
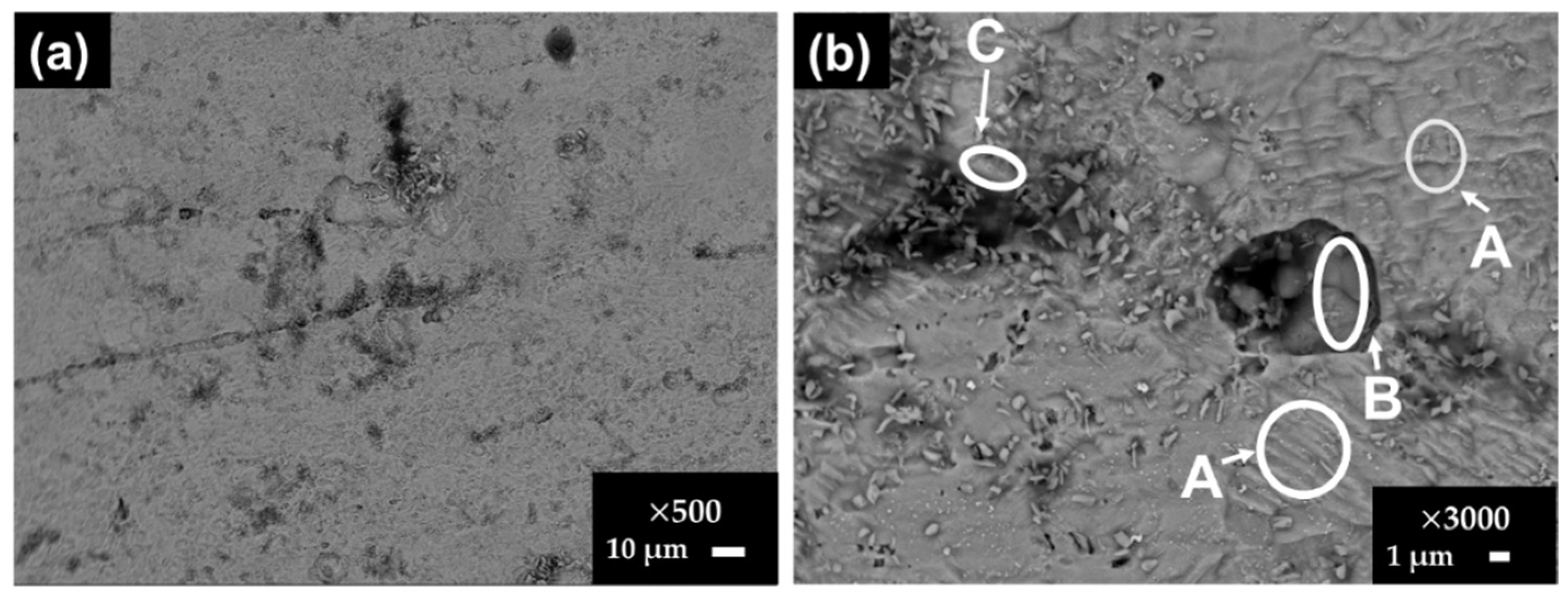
3.4. Stainless Steel SS430 Surface Characterization after Exposure to SS1 Cement Extract Solution
3.5. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Spectra
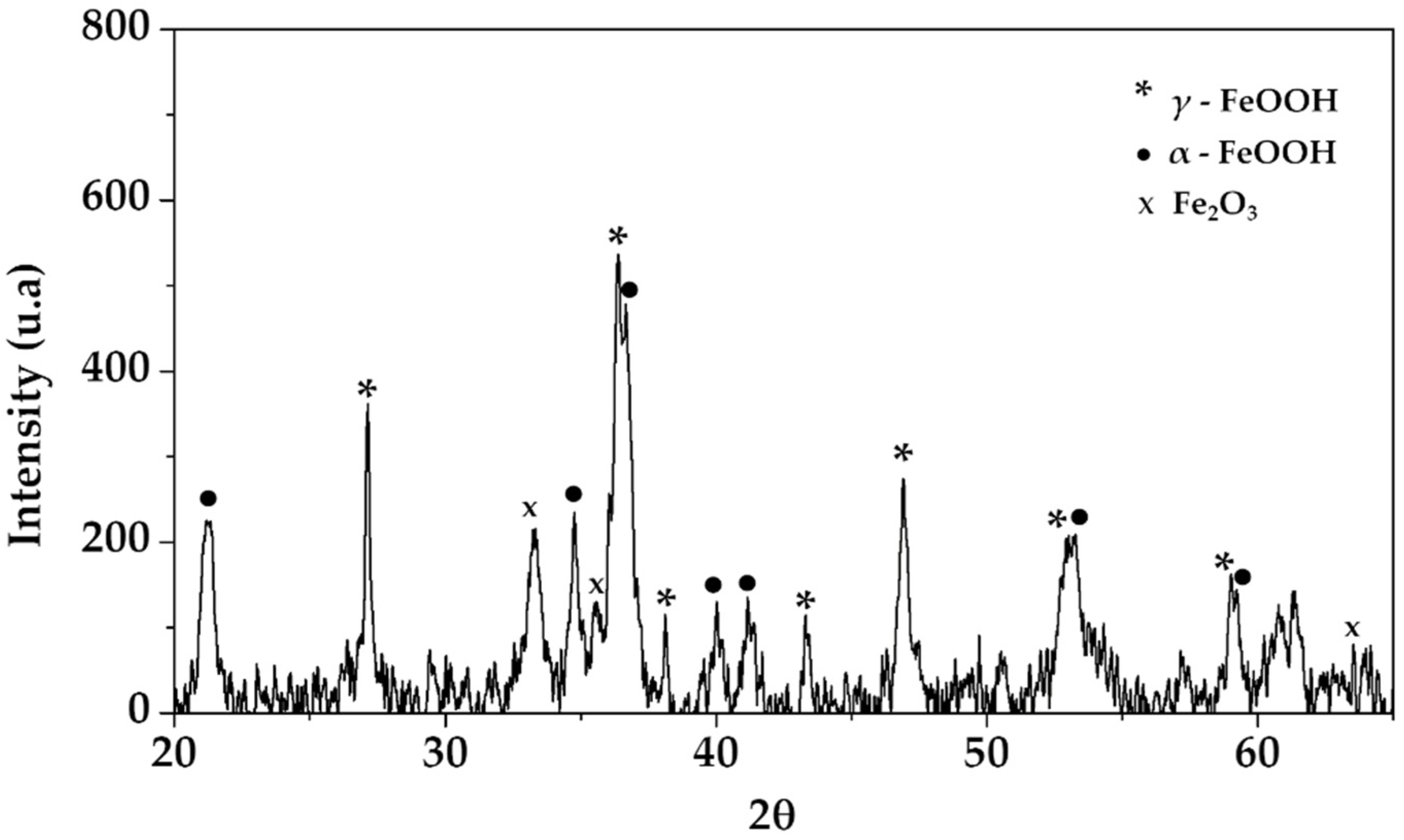
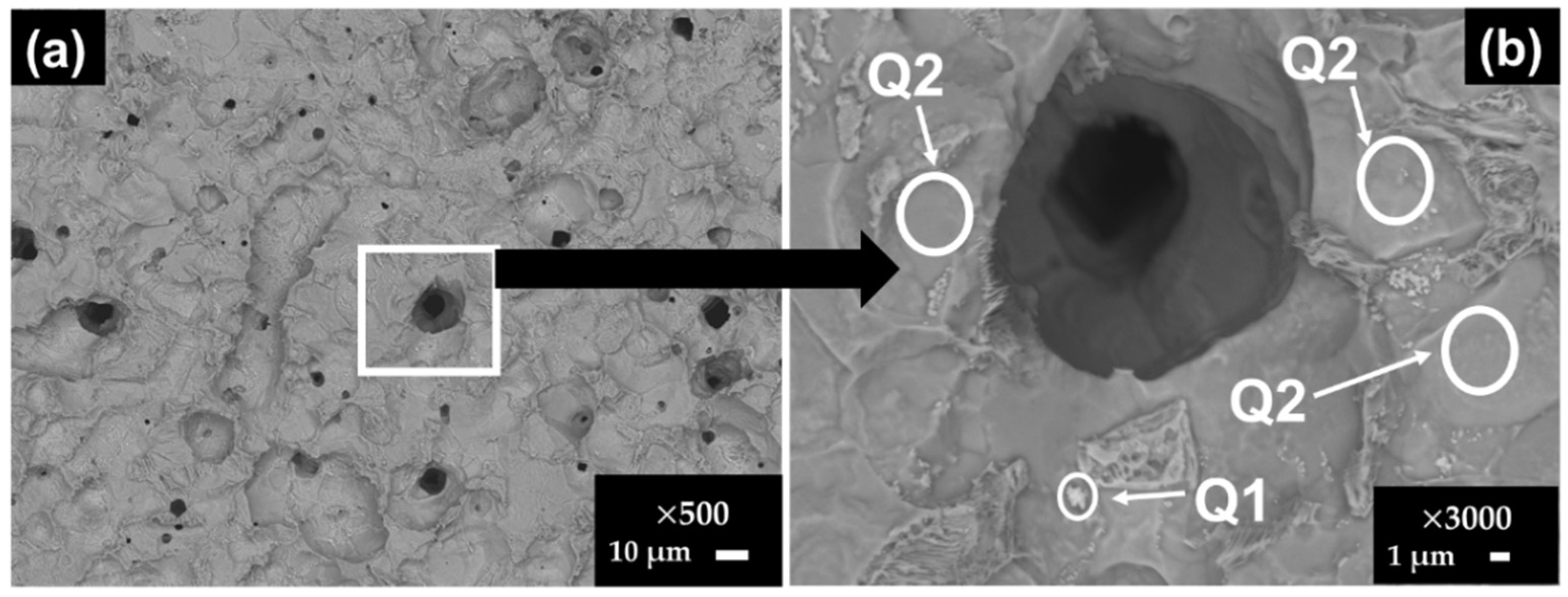
3.6. Steel Surface Damage after Exposure to SS1 Cement Extract Solution
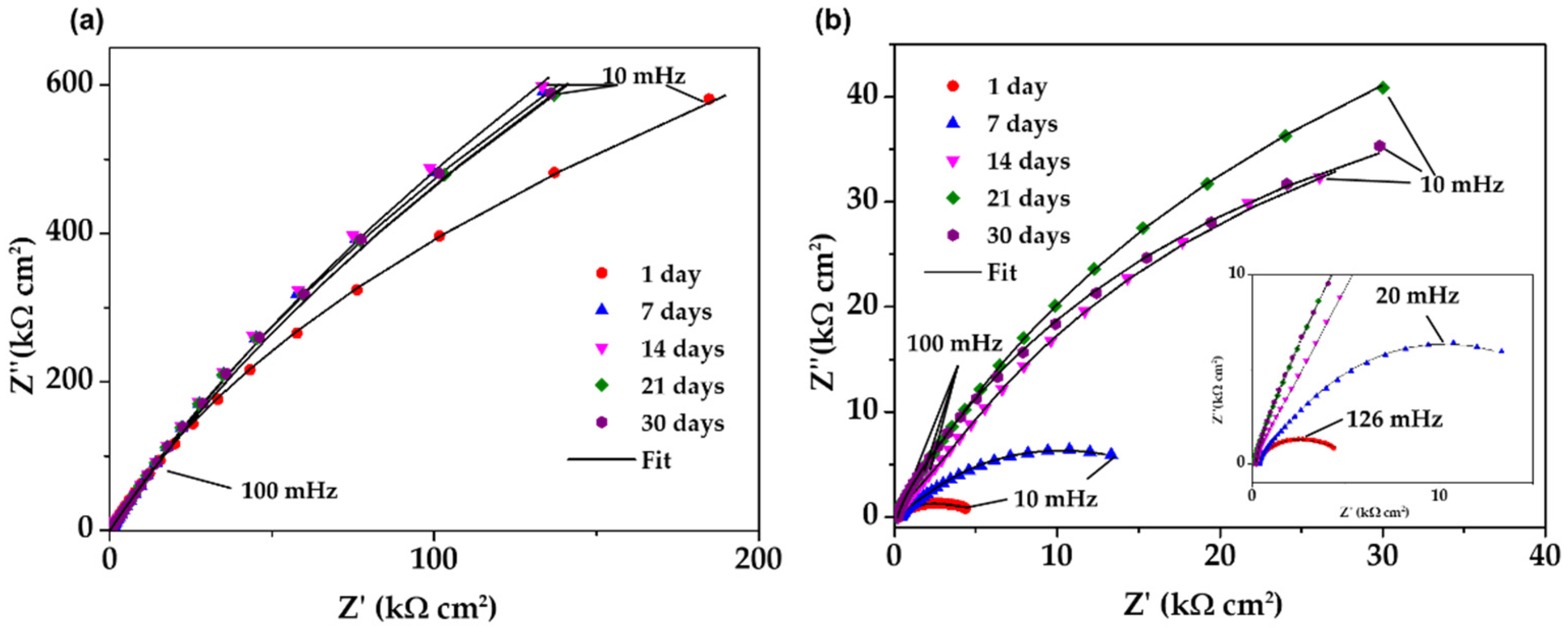
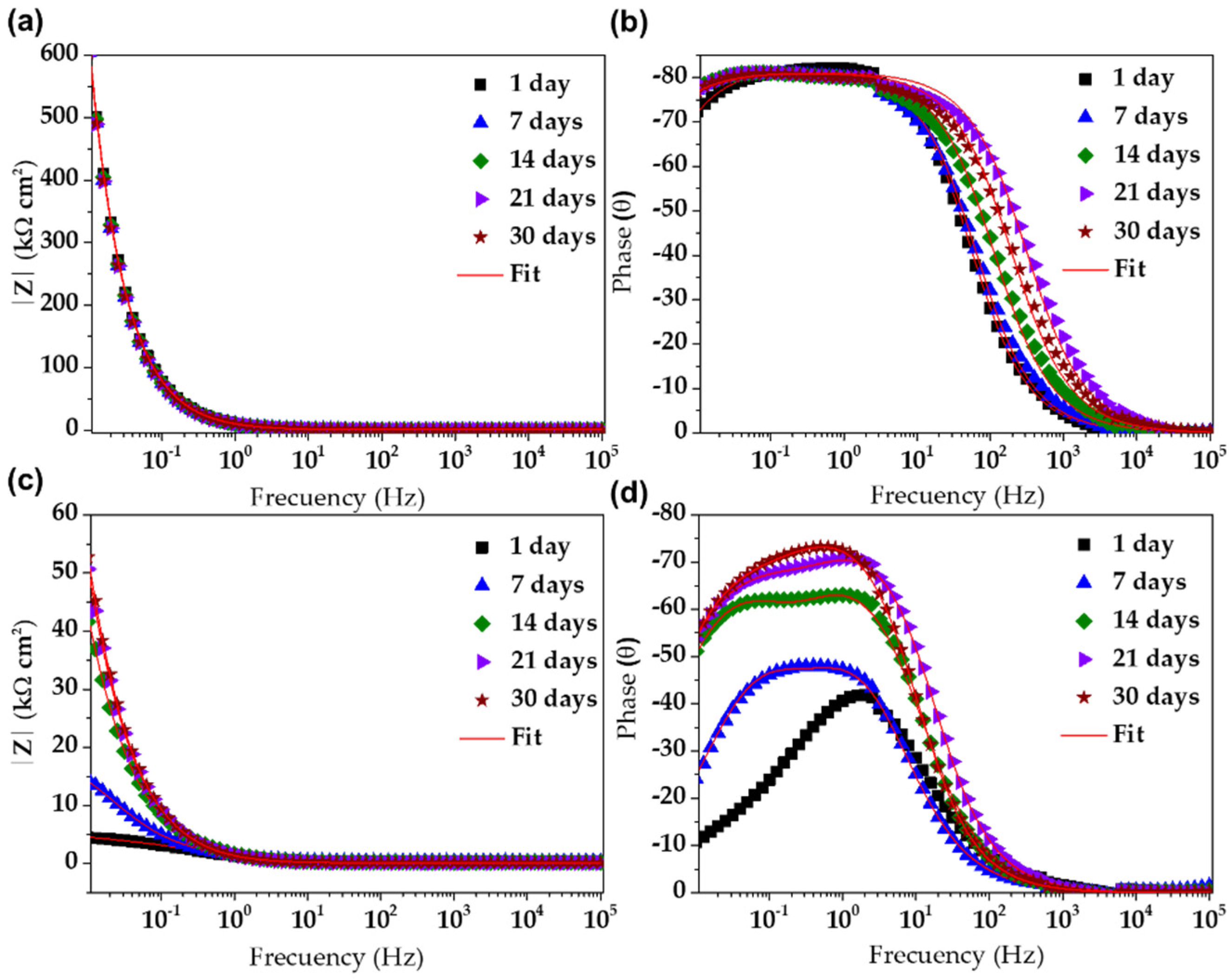
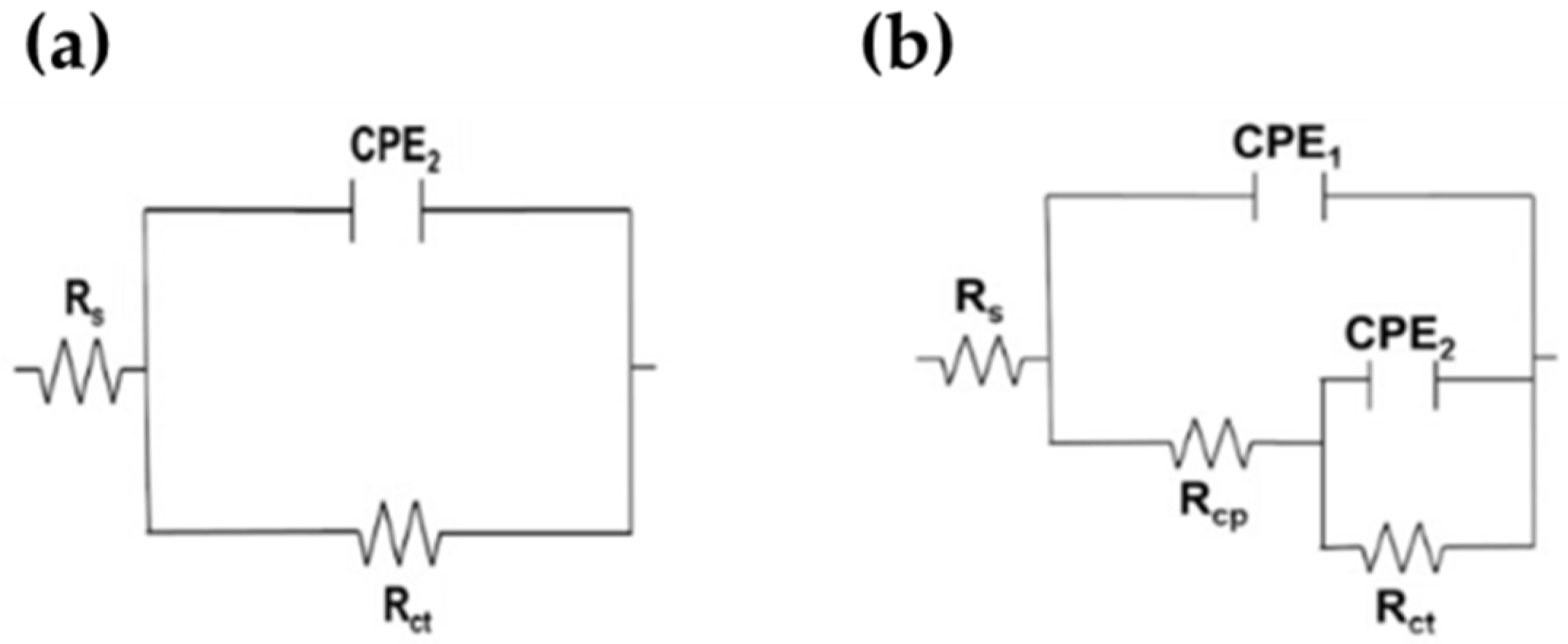
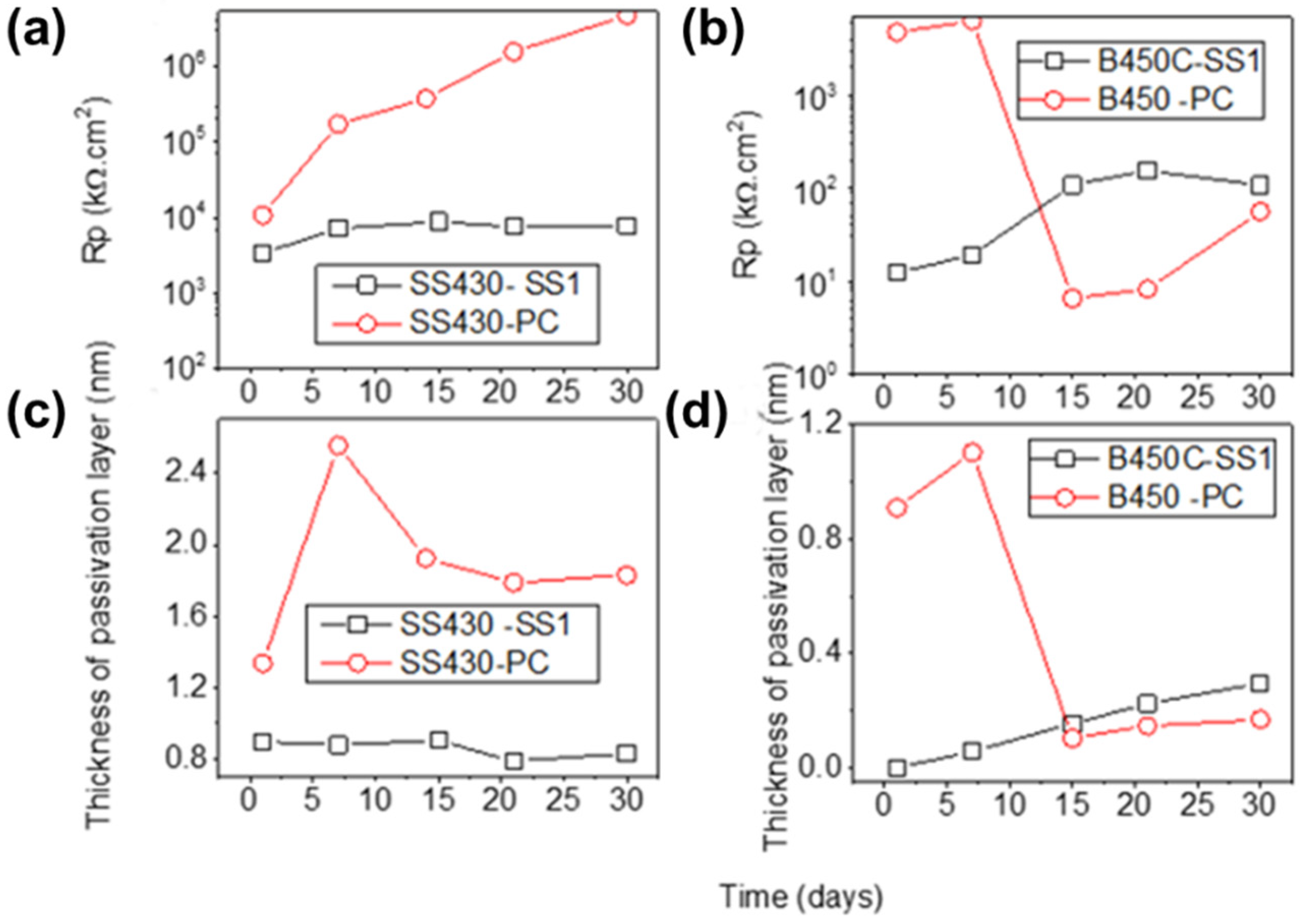
3.7. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pourbaix, M. Atlas of Electrochemical Equilibria in Aqueous Solutions, 2nd ed.; NACE: Houston, TX, USA, 1974; p. 561. [Google Scholar]
- Callaghan, B.G. The performance of a 12% chromium steel in concrete in severe marine environments. Corros. Sci. 1993, 35, 1535–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagayama, M.; Cohen, M. The anodic oxidation of iron in a neutral solution: II. Efect of ferrous ion and pH on the behavior of passive iron. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1963, 110, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, J.; Calvert, J.P. Closure to “Discussion of Ellipsometric-potentiostatic studies of iron passivity, I. anodic film growth in slightly basic solutions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1967, 114, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, P.; Veleva, L.; Balancan, M. Corrosion of reinforced concrete in a tropical marine environment and in accelerated test. Constr. Build. Mater. 1997, 11, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, M.P.; Toney, M.F.; Davenport, A.J.; Oblonsky., L.J. In situ X-ray-difraction studies of passive oxide films. MRS Bull. 1999, 24, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedriks, A.J. Corrosion of stainless steels. In Encyclopedia of Materials: Science and Technology, 2nd ed.; Jürgen, B., Flemings, M., Kramer, E., Veyssière, P., Cahn, R., Ilschner, B., Mahajna, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 1707–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, A.-M.; Mejía, R. Durability of reinforced concrete exposed to aggressive conditions. Mater. Construcc. 2013, 63, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freire, L.; Carmezim, M.J.; Ferreira, M.G.S.; Montemor, M.F. The passive behaviour of AISI 316 in alkaline media and the effect of pH: A combined electrochemical and analytical study. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 21, 6174–6181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, R.M. Global CO2 emissions from cement production. Earth Syst. Sci. Data. 2018, 10, 2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Juenger, M.; Snellings, R.; Bernal, S. Supplementary cementitious materials: New sources, characterization and performance insights. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 122, 257–273. [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi, H.J.; Ahmad, J.; Majdi, A.; Saleem, M.U.; Al Fuhaid, A.F.; Arifussaman, M. A Study on Sustainable Concrete with Partial Substitution of Cement with Red Mud: A Review. Materials 2022, 15, 7761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, T.; Yang, Q. Mechanical Properties and Damage Layer Thickness of Green Concrete under a Low-Temperature Environment. Materials 2022, 15, 7409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-H.; Jeong, S.T.; Bui, Q.T.; Yang, I.-H. Strength and Permeability Properties of Pervious Concrete Containing Coal Bottom Ash Aggregates. Materials 2022, 15, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulbul, A.M.; Khan, K.; Nafees, A.; Amin, M.N.; Ahmad, W.; Usman, M.; Nazara, S.; Abu Arab, A.M. In-Depth Analysis of Cement-Based Material Incorporating Metakaolin Using Individual and Ensemble Machine Learning Approaches. Materials 2022, 15, 7764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, H.F.W. Cement Chemistry, 2nd ed.; Thomas Telford Publishing, Ltd.: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Matschei, T.; Bellmann, E.; Stirk, J. Hydration behavior of sulphate-activated slag cements. Adv. Cem. Res. 2005, 17, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrotra, V.P.; Sai, A.S.R.; Kapur, P.C. Plaster of Paris activated supersulfated slag cement. Cement Concr. Res. 1982, 12, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menchaca-Ballinas, L.E.; Escalante-Garcia, J.I. Low CO2 emission cements of waste glass activated by CaO and NaOH. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 239, 117992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aygun, Z.; Aygun, M. Spectroscopic analysis of Ahlat stone (ignimbrite) and pumice formed by volcanic activity. Spectrochim. Acta Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2016, 166, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Luna, K.; Maldonado-Bandala, E.E.; Nieves-Mendoza, D.; Castro-Borges, P.; Escalante García, J.I. Supersulfated cements based on pumice with quicklime, anhydrite, and hemihydrate; characterization and environmental impact. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 124, 104236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, K.M.A. Blended cement using volcanic ash and pumice. Cem. Concr. Res. 2003, 33, 1601–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahverdi, A.; Abolhasani, S. Binary mixture of natural pozzolana/gypsum activated with Portland cement clinker and chemical activators. Cem. Wapno Bet. 2011, 16, 139–147. [Google Scholar]
- Yasar, E.; Atis, C.D.; Kilic, A.; Gulsen, H. Strength properties of lightweight concrete made with basaltic pumice and fly ash. Mater. Lett. 2003, 57, 2267–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, D.; Pasamehmetoglu, A.G. The effects of gradation and admixture on the pumice lightweight concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahverdi, A.; Mehrpour, K.; Najafi Kani, E. Investigation the possibility of utilizing pumice-type natural pozzonal in production of geopolymer cement. Ceram. Silikaty. 2008, 52, 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Midgley, H.G.; Pettifer, K. The micro structure of hydrated super sulphated cement. Cement Concr. Res. 1971, 1, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grounds, T.; Nowell, D.V.; Wilburn, F.W. Resistance of supersulfated cement to strong sulfate solutions. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2003, 72, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Luna, K.; Maldonado-Bandala, E.E.; Nieves-Mendoza, D.; Castro-Borges, P.; Escalante García., J.I. Novel low emissions supersulfated cements of pumice in concrete; mechanical and electrochemical characterization. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 272, 122520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, C.L.; Treadaway, K.W.J. Aspects of the electrochemistry of steel in concrete. Nature 1982, 297, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poursaee, A. Corrosion of steel bars in saturated Ca(OH)2 and concrete pore solution. Concr. Res. Lett. 2010, 1, 90–97. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Sagüés, A.A. Chloride corrosion threshold of reinforcing steel in alkaline solutions-open circuit immersion tests. Corrosion 2001, 57, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oranowska, H.; Szklarska-Smialowska, Z. An electrochemical and ellipsometric investigation of surface films grown on iron in saturad calcium hydroxide solutions with or without chloride ions. Corros. Sci. 1981, 21, 735–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Jinshan, P.; Changjian, L. Localized corrosion behaviour of reinforcement steel in simulated concrete pore solution. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 2130–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, P.K.; Misra, S.; Mondal, K. Corrosion Behavior of Strained Rebar in Simulated Concrete Pore Solution. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2020, 29, 1939–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokorný, P.; Vacek, V.; Prodanovic, N.; Zabloudil, A.; Fojt, J.; Johánekm, V. The Influence of Graded Amount of Potassium Permanganate on Corrosion of Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel in Simulated Concrete Pore Solutions. Materials 2022, 15, 7864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakroczymski, T.; Fan, C.J.; Szklarska-Smialowska, Z. Kinetics of passive film formation on iron in 0.05M NaOH. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1985, 132, 2282–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montemor, M.F.; Simoes, A.M.; Ferreira, M.G. Analytical characterization of the passive film formed on steel in solutions simulating the concrete interstitial electrolyte. Corrosion 1998, 54, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veleva, L.; Alpuche-Aviles, M.A.; Graves-Brook, M.K.; Wipf, D.O. Comparative cyclic voltammetry and surface analysis of passive films grown on stainless steel 316 in concrete pore model solutions. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2002, 537, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veleva, L.; Alpuche-Aviles, M.A.; Graves-Brook, M.K.; Wipf, D.O. Voltammetry and surface analysis of AISI 316 stainless steel in chloride-containing simulated concrete pore environment. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2005, 578, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacelis, A.; Veleva, L.; Feliu, S.; Cabrini, M.; Lorenzi, S. Corrosion Activity of Carbon Steel B450C and Low Chromium Ferritic Stainless Steel 430 in Cement Extract Solution. Buildings 2021, 11, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Z.; Hu, J.; Xu, Z.; Huang, H.; Yin, S.; Ma, Y.; Wei, J.; Yu, Q. Degradation process of Ag/AgCl chloride-sensing electrode in cement extrat with low chloride concentration. Corros. Sci. 2022, 198, 110107. [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita, T.; Hayes, P. Analysis of XPS spectra of Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions in oxide materials. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 254, 2441–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippold, J.C.; Kotecki, D.J. Welding Metallurgy and Weldability of Stainless Steels, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 19–55. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, T.; Ni, R.; Wang, H.; Shen, J.; Wang, Z. Investigation on the formation of Cr-rich precipitates at the interphase boundary in type 430 stainless steel based on austenite–ferrite transformation kinetics. Metals 2019, 9, 1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heo, S.Y.; Shin, J.H.; Kim, D.-I.; Oh, J.Y.; Zhang, S.H.; Kim, K.H. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Cr–V–C–N films. Surf. Eng. 2015, 31, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolopoulos, C.; Drakakaki, A.; Apostolopoulos, A.; Koulouris, K. Comparison of the mechanical response of B400c and B450c dual phase steel bar categories, in long terms. Frat. Integrità Strutt. 2019, 50, 548–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Apostolopoulos, C.; Drakakaki, A.; Apostolopoulos, A.; Matikas, T.; Rudskoi, A.I.; Kodzhaspirov, G. Characteristic defects corrosion damage and mechanical behavior of dual phase rebar. Mater. Phys. Mech. 2017, 30, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Cabrera-Luna, K.; Maldonado-Bandala, E.E.; Nieves-Mendoza, D.; Escalante García, J.I. Supersulfated binders based on volcanic raw material; optimization, microstructure and reaction products. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 176, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhan, S.; Tang, X.; Xiu, Q.; Qian, K. Pore solution chemistry of calcium sulfoaluminate cement and its effects on steel passivation. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ASTM-NACE/ASTM G31-12a; Standard Guide for Laboratory Immersion Corrosion Testing of Metals. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2012.
- ASTM G1-03; Standard Practice for Preparing, Cleaning, and Evaluating Corrosion Test Specimens. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- ASTM-C876; Standard Test Method for Corrosion Potentials of Uncoated Reinforcing Steel in Concrete. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2012.
- Mursalo, N.; Tullmln, M.; Pa Robinson, F. The Corrosion behaviour of mild steel, 3CR12 and AISI type 316L in synthetic mine waters. J. South Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 1988, 88, 249–256. [Google Scholar]
- Premlall, K.; Herman Potgieter, J.; Potgieter-Vermaak, S. Laser surface treatment to inhibit observed corrosion of reinforcing steel in sulphate alkaline media. Anti-Corros. Methods Mater. 2011, 58, 267–284. [Google Scholar]
- Veleva, L. Memorias en extenso del congreso. Corrosion 2003, 2003, 03602. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, S.; Cook, D.C.; Townsend, H.E. Characterization of Iron Oxides Commonly Formed as Corrosion Products on Steel. Hyperfine Interact. 1998, 112, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouglova, A.; Berthaud, Y.; François, M.; Foct, F. Mechanical Properties of an Iron Oxide Formed by Corrosion in Reinforced Concrete Structures. Corros. Sci. 2006, 48, 3988–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goti´c, M.; Musi´c, S. FT-IR and FE SEM Investigation of Iron Oxides Precipitated from FeSO4 Solutions. J. Mol. Struct. 2007, 834–836, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mataferia, I.A. Characterization of Steel Corrosion Products in Reinforced Concrete. Master’s Thesis, University of Ottawa, Ottawa, CA, Canada, 14 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Weissenrieder, J.; Leygrad, C. In Situ Studies of Filiform Corrosion on Iron. J. Elchem. Soc. 2004, 151, B165–B173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, R.; Costa, I.; Araujo, D. Characterization of Corrosion Products Formed on Steels in the First Months of Atmospheric Exposure. Mater. Res. 2003, 6, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vera, R.; Costa, I.; Villarroel, M.; Carvajal, A.M.; Vera, E.; Ortiz, C. Corrosion Products of Reinforcement in Concrete in Marine and Industrial Environments. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 114, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, S. Atmospheric corrosion of carbon steel at marine sites in Saudi Arabia. Mater. Corros. 2010, 61, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramana, K.V.S.; Kaliappan, S.; Ramanathan, N.; Kavitha, V. Characterization of rust phases formed on low carbon steel exposed to natural marine environment of Chennal harbour. Mater. Corros. 2007, 58, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhawat, M.; Hammed, O.; Araba, A. Study of corrosion products induced under different environmental conditions. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1090, 012050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Su, H.; Dong, C.; Xiao, K.; Li, X. Electrochemical and passivation behavior investigation of ferritic stainless steel in alkaline environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 96, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Zhao, X.; Du, Y.; Yang, S.; Wang, D.; Zhao, T.; Bai, Y. Comprehensive properties of passive film formed in simulated pore solution of alkali-activated concrete. Const. Build. Mater. 2022, 319, 126142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulder, J.F.; Stickle, W.F.; Sobol, P.E.; Bomben, K.D. Handbook of X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy: A Reference Book of Standard Spectra for Identification and Interpretation of XPS Data; Physical Electronics: Chanhassen, MN, USA, 1995; p. 81. [Google Scholar]
- Sarango de Souza, J.; De Oliveira, L.A.; Sayeg, I.J.; Antunes, R.A. Electrochemical study of the AISI 409 ferritic stainless steel: Passive film stability and pitting nucleation and growth. Mater. Res. 2017, 20, 1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, J.; Wu, M.; Ming, J. Degradation effect of carbonation on electrochemical behavior of 2304 duplex stainless steel in simulated concrete pore solutions. Corros. Sci. 2020, 177, 109006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, M.; Huang, R. Study of depassivation of carbon steel in simulated concrete pore solution using different equivalent circuits. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 157, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Ma, H.; Shi, J. Enhanced corrosion resistance of reinforcing steels in simulated concrete pore solution with low mo-lybdate to chloride ratios. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2020, 110, 103589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Xiong, C.; Zhao, T.; Du, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, N.; Yu, Y.; Wang., P. Passivation ad depassivation properties of Cr-Mo alloyed corrosion-resistant steel in simulated concrete pore solution. Cem. Conr. Compos. 2022, 126, 104375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Ni, Z.; Huang., R. Corrosion behavior of steel submitted to chloride and sulphate ions in simulated concrete pore solution. Const. Build. Mater. 2016, 115, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, L.; Carmezim, M.J.; Ferreira, M.G.S.; Montermor, M.F. The electrochemical behaviour of stainless steel AISI 304 in alkaline solutions with different pH in the presence of chlorides. Electrochim. Acta. 2011, 56, 5280–5289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Dong, S.; Zhang, X. EIS analysis on chloride-induced corrosion behavior of reinforcement steel in simulated carbonated concrete pore solutions. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2013, 688, 275–281. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.; Su, H.; Dong, C.; Li, X. Passivation and electrochemical behavior of 316L stainless steel in chlorinated simulated concrete pore solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 400, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Wu, M.; Ming, J. Long-term corrosion resistance of reinforcing steel in alkali-activated slag mortar after exposure to marine environments. Corros. Sci. 2021, 179, 109175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujar, M.G.; Parvathavarthini, N.; Dayal, R.K. Some aspects of corrosion and film formation of austenitic stainless steel type 316LN using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 4535–4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orazem, M.; Frateur, I.; Tribollet, B.; Vivier, V.; Marcelin, S.; Pebere, N.; Bunge, A.L.; White, E.A.; Riemer, D.P.; Musiani, M. Dielectric properties of materials showing constant-phase-element (CPE) impedance response. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2013, 160, C215–C225Z. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carmezim, M.J.; Simões, A.M.; Montemor, M.F.; Da Cunha Belo, M. Capacitance behaviour of passive films on ferritic and austenitic stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 2005, 47, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Element (wt.%) | C | Cr | N | Cu | P | S | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SS430 | 0.25 | 16.2 | - | - | - | - | Balance |
| B450C | 0.22 | - | 0.12 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.5 | Balance |
| SS1 | CPC30 | CaO | Hh (CS) (CaSO4·1/2H2O) | Pumice (SiO2/Al2O3) | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt.% | 6.89 | 6.89 | 34.48 | 51.72 | 100 |
| SS1 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | MgO | SO3 | K2O | Na2O | TiO2 | Cl | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt.% | 38.22 | 7.82 | 1.63 | 26.07 | 0.49 | 19.46 | 2.98 | 2.00 | 0.24 | 0.06 | 1.03 |
| Element (mg/L) | Li+ | K+ | Na+ | Al3+ | Ca2+ | Si | SO42− | Sr | Cl− |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SS1 | 0.184 | 496.8 | 310.2 | 0.185 | 396.6 | 5.4 | 563.5 | 9.02 | 45.4 |
| pH vs. Time (Days) | Initial | 1 | 7 | 14 | 21 | 30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B450C (SS1) | 12.38 | 9.56 | 7.80 | 7.66 | 7.64 | 7.84 |
| SS430 (SS1) | 12.38 | 9.60 | 7.92 | 7.97 | 7.63 | 7.80 |
| OCP (mV) vs. SHE Time (Days) | Initial | 1 | 7 | 14 | 21 | 30 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B450C (SS1) | −206.54 | −466.34 | −481.17 | −476.10 | −477.44 | −480.74 |
| SS430 (SS1) | −20.28 | 104.17 | 171.51 | 173.56 | 178.92 | 182.50 |
| Days/wt.% | Fe | O | Mn | Zn | Ca | C | Na | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | A | 85.02 | 9.27 | 0.89 | - | - | 4.81 | - |
| B | 58.52 | 32.27 | 1.58 | 1.30 | 1.16 | 5.17 | - | |
| C | 26.18 | 44.43 | 0.82 | - | 14.24 | 14.14 | - | |
| 30 | D | 48.85 | 47.55 | 0.48 | - | - | 1.81 | 0.96 |
| Days/wt.% | Fe | O | Cr | C | S | Na | Cl | K | Si | Mn | Ca | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | A | 58.67 | 5.90 | 12.86 | 15.04 | 0.52 | 2.67 | 0.50 | 0.28 | 0.78 | - | - |
| B | 8.46 | 40.20 | 2.31 | 4.98 | 14.81 | 14.60 | 0.67 | 13.02 | 0.65 | - | - | |
| C | 77.84 | 1.26 | 16.59 | 2.61 | - | - | - | - | 0.73 | 0.98 | - | |
| 30 | Q1 | 1.80 | 38.66 | 0.53 | 26.90 | - | 1.99 | 7.52 | 5.91 | 0.53 | - | 15.69 |
| Q2 | 1.23 | 3.97 | 0.46 | - | - | 0.58 | 44.98 | 48.78 | - | - | - | |
| Q3 | 0.93 | 11.98 | - | 28.89 | - | 0.68 | 29.51 | 28.01 | - | - | - | |
| Q4 | 62.59 | 4.46 | 13.50 | 16.30 | . | 1.46 | 0.92 | 0.32 | 0.26 | - | - | |
| wt.% | C | Cr | Mn | O | V | N | S | Fe | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SS430 | A | 2.35 | 16.92 | 0.77 | 0.83 | - | - | - | 78.83 |
| B | 16.37 | 27.69 | 9.78 | 23.01 | 1.13 | 0.37 | 0.21 | 18.61 | |
| C | 28.57 | 24.17 | - | 8.86 | 1.24 | 16.11 | 0.28 | 20.07 | |
| wt.% | C | Mn | O | Cu | Fe | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B450C | Q1 | 2.72 | - | 1.66 | 64.08 | 31.54 |
| Q2 | 0.84 | 0.54 | - | - | 98.62 | |
| Steel | Days | Rsol kΩ cm2 | Rcp kΩ cm2 | CPE1 μSsncm−2 | n1 | Rct kΩ cm2 | CPE2 μSsncm−2 | n2 | Rp kΩ cm2 | c2 10−4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SS430 | 1 | 0.24 | - | - | - | 3356 | 19.74 | 0.91 | 3356 | 1.86 |
| 7 | 0.21 | - | - | - | 7217 | 19.81 | 0.91 | 7217 | 0.1 | |
| 14 | 0.14 | - | - | - | 8839 | 19.06 | 0.9 | 8839 | 0.23 | |
| 21 | 0.05 | - | - | - | 7622 | 19.4 | 0.9 | 7622 | 0.29 | |
| 30 | 0.08 | - | - | - | 7806 | 19.41 | 0.9 | 7806 | 0.24 | |
| B450C | 1 | 0.29 | 2.89 | 186.6 | 0.73 | 9.567 | 972.6 | 0.25 | 12.46 | 1.37 |
| 7 | 0.36 | 3.98 | 160.1 | 0.81 | 14.94 | 222.3 | 0.75 | 18.92 | 0.98 | |
| 14 | 0.21 | 11.06 | 121.7 | 0.85 | 97.68 | 89.06 | 0.79 | 108.74 | 3.64 | |
| 21 | 0.12 | 8.97 | 116 | 0.9 | 145.7 | 63.69 | 0.71 | 154.67 | 0.44 | |
| 30 | 0.2 | 13.77 | 140.6 | 0.9 | 93.81 | 61.58 | 0.7 | 107.58 | 0.53 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bonfil, D.; Veleva, L.; Feliu, S., Jr.; Escalante-García, J.I. Corrosion Activity of Carbon Steel B450C and Stainless Steel SS430 Exposed to Extract Solution of a Supersulfated Cement. Materials 2022, 15, 8782. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15248782
Bonfil D, Veleva L, Feliu S Jr., Escalante-García JI. Corrosion Activity of Carbon Steel B450C and Stainless Steel SS430 Exposed to Extract Solution of a Supersulfated Cement. Materials. 2022; 15(24):8782. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15248782
Chicago/Turabian StyleBonfil, David, Lucien Veleva, Sebastian Feliu, Jr., and José Iván Escalante-García. 2022. "Corrosion Activity of Carbon Steel B450C and Stainless Steel SS430 Exposed to Extract Solution of a Supersulfated Cement" Materials 15, no. 24: 8782. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15248782
APA StyleBonfil, D., Veleva, L., Feliu, S., Jr., & Escalante-García, J. I. (2022). Corrosion Activity of Carbon Steel B450C and Stainless Steel SS430 Exposed to Extract Solution of a Supersulfated Cement. Materials, 15(24), 8782. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15248782








