Unveiling the Hidden Entropy in ZnFe2O4
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
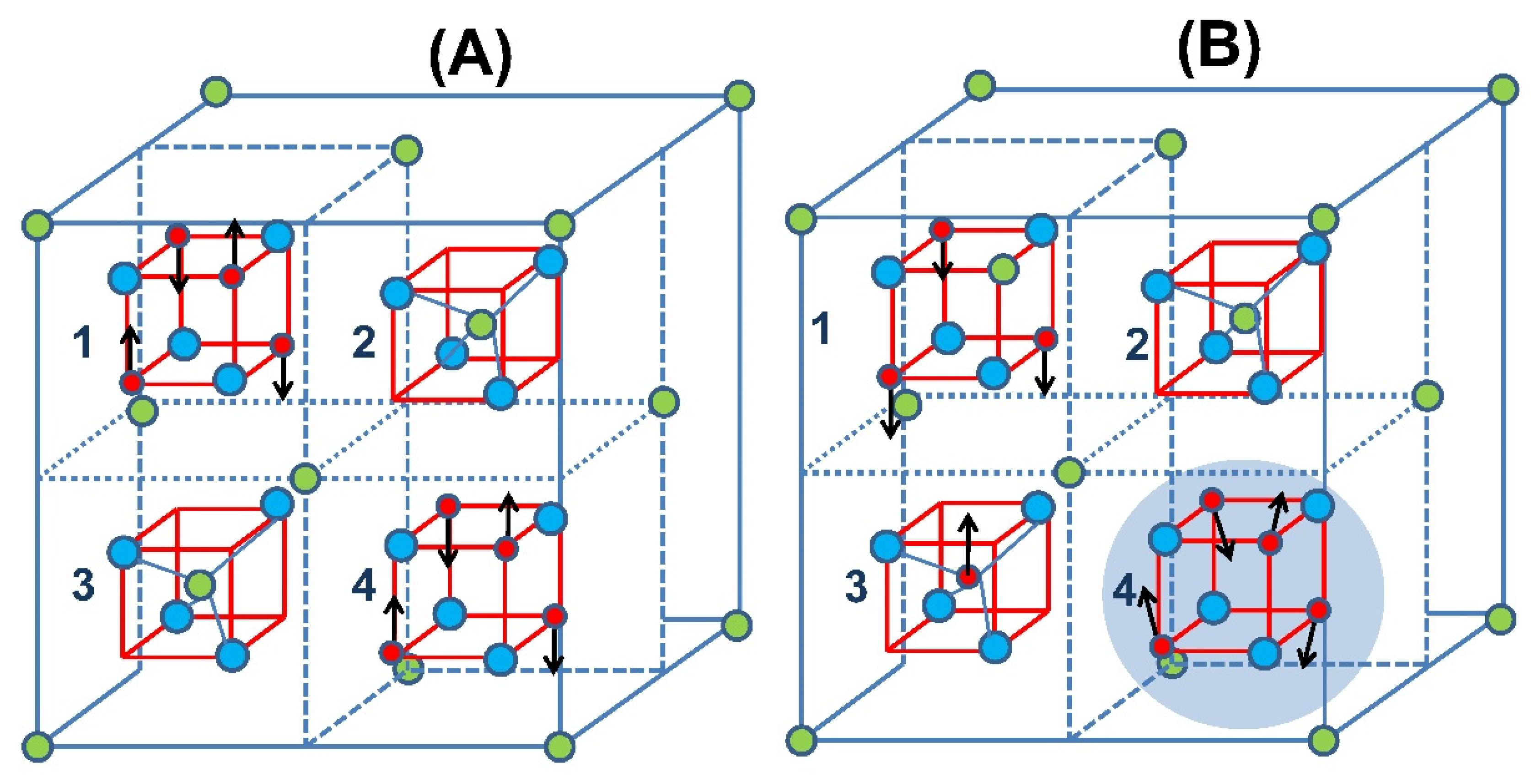
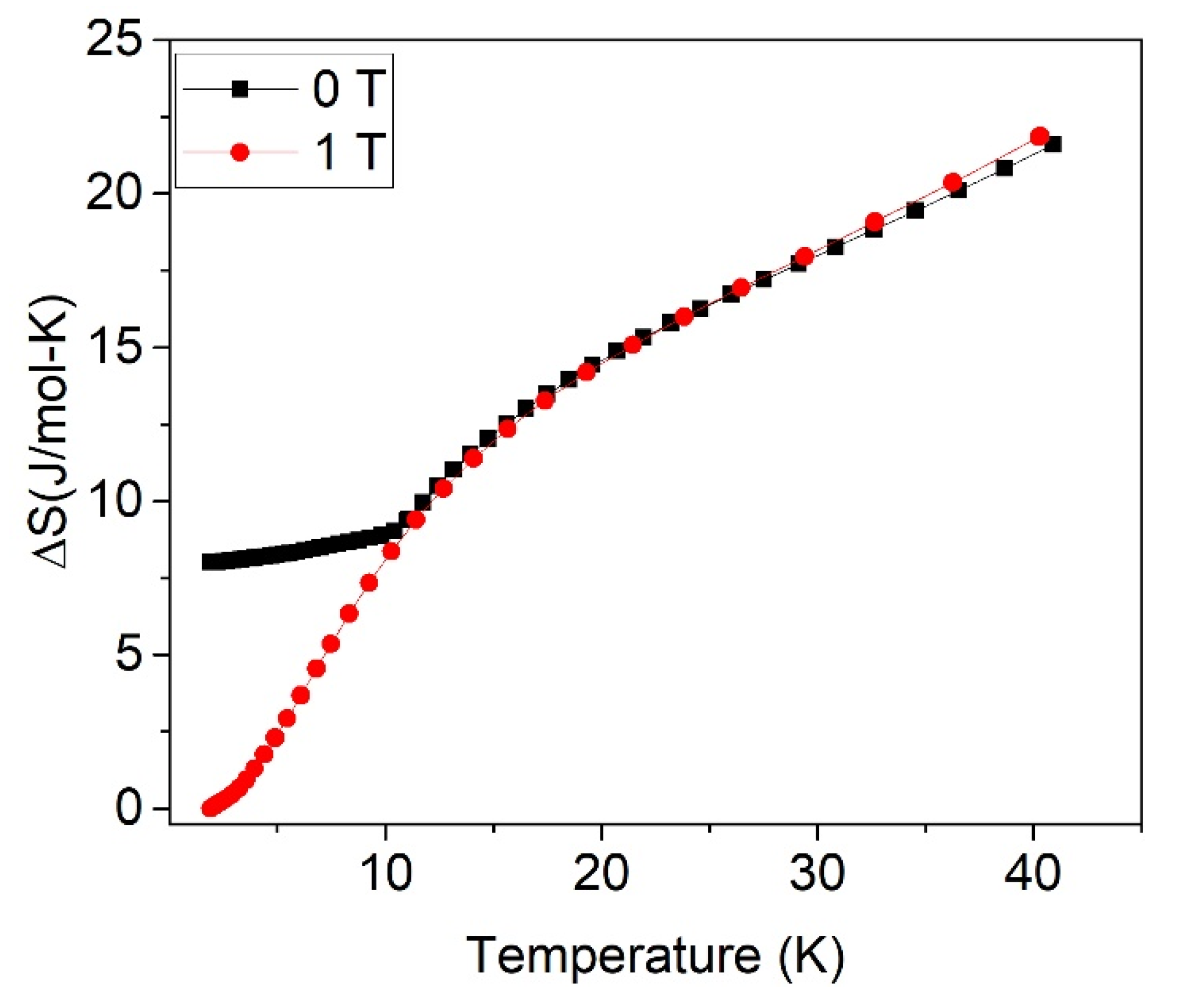
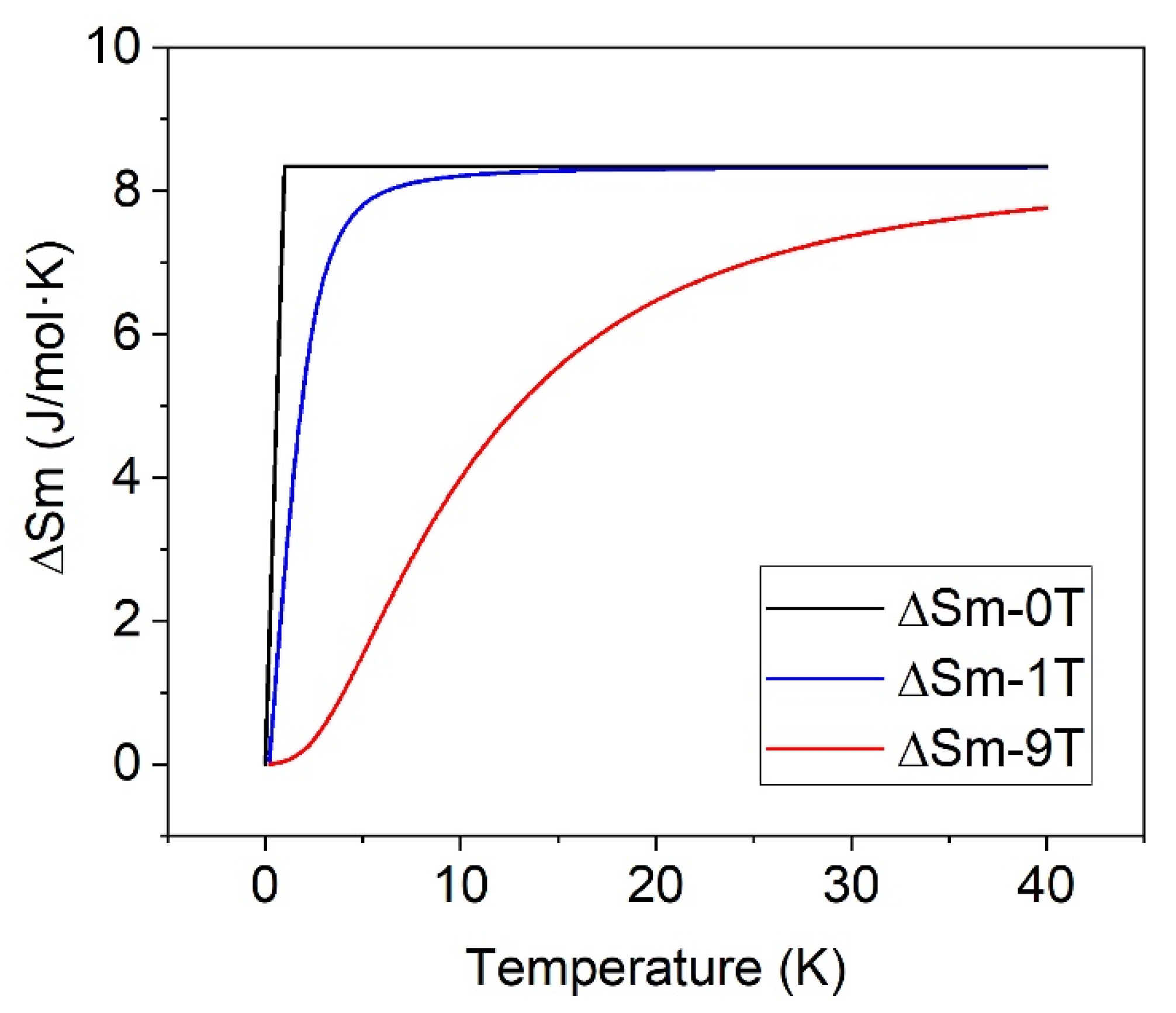
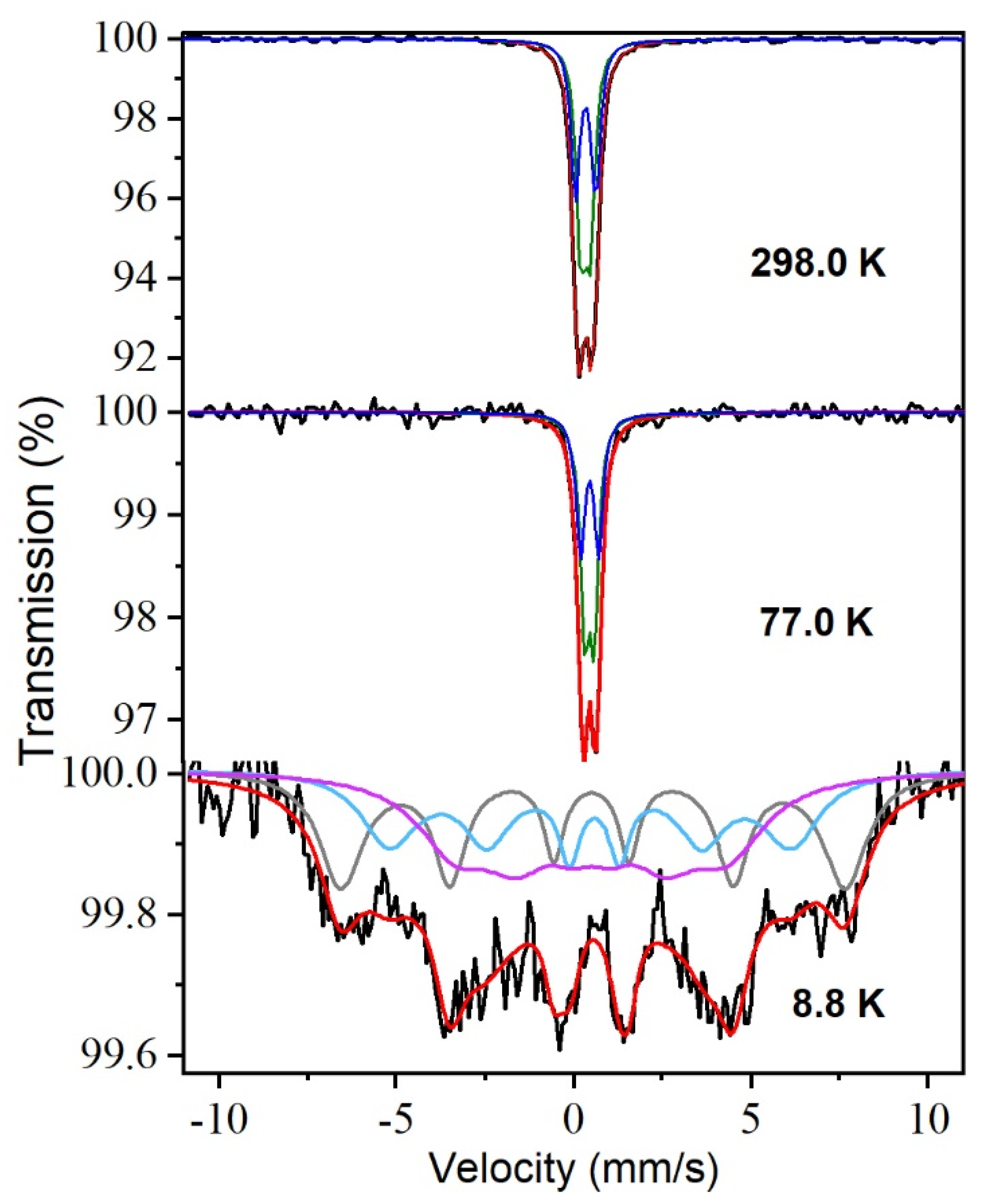
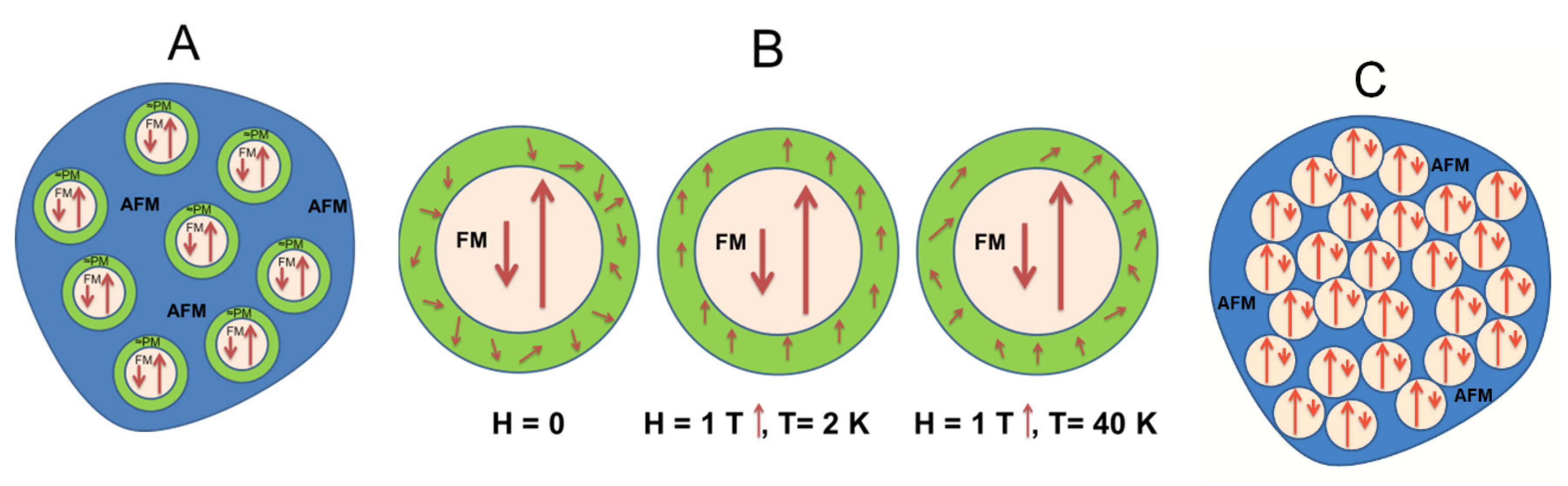
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dolcet, P.; Kirchberg, K.; Antonello, A.; Suchomski, C.; Marschall, R.; Diodati, S.; Munoz-Espi, R.; Landfester, K.; Gross, S. Exploring wet chemistry approaches to ZnFe2O4 spinel ferrite nanoparticles with different inversion degrees: A comparative study. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2019, 6, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohra, M.; Alman, V.; Arras, R. Nanostructured ZnFe2O4: An Exotic Energy Material. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sai, R.; Arackal, S.; Kahmei, R.D.R.; Bhat, N.; Yamaguchi, M.; Shivashankar, S.A. Crystallographic inversion-mediated superparamagnetic relaxation in Zn-ferrite nanocrystals. AIP Adv. 2020, 10, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobos, M.A.; de la Presa, P.; Llorente, I.; Alonso, J.M.; Garcia-Escorial, A.; Marin, P.; Hernando, A.; Jimenez, J.A. Magnetic Phase Diagram of Nanostructured Zinc Ferrite as a Function of Inversion Degree delta. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 17472–17482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yafet, Y.; Kittel, C. Antiferromagnetic Arrangements in Ferrites. Phys. Rev. 1952, 87, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastings, J.M.; Corliss, L.M. An Antiferromagnetic Transition In Zinc Ferrite. Phys. Rev. 1956, 102, 1460–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, M.; Campbell, S.J.; Ehrhardt, H.; Feyerherm, R. The magnetic behaviour of nanostructured zinc ferrite. J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 39, 5057–5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrhardt, H.; Campbell, S.J.; Hofmann, M. Magnetism of the nanostructured spinel zinc ferrite. Scr. Mater. 2003, 48, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usa, T.; Kamazawa, K.; Sekiya, H.; Nakamura, S.; Tsunoda, Y.; Kohn, K.; Tanaka, M. Magnetic Properties of ZnFe2O4 as a 3-D Geometrical Spin Frustration System. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2004, 73, 2834–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiessl, W.; Potzel, W.; Karzel, H.; Steiner, M.; Kalvius, G.M.; Martin, A.; Krause, M.K.; Halevy, I.; Gal, J.; Schäfer, W.; et al. Magnetic properties of the ZnFe2O4 spinel. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 53, 9143–9152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oneill, H.S. Temperature-Dependence Of The Cation Distribution In Zinc Ferrite (ZnFe2O4) From Powder Xrd Structural Refinements. Eur. J. Mineral. 1992, 4, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.S.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.B.; Zhou, Q.G.; Zhou, X.Z.; Kunkel, H.P.; Williams, G. Site preference of Fe in nanoparticles of ZnFe2O4. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2004, 268, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobos, M.Á.; de la Presa, P.; Puente-Orench, I.; Llorente, I.; Morales, I.; García-Escorial, A.; Hernando, A.; Jiménez, J.A. Coexistence of antiferro- and ferrimagnetism in the spinel ZnFe2O4 with an inversion degree delta lower than 0.3. Ceram. Int. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimes, N.W. On the specific-heat of compounds with spinel structure—II Zinc ferrite, a paramagnetic compound with magnetic ion occupying octahedral site. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A-Math. Phys. Sci. 1974, 338, 223–233. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, J.C.; Hamdeh, H.H.; Chen, Y.Y.; Lin, S.H.; Yao, Y.D.; Willey, R.J.; Oliver, S.A. Low-temperature calorimetric properties of zinc ferrite nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B 1995, 52, 10122–10126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westrum, E.F.; Grimes, D.M. Low temperature heat capacity and thermodynamic properties of zinc ferrite. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1957, 3, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.N.; Shi, Q.; Schliesser, J.; Woodfield, B.F.; Nan, Z.D. Magnetic and Thermodynamic Properties of Nanosized Zn Ferrite with Normal Spinal Structure Synthesized Using a Facile Method. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 10463–10470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamazawa, K.; Tsunoda, Y.; Kadowaki, H.; Kohn, K. Magnetic neutron scattering measurements on a single crystal of frustrated ZnFe2O4. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 68, 024412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashley, J.C.; Stevens, R.; Crawford, M.K.; Boerio-Goates, J.; Woodfield, B.F.; Qiu, Y.; Lynn, J.W.; Goddard, P.A.; Fisher, R.A. Specific heat and magnetic susceptibility of the spinels GeNi(2)O(4) and GeCo(2)O(4). Phys. Rev. B 2008, 78, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenner, L.A.; Wills, A.S.; Bramwell, S.T.; Dahlberg, M.; Schiffer, P. Zero-point entropy of the spinel spin glasses CuGa2O4 and CuAl2O4. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2009, 145, 012029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, J.Z.; Wynn, P.; Morup, S.; Okada, T.; Berry, F.J. Magnetic structure evolution bn mechanically milled nanostructured ZnFe2O4 particles. Nanostruct. Mater. 1999, 12, 737–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, D.S.; Juang, R.S. An overview of the structure and magnetism of spinel ferrite nanoparticles and their synthesis in microemulsions. Chem. Eng. J. 2007, 129, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnasamy, C.N.; Narayanasamy, A.; Ponpandian, N.; Chattopadhyay, K.; Guerault, H.; Greneche, J.M. Magnetic properties of nanostructured ferrimagnetic zinc ferrite. J. Phys.-Condes. Matter 2000, 12, 7795–7805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.W.; Zeng, Q.S.; Goya, G.F.; Torres, T.; Liu, J.F.; Wu, H.P.; Ge, M.Y.; Zeng, Y.W.; Wang, Y.W.; Jiang, J.Z. ZnFe2O4 nanocrystals: Synthesis and magnetic properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 12274–12278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jimenez, J.A.; Cobos, M.A.; Llorente, I.; Nassif, V.; Puente Orench, I. Evolution of the Magnetic Properties with Annealing Temperature of Spinel Zinc Ferrite Disordered by Ball Milling; Institut Laue-Langevin (ILL): Grenoble, France, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez, J.A.; Cobos, M.A.; Llorente, I.; Puente Orench, I. Effect of Microstructural Features and Defects Introduced by Mechanical Milling and Thermal Treatments on the Magnetic Order of Spinel Zinc; Institut Laue-Langevin (ILL): Grenoble, France, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez, J.A.; Cobos, M.A.; Llorente, I.; Puente Orench, I. Effect of Inversion Degree on the Magnetic Properties of Spinel Zinc Ferrite; Institut Laue-Langevin (ILL): Grenoble, France, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Villars, P.; Cenzual, K. Pearson’s Crystal Data: Crystal Structure Database for Inorganic Compounds; ASM International®: Materials Park, OH, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, E.; Schafer, W.; Will, G. R values in analysis of powder diffraction data using Rietveld refinement. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1994, 27, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobos, M.A.; de la Presa, P.; Llorente, I.; García-Escorial, A.; Hernando, A.; Jiménez, J.A. Effect of preparation methods on magnetic properties of stoichiometric zinc ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 849, 156353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberghe, R.E.; De Grave, E. Mössbauer Effect Studies of Oxidic Spinels. In Mössbauer Spectroscopy Applied to Inorganic Chemistry; Long, G.J., Grandjean, F., Eds.; Springer US: Boston, MA, USA, 1989; pp. 59–182. [Google Scholar]
- Goya, G.F.; Leite, E.R. Ferrimagnetism and spin canting of Zn57Fe2O4nanoparticles embedded in ZnO matrix. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2003, 15, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rancourt, D.G. Analytical Methods for Mössbauer Spectral Analysis of Complex Materials. In Mössbauer Spectroscopy Applied to Magnetism and Materials Science; Long, G.J., Grandjean, F., Eds.; Springer US: Boston, MA, USA, 1996; pp. 105–124. [Google Scholar]
- Blume, M.; Tjon, J.A. Mossbauer Spectra in a Fluctuating Environment. Phys. Rev. 1968, 165, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
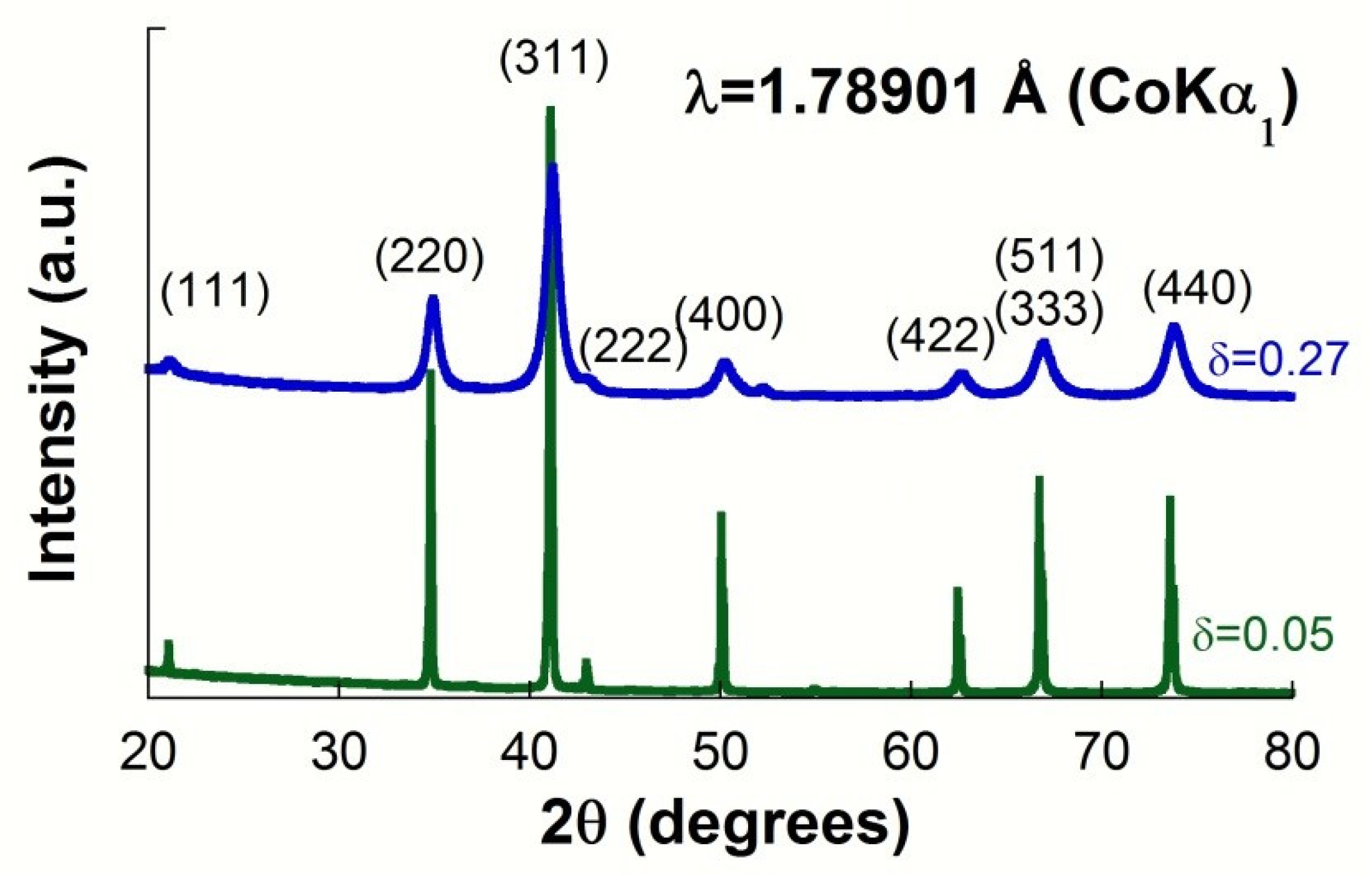
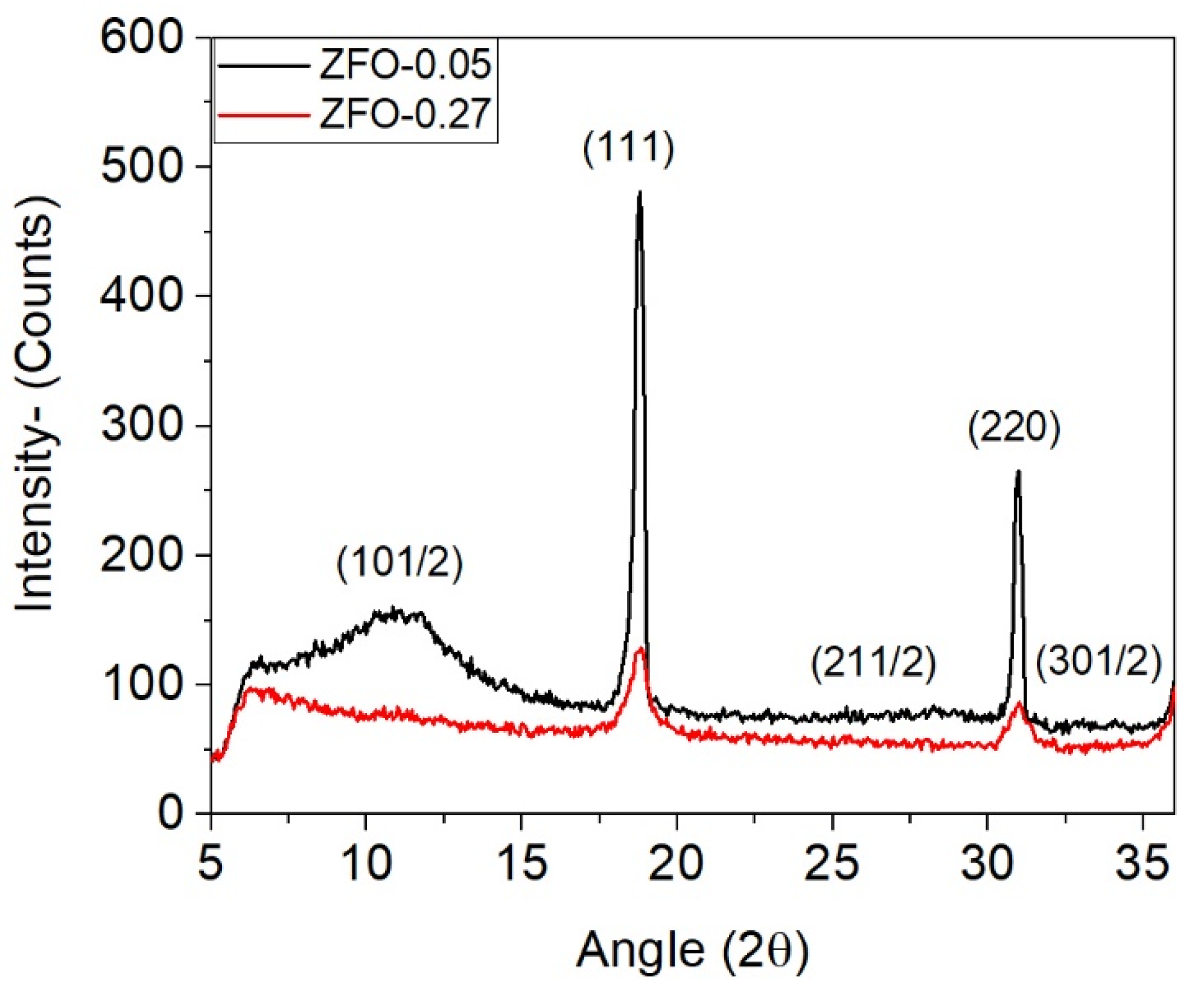
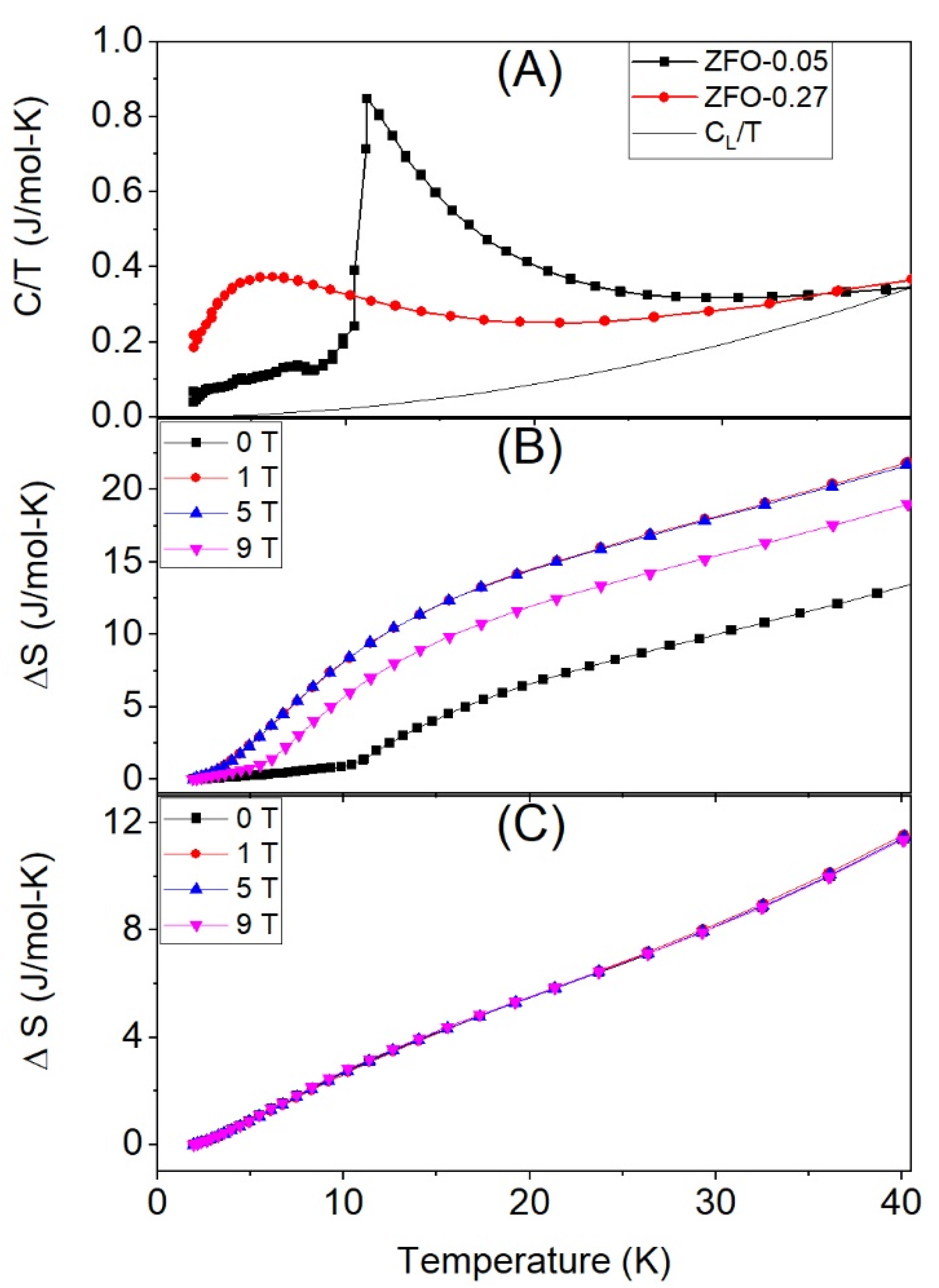
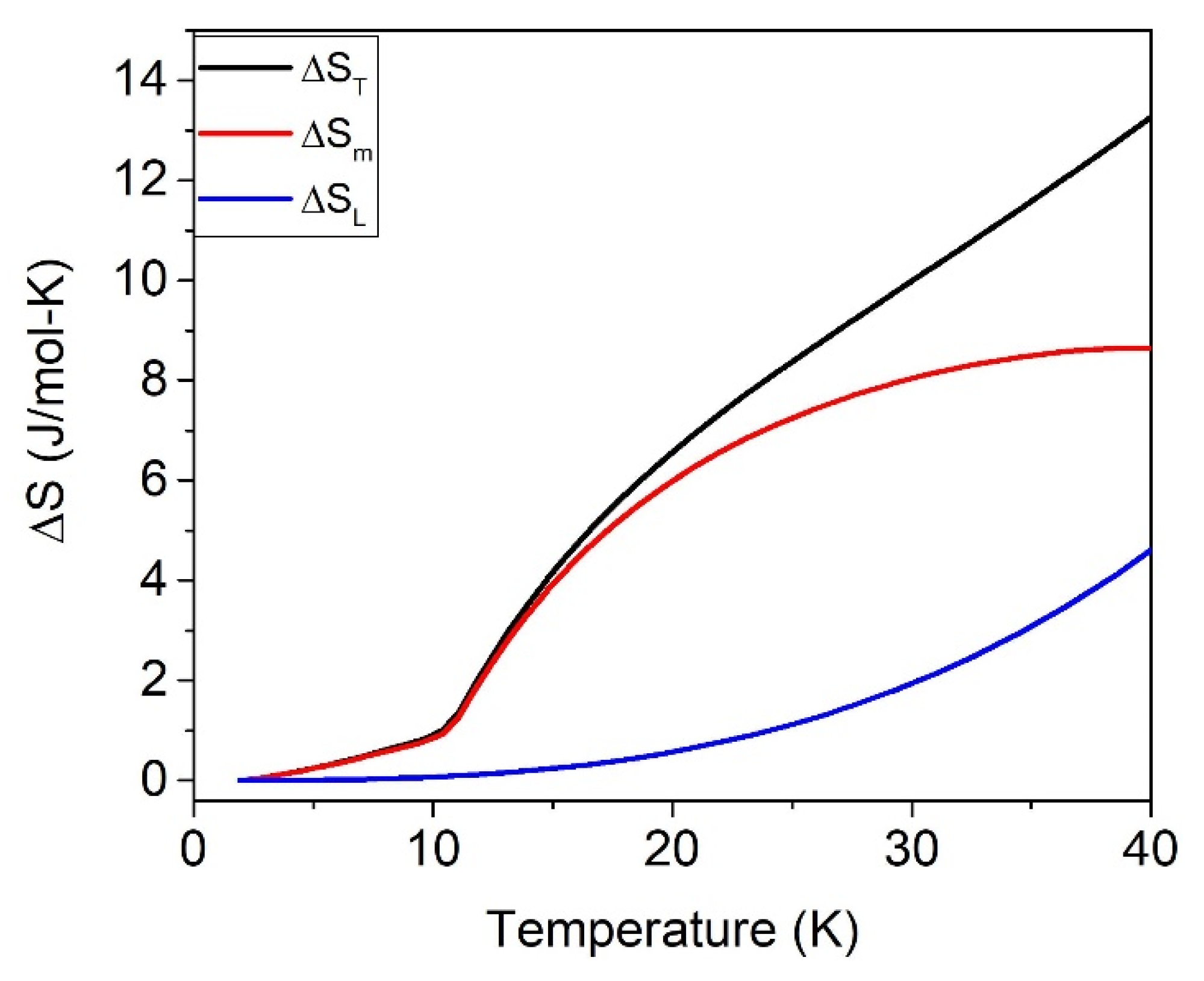
| Sample | Source | Lattice Parameter (Å) | Inversion Degree(δ) | O-Position (x = y = z) | Crystal Size (nm) | μ-Deformation (ε) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZFO-0.05 | XRD | 8.4489(5) | 0.05(1) | 0.2416(9) | >150 | - |
| NPD | 8.4498(5) | 0.05(1) | 0.2397(3) | >150 | - | |
| ZFO-0.27 | XRD | 8.4322(5) | 0.28(2) | 0.2424(5) | 15(1) | 0.0020(2) |
| NPD | 8.4373(5) | 0.20(2) | 0.2414(3) | 14(1) | 0.0019(2) |
| H (T) | 40 K | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ΔST | ΔSm | ΔSL | |
| 0 | 13.2 (1) | 8.7 (1) | 4.6 (1) |
| 1–5 | 21.7 (1) | 17.1 (1) | 4.6 (1) |
| 9 | 18.9 (1) | 14.2 (1) | 4.7 (1) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cobos, M.A.; Hernando, A.; Marco, J.F.; Puente-Orench, I.; Jiménez, J.A.; Llorente, I.; García-Escorial, A.; de la Presa, P. Unveiling the Hidden Entropy in ZnFe2O4. Materials 2022, 15, 1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031198
Cobos MA, Hernando A, Marco JF, Puente-Orench I, Jiménez JA, Llorente I, García-Escorial A, de la Presa P. Unveiling the Hidden Entropy in ZnFe2O4. Materials. 2022; 15(3):1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031198
Chicago/Turabian StyleCobos, Miguel Angel, Antonio Hernando, José Francisco Marco, Inés Puente-Orench, José Antonio Jiménez, Irene Llorente, Asunción García-Escorial, and Patricia de la Presa. 2022. "Unveiling the Hidden Entropy in ZnFe2O4" Materials 15, no. 3: 1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031198
APA StyleCobos, M. A., Hernando, A., Marco, J. F., Puente-Orench, I., Jiménez, J. A., Llorente, I., García-Escorial, A., & de la Presa, P. (2022). Unveiling the Hidden Entropy in ZnFe2O4. Materials, 15(3), 1198. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031198








