Study on the Durability of Acid Rain Erosion-Resistant Asphalt Mixtures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Asphalt
2.1.2. Aggregates and Gradation Composition Design
2.1.3. Waste Rubber Powder and Modified Bamboo Fiber
2.2. Experiments
2.2.1. Physical Properties of Asphalt Binder
2.2.2. Preparation of Asphalt Mixture
2.2.3. Periodic Dry–Wet Cycle Immersion Test
2.2.4. Aging Test
2.2.5. Low-Temperature Stability Test
2.2.6. Moisture Stability Test
2.2.7. Fatigue Life Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Performance Analysis of Asphalt Binder
3.1.1. Physical Performance
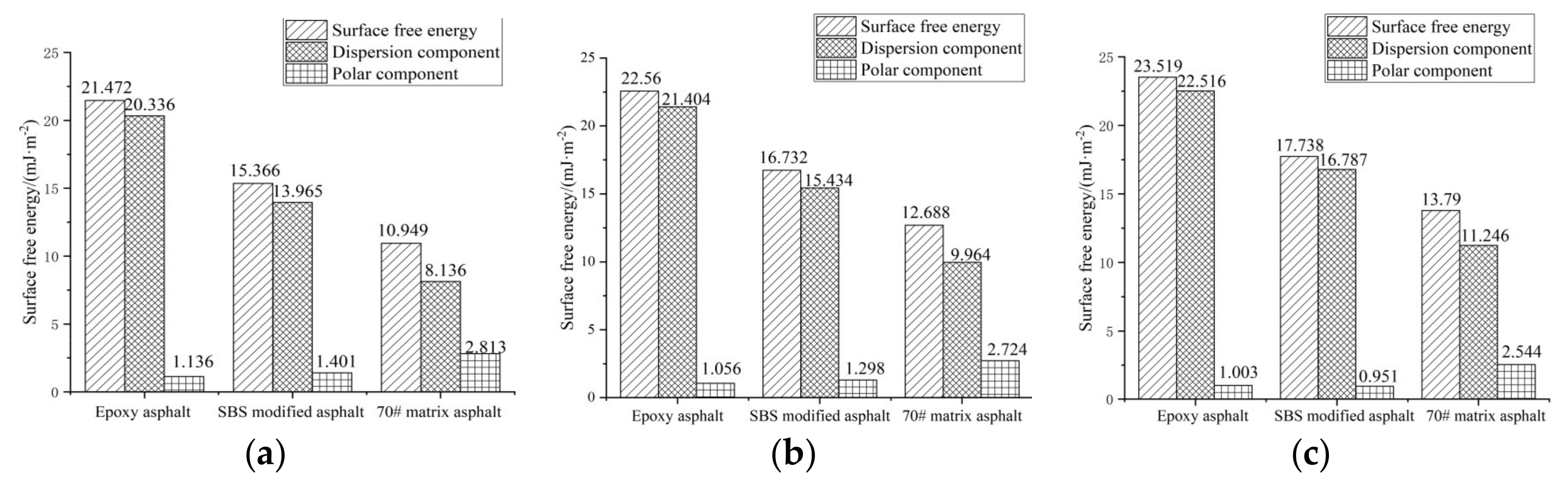
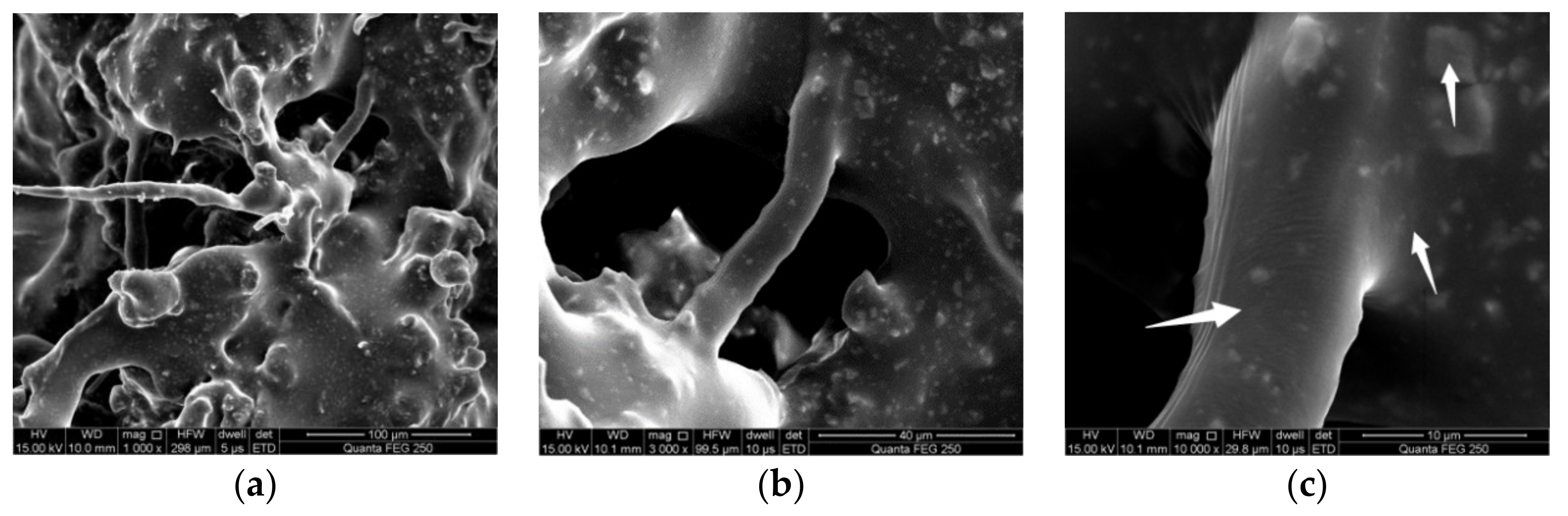
3.1.2. Adhesion Performance
3.2. Anti-Aging Properties of Asphalt Mixture
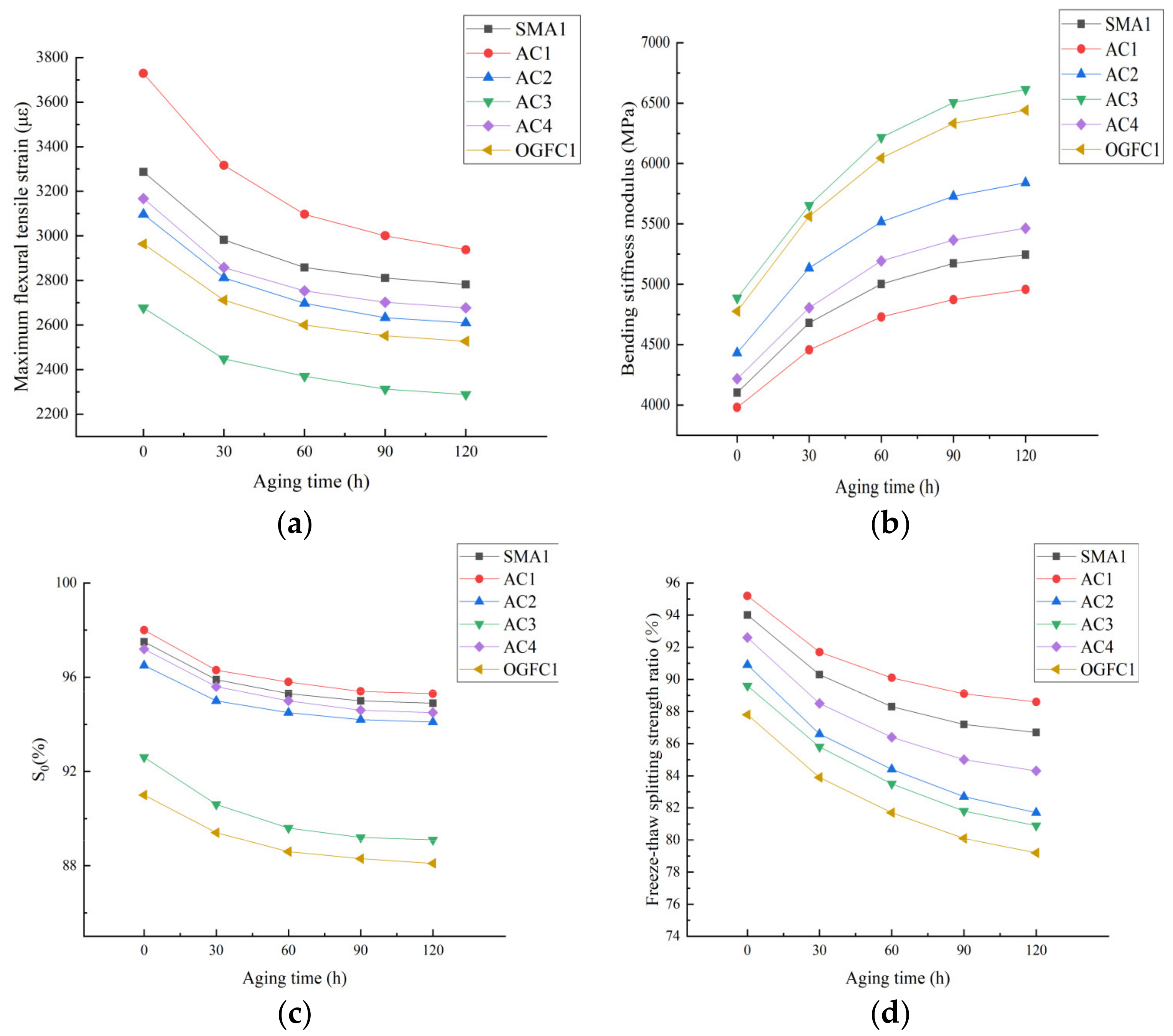
3.2.1. Different Aging Time
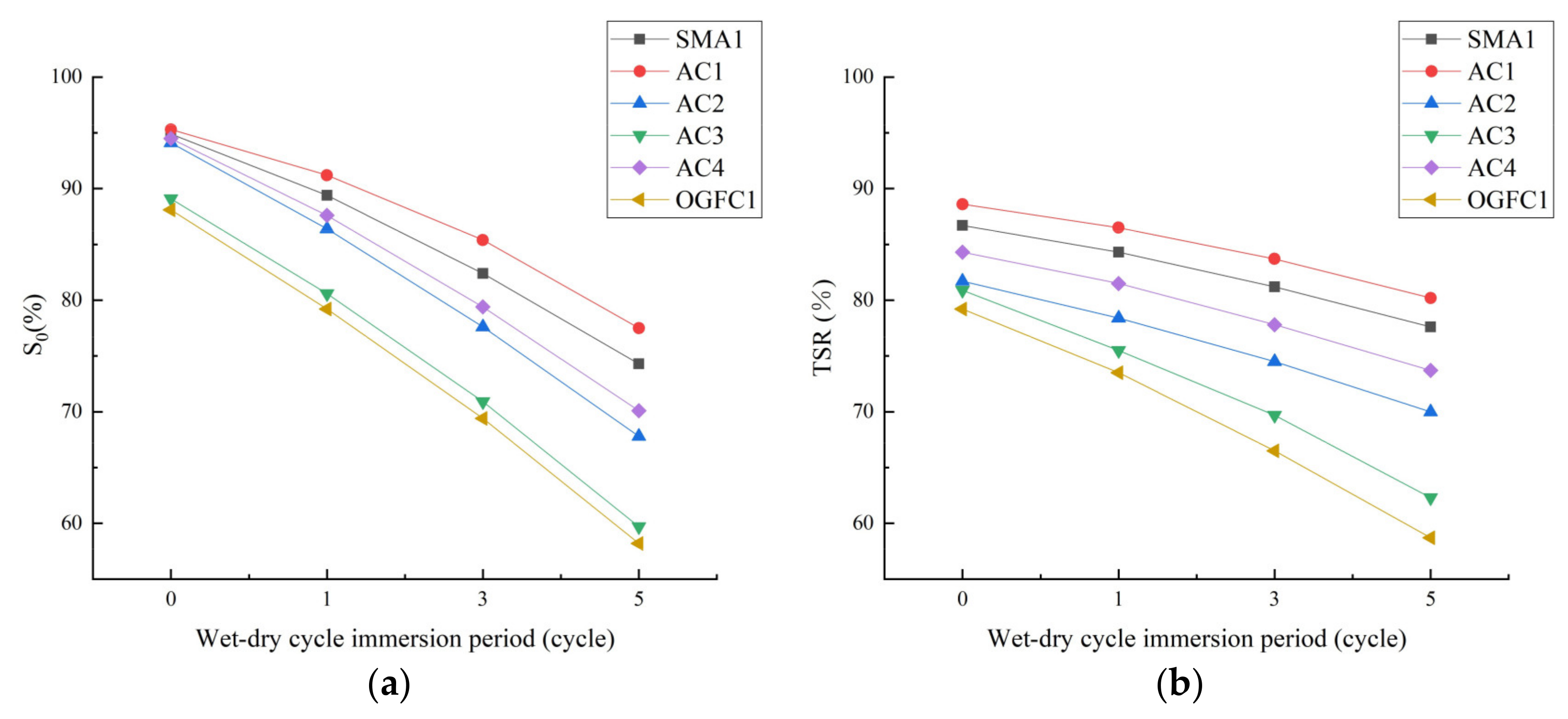
3.2.2. Different Acidic Conditions
Low-Temperature Performance
Moisture Stability
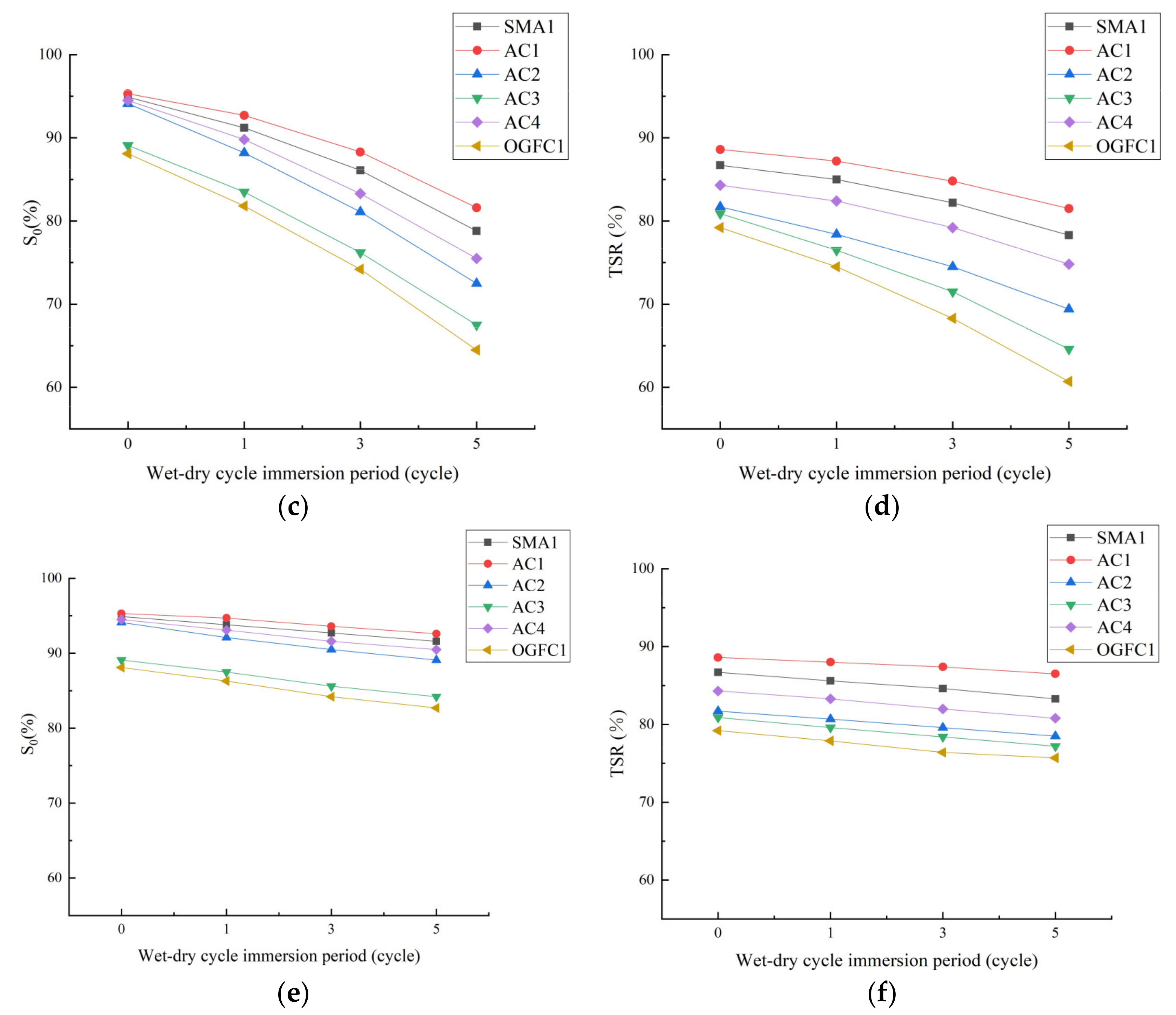
3.3. Freeze–Thaw Cycle Durability of Asphalt Mixture
3.4. Fatigue Property of Asphalt Mixture
3.5. Grey Correlation Analysis
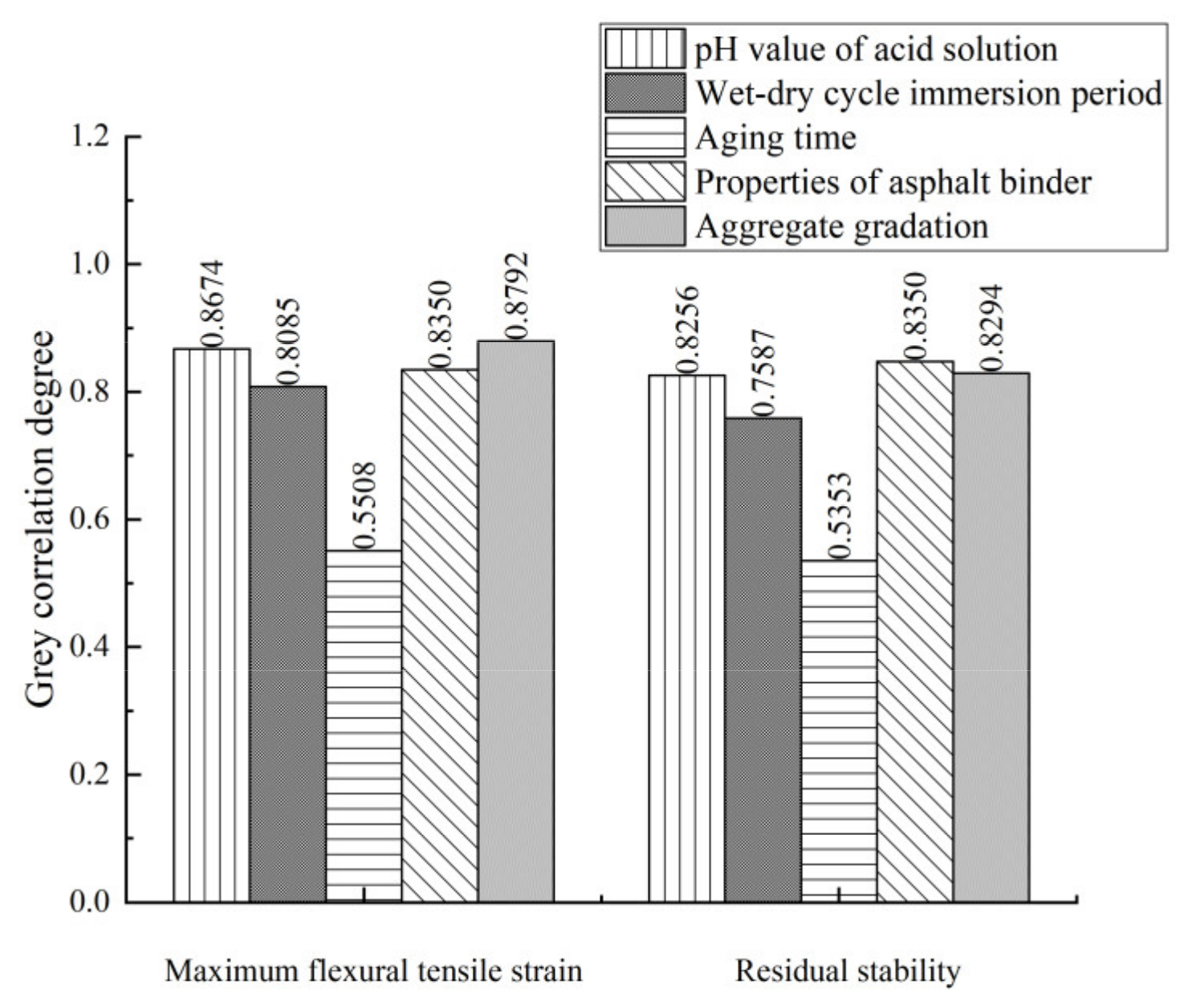
3.5.1. Anti-Aging Properties of Asphalt Mixtures
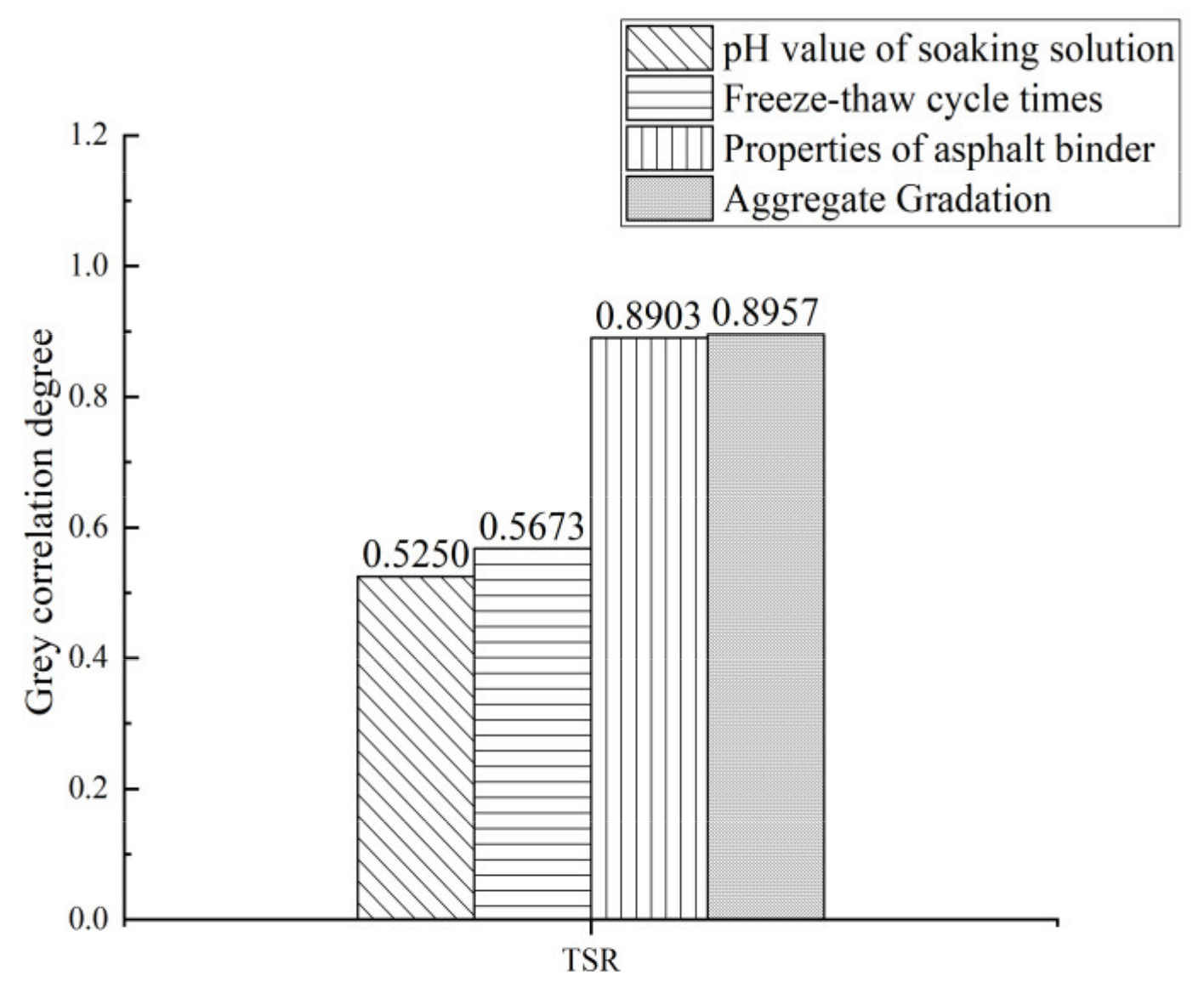
3.5.2. Freeze–Thaw Cycle Durability of Asphalt Mixtures
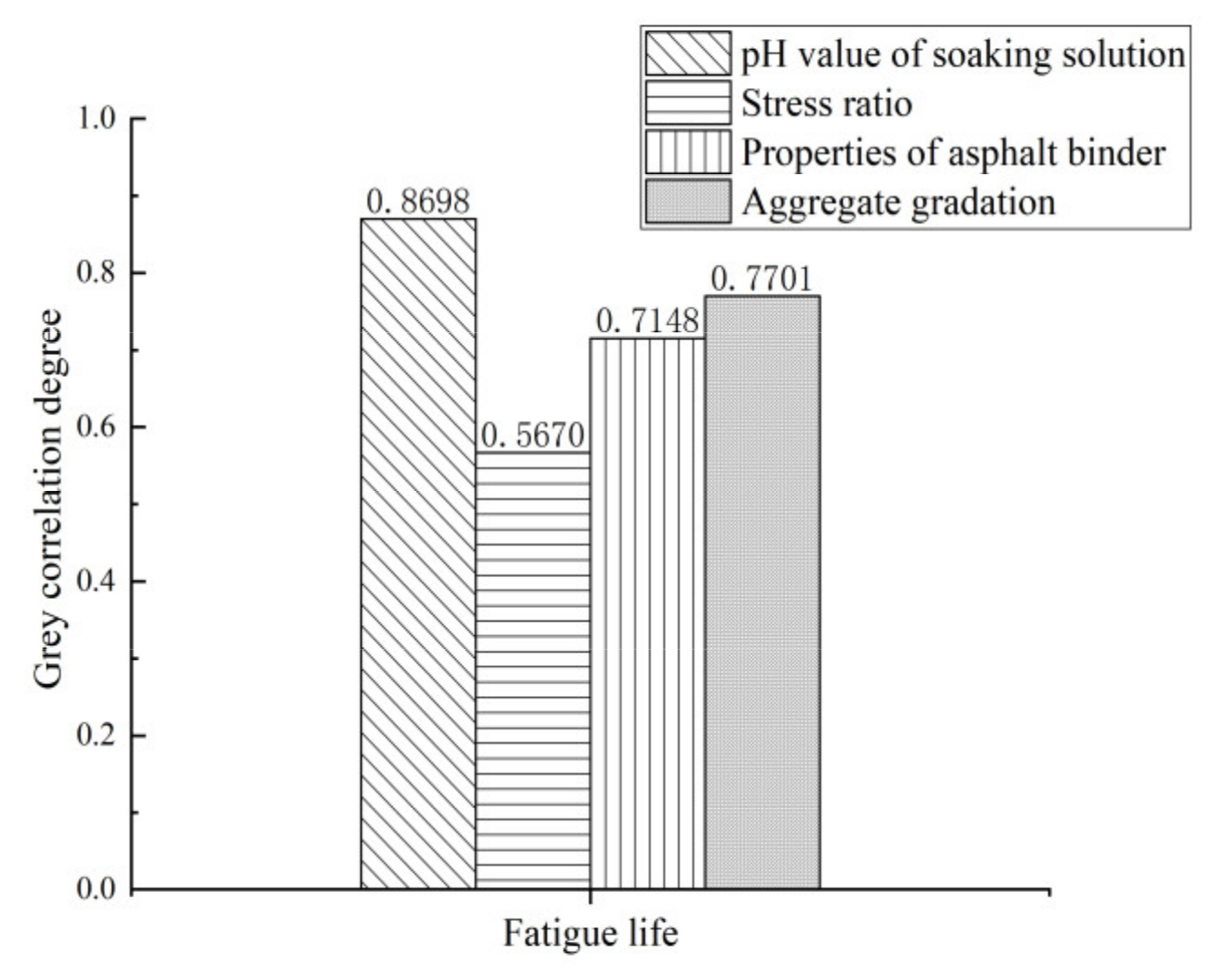
3.5.3. Fatigue Property of Asphalt Mixtures
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Larssen, T.; Lydersen, E.; Tang, D. Acid rain in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 2, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagase, Y.; Silva, E. Acid rain in China and Japan: A Game-theoretic Analysis. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2007, 37, 100–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larssen, T.; Carmichael, G.R. Acid rain and acidification in China: The importance of base cation deposition. Environ. Pollut. 2000, 1, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-hasan, S.J.A.; Balamuralikrishnan, R.; Altarawneh, M. Eco-Friendly asphalt approach for the development of sustainable roads. J. Human Earth Future 2020, 1, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadhim, Y.N.; Hussain, W.A.M.; Abdulrasool, A.T. The effect of animal bone ash on the mechanical properties of asphalt concrete. Civ. Eng. J. 2021, 7, 1741–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Guo, H.; Yang, B. Aging characteristics of bitumen from different bituminous pavement structures in service. Materials 2019, 12, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohammed, S.F.; Ismael, M.Q. Effect of polypropylene fibers on moisture susceptibility of warm mix asphalt. Civ. Eng. J. 2021, 7, 988–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, D.B.; Kern, L.; Loendersloot, R. A methodology based on pulse-velocity measurements to quantify the chemical degradation levels in thin mortar specimens. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 2018, 37, 37–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, L.; Visintin, P.; Bennett, T. Evaluation of accelerated degradation test methods for cementitious composites subject to sulfuric acid attack; application to conventional and alkali-activated concretes. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2017, 15, 87–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Che, Y.; Leng, F. Calcium leaching behavior of cementitious materials in hydrochloric acid solution. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Cheng, Z.; Tong, Z.; Wang, F.; Xie, S. The influence of acid rain on the performance of building mortar. J. Shenyang Jianzhu Univ. Nat. Sci. 2016, 32, 658–666. [Google Scholar]
- Eyssautier, S.; Marin, B.; Thomachot, C. Simulation of acid rain weathering effect on natural and artificial carbonate stones. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 748–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.; Zhang, X.; Wu, S. Influence of water solute exposure on the chemical evolution and rheological properties of asphalt. Materials 2018, 11, 983–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, G. Study on the effect of acid rain erosion on the road performance of steel slag asphalt mixture. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1972, 012108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Li, Y.; Ran, Y. Deterioration mechanism of CA mortar due to simulated acid rain. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 168, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Su, W.; Liu, Y. Laboratory investigation on the microstructure and performance of SBS modified epoxy asphalt binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 3, 270–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Bors, J. Alternate uses of epoxy asphalt on bridge decks and roadways. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 78, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Wen, X.J.; Jian, X. Study on viscosity evaluation of foamed epoxy asphalt. Adv. Mater. Res. 2015, 1082, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Hong, R.; Gu, C. Influence of fiber type on low-temperature fracture performance of presawed asphalt mixture beams. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 2018, 5087395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, C.; Wu, C.; Liu, K. Study on the durability of bamboo fiber asphalt mixture. Materials 2021, 7, 1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Han, S.; Jia, Z.Q. Research of the crack resistance of asphalt mixture based on the low-temperature bending test. J. Shandong. Univ. 2010, 75, 569–576. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, D.; Yan, K.; Ye, F. The laboratory performance of asphalt mixture with Amorphous poly alpha olefins (APAO) modified asphalt binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 188, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.T.; Zhen, J.L. Normalization method for asphalt mixture fatigue equation under different loading frequencies. J. Cent. South Univ. 2015, 22, 2761–2767. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, X.; Chen, Z.; Jiao, Z. Study on microstructure, rheology and thermal stability of cement epoxy asphalt mortar multiphase materials. Mag. Concr. Res. 2013, 65, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, K. Thermal, mechanical properties, and low-temperature performance of fibrous nanoclay-reinforced epoxy asphalt composites and their concretes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 12, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Qiang, W.; Jin, R. Rubber-like quasi-thermosetting polyetheramine-cured epoxy asphalt composites capable of being opened to traffic immediately. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18882. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, K.; Liu, K. Adhesion characteristics of graphene oxide modified asphalt unveiled by surface free energy and AFM-scanned micro-morphology. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 244, 404–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, G. Study on the effect of waterborne epoxy resins on the performance and microstructure of cement paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 10, 831–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Yang, K.; Qiu, X. Degradation mechanism of CA mortar in CRTS I slab ballastless railway track in the Southwest acid rain region of China—Materials analysis—ScienceDirect. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 149, 921–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Yan, X.; Cheng, Z. Mechanism of WMA splitting strength of Sasobit based on surface free energy. J. Build. Mater. 2015, 18, 669–673. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Guo, Q.; Tao, J. Aging mechanism of a diatomite-modified asphalt binder using Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy analysis. Materials 2019, 6, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Mills, J.; You, Z. Chemical characterization and oxidative aging of bio-asphalt and its compatibility with petroleum asphalt. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 1837–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Qian, Z. Research on low temperature performance of epoxy asphalt mixture. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2010, 34, 1124–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Mao, X.; Zhu, H. Water and erosion resistance of epoxy–acrylic–amine waterborne coatings: Effects of resin molecular weight, polar group and hydrophobic segment. Corros. Sci. 2013, 75, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.F.; Li, T.; Wu, C.F. Bamboo fiber has engineering properties and performance suitable as reinforcement for asphalt mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 290, 123240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, L.; Ren, M.; Shi, J. Experimental investigation on performance deterioration of asphalt mixture under freeze-thaw cycles. Int. J. Trans. Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R. Negative Temperature Gradient (in Ice); Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Zhang, Y. Analysis of leachate contaminants metals in polyphthalamide-modified asphalt and their environmental effects. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 275, 239–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Xiong, X. Erosion effect of acid rain on the technical properties of mineral aggregates. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 690, 3576–3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Guo, W.; Tan, Y. Permeability of asphalt mixtures exposed to freeze–thaw cycles. Cold. Reg. Sci. Technol. 2016, 123, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Li, H.; Guo, P. Effect of fibers on mixture design of stone matrix asphalt. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, C.; Zhang, H.; Huang, L. Long-term performance and microstructure of asphalt emulsion cold recycled mixture with different gradations. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 1, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Y.; Dang, S.Y.; Cui, D.Y. Durability test research of asphalt mixture with rubber particles under the condition of freeze-thaw cycle. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 919, 1096–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, R.; Wang, L. Durability prediction of asphalt mixture under freeze-thaw cycle based on GM (1,N) grey model. Adv. Mater. Res. 2015, 744, 1244–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Property | Penetration (25 °C, 0.1 mm) | Softening Point (°C) | Ductility (10 °C, cm) | Dynamic Viscosity (60 °C, Pa·s) | Mass Change after TFOT * (%) | Residual Penetration after TFOT (25 °C, %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epoxy asphalt | 39.8 | 98.0 | 45.0 | 29,365 | 0.00 | 91.3 |
| SBS-modified asphalt | 49.0 | 87.5 | 34.0 | 24,564 | −0.01 | 76.4 |
| 70# matrix asphalt | 64.0 | 48.0 | 24.7 | 500 | −0.02 | 69.8 |
| Mixture Type | Passing Rate (mm) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16 | 13.2 | 9.5 | 4.75 | 2.36 | 1.18 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.15 | 0.075 | |
| AC-13 | 100 | 94.7 | 75.5 | 43.6 | 30.0 | 23.1 | 15.7 | 11.2 | 9.4 | 7.4 |
| SMA-13 | 100 | 92.2 | 64.9 | 27.6 | 23.1 | 19.2 | 16.6 | 14.6 | 13.1 | 10.3 |
| OGFC-13 | 100 | 92.3 | 64.6 | 24.8 | 16.9 | 13.0 | 8.9 | 6.4 | 5.4 | 4.3 |
| Mixture Type | Gradation Type | Asphalt Type | Waste Rubber Powder | Modified Bamboo Fiber | Optimum Asphalt Content (%) | Void Fraction (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epoxy Asphalt | SBS-Modified Asphalt | 70# Matrix Asphalt | ||||||
| AC1 | AC-13 | √ | √ | √ | 5.5 | 3.0 | ||
| AC2 | √ | √ | √ | 5.3 | 3.0 | |||
| AC3 | √ | √ | √ | 5.0 | 3.0 | |||
| AC4 | √ | 4.9 | 3.5 | |||||
| SMA | SMA-13 | √ | √ | √ | 6.2 | 4.0 | ||
| OGFC | OGFC-13 | √ | √ | √ | 4.6 | 19.7 | ||
| Technical Index | Epoxy Asphalt | SBS-Modified Asphalt | 70# Matrix Asphalt |
|---|---|---|---|
| Softening point (°C) | 98.5 | 88.1 | 51.2 |
| Penetration (25 °C, 0.1 mm) | 38.2 | 47.6 | 73.0 |
| Ductility (10 °C, cm) | 45.3 | 34.5 | 25.2 |
| Dynamic viscosity(60 °C, Pa·s) | 29,524 | 24,713 | 517 |
| Sticky toughness(25 °C, N·m) | 21.4 | 19.2 | 12.6 |
| Toughness(25 °C, N·m) | 18.8 | 17.6 | 12.4 |
| Elastic recovery rate (%) | 93 | 86 | 82 |
| Mixture Type | pH = 2 | R2 | pH = 4.5 | R2 | pH = 7 | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AC1 | y = −4.7491x + 6.3062 | 0.9921 | y = −4.6516x + 6.58973 | 0.9913 | y = −4.1363x + 6.66242 | 0.9987 |
| AC2 | y = −5.7637x + 5.9202 | 0.9932 | y = −5.3321x + 6.08838 | 0.9947 | y = −4.7697x + 6.17921 | 0.9919 |
| AC3 | y = −5.9980x + 5.6859 | 0.9945 | y = −5.2070x + 5.82755 | 0.9991 | y = −5.9980x + 5.68598 | 0.9995 |
| AC4 | y = −4.8106x + 5.9741 | 0.9966 | y = −4.8006x + 6.38764 | 0.9928 | y = −4.8106x + 5.97415 | 0.9955 |
| SMA | y = −4.6722x + 6.0570 | 0.9917 | y = −4.4152x + 6.44897 | 0.9932 | y = −4.1029x + 6.54462 | 0.9908 |
| OGFC | y = −6.8321x + 5.5940 | 0.9918 | y = −5.2975x + 5.62817 | 0.9954 | y = −4.8933x + 5.75816 | 0.9908 |
| Evaluation Index | Serial Number | Maximum Flexural Tensile Strain (×10−6 με) | S0 (%) | Aging Time (h) | pH Value of Acid Solution | Wet-Dry Cycle Immersion Period (Cycle) | 4.75 mm Pass Rate (%) | Ductility (10 °C, cm) | Dynamic Viscosity (60 °C, Pa·s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low-temperature stability | 1 | 3483 | 0 | 7 | 1 | 43.6 | 24.7 | ||
| 2 | 2063 | 30 | 4.5 | 3 | 24.8 | 34 | |||
| 3 | 2307 | 90 | 2 | 3 | 27.6 | 45 | |||
| 4 | 2514 | 60 | 4.5 | 5 | 43.6 | 45 | |||
| 5 | 3014 | 120 | 7 | 5 | 27.6 | 24.7 | |||
| 6 | 1874 | 120 | 2 | 1 | 24.8 | 34 | |||
| Moisture stability | 1 | 96 | 0 | 7 | 1 | 43.6 | 29,365 | ||
| 2 | 91.5 | 30 | 4.5 | 3 | 24.8 | 24,564 | |||
| 3 | 65.7 | 60 | 2 | 3 | 27.6 | 500 | |||
| 4 | 74.2 | 90 | 4.5 | 5 | 43.6 | 500 | |||
| 5 | 86.5 | 120 | 7 | 5 | 27.6 | 29,365 | |||
| 6 | 87.2 | 120 | 2 | 1 | 24.8 | 24,564 |
| Serial Number | TSR (%) | pH Value of Acid Solution | Freeze-Thaw Cycle Times (Cycle) | Dynamic Viscosity (60 °C, Pa·s) | 4.75 mm PASS Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 84.9 | 2 | 2 | 29,365 | 43.6 |
| 2 | 77.3 | 4.5 | 4 | 24,564 | 27.6 |
| 3 | 63.4 | 4.5 | 6 | 500 | 24.8 |
| 4 | 78.4 | 7 | 4 | 24,564 | 43.6 |
| 5 | 76.3 | 7 | 6 | 29,365 | 27.6 |
| Serial Number | Fatigue Life (Times) | pH Value of Soaking Solution | Tensile Stress Level | Elastic Recovery Rate (%) | 4.75 mm Pass Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 21,244 | 7 | 0.3 | 93 | 43.6 |
| 2 | 17,643 | 7 | 0.4 | 86 | 27.6 |
| 3 | 9477 | 4.5 | 0.5 | 82 | 43.6 |
| 4 | 12,737 | 4.5 | 0.3 | 86 | 27.6 |
| 5 | 4227 | 2 | 0.4 | 82 | 24.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, J.; Chen, Q.; Du, J.; Liu, K.; Jiang, K. Study on the Durability of Acid Rain Erosion-Resistant Asphalt Mixtures. Materials 2022, 15, 1849. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15051849
Wei J, Chen Q, Du J, Liu K, Jiang K. Study on the Durability of Acid Rain Erosion-Resistant Asphalt Mixtures. Materials. 2022; 15(5):1849. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15051849
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Jiatuo, Quansheng Chen, Jiaying Du, Kefei Liu, and Kang Jiang. 2022. "Study on the Durability of Acid Rain Erosion-Resistant Asphalt Mixtures" Materials 15, no. 5: 1849. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15051849
APA StyleWei, J., Chen, Q., Du, J., Liu, K., & Jiang, K. (2022). Study on the Durability of Acid Rain Erosion-Resistant Asphalt Mixtures. Materials, 15(5), 1849. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15051849





