Failure Analysis of a C-276 Alloy Pipe in a Controlled Decomposition Reactor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Experimental Procedures
3. Results
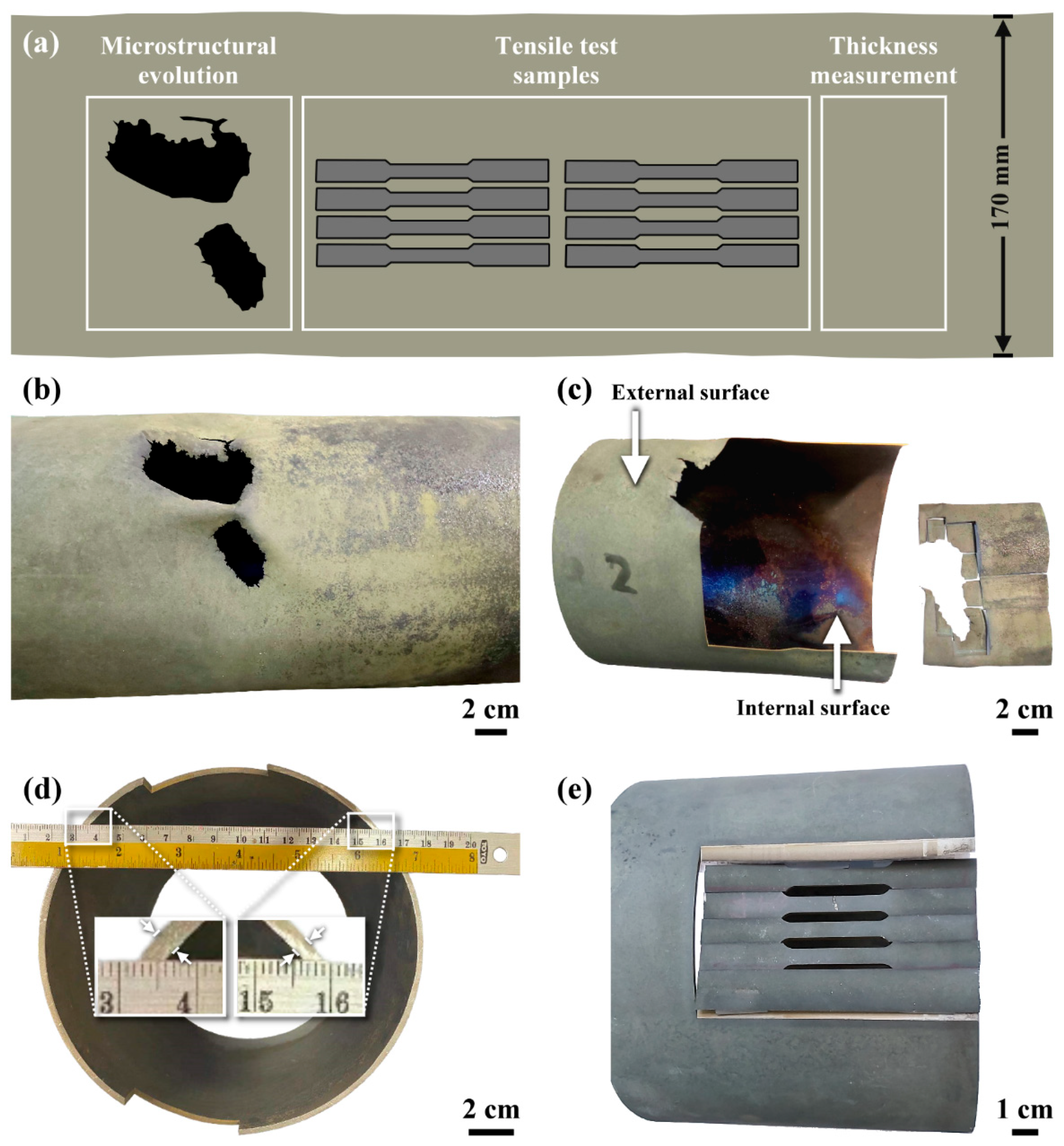
3.1. Visual Inspection
3.2. Mechanical Properties Evaluation
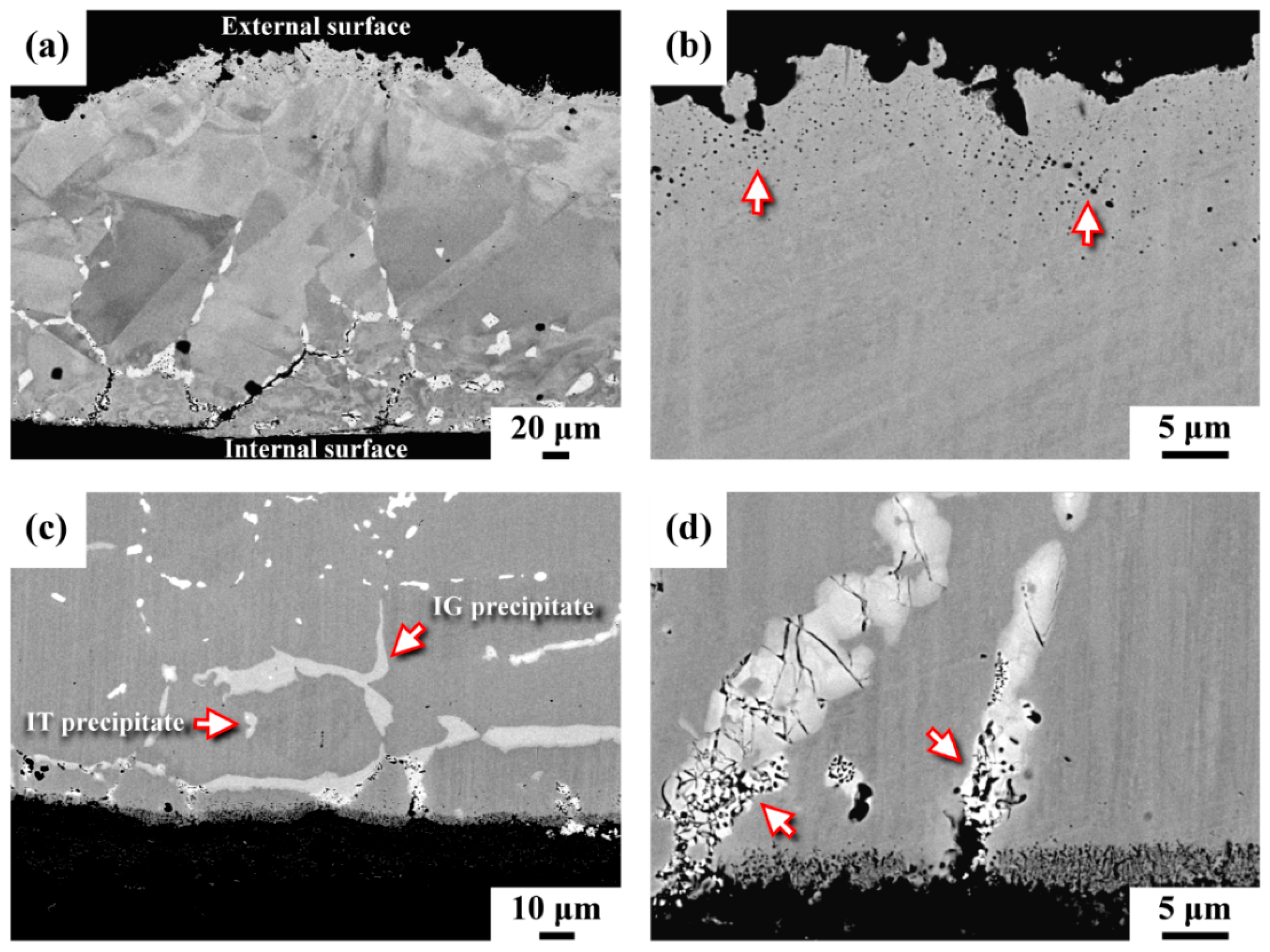
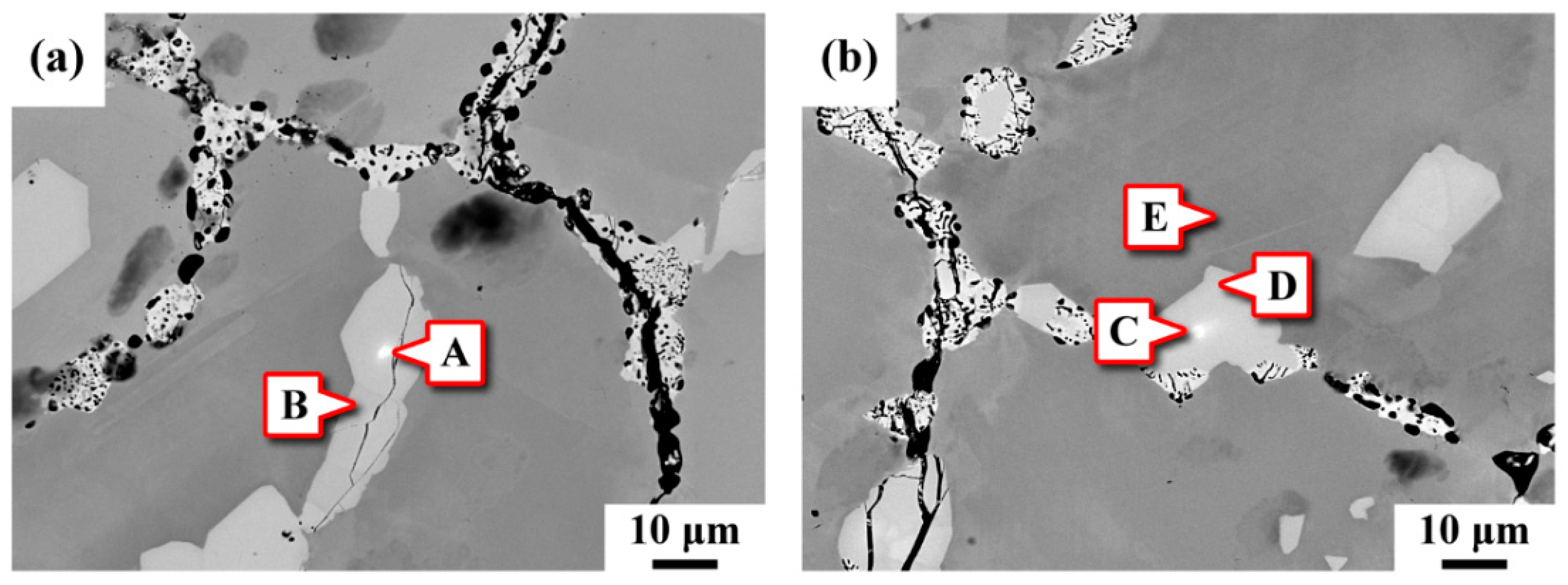
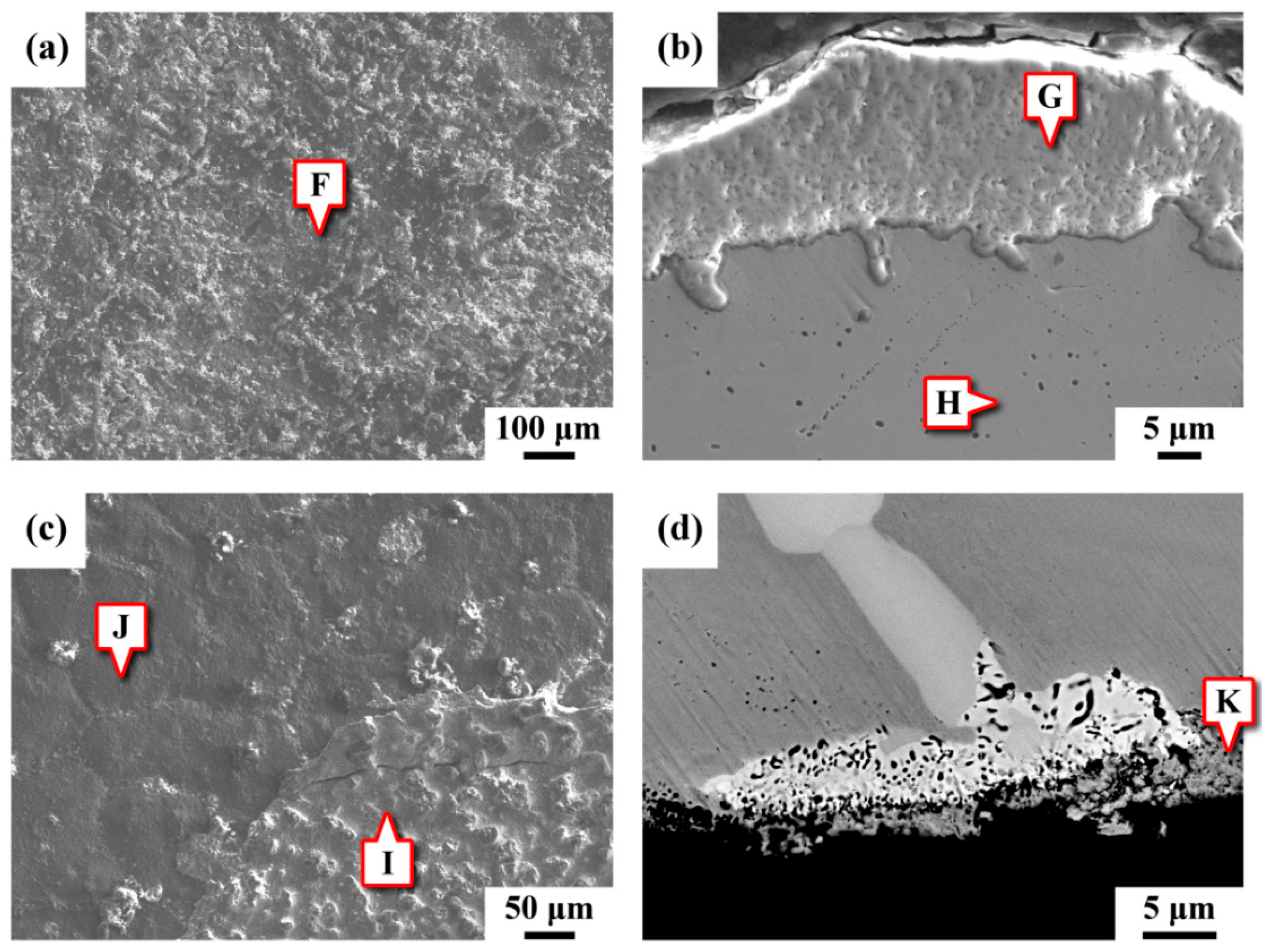
3.3. Microstructural Observation
3.4. Chemical Composition Analysis
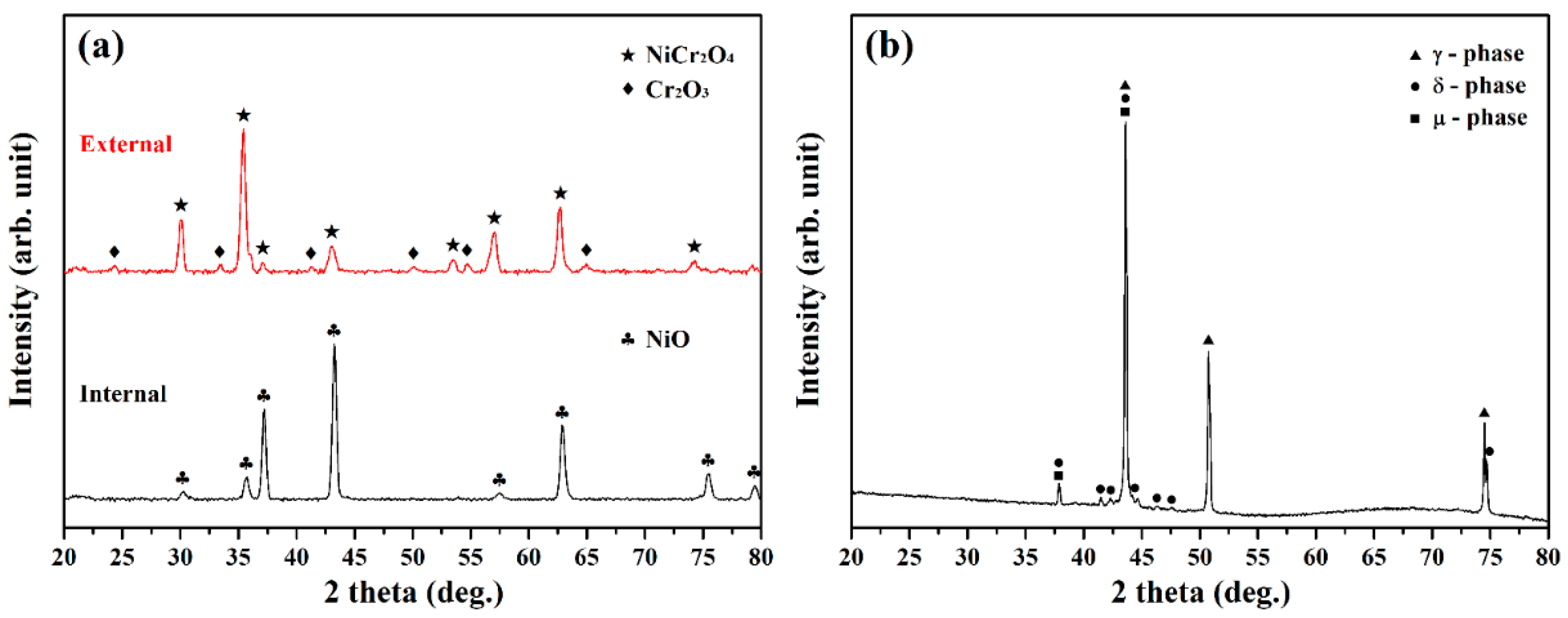
3.5. Crystal Structure Determination
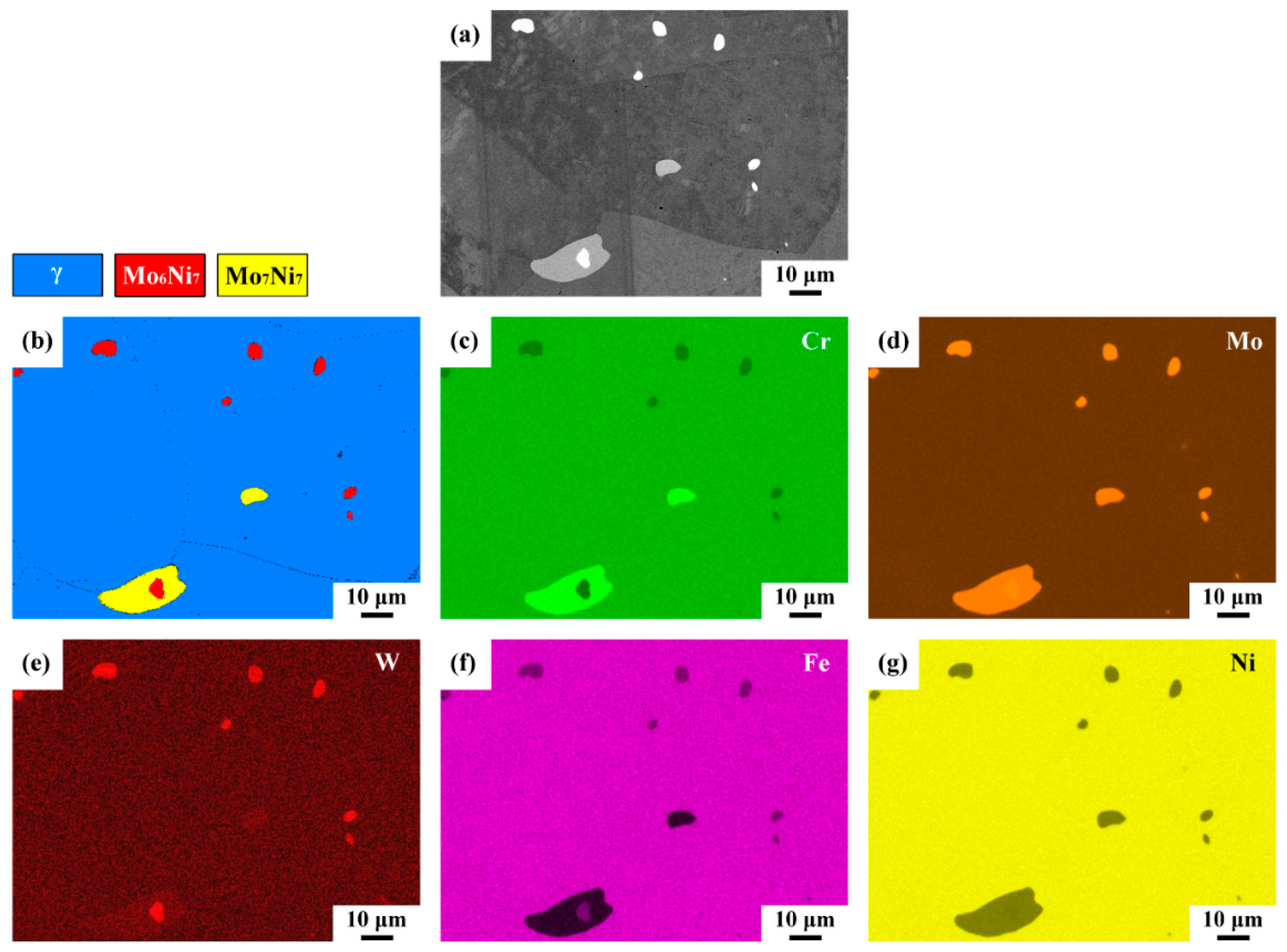
3.6. Results of Phase and Elemental Mapping
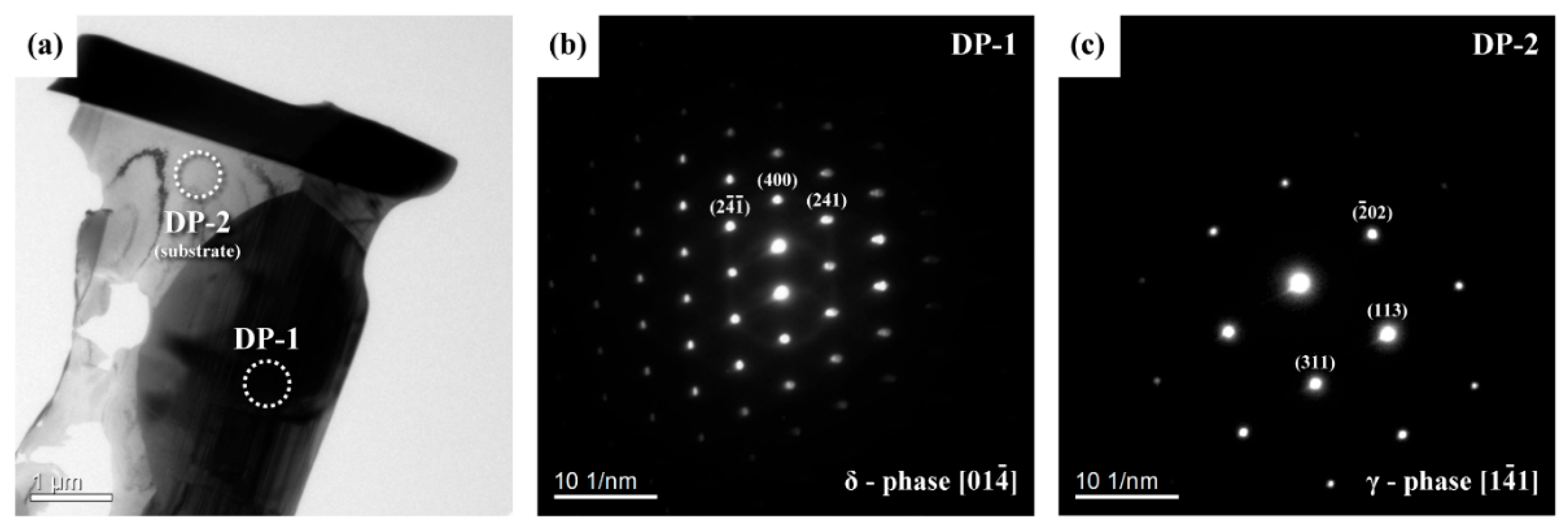
3.7. Results of TEM Analysis
3.8. SEM Fractography
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The C-276 pipe used in a CDR system to catch decomposed perfluorinated compounds was etched to uneven thickness. The zone near the external surface had a porous structure, whereas the microcracks tended to initiate and grow from the inner surface of the pipe. The induced thermal stress in the pipe caused severe cracking of the grain boundary precipitates. Moreover, the grain boundary precipitates were corroded preferentially, resulting in the formation of fine pores within the precipitates and around them. The spalling of the corroded segments was responsible for the rapid thinning in the wall of the C-276 pipe.
- Two kinds of precipitates were present in the ruptured C-276 pipe; the intergranular (IG) precipitates were coarser and greater in amount than the intragranular (IT) precipitates. The coarse precipitates at the grain boundaries were Mo7Ni7 (δ) phase, which was rich in Mo and Cr. By contrast, the fine precipitates dispersed intragranularly or embedded in the δ phase were the μ phase (Mo6Ni7) enriched in Mo and W.
- After service at elevated temperature, the aggregation of W assisted the transformation of δ to μ phase in the aged C-276 pipe. Therefore, fine μ precipitates were found to be embedded in the coarse δ in the ruptured pipe. Moreover, numerous precipitates present in the matrix and along the grain boundaries caused a significant loss in the strength and ductility of the C-276 pipe.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tawancy, H.M.; Herchenroeder, R.B.; Asphahani, A.I. High-Performance Ni-Cr-Mo-W Alloys. JOM 1983, 35, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, M.; Berkowitz, B.J.; Scanlon, J.C. Electron Microscopic Analysis of Heterogeneous Precipitates in Hastelloy C-276. Metall. Trans. A 1982, 13, 979–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawancy, H.M. Precipitation characteristics of μ-phase in wrought nickel-base alloys and its effect on their propert. J. Mater. Sci. 1996, 31, 3929–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, J.I.; Shaikh, M.A.; Ahmad, M.; Iqbal, M.; Shoaib, K.A.; Ahmad, W. Effect of aging on the hardness and impact properties of Hastelloy C-276. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 2001, 20, 333–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Ma, Y.H.; Lou, L.H.; Hu, Z.Q. μ phase in a nickel base directionally solidified alloy. Mater. Trans. 2005, 46, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, L.; Cui, Y.; Feng, Q.; Cheng, C. Effects of High-Temperature Aging on Precipitation and Corrosion Behavior of a Ni-Cr-Mo-Based Hastelloy C276 Superalloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2020, 29, 2026–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.-T.; Chen, H.-P.; Hsien, W.-Y. A review of uses, environmental hazards and recovery/recycle technologies of perfluorocarbons (PFCs) emissions from the semiconductor manufacturing processes. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2002, 15, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.Y.-C.; Panchangam, S.C.; Lo, C.-C. The impact of semiconductor, electronics and optoelectronic industries on downstream perfluorinated chemical contamination in Taiwanese rivers. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1365–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golja, B.; Barkanic, J.A.; Hoff, A. A review of nitrogen trifluoride for dry etching in microelectronics processing. Microelectron. J. 1985, 16, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.-T. Environmental and health risk analysis of nitrogen trifluoride (NF3), a toxic and potent greenhouse gas. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 159, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, R.F.; Mühle, J.; Salameh, P.K.; Harth, C.M. Nitrogen trifluoride in the global atmosphere. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L20821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robson, J.I.; Gohar, L.K.; Hurley, M.D.; Shine, K.P.; Wallington, T.J. Revised IR spectrum, radiative efficiency and global warming potential of nitrogen trifluoride. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L10817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakkar, A.; Ahmed, M.M.Z.; Alsaleh, N.A.; Seleman, M.M.E.-S.; Ataya, S. Microstructure, wear, and corrosion characterization of high TiC content Inconel 625 matrix composites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 1102–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, M.; Arivazhagan, N.; Nageswara Rao, M.; Madhusudhan Reddy, G. Improvement of Microstructure and Mechanical Behavior of Gas Tungsten Arc Weldments of Alloy C-276 by Current Pulsing. Acta Metall. Sin. 2015, 28, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, M.; Akhter, J.I.; Akhtar, M.; Iqbal, M.; Ahmed, E.; Choudhry, M.A. Microstructure and hardness studies of the electron beam welded zone of Hastelloy C-276. J. Alloys Compd. 2005, 390, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikandan, M.; Hari, P.; Vishnu, G.; Arivarasu, M.; Ramkumar, K.D.; Arivazhagan, N.; Rao, M.N.; Reddy, G. Investigation of microstructure and mechanical properties of super alloy C-276 by continuous Nd: YAG laser welding. Procedia Mater. Sci. 2014, 5, 2233–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gozlan, E.; Bamberger, M.; Dirnfeld, S.F.; Prinz, B.; Klodt, J. Topologically close-packed precipitations and phase diagrams of Ni-Mo-Cr and Ni-Mo-Fe and of Ni-Mo-Fe with constant additions of chromium. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1991, 141, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoemaker, C.B.; Shoemaker, D.P. The crystal structure of the δ phase Mo-Ni. Acta Crystallogr. 1963, 16, 997–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaev, S.V.; Kerimov, E.Y.; Slyusarenko, E.M. Phase equilibria in four-component system Ni-Nb-Mo-Re at 1375 K. Inorg. Mater. Appl. Res. 2014, 5, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Lu, Y.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Zhou, X. Effect of long-term aging on microstructure and mechanical properties of alloy C276. Acta Metall. Sin. 2013, 49, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, R.B. Thermal Stability of Hastelloy Alloy C-276. Corrosion 2013, 25, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthew, F. Updated Sublattice Models of Topologically Close Packed Phases with a Revised Phase Description of σ Phase. Master’s Thesis, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Tang, R.; Yin, K.; Luo, X.; Zhang, L. Corrosion behavior of Hastelloy C-276 in supercritical water. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 2092–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Sridharan, K.; Allen, T.R. Corrosion Behavior of Alloys 625 and 718 in Supercritical Water. Corrosion 2007, 63, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | Thickness (mm) | Yield Strength (MPa) | Ultimate Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 2.55 | 297 | 550 | 27 |
| A2 | 2.52 | 281 | 540 | 31 |
| A3 | 2.51 | 290 | 577 | 35 |
| B1 | 0.85 | 271 | 505 | 11 |
| B2 | 0.71 | 266 | 454 | 5 |
| B3 | 0.66 | 252 | 452 | 4 |
| Element | Site A | Site B | Site C | Site D | Site E | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt.% | at. % | wt.% | at. % | wt.% | at. % | wt.% | at. % | wt.% | at. % | |
| C | 0.1 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 0.1 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 1.0 |
| O | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Cr | 7.1 | 12.1 | 21.4 | 30.3 | 7.0 | 12.3 | 21.5 | 30.3 | 13.2 | 15.8 |
| Mo | 37.9 | 35.1 | 36.0 | 27.7 | 34.2 | 32.5 | 36.7 | 28.0 | 9.0 | 5.8 |
| W | 23.6 | 11.4 | 4.5 | 1.8 | 26.4 | 13.1 | 4.9 | 2.0 | 1.8 | 0.5 |
| Fe | 2.1 | 3.3 | 1.2 | 1.6 | 2.0 | 3.3 | 1.1 | 1.5 | 6.7 | 7.4 |
| Ni | bal. | bal. | bal. | bal. | bal. | bal. | bal. | bal. | bal. | bal. |
| Element | Site F | Site G | Site H | Site I | Site J | Site K | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt.% | at. % | wt.% | at. % | wt.% | at. % | wt.% | at. % | wt.% | at. % | wt.% | at. % | |
| C | 0.9 | 2.6 | 0.5 | 1.3 | 0.2 | 1.0 | 1.6 | 5.5 | 2.4 | 7.4 | 0.4 | 1.4 |
| O | 26.4 | 55.0 | 37.2 | 68.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 12.8 | 33.5 | 24.4 | 56.8 | 9.1 | 28.5 |
| Cr | 51.4 | 32.9 | 58.3 | 30.1 | 7.1 | 8.7 | 6.9 | 5.5 | 9.5 | 6.8 | 11.6 | 11.2 |
| Mo | 9.1 | 3.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 18.2 | 12.1 | 0.4 | 0.2 | 38.6 | 15.0 | 14.2 | 7.4 |
| W | 1.6 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 3.7 | 1.3 | 1.7 | 0.1 | 4.6 | 0.9 | 3.0 | 0.8 |
| Fe | 1.9 | 1.1 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 6.2 | 7.1 | 2.8 | 2.1 | 1.9 | 1.1 | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| Ni | bal. | bal. | bal. | bal. | bal. | bal. | bal. | bal. | bal. | bal. | bal. | bal. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, T.-C.; Yue, G.-L.; Kai, W.; Shiue, R.-K.; Tsay, L.-W. Failure Analysis of a C-276 Alloy Pipe in a Controlled Decomposition Reactor. Materials 2022, 15, 2483. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15072483
Chen T-C, Yue G-L, Kai W, Shiue R-K, Tsay L-W. Failure Analysis of a C-276 Alloy Pipe in a Controlled Decomposition Reactor. Materials. 2022; 15(7):2483. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15072483
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Tai-Cheng, Gui-Lin Yue, Wu Kai, Ren-Kae Shiue, and Leu-Wen Tsay. 2022. "Failure Analysis of a C-276 Alloy Pipe in a Controlled Decomposition Reactor" Materials 15, no. 7: 2483. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15072483
APA StyleChen, T.-C., Yue, G.-L., Kai, W., Shiue, R.-K., & Tsay, L.-W. (2022). Failure Analysis of a C-276 Alloy Pipe in a Controlled Decomposition Reactor. Materials, 15(7), 2483. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15072483








