Oxidation of Cyclohexane/Cyclohexanone Mixture with Oxygen as Alternative Method of Adipic Acid Synthesis
Abstract
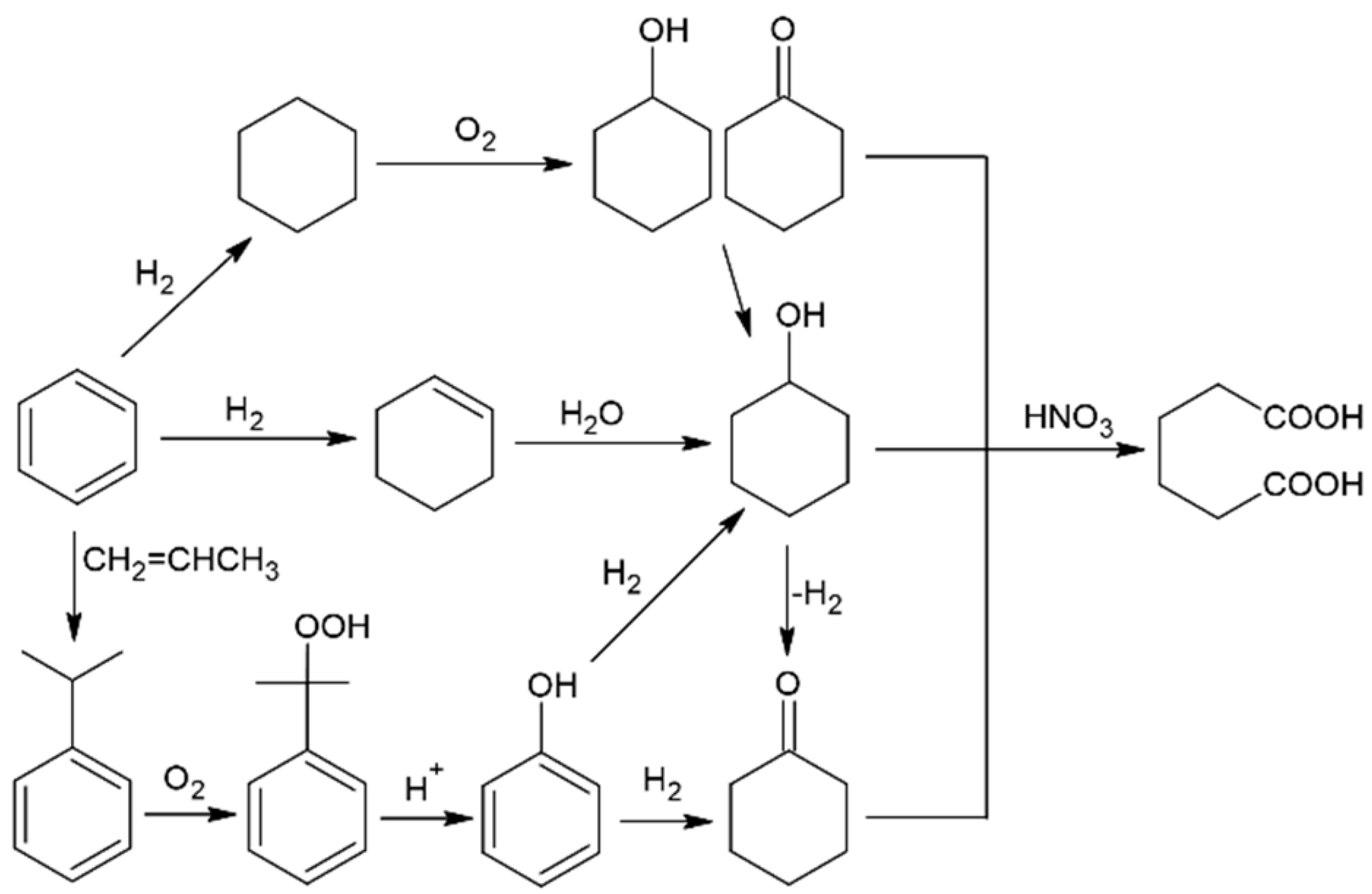
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Oxidation Process
2.3. GC Analysis
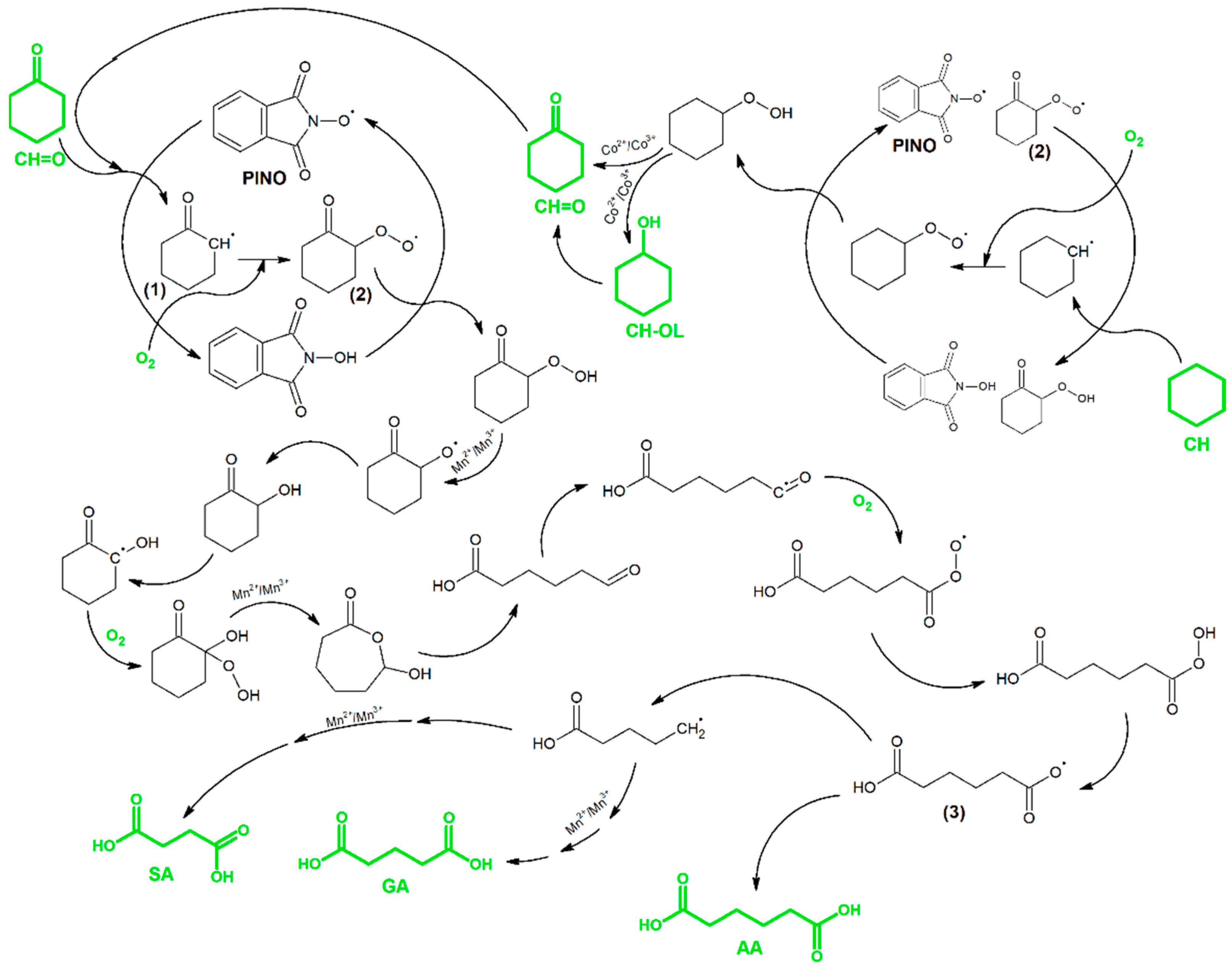
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Influence of Solvent
- type and amount of catalyst,
- cyclohexane to cyclohexanone ratio (v/v),
- temperature,
- time,
- type of oxidizing agent.
3.2. Influence of Catalyst Type and Amount
3.3. Effect of CH/CH=O Ratio
3.4. Influence of Temperature and Reaction Time
3.5. Influence of the Oxidizing Agent
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lisicki, D.; Orlińska, B. Oxidation of cyclic ketones to dicarboxylic acids. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2018, 20, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Musser, M.T. Adipic Acid. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios, J.; Lebeau, J.; Yang, T.; Li, S.; Lynch, M.D. A critical review on the progress and challenges to a more sustainable, cost competitive synthesis of adipic acid. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 3172–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwahama, T.; Syojyo, K.; Sakaguchi, S.; Ishii, Y. Direct Conversion of Cyclohexane into Adipic Acid with Molecular Ox-ygen Catalyzed by N -Hydroxyphthalimide Combined with Mn(Acac)2 and Co(OAc)2. Org. Process Res. Dev. 1998, 2, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavani, F.; Ferroni, L.; Frattini, A.; Lucarelli, C.; Mazzini, A.; Raabova, K.; Alini, S.; Accorinti, P.; Babini, P. Evidence for the presence of alternative mechanisms in the oxidation of cyclohexanone to adipic acid with oxygen, catalysed by Keggin polyoxometalates. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2011, 391, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besson, M.; Gauthard, F.; Horvath, B.; Gallezot, P. Catalytic Oxidation with Air of Cyclohexanone to Dicarboxylic Acids on Synthetic Carbons. Effect of Supported Metals and Solvents. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 2461–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhandari, S.; Khatun, R.; Poddar, M.K.; Kothari, A.C.; Bal, R. Direct oxidation of cyclohexane to adipic acid in air over Co3O4@ZrO2 nanostructured catalyst. Mol. Catal. 2022, 528, 112473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damm, M.; Gutmann, B.; Kappe, C.O. Continuous-Flow Synthesis of Adipic Acid from Cyclohexene Using Hydrogen Peroxide in High-Temperature Explosive Regimes. ChemSusChem 2013, 6, 978–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- She, M.; Gu, R.; Meng, D.; Yang, H.; Wen, Y.; Qian, X.; Guo, X.; Ding, W. Nanosheets of Ni-SAPO-34 Molecular Sieve for Selective Oxidation of Cyclohexanone to Adipic Acid. Chem. A Eur. J. 2022, 28, e202200696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mekala, S.P.; Prabu, M.; Gawali, S.D.; Gopakumar, K.; Gogoi, P.; Bhatkar, A.R.; Mohapatra, G.; Unnikrishanan, E.; Raja, T. Green synthesis of cyclohexanone to adipic acid over Fe–W oxides incorporated mesoporous carbon support. Catal. Commun. 2022, 168, 106466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tella, A.C.; Isaac, A.Y.; Clayton, H.S.; Ogunlaja, A.S.; Venugopalan, A.T.; Marimuthu, P.; Thirumalaiswamy, R. Synthesis and Crystal Structures of Mn(II) and Co(II) Complexes as Catalysts for Oxidation of Cyclohexanone. Inorganics 2022, 10, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.P.C.; Martins, L.M.D.R.S.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. N2O-Free single-pot conversion of cyclohexane to adipic acid catalysed by an iron(ii) scorpionate complex. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 1499–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noyori, R.; Aoki, M.; Sato, K. Green Oxidation with Aqueous Hydrogen Peroxide. Chem. Commun. 2003, 3, 1977–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peckh, K.; Lisicki, D.; Pabich, E.; Orlińska, B. Oxidation of 1,2-cyclohexanediol as a step for adipic acid synthesis. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 110, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, M.; Li, H. Sustainable Routes for the Synthesis of Renewable Adipic Acid from Biomass Derivatives. ChemSusChem 2022, 15, e202101531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, M.A.; Martins, L.M.D.R.S. Organocatalysis Meets Hydrocarbon Oxyfunctionalization: The Role of N -Hydroxyimides. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 2021, 4715–4727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melone, L.; Punta, C. Metal-Free Aerobic Oxidations Mediated by N-Hydroxyphthalimide. A Concise Review. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2013, 9, 1296–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kulsrestha, G.N.; Shankar, U.; Sharma, J.S.; Singh, J. One-step oxidation of cyclohexane to adipic acid. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1991, 50, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermans, I.; Jacobs, P.A.; Peeters, J. To the Core of Autocatalysis in Cyclohexane Autoxidation. Chem. A Eur. J. 2006, 12, 4229–4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, A.; Tanaka, K.; Ogawa, H.; Matsuoka, Y.; Fujimori, M.; Nagamori, Y.; Hamachi, H.; Kimura, K. An Industrial Process for Adipic Acid Production by the Liquid-Phase Oxidation of Cyclohexanone with Molecular Oxygen. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2003, 76, 1993–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlińska, B.; Zawadiak, J. Aerobic oxidation of isopropylaromatic hydrocarbons to hydroperoxides catalyzed by N-hydroxyphthalimide. React. Kinet. Mech. Catal. 2013, 110, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Entry | Solvent | Solvent:CH:CH=O v/v/v | Conv.CH [%] | Conv.CH=O [%] | Sel.CH-OL [%] | Sel.AA [%] | Sel.GA [%] | Sel.SA [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | 0:1:0 | -(1) | traces (2) | traces | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | - | 0:1:1 | 37 | 69 | 3 | 36 | 9 | 8 |
| 3 | MeCN | 2:1:1 | 66 | 65 | 1 | 40 | 12 | 10 |
| 4 | PhCN | 2:1:1 | 53 | 84 | 2 | 43 | 11 | 10 |
| 5 | AcOH | 2:1:1 | 68 | 99 | 1 | 49 | 13 | 12 |
| 6 | AcOH | 2:1:0 | 39 | 0 (2) | 0 | 31 | 4 | 2 |
| Entry | Co(acac)2 [mol%] | Mn(acac)2 [mol%] | NHPI [mol%] | Conv.CH [%] | Conv.CH=O [%] | Sel.CH-OL [%] | Sel.AA [%] | Sel.GA [%] | Sel.SA [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.050 | 0.025 | 0.50 | 37 | 65 | 4 | 37 | 11 | 10 |
| 2 | 0.125 | 0.025 | 0.50 | 58 | 68 | 1 | 28 | 8 | 7 |
| 3 | 0.250 | 0.025 | 0.50 | 59 | 65 | 0 | 26 | 8 | 7 |
| 4 | - | 0.250 | 0.50 | 18 | 26 | 7 | 50 | 15 | 11 |
| 5 | 0.025 | 0.250 | 0.50 | 38 | 75 | 2 | 41 | 10 | 8 |
| 6 | 0.050 | 0.250 | 0.50 | 51 | 78 | 0 | 35 | 8 | 7 |
| 7 | 0.250 | 0.250 | 0.50 | 56 | 76 | 0 | 27 | 2 | 1 |
| 8 | 0.050 | - | 0.50 | 42 | 27 | 6 | 29 | 13 | 11 |
| 9 | 0.050 | 0.025 | 0.50 | 37 | 65 | 4 | 37 | 11 | 10 |
| 10 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 0.50 | 40 | 75 | 3 | 44 | 11 | 10 |
| 11 | 0.050 | 0.125 | 0.50 | 38 | 83 | 1 | 46 | 11 | 10 |
| 12 | 0.050 | 0.250 | 0.50 | 51 | 78 | 0 | 35 | 8 | 7 |
| 13 | 0.050 | 0.250 | 0.00 | 41 | 77 | 2 | 36 | 9 | 8 |
| 14 | 0.050 | 0.250 | 0.25 | 40 | 75 | 2 | 35 | 7 | 6 |
| 15 | 0.050 | 0.250 | 0.50 | 51 | 78 | 0 | 35 | 8 | 7 |
| 16 | 0.050 | 0.250 | 2.50 | 51 | 67 | 1 | 37 | 9 | 8 |
| Entry | CH:CH=O [v/v] | Conv.CH [%] | Conv.CH=O [%] | Sel.CH-OL [%] | Sel.AA [%] | Sel.GA [%] | Sel.SA [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cyclohexane | -1 | - | traces | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | Cyclohexanone | - | 55 | - | 30 | 8 | 7 |
| 3 | 7:1 | 30 | 96 | 1 | 43 | 11 | 9 |
| 4 | 3:1 | 37 | 80 | 2 | 46 | 11 | 10 |
| 5 | 1:1 | 37 | 69 | 3 | 36 | 9 | 8 |
| Entry | Temp. [°C] | Time [h] | Conv.CH [%] | Conv.CH=O [%] | Sel.CH-OL [%] | Sel.AA [%] | Sel.GA [%] | Sel.SA [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 70 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 14 | 53 | 10 | 10 |
| 2 | 80 | 2 | 40 | 78 | 2 | 49 | 11 | 10 |
| 3 | 90 | 2 | 53 | 81 | 2 | 48 | 10 | 10 |
| 4 | 100 | 2 | 51 | 67 | 1 | 37 | 9 | 8 |
| 5 | 80 | 2 | 40 | 78 | 2 | 49 | 11 | 10 |
| 6 | 80 | 4 | 57 | 88 | 2 | 44 | 9 | 8 |
| 7 | 80 | 6 | 68 | 86 | 1 | 37 | 8 | 9 |
| 8 | 80 | 8 | 77 | 89 | 1 | 33 | 8 | 9 |
| Entry | Oxidizer | Pressure [MPa] | Time [h] | Conv.CH [%] | Conv.CH=O [%] | Sel.CH-OL [%] | Sel.AA [%] | Sel.GA [%] | Sel.SA [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Oxygen | 1 | 2 | 51 | 67 | 1 | 37 | 9 | 8 |
| 2 | Air | 2 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 29 | 28 | 2 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lisicki, D.; Orlińska, B.; Marek, A.A.; Bińczak, J.; Dziuba, K.; Martyniuk, T. Oxidation of Cyclohexane/Cyclohexanone Mixture with Oxygen as Alternative Method of Adipic Acid Synthesis. Materials 2023, 16, 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16010298
Lisicki D, Orlińska B, Marek AA, Bińczak J, Dziuba K, Martyniuk T. Oxidation of Cyclohexane/Cyclohexanone Mixture with Oxygen as Alternative Method of Adipic Acid Synthesis. Materials. 2023; 16(1):298. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16010298
Chicago/Turabian StyleLisicki, Dawid, Beata Orlińska, Adam A. Marek, Jakub Bińczak, Krzysztof Dziuba, and Tomasz Martyniuk. 2023. "Oxidation of Cyclohexane/Cyclohexanone Mixture with Oxygen as Alternative Method of Adipic Acid Synthesis" Materials 16, no. 1: 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16010298
APA StyleLisicki, D., Orlińska, B., Marek, A. A., Bińczak, J., Dziuba, K., & Martyniuk, T. (2023). Oxidation of Cyclohexane/Cyclohexanone Mixture with Oxygen as Alternative Method of Adipic Acid Synthesis. Materials, 16(1), 298. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16010298







