The Influence of Annealing and Film Thickness on the Specific Properties of Co40Fe40Y20 Films
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
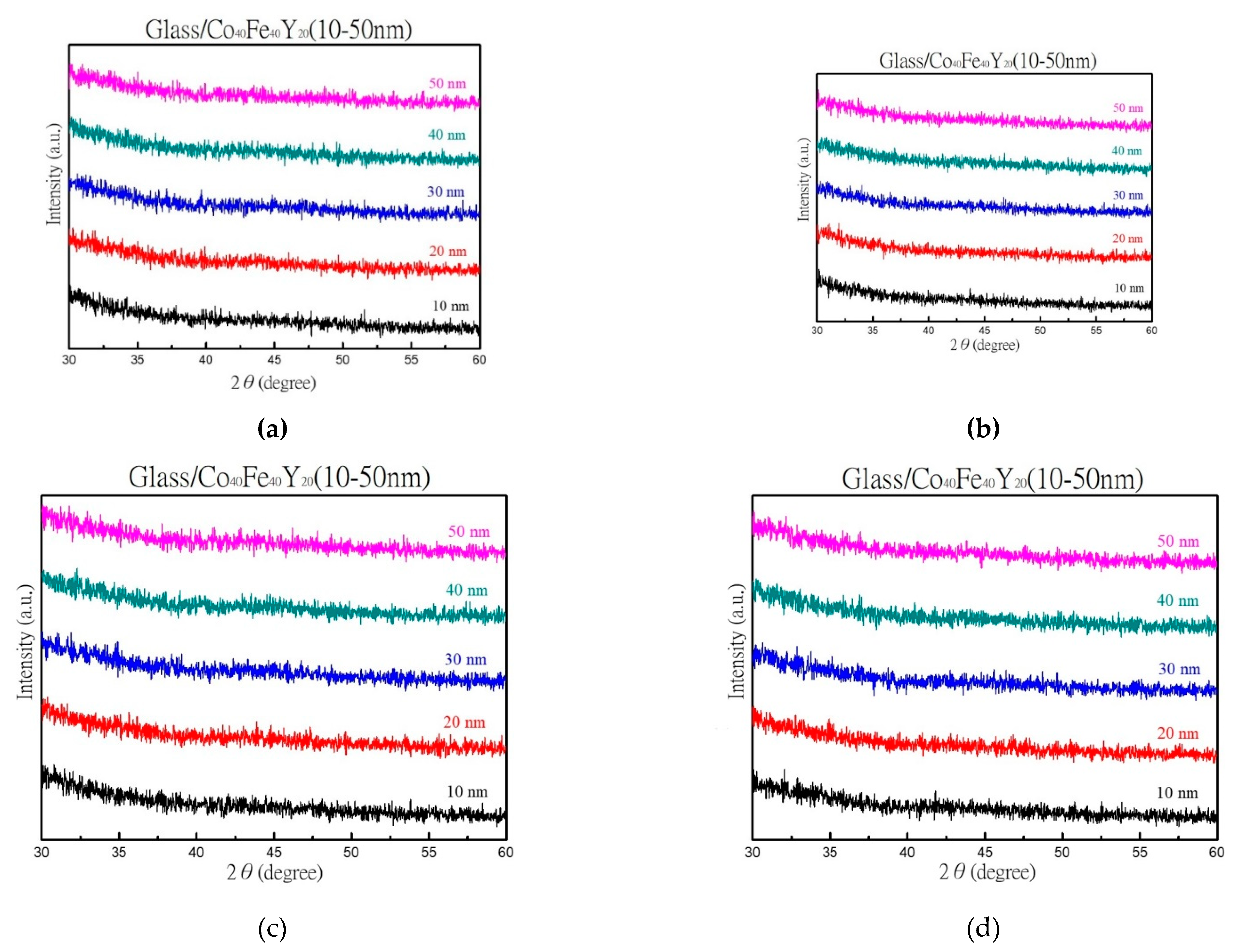
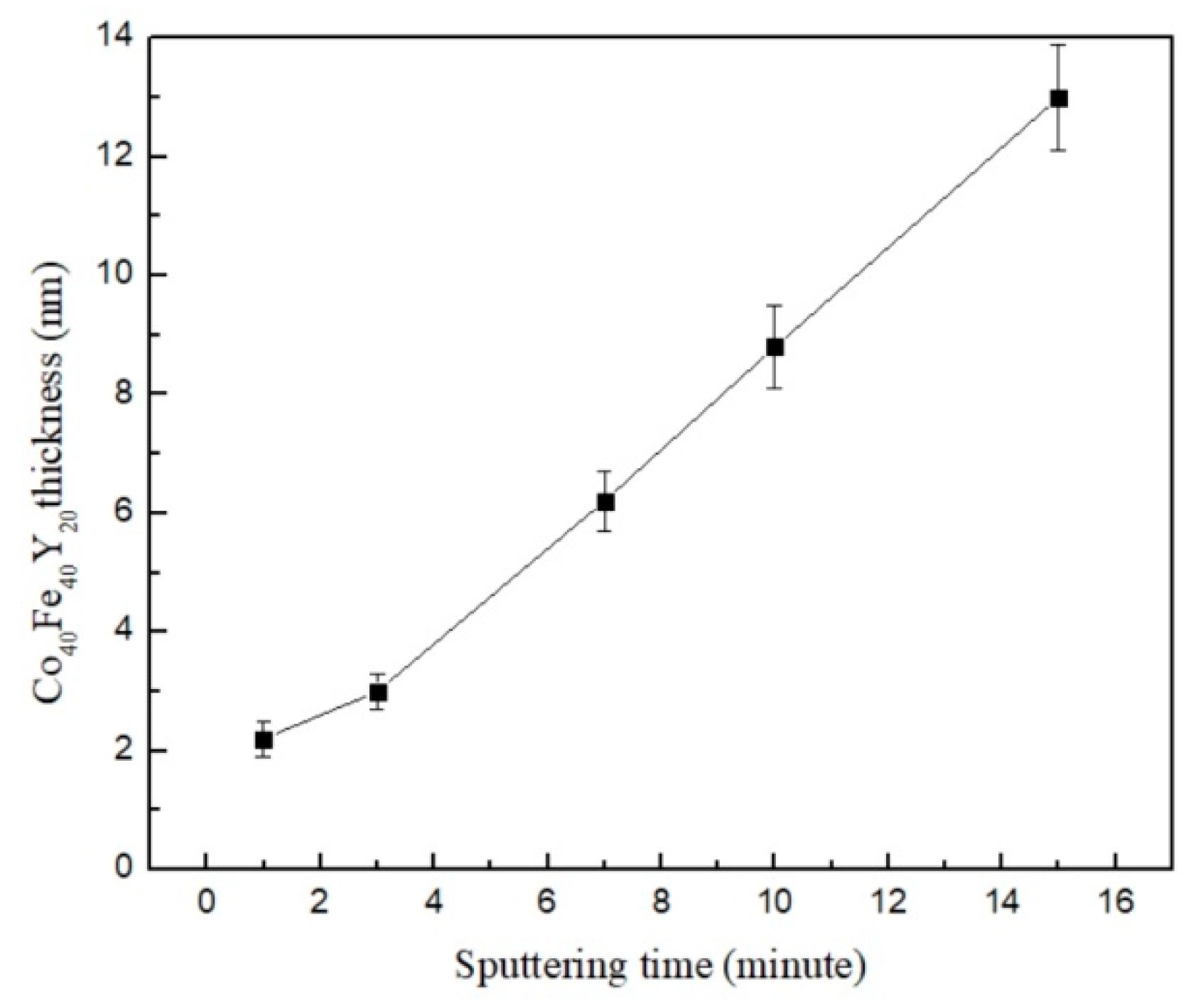
3.1. XRD, EDX, and AFM Morphology
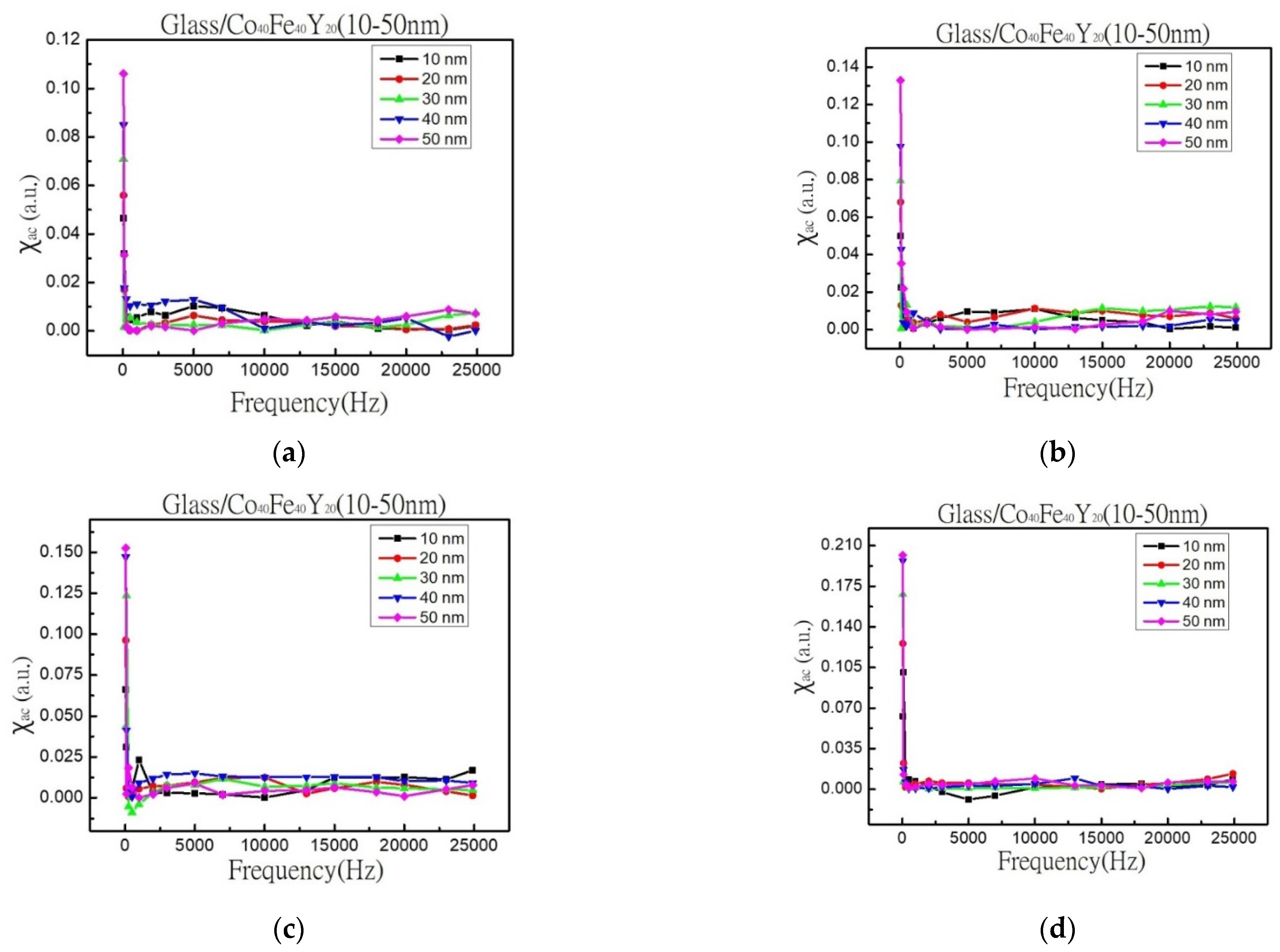
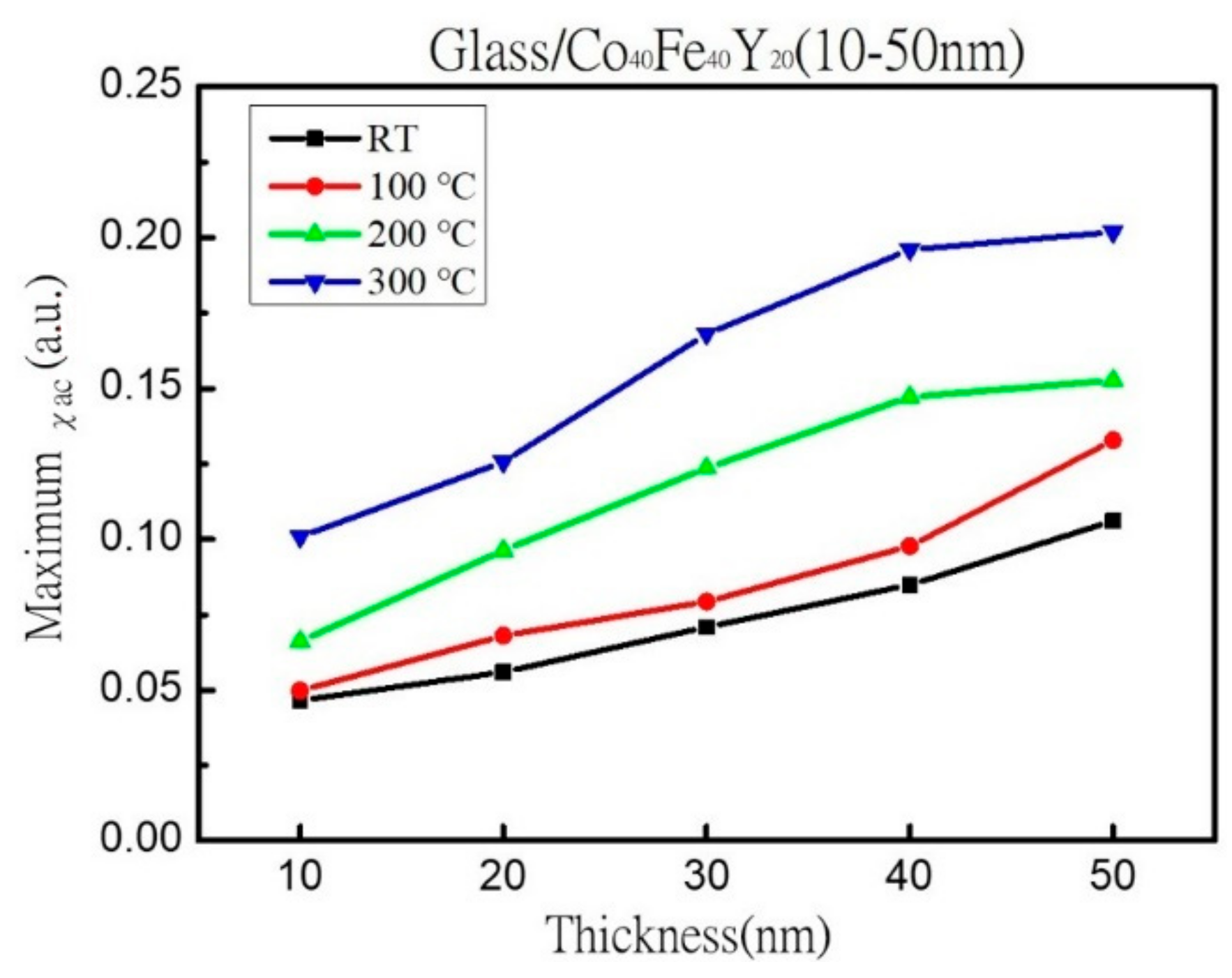
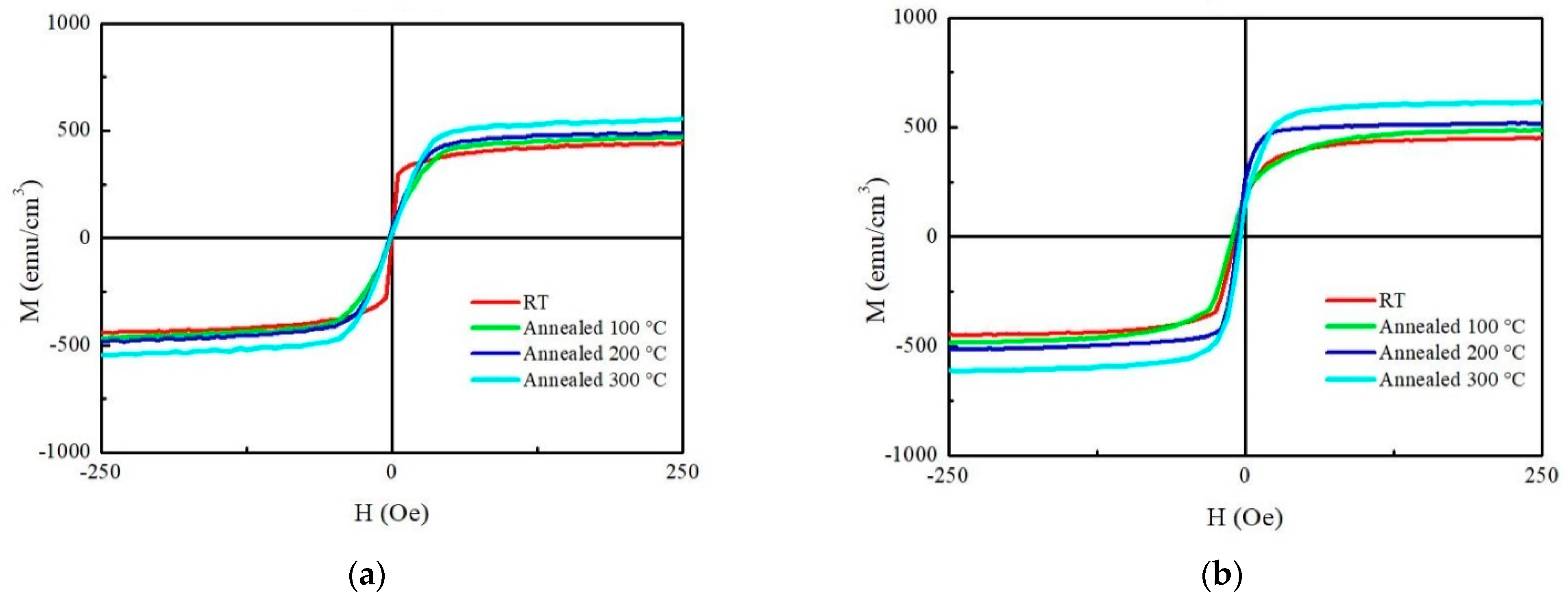
3.2. Magnetic Property
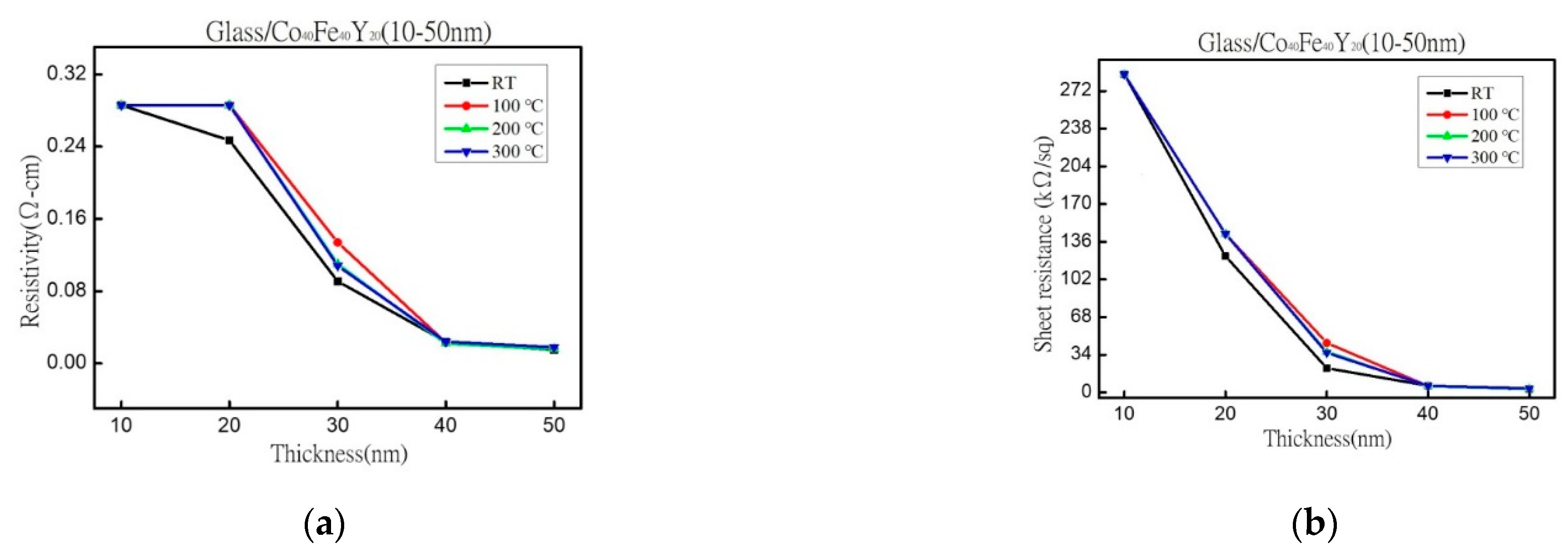
3.3. Electrical Properties
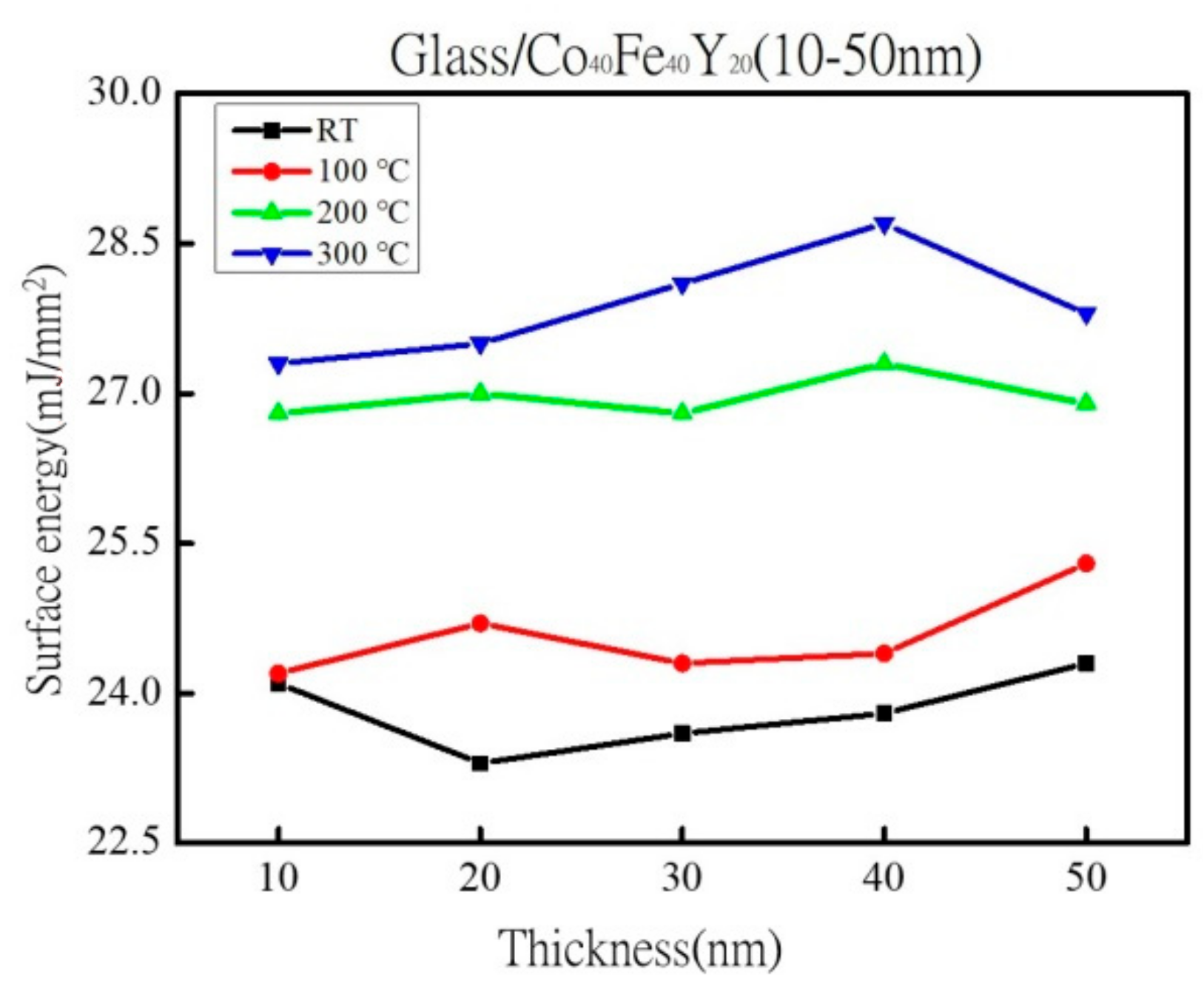
3.4. Analysis of Surface Energy and Adhesion
3.5. Analysis of Optical Property
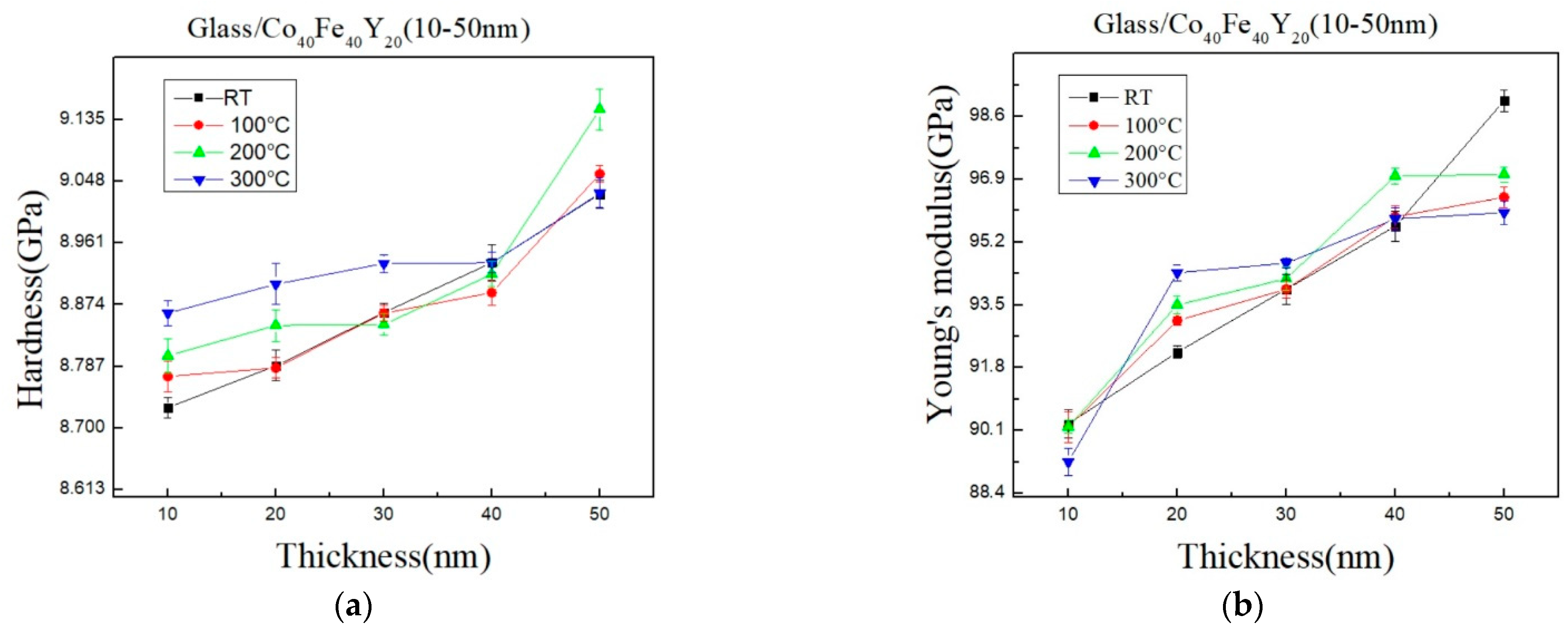
3.6. Hardness and Young’s Modulus
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scheunert, G.; Heinonen, O.; Hardeman, R.; Lapicki, A.; Gubbins, M.; Bowman, R.M. A review of high magnetic moment thin films for microscale and nanotechnology applications. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2016, 3, 011301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sunder, R.S.; Deevi, S. Soft magnetic FeCo alloys: Alloy development, processing, and properties. Int. Mater. Rev. 2005, 50, 157–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, S.; Tagawa, I.; Uehara, Y.; Kubomiya, T.; Kane, J.; Kakehi, A.; Chikazawa, A. Write heads with pole tip consisting of high-Bs FeCoAlO films. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2002, 38, 2219–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, P.; Hong, Y.; Ci, S.; Wen, Z. In situ integration of CoFe alloy nanoparticles with nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes as advanced bifunctional cathode catalysts for Zneair batteries. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 20048–20055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaka, K.; Saidoh, N.; Nishiyama, N.; Ishimaru, M.; Inoue, A. Novel soft-magnetic underlayer of a bit-patterned media using CoFe-based amorphous alloy thin film. Intermetallics 2012, 30, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, M.; Ruban, A.V.; Mookerjee, A.; Johansson, B. Magnetic state effect upon the order-disorder phase transition in Fe-Co alloys: A first-principles study. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 83, 054202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, H.L.B.; Wenny, D.H. Supermendur: A new rectangular-loop magnetic material. Electr. Eng. 1957, 76, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakita, A.; Passamani, E.; Kumar, H.; Cornejo, D.; Fugivara, C.; Noce, R.; Benedetti, A. Influence of current density on crystalline structure and magnetic properties of electrodeposited Co-rich CoNiW alloys. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2013, 141, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogachi, M.; Tadachi, N.; Kohata, H.; Ishibashi, H. Magnetism and point defect in B2-type CoFe alloys. Intermetallics 2005, 13, 535–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Jen, S.; Yao, Y.; Wu, J.; Hwang, G.; Tsai, T.; Chang, Y.; Sun, A. Magnetic, structural and electrical properties of ordered and disordered Co50Fe50 films. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2006, 304, e71–e74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kockar, H.; Ozergin, E.; Karaagac, O.; Alper, M. Characterisations of CoFeCu films: Influence of Fe concentration. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 586, S326–S330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihajlovic, J.; Rinklebe, J. Rare earth elements in German soils—A review. Chemosphere 2018, 205, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.-Q.; Zhou, L.-X.; Zhu, K.-J.; Gu, J.; Zheng, S.-H. Isothermal oxidation behavior of scandium and yttrium co-doped B2-type iron–aluminum intermetallics at elevated temperature. Rare Met. 2018, 37, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wu, Q.; Yan, H.; Zhong, S.; Huang, Z. Effect of Trace Yttrium Addition and Heat Treatmenton the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of As-Cast ADC12 Aluminum Alloy. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baulin, O.; Bugnet, M.; Fabrègue, D.; Lenain, A.; Gravier, S.; Cazottes, S.; Kapelski, G.; Ovanessian, B.T.; Balvay, S.; Hartmann, D.J.; et al. Improvement of mechanical, thermal, and corrosion properties of Ni- and Al-free Cu–Zr–Ti metallic glass with yttrium addition. Materialia 2018, 1, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Qian, D.; Zhao, L.; Zheng, Z.; Gao, X.; Ramanujan, R. Enhancing the coercivity, thermal stability and exchange coupling of nano-composite (Nd,Dy,Y)–Fe–B alloys with reduced Dy content by Zr addition. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 606, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Qian, D.; Zeng, D. Reducing Dy Content by Y Substitution in Nanocomposite NdFeB Alloys With Enhanced Magnetic Properties and Thermal Stability. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 2797–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.H.; Luo, Y.; Yu, D.B.; Quan, N.T.; Wu, G.Y.; Dou, Y.K.; Hu, Z.; Wang, Z.L. Permanent magnetic properties of Nd–Fe–B melt-spun ribbons with Y substitution. Rare Metals 2020, 39, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courcot, E.; Rebillat, F.; Teyssandier, F.; Louchet-Pouillerie, C. Stability of rare earth oxides in a moist environment at elevated temperatures—Experimental and thermodynamic studies: Part II: Comparison of the rare earth oxides. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 30, 1911–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghazadeh, M.; Barmi, A.-A.M.; Shiri, H.M. Cathodic electrodeposition and characterization of nanostructured Y2O3 from chloride solution Part I: Effect of current density. Russ. J. Electrochem. 2013, 49, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Liu, Z.T.; Liu, W.T. The preparation and properties of Y2O3/AlN anti-reflection films on chemical vapor deposition diamond. Thin Solid Films 2011, 520, 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, S.J.; Parker, G.J.; Charlton, M.D.B.; Wilkinson, J.S. Structural and optical properties of yttrium oxide thin films for planar wave guiding application. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2010, 28, 1388–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.J.; Ou, S.L.; Chang, Y.H.; Chen, Y.T.; Chiang, M.R.; Hsu, S.C.; Chu, C.L. Adhesive characteristic, surface mor-phology, and optical properties of Co40Fe40V20 films. Opt.-Int. J. Light Electron Opt. 2020, 216, 164587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.J.; Chen, Y.T.; Chang, Y.H.; Chiang, M.R.; Li, W.H.; Tseng, J.Y.; Chi, P.W.; Wu, T.H. Structure and magnetic properties of Co40Fe40V20 Thin Films. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 19, 5974–5978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.J.; Chang, Y.H.; Ou, S.L.; Chen, Y.T.; Li, W.H.; Jhou, T.Y.; Chu, C.C.; Wu, T.H.; Tseng, S.W. Effect of annealing on the structural, magnetic, surface energy and optical properties of Co32Fe30W38 films deposited by direct-current magnetron sputtering. Coatings 2020, 10, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.J.; Chang, Y.H.; Chiang, C.C.; Chen, Y.T.; Chen, Y.S.; Liao, H.W.; Wu, T.H.; Lin, S.H.; Chi, P.W. Effect of annealing and thickness of Co40Fe40Yb20 thinfilms on various physical properties on a glass substrate. Materials 2022, 15, 8509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-J.; Chang, Y.-H.; Chiang, C.-C.; Chen, Y.-T.; Liu, Y.-C.; Ou, S.-L.; Li, S.-Y.; Chi, P.-W. Co40Fe40Y20 Nanofilms’ Structural, Magnetic, Electrical, and Nanomechanical Characteristics as a Function of Annealing Temperature and Thickness. Coatings 2023, 13, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankl, M.; Laib, S.; Seeger, S. Surface tension properties of surface-coatings for application in biodiagnostics determined by contact angle measurements. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2003, 30, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Zhu, J.-G.; Moneck, M.T.; Peng, Y.; Laughlin, D.E. Annealing effects on structural and transport properties of rf-sputtered CoFeB/MgO/CoFeB magnetic tunnel junctions. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 99, 08A901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto, M.; Marukame, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Matsuda, K.; Uemura, T.; Arita, M. Fabrication of fully epitaxial magnetic tunnel junctions using cobalt-based full-Heusler alloy thin film and their tunnel magnetoresistance characteristics. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2006, 39, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchaneck, G.; Artiukh, E.; Sobolev, N.A.; Telesh, E.; Kalanda, N.; Kiselev, D.A.; Ilina, T.S.; Gerlach, G. Strontium Ferro-molybdate-Based Magnetic Tunnel Junctions. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Chung, T.S.; Good, R.J. Surface energy of thermotropic liquid crystalline polyesters and polyesteramide. J. Polym. Sci. 1998, 36, 2327–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, D.K.; Wendt, R.C. Estimation of the surface free energy of polymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1969, 13, 1741–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaelble, D.H.; Uy, K.C. A Reinterpretation of Organic Liquid-Polytetrafluoroethylene Surface Interactions. J. Adhes. 1970, 2, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, D.; Shen, J.; Fan, H.; Sun, J. Effect of yttrium on the glass-forming ability of Fe-Cr-Mo-C-B bulk amorphous alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 427, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kube, S.A.; Xing, W.; Kalidindi, A.; Sohn, S.; Datye, A.; Amram, D.; Schuh, C.A.; Schroers, J. Combinatorial study of thermal stability in ternary nanocrystalline alloys. Acta Mater. 2020, 188, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Huang, L.; Liu, F. A thermo-kinetic correlation for grain growth in nanocrystalline alloys. Mater. Lett. 2018, 219, 276–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luborsky, F.; Walter, J. Magnetic anneal anisotropy in amorphous alloys. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1977, 13, 953–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Luo, J.; Sui, Y.; Guo, Z. Effect of yttrium substitution on magnetic properties and microstructure of Nd-Y-Fe-B nanocomposite magnets. J. Rare Earths 2010, 28, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Khan, A.J.; Yu, H.; Zhong, X.; Liu, Z. Performance improvement and element segregation behavior in Y substituted nanocrystalline (La,Ce)–Fe–B permanent magnetic alloys without critical RE elements. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 834, 155226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.M.; Han, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Choi, D.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, J. Thickness effects on magnetic properties and ferromagnetic resonance in Co–Ni–Fe–N soft magnetic thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 91, 8462–8464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-J.; Chang, Y.-H.; Chen, Y.-T.; Chiang, Y.-C.; Tsai, D.-Y.; Wu, T.-H.; Chi, P.-W. Effect of Annealing on the Characteristics of CoFeBY Thin Films. Coatings 2021, 11, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, T.P.; Raja, M.M.; Kumar, A.; Srinath, S.; Kamat, S. Effect of thickness on structure, microstructure, residual stress and soft magnetic properties of DC sputtered Fe65Co35 soft magnetic thin films. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2014, 365, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almasi-Kashi, M.; Ramazani, A.; Kheyri, F.; Jafari-Khamse, E. The effect of magnetic layer thickness on magnetic properties of Fe/Cu multilayer nanowires. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2014, 144, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Kar, M. Effect of Annealing Temperature and Preparation Condition on Magnetic Anisotropy in Nanocrystalline Cobalt Ferrite. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 47, 3645–3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jen, S.U.; Yao, Y.D.; Chen, Y.T.; Wu, J.M.; Lee, C.C.; Tsai, T.L.; Chang, Y.C. Magnetic and electrical properties of amorphous CoFeB films. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 99, 053701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.M.; Hsieh, J.H.; Li, C. Electrical and piezoresistive properties of TaN-Cu nanocomposite thin films. Thin Solid Films 2004, 469–470, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.H.; Okamoto, T.; Nakagawa, S. [Ni-Fe/Si] double seedlayer with low surface energy for Fe-Co-B soft magnetic underlayer with high Hk for perpendicular magnetic recording media. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2004, 40, 2389–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, D.A.; Easterling, K.E. Phase Transformations in Metals and Alloy, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: London, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Absolom, D.; Eom, K.; Vargha-Butler, E.; Hamza, H.; Neumann, A. Surface properties of coal particles in aqueous media II. Adhesion of coal particles to polymeric substrates. Colloids Surf. 1986, 17, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapustianyk, V.; Turko, B.; Kostruba, A.; Sofiani, Z.; Derkowska, B.; Dabos-Seignon, S.; Barwiński, B.; Eliyashevskyi, Y.; Sahraoui, B. Influence of size effect and sputtering conditions on the crystallinity and optical properties of ZnO thin films. Opt. Commun. 2007, 269, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, W.C.; Pharr, G.M. An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and dis-placement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 1992, 7, 1564–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, L.; Wang, T. Investigation of the mechanical properties of thin films by nanoindentation, considering the effects of thickness and different coating–substrate combinations. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 191, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashgari, H.; Cadogan, J.; Chu, D.; Li, S. The effect of heat treatment and cyclic loading on nanoindentation behaviour of FeSiB amorphous alloy. Mater. Des. 2016, 92, 919–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Song, M.; Liao, X.; Sha, G.; He, Y. Effects of isothermal annealing on the microstructures and mechanical properties of a FeCuSiBAl amorphous alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 543, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Song, M.; Ni, S.; Guo, S.; He, Y. Effects of annealing on the hardness and elastic modulus of a Cu36Zr48Al8Ag8 bulk metallic glass. Mater. Des. 2013, 47, 706–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbull, D.; Cohen, M.H. On the free volume model of liquid glass transition. J. Chem. Phys. 1970, 52, 3038–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Abbreviation | Full Name |
|---|---|
| CoFeY | Cobalt Iron Yttrium |
| Y | Yttrium |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| χac | Low-frequency alternate-current magnetic susceptibility |
| Ms | Saturation magnetization |
| Hc | Coercivity |
| CoFe | Cobalt Iron |
| MRAM | Magnetic random-access memory |
| RE | Rare earth |
| Y2O3 | Yttrium oxide |
| Co40Fe40B20 | Cobalt Iron Boron |
| MTJ | Magnetic tunneling junction |
| RT | Room temperature |
| CoFeV | Cobalt Iron Vanadium |
| CoFeW | Cobalt Iron Tungsten |
| CoFeYb | Cobalt Iron Ytterbium |
| DC | Direct current |
| TA | Annealed temperature |
| Ar | Argon |
| GIXRD | Grazing incidence X-ray diffraction |
| EDX | Energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy |
| AFM | Atomic force microscopy |
| a.u. | Arbitrary unit |
| ƒres | Optimal resonance frequency |
| VSM | Vibrating sample magnetometer |
| θ | Contact angle |
| DI | Deionized |
| CSM | Continuous stiffness measurement |
| M | Magnetization |
| Hext | External field |
| FEP | Fluorinated ethylene propylene copolymer |
| PS | Polystyrene |
| W | Tungsten |
| H | Hardness |
| E | Young’s modulus |
| Materials | Maximum χac (a.u.) | Surface Energy (mJ/mm2) | Transmittance (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glass substrate/Co40Fe40V20 [23,24] 10–100 nm at RT | 0.02–0.04 | 27.8–45.4 | x |
| Glass substrate/Co32Fe30W38 [25] 10-50 nm at RT and annealed conditions | 0.02–0.52 | 22.3–28.4 | x |
| Glass substrate/Co40Fe40Yb20 [26] 10–50 nm at RT and annealed conditions | 0.04–0.35 | 28.6–34.5 | 22.3–80.5 |
| Si(100) substrate/Co40Fe40Y20 [27] 10–50 nm at RT and annealed conditions | 0.03–0.16 | 22.7–31.1 | x |
| Glass substrate/Co40Fe40Y20 10–50 nm at RT and annealed conditions (Current research) | 0.04–0.20 | 23.3–28.7 | 20.1–81.7 |
| Element | Weight% | Atomic% |
|---|---|---|
| Fe | 28.06 | 36.56 |
| Co | 38.12 | 47.07 |
| Y | 33.82 | 16.37 |
| Totals | 100.00 |
| Process | Thickness | Minimum Transmittance (%) | Maximum Transmittance (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| As-deposited | 10 nm | 65.1 | 81.7 |
| 20 nm | 62.3 | 78.8 | |
| 30 nm | 34.3 | 41.4 | |
| 40 nm | 23.2 | 34.5 | |
| 50 nm | 21.4 | 32.5 | |
| Annealing 100 °C | 10 nm | 66.5 | 78.6 |
| 20 nm | 58.7 | 74.6 | |
| 30 nm | 39.1 | 42.3 | |
| 40 nm | 24.2 | 31.2 | |
| 50 nm | 20.1 | 29.4 | |
| Annealing 200 °C | 10 nm | 66.7 | 80.5 |
| 20 nm | 61.1 | 72.2 | |
| 30 nm | 38.2 | 41.2 | |
| 40 nm | 25.1 | 30.8 | |
| 50 nm | 22.4 | 29.5 | |
| Annealing 300 °C | 10 nm | 70.7 | 78.4 |
| 20 nm | 60.1 | 66.6 | |
| 30 nm | 31.1 | 36.1 | |
| 40 nm | 22.4 | 29.1 | |
| 50 nm | 20.8 | 28.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, W.-J.; Chang, Y.-H.; Chiang, C.-C.; Chen, Y.-T.; Liu, Y.-C.; Huang, Y.-J.; Chi, P.-W. The Influence of Annealing and Film Thickness on the Specific Properties of Co40Fe40Y20 Films. Materials 2023, 16, 2490. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16062490
Liu W-J, Chang Y-H, Chiang C-C, Chen Y-T, Liu Y-C, Huang Y-J, Chi P-W. The Influence of Annealing and Film Thickness on the Specific Properties of Co40Fe40Y20 Films. Materials. 2023; 16(6):2490. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16062490
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Wen-Jen, Yung-Huang Chang, Chia-Chin Chiang, Yuan-Tsung Chen, Yu-Chi Liu, Yu-Jie Huang, and Po-Wei Chi. 2023. "The Influence of Annealing and Film Thickness on the Specific Properties of Co40Fe40Y20 Films" Materials 16, no. 6: 2490. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16062490
APA StyleLiu, W.-J., Chang, Y.-H., Chiang, C.-C., Chen, Y.-T., Liu, Y.-C., Huang, Y.-J., & Chi, P.-W. (2023). The Influence of Annealing and Film Thickness on the Specific Properties of Co40Fe40Y20 Films. Materials, 16(6), 2490. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16062490








