Comprehensive Assessment of Cyclic Fatigue Strength in Five Multiple-File Nickel–Titanium Endodontic Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Geometric Design Analysis
2.2. Metallurgical Features Analysis
2.3. Cyclic Fatigue Testing
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Geometric Design Analysis
3.2. Metallurgical Features Analysis
3.3. Cyclic Fatigue Testing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hülsmann, M.; Peters, O.A.; Dummer, P.M. Mechanical preparation of root canals: Shaping goals, techniques and means. Endod. Top. 2005, 10, 30–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirani, C.; Cirulli, P.P.; Chersoni, S.; Micele, L.; Ruggeri, O.; Prati, C. Cyclic fatigue testing and metallographic analysis of nickel-titanium rotary instruments. J. Endod. 2011, 37, 1013–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sattapan, B.; Nervo, G.J.; Palamara, J.E.; Messer, H.H. Defects in rotary nickel-titanium files after clinical use. J. Endod. 2000, 26, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plotino, G.; Grande, N.M.; Cordaro, M.; Testarelli, L.; Gambarini, G. A review of cyclic fatigue testing of nickel-titanium rotary instruments. J. Endod. 2009, 35, 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keles, A.; Eymirli, A.; Uyanik, O.; Nagas, E. Influence of static and dynamic cyclic fatigue tests on the lifespan of four reciprocating systems at different temperatures. Int. Endod. J. 2019, 52, 880–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.N.R.; Martins, R.F.; Braz Fernandes, F.M.; Silva, E. What meaningful information are the instruments mechanical testing giving us? A comprehensive review. J. Endod. 2022, 48, 985–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.N.R.; Nogueira Leal Silva, E.J.; Marques, D.; Ginjeira, A.; Braz Fernandes, F.M.; De Deus, G.; Versiani, M.A. Influence of kinematics on the cyclic fatigue resistance of replicalike and original brand rotary instruments. J. Endod. 2020, 46, 1136–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruthi, P.J.; Nawal, R.R.; Talwar, S.; Verma, M. Comparative evaluation of the effectiveness of ultrasonic tips versus the Terauchi file retrieval kit for the removal of separated endodontic instruments. Rest. Dent. Endod. 2020, 45, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, E.; Pena-Bengoa, F.; Ajuz, N.C.; Vieira, V.T.L.; Martins, J.N.R.; Marques, D.; Pinto, R.; Rito Pereira, M.; Braz-Fernandes, F.M.; Versiani, M.A. Multimethod analysis of large- and low-tapered single file reciprocating instruments: Design, metallurgy, mechanical performance, and irrigation flow. Int. Endod. J. 2024, 57, 601–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASTM:F2004−17; Standard Test Method for Transformation Temperature of Nickel-Titanium Alloys by Thermal Analysis. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2004; pp. 1–5.
- Dentsply Maillefer. ProTaper Gold Treatment—Directions for Use. 2016. 1–7. Available online: https://assets.dentsplysirona.com/dentsply/web/Endodontics/global-page-templates-assets/download-pdf%27s/protaper-gold/ProTaper%20Gold%20ROW%20DFU%20EN.pdf (accessed on 22 April 2024).
- Herold, K.S.; Johnson, B.R.; Wenckus, C.S. A scanning electron microscopy evaluation of microfractures, deformation and separation in EndoSequence and Profile nickel-titanium rotary files using an extracted molar tooth model. J. Endod. 2007, 33, 712–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, E.; Martins, J.N.R.; Versiani, M.A. Advancing insights in contemporary endodontics: Proposing a multimethod approach for comprehensive evaluation of NiTi instruments. Int. Endod. J. 2024, 57, 116–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, M.E.; Price, J.W.; Parashos, P. Fracture resistance of electropolished rotary nickel-titanium endodontic instruments. J. Endod. 2007, 33, 1212–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duke, F.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, H.; Ruse, N.D.; Wang, Z.J.; Hieawy, A.; Haapasalo, M. Cyclic fatigue of ProFile Vortex and Vortex Blue nickel-titanium files in single and double curvatures. J. Endod. 2015, 41, 1686–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramkowski, R.; Bahcall, J. An in vitro comparison of torsional stress and cyclic fatigue resistance of ProFile GT and ProFile GT Series X rotary nickel-titanium files. J. Endod. 2009, 35, 404–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McSpadden, J.T. Mastering Instrument Designs. In Mastering Endodontics Instrumentation; McSpadden, J.T., Ed.; Cloudland Institute: Chattanooga, TN, USA, 2007; pp. 37–97. [Google Scholar]
- Elnaghy, A.M.; Elsaka, S.E. Mechanical properties of ProTaper Gold nickel-titanium rotary instruments. Int. Endod. J. 2016, 49, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Peng, B.; Zheng, Y. An overview of the mechanical properties of nickel–titanium endodontic instruments. Endod. Top. 2013, 29, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupanc, J.; Vahdat-Pajouh, N.; Schafer, E. New thermomechanically treated NiTi alloys—A review. Int. Endod. J. 2018, 51, 1088–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keskin, C.; Inan, U.; Demiral, M.; Keles, A. Cyclic fatigue resistance of Reciproc Blue, Reciproc, and WaveOne Gold reciprocating instruments. J. Endod. 2017, 43, 1360–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plotino, G.; Grande, N.M.; Mercade Bellido, M.; Testarelli, L.; Gambarini, G. Influence of temperature on cyclic fatigue resistance of ProTaper Gold and ProTaper Universal rotary files. J. Endod. 2017, 43, 200–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grande, N.M.; Plotino, G.; Silla, E.; Pedulla, E.; De Deus, G.; Gambarini, G.; Somma, F. Environmental temperature drastically affects flexural fatigue resistance of nickel-titanium rotary files. J. Endod. 2017, 43, 1157–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.N.R.; Silva, E.; Marques, D.; Belladonna, F.G.; Simoes-Carvalho, M.; da Costa, R.P.; Ginjeira, A.; Braz Fernandes, F.M.; Versiani, M.A. Comparison of five rotary systems regarding design, metallurgy, mechanical performance, and canal preparation-a multimethod research. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2022, 26, 3299–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruett, J.P.; Clement, D.J.; Carnes, D.L., Jr. Cyclic fatigue testing of nickel-titanium endodontic instruments. J. Endod. 1997, 23, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grande, N.M.; Plotino, G.; Pecci, R.; Bedini, R.; Malagnino, V.A.; Somma, F. Cyclic fatigue resistance and three-dimensional analysis of instruments from two nickel-titanium rotary systems. Int. Endod. J. 2006, 39, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASTM International. ASTM:F2516-07—Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Nickel-Titanium Superelastic Materials; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2007; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, O.A.; Arias, A.; Choi, A. Mechanical properties of a novel nickel-titanium root canal instrument: Stationary and dynamic tests. J. Endod. 2020, 46, 994–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 3630-3631:2008; Dentistry—Root Canal Instruments—Part 1: General Requirements and Test Methods. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008.

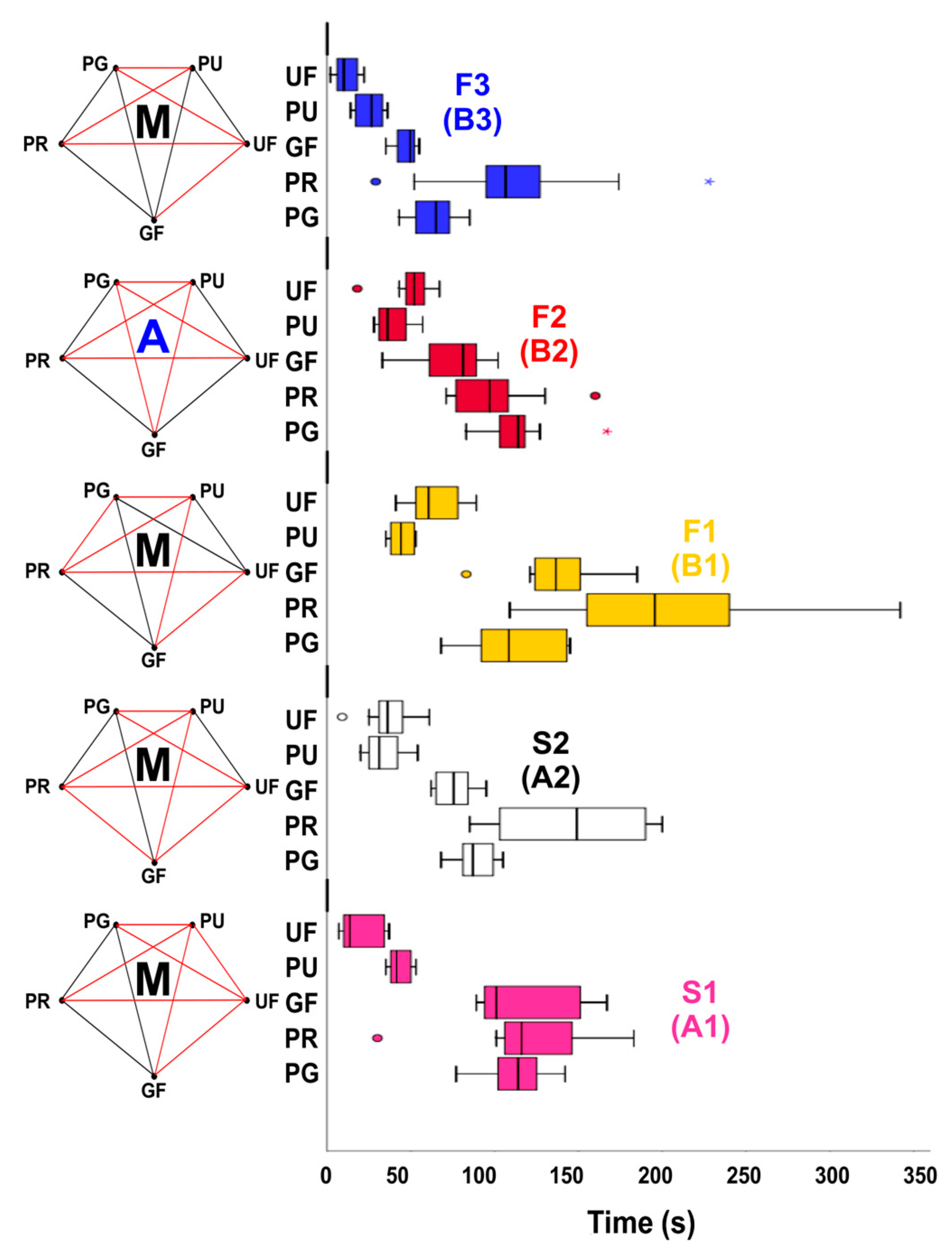
| Instruments | Geometric Design | Cyclic Fatigue Test 1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apical Size/Taper 2 | Active Blade Length (mm) | Number of Spirals | Spirals per Millimetre | Helical Angle (°) | Time to Fracture (s) | Fragment Length (mm) | |
| ProTaper Gold S1 | 18/0.02 v | 15 | 11 | 0.73 | 21.7° | 114 [99–128] | 8.0 [7.6–8.1] |
| Premium Taper Gold S1 | 18/0.02 v | 17 | 12 | 0.71 | 24.3° | 116 [104–148] | 7.4 [7.4–7.5] |
| Go-Taper Flex A1 | 18/0.02 v | 16 | 11 | 0.69 | 19.6° | 101 [93–154] | 7.7 [7.4–7.9] |
| ProTaper Universal S1 | 17/0.02 v | 15 | 11 | 0.73 | 21.6° | 41 [37–50] | 7.5 [6.9–7.7] |
| U-File S1 | 17/0.02 v | 15 | 11 | 0.73 | 20.3° | 13 [10–34] | 7.5 [7.2–7.9] |
| ProTaper Gold S2 | 20/0.04 v | 17 | 11 | 0.65 | 22.4° | 87 [80–100] | 7.7 [7.4–8.2] |
| Premium Taper Gold S2 | 20/0.04 v | 17 | 14 | 0.82 | 29.6° | 149 [102–192] | 7.7 [7.4–7.8] |
| Go-Taper Flex A2 | 20/0.04 v | 17 | 11 | 0.65 | 23.6° | 75 [65–86] | 7.8 [7.4–7.9] |
| ProTaper Universal S2 | 20/0.04 v | 17 | 11 | 0.65 | 22.3° | 31 [24–42] | 7.2 [6.9–7.8] |
| U-File S2 | 20/0.04 v | 17 | 11 | 0.65 | 21.4° | 36 [29–47] | 7.3 [7.0–7.8] |
| ProTaper Gold F1 | 20/0.07 v | 17 | 12 | 0.71 | 24.7° | 108 [89–143] | 7.6 [7.0–7.9] |
| Premium Taper Gold F1 | 20/0.07 v | 17 | 15 | 0.88 | 29.7° | 186 [140–236] | 7.9 [7.7–8.0] |
| Go-Taper Flex B1 | 20/0.07 v | 17 | 12 | 0.71 | 25.8° | 136 [123–151] | 8.0 [7.4–8.2] |
| ProTaper Universal F1 | 20/0.07 v | 17 | 12 | 0.71 | 25.4° | 44 [38–52] | 7.8 [7.6–8.0] |
| U-File F1 | 20/0.07 v | 17 | 12 | 0.71 | 24.4° | 60 [52–79] | 7.3 [7.1–7.6] |
| ProTaper Gold F2 | 25/0.08 v | 17 | 10 | 0.59 | 22.0° | 114 [100–120] | 8.3 [7.6–8.9] |
| Premium Taper Gold F2 | 25/0.08 v | 17 | 11 | 0.65 | 25.1° | 97 [76–113] | 7.9 [7.7–8.1] |
| Go-Taper Flex B2 | 25/0.08 v | 17 | 10 | 0.59 | 23.3° | 81 [59–90] | 7.7 [7.5–8.4] |
| ProTaper Universal F2 | 25/0.08 v | 17 | 10 | 0.59 | 22.3° | 36 [30–47] | 7.1 [6.9–7.5] |
| U-File F2 | 25/0.08 v | 17 | 11 | 0.65 | 25.6° | 52 [46–58] | 7.3 [6.3–8.2] |
| ProTaper Gold F3 | 30/0.09 v | 17 | 9 | 0.53 | 21.5° | 65 [52–74] | 8.4 [7.8–8.6] |
| Premium Taper Gold F3 | 30/0.09 v | 17 | 11 | 0.65 | 27.4° | 106 [84–138] | 8.1 [6.5–10.4] |
| Go-Taper Flex B3 | 30/0.09 v | 16 | 9 | 0.56 | 22.1° | 49 [40–52] | 8.4 [7.9–8.9] |
| ProTaper Universal F3 | 30/0.09 v | 17 | 9 | 0.53 | 21.6° | 26 [16–33] | 8.1 [7.5–9.8] |
| U-File F3 | 30/0.09 v | 16 | 9 | 0.56 | 23.1° | 10 [5–18] | 8.2 [7.2–9.4] |
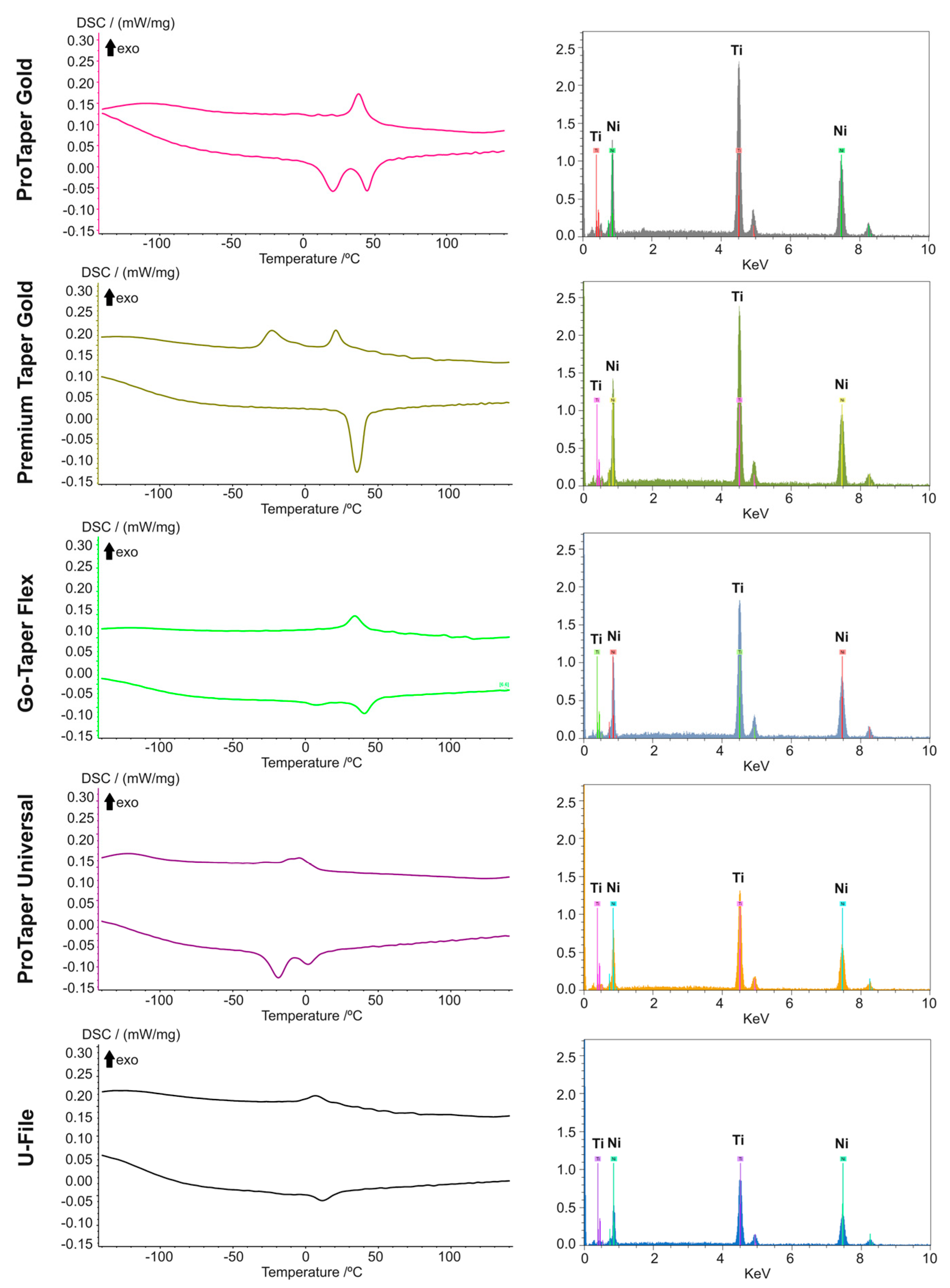
| Instruments * | Phase Transformation Temperatures | Elements Composition | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rs °C Cooling | Rf °C Cooling | As °C Heating | Af °C Heating | Nickel (Atomic %) | Titanium (Atomic %) | Nickel/Titanium Ratio | |
| ProTaper Gold F1 | 49.3 °C | 30.7 °C | 8.9 °C | 51.3 °C | 51.58 | 48.42 | 1.065 |
| Premium Taper Gold F1 | 26.6 °C | 16.5 °C | 27.5 °C | 42.8 °C | 51.20 | 48.80 | 1.049 |
| Go-Taper Flex B1 | 43.0 °C | 23.8 °C | −0.8 °C | 49.1 °C | 50.72 | 49.28 | 1.029 |
| ProTaper Universal F1 | 10.1 °C | −16.9 °C | −30.2 °C | 12.1 °C | 50.47 | 49.53 | 1.019 |
| U-File F1 | 18.7 °C | −4.4 °C | 3.6 °C | 24.8 °C | 50.23 | 49.77 | 1.009 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martins, J.N.R.; Silva, E.J.N.L.; Marques, D.; Braz Fernandes, F.M.; Versiani, M.A. Comprehensive Assessment of Cyclic Fatigue Strength in Five Multiple-File Nickel–Titanium Endodontic Systems. Materials 2024, 17, 2345. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17102345
Martins JNR, Silva EJNL, Marques D, Braz Fernandes FM, Versiani MA. Comprehensive Assessment of Cyclic Fatigue Strength in Five Multiple-File Nickel–Titanium Endodontic Systems. Materials. 2024; 17(10):2345. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17102345
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartins, Jorge N. R., Emmanuel J. N. L. Silva, Duarte Marques, Francisco M. Braz Fernandes, and Marco A. Versiani. 2024. "Comprehensive Assessment of Cyclic Fatigue Strength in Five Multiple-File Nickel–Titanium Endodontic Systems" Materials 17, no. 10: 2345. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17102345
APA StyleMartins, J. N. R., Silva, E. J. N. L., Marques, D., Braz Fernandes, F. M., & Versiani, M. A. (2024). Comprehensive Assessment of Cyclic Fatigue Strength in Five Multiple-File Nickel–Titanium Endodontic Systems. Materials, 17(10), 2345. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17102345








