Effects of Thermoforming Parameters on Woven Carbon Fiber Thermoplastic Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
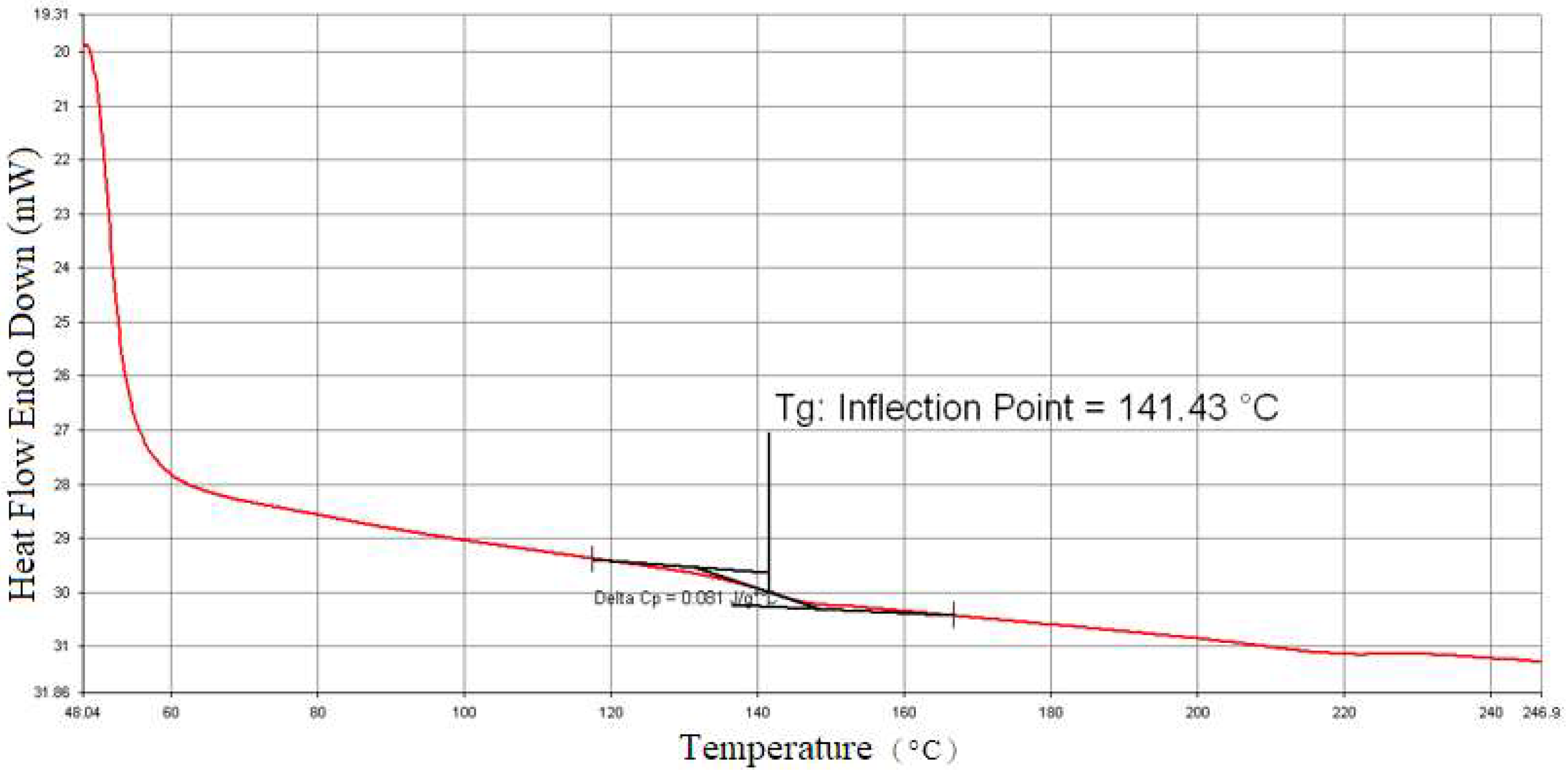
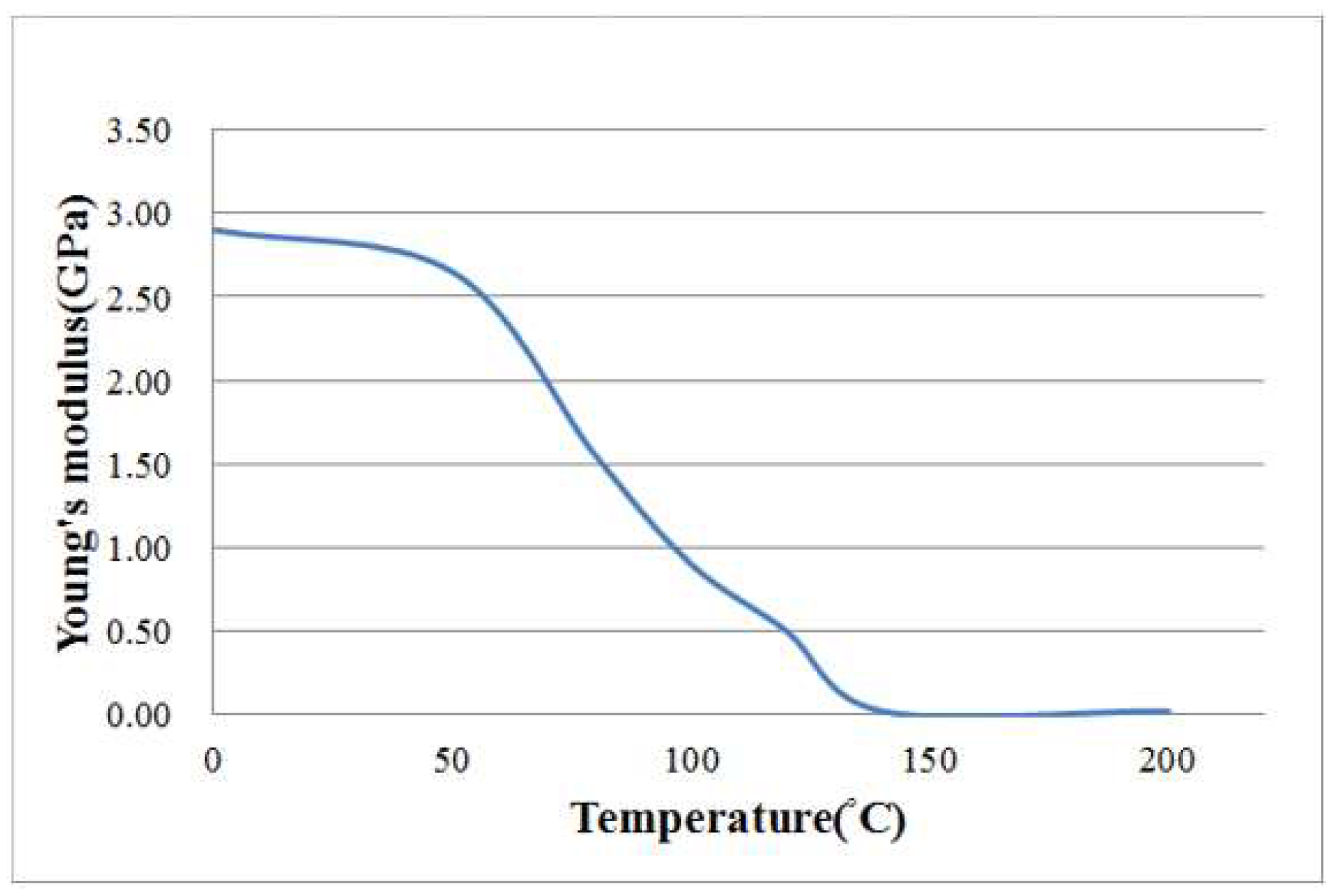
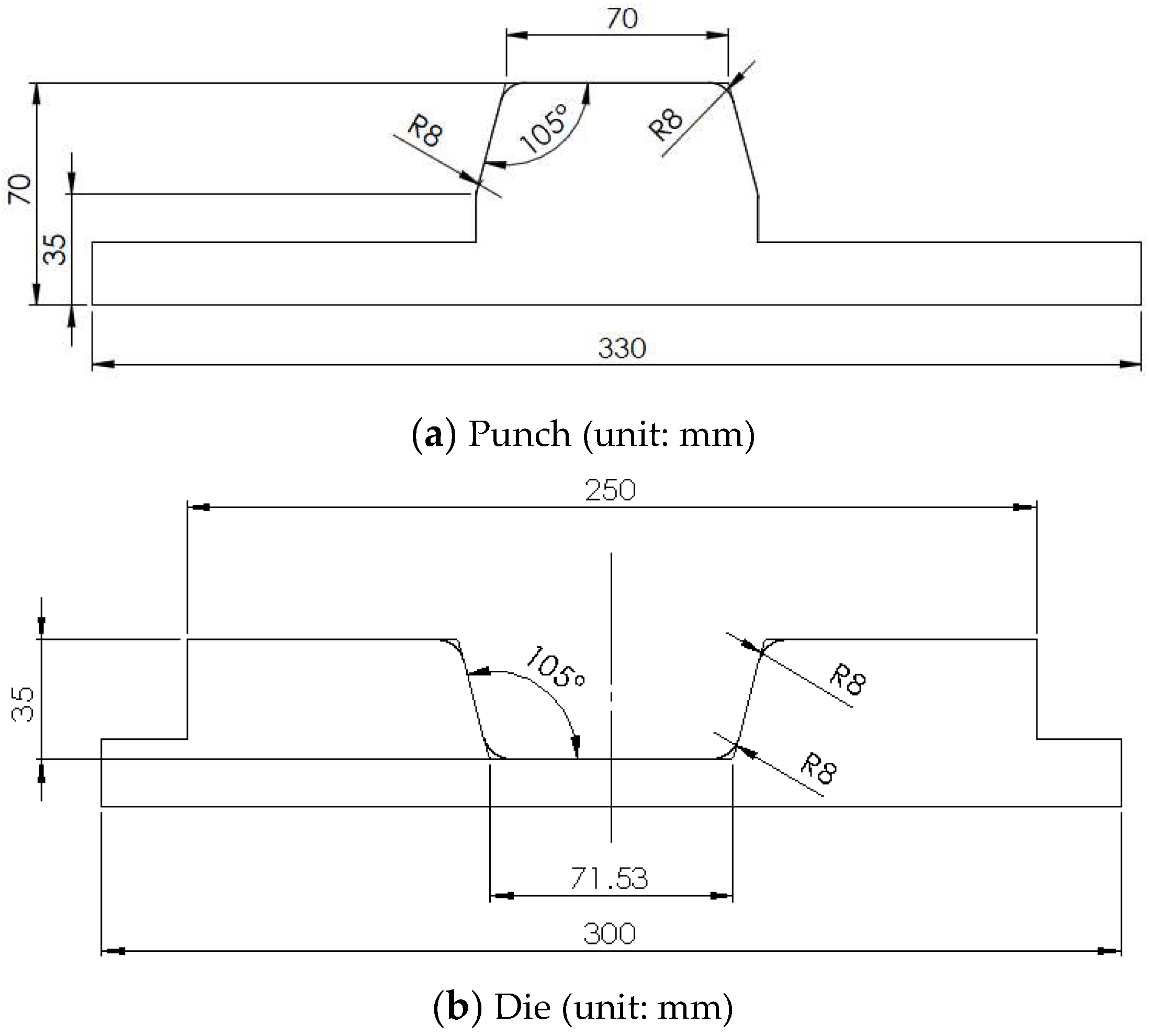
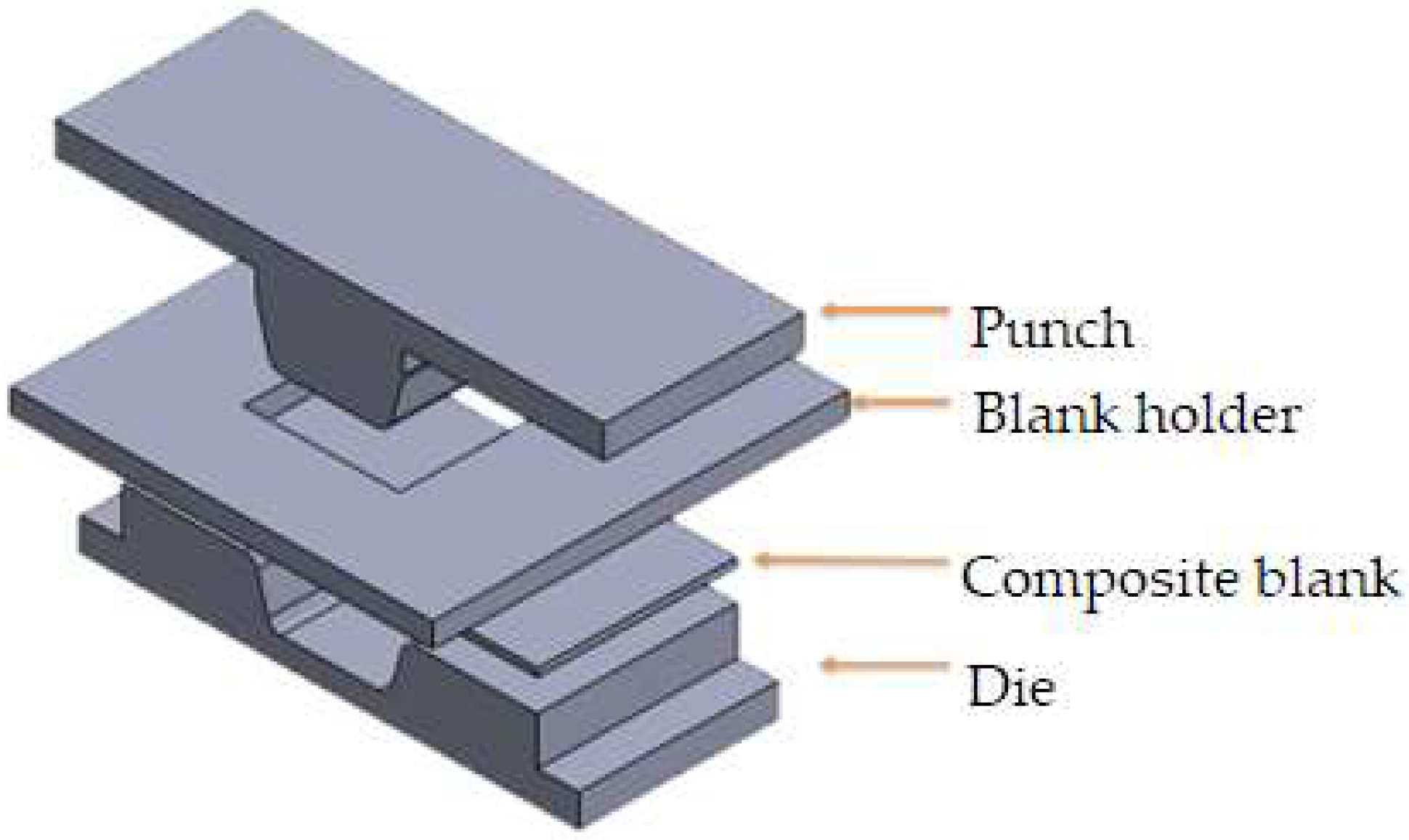
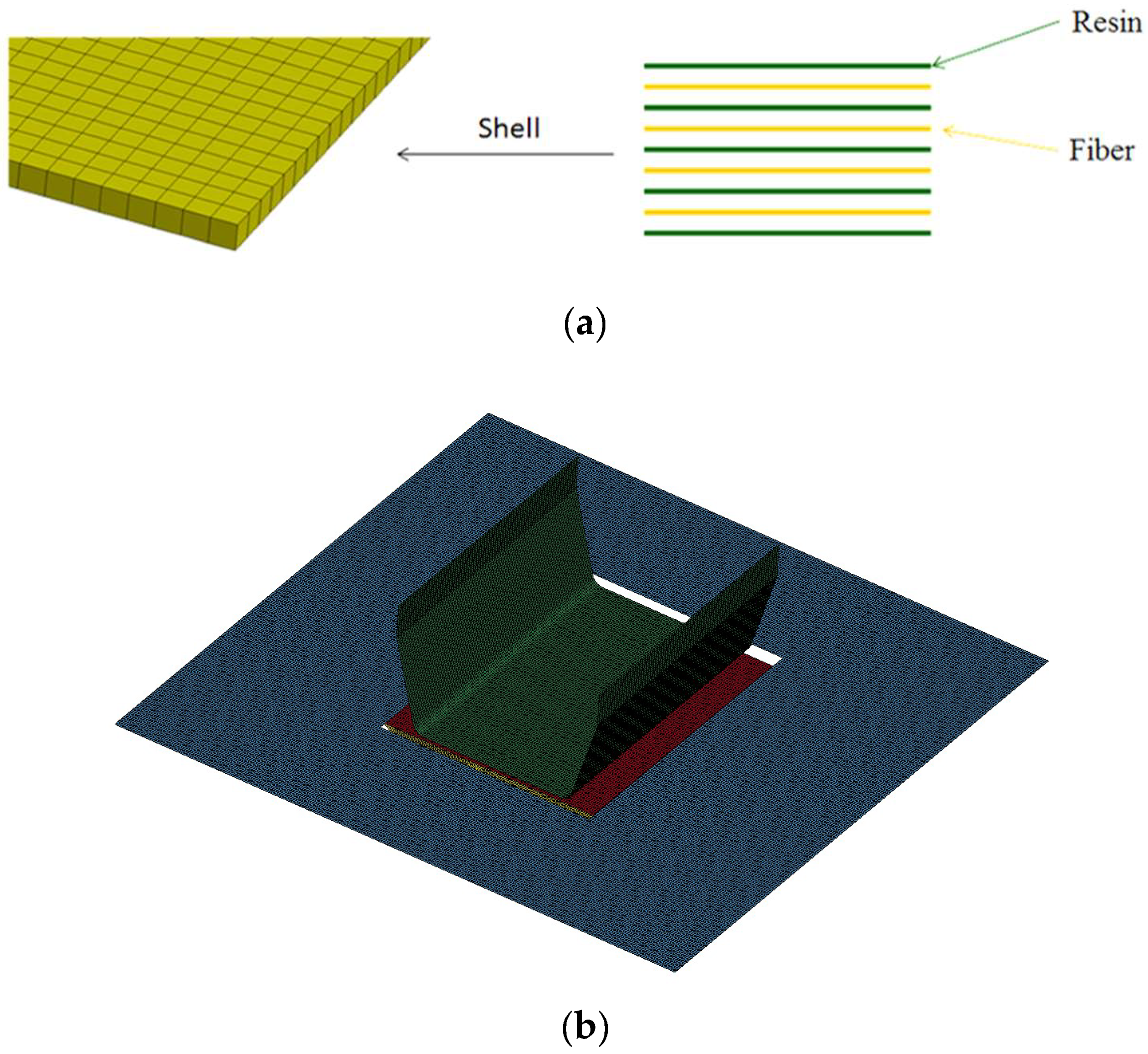
2. Thermoplastic Composite Material and Thermoforming Process
3. Finite Element Simulation
4. Results and Discussion
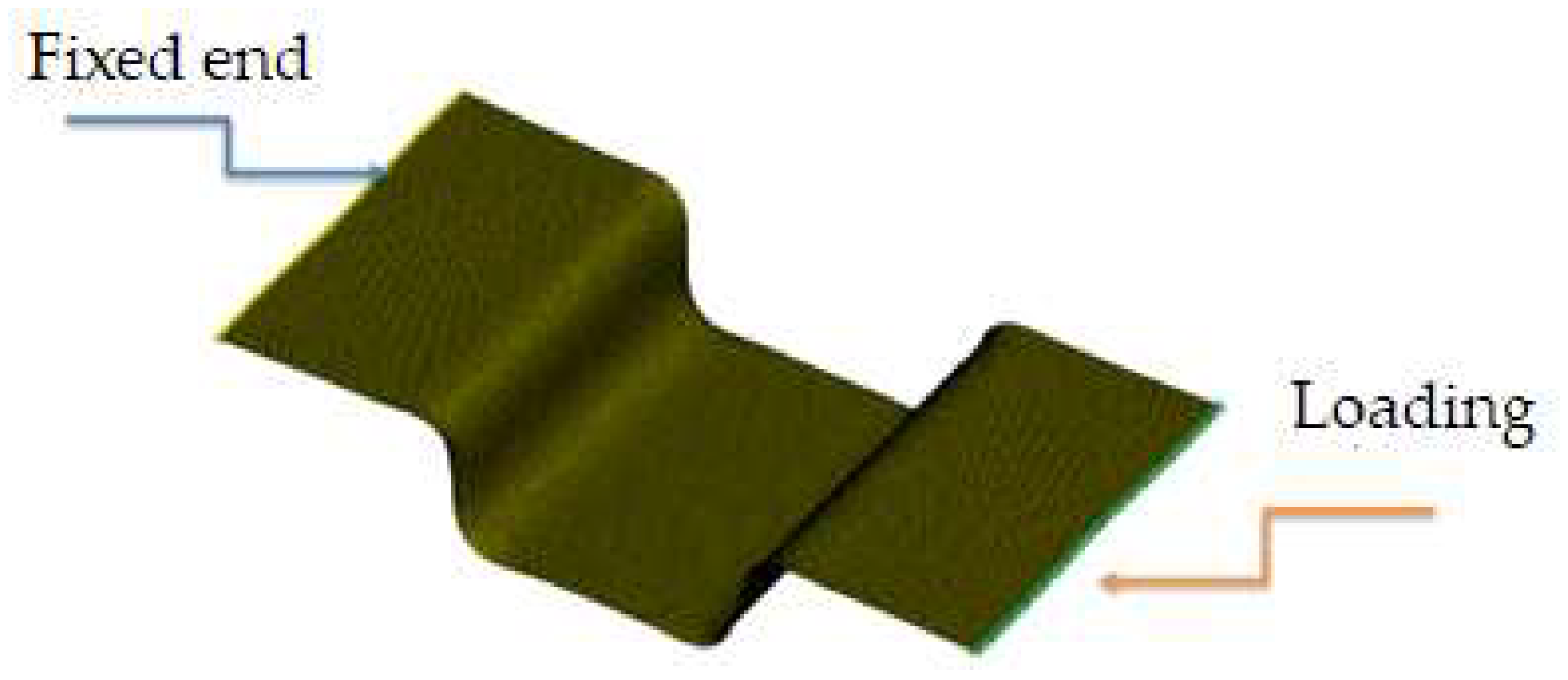
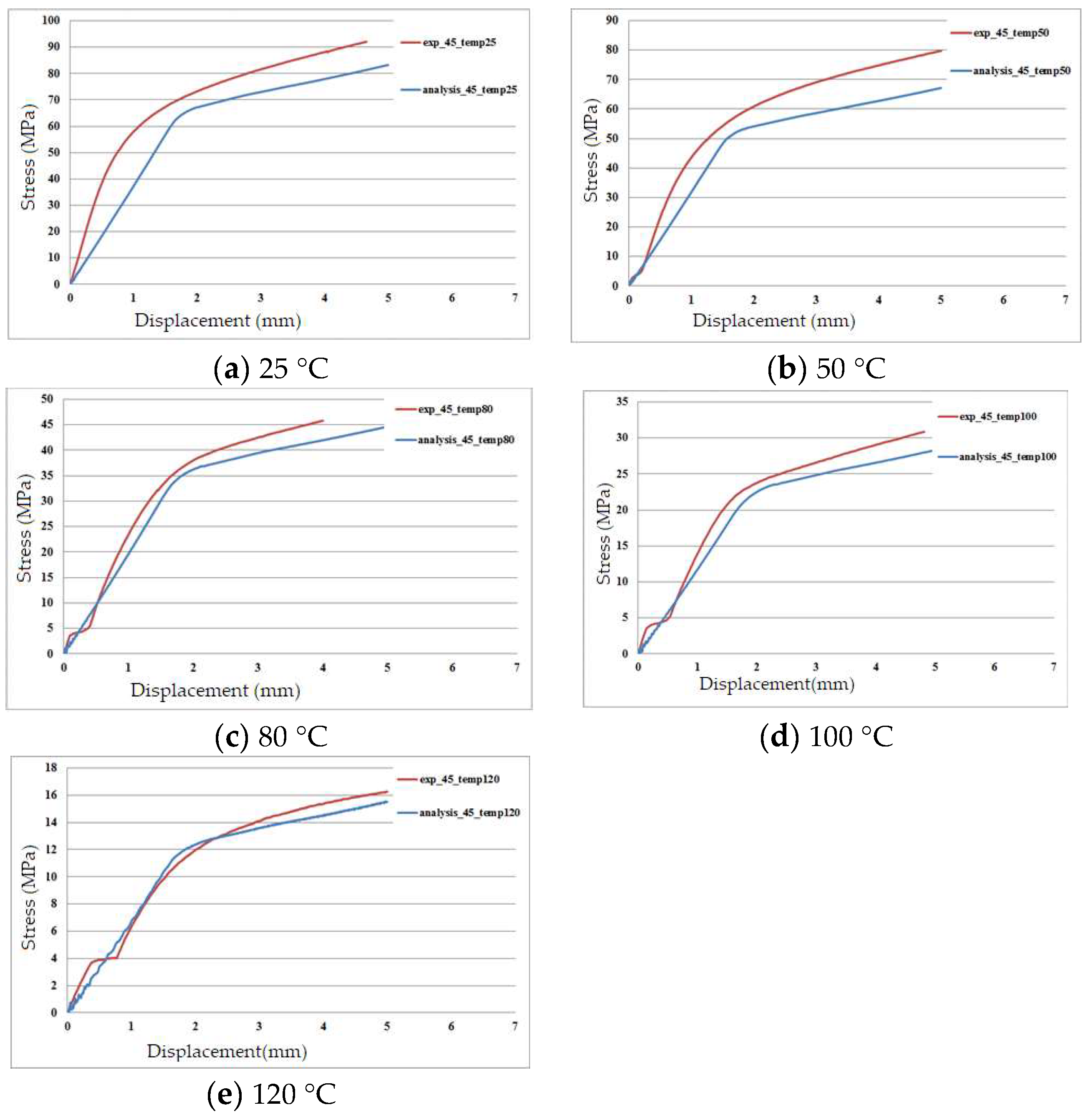
4.1. Bias Extension Test
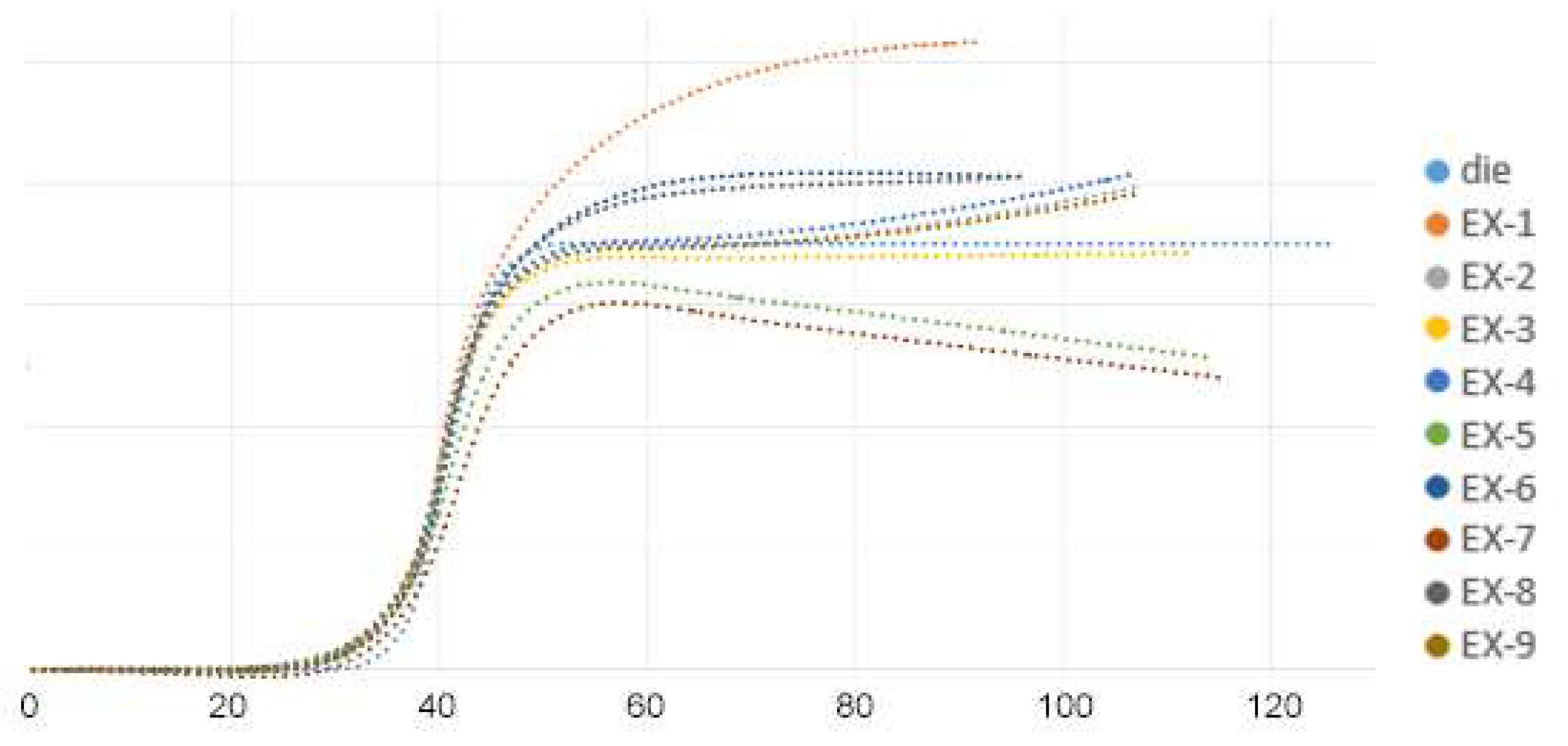
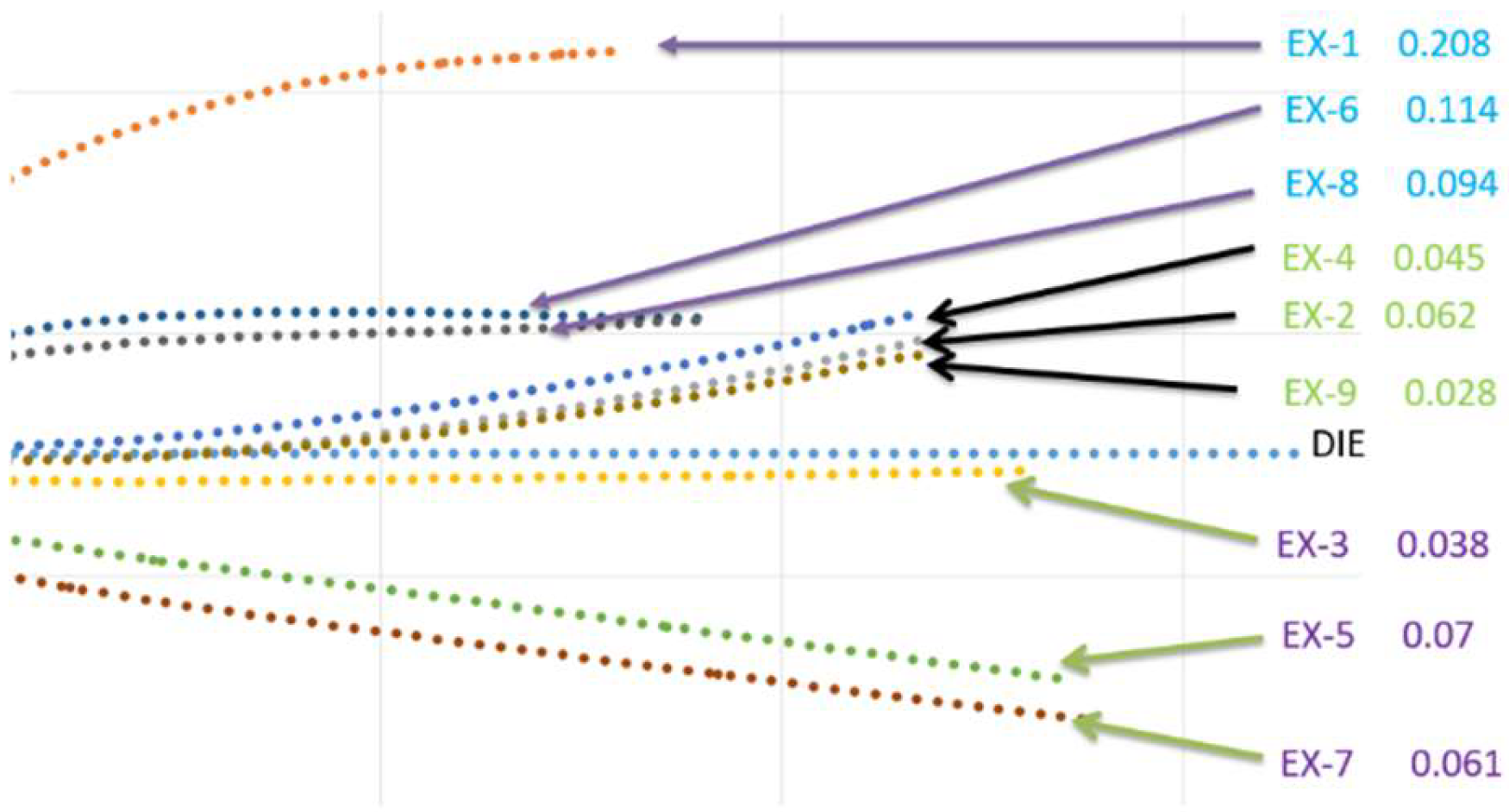
4.2. Results from the Taguchi Orthogonal Array
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- van Rijswijk, K.; Bersee, H.E.N. Reactive processing of textile fiber-reinforced thermoplastic composites—An overview. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2007, 38, 666–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malcolm, W.; Todd, E. Carbon fiber reinforced PPS thermoplastic materials implemented in cost sensitive commercial applications. In Proceedings of the 38th International SAMPE Symposium, Anaheim, CA, USA, 10–13 May 1993; pp. 2055–2065. [Google Scholar]
- Zampaloni, M.A.; Pourboghrat, F.; Yu, W.R. Stamp thermo-hydroforming: A new method for processing fiber-reinforced thermoplastic composite sheets. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2004, 17, 31–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, M.; Rossitti, I.; Sambucci, M. Different production processes for thermoplastic composite materials: Sustainability versus mechanical properties and processes parameter. Polymers 2023, 15, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offringa, A.R. Thermoplastic composites-rapid processing applications. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 1996, 27, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, B.; Raatz, A.; Hubner, S.; Bonk, C.; Bohne, F.; Bruns, C.; Micke-Camuz, M. Automated stamp forming of continuous fiber reinforced thermoplastics for complex shell geometries. Procedia CIRP 2017, 66, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Striewea, J.; Reutera, C.; Sauerlandb, K.H.; Tröstera, T. Manufacturing and crashworthiness of fabric-reinforced thermoplastic Composites. Thin-Walled Struct. 2018, 123, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maron, B.; Garthaus, C.; Hornig, A.; Lenz, F.; Hubner, M. Forming of carbon fiber reinforced thermoplastic composite tubes—Experimental and numerical approaches. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2017, 18, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlevliet, P.P.; Bersee, H.E.N.; Beukers, A. Residual stresses in thermoplastic composites-a study of the literature-part I: Formation of residual stresses. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2006, 37, 1847–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlevliet, P.P.; Bersee, H.E.N.; Beukers, A. Residual stresses in thermoplastic composites-a study of the literature-part II: Experimental techniques. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2007, 38, 651–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlevliet, P.P.; Bersee, H.E.N.; Beukers, A. Residual stresses in thermoplastic composites-a study of the literature-part III: Effect of thermal residual stresses. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2007, 38, 1581–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Butterfield, J.; Price, M.; Buchanan, S.; Murphy, A. Experimental investigation of thermoforming carbon fibre-reinforced polyphenylene sulphide composites. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2015, 28, 529–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Peng, X.; Du, T.; Chen, J. Forming of thermoplastic plain woven carbon composites: An experimental investigation. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2015, 28, 730–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadighi, M.; Radizadeh, E.; Kermansaravi, F. Effects of laminate sequencing on thermoforming of thermoplastic matrix Composites. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2008, 201, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.G.; Kim, D.H.; Jung, K.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, H.S. Effect of the cooling rate on the mechanical properties of glass fiber reinforced thermoplastic composites. Compos. Struct. 2017, 177, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorr, D.; Schirmaier, F.J.; Henning, F.; Karger, L. A viscoelastic approach for modeling bending behavior in finite element forming simulation of continuously fiber reinforced composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2017, 94, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman-Maldonado, E.; Hamila, N.; Naouar, N.; Moulin, G.; Boisse, P. Simulation of thermoplastic prepreg thermoforming based on a visco-hyperelastic model and a thermal homogenization. Mater. Design 2016, 93, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman-Maldonado, E.; Hamila, N.; Boisse, P.; Bikard, J. Thermomechanical analysis, modelling and simulation of the forming of pre-impregnated thermoplastics composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2015, 78, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margossian, A.; Bel, S.; Hinterhoelzl, R. On the characterisation of transverse tensile properties of molten unidirectional thermoplastic composite tapes for thermoforming simulations. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 88, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauffres, D.; Sherwood, J.A.; Morris, C.D.; Chen, J. Discrete mesoscopic modeling for the simulation of woven-fabric reinforcement forming. Int. J. Mater. Form. 2010, 3, S1205–S1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabiei, A.; Murugesan, R. Thermal structural forming simulation of carbon and glass fiber reinforced plastics composites. Int. J. Compos. Mater. 2015, 5, 182–194. [Google Scholar]
- Tabiei, A.; Ivanov, I. Computational micro-mechanical model of flexible woven fabric for finite element impact simulation. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2002, 53, 1259–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, I.; Tabiei, A. Loosely woven fabric model with viscoelastic crimped fibers for ballistic impact simulations. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2004, 61, 1565–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Hamila, N.; Boisse, P. Thermoforming simulation of multilayer composites with continuous fibers and thermoplastic matrix. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 52, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamila, N.; Boisse, P. Simulations of textile composite reinforcement draping using a new semi-discrete three node finite element. Compos. Part B Eng. 2008, 39, 999–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luycker, E.; Morestin, F.; Boisse, P.; Marsal, D. Simulation of 3D interlock composite preforming. Compos. Struct. 2009, 88, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charmetant, A.; Vidal-Salle, E.; Boisse, P. Hyperelastic modelling for mesoscopic analyses of composite reinforcements. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2011, 71, 1623–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, R.M.J.S.; Averill, R.C.; Riaz, M.; Pourboghrat, F. Finite element analysis of textile composite preform stamping. Compos. Struct. 2001, 52, 483–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.F.; Yu, C.X. Spring-in behavior of woven carbon fiber/polycarbonate thermoplastic composites. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2024, 37, 293–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Ding, F. Validation of a non-orthogonal constitutive model for woven composite fabrics via hemispherical stamping simulation. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2011, 42, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Property | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 1.8 | g/cm3 |
| Longitudinal Young’s modulus | 230 | GPa |
| Transverse Young’s modulus | 25.3 | GPa |
| Shear modulus | 12 | GPa |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.24 | |
| Heat capacity | 720 | J·°C−1 |
| Longitudinal thermal conductivity | −0.18 | W/m·K |
| Transverse thermal conductivity | 0.18 | W/m·K |
| Coefficient of thermal expansion | −1 × 10−6 | 1/°C |
| Ultimate strain at failure | 0.03 | |
| Yarn locking angle | 5 | Degree |
| Property | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 1.2 | g/cm3 |
| Young’s modulus | 2.9 | GPa |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.39 | |
| Heat capacity | 1250 | J·°C−1 |
| Thermal conductivity | 2 | W/m·K |
| Coefficient of thermal expansion | 67 × 10−6 | 1/°C |
| Factor | Blank Temperature | Mold Temperature | Blank Holding Pressure |
|---|---|---|---|
| EX-1 | 230 °C | 230 °C | 0 kPa |
| EX-2 | 230 °C | 190 °C | 1.18 kPa |
| EX-3 | 230 °C | 160 °C | 2.36 kPa |
| EX-4 | 190 °C | 230 °C | 1.18 kPa |
| EX-5 | 190 °C | 190 °C | 2.36 kPa |
| EX-6 | 190 °C | 160 °C | 0 kPa |
| EX-7 | 160 °C | 230 °C | 2.36 kPa |
| EX-8 | 160 °C | 190 °C | 0 kPa |
| EX-9 | 160 °C | 160 °C | 1.18 kPa |
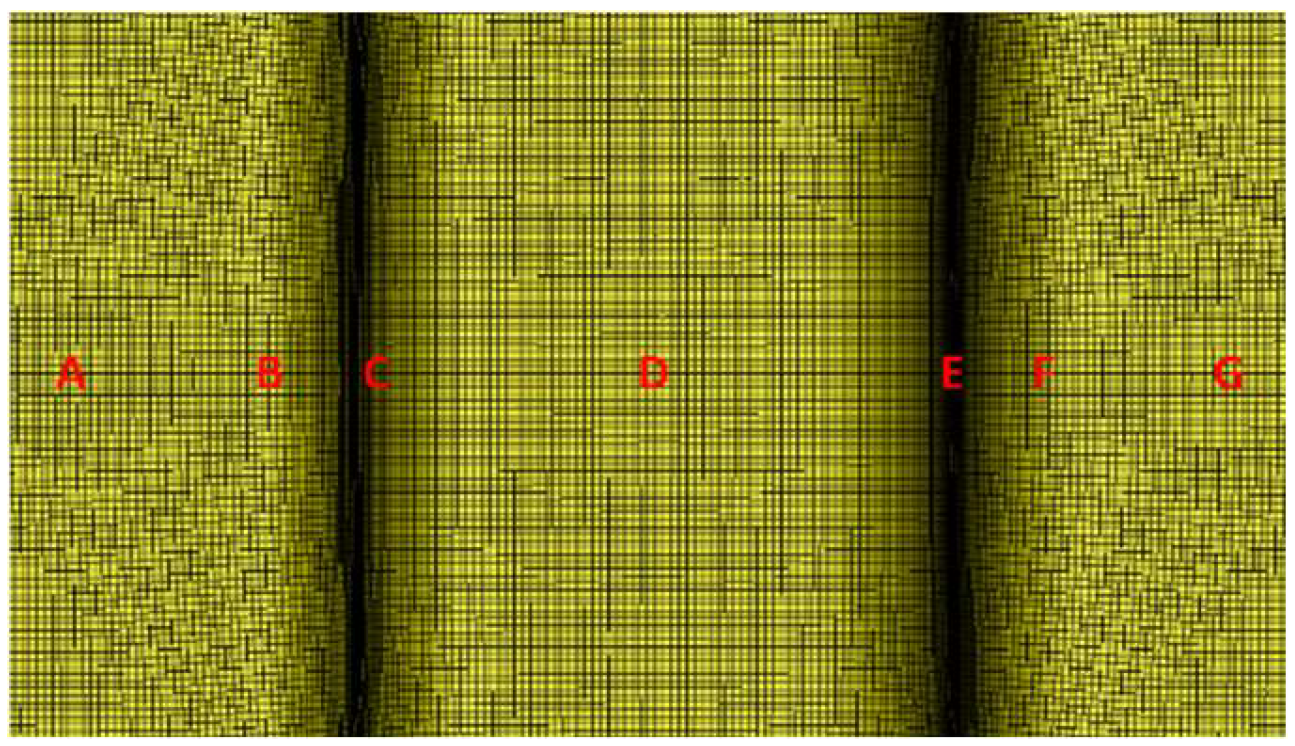
| A | B | C | D | E | F | G | Ave. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EX-1 | 94.48° | 96.44° | 94.48° | 96.44° | 94.48° | 96.44° | 94.48° | 95.32° |
| EX-2 | 95.04° | 89.10° | 81.16° | 83.14° | 81.16° | 89.10° | 95.04° | 87.68° |
| EX-3 | 84.56° | 84.56° | 80.34° | 83.16° | 80.34° | 84.56° | 84.56° | 83.16° |
| EX-4 | 95.16° | 89.18° | 81.20° | 83.20° | 81.20° | 89.18° | 95.16° | 87.74° |
| EX-5 | 84.34° | 84.34° | 78.34° | 81.34° | 78.34° | 84.34° | 84.34° | 82.18° |
| EX-6 | 95.82° | 97.94° | 93.58° | 95.82° | 95.82° | 97.94° | 95.82° | 96.10° |
| EX-7 | 84.88° | 84.8°8 | 80.34° | 82.60° | 80.34° | 84.88° | 84.88° | 83.26° |
| EX-8 | 95.16° | 97.20° | 95.16° | 95.16° | 95.16° | 97.20° | 95.16° | 96.02° |
| EX-9 | 95.22° | 89.30° | 81.40° | 83.38° | 81.40° | 89.30° | 95.22° | 87.88° |
| Spring-Back Angle | Fitness | Strain | |
|---|---|---|---|
| EX-1 | −3.65° | 19.77 | 0.208 |
| EX-2 | −0.32° | 2.00 | 0.062 |
| EX-3 | 0.23° | 3.41 | 0.038 |
| EX-4 | −0.08° | 3.00 | 0.045 |
| EX-5 | 4.61° | 4.99 | 0.070 |
| EX-6 | −1.45° | 9.44 | 0.114 |
| EX-7 | 13.07° | 6.44 | 0.061 |
| EX-8 | −2.60° | 7.06 | 0.094 |
| EX-9 | 0.43° | 3.59 | 0.062 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hwang, S.-F.; Yang, C.-Y.; Huang, S.-H. Effects of Thermoforming Parameters on Woven Carbon Fiber Thermoplastic Composites. Materials 2024, 17, 3932. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17163932
Hwang S-F, Yang C-Y, Huang S-H. Effects of Thermoforming Parameters on Woven Carbon Fiber Thermoplastic Composites. Materials. 2024; 17(16):3932. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17163932
Chicago/Turabian StyleHwang, Shun-Fa, Cheng-Yi Yang, and Shao-Hao Huang. 2024. "Effects of Thermoforming Parameters on Woven Carbon Fiber Thermoplastic Composites" Materials 17, no. 16: 3932. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17163932
APA StyleHwang, S.-F., Yang, C.-Y., & Huang, S.-H. (2024). Effects of Thermoforming Parameters on Woven Carbon Fiber Thermoplastic Composites. Materials, 17(16), 3932. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17163932







