Continuous and Stable Printing Method of Planar Microstructure Based on Meniscus-Confined Electrodeposition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Principles and Methods
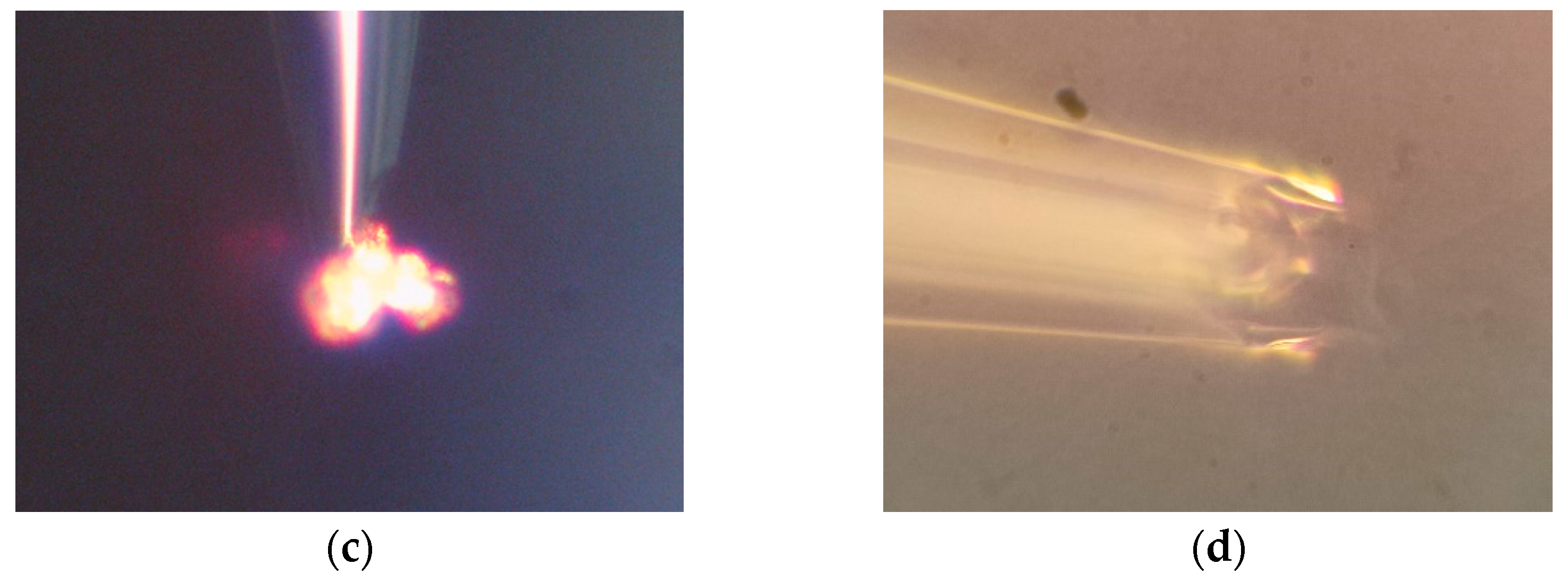
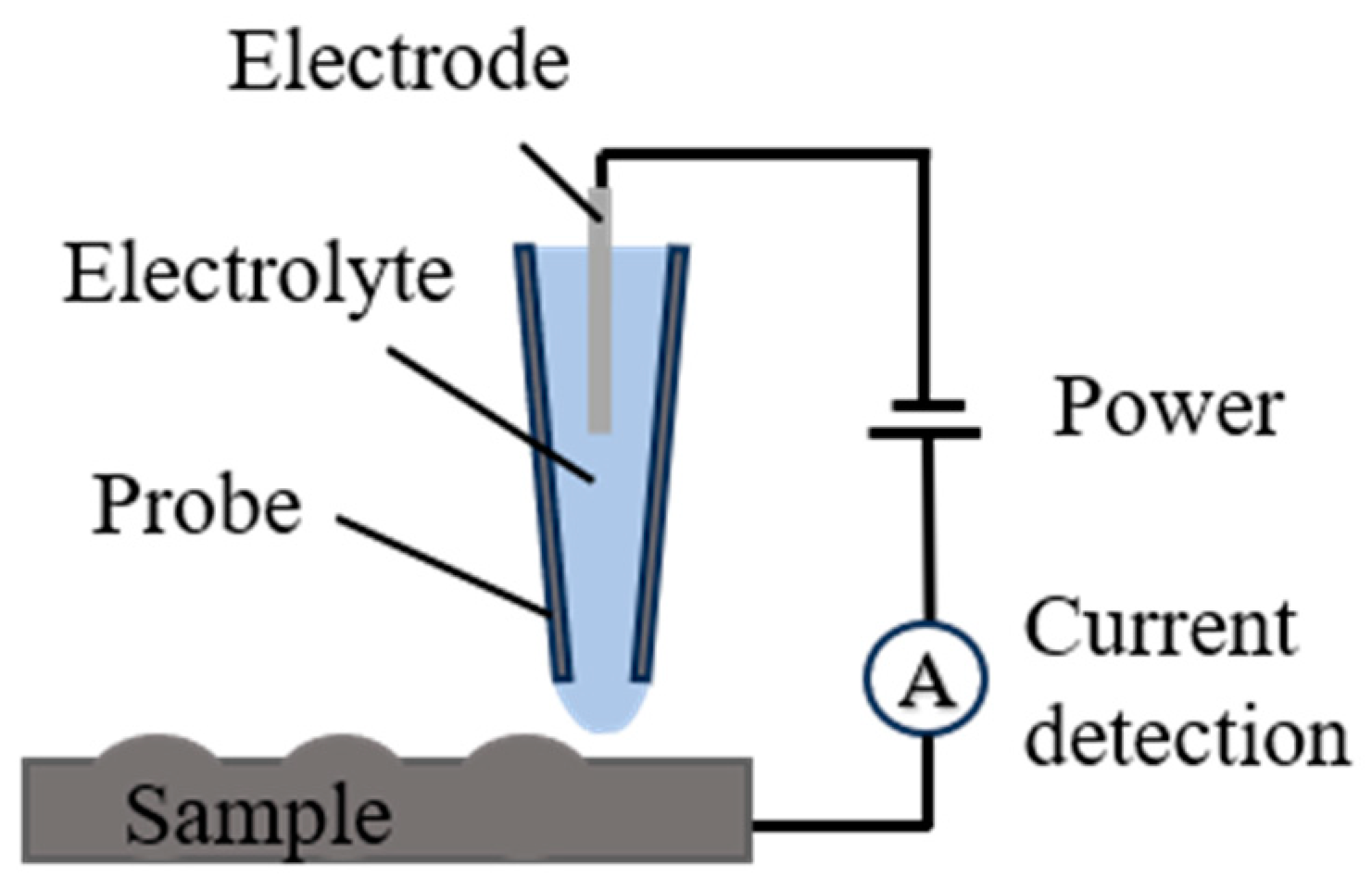
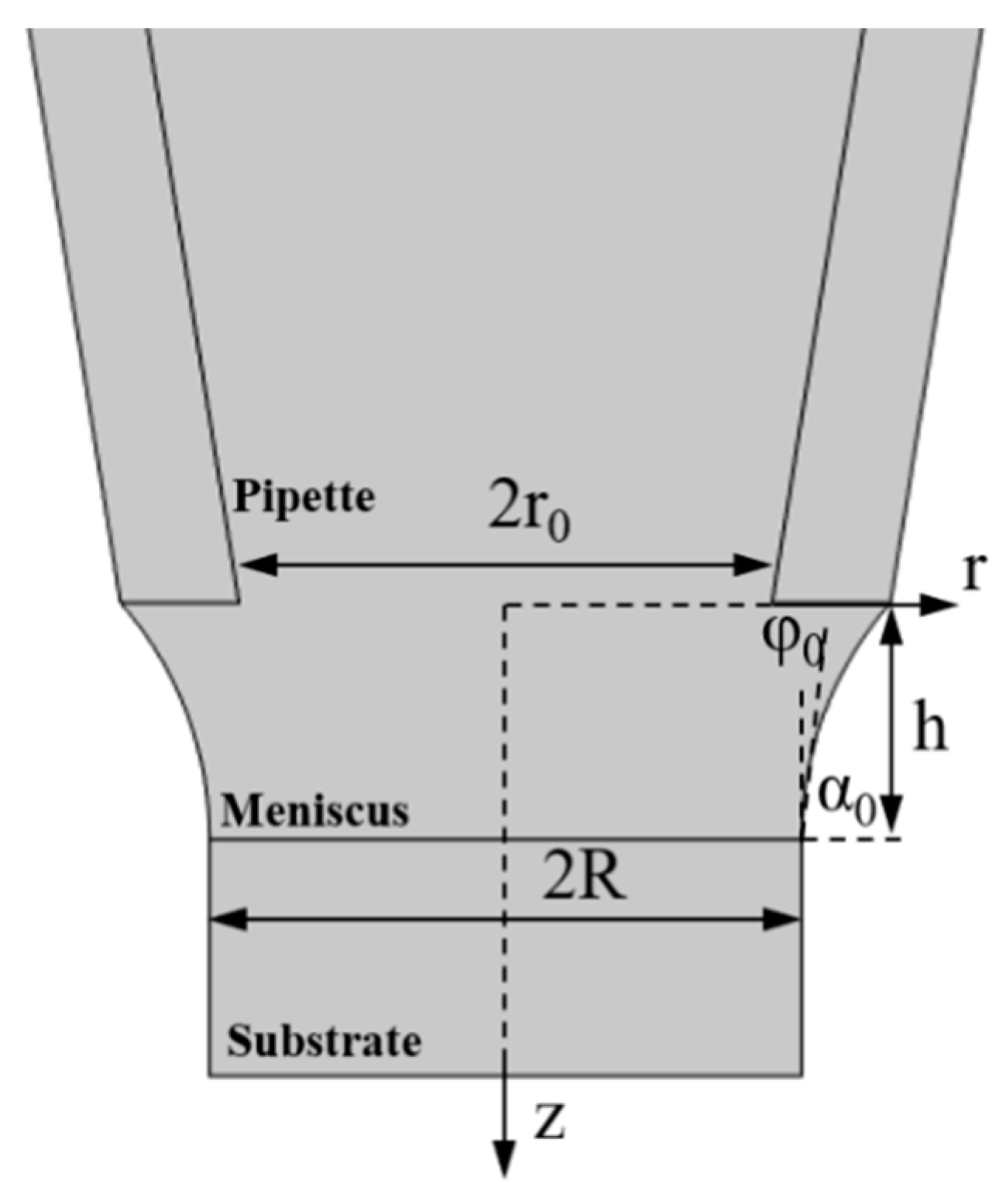
2.1. Principle of Meniscus-Confined Electrodeposition
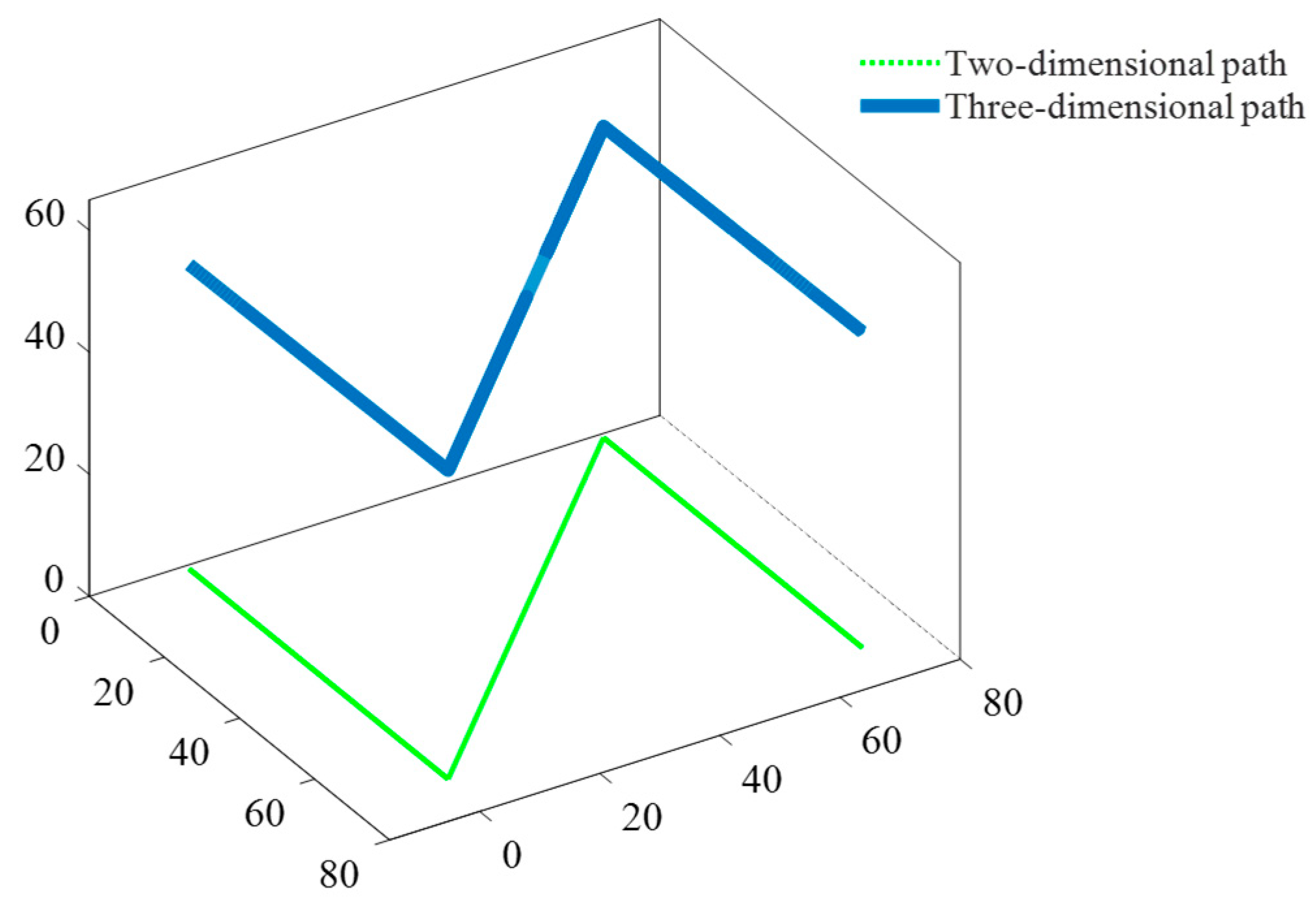
2.2. Planar Adaptive Micro-Tuning Deposition Method (PAMTDM)
2.2.1. SVD Plane Fitting
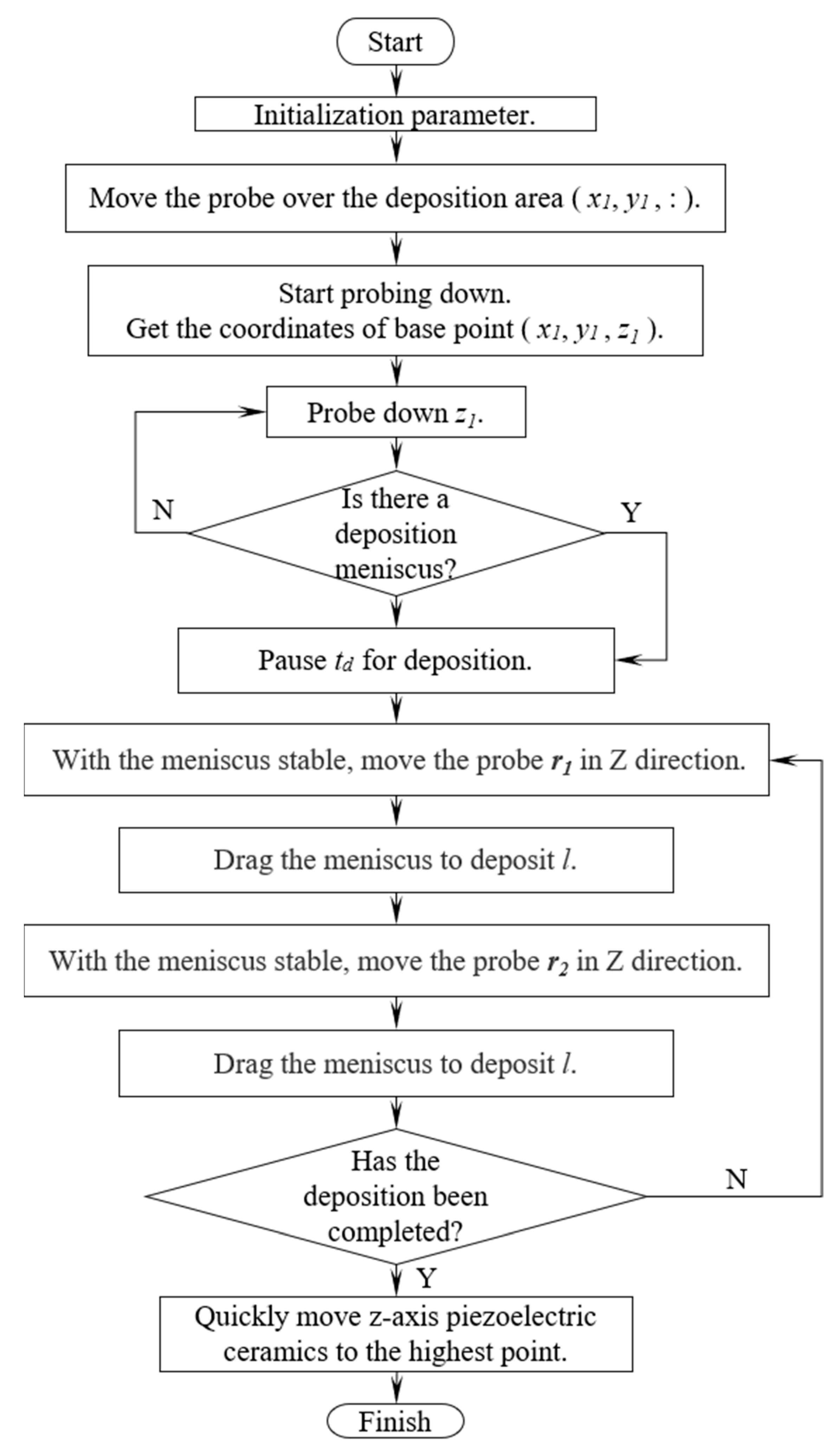
2.2.2. Motion Method
- Preparation: Move the probe above the deposition point with a distance from the deposition plane not exceeding 80 μm (Z-axis range: 0–80 μm). Using the SECCM positioning principle, obtain the Z-coordinate of and set this point as the reference point.
- Initial Deposition: If deposition proceeds along the x-axis, lower the probe from the reference point by and observe whether a meniscus forms. If a deposition meniscus forms, time is paused to perform the deposition.
- Upward Lift and Lateral Movement: Lift the probe by , maintain the meniscus, and move by a distance of l. The new position is .
- Meniscus Stability Adjustment: To ensure continuous liquid flow at the probe tip and prevent tip clogging due to a small probe opening, lower the glass microprobe by a distance ( to maintain a safe distance from the substrate and avoid collision). The probe tip coordinates at this point are , which stabilize the meniscus through slight pressure.
- Further Deposition: Move a distance l for deposition, reaching point .
- Repetition: Lift the probe to point , continue moving the distance l, and repeat the above steps.
- Termination: Upon reaching the endpoint, hold the probe in place for to complete the deposition. Finally, lift the probe quickly to complete the deposition process.
3. Experimental Platform and Model
3.1. Experimental Platform
3.2. Multi-Physics Model
4. Optimal Parameter Determination and Experimental Verification
4.1. Optimal Parameter Determination
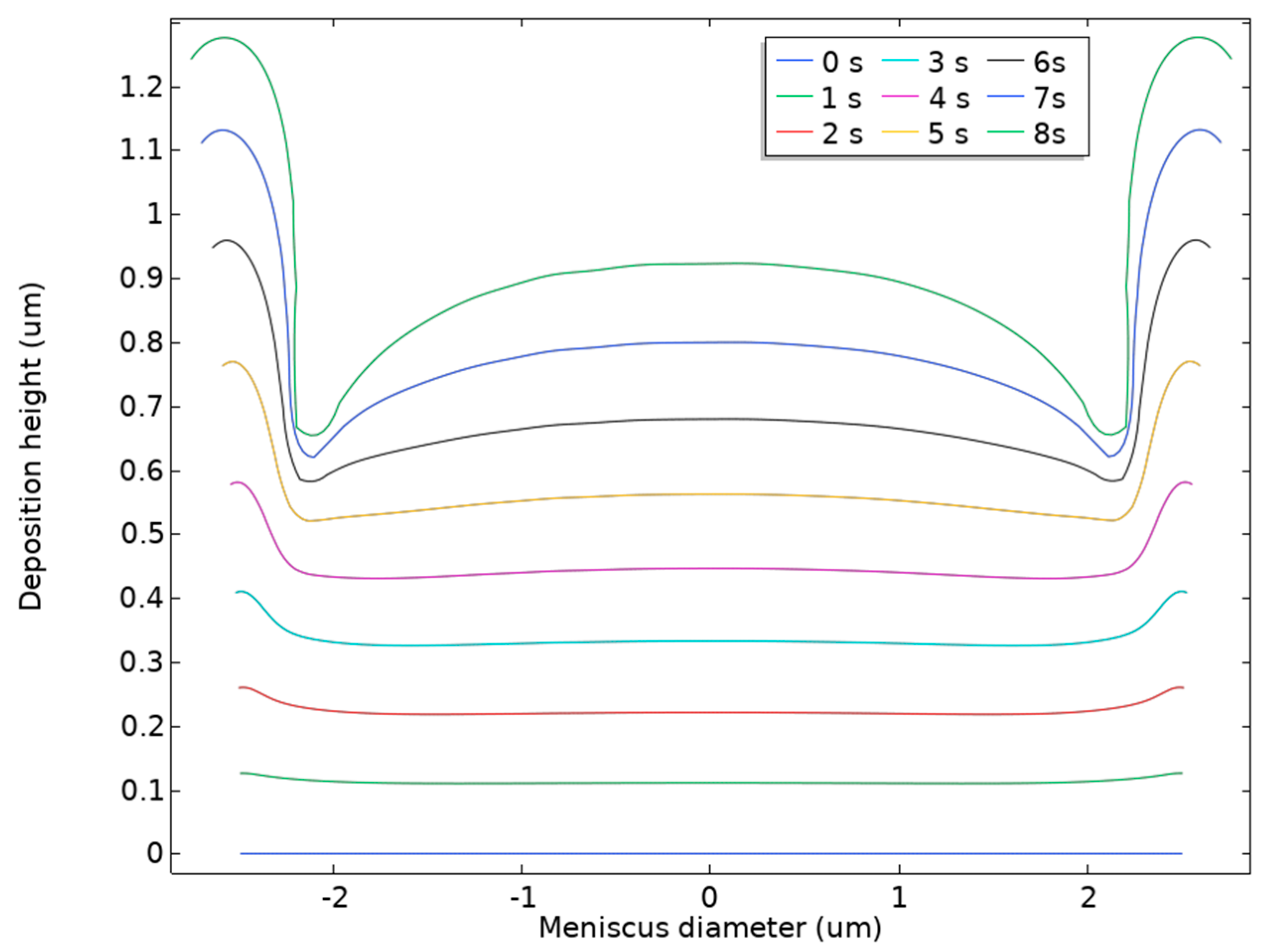
4.1.1. Analysis of Simulation Results
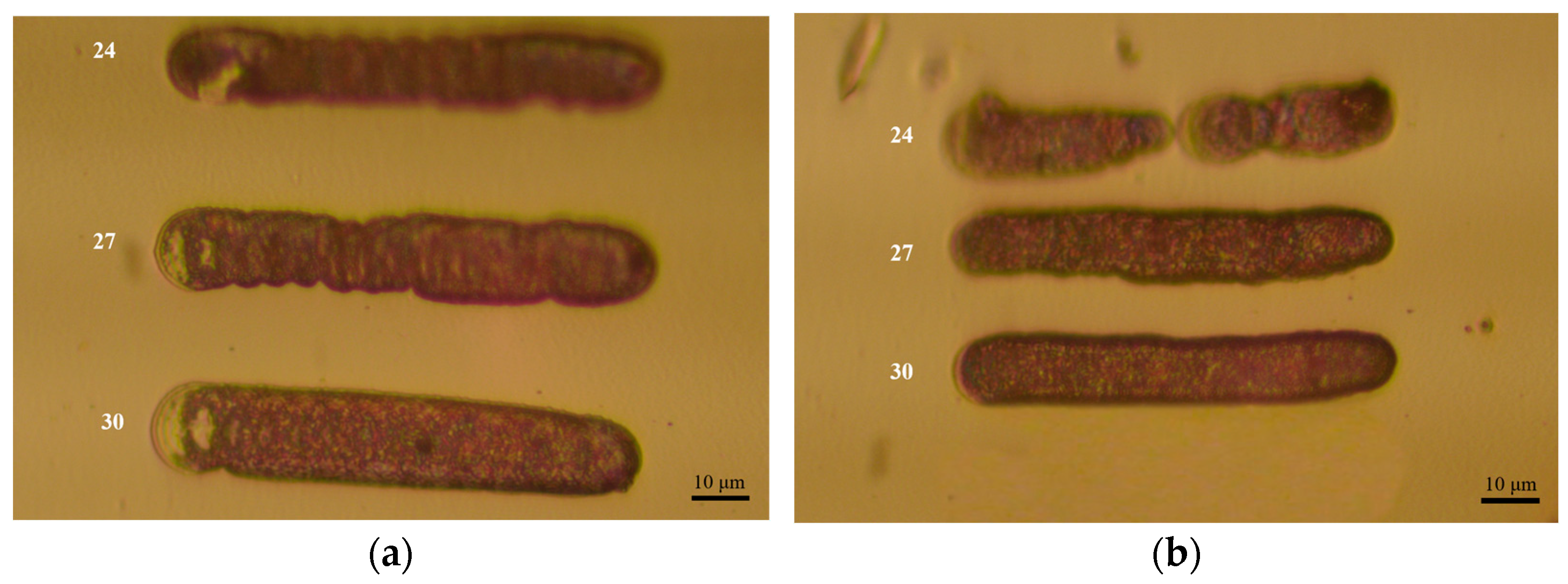
4.1.2. Optimal Parameters Based on Experimental Results
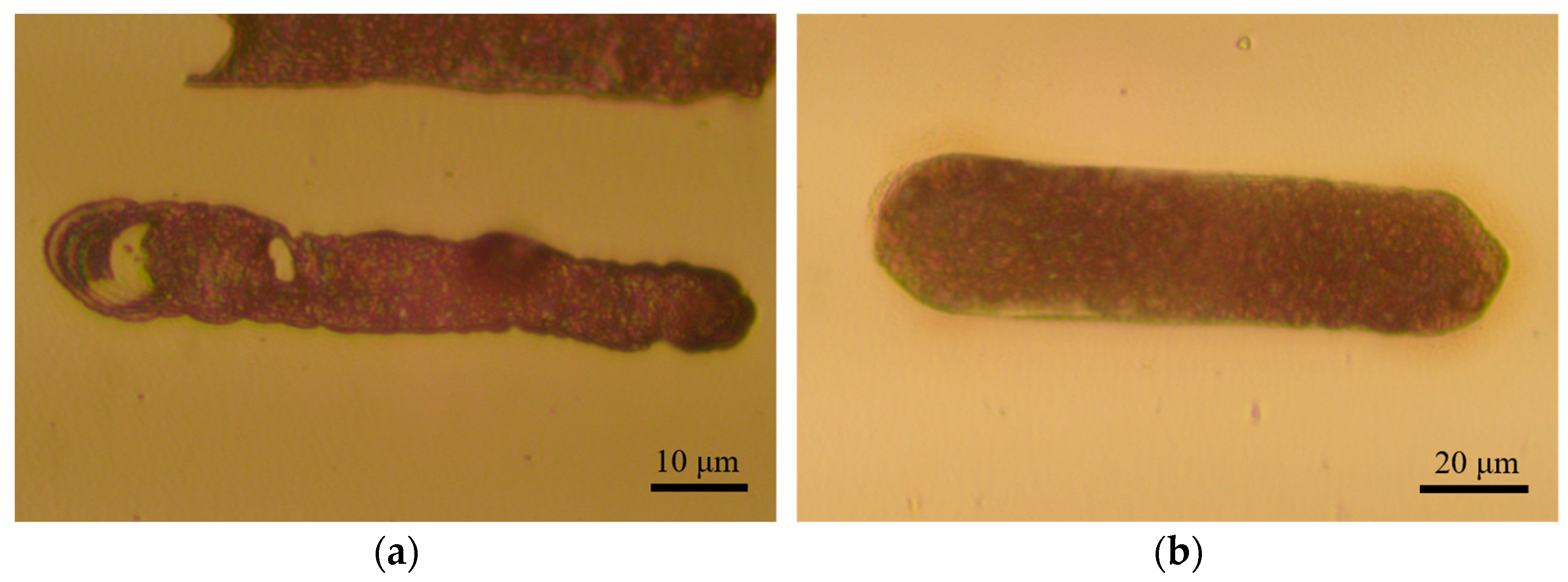
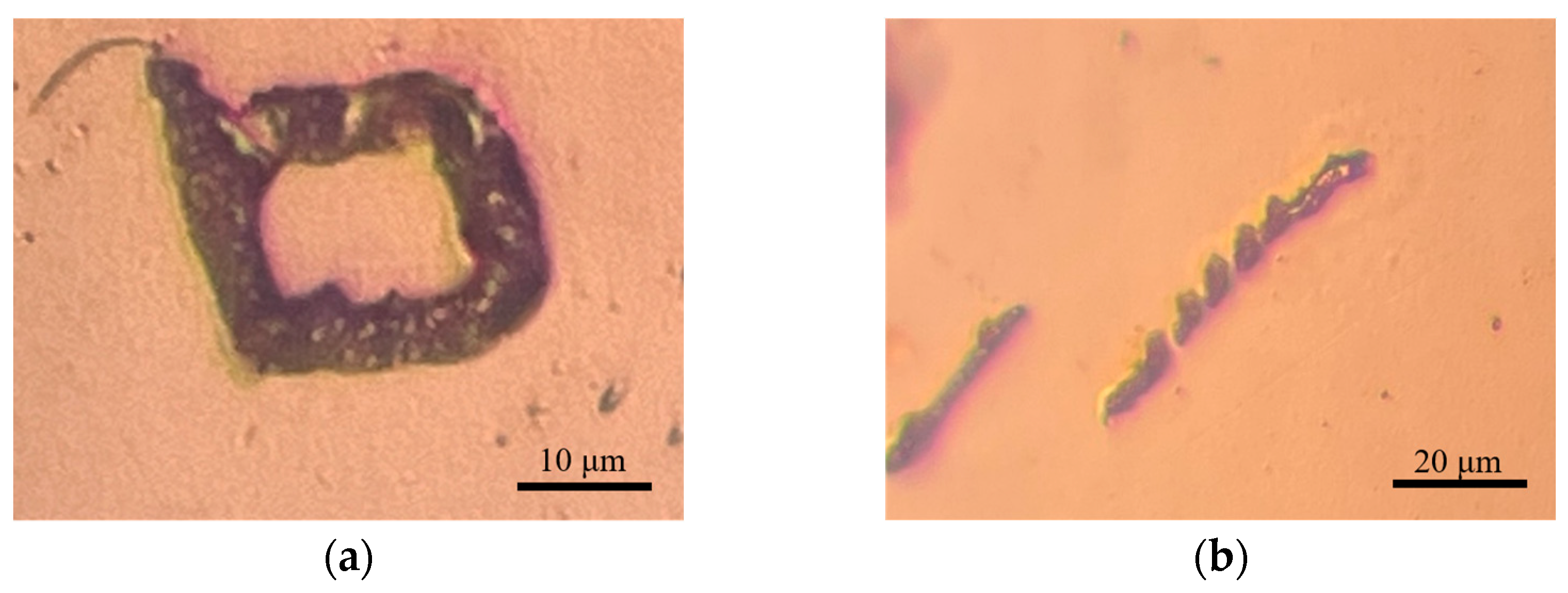
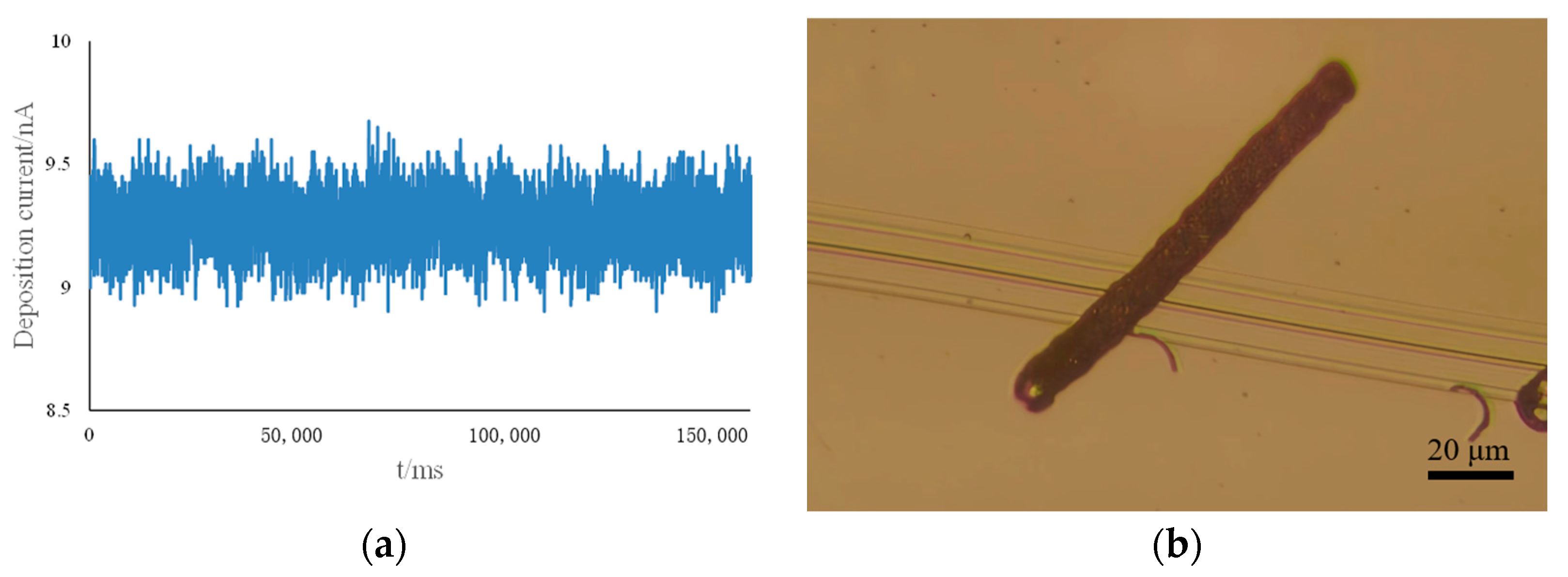
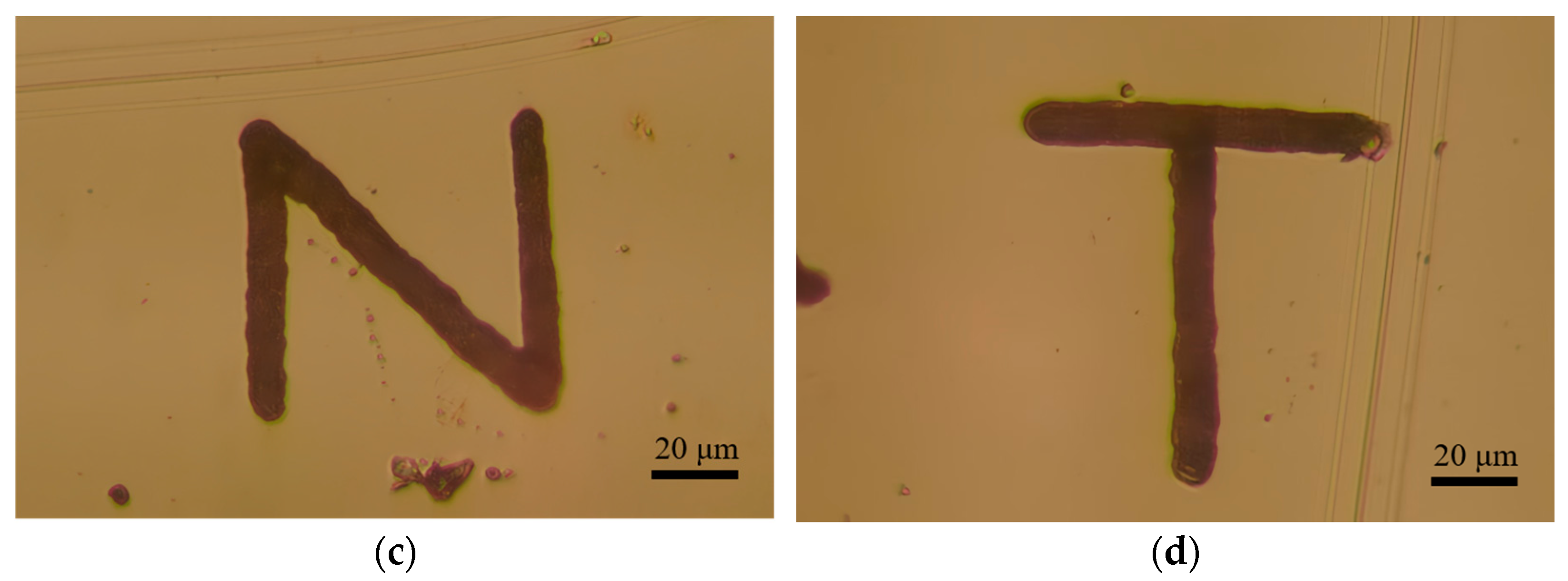
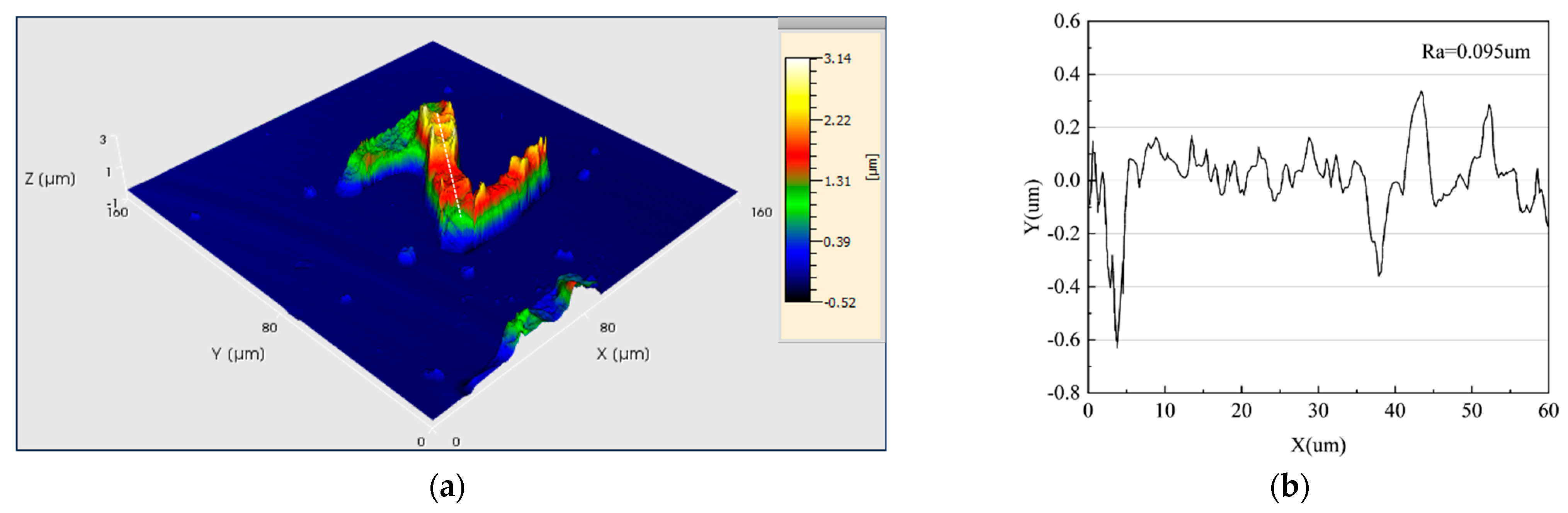
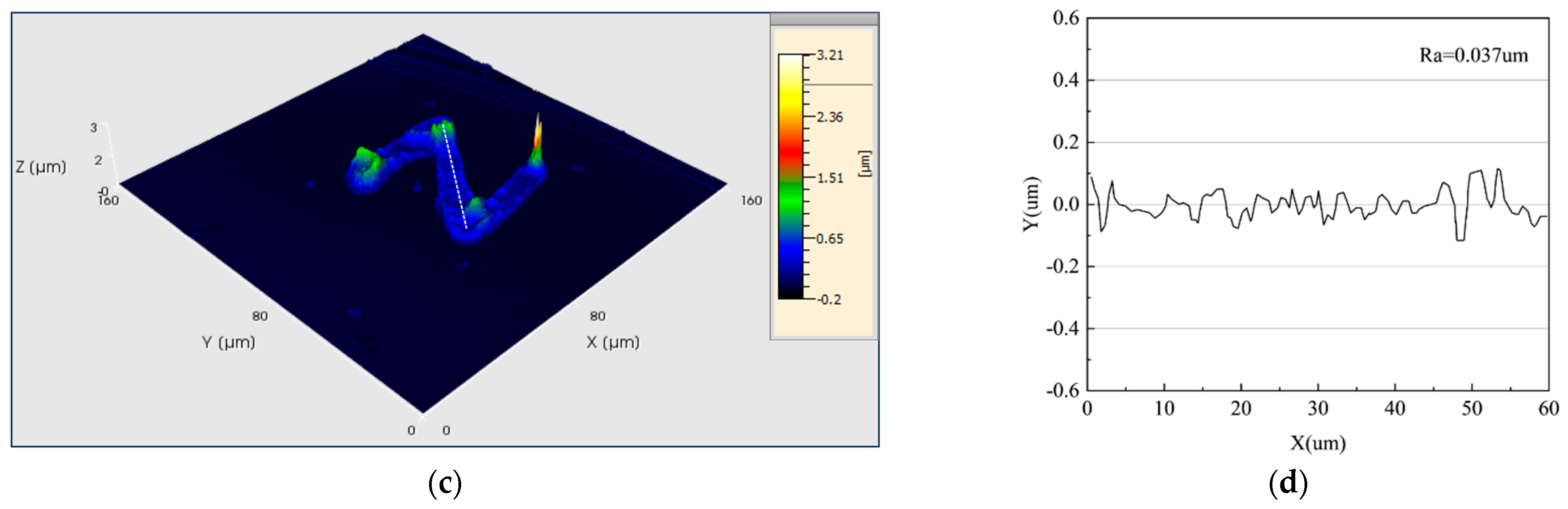
4.2. Verification of Deposition Effect of PAMTDM
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pingmei, M.; Xinchao, L.I.; Xinmin, Z.; Ge, Q.; Liang, Y.; Junzhong, Z.; Xiaodi, L. Research progress of electrochemical three-dimensional micro-deposition technology. Sci. Sin. (Technol.) 2018, 48, 347–359. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, E.W.; Ehrfeld, W.; Hagmann, P.; Maner, A.; Münchmeyer, D. Fabrication of microstructures with high aspect ratios and great structural heights by synchrotron radiation lithography, galvanoforming, and plastic moulding (LIGA process). Microelectron. Eng. 1986, 4, 35–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirt, L.; Reiser, A.; Spolenak, R.; Zambelli, T. Additive Manufacturing of Metal Structures at the Micrometer Scale. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calignano, F.; Manfredi, D.; Ambrosio, E.P.; Biamino, S.; Lombardi, M.; Atzeni, E.; Salmi, A.; Minetola, P.; Iuliano, L.; Fino, P. Overview on Additive Manufacturing Technologies. Proc. IEEE 2017, 105, 593–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamayo-Dominguez, A.; Fernandez-Gonzalez, J.M.; Sierra-Perez, M. Metal-Coated 3D-Printed Waveguide Devices for mm-Wave Applications [Application Notes]. IEEE Microw. Mag. 2019, 20, 18–31. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, W.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Q.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, L.; Cheng, Y.; Sun, A.; Wang, G. Direct Writing of Shape-Gradient Magnetic Alloy Microwire Arrays with Meniscus-Confined Electrodeposition Process. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 7, 2200024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J. Interfacial Physics in Meniscus-Confined Electrodeposition and Its Applications for Fabricating Electronic Structures. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Champaign, IL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Seol, S.K.; Kim, D.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.H.; Chang, W.S.; Kim, J.T. Electrodeposition-based 3D Printing of Metallic Microarchitectures with Controlled Internal Structures. Small 2015, 11, 3896–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Liao, X.; Deng, Y.; Cheng, L.; Zia, A.A.; Cai, Y.; Zhou, M. A circuit model for SECCM and topographic imaging method in AC mode. Micron 2019, 126, 102738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Zhuang, J.; Deng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lu, X. A closed-loop constant deposition current control method based on MCED circuit model. AIP Adv. 2020, 10, 045118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xu, Z.; Ren, W.; Zou, Z.; Wang, X. Simulation and Experimental Study on Metal Microstructure of Meniscus-Confined Electrodeposition. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2022, 24, 2200654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xiong, X.; Ju, B.F.; Chen, Y.L. Voxelated meniscus-confined electrodeposition of 3D metallic microstructures. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. Des. Res. Appl. 2022, 174, 103850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, Z. A review of modern advancements in micro drilling techniques. J. Manuf. Process. 2017, 29, 343–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behroozfar, A.; Daryadel, S.; Morsali, S.R.; Moreno, S.; Baniasadi, M.; Bernal, R.A.; Minary-Jolandan, M. Microscale 3D Printing of Nanotwinned Copper. Adv. Mater. 2017, 30, 1705107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xu, D.; Yu, M.F.; Yi, Z.; Li, Z.; Sun, A.; Xu, G.; Cui, P.; Guo, J. Dynamic “Scanning-Mode” Meniscus Confined Electrodepositing and Micropatterning of Individually Addressable Ultraconductive Copper Line Arrays. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 2380–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Y.; Gao, F.; Guo, J.; Xu, G.; Yang, Y. Microfabrication of conductive copper patterns by meniscus-confined electrodeposition. Integr. Ferroelectr. 2018, 190, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.G.; Edwards, M.A.; Colley, A.L.; Macpherson, J.V.; Unwin, P.R. Scanning micropipet contact method for high-resolution imaging of electrode surface redox activity. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 2486–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebejer, N.; Schnippering, M.; Colburn, A.W.; Edwards, M.A.; Unwin, P.R. Localized high resolution electrochemistry and multifunctional imaging: Scanning electrochemical cell microscopy. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 9141–9145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, B.; Unwin, P.R.; Bentley, C.L. Nanoscale Variations in the Electrocatalytic Activity of Layered Transition-Metal Dichalcogenides. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Kumatani, A.; Munakata, H.; Inomata, H.; Ito, K.; Ino, K.; Shiku, H.; Unwin, P.R.; Korchev, Y.E.; Kanamura, K. Nanoscale visualization of redox activity at lithium-ion battery cathodes. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Zhuang, J.; Cheng, L.; Yang, J.; Zheng, Q. Environmental humidity control method for structural reading and writing based on micropipette probe. Opt. Precis. Eng. 2021, 29, 2432–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.T.; Seol, S.K.; Pyo, J.; Lee, J.S.; Je, J.H.; Margaritondo, G. Three-Dimensional Writing of Conducting Polymer Nanowire Arrays by Meniscus-Guided Polymerization. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Study of Microscale Meniscus Confined Electrodeposition Based on COMSOL. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Copper ion solution | CuSO4 (0.1 M) |
| Glass pipette aperture | 5 µm |
| Rate of travel | 1.5 μm/s |
| Ambient temperature | Room temperature (20 °C) |
| Environment humidity | 40% |
| Levels | Factors | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| l | |||
| 1 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 2 |
| 2 | 0.8 | 0.4 | 3 |
| 3 | 1.0 | 0.6 | 4 |
| 4 | 1.2 | 0.8 | 5 |
| Experimental Serial Number | /(μm) | /(μm) | l/(μm) | RMSE/(nA) | /(μm/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 2 | 0.2286 | 0.304 |
| 2 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 3 | 0.1976 | 0.421 |
| 3 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 4 | 0.1923 | 0.482 |
| 4 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 2 | 0.2196 | 0.337 |
| 5 | 0.8 | 0.4 | 3 | 0.1872 | 0.404 |
| 6 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 4 | 0.1936 | 0.464 |
| 7 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 5 | 0.2062 | 0.486 |
| 8 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 3 | 0.1971 | 0.377 |
| 9 | 1.0 | 0.4 | 2 | 0.1876 | 0.337 |
| 10 | 1.0 | 0.6 | 5 | 0.1987 | 0.461 |
| 11 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 4 | 0.2033 | 0.464 |
| 12 | 1.2 | 0.2 | 3 | 0.1896 | 0.362 |
| 13 | 1.2 | 0.4 | 2 | 0.2017 | 0.315 |
| 14 | 1.2 | 0.6 | 5 | 0.1992 | 0.446 |
| 15 | 1.2 | 0.8 | 4 | 0.1929 | 0.446 |
| 16 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 5 | 0.2004 | 0.458 |
| 17 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 4 | 0.1918 | 0.461 |
| 18 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 3 | 0.1953 | 0.442 |
| 19 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 5 | 0.1960 | 0.449 |
| 20 | 0.8 | 0.4 | 4 | 0.2007 | 0.456 |
| 21 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 3 | 0.1908 | 0.421 |
| 22 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 2 | 0.1884 | 0.368 |
| 23 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 4 | 0.1968 | 0.424 |
| 24 | 1.0 | 0.4 | 5 | 0.2014 | 0.443 |
| 25 | 1.0 | 0.6 | 2 | 0.1877 | 0.352 |
| 26 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 3 | 0.1863 | 0.414 |
| 27 | 1.2 | 0.2 | 4 | 0.1965 | 0.409 |
| 28 | 1.2 | 0.4 | 5 | 0.1989 | 0.435 |
| 29 | 1.2 | 0.6 | 2 | 0.1901 | 0.338 |
| 30 | 1.2 | 0.8 | 3 | 0.1861 | 0.4 |
| Experimental Serial Number | RMSE1/(nA) | RMSE2/(nA) |
|---|---|---|
| 24 | 0.1944 | 0.2153 |
| 27 | 0.1596 | 0.136 |
| 30 | 0.1157 | 0.1197 |
| Deposition Parameters | |
|---|---|
| r1/µm | 1.2 |
| r2/µm | 0.8 |
| td/ms | 5000 |
| l/µm | 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Wan, H.; Xing, Q.; Zhang, X.; Xu, H. Continuous and Stable Printing Method of Planar Microstructure Based on Meniscus-Confined Electrodeposition. Materials 2024, 17, 4650. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17184650
Yang Y, Wan H, Xing Q, Zhang X, Xu H. Continuous and Stable Printing Method of Planar Microstructure Based on Meniscus-Confined Electrodeposition. Materials. 2024; 17(18):4650. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17184650
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yawen, Hanchi Wan, Qiang Xing, Xiaoping Zhang, and Haili Xu. 2024. "Continuous and Stable Printing Method of Planar Microstructure Based on Meniscus-Confined Electrodeposition" Materials 17, no. 18: 4650. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17184650
APA StyleYang, Y., Wan, H., Xing, Q., Zhang, X., & Xu, H. (2024). Continuous and Stable Printing Method of Planar Microstructure Based on Meniscus-Confined Electrodeposition. Materials, 17(18), 4650. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17184650







