Fluorescence Output Enhancement of Ce3+:YAG Transparent Ceramics by Eutectic Soldering Packaging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
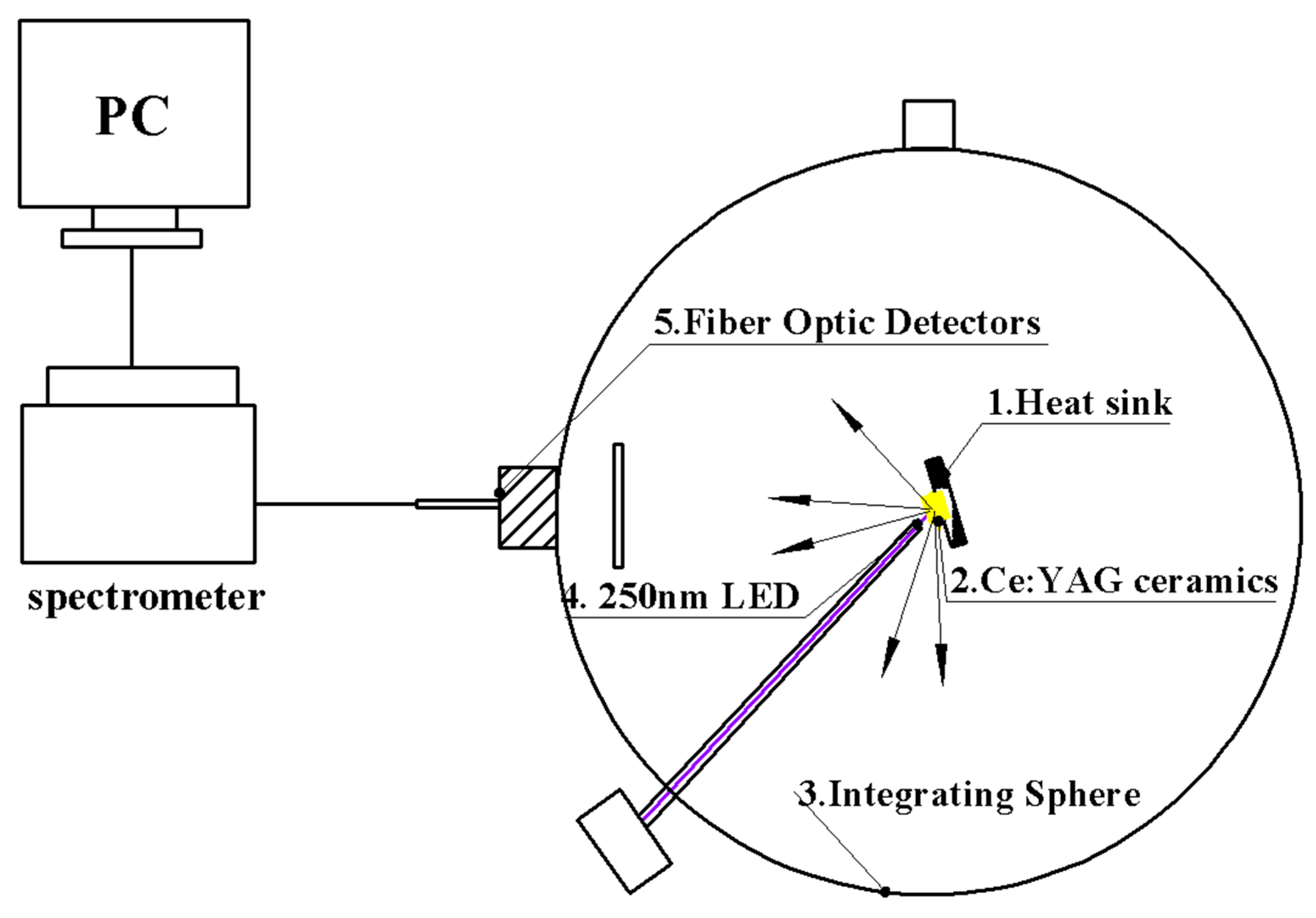
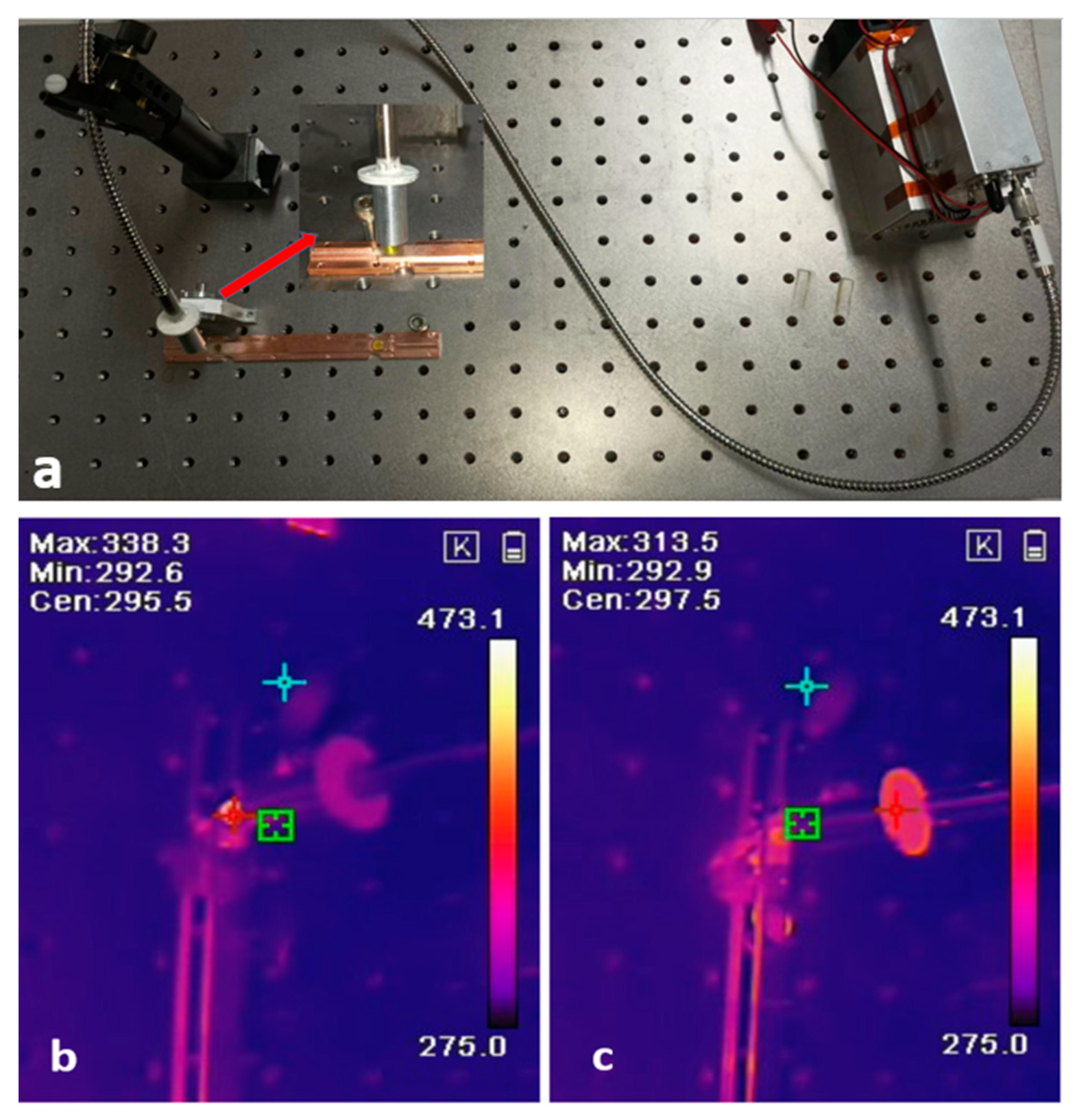
2. Experimental
3. Results and Discussion
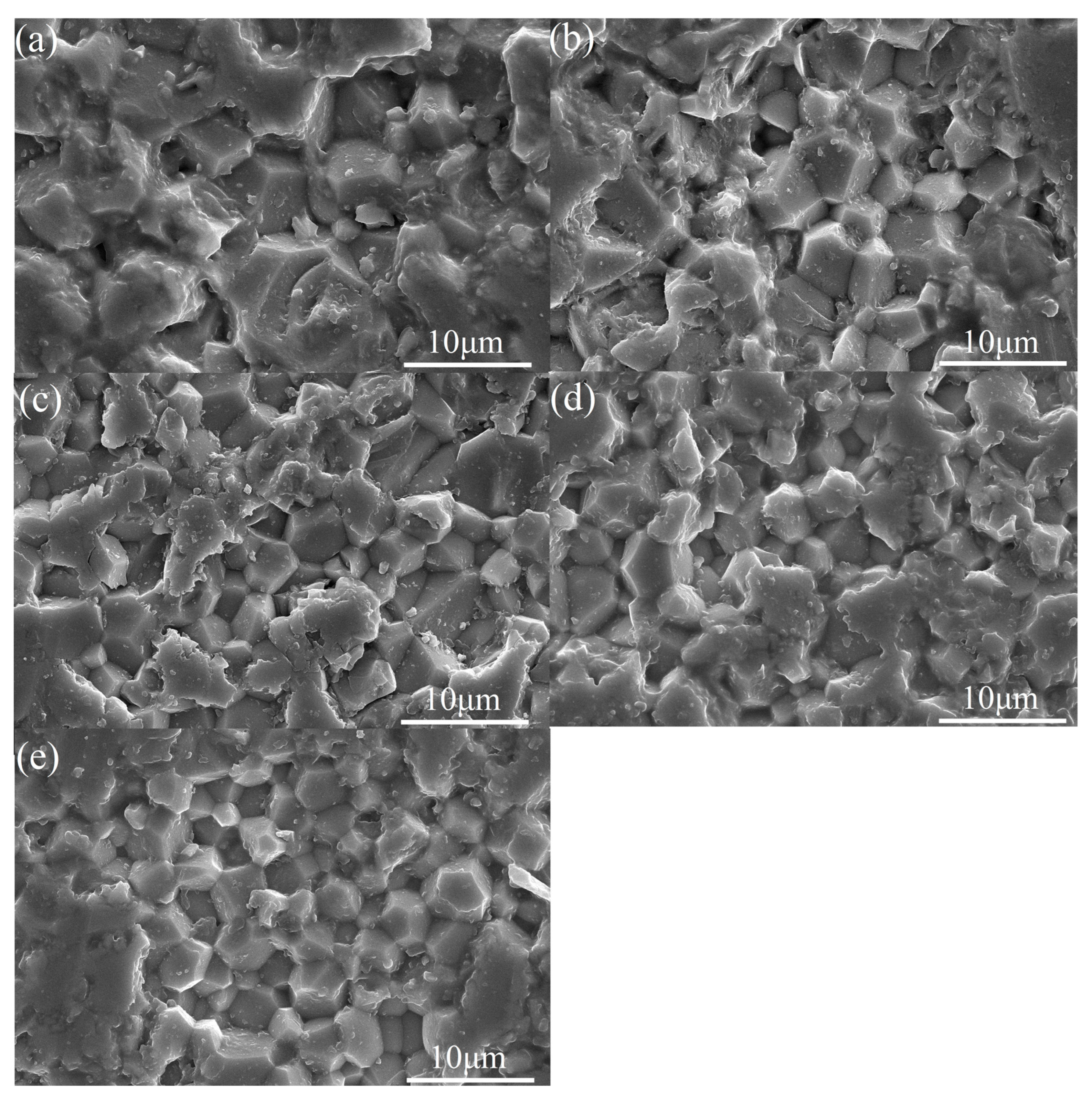
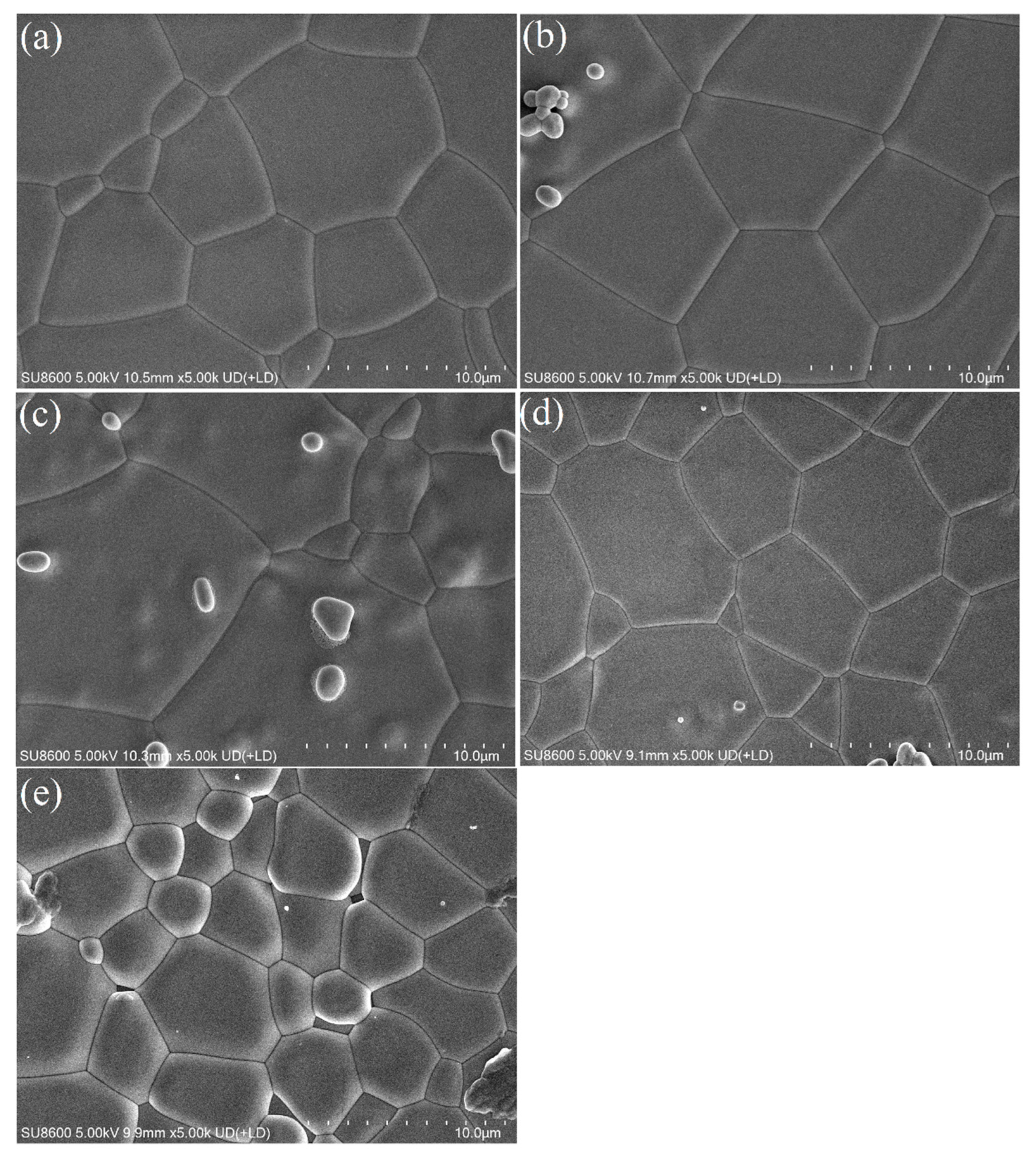
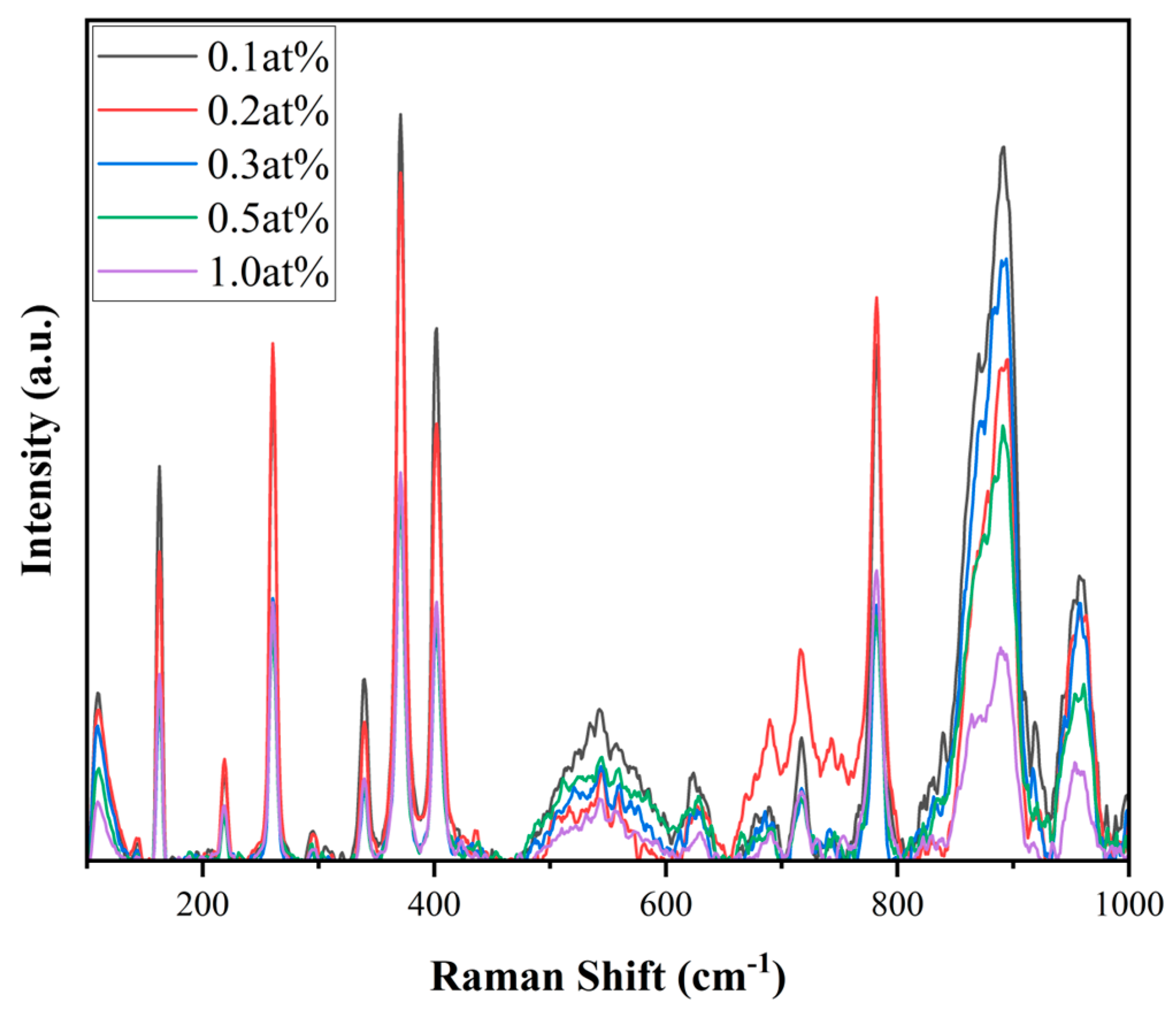
3.1. Concentration Optimization Experiment
3.2. Eutectic Welding Experiment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agaker, M.; Andersson, J.; Englund, J.C.; Rausch, J.; Rubensson, J.E.; Nordgren, J. Spectroscopy in the vacuum-ultraviolet. Nat. Photonics 2011, 5, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pile, D.F.P. Vacuum-ultraviolet source. Nat. Photonics 2018, 12, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, M.A.; De Marco, O. Analysis of far-UV data of central stars of planetary nebulae: Occurrence and variability of stellar winds. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 553, A126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, D.N.; Kanekal, S.G.; Li, X.; Monk, S.P.; Goldstein, J.; Burch, J.L. An extreme distortion of the Van Allen belt arising from the ‘Halloween’ solar storm in 2003. Nature 2004, 432, 878–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.; Zheng, W.; Huang, F. Vacuum-ultraviolet photodetectors. Photonix 2020, 1, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D. Gelcasting of High Performance Carbide Ceramics with Larger Size/Complex Shape. In Advanced Processing and Manufacturing Technologies for Structural and Multifunctional Materials IV: Ceramic Engineering and Science Proceeding; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; Volume 31, pp. 195–211. [Google Scholar]
- Brinkmann, K.T.; Borisevich, A.; Diehl, S.; Dormenev, V.; Houzvicka, J.; Korjik, M.; Novotny, R.W.; Zaunick, H.G.; Zimmermann, S. Research activity with different types of scintillation materials. In Proceedings of the Applications of Novel Scintillators for Research and Industry (ANSRI), University College Dublin, Dublin, Ireland, 11–13 May 2016; 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Selim, F.A.; Khamehchi, A.; Winarski, D.; Agarwal, S. Synthesis and characterization of Ce:YAG nanophosphors and ceramics. Opt. Mater. Express 2016, 6, 3704–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagida, T.; Fujimoto, Y.; Kurosawa, S.; Kamada, K.; Takahashi, H.; Fukazawa, Y.; Nikl, M.; Chani, V. Temperature Dependence of Scintillation Properties of Bright Oxide Scintillators for Well-Logging. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 52, 076401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhu, Q.; Tang, D.; Liu, X.; Ouyang, G.; Cao, L.; Hirosaki, N.; Nishimura, T.; Huang, Z.; Xie, R.-J. Al2O3-YAG:Ce composite phosphor ceramic: A thermally robust and efficient color converter for solid state laser lighting. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 8648–8654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, G.; Zhou, Z.; Li, J.; Zeng, L.; Lin, S.; Wang, P.; Lin, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Huang, F.; et al. Transparent Composite Ceramic@aluminum with Ultra-High Thermal Conductivity for High-Brightness Laser-Driven Lighting. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2401026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.N.; Sharif, A.; Chan, Y.C. Effect of volume in interfacial reaction between eutectic Sn-3.5% Ag-0.5% Cu solder and Cu metallization in microelectronic packaging. J. Electron. Mater. 2005, 34, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Ritzdorf, T. Electrodeposition of near-eutectic SnAg solders for wafer-level packaging. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2003, 150, C577–C584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, R.M. Development of holmium doped eutectic Sn-Ag lead-free solder for electronic packaging. Solder. Surf. Mt. Technol. 2022, 34, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, J.; Dorenbos, P.; Bos, A.J.J.; Meijerink, A.; Tanabe, S. Insight into the Thermal Quenching Mechanism for Y3Al5O12:Ce3+ through Thermo luminescence Excitation Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 25003–25008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Kang, J.; Shao, C.; Zhang, L.; Zou, J. Laser light illuminant based on YAG: Ce phosphor ceramic with ultra-high luminance, stable output, and excellent heat dissipation. Opt. Mater. 2024, 157, 116410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Z.; Meijerink, A. Ce3+-Doped garnet phosphors: Composition modification, luminescence properties and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 275–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, N.C.; Denault, K.A.; Seshadri, R. Phosphors for Solid-State White Lighting. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2013, 43, 481–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukyashin, K.E.; Shitov, V.A.; Medvedev, A.I.; Ishchenko, A.V.; Shevelev, V.S.; Shulgin, B.V.; Basyrova, L.R. Ce:YAG ceramics: The influence of the synthesis technology features on the luminescent and the optical properties. In Proceedings of the 3rd Interdisciplinary Youth Scientific Forum with International Participation on New Materials, Russian Acad Sci Presidium, Moscow, Russia, 21–24 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lukyashin, K.E.; Ishchenko, A.V.; Shitov, V.A.; Shevelev, V.S.; Victorov, L.V. Effect of the sintering aids on optical and luminescence properties of Ce:YAG ceramics. In Proceedings of the 4th Interdisciplinary Scientific Forum on New Materials and Promising Technologies, Russian Acad Sci, Moscow, Russia, 27–30 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, H.; Hu, P.; Liu, Z.; Sun, P.; Liu, Y.; Luo, Z.; Chao, K.; Jiang, H.; Jiang, J. Effect of Ca2+-Si4+ on Y3Al5O12:Ce ceramic phosphors for white laser-diodes lighting. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2021, 118, 211902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Zhang, N.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, L.; Cai, W. Extreme Ultraviolet Detectors: A Review. Chin. J. Lasers-Zhongguo Jiguang 2024, 51, 0701008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berends, A.C.; van de Haar, M.A.; Krames, M.R. YAG:Ce3+ Phosphor: From Micron-Sized Workhorse for General Lighting to a Bright Future on the Nanoscale. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 13461–13479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikl, M.; Yoshikawa, A. Recent R&D Trends in Inorganic Single-Crystal Scintillator Materials for Radiation Detection. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2015, 3, 463–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimov, A.A.; Santos, J.C.A.; Sampaio, D.V.; Silva, R.S.; DeVol, T.A.; Jacobsohn, L.G. Microstructure, luminescence and thermoluminescence of laser-sintered polycrystalline ceramic YAG:Ce scintillators. J. Lumin. 2022, 251, 119206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisevich, A.; Dosovitsky, A.; Fedorov, A.; Khasanov, O.; Korzhik, M.; Mechinsky, V.; Missevitch, O.; Shevchenko, G. On the development of heavy and fast scintillation nano-ceramics. In Proceedings of the IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium/Medical Imaging Conference, Dresden, Germany, 19–25 October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Moszynki, M.; Ludziejewski, T.; Wolski, D.; Klamra, W.; Norlin, L.O. Properties of the YAG:Ce scintillator. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 1994, 345, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiura, S.; Tanabe, S.; Fujioka, K.; Fujimoto, Y. Properties of transparent Ce:YAG ceramic phosphors for white LED. Opt. Mater. 2011, 33, 688–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Haseman, M.S.; Khamehchi, A.; Saadatkia, P.; Winarski, D.J.; Selim, F.A. Physical and optical properties of Ce: YAG nanophosphors and transparent ceramics and observation of novel luminescence phenomenon. Opt. Mater. Express 2017, 7, 1055–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.C.; Tang, X.Y.; Zheng, P.; Li, S.X.; Zhou, T.L.; Xie, R.J. Thermally self-managing YAG:Ce-Al2O3 color converters enabling high-brightness laser-driven solid state lighting in a transmissive configuration. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 3901–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dosovitskiy, G.; Fedorov, A.; Karpyuk, P.; Kuznetsova, D.; Mikhlin, A.; Kozlov, D.; Dosovitskiy, A.; Korjik, M. Polycrystalline scintillators for large area detectors in HEP experiments. J. Instrum. 2017, 12, C06045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Yu, S.; Li, Y.; Ruan, S.; Kong, L.B.; Huang, Q.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, K.; Su, H.; Yao, Z.; et al. Materials development and potential applications of transparent ceramics: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. R-Rep. 2020, 139, 100518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagida, T.; Kato, T.; Nakauchi, D.; Kawaguchi, N. Fundamental aspects, recent progress and future prospects of inorganic scintillators. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2023, 62, 010508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Chen, H.; Zhou, G.; He, Y.; Zhang, S.; Tang, B. Co-effects of Nb2O5 and stoichiometric deviations on the microwave dielectric properties of Y3Al5O12. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 18651–18657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senden, T.; van Dijk-Moes, R.J.A.; Meijerink, A. Quenching of the red Mn4+ luminescence in Mn4+-doped fluoride LED phosphors. Light-Sci. Appl. 2018, 7, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodama, N.; Yamaga, M.; Kurahashi, T. Crystal field splitting and symmetry of Ce3+ polyhedra in oxide crystals. Radiat. Eff. Defects Solids 1999, 151, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotman, S.R. Crystal-field splitting of Ce3+5d levels in yttrium aluminum garnet. Phys. Status Solidi A 1992, 132, K61–K63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, R.G. Mineralogical Applications of Crystal Field Theory; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005; Volume 39, p. 123. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Q.; Hu, P.; Sun, P.; Liu, M.; Dong, R.; Chao, K.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Jiang, H. YAG:Ce3+ Transparent Ceramic Phosphors Brighten the Next-Generation Laser-Driven Lighting. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1907888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.; Chen, Z.; Meng, Y.; Cao, X.; Xiong, D.; Huang, Y. Micro-defects and optical properties of YAG:Ce crystals prepared by optical floating zone method. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 2017, 31, 1744068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, M.; Fan, J.; Lian, H.; Zhang, Y.; Geng, D.; Lin, J. A Double Substitution of Mg2+-Si4+/Ge4+ for Al(1)3+-Al(2)3+ in Ce3+-Doped Garnet Phosphor for White LEDs. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 7748–7755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




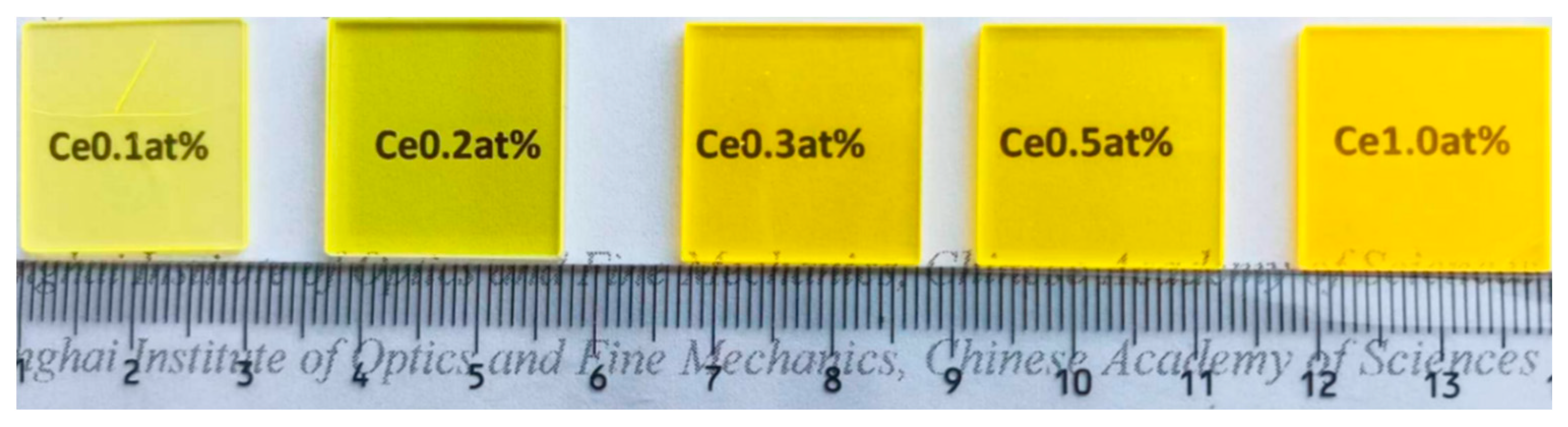
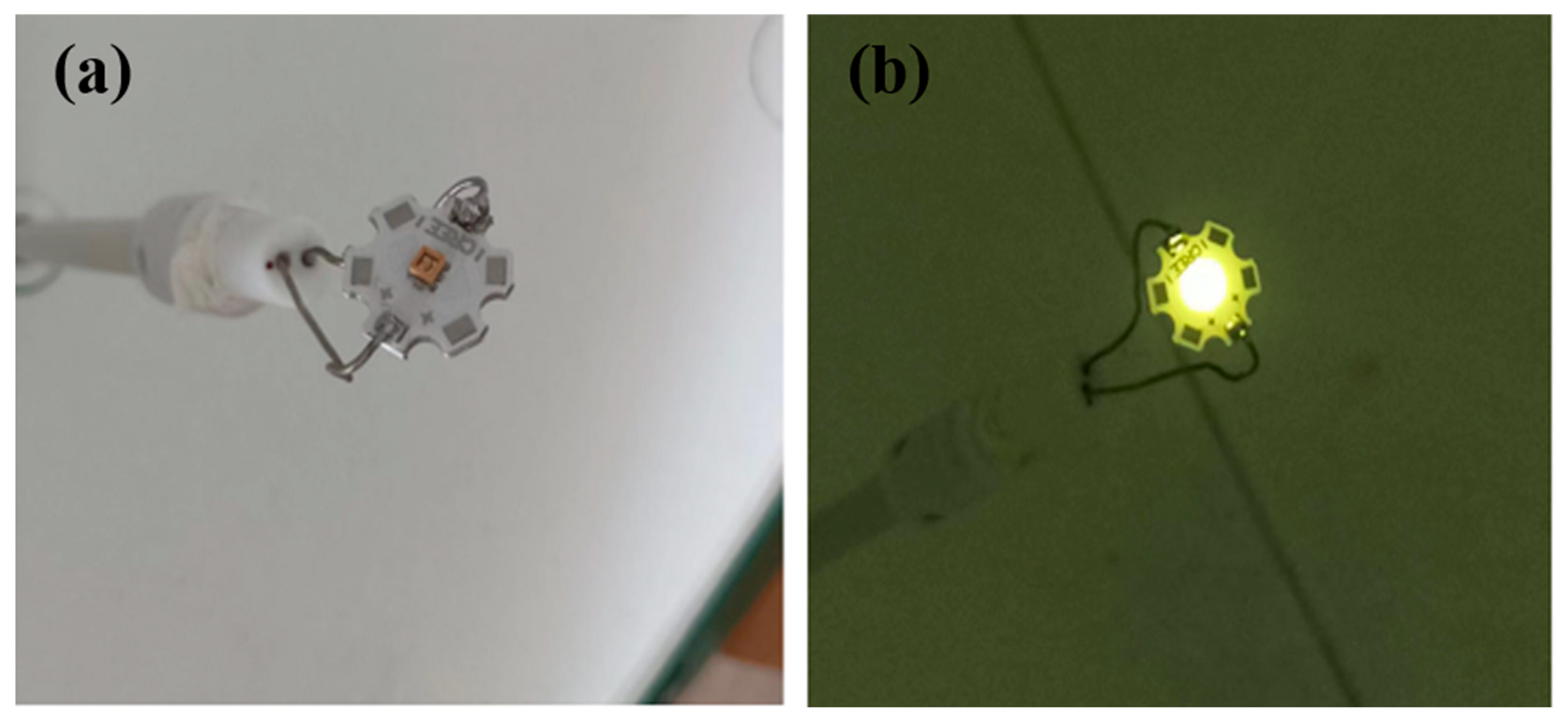
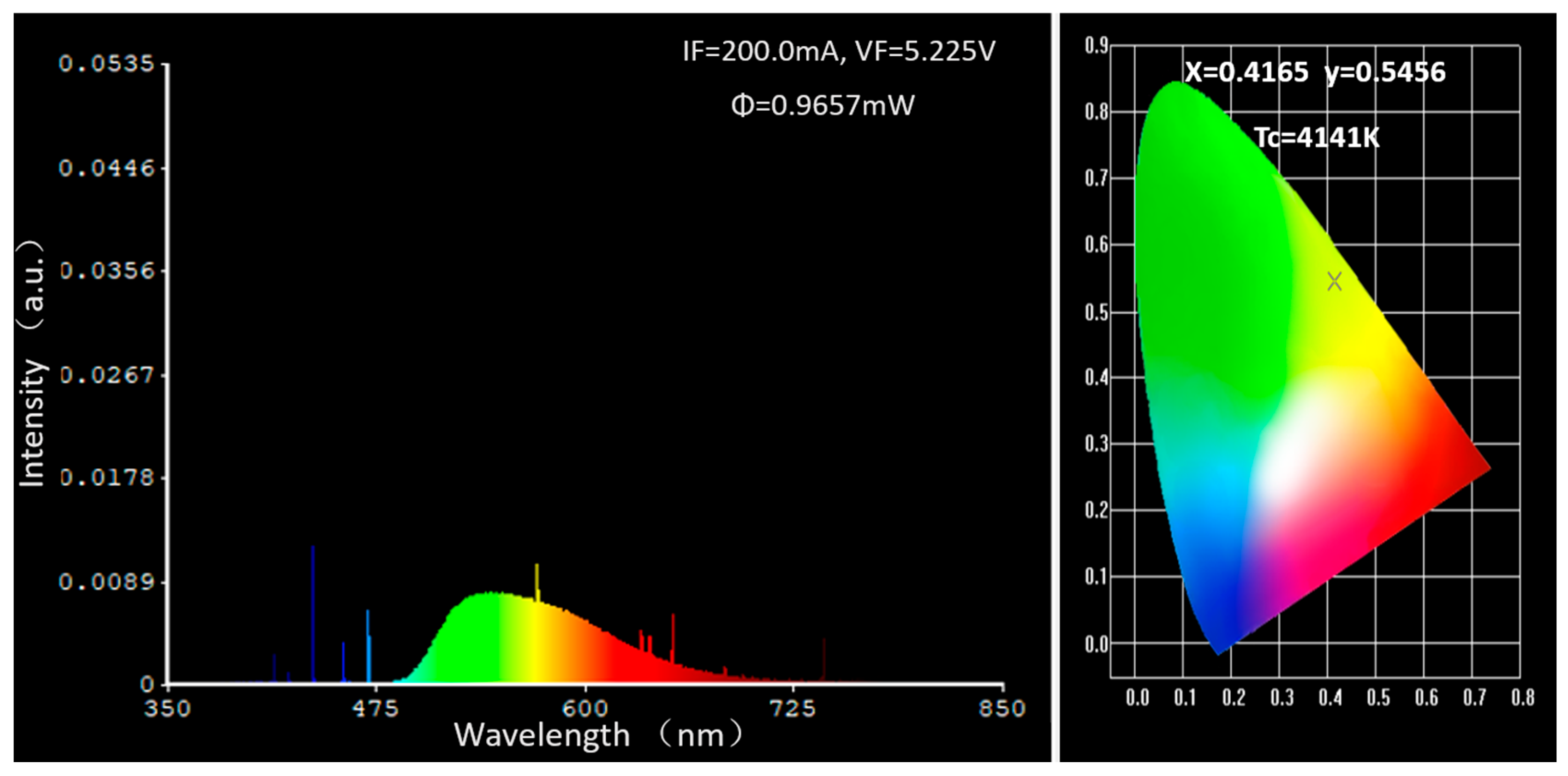
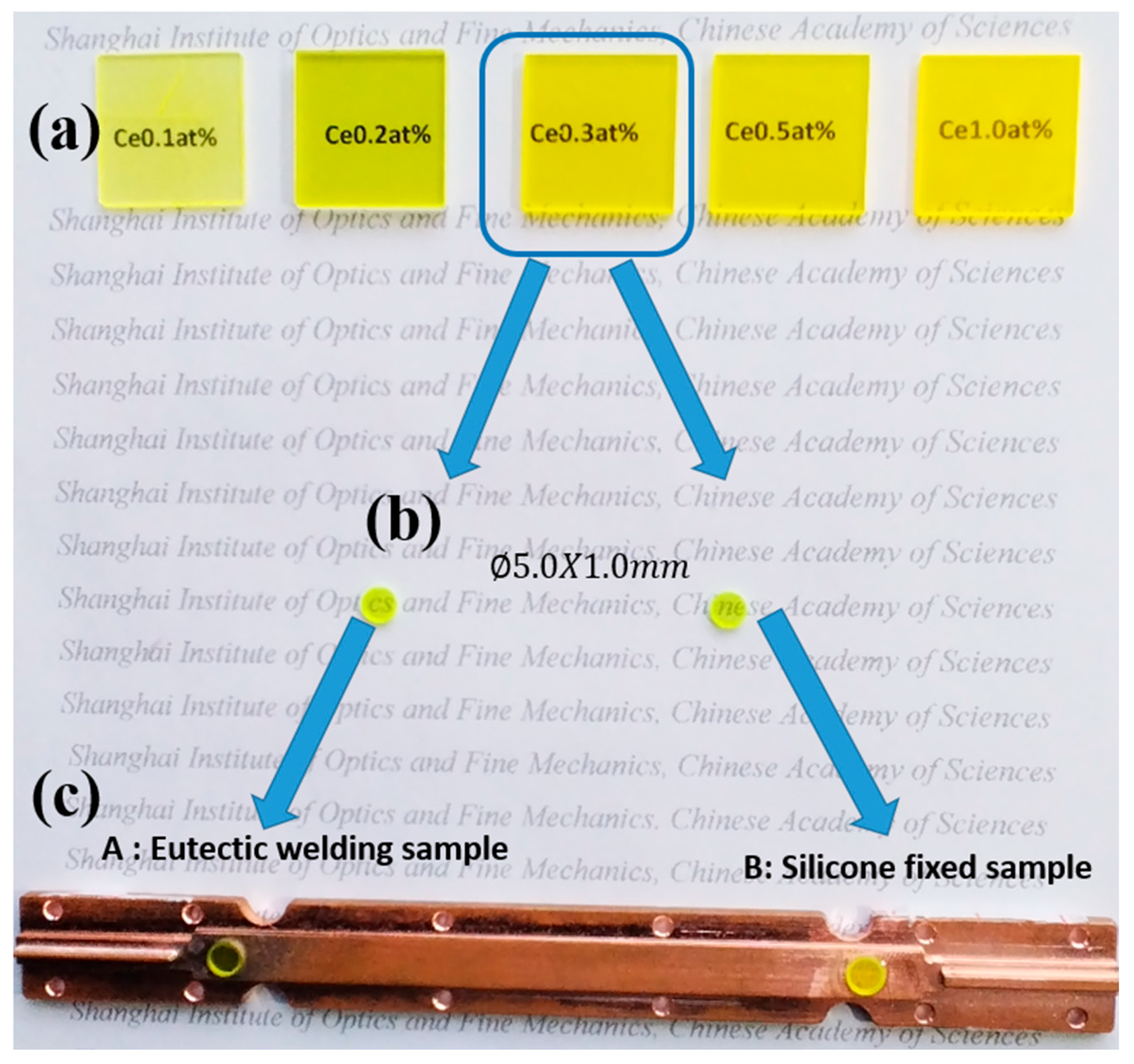

| Doping Concentration of Ce | 0.1 at% | 0.2 at% | 0.3 at% | 0.5 at% | 1.0 at% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Output energy (mW) | 0.3002 | 0.4022 | 0.9657 | 0.8011 | 0.7160 |
| Energy conversion efficiency | 1.20% | 1.61% | 3.86% | 3.20% | 2.86% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yi, X.; Sai, Q.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, R.; Li, M. Fluorescence Output Enhancement of Ce3+:YAG Transparent Ceramics by Eutectic Soldering Packaging. Materials 2025, 18, 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18051081
Yi X, Sai Q, Tian Y, Jiang R, Li M. Fluorescence Output Enhancement of Ce3+:YAG Transparent Ceramics by Eutectic Soldering Packaging. Materials. 2025; 18(5):1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18051081
Chicago/Turabian StyleYi, Xuezhuan, Qinglin Sai, Yanna Tian, Renjie Jiang, and Mingqin Li. 2025. "Fluorescence Output Enhancement of Ce3+:YAG Transparent Ceramics by Eutectic Soldering Packaging" Materials 18, no. 5: 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18051081
APA StyleYi, X., Sai, Q., Tian, Y., Jiang, R., & Li, M. (2025). Fluorescence Output Enhancement of Ce3+:YAG Transparent Ceramics by Eutectic Soldering Packaging. Materials, 18(5), 1081. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18051081






