Evaluation of Fresh Property, Compressive Strength and Environmental Impact of Low-Carbon Geopolymer Based on Ladle Furnace Slag and Soda Residue
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experiments
2.1. Materials
2.2. Mix Proportions and Specimen Preparation
2.3. Test Methods
2.3.1. Fresh Properties Test
2.3.2. Compressive Strength Test
2.3.3. Microstructure Test
2.3.4. Calculation of Embodied Carbon
3. Results
3.1. Fresh Properties
3.1.1. Setting Time
3.1.2. Rheology Property
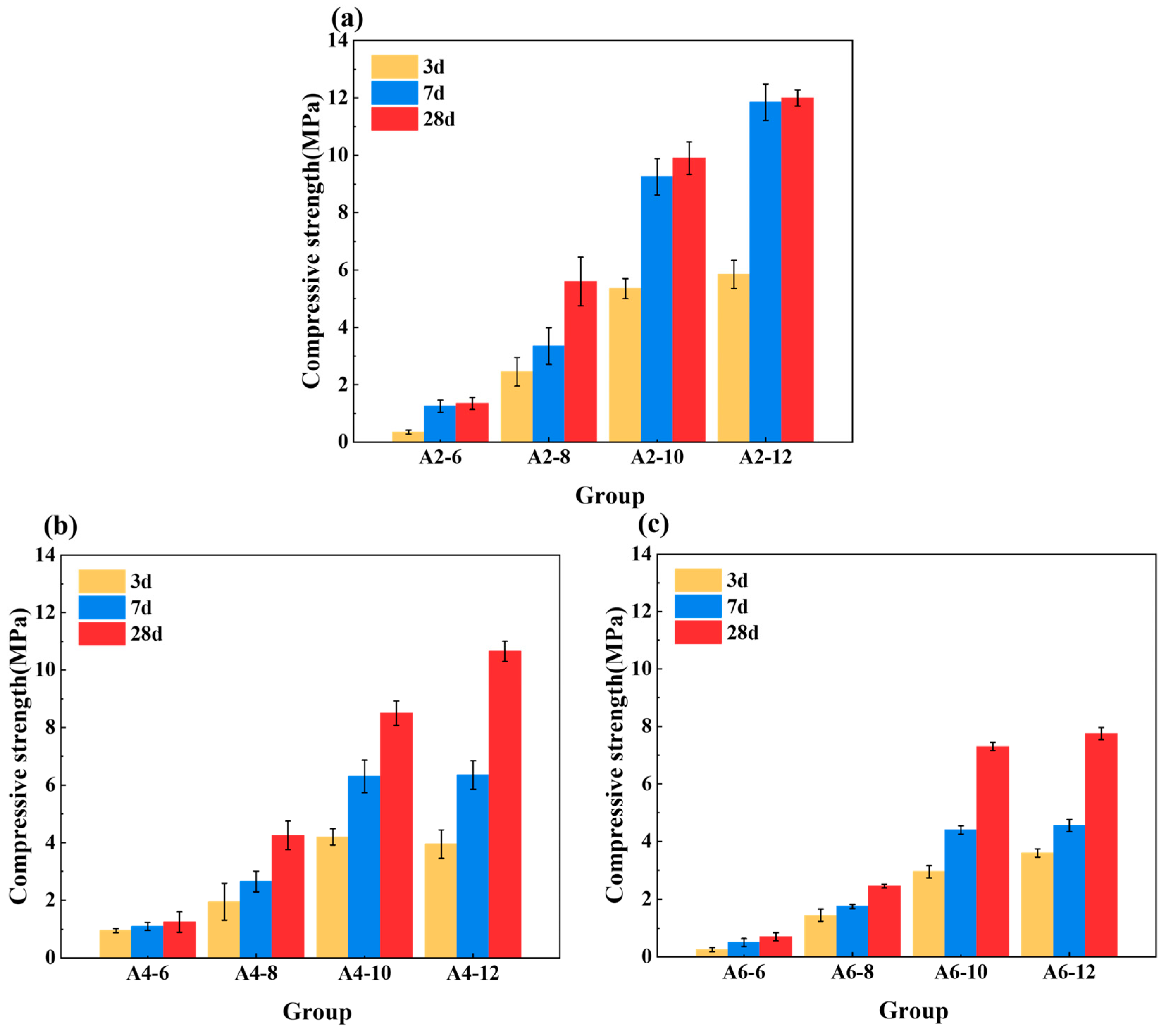
3.2. Compressive Strength
3.3. Microstructure Analysis
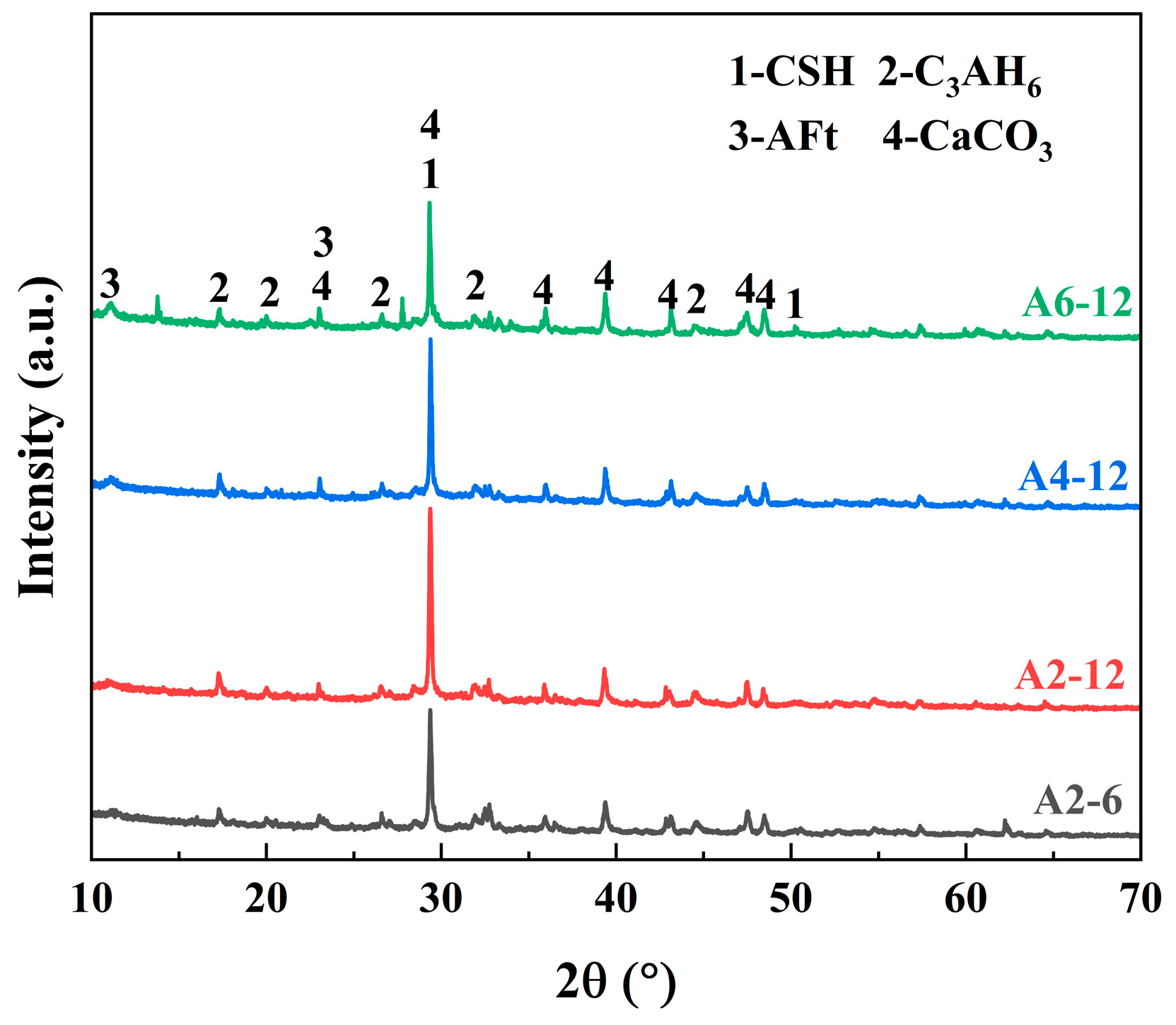
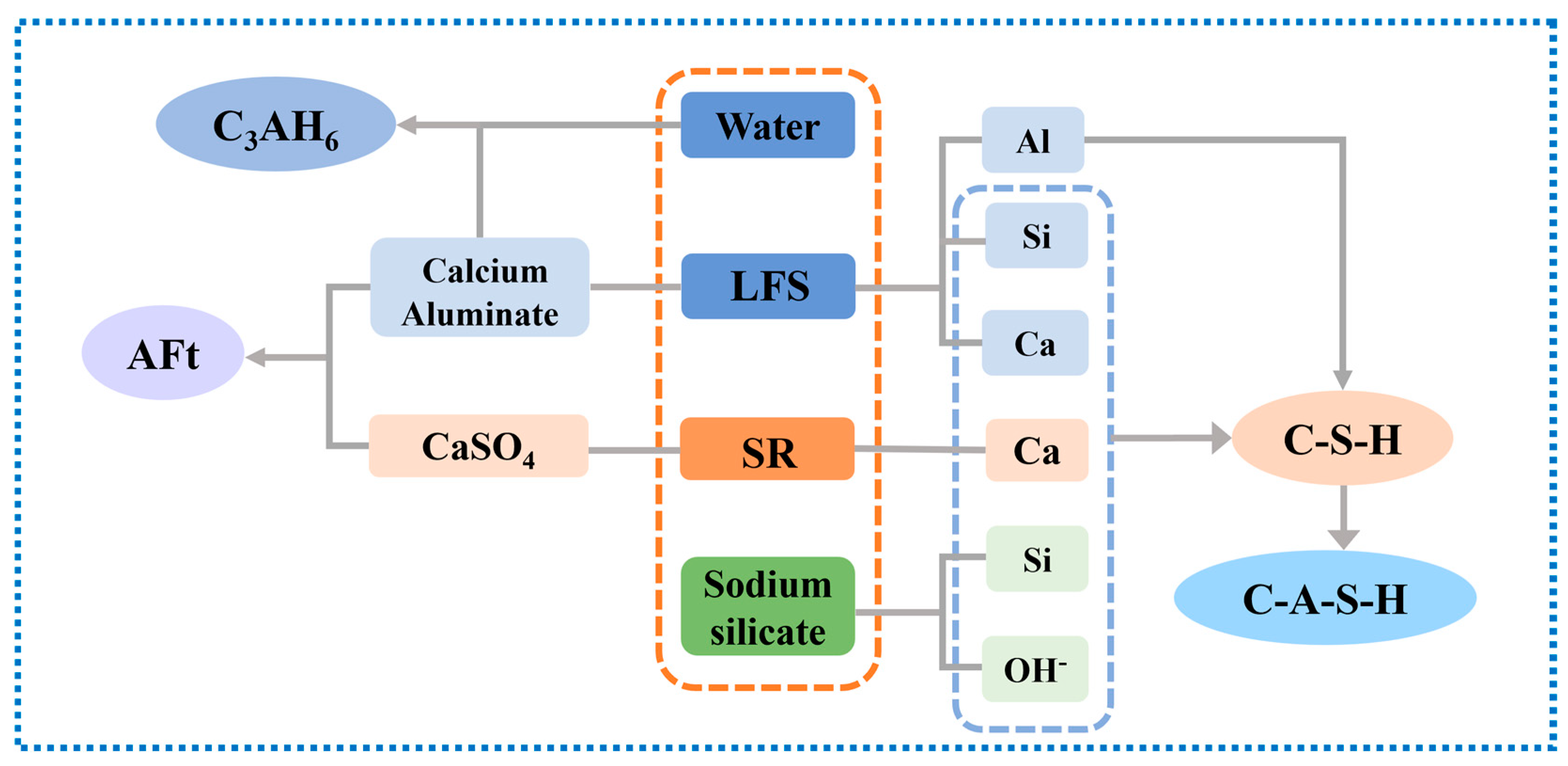
3.3.1. XRD Analysis
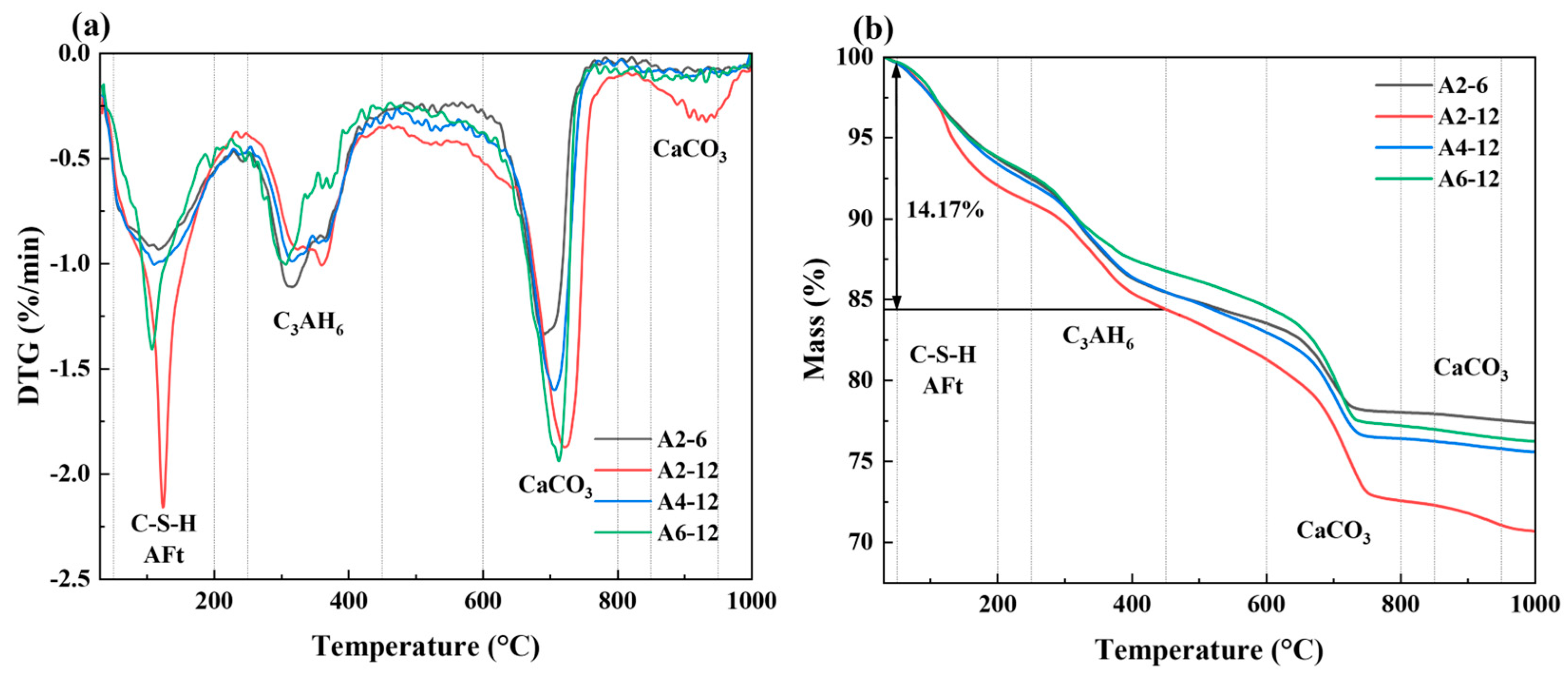
3.3.2. TG/DTG Analysis
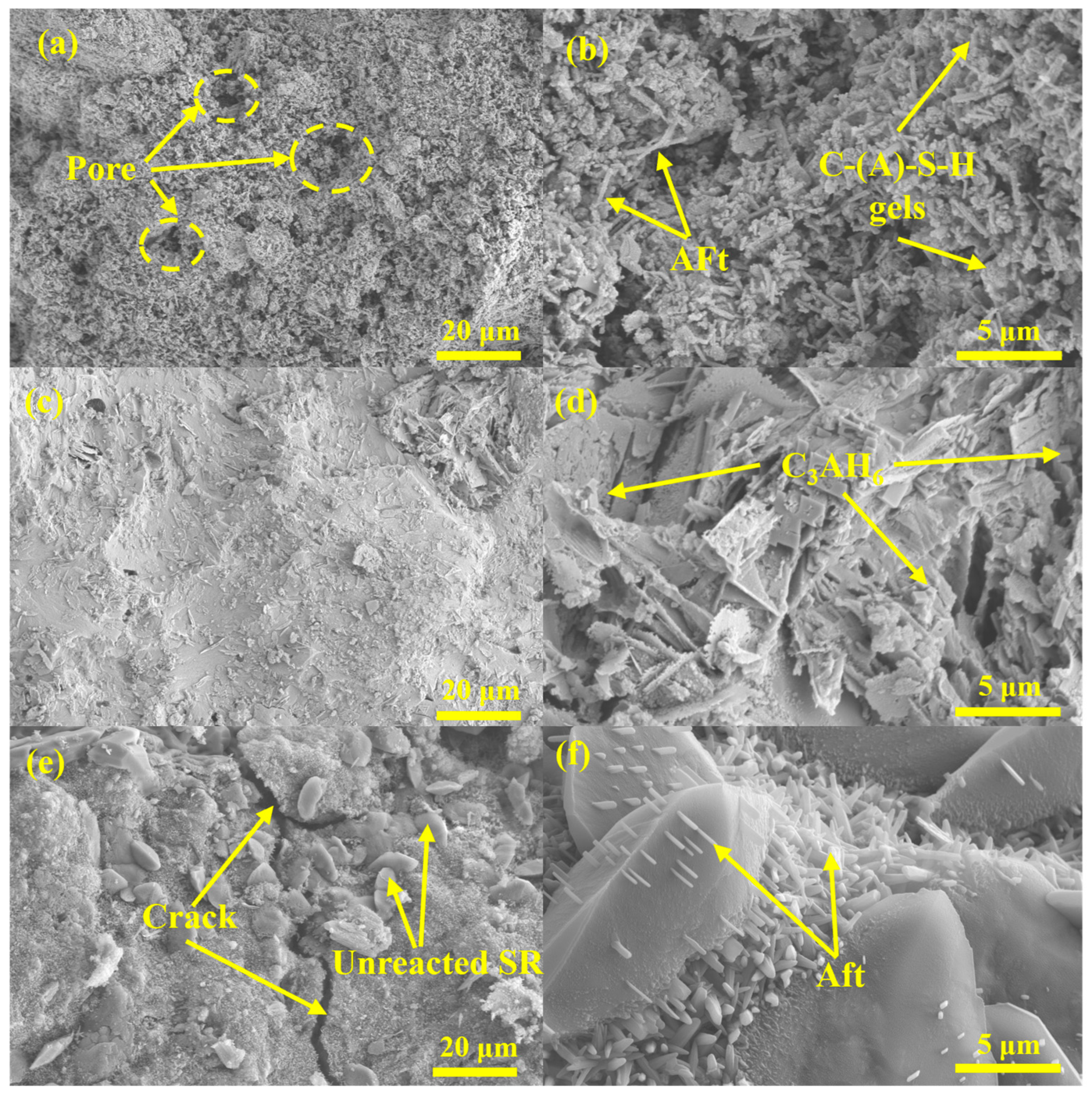
3.3.3. SEM Analysis
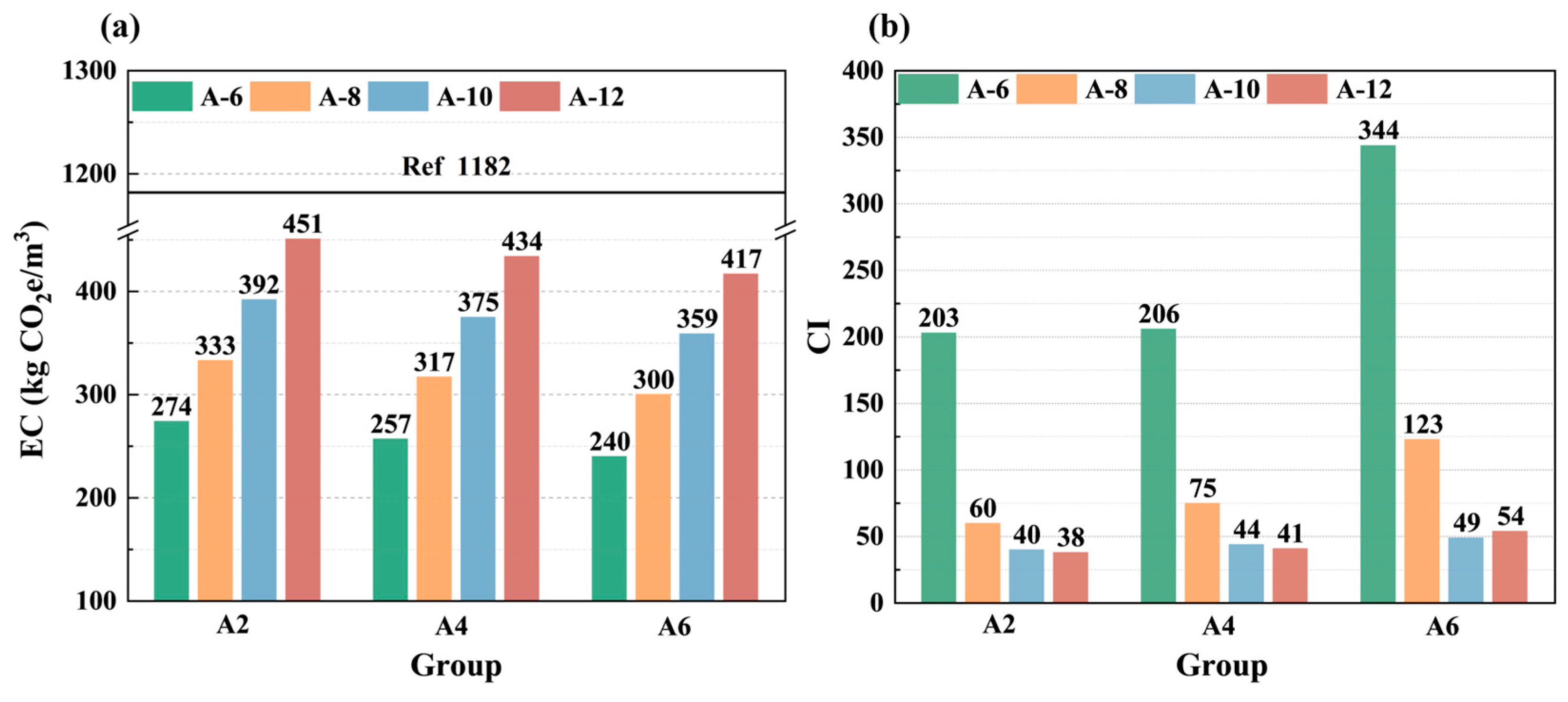
3.4. Calculation of Embodied Carbon
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IEA. Global Energy Review 2025; International Energy Agency: Paris, France, 2025.
- Barbhuiya, S.; Kanavaris, F.; Das, B.B.; Idrees, M. Decarbonising cement and concrete production: Strategies, challenges and pathways for sustainable development. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 86, 108861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, X.; Yin, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, N. Intermediate-calcium based cementitious materials prepared by MSWI fly ash and other solid wastes: Hydration characteristics and heavy metals solidification behavior. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 349, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Wang, L.; Ma, G.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, X. Preparation and properties of bio-geopolymer composites with waste cotton stalk materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 245, 118842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadsetan, S.; Siad, H.; Lachemi, M.; Mahmoodi, O.; Sahmaran, M. Development of ambient cured geopolymer binders based on brick waste and processed glass waste. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 80755–80774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadsetan, S.; Siad, H.; Lachemi, M.; Mahmoodi, O.; Sahmaran, M. Optimization and characterization of geopolymer binders from ceramic waste, glass waste and sodium glass liquid. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 342, 130931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Feky, M.S.; Kohail, M.; El-Tair, A.M.; Serag, M.I. Effect of microwave curing as compared with conventional regimes on the performance of alkali activated slag pastes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 233, 117268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najimi, M.; Ghafoori, N. Engineering properties of natural pozzolan/slag based alkali-activated concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 208, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.; Zhao, Y.; Lv, G.; Duan, Y.; Liu, X.; Jiang, X. Improving stabilization/solidification of MSWI fly ash with coal gangue based geopolymer via increasing active calcium content. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 854, 158594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Wang, B.; Ai, H.; Qi, Y.; Liu, Z. A comparative study on solidification/stabilization characteristics of coal fly ash-based geopolymer and Portland cement on heavy metals in MSWI fly ash. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 319, 128790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Tan, J.; Li, X. Thermoelectric behaviors of fly ash and metakaolin based geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 237, 117757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Gu, G.; Shi, Y.; Xu, F.; Ma, T. Understanding the role of epoxy resin and polyurethane in toughening metakaolin-based geopolymer matrix. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e02919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tay, B.W.Y.; Lei, J.; Yang, E.-H. Experimental investigation of Seebeck effect in metakaolin-based geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 272, 121615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Bao, Y.; Wang, M. Steel slag in China: Treatment, recycling, and management. Waste Manag. 2018, 78, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altiner, M.; Yildirim, M. Production and characterization of synthetic aragonite prepared from dolomite by eco-friendly leaching–carbonation process. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Ma, M.; He, X.; Zheng, Z.; Su, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhao, H. Effect of wet-grinding steel slag on the properties of Portland cement: An activated method and rheology analysis. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 286, 122823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacobescu, R.I.; Angelopoulos, G.N.; Jones, P.T.; Blanpain, B.; Pontikes, Y. Ladle metallurgy stainless steel slag as a raw material in Ordinary Portland Cement production: A possibility for industrial symbiosis. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 872–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serjun, V.Z.; Mladenovič, A.; Mirtič, B.; Meden, A.; Ščančar, J.; Milačič, R. Recycling of ladle slag in cement composites: Environmental impacts. Waste Manag. 2015, 43, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesanya, E.; Sreenivasan, H.; Kantola, A.M.; Telkki, V.-V.; Ohenoja, K.; Kinnunen, P.; Illikainen, M. Ladle slag cement—Characterization of hydration and conversion. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 193, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adolfsson, D.; Robinson, R.; Engström, F.; Björkman, B. Influence of mineralogy on the hydraulic properties of ladle slag. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 865–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesanya, E.; Ohenoja, K.; Kinnunen, P.; Illikainen, M. Alkali Activation of Ladle Slag from Steel-Making Process. J. Sustain. Metall. 2017, 3, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancellotti, I.; Ponzoni, C.; Bignozzi, M.C.; Barbieri, L.; Leonelli, C. Incinerator Bottom Ash and Ladle Slag for Geopolymers Preparation. Waste Biomass Valorization 2014, 5, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bignozzi, M.C.; Manzi, S.; Lancellotti, I.; Kamseu, E.; Barbieri, L.; Leonelli, C. Mix-design and characterization of alkali activated materials based on metakaolin and ladle slag. Appl. Clay Sci. 2013, 73, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbarey, M.S.; El-Sayed Seleman, M.M.; El Kheshen, A.A.; Zawrah, M.F. Utilization of ladle furnace slag for fabrication of geopolymer: Its application as catalyst for biodiesel production. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natali Murri, A.; Rickard, W.D.A.; Bignozzi, M.C.; van Riessen, A. High temperature behaviour of ambient cured alkali-activated materials based on ladle slag. Cem. Concr. Res. 2013, 43, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong-Sing, N.; Yun-Ming, L.; Cheng-Yong, H.; Abdullah, M.M.A.B.; Chan, L.W.L.; Hui-Teng, N.; Shee-Ween, O.; Wan-En, O.; Yong-Jie, H. Evaluation of flexural properties and characterisation of 10-mm thin geopolymer based on fly ash and ladle furnace slag. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-C.; Wang, H.-Y.; Tsai, H.-C. Study on engineering properties of alkali-activated ladle furnace slag geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 123, 800–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najm, O.; El-Hassan, H.; El-Dieb, A. Optimization of alkali-activated ladle slag composites mix design using taguchi-based TOPSIS method. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 327, 126946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obrenović, M.Č.; Iličković, Z.; Andrejaš, F. Utilization of Soda Ash Plant Solid Wastes in Production of Geopolymers. Int. J. Eng. Innov. Res. 2017, 6, 273–277. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Li, J.; Yao, G.; Zhu, X.; Hu, S.; Qiu, J.; Chen, P.; Lyu, X. Characterization of the mechanical properties and microcosmic mechanism of Portland cement prepared with soda residue. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 241, 117994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, C.; Zuo, L.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, B. Synthesis and characterization of fly ash geopolymer paste for goaf backfill: Reuse of soda residue. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 260, 121045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Qi, F.; Seshadri, B.; Xu, Y.; Hou, J.; Ok, Y.S.; Dong, X.; Li, Q.; Sun, X.; Wang, L.; et al. Utilization of phosphorus loaded alkaline residue to immobilize lead in a shooting range soil. Chemosphere 2016, 162, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zha, F.; Pan, D.; Xu, L.; Kang, B.; Yang, C.; Chu, C. Investigations on engineering properties of solidified/stabilized pb-contaminated soil based on alkaline residue. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2018, 2018, 8595419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; He, Y.; Wu, Y.; Dian, B.; Zhang, J.; Li, T.; Jiang, M. Solidification/stabilization of soil heavy metals by alkaline industrial wastes: A critical review. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 312, 120094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Huang, Y.; Huang, L.; Huang, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, S.; Liu, C.; Liu, Z. Combined biochar and soda residues increases maize yields and decreases grain Cd/Pb in a highly Cd/Pb-polluted acid udults soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 306, 107198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, V.F.F.; MacKenzie, K.J.D.; Thaumaturgo, C. Synthesis and characterisation of materials based on inorganic polymers of alumina and silica: Sodium polysialate polymers. Int. J. Inorg. Mater. 2000, 2, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikan, H.; Justnes, H. Rheology of cementitious paste with silica fume or limestone. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 1512–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xie, X.; Liu, R.; Lyu, K.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Fu, F.; Wu, C.; Zuo, J. Manufacture of alkali-activated cementitious materials using municipal solid waste incineration fly ash (MSWIFA): The effect of the Si/Al molar ratio on fresh and hardened properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 409, 134075. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Wang, T.; Kolosz, B.; Andresen, J.; Garcia, S.; Fang, M.; Maroto-Valer, M.M. Life-cycle assessment of emerging CO2 mineral carbonation-cured concrete blocks: Comparative analysis of CO2 reduction potential and optimization of environmental impacts. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 241, 118359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Long, G.; Ma, C.; Xie, Y.; He, J. Design and preparation of ultra-high performance concrete with low environmental impact. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 214, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocharla, I.R.; Selvam, R.; Govindaraj, V.; Muthu, M. Performance and life-cycle assessment of high-volume fly ash concrete mixes containing steel slag sand. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 341, 127814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Luo, S.-R.; Li, W.-J.; Kang, D.-Y.; Zuo, Z.-W. Capillary water absorption and strength of solidified marine soft soil. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 423, 135729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zareechian, M.; Siad, H.; Lachemi, M.; Sahmaran, M. Advancements in cleaner production of one-part geopolymers: A comprehensive review of mechanical properties, durability, and microstructure. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 409, 133876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Heede, P.; De Belie, N. Environmental impact and life cycle assessment (LCA) of traditional and ‘green’ concretes: Literature review and theoretical calculations. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2012, 34, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, R.; Lyu, K.; Zhu, Y.; Zuo, J.; Zhang, P.; Wu, C.; Shah, S.P. Optimization formulation of low carbon MSWIFA cement-based composites modified by nano SiO2. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 80, 108043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Wang, Q.; Luo, T. Understanding the workability of alkali-activated phosphorus slag pastes: Effects of alkali dose and silicate modulus on early-age hydration reactions. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2022, 133, 104649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Ni, W.; Wang, Q.; Xu, C.; Li, K. Ammonia-soda residue and metallurgical slags from iron and steel industries as cementitious materials for clinker-free concretes. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 307, 127262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Xu, D.; Zhao, X. Effect of soda residue addition and its chemical composition on physical properties and hydration products of soda residue-activated slag cementitious materials. Materials 2020, 13, 1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heikal, M.; El-Didamony, H.; Morsy, M.S. Limestone-filled pozzolanic cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 1827–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios, M.; Gismera, S.; Alonso, M.M.; d’Espinose de Lacaillerie, J.B.; Lothenbach, B.; Favier, A.; Brumaud, C.; Puertas, F. Early reactivity of sodium silicate-activated slag pastes and its impact on rheological properties. Cem. Concr. Res. 2021, 140, 106302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Shrivastava, S. Influence of molarity and alkali mixture ratio on ambient temperature cured waste cement concrete based geopolymer mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 301, 124380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papayianni, I.; Anastasiou, E. Effect of granulometry on cementitious properties of ladle furnace slag. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2012, 34, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-M.; Choi, S.-M.; Han, D. Improving the mechanical properties of rapid air cooled ladle furnace slag powder by gypsum. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 127, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, A.M.; Oliveira, A.P.; Vieira, J.D.; Junior, A.N.; Cascudo, O. Study of the development of hydration of ternary cement pastes using X-ray computed microtomography, XRD-Rietveld method, TG/DTG, DSC, calorimetry and FTIR techniques. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 64, 105616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, W.; Pereira, G.B. Differential scanning calorimetry study of hydrated ground granulated blast-furnace slag. Cem. Concr. Res. 2001, 31, 327–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, N.C. Transition and Decomposition Temperatures of Cement Phases—A Collection of Thermal Analysis Data. Ceram.-Silik. 2016, 60, 338–343. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, H.; Adesanya, E.; Ohenoja, K.; Kriskova, L.; Pontikes, Y.; Kinnunen, P.; Illikainen, M. Byproduct-based ettringite binder—A synergy between ladle slag and gypsum. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 197, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Q.; Pan, H.; Zhao, Q.; Du, S.; Wang, D. Strength development and microstructure of recycled gypsum-soda residue-GGBS based geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 331, 127312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Wu, P.; Lyu, X. Recovered soda residue as alkaline activator of furnace slag: Geopolymer prepared from furnace slag incorporated with soda residue and its reuse in composite cement. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2023, 25, 1525–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

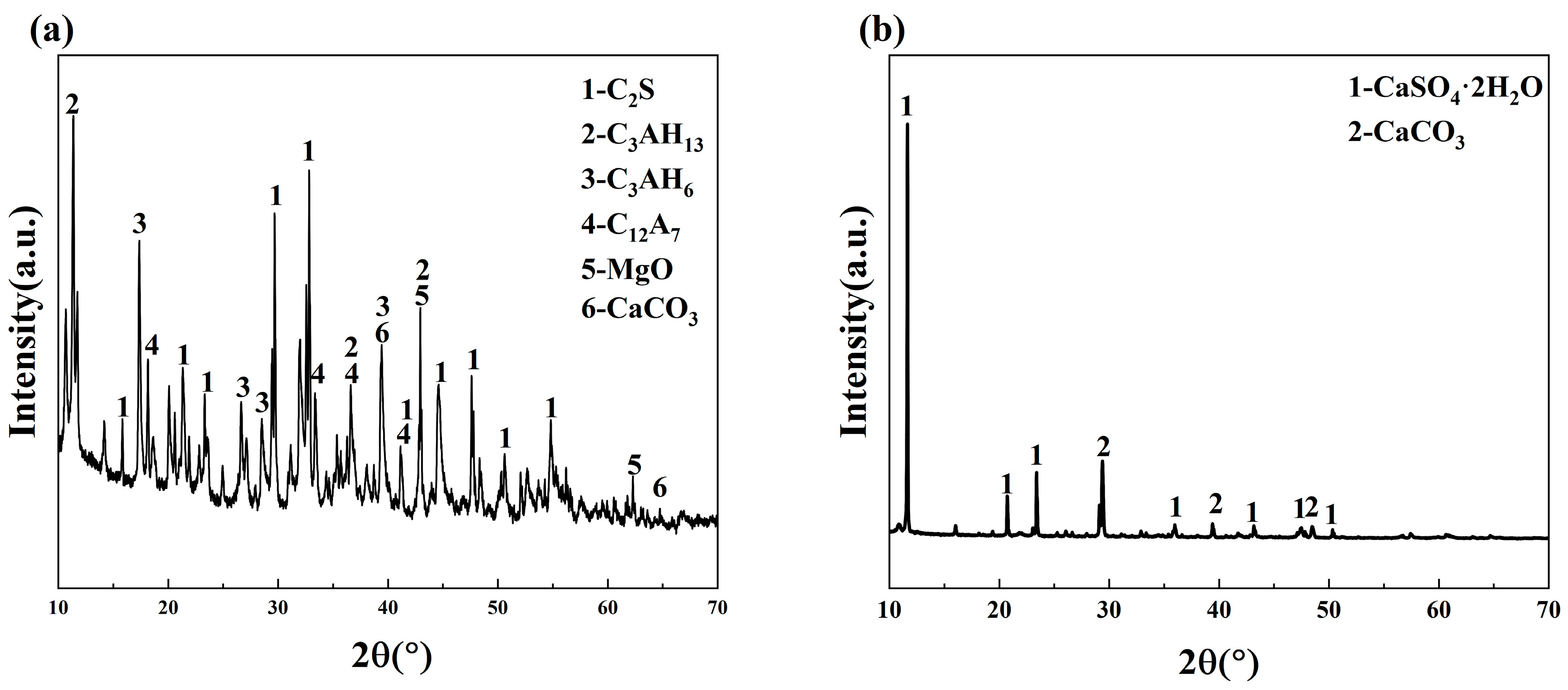
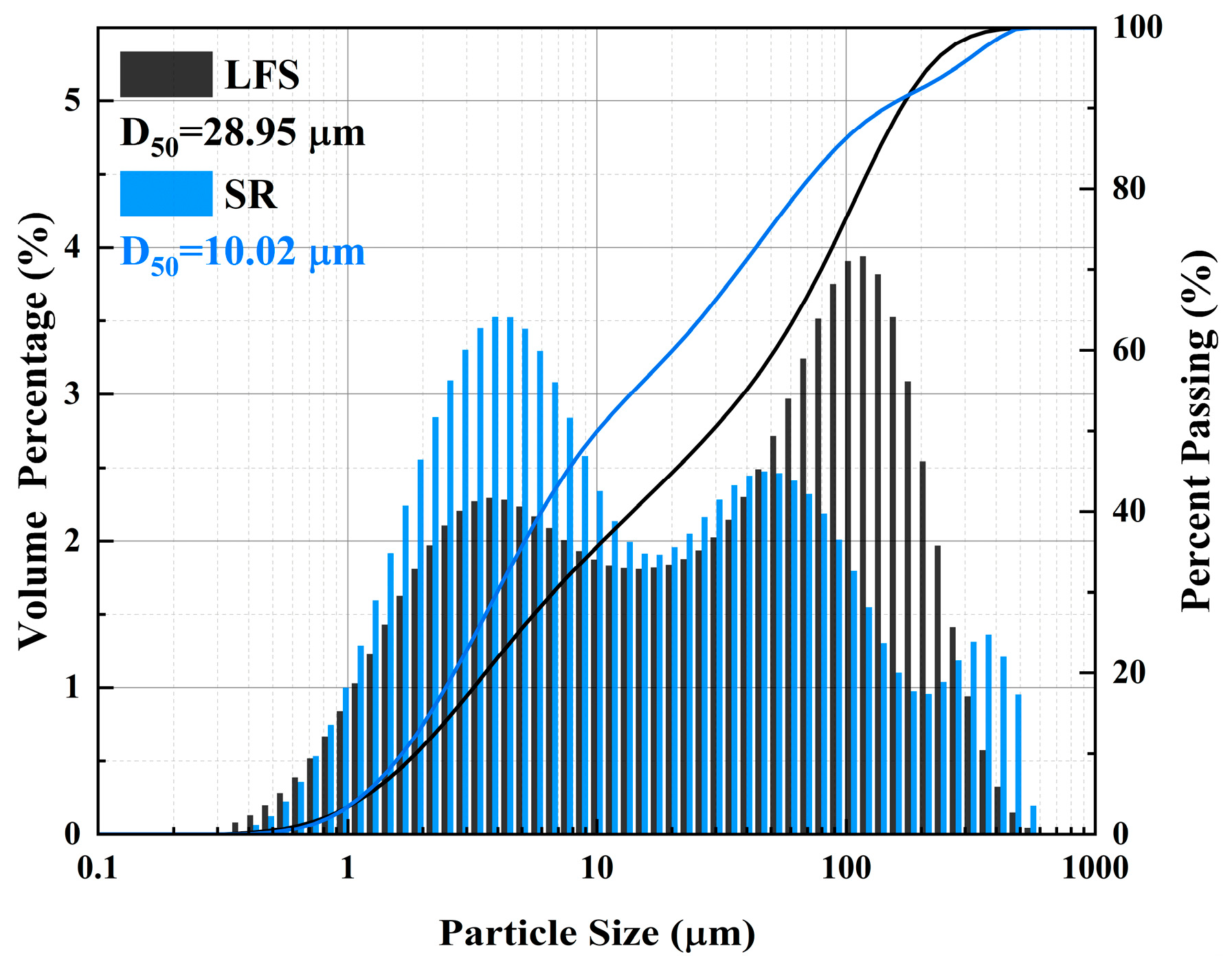
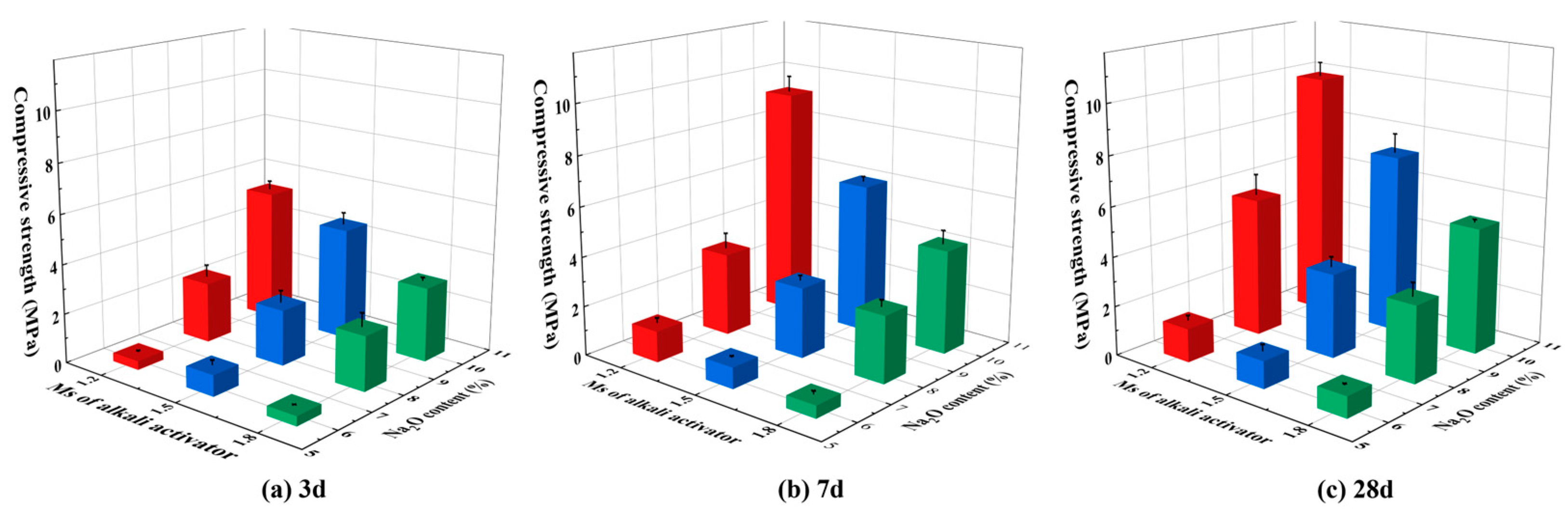

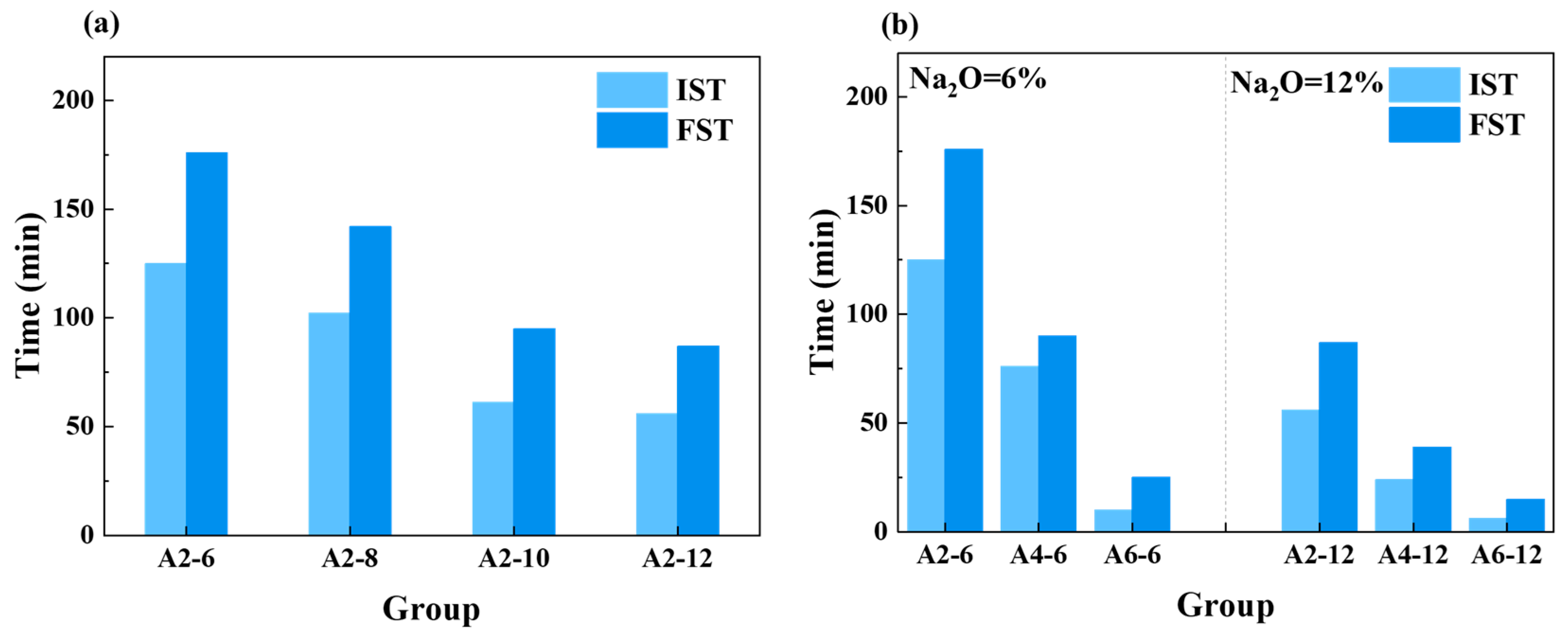

| CaO | Al2O3 | SiO2 | MgO | SO3 | Fe2O3 | TiO2 | MnO | Cl | Na2O | P2O5 | LOI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LFS | 51.75 | 25.45 | 13.97 | 3.75 | 2.35 | 1.20 | 0.73 | 0.29 | 0.18 | 0.12 | 0.05 | 0.16 |
| SR | 51.44 | 4.79 | 11.79 | 12.49 | 11.76 | 2.95 | 0.28 | 0.26 | 3.19 | 0.49 | 0.14 | 0.42 |
| Sample | Ms of Alkali Activator | Na2O (%) | SR (%) | LFS (%) | Water-to-Binder | Superplasticizer (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A2-6 | 1.2 | 6 | 20 | 80 | 0.45 | 2 |
| A2-8 | 1.2 | 8 | 20 | 80 | 0.45 | 2 |
| A2-10 | 1.2 | 10 | 20 | 80 | 0.45 | 2 |
| A2-12 | 1.2 | 12 | 20 | 80 | 0.45 | 2 |
| A4-6 | 1.2 | 6 | 40 | 60 | 0.45 | 2 |
| A4-8 | 1.2 | 8 | 40 | 60 | 0.45 | 2 |
| A4-10 | 1.2 | 10 | 40 | 60 | 0.45 | 2 |
| A4-12 | 1.2 | 12 | 40 | 60 | 0.45 | 2 |
| A6-6 | 1.2 | 6 | 60 | 40 | 0.45 | 2 |
| A6-8 | 1.2 | 8 | 60 | 40 | 0.45 | 2 |
| A6-10 | 1.2 | 10 | 60 | 40 | 0.45 | 2 |
| A6-12 | 1.2 | 12 | 60 | 40 | 0.45 | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Zuo, Y.; Yang, F.; Zuo, J.; Liu, A.; Huangfu, H.; Lyu, K.; Xie, X.; Shah, S.P. Evaluation of Fresh Property, Compressive Strength and Environmental Impact of Low-Carbon Geopolymer Based on Ladle Furnace Slag and Soda Residue. Materials 2025, 18, 1552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071552
Liu X, Zuo Y, Yang F, Zuo J, Liu A, Huangfu H, Lyu K, Xie X, Shah SP. Evaluation of Fresh Property, Compressive Strength and Environmental Impact of Low-Carbon Geopolymer Based on Ladle Furnace Slag and Soda Residue. Materials. 2025; 18(7):1552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071552
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xiaoyan, Yulan Zuo, Fengming Yang, Junqing Zuo, Aihua Liu, Huang Huangfu, Kai Lyu, Xian Xie, and Surendra P. Shah. 2025. "Evaluation of Fresh Property, Compressive Strength and Environmental Impact of Low-Carbon Geopolymer Based on Ladle Furnace Slag and Soda Residue" Materials 18, no. 7: 1552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071552
APA StyleLiu, X., Zuo, Y., Yang, F., Zuo, J., Liu, A., Huangfu, H., Lyu, K., Xie, X., & Shah, S. P. (2025). Evaluation of Fresh Property, Compressive Strength and Environmental Impact of Low-Carbon Geopolymer Based on Ladle Furnace Slag and Soda Residue. Materials, 18(7), 1552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18071552






