Effect of Chromium on Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Behavior of Copper–Nickel Alloy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
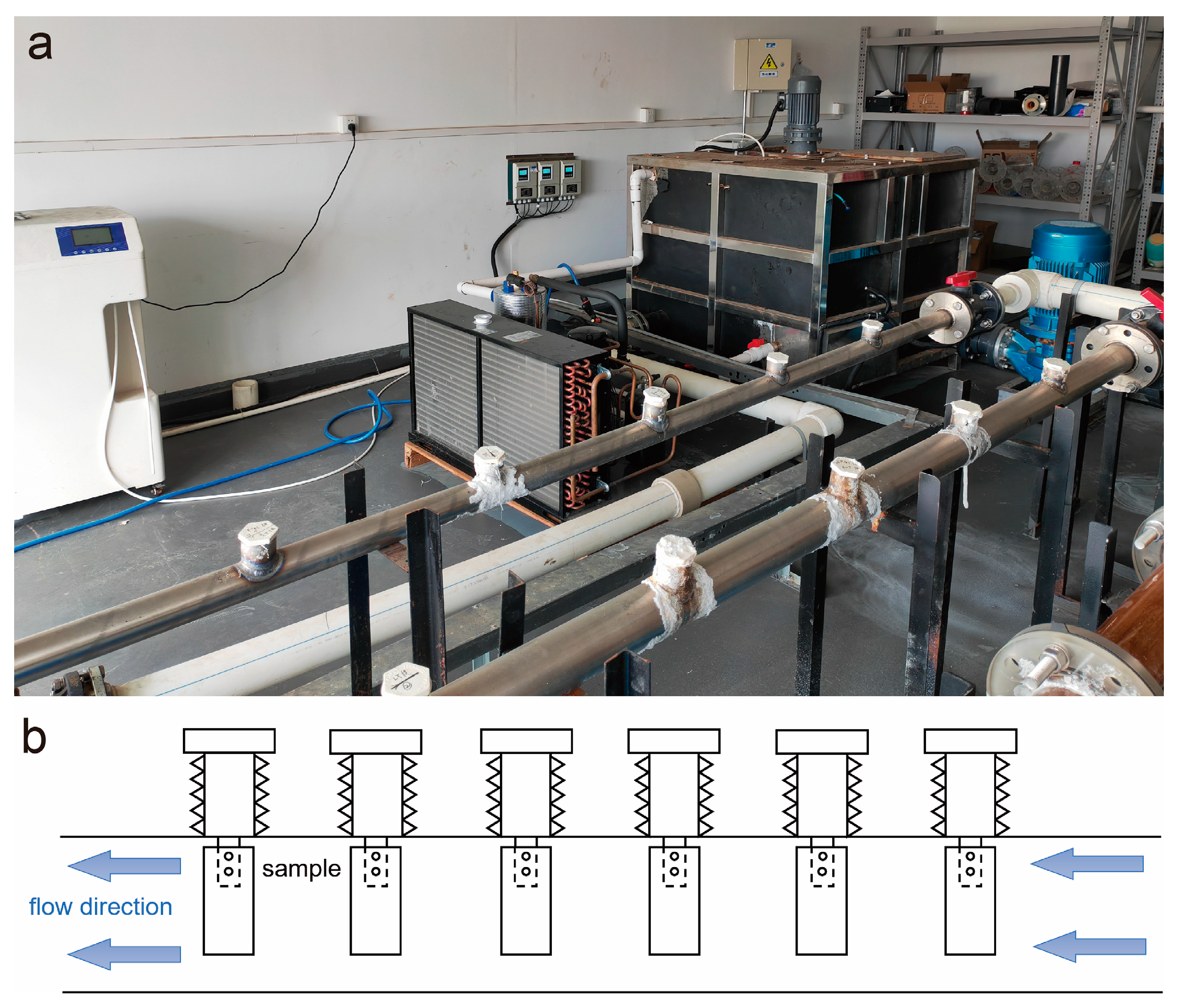
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Alloy Performance Tests
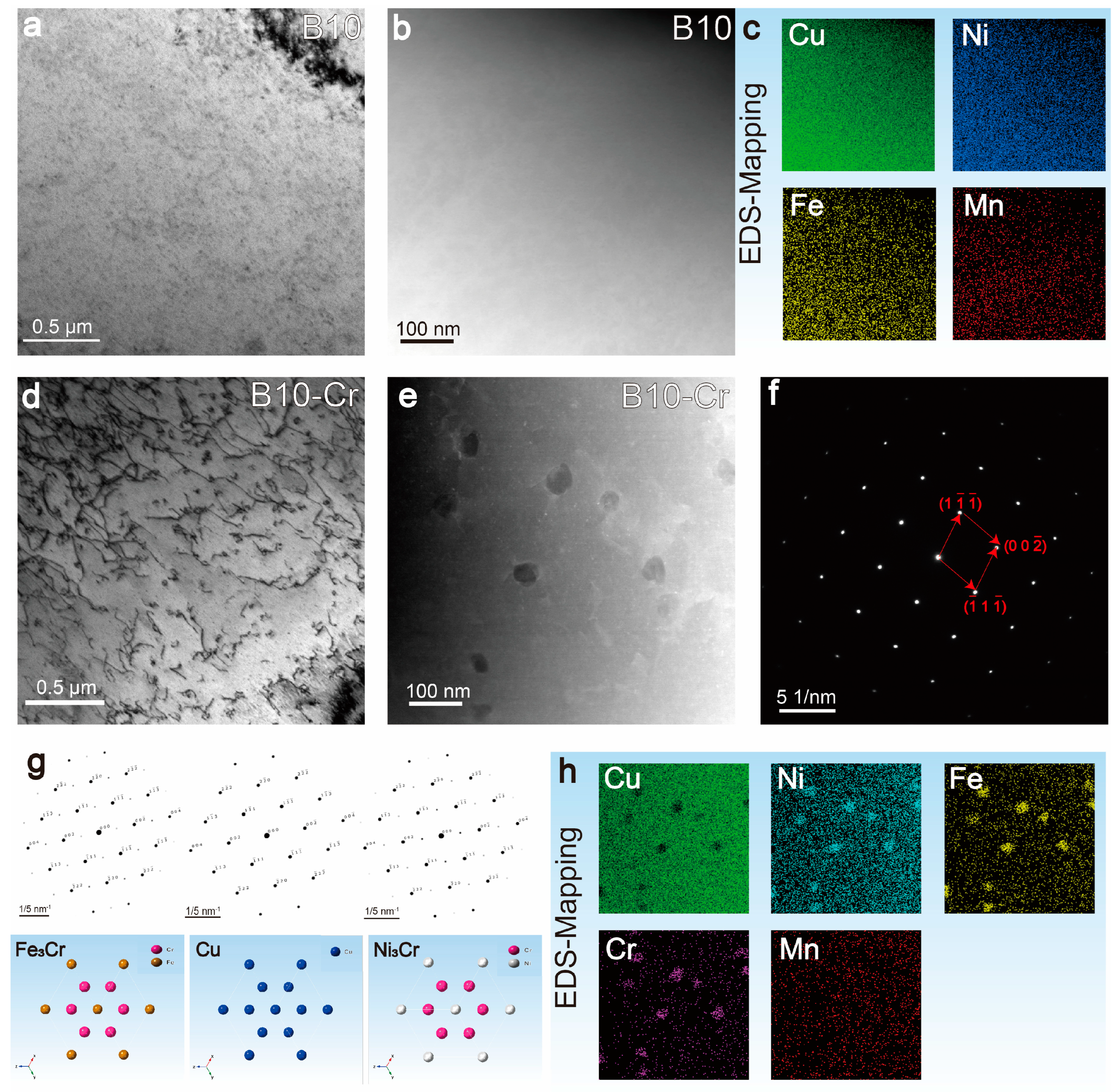
3.2. Microstructure of the Alloy
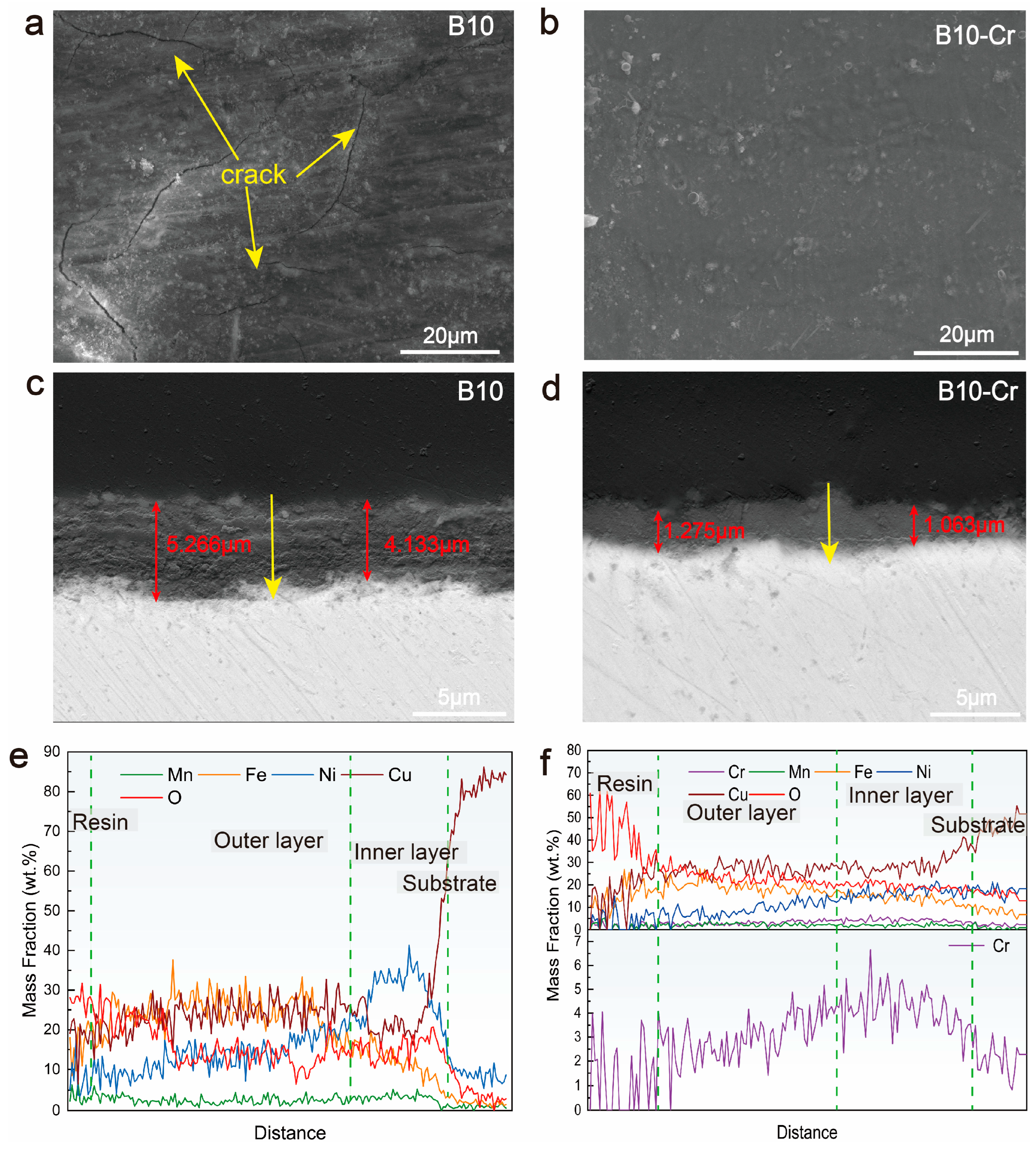
3.3. Microstructure of Corrosion Product Film
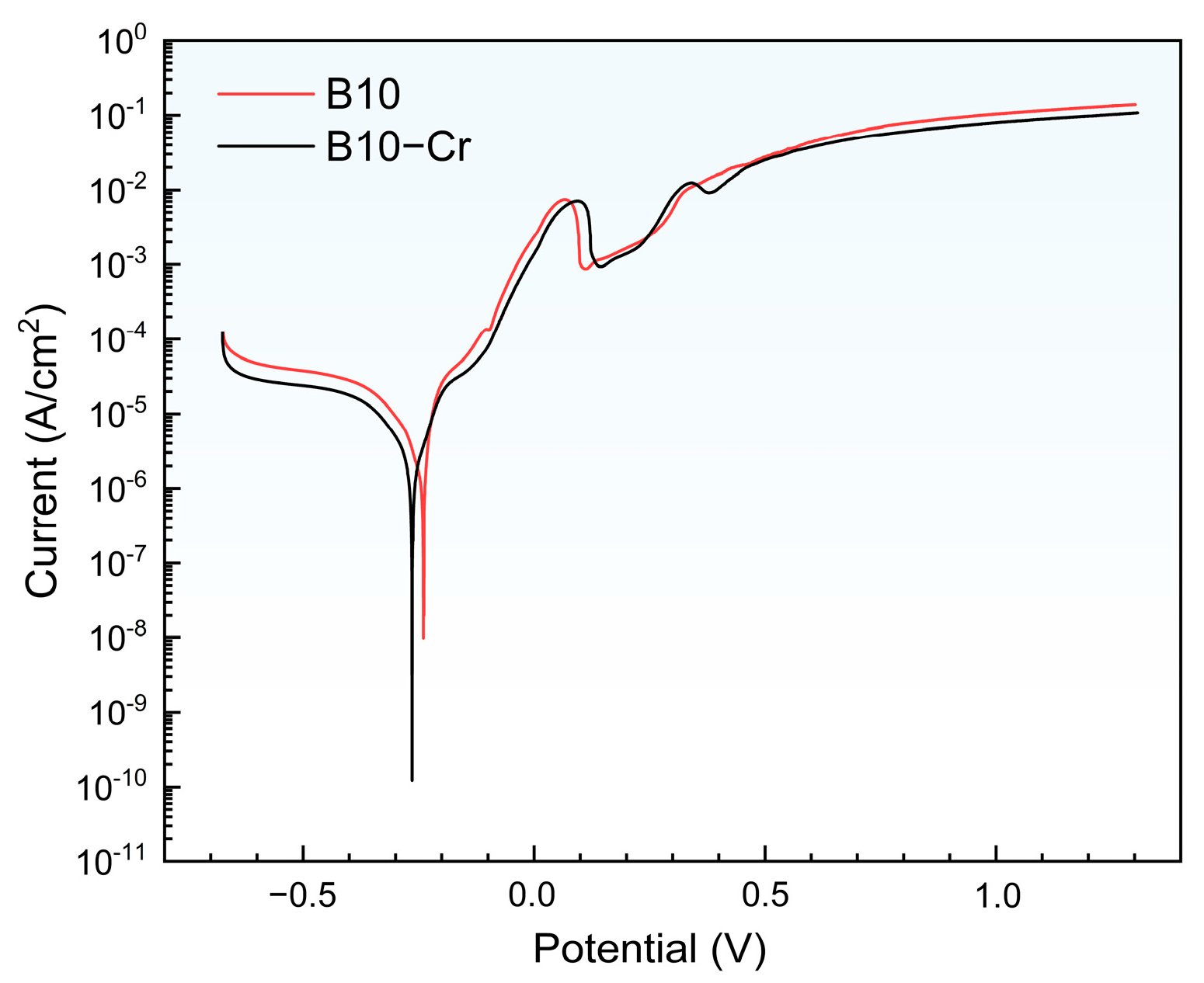
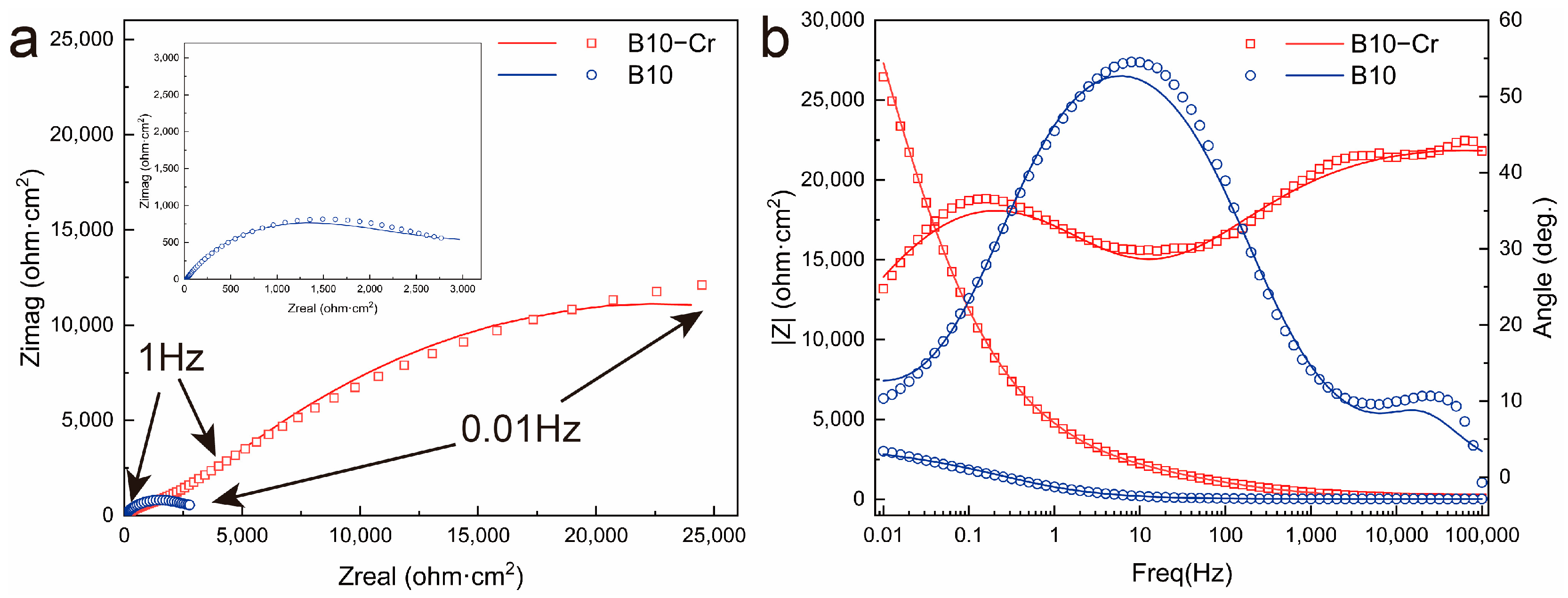
3.4. Electrochemical Performance Characterization of Alloys
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Cr has a notable synergistic effect on the erosion–corrosion resistance and strength of cupronickel alloys, with optimum alloy properties achieved with the addition of 0.3 wt.% Cr, increasing the ultimate tensile strength of cupronickel alloys by 30% to 350 MPa and reducing the erosion–corrosion rate by 70% to 0.0603 mm/a.
- (2)
- The addition of Cr has almost no effect on the grain size and the proportion of special grain boundaries in the alloy. However, TEM results show that the addition of Cr forms fine, dispersed (Ni/Fe)3Cr phases in the matrix, which is the main reason for the increased strength of the alloy. At the same time, this also improves the erosion resistance of the alloy matrix.
- (3)
- Characterization of the corrosion products revealed that the B10-Cr alloy formed smoother films with fewer cracks, and there is also an enrichment of Cr in the corrosion products. This indicates that Cr can partially fill the cation vacancies in Cu2O, thereby reducing the ion diffusion pathways. The results of the polarization curves show that the B10-Cr alloy is easier to passivate, which allows the alloy matrix to be protected by the passive film at an earlier stage. The EIS results show that the addition of Cr greatly improves the resistance to charge transfer, thereby improving the corrosion performance of the alloy.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kear, G.; Barker, B.D.; Walsh, F.C. Electrochemical corrosion of unalloyed copper in chloride media—A critical review. Corros. Sci. 2004, 46, 109–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, A.L.; Jiang, S.L.; Zheng, Y.G.; Ke, W. Corrosion product film formed on the 90/10 copper–nickel tube in natural seawater: Composition/structure and formation mechanism. Corros. Sci. 2015, 91, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- North, R.F.; Pryor, M.J. The influence of corrosion product structure on the corrosion rate of Cu-Ni alloys. Corros. Sci. 1970, 10, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.Z.; Zhang, W.F.; Li, N.; Liu, X.R.; Han, L.; Dai, W. Surface Characterization and Corrosion Behavior of 90/10 Copper-Nickel Alloy in Marine Environment. Materials 2019, 12, 1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.J.; Pehkonen, S.O. Surface characterization and corrosion behavior of 70/30 Cu–Ni alloy in pristine and sulfide-containing simulated seawater. Corros. Sci. 2007, 49, 1276–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, C.; Cao, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Yang, B. Microstructure and Corrosion Behavior of as-cast 90Cu-10Ni Alloys with Different Yttrium Content. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2020, 15, 4161–4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Peng, L.; Xie, H.; Zhang, W.; Huang, S.; Yang, Z.; Li, Z.; Mi, X. Enhancing the erosion-corrosion resistance of cupronickel alloy through grain boundary engineering. Corros. Sci. 2023, 219, 111228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.X.; Zhang, B.; Wu, B.; Wang, Y.J.; Tian, X.H.; Yang, L.X.; Oguzie, E.E.; Ma, X.L. Enhanced corrosion resistance by engineering crystallography on metals. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.B.; Chen, X.H.; Liu, P.; Fu, S.L.; Zhou, H.L.; Wu, J.Y. Effect of iron on the composition and structure of corrosion product film formed in 70/30 copper-nickel alloy. Anti-Corros. Methods Mater. 2021, 68, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drolenga, L.J.P.; Ijsseling, F.P.; Kolster, B.H. The Influence of Alloy Composition and Microstructure on the Corrosion Behavior of Cu-Ni Alloys in Seawater. Werkst. Und Korros.-Mater. Corros. 1983, 34, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, G.; Gao, Y.; Wu, J.; Liu, P.; Zhang, K.; Li, W.; Ma, F.; Zhou, H.; Chen, X. Effect of Fe/Mn content on mechanical and corrosion properties of 90/10 copper-nickel alloy. Mater. Corros.-Werkst. Korros. 2022, 73, 1085–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Li, S.; Zhang, R. Investigation of corrosion characteristics of Cu-10Ni-1.2Fe-xMn (x = 0.53, 0.87, 1.19) alloy in 3.5% NaCl solution. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 11318–11328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Pan, L.; Jin, Q.; Wang, C.; Jiang, Y. Effects of B on Microstructure and Properties of White Copper Alloys. Spec. Cast. Non-Ferr. Alloys 2010, 30, 385–388. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.; Hong, S.; Zhang, S. Effect of Al Content on the Corrosion Resistance of Cu-Ni Powder Metallurgy Alloy. Mater. Prot. 2023, 56, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Z.; Jia, S.; Zhou, Y.; Song, K.; Mi, X.; Li, Z. Effect of homogenization annealing on corrosion resistance of new Cu-Ni-Al alloy. Trans. Mater. Heat Treat. 2018, 39, 78–83. [Google Scholar]
- Tandon, V.; Patil, A.P.; Bansod, A. Effect of Zn addition on corrosion resistance of Cu-10Ni alloy in clean and sulphide contaminated seawater. Can. Metall. Q. 2018, 57, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Tang, H.; Wang, C.; Han, Z.; Li, S. Effects of Alloying Elements and Microstructure on Stainless Steel Corrosion: A Review. Steel Res. Int. 2022, 93, 2100450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, G. Chemical Composition Optimization and Sea Water Corrosion Resistance of a Ductile Cast Iron. J. Chin. Soc. Corros. Prot. 2014, 34, 537–543. [Google Scholar]
- Tomaru, M.; Yakou, T. Effect of Cr Contents on Corrosion Resistance of FeAl in HCl Solution. Tetsu Hagane-J. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 2011, 97, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Shu, Y. Influence of Cr content on the corrosion of Fe-Cr alloys: The synergistic effect of NaCl and water vapor. Oxid. Met. 2003, 59, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquivel, J.; Gupta, R.K. Review—Corrosion-Resistant Metastable Al Alloys: An Overview of Corrosion Mechanisms. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 081504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.C.; Chao, H.; Chen, K.H. Effect of Zr, Er and Cr additions on microstructures and properties of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A-Struct. Mater. Prop. Microstruct. Process. 2014, 610, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.C.; Chen, K.H.; Chen, X.; Chao, H.; Peng, G.S. Effect of Cr, Yb and Zr additions on localized corrosion of Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 2872–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, G.; Lee, E.K.Y. Simultaneous refinement in 0′ precipitation and corrosion behavior of a 2xxx series Al-Cu alloys modified via the sole or joint addition of Cr, Mn and Zr. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 40, 109578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.N.; Zi, J.L.; Zheng, M.S.; Zhu, J.W. Corrosion behavior of copper with minor alloying addition in chloride solution. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 462, 240–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Xu, X.; Chen, M.; Xie, J. Corrosion mechanism and corrosion behavior prediction of Cu-10Ni-X alloys in NaCl solution combining DFT calculation and experiments. Corros. Sci. 2024, 227, 111671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Fang, M.; Xiao, Z.; Meng, X.; Lei, Q.; Jia, Y. Effect of Cr addition on corrosion behavior of cupronickel alloy in 3.5 wt% NaCl solution. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 22, 2222–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, N.N.; Zhou, W. Effect of grain size and twins on corrosion behaviour of AZ31B magnesium alloy. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollapudi, S. Grain size distribution effects on the corrosion behaviour of materials. Corros. Sci. 2012, 62, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralston, K.D.; Fabijanic, D.; Birbilis, N. Effect of grain size on corrosion of high purity aluminium. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 1729–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X. Effect of Grain Size on Atmospheric Corrosion Resistance of Ultra-Low Carbon If Steel. Acta Metall. Sin. 2012, 48, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Xu, Y.; Ma, A.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, Y. Influence of pre-immersion aeration conditions on corrosion product films and erosion-corrosion resistance of 90/10 and 70/30 copper-nickel tubes in 1 wt% NaCl solution. Corros. Sci. 2024, 228, 111817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, S.A.; Radford, G.J.W.; Tuck, C.D.S.; Barker, B.D. Corrosion and Galvanic Compatibility Studies of a High-Strength Copper-Nickel Alloy. Corrosion 2002, 58, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ura-Binczyk, E.; Homazava, N.; Ulrich, A.; Hauert, R.; Lewandowska, M.; Kurzydlowski, K.J.; Schmutz, P. Passivation of Al–Cr–Fe and Al–Cu–Fe–Cr complex metallic alloys in 1M H2SO4 and 1M NaOH solutions. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 1825–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Li, K.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yao, L.; Fa, Y.; Jian, Z. Microstructure, Corrosion Behaviour and Microhardness of Non-equiatomic Fe1.5CoNiCrCux (0.5 ≤ x ≤ 2.0) High-Entropy Alloys. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2020, 73, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample | Ni (wt.%) | Fe (wt.%) | Mn (wt.%) | Cr (wt.%) | Cu (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B10 | 9.98 ± 0.02 | 1.89 ± 0.01 | 0.90 ± 0.02 | - | Bal. |
| B10-0.3Cr | 9.98 ± 0.02 | 1.93 ± 0.01 | 0.90 ± 0.03 | 0.29 ± 0.01 | Bal. |
| B10-0.4Cr | 9.96 ± 0.02 | 1.93 ± 0.02 | 0.90 ± 0.03 | 0.41 ± 0.01 | Bal. |
| B10-0.5Cr | 9.98 ± 0.04 | 1.93 ± 0.02 | 0.90 ± 0.01 | 0.52 ± 0.02 | Bal. |
| Sample | Rs (Ω·cm2) | C1 × 10−6 (F·cm2) | n1 | Rf (Ω·cm2) | C2 × 10−6 (F·cm−2) | n2 | Rct (Ω·cm2) | W × 103 (Ω−1·cm−2·s−0.5) | ∑x2 × 10−3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B10 | 19.86 | 31.65 | 0.68 | 2211 | 20.59 | 0.82 | 5184 | 7.15 | 2.549 |
| B10-Cr | 1.28 | 27.42 | 0.53 | 2798 | 77.37 | 0.73 | 5.762 × 104 | 5.139 | 0.523 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chu, H.; Yang, Z.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xie, H.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, H.; Yue, D. Effect of Chromium on Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Behavior of Copper–Nickel Alloy. Materials 2025, 18, 1799. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081799
Chu H, Yang Z, Cao Y, Zhang W, Xie H, Yuan Y, Wang H, Yue D. Effect of Chromium on Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Behavior of Copper–Nickel Alloy. Materials. 2025; 18(8):1799. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081799
Chicago/Turabian StyleChu, Hao, Zhen Yang, Yicheng Cao, Wenjing Zhang, Haofeng Xie, Yi Yuan, Hongqian Wang, and Dongyan Yue. 2025. "Effect of Chromium on Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Behavior of Copper–Nickel Alloy" Materials 18, no. 8: 1799. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081799
APA StyleChu, H., Yang, Z., Cao, Y., Zhang, W., Xie, H., Yuan, Y., Wang, H., & Yue, D. (2025). Effect of Chromium on Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Behavior of Copper–Nickel Alloy. Materials, 18(8), 1799. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081799






