The Effect of Aging Treatment on the Corrosion Behavior of 17-4PH Stainless Steel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiments
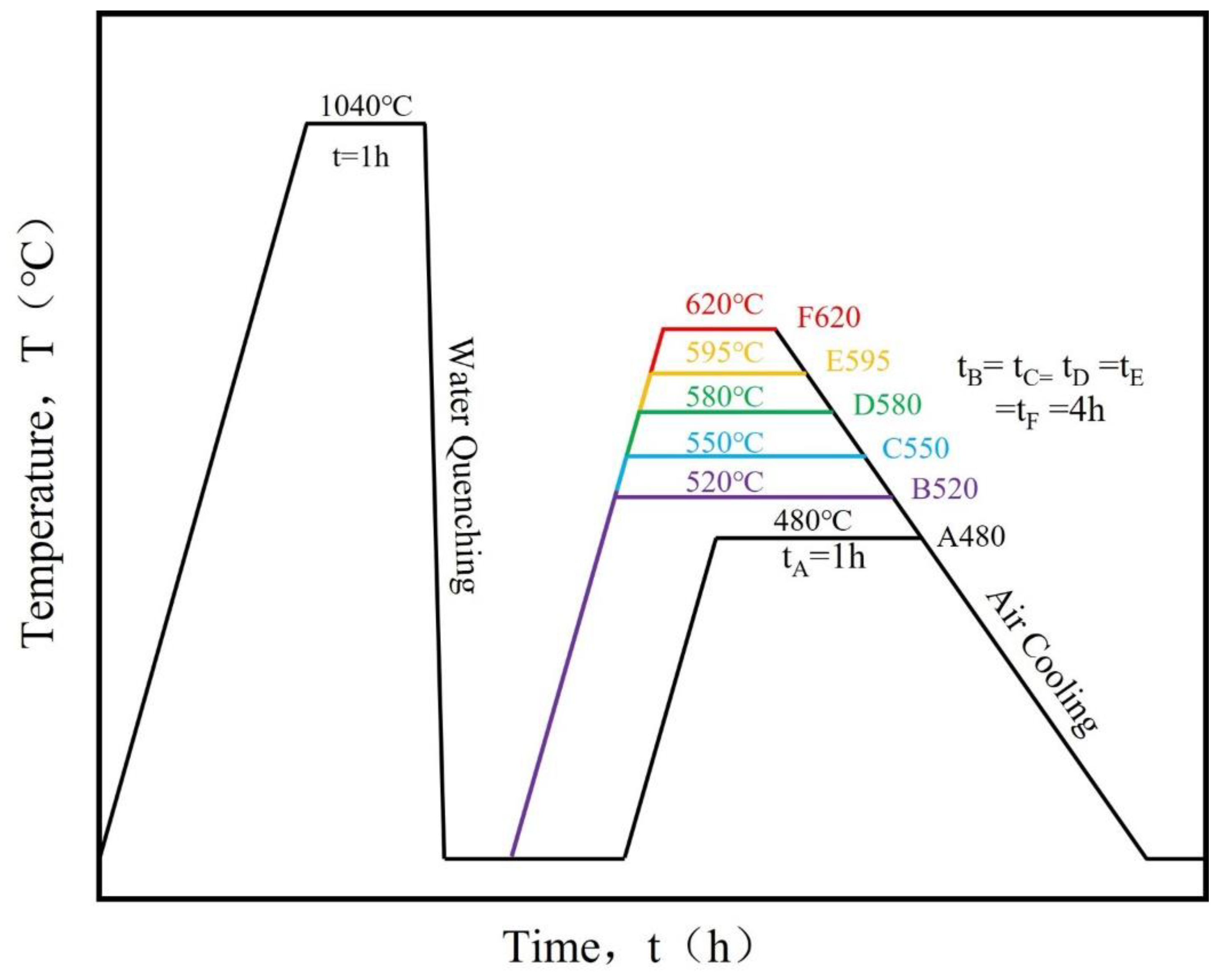
2.1. Materials and Samples
2.2. Electrochemical Measurements
2.3. Microstructural Characterization
3. Results
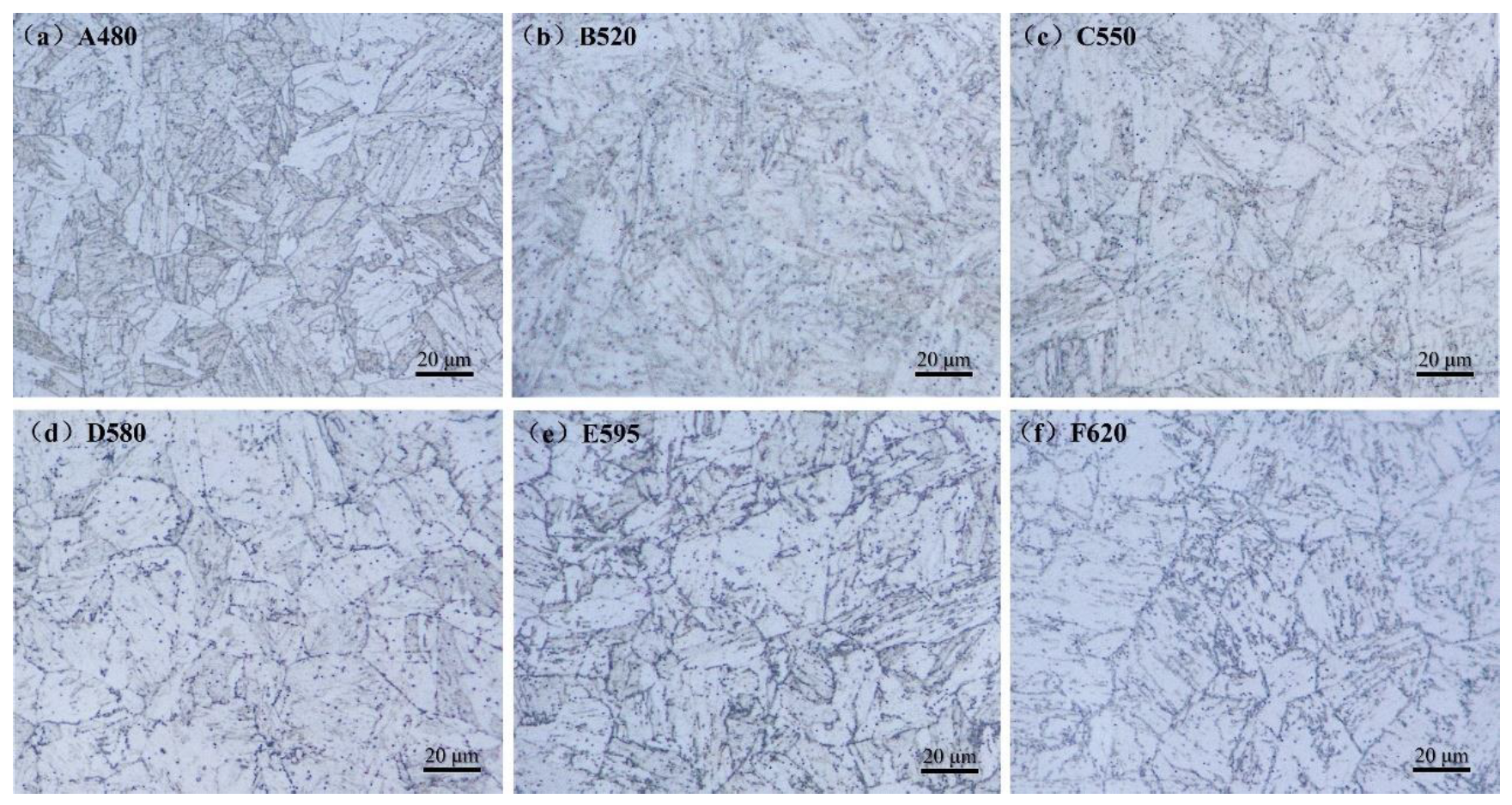
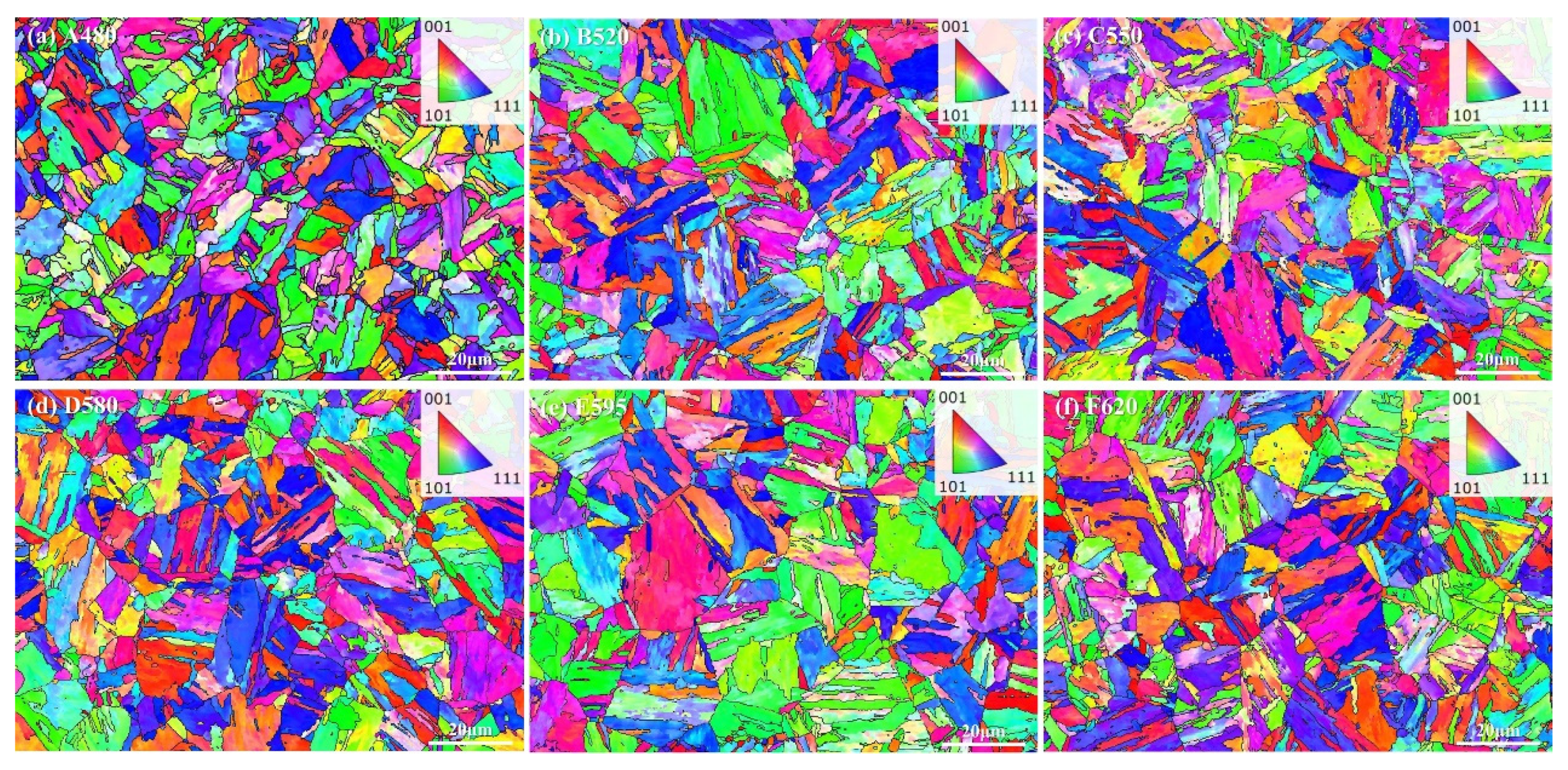
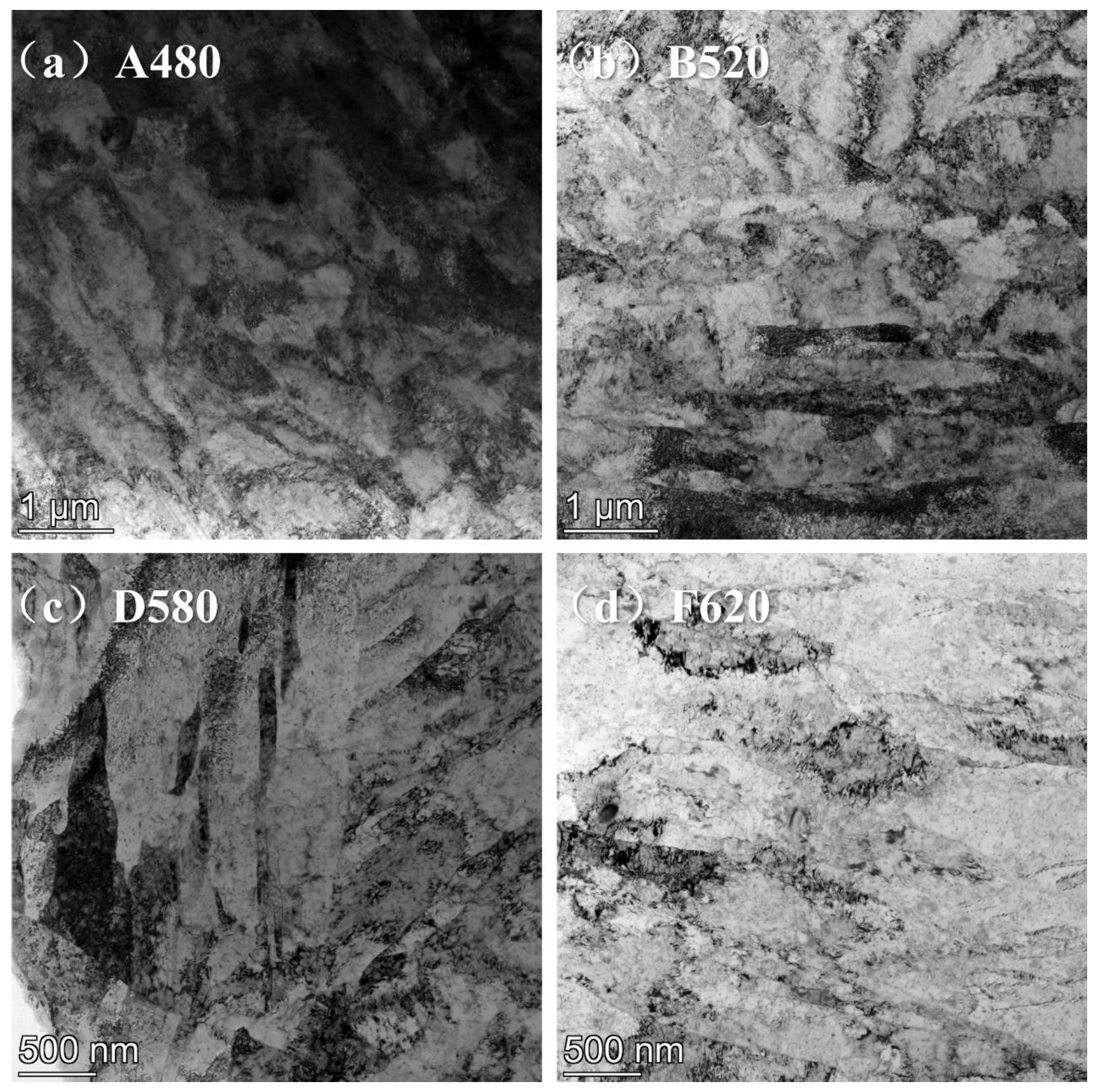
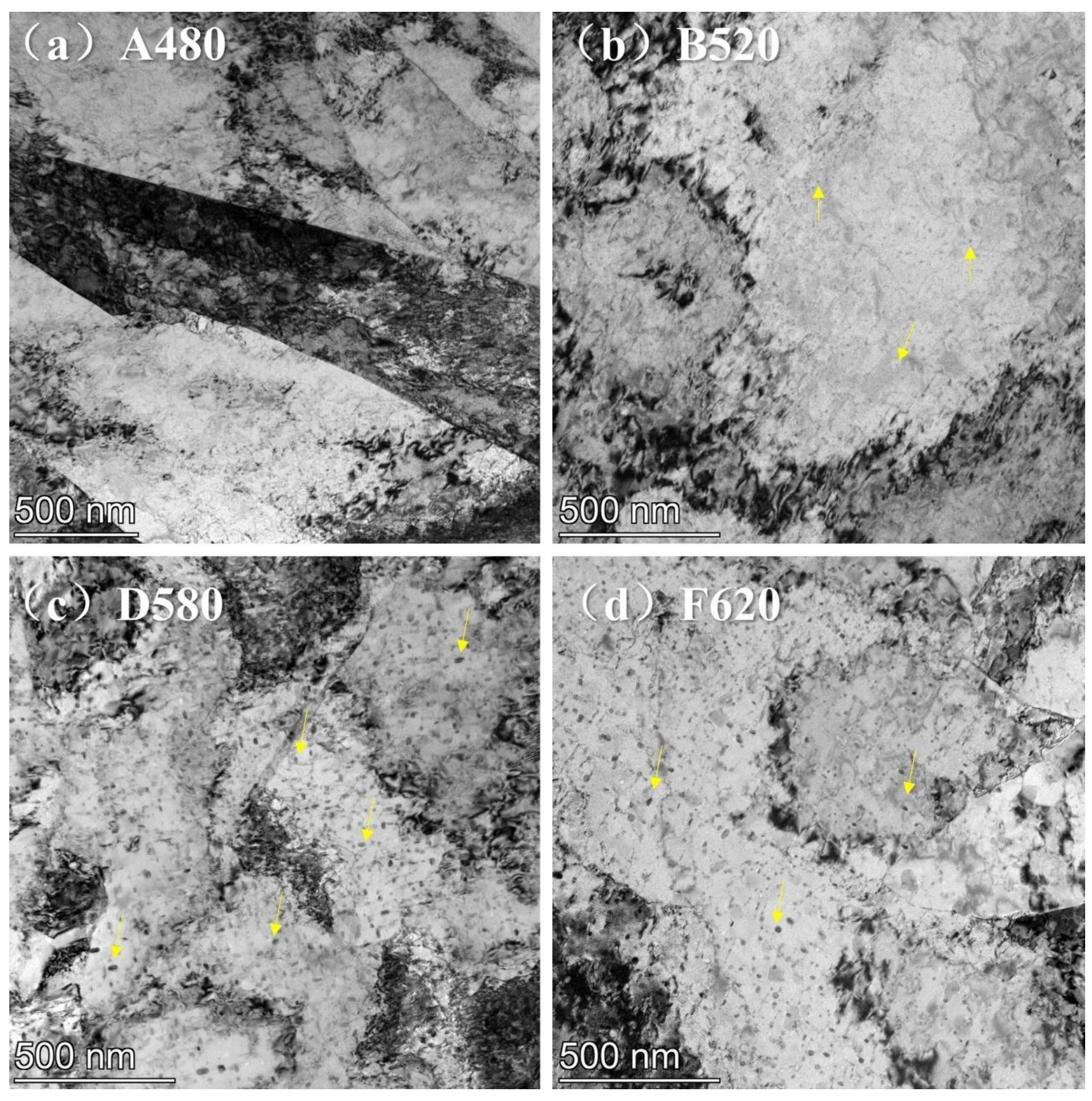
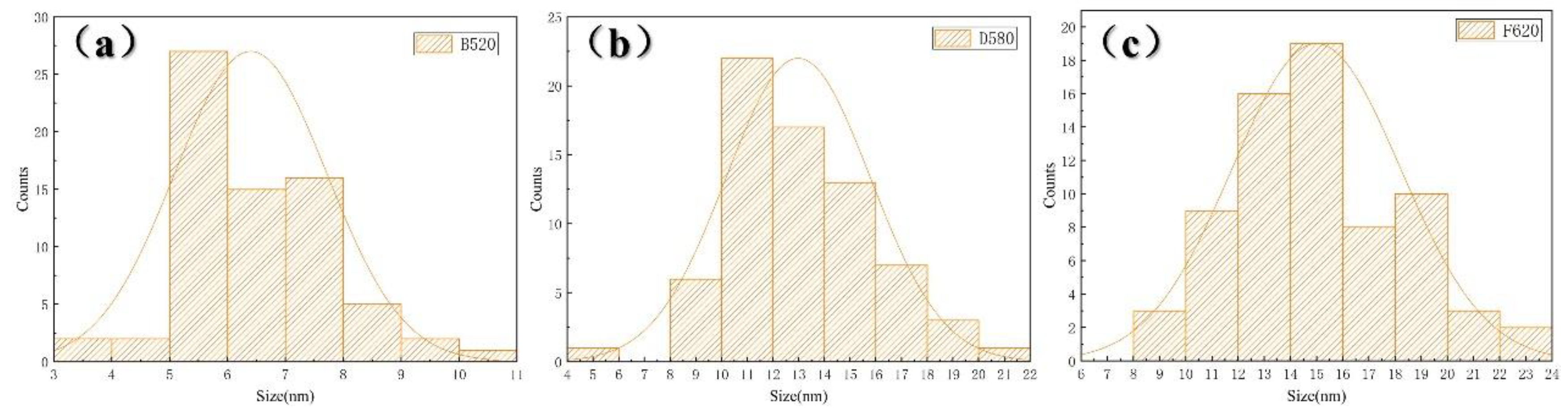
3.1. Effect of Aging Treatment on Microstructural Evolution
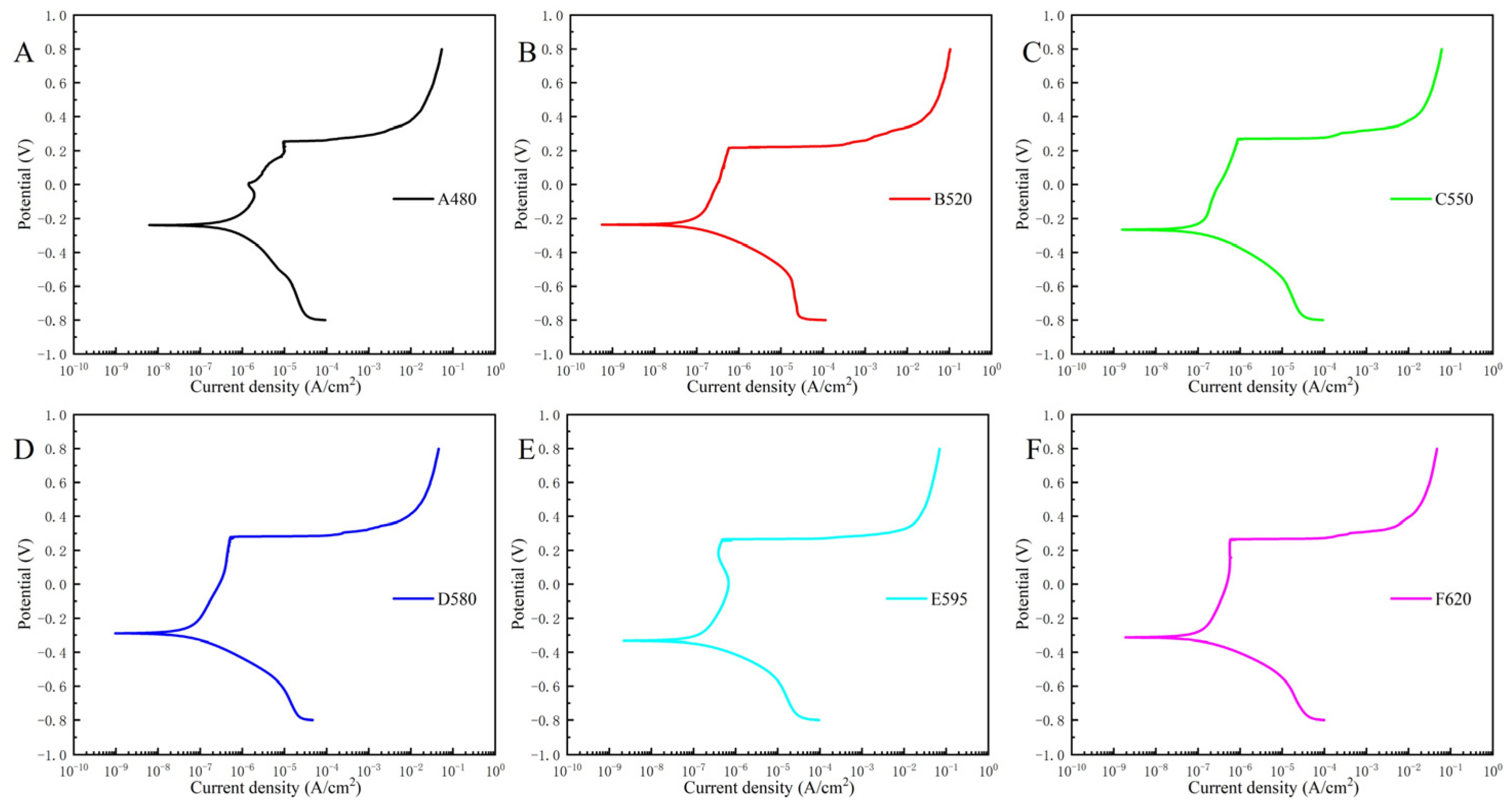
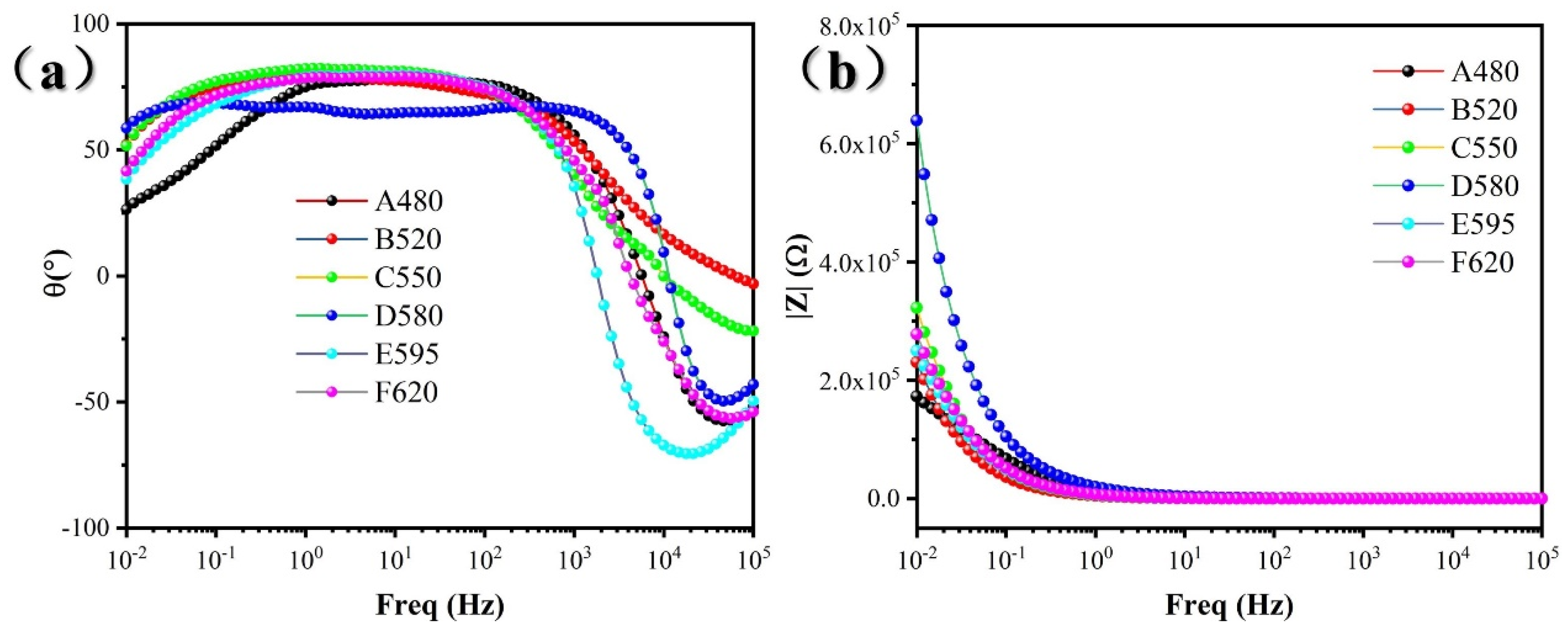
3.2. Electrochemical Test Result
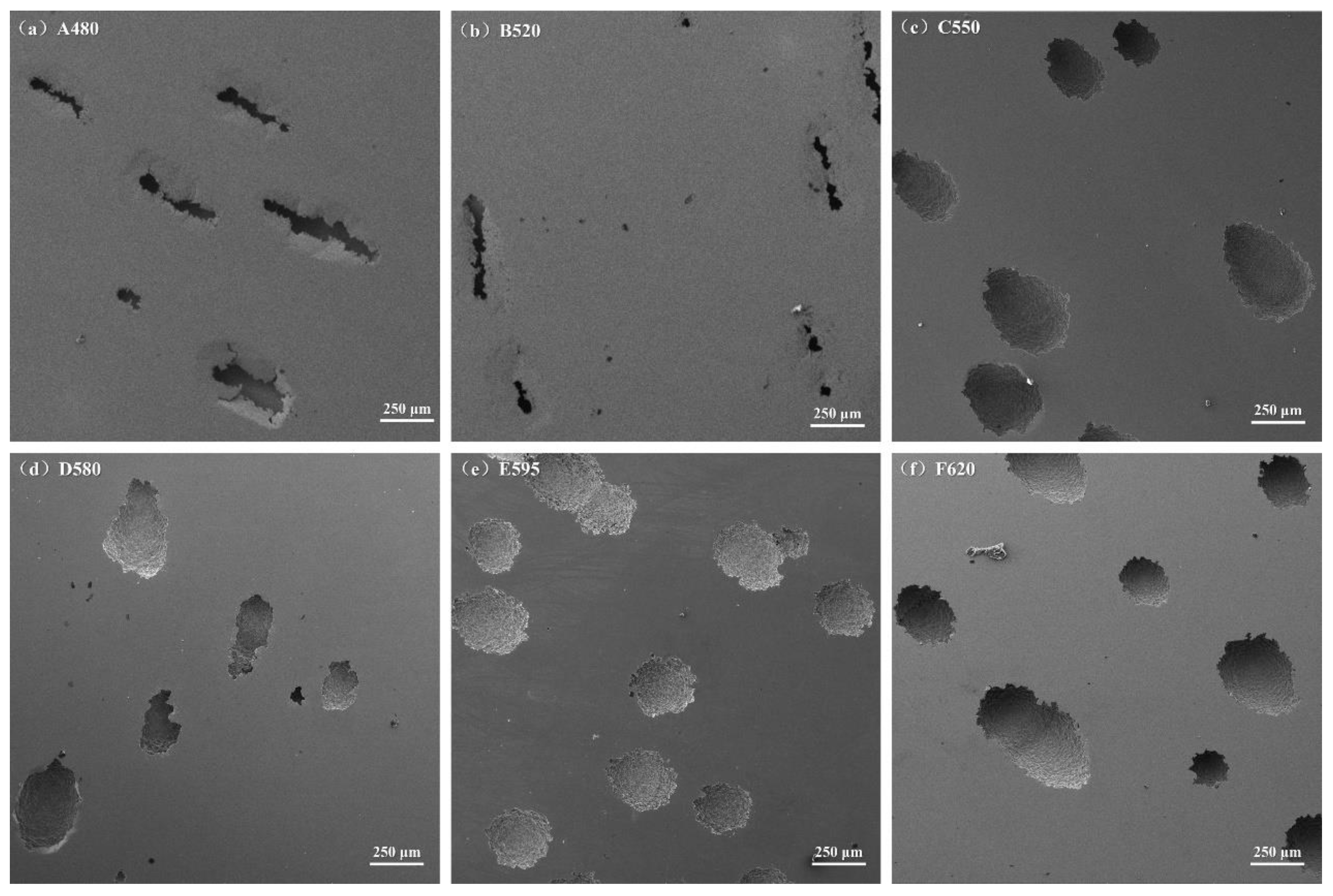
3.3. Surface Morphology of the Samples After Electrochemical Testing
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- As the aging temperature increases from 480 °C to 620 °C, the number of dislocations within the matrix gradually decreases. Precipitation behavior exhibited a sequential evolution: initial nucleation of Cu-rich precipitates at lower aging temperatures, followed by coarsening and agglomeration at elevated temperatures, accompanied by a corresponding decrease in precipitate population density.
- The corrosion resistance of 17-4PH stainless steel in 3.5 wt% NaCl solution first improved and then deteriorated with the aging temperature increasing, and the corrosion pit also changed from strip shape to oval shape. The corrosion resistance of the D580 sample was the best, and that of the A480 sample was the worst.
- Pitting susceptibility was governed by synergistic effects of dislocation distribution and copper-rich phase evolution. The regional distribution of dislocation leads to electrochemical potential difference between different regions, which leads to pitting corrosion. The degree of segregation of Cu-rich precipitates can also cause pitting corrosion.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Esfandiari, M.; Dong, H. The corrosion and corrosion–wear behaviour of plasma nitrided 17-4PH precipitation hardening stainless steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 202, 466–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Che, Z.; Liu, W.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, X.; Liu, C.; Li, X. Influence mechanism of heat treatment on corrosion resistance of Te-containing 15–5PH stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 2023, 225, 111610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabzi, H.E.; Lim, S.H.; Della Crociata, D.; Castellote-Alvarez, R.; Simonelli, M.; San-Martín, D.; Hao, X.; Choi, P.P.; Rivera-Díaz-del-Castillo, P.E. Genetic design of precipitation-hardening stainless steels for additive manufacturing. Acta Mater. 2024, 274, 120018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, W.-T.; Tsai, C.-S. The investigation on the prediction of tool wear and the determination of optimum cutting conditions in machining 17-4PH stainless steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2003, 140, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, S.V.; Ghosn, L.J.; Lerch, B.A.; Hebsur, M.; Cosgriff, L.M.; Fedor, J. Mechanical properties of 17-4PH stainless steel foam panels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 456, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arisoy, C.F.; Başman, G.; Şeşen, M.K. Failure of a 17-4 PH stainless steel sailboat propeller shaft. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2003, 10, 711–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, P.; Nan, Y.; Yang, G.; Song, X. Effect of solution-treated temperature on hydrogen embrittlement of 17-4 PH stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 703, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zou, H.; Li, C.; Peng, Y.; Qiu, S.; Shen, B. The microstructure evolution of type 17-4PH stainless steel during long-term aging at 350 °C. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2006, 236, 2531–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, S.S.; Machado, C.L.; Oliveira, I.G.; Martins, T.R.; Masoumi, M. Damage associated with the interaction between hydrogen and microstructure in a high sulfur 17-4PH steel for studs. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2017, 82, 642–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamabe, J.; Sezgin, J.-G.; Wada, K. Fatigue crack threshold and crack growth behavior of 17–4 PH steel determined with internal hydrogen. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2022, 276, 108882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Wu, M.; Cui, C.; Miao, X.; Gong, Y. Effects of laser energy density on microstructure and corrosion resistance of FeCrNiMnAl high entropy alloy coating. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 152, 108188. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Mao, J.; Xue, C.; Ge, H.; Dong, G.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, J. Cavitation-Erosion behavior of laser cladded Low-Carbon Cobalt-Based alloys on 17-4PH stainless steel. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 158, 108761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Cai, Q.; Wei, B.; Zhang, X. Effect of Aging Temperature on Erosion-Corrosion Behavior of 17-4PH Stainless Steels in Dilute Sulphuric Acid Slurry. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2006, 13, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujiro, T.; Satoh, S.; Staehle, R.; Smyrl, W. Effect of alloying Cu on the corrosion resistance of stainless steels in chloride media. Corros. Sci. 2001, 43, 2185–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Jin, Y.; Chen, H.; Hu, S.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, M.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, W.; Li, W. Cellular automata simulation of pitting corrosion of stainless steel in marine environments. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 41, 110555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, A.K.; Sreekumar, K. Intergranular corrosion of a stud used in safety relief valve. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2009, 16, 1379–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhao, J.; Xie, D.; Lv, F.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H. Improved mechanical properties of laser-repaired 15-5PH stainless steel by in-situ heat treatment and grain refinement. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 150, 107999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xun, M.; Ma, J.; Liang, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, H.; Jiang, Z.; Fan, G.; Han, P. Effects of heat treatment on precipitation and corrosion resistance of cerium-containing super austenitic stainless steel S31254. Corros. Commun. 2022, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.-S.; Kim, J.-G.; Park, Y.-S.; Park, J.-Y. Austenitizing treatment influence on the electrochemical corrosion behavior of 0.3C–14Cr–3Mo martensitic stainless steel. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 244–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, H.; Huo, P.; Bai, P.; Du, W.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, W. Effect of Solution Temperature on the Microstructure and Properties of 17-4PH High-Strength Steel Samples Formed by Selective Laser Melting. Metals 2022, 12, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, C.N.; Chiou, C.S.; Yang, J.R. Aging reactions in a 17-4 PH stainless steel. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2002, 74, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavares, S.S.M.; Da Silva, F.J.; Scandian, C.; Da Silva, G.F.; De Abreu, H.F.G. Microstructure and intergranular corrosion resistance of UNS S17400 (17-4PH) stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 3835–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.-Y.; Tzeng, Y.-C. Effects of aging treatment on the precipitation behavior of ε-Cu phase and mechanical properties of metal injection molding 17-4PH stainless steel. Mater. Lett. 2019, 237, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Lv, W.; Yang, Y.; Li, D.; Yan, L.; Pang, X.; He, Y.; Gao, K. Optimizing the hydrogen embrittlement resistance by tuning the structures of Cu-rich nanoprecipitates in high strength martensite stainless steels. Acta Mater. 2023, 246, 118722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Zhong, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Guan, K. Hydrogen embrittlement induced fracture of 17-4 PH stainless steel valve stem. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2020, 113, 104576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, W.; Wang, H.; Sun, Z.; Yang, Y.; He, W.; Xu, J.; Xia, Y.; Yin, W.; et al. Effect of Si on the dislocation state within martensite of ultra-high strength hot-rolled medium Mn steel with good ductility. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 869, 144825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Z.; Xue, H.; Liu, J.; Zhou, X.; Liu, W.; Yang, S.; Du, Y.; Cheng, X.; Li, X.; Liu, C. A novel understanding of dislocation density effect on the corrosion resistance of 316L stainless steel with passive film nucleation growth kinetic calculation. Corros. Sci. 2025, 248, 112810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.G.; Jiang, X.J.; Ran, Q.X.; Wang, S.Q.; Han, R.H. Corrosion resistance improvement of 430 stainless steel via plastic deformation induced uniform substructure. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; He, J.; Liu, M.; Wu, Z.; Wu, N.; Luo, F. Effect of cold-rolling on the corrosion resistance of 316L SS in simulated PEMFCs cathode environment. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 93, 1100–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurice, V.; Marcus, P. Progress in corrosion science at atomic and nanometric scales. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2018, 95, 132–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayani, S.H.; Ha, H.Y.; Cho, Y.H.; Son, H.W.; Lee, J.M. Dislocation-assisted localised pitting corrosion behaviour of AlSiMgCuMn alloy. Corros. Sci. 2023, 221, 111372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Oguzie, E.E.; Li, Y.; Chen, D.; Yang, K.; Wang, F. Electrochemical corrosion behavior of a novel antibacterial stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 1083–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kear, G.; Barker, B.D.; Walsh, F.C. Electrochemical corrosion of unalloyed copper in chloride media—A critical review. Corros. Sci. 2004, 46, 109–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Yan, L.; Pang, X.; Gao, K. Hydrogen trapping and hydrogen embrittlement in 15-5PH stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 2022, 205, 110416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Shen, Q.; Liu, W.; Wang, Z. Nano-precipitates evolution and their effects on mechanical properties of 17-4 precipitation-hardening stainless steel. Acta Mater. 2018, 156, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Chen, C.; Li, Y.; Zhou, W.; Ren, X. Effect of surface morphology and microstructure on the hot corrosion behavior of TiC/IN625 coatings prepared by extreme high-speed laser cladding. Corros. Sci. 2022, 201, 110271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, A.; Merino, M.; Carboneras, M.; Viejo, F.; Arrabal, R.; Muñoz, J. Influence of Cu and Sn content in the corrosion of AISI 304 and 316 stainless steels in H2SO4. Corros. Sci. 2006, 48, 1075–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguzie, E.E.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, D.; Li, Y.; Yang, K.; Wang, F. The effect of Cu addition on the electrochemical corrosion and passivation behavior of stainless steels. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 5028–5035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zou, D.-N.; Yan, X.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-B.; Pan, J.-X.; Cheng, Y.-X.; Xu, R.; Jiang, Y.-C. Phase precipitation and corrosion properties of copper-bearing ferritic stainless steels by annealing process. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2023, 30, 2280–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Qian, H.; Chang, W.; Guo, D.; Kwok, C.T.; Tam, L.M.; Zhang, D. Effect of aging heat treatment on microbiologically influenced corrosion of 17–4PH stainless steel by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Corros. Sci. 2024, 227, 111739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banas, J.; Mazurkiewicz, A. The effect of copper on passivity and corrosion behaviour of ferritic and ferritic–austenitic stainless steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2000, 277, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-M.; Tsai, H.-L.; Bor, H.-Y. Effect of aging treatment on microstructure and properties of high-entropy Cu0.5CoCrFeNi alloy. Intermetallics 2010, 18, 1244–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| C | Si | Mn | Ni | P | S | Cr | Cu | Nb | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.031 | 0.53 | 0.58 | 3.87 | 0.018 | 0.0005 | 16.41 | 3.78 | 0.28 | balance |
| Samples | Icorr (nA/cm2) | Ecorr (VSCE) | Epit (VSCE) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A480 | 375 | −0.241 | 0.254 |
| B520 | 73.7 | −0.236 | 0.217 |
| C550 | 94.9 | −0.265 | 0.266 |
| D580 | 43.8 | −0.288 | 0.279 |
| E595 | 112 | −0.327 | 0.265 |
| F620 | 94.2 | −0.311 | 0.262 |
| Fe (at%) | Cr (at%) | Ni (at%) | Cu (at%) | Nb (at%) | Si (at%) | O (at%) | C (at%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a1 | 79.76 | 16.39 | 3.85 | |||||
| a2 | 58.85 | 19.67 | 16.03 | 2.76 | 2.69 | |||
| b1 | 77.19 | 16.99 | 3.04 | 2.78 | ||||
| b2 | 63.82 | 14.71 | 3.37 | 4.53 | 0.71 | 2.91 | 9.95 | |
| c1 | 76.10 | 15.83 | 3.61 | 3.32 | 1.14 | |||
| c2 | 44.79 | 17.30 | 2.31 | 8.09 | 2.18 | 1.47 | 5.48 | 18.39 |
| d1 | 65.03 | 14.09 | 3.59 | 0.87 | 16.42 | |||
| d2 | 63.28 | 14.52 | 3.85 | 8.82 | 1.68 | 0.96 | 6.88 | |
| e1 | 73.35 | 16.60 | 3.63 | 3.52 | 0.90 | |||
| e2 | 33.00 | 17.35 | 1.73 | 4.72 | 2.51 | 1.33 | 13.35 | 26.01 |
| f1 | 79.33 | 19.62 | 1.05 | |||||
| f2 | 55.00 | 12.14 | 2.31 | 5.44 | 1.15 | 1.33 | 7.62 | 14.32 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, C.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, L. The Effect of Aging Treatment on the Corrosion Behavior of 17-4PH Stainless Steel. Materials 2025, 18, 1823. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081823
Zhou C, Lv Y, Zhang L. The Effect of Aging Treatment on the Corrosion Behavior of 17-4PH Stainless Steel. Materials. 2025; 18(8):1823. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081823
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Chengshuang, Yin Lv, and Lin Zhang. 2025. "The Effect of Aging Treatment on the Corrosion Behavior of 17-4PH Stainless Steel" Materials 18, no. 8: 1823. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081823
APA StyleZhou, C., Lv, Y., & Zhang, L. (2025). The Effect of Aging Treatment on the Corrosion Behavior of 17-4PH Stainless Steel. Materials, 18(8), 1823. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081823





