Characteristics of Lightweight Foam Concrete Manufactured Using Water-Soluble Polymers and Lightweight Aggregates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
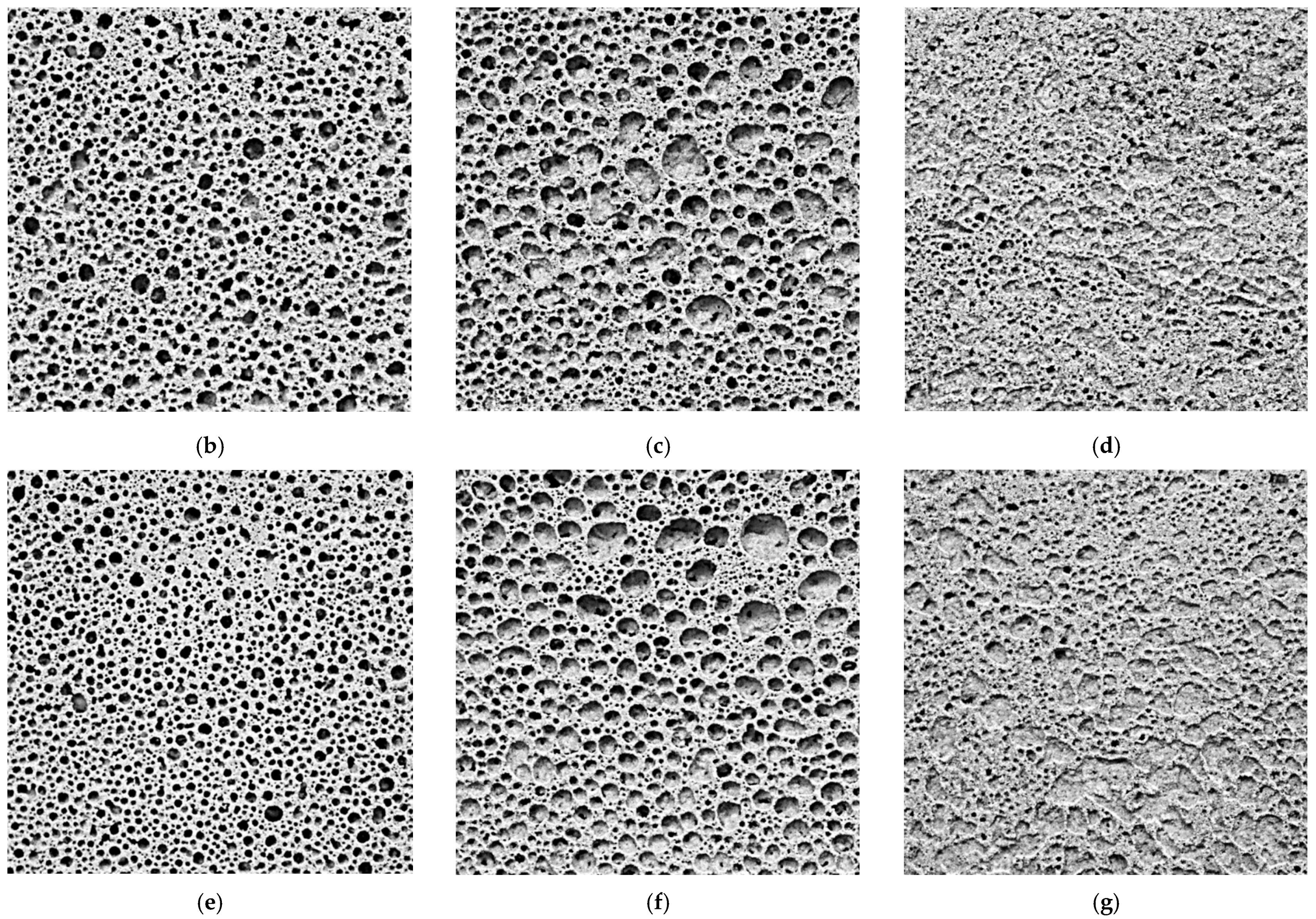
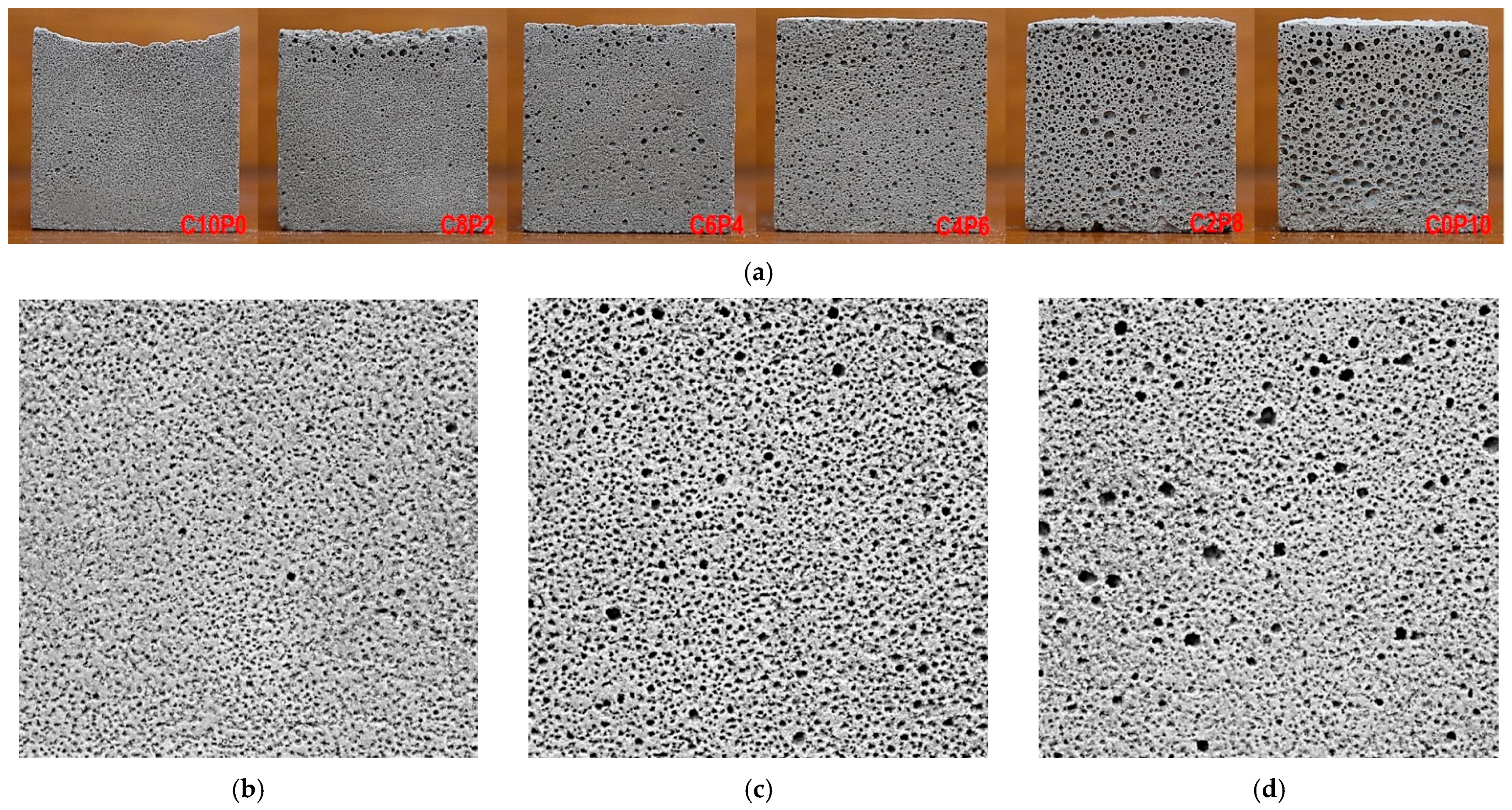
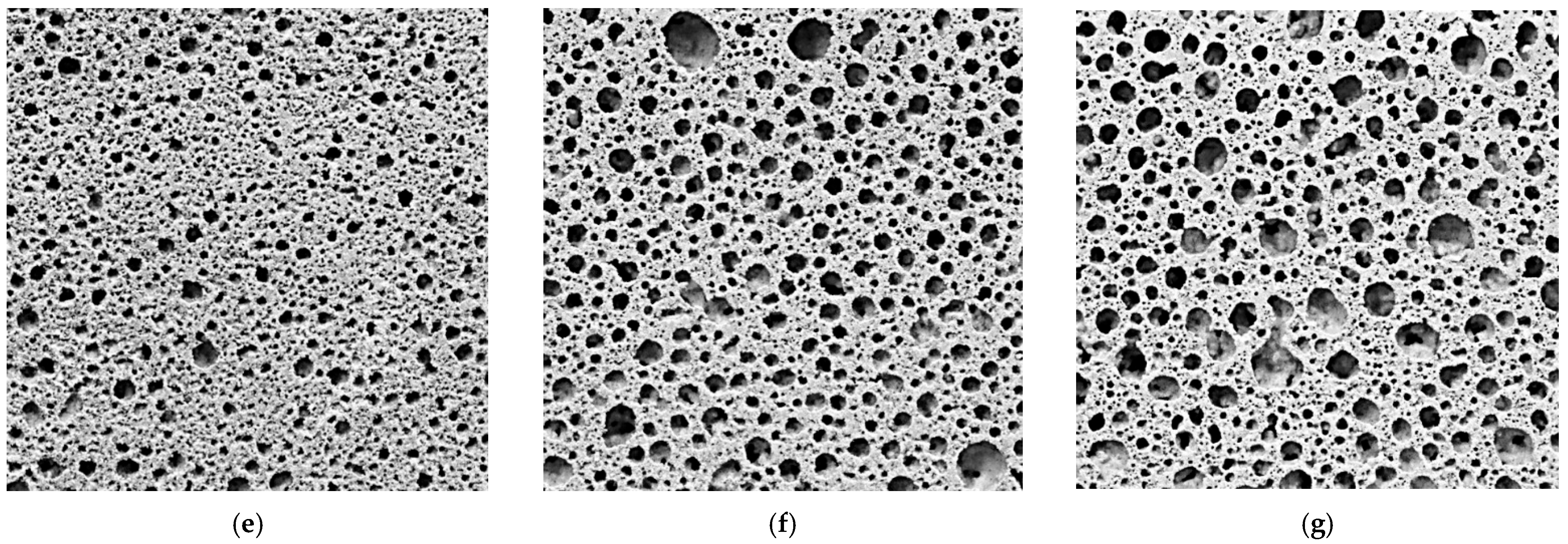
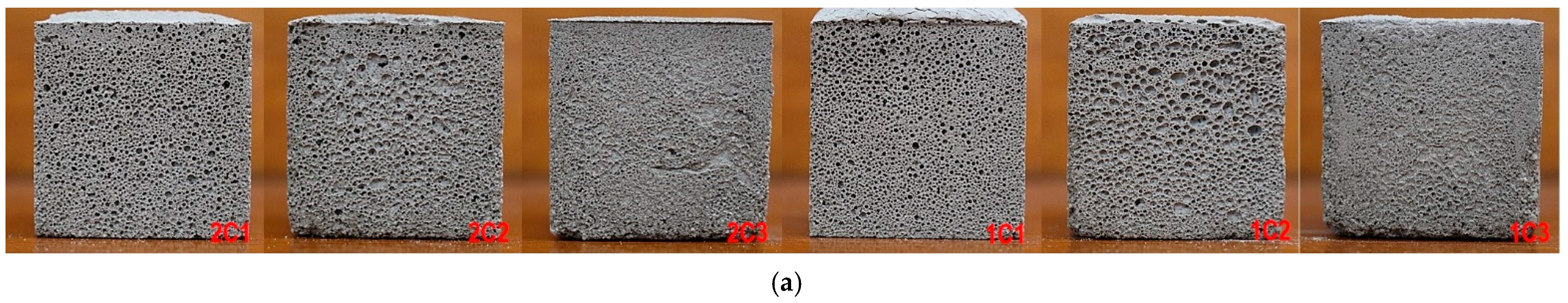
3.1. Foaming and Microporosity
3.2. Average Pore Diameter
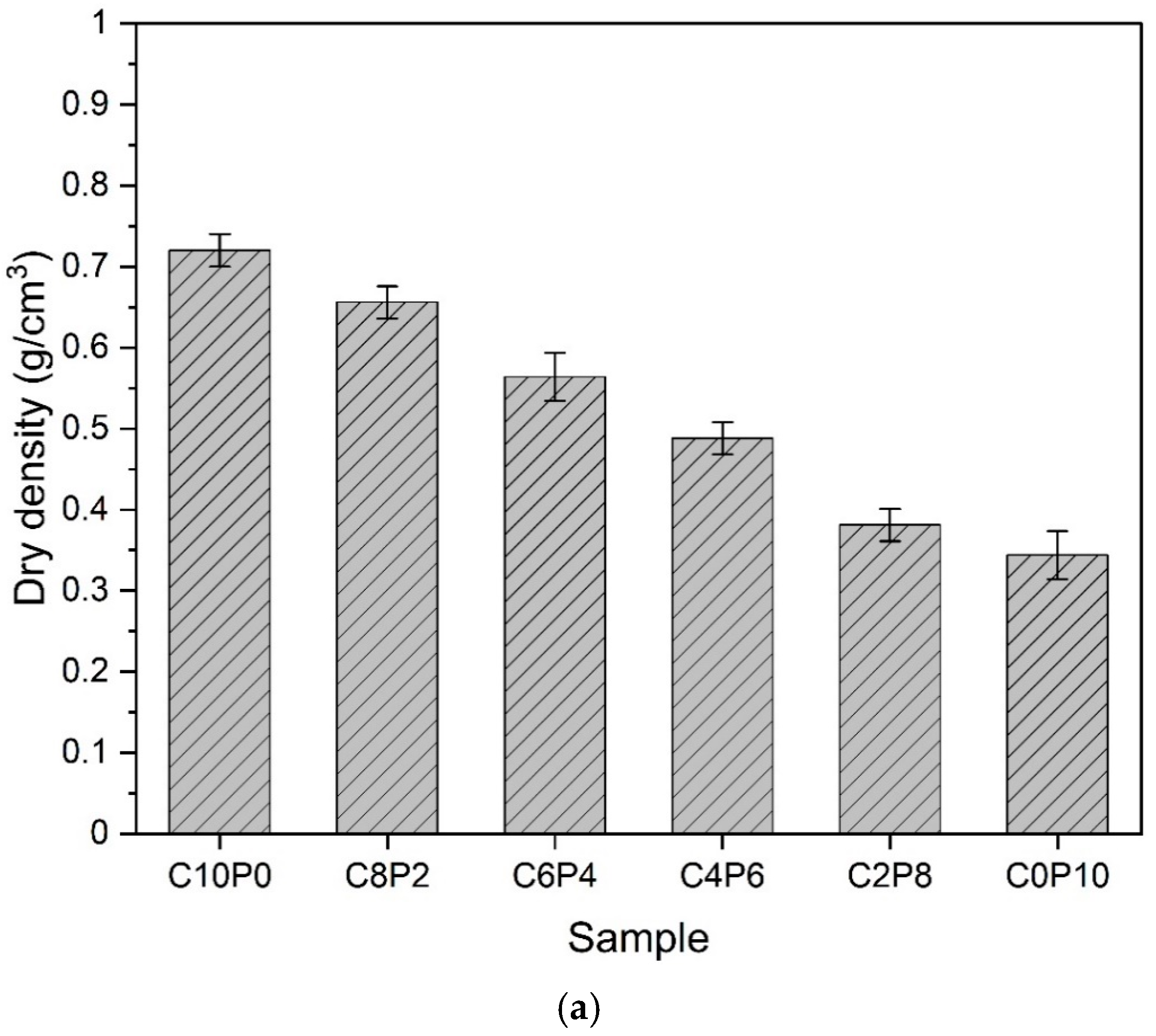
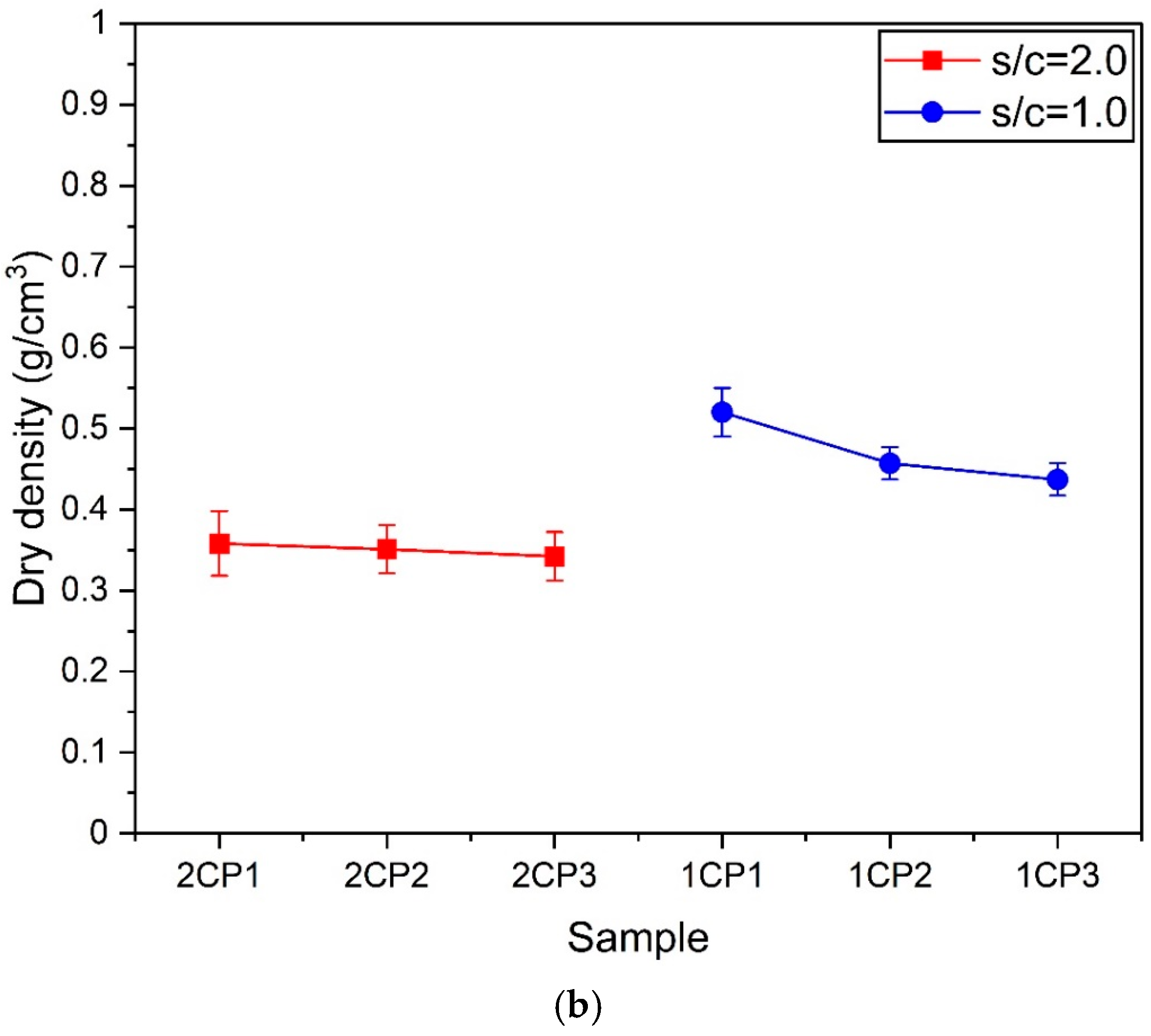
3.3. Dry Density
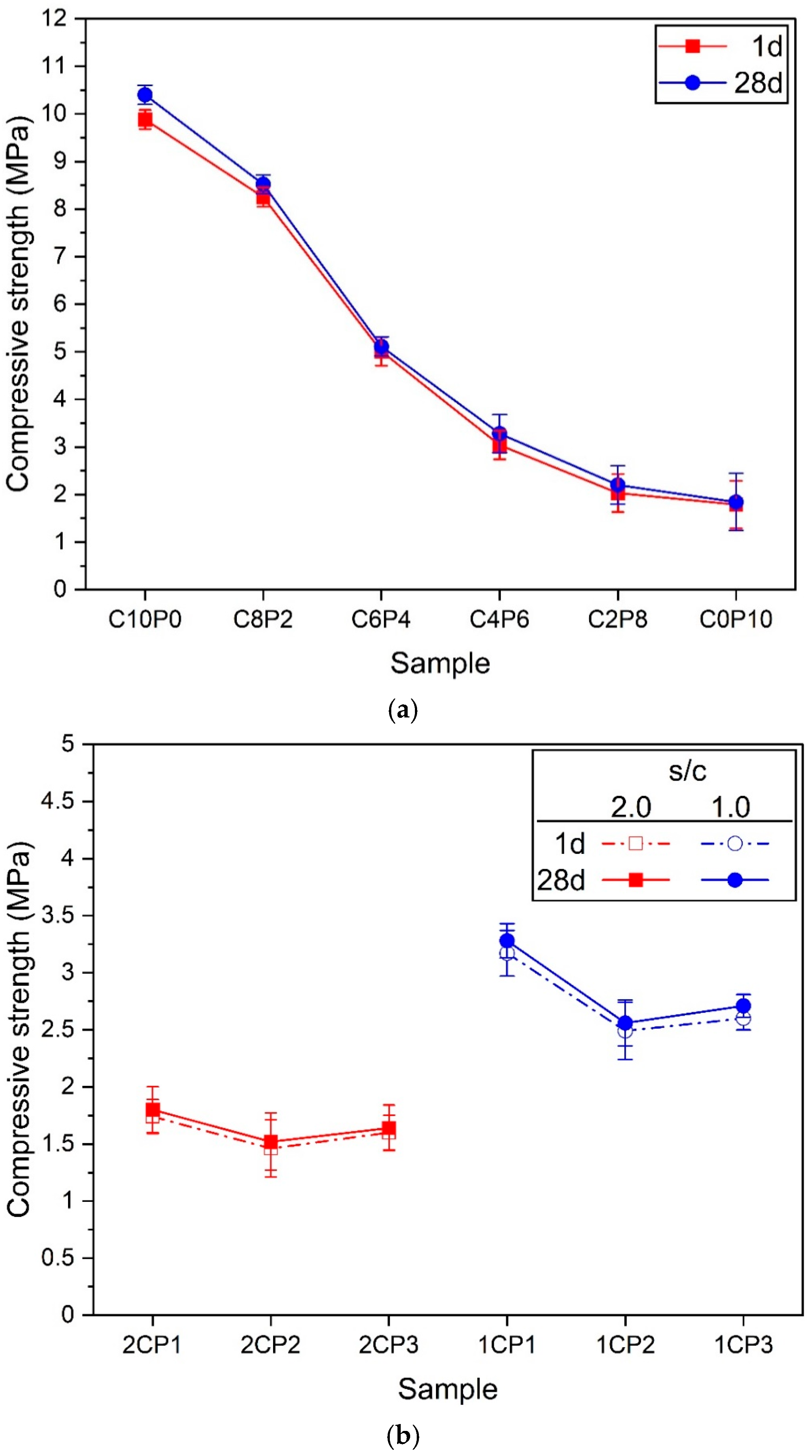
3.4. Compressive Strength
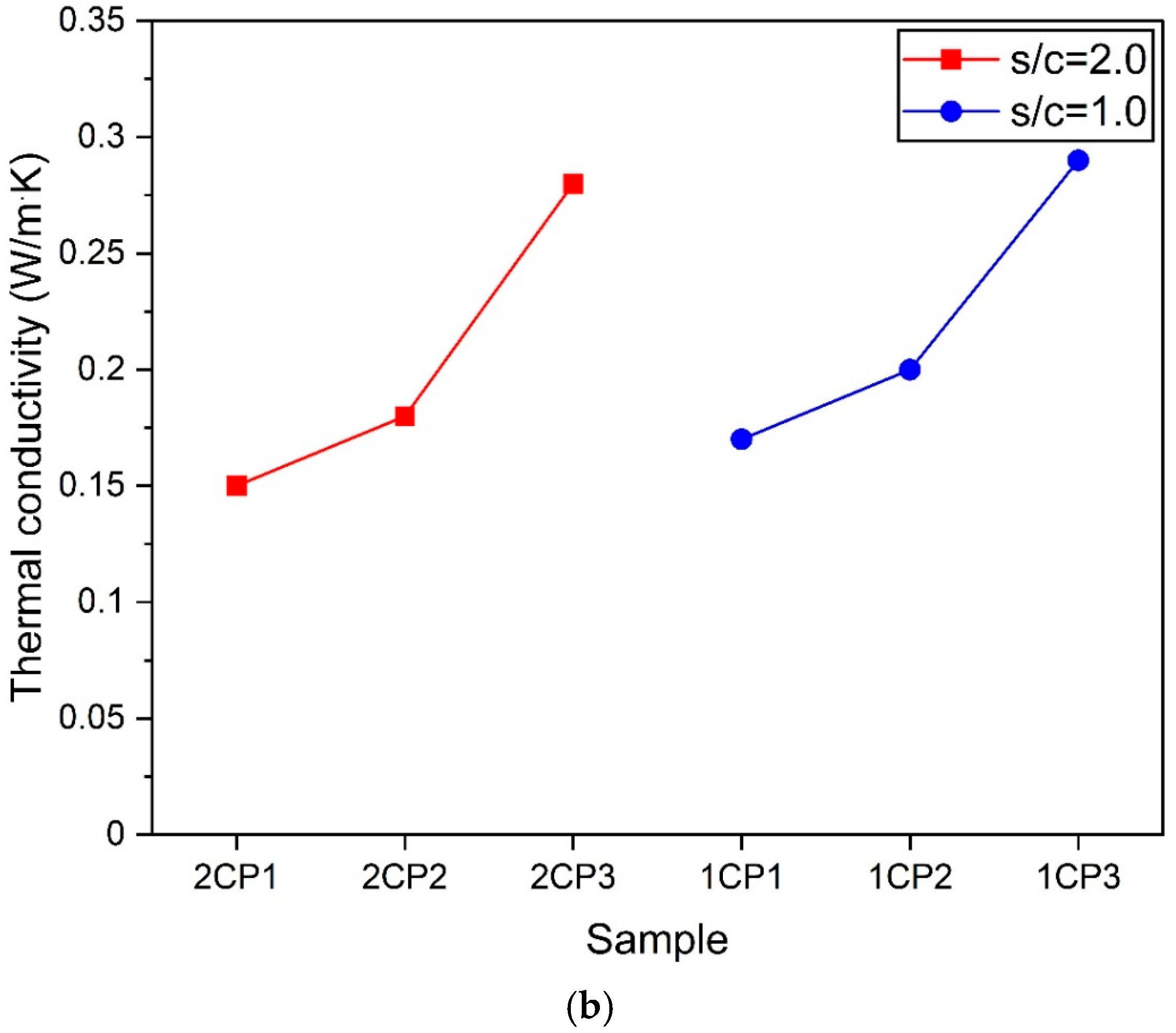
3.5. Thermal Conductivity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nigro, L.; Magni, S.; Ortenzi, M.A.; Gazzotti, S.; Torre, C.D.; Binelli, A. Are “liquid plastics” a new environmental threat? The case of polyvinyl alcohol. Aquat. Toxicol. 2022, 248, 106200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Hanif, A.; Lu, C.; Sun, G.; Cheng, Y.; Li, Z. Thermal, mechanical, and surface properties of poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) polymer modified cementitious composites for sustainable development. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Gu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Jin, W.; Lyu, K.; Guo, M. Effect of polyvinyl alcohol on the performance of carbon fixation foam concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 390, 131775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarnowiecka-Kuca, A.; Peeters, R.; Bamps, B.; Stobińska, M.; Kamola, P.; Wierzchowski, A.; Bartkowiak, A.; Mizielińska, M. Paper Coatings Based on Polyvinyl Alcohol and Cellulose Nanocrystals Using Various Coating Techniques and Determination of Their Barrier Properties. Coatings 2023, 13, 1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Ge, Y.; Ruan, W.; Meng, J. Effects of PVA fiber on shrinkage deformation and mechanical properties of ultra-high performance concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 417, 135399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.P.; Gunasekara, C.; Law, D.W.; Houshyar, S.; Setunge, S. Microstructural characterisation of cementitious composite incorporating polymeric fiber: A comprehensive review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 335, 127497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Guo, Q.; Wu, X.; Zhao, R. Research on different types of fiber reinforced concrete in recent years: An overview. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 365, 130075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moukwa, M.; Youn, D.; Hassanali, M. Effects of degree of polymerization of water soluble polymers on concrete properties. Cem. Concr. Res. 1993, 23, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.B.; Rai, S. Effect of polyvinyl alcohol on the hydration of cement with rice husk ash. Cem. Concr. Res. 2001, 31, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.S.; Rodrigues, F.A.; Segre, N.; Joekes, I. Macro-defect free cements influence of poly(vinyl alcohol), cement type, and silica fume. Cem. Concr. Res. 1999, 29, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.D.; Devlin, L.P.; Koshy, P.; Sorrell, C.C. Effects of chemical nature of polyvinyl alcohol on early hydration of Portland cement. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 123, 1439–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Wang, B. Effect of the Chemical Nature of Polyvinyl Alcohol on the Microstructure of Cement Hydration Products. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2023, 35, 04023201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, S.C.; Poon, C.S. Properties of concrete prepared with PVA-impregnated recycled concrete aggregates. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2010, 32, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huiwen, W.; Liyuan, Y.; Zhonghe, S. Modificatin of ITZ structure and properties of regenerated concrete. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Ed. 2006, 21, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannan, M.A.; Alexander, J.; Ganapathy, C.; Teo, D.C.L. Quality improvement of oil palm shell (OPS) as coarse aggregate in lightweight concrete. Build. Environ. 2006, 41, 1239–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thong, C.C.; Teo, D.C.L.; Ng, C.K. Application of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) in cement-based composite materials: A review of its engineering properties and microstructure behavior. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 107, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahverdi, A.; Kianpur, K.; Moghbeli, M.R. Effect of polyvinyl alcohol on flexural strength and some important physical properties of Portland cement paste. Iran. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2010, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ohama, Y. Polymer-based admixtures. Cem. Concr. Compos. 1998, 20, 189–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Robertson, R.E.; Naaman, A.E. Structure and properties of poly(vinyl alcohol)—Modified mortar and concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 1999, 29, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Robertson, R.E. Effects of polyvinyl alcohol on aggregate-paste bond strength and the interfacial transition zone. Adv. Cem. Based Mater. 1998, 8, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Han, H.; Xu, L.; Gao, Y.; Yang, Z.; Jiang, Z.; De Schutter, G. The improvement of freezing–thawing resistance of concrete by cellulose/polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 291, 123274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morlat, R.; Orange, G.; Bomal, Y.; Godard, P. Reinforcement of hydrated portland cement with high molecular mass water-soluble polymers. J. Mater. Sci. 2007, 42, 4858–4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pique, T.M.; Vazquez, A. Control of hydration rate of polymer modified cements by the addition of organically modified montmorillonites. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2013, 37, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, B.; Xing, Y.; Zhang, K.; Jiang, W. Effect of Polyvinyl Alcohol on the Rheological Properties of Cement Mortar. Molecules 2020, 25, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Robertson, R.E. Prevention of air void formation in polymer-modified cement mortar by pre-wetting. Cem. Concr. Res. 1997, 27, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, S.; Family, R.; Menguc, M.P. Analysis of perlite and pumice based building insulation materials. J. Build. Eng. 2016, 6, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davraz, M.; Koru, M.; Akdağ Kılınçarslan, A.E.; Delikanlı, Y.E.; Çabuk, M. Investigating the use of raw perlite to produce monolithic thermal insulation material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 263, 120674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshi, M.; Dalalbashi, A.; Soheili, H. Energy dissipation capacity of an optimized structural lightweight perlite concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 389, 131765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengul, O.; Azizi, S.; Karaosmanoglu, F.; Tasdemir, M.A. Effect of expanded perlite on the mechanical properties and thermal conductivity of lightweight concrete. Energy Build. 2011, 43, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirboga, R.; Gül, R. The effects of expanded perlite aggregate, silica fume and fly ash on the thermal conductivity of lightweight concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2003, 33, 723–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.; Ahmad, A.; Barry, M.S.; Alhems, L.M.; Mohamed Suhoothi, A.C. Durability of structural lightweight concrete containing expanded perlite aggregate. Int. J. Concr. Struct. Mater. 2020, 14, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexa-Stratulat, S.; Taranu, G.; Toma, A.; Olteanu, I.; Pastia, C.; Bunea, G.; Toma, I. Effect of expanded perlite aggregates and temperature on the strength and dynamic elastic properties of cement mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 438, 137229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, N.; Kuenzel, C. Cenospheres: A review. Fuel 2017, 207, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesina, A. Sustainable application of cenospheres in cementitious materials–Overview of performance. Dev. Built Environ. 2020, 4, 100029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Qi, Z.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Z. Effects of cenosphere on the mechanical properties of cement-based composites. Construct. Build. Mater. 2020, 261, 120527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, J.-Y.; Monteiro, P.J.M.; Zhang, M.-H. Development of ultra-lightweight cement composites with low thermal conductivity and high specific strength for energy efficient buildings. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 87, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, H.; Elchalakani, M.; Ayough, P.; Lyu, X.; Sadakkathulla, M.A.; Cai, J.; Xie, T. Enhanced thermal insulation and structural health monitoring with ultra-lightweight ECC incorporating air entrainment and cenospheres. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2024, 154, 105768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T. Characteristics of alkali-activated slag cement-based ultra-lightweight concrete with high-volume cenosphere. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 302, 124165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, H.; Elchalakani, M.; Liu, H.; Yehia, S.; Yang, B. Development and characteristics of multifunctional ultra-lightweight engineered cementitious composites incorporating cenospheres and PE fibre. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2023, 140, 105084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.W.; Xu, T.T.; Wu, M. Mechanical properties and durability of lightweight cenosphere cementitious composites under coupling effect of dry-wet cycles and salt erosion. Structures 2024, 69, 107436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish, A.; Mosaberpanah, M.A.; Tuladhar, R.; Salim, M.U.; Yaqub, M.A.; Ahmad, N. Effect of cenospheres on the engineering properties of lightweight cementitious composites: A comprehensive review. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 49, 104016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.D.; Devlin, L.P.; Koshy, P.; Sorrell, C.C. Effect of polyvinyl alcohol on rheology of portland cement pastes. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 51, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM C305; Standard Practice for Mechanical Mixing of Hydraulic Cement Pastes and Mortars of Plastic Consistency. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- ASTM C109; Standard Test Method for Compressive Strength of Hydraulic Cement Mortars (Using 2-in. or [50-mm] Cube Specimens). ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- ASTM D7984; Standard Test Method for Measurement of Thermal Effusivity of Fabrics Using a Modified Transient Plane Source (MTPS) Instrument. ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021.
- Topic, J.; Prošek, Z.; Indrová, K.; Plachý, T.; Nežerka, V.; Kopecký, L.; Tesárek, P. Effect of PVA modification on the properties of cement of composites. Acta Polytech. 2015, 55, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Chemical Composition (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | CaO | K2O | SO3 | Na2O | |
| OPC | 22.63 | 5.81 | 2.54 | 3.02 | 62.19 | 0.67 | 2.8 | 0.13 |
| CP | 61.07 | 29.46 | 3.17 | 1.24 | 2.06 | 1.59 | 1.01 | 0.17 |
| PL | 76.85 | 14.06 | 0.93 | 0.21 | 1.37 | 2.65 | - | 3.49 |
| Level | PVA Dosage (%) | PVA Sol. (g) | OPC (g) | CP (g) | PL (g) | s/c | s/ (c + CP + PL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C10P0 | 5 | 300 | 200 | 100 | 0 | 1.5 | 1.0 |
| C8P2 | 80 | 20 | |||||
| C6P4 | 60 | 40 | |||||
| C4P6 | 40 | 60 | |||||
| C2P8 | 20 | 80 | |||||
| C0P10 | 0 | 100 | |||||
| 2CP1 | 5 | 300 | 150 | 100 | 100 | 2.0 | 0.85 |
| 2CP2 | 200 | 100 | 0.67 | ||||
| 2CP3 | 300 | 100 | 0.54 | ||||
| 1CP1 | 300 | 100 | 100 | 1.0 | 0.60 | ||
| 1CP2 | 200 | 100 | 0.50 | ||||
| 1CP3 | 300 | 100 | 0.43 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, C.; Seo, K.-Y.; Park, Y.-M.; Kim, T. Characteristics of Lightweight Foam Concrete Manufactured Using Water-Soluble Polymers and Lightweight Aggregates. Materials 2025, 18, 1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081881
Kang C, Seo K-Y, Park Y-M, Kim T. Characteristics of Lightweight Foam Concrete Manufactured Using Water-Soluble Polymers and Lightweight Aggregates. Materials. 2025; 18(8):1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081881
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Choonghyun, Ki-Young Seo, Yong-Myung Park, and Taewan Kim. 2025. "Characteristics of Lightweight Foam Concrete Manufactured Using Water-Soluble Polymers and Lightweight Aggregates" Materials 18, no. 8: 1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081881
APA StyleKang, C., Seo, K.-Y., Park, Y.-M., & Kim, T. (2025). Characteristics of Lightweight Foam Concrete Manufactured Using Water-Soluble Polymers and Lightweight Aggregates. Materials, 18(8), 1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18081881






