Effect of Nb/C Ratio on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of B50A789G Precipitation Hardening Stainless Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Material
2.2. Mechanical Properties Testing
2.3. Microstructure Characterization
3. Results
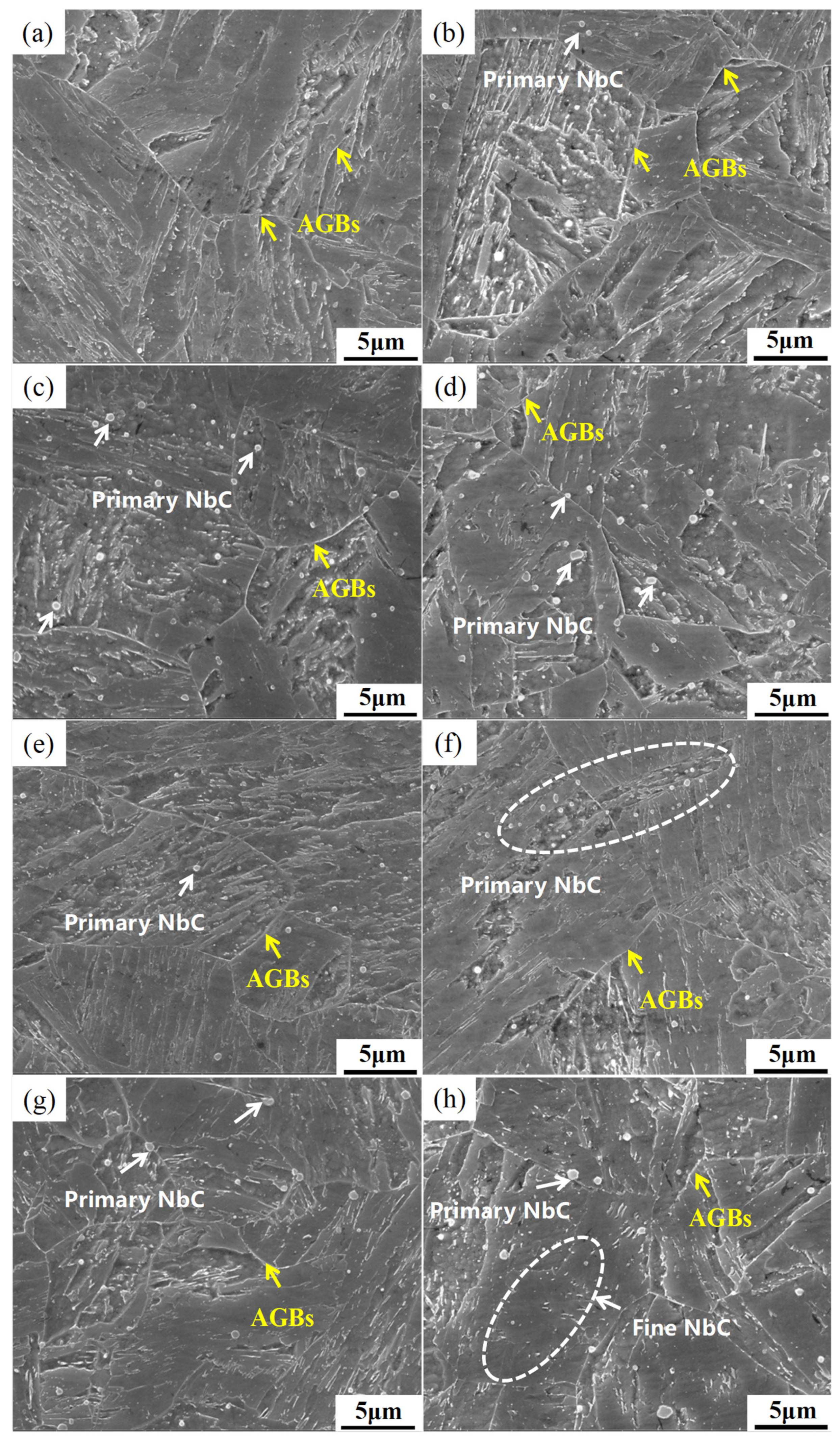
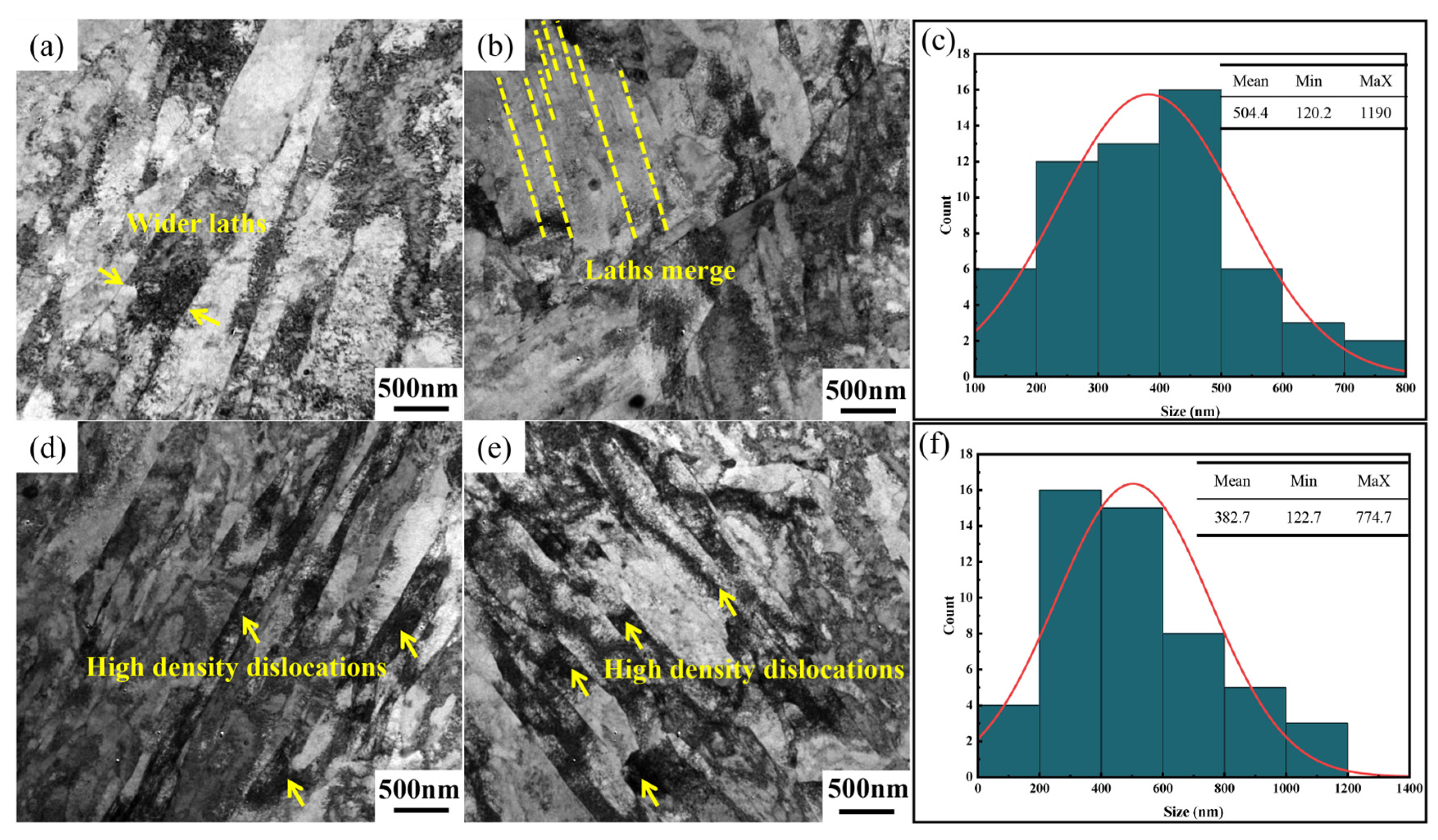
3.1. Effect of Nb/C Ratio on Microstructure
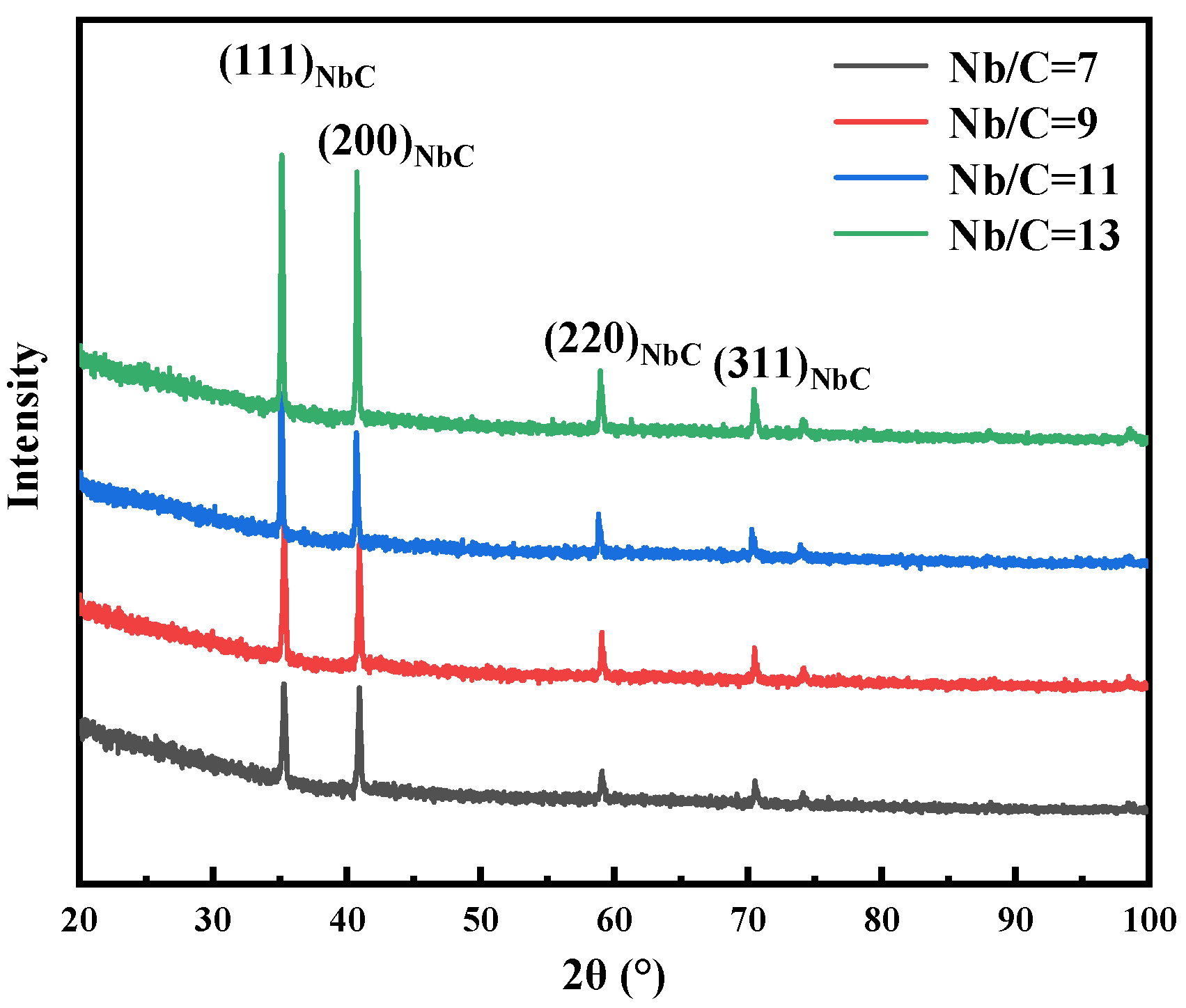
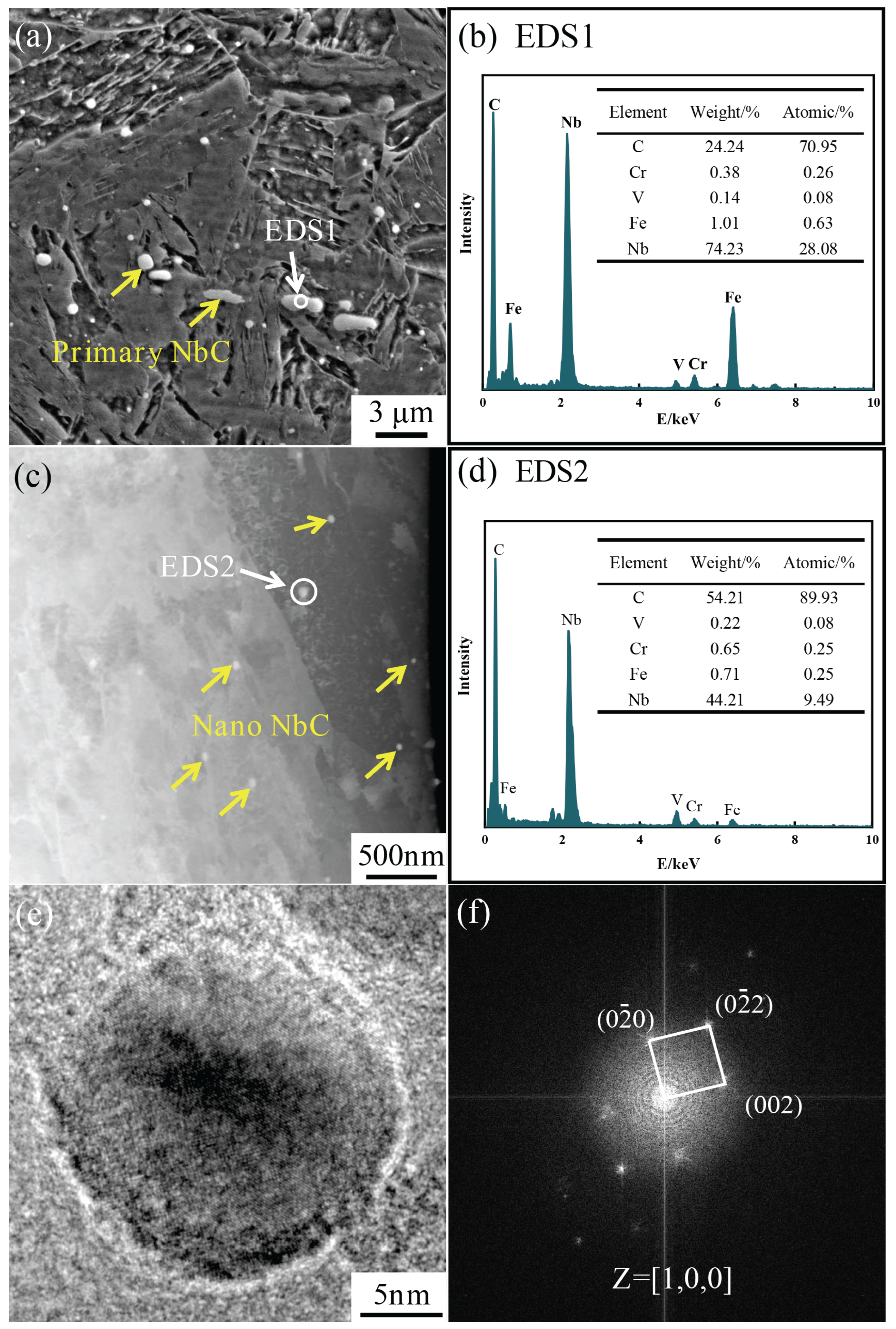
3.2. Effect of Nb/C Ratio on NbC
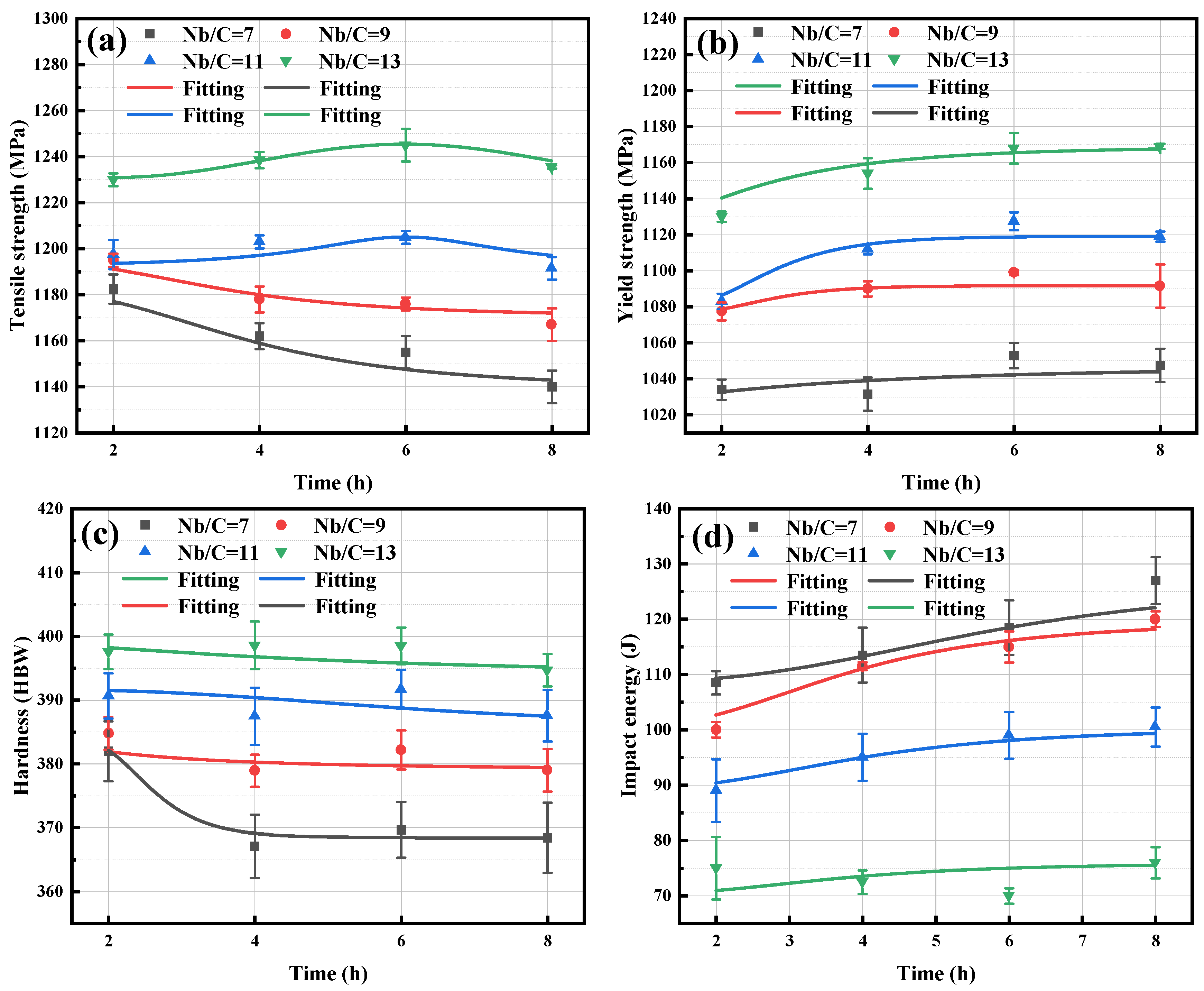
3.3. Effect of Nb/C Ratio on Mechanical Properties
4. Discussion
4.1. Grain Refinement Strengthening Effect of Nb
4.2. Precipitation Strengthening Effect of NbC Phase
5. Conclusions
- At the same tempering time, increasing the Nb/C ratio enhances the strength and hardness of B50A789G steel but reduces its toughness. Notably, the impact energy decreases significantly when the Nb/C ratio reaches 13. With prolonged tempering time, the tensile strength of B50A789G steel gradually decreases. For steels with Nb/C ratios of 7 and 9, the tensile strength exhibits a continuous decline. However, when the Nb/C ratio is increased to 11 and 13, the decline in tensile strength is delayed.
- Increasing the Nb/C ratio leads to a higher volume fraction of nanoscale NbC precipitates, which enhances their pinning effect on dislocations. This retards the widening of martensitic laths and delays the onset of lath decomposition. Simultaneously, the amount of coarse primary NbC precipitates in the steel also increases with the Nb/C ratio.
- For steels with Nb/C ≤ 11, the prior austenite grain size gradually refines as the Nb/C ratio increases. During this stage, the improvement in material strength is primarily attributed to the combined effects of grain refinement strengthening and precipitation strengthening provided by Nb. However, when the Nb/C ratio is further increased to 13, the grain refinement strengthening effect of Nb becomes less significant, and the increase in strength is mainly driven by the precipitation strengthening effect of a higher volume fraction of nanoscale NbC precipitates.
- The results show that increasing the Nb/C ratio in B50A789G steel can effectively improve the strength of the steel. However, a high Nb/C ratio will cause a large amount of precipitation of the primary NbC phase in the steel, resulting in a significant decrease in the impact energy. For practical applications, further refinement studies on Nb and C contents should be conducted according to specific requirements to determine the optimal Nb/C ratio.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, K.; Zhan, J.; Yang, T.; To, A.C.; Tan, S.; Tang, Q.; Cao, H.; Murr, L.E. Homogenization Timing Effect on Microstructure and Precipitation Strengthening of 17–4PH Stainless Steel Fabricated by Laser Powder Bed Fusion. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 52, 102672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, H.J.; Ryou, K.; Kang, T.H.; Jimbo, S.; Nambu, S.; Han, J.; Choi, P.-P. Thermally Driven Changes in the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Martensitic 15–5 Precipitation-Hardened Stainless Steel during Directed Energy Deposition. Addit. Manuf. 2023, 74, 103729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vite-Torres, M.; Moreno-Ríos, M.; Villanueva-Zavala, A.; Gallardo-Hernández, E.A.; Farfán-Cabrera, L.; Mesa-Grajales, D.H. Study of Cavitation Erosion Phenomenon at Stainless Steel AISI 304 Base and with SiC Coating. Appl. Eng. Lett. 2022, 7, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, R.A.; Ibrahim, M.E.; Gujba, A.K.; Pugh, M.D.; Medraj, M. On the Role of Strain Hardening and Mechanical Properties in Water Droplet Erosion of Metals. Tribol. Int. 2022, 173, 107649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Hu, R.; Zhang, C.; Xue, J.; Yang, W. Effect of Precipitates on Hardening of 17-4PH Martensitic Stainless Steel Serviced at 300 C in Nuclear Power Plant. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2021, 154, 108123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Li, D.; Diao, Y.; He, Y.; Yan, L.; Pang, X.; Gao, K. Nanoscale Cu Particle Evolution and Its Impact on the Mechanical Properties and Strengthening Mechanism in Precipitation-Hardening Stainless Steel. Mater. Charact. 2022, 188, 111885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Li, D.; Yan, L.; Pang, X.; Gao, K. Simultaneous Enhancement of Strength-Ductility via Multiple Precipitates and Austenite in a Novel Precipitation-Hardened Martensitic Stainless Steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 873, 145062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, P.; Xing, G.; Nong, Z.; Chen, L.; Lai, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, J. Recent Advances on Composition-Microstructure-Properties Relationships of Precipitation Hardening Stainless Steel. Materials 2022, 15, 8443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanuma, T. 14—Development of Last-Stage Long Blades for Steam Turbines. In Advances in Steam Turbines for Modern Power Plants, 2nd ed.; Tanuma, T., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Energy; Woodhead Publishing: London, UK, 2022; pp. 329–357. ISBN 978-0-12-824359-6. [Google Scholar]
- Adnyana, D.N. Corrosion Fatigue of a Low-Pressure Steam Turbine Blade. J. Fail. Anal. Preven. 2018, 18, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Fu, Q.; Akiyama, E.; Song, X.; Shen, S.; Li, Q. Hydrogen Embrittlement of High Strength Steam Turbine Last Stage Blade Steels: Comparison between PH17-4 Steel and PH13-8Mo Steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 742, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, E.; Matsuno, N.; Tanaka, K.; Nishimoto, S.; Yamamoto, R.; Imano, S. Latest Technologies and Future Prospects for a New Steam Turbine. Mitsubishi Heavy Ind. Tech. Rev. 2015, 52, 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Cao, L.; Song, L. Structure and Modal Analysis of the Last Stage Blade in Steam Turbine under Low Volume Flow Conditions. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 131, 105820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, L.; Jalalahmadi, B.; Ashtekar, A.; Jiang, Y. Cyclic Deformation and Fatigue Behavior of Additively Manufactured 17–4 PH Stainless Steel. Int. J. Fatigue 2019, 123, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabooni, S.; Chabok, A.; Feng, S.C.; Blaauw, H.; Pijper, T.C.; Yang, H.J.; Pei, Y.T. Laser Powder Bed Fusion of 17–4 PH Stainless Steel: A Comparative Study on the Effect of Heat Treatment on the Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 46, 102176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yubing, P.; Tianjian, W.; Zhenhuan, G.; Hua, F.; Gongxian, Y. Effects of Mo Content on Microstructure and Mechanical Property of PH13-8Mo Martensitic Precipitation-Hardened Stainless Steel. In Energy Materials 2014; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 321–326. ISBN 978-3-319-48598-0. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, C.; Liu, C. Effect of Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Selective Laser-Melted PH13-8Mo Stainless Steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2024, 31, 945–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Mi, P.; Hao, L.; Zhou, H.; Yan, W.; Zhao, K.; Xu, B.; Sun, M. Evolution of Toughening Mechanisms in PH13-8Mo Stainless Steel during Aging Treatment. Materials 2023, 16, 3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badaruddiny, M.; Diarko, P.; Asmi, D.; Wardono, H. Influence of Single- and Multi-Stage Austempering Treatments on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of AISI 4140 Steel. Tribol. Mater. 2024, 3, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Shen, Q.; Liu, W.; Wang, Z. Nano-Precipitates Evolution and Their Effects on Mechanical Properties of 17-4 Precipitation-Hardening Stainless Steel. Acta Mater. 2018, 156, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Huang, D.; Liu, W.; Li, F.; Lu, Q. Effect of Cu Content on the Precipitation Behavior of Cu-Rich and NiAl Phases in Steel. Mater. Charact. 2022, 187, 111849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Miyamoto, G.; Shinbo, K.; Furuhara, T. Comparative Study of VC, NbC, and TiC Interphase Precipitation in Microalloyed Low-Carbon Steels. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2020, 51, 6149–6158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Zhu, X.; Zheng, X.; Lan, P.; Li, J. Precipitation and Growth of Laves Phase and NbC during Aging and Its Effect on Tensile Properties of a Novel 15Cr–22Ni–1Nb Austenitic Heat-Resistant Steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 854, 143822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, L. Formation Mechanism of NbC Precipitates in Micro-Alloyed Nb High-Strength Steel. Chin. J. Eng. 2023, 45, 1729–1739. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Qiao, Z.; Dong, J. Effect of Tempering Time on Carbide Evolution and Mechanical Properties of a Nb-V-Ti Micro-Alloyed Steel. Metals 2023, 13, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Sun, M.; Ren, Y.; Li, M.; Yang, H.; Wang, H. A Heat-Resistant Steel with Excellent High-Temperature Strength-Ductility Based on a Combination of Solid-Solution Strengthening and Precipitation Hardening. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2024, 915, 147218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinkenberg, C.; Hulka, K.; Bleck, W. Niobium Carbide Precipitation in Microalloyed Steel. Steel Res. Int. 2004, 75, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.-H.; Song, S.-Q.; Cromarty, R.; Chen, Y.-L.; Xue, Z.-L. The Precipitation of Niobium Carbide and Its Influence on the Structure of HT250 for Automobile Wheel Hubs. Materials 2021, 14, 6109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, B.; Qiao, G.; Yuan, N.; Xiao, F. Refinement Effect of NbC Particle Additions on the Microstructure of High-Speed Steel Rolls. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 1697–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varanasi, R.S.; Gault, B.; Ponge, D. Effect of Nb Micro-Alloying on Austenite Nucleation and Growth in a Medium Manganese Steel during Intercritical Annealing. Acta Mater. 2022, 229, 117786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.-F.; Wang, F.-M.; Sun, G.-L.; Yang, Z.-B.; Li, C.-R. DICTRA Simulation of Holding Time Dependence of NbC Size and Experimental Study of Effect of NbC on Austenite Grain Growth. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2015, 46, 3670–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 228.1; Metallic Materials—Tensile Testing—Part 1: Method of Test at Room Temperature. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2021.
- GB/T 229; Metallic Materials—Charpy Pendulum Impact Test Method. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Ji, F.; Xu, R.; Gao, Y.; Tian, Q.; Wang, L.; Xiao, Z.; Yin, F. Effect of Ti and Rare Earth on Microsegregation and Large-Sized Precipitates of H13 Steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2021, 28, 1591–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enloe, C.M.; Findley, K.O.; Speer, J.G. Austenite Grain Growth and Precipitate Evolution in a Carburizing Steel with Combined Niobium and Molybdenum Additions. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2015, 46, 5308–5328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Mao, W.M.; Chen, Y.J.; Jing, J.; Cheng, M. Influence of Nb Content on Grain Size and Mechanical Properties of 18 Wt% Cr Ferritic Stainless Steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 677, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisko, A.; Talonen, J.; Porter, D.A.; Karjalainen, L.P. Effect of Nb Microalloying on Reversion and Grain Growth in a High-Mn 204Cu Austenitic Stainless Steel. ISIJ Int. 2015, 55, 2217–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.C.; Wang, Z.X.; Cong, J.H.; Misra, R.D.K.; Wang, X.M.; Guo, A.M.; Zhang, Y.Q. The Significance of Nb Interface Segregation in Governing Pearlitic Refinement in High Carbon Steels. Mater. Lett. 2020, 279, 128520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, Z.; Ghaemifar, S.; Naghizadeh, M.; Mirzadeh, H. Thermal Mechanisms of Grain Refinement in Steels: A Review. Met. Mater. Int. 2021, 27, 2078–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Liu, X.; Xu, X.; Lei, S.; Li, H.; Zhai, Q. Review on Niobium Application in Microalloyed Steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2022, 29, 1513–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashima, K.; Sakamoto, S.; Hara, T. Austenite Grain Growth Behavior after Recrystallization Considering Solute-Drag Effect and Pinning Effect. Int. J. Offshore Polar Eng. 2019, 29, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Zhang, Y.; Miyamoto, G.; Inomoto, M.; Chen, H.; Yang, Z.; Furuhara, T. Unraveling the Effects of Nb Interface Segregation on Ferrite Transformation Kinetics in Low Carbon Steels. Acta Mater. 2021, 215, 117081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Wei, R.; Jin, D.; Wang, H.; Wan, X.; Hu, C.; Wu, K. Influence of Solute Drag Effect and Interphase Precipitation of Nb on Ferrite Transformation. Materials 2024, 17, 2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, P.R. Niobium Solubility in Austenite in the Presence of Niobium Carbides, Nitrides and Carbonitrides. In Proceedings of the Defect and Diffusion Forum; Trans Tech Publications, Ltd.: Wollerau, Switzerland, 2025; Volume 439, pp. 35–52. [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair, C.W.; Hutchinson, C.R.; Bréchet, Y. The Effect of Nb on the Recrystallization and Grain Growth of Ultra-High-Purity α-Fe: A Combinatorial Approach. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2007, 38, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, L.; Gao, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, P.; Wei, X.; Ma, T. Effect of Nb Alloying and Solution Treatment on the Mechanical Properties of Cold-Rolled Fe-Mn-Al-C Low-Density Steel. Metals 2025, 15, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Wang, Q.; Dou, Y.; Wang, Q.; Xu, X.; Wang, Q. Comparison of Strengthening Mechanism of the Nb, V, and Nb-V Micro-Alloyed High-Strength Bolt Steels Investigated by Microstructural Evolution and Strength Modeling. Metals 2024, 14, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Wang, E.; Wu, H. Precipitation Behavior and Strengthening–Toughening Mechanism of Nb Micro-Alloyed Direct-Quenched and Tempered 1000 MPa Grade High-Strength Hydropower Steel. Metals 2024, 14, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Jin, R.; Han, L.; Xie, D.; Sun, T.; Wang, M.; Shi, J. Effect of Ti and TiNb Microalloying on Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of 2200 MPa Low-Alloy Ultra-High-Strength Steels. Metals 2025, 15, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladman, T. Precipitation Hardening in Metals. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1999, 15, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Gao, P.; Wang, S.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, Z. Strengthening Mechanisms of Nb and V Microalloying High Strength Hot-Stamped Steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 797, 140115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Nb/C | C | Mn | Si | Cr | Ni | Mo | Cu | Nb | V | N | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.03–0.05 | 0.3–0.8 | 0.2–0.5 | 14.0–16.0 | 6.2–6.8 | 0.6–1.0 | 1.35–1.75 | 0.3–0.6 | ≤0.10 | ≤0.030 | Bal. | |
| 7 | 0.046 | 0.48 | 0.43 | 14.43 | 6.5 | 0.83 | 1.58 | 0.32 | 0.059 | 0.028 | Bal. |
| 9 | 0.044 | 0.48 | 0.43 | 14.43 | 6.5 | 0.84 | 1.6 | 0.39 | 0.062 | 0.028 | Bal. |
| 11 | 0.044 | 0.48 | 0.42 | 14.28 | 6.52 | 0.84 | 1.58 | 0.5 | 0.058 | 0.031 | Bal. |
| 13 | 0.045 | 0.47 | 0.43 | 14.51 | 6.48 | 0.83 | 1.56 | 0.58 | 0.058 | 0.031 | Bal. |
| Nb/C | 7 | 9 | 11 | 13 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content of Nb in steel (wt%) | 0.32 | 0.39 | 0.5 | 0.58 |
| Solid solution of Nb in steel (wt%) | 0.09 | 0.14 | 0.29 | 0.28 |
| Nb/C | 7 | 9 | 11 | 13 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial full austenite temperature (°C) | 1327 | 1317 | 1316 | 1295 |
| Primary NbC precipitation amount (wt%) | 0 | 0.05 | 0.15 | 0.23 |
| Nb/C | Mass Fractions of NbC (wt%) | Yield Strength Increments (MPa) |
|---|---|---|
| 9 | 0.306 | 136.9 |
| 13 | 0.404 | 207.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Zhao, J.; Xin, R.; He, Y.; Yang, G.; Yang, B. Effect of Nb/C Ratio on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of B50A789G Precipitation Hardening Stainless Steel. Materials 2025, 18, 1917. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18091917
Liu S, Zhao J, Xin R, He Y, Yang G, Yang B. Effect of Nb/C Ratio on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of B50A789G Precipitation Hardening Stainless Steel. Materials. 2025; 18(9):1917. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18091917
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Shuai, Jiqing Zhao, Ruishan Xin, Yudong He, Gang Yang, and Bin Yang. 2025. "Effect of Nb/C Ratio on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of B50A789G Precipitation Hardening Stainless Steel" Materials 18, no. 9: 1917. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18091917
APA StyleLiu, S., Zhao, J., Xin, R., He, Y., Yang, G., & Yang, B. (2025). Effect of Nb/C Ratio on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of B50A789G Precipitation Hardening Stainless Steel. Materials, 18(9), 1917. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18091917






