Influence and Mechanism of Coal Gangue Sand on the Properties and Microstructure of Shotcrete Mortar
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Program
2.1. Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Test Method
2.3.1. Setting Time
2.3.2. Compressive Strength Test
2.3.3. Water Absorption Test
2.3.4. Microscopic Characterization
3. Result and Discussion
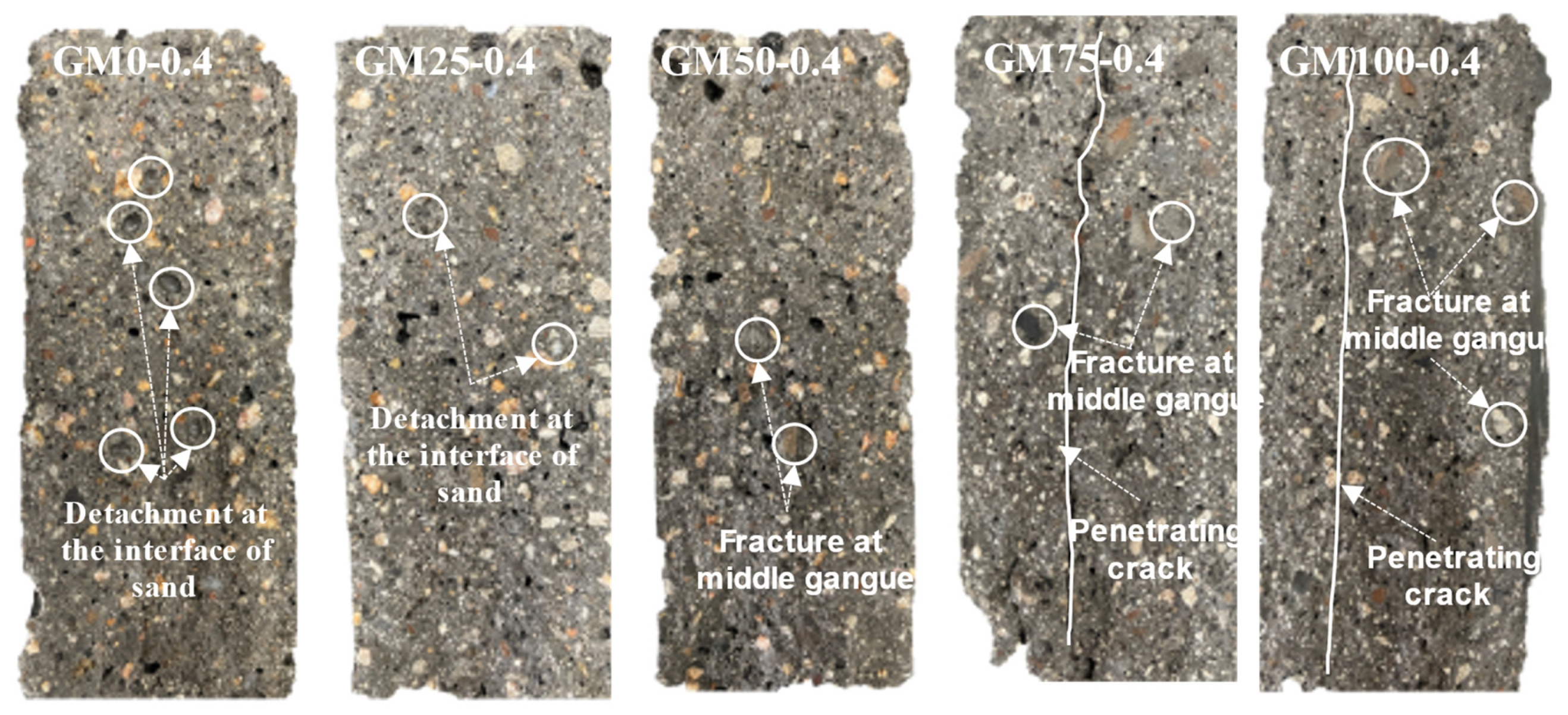
3.1. Surface Condition
3.2. Setting Time
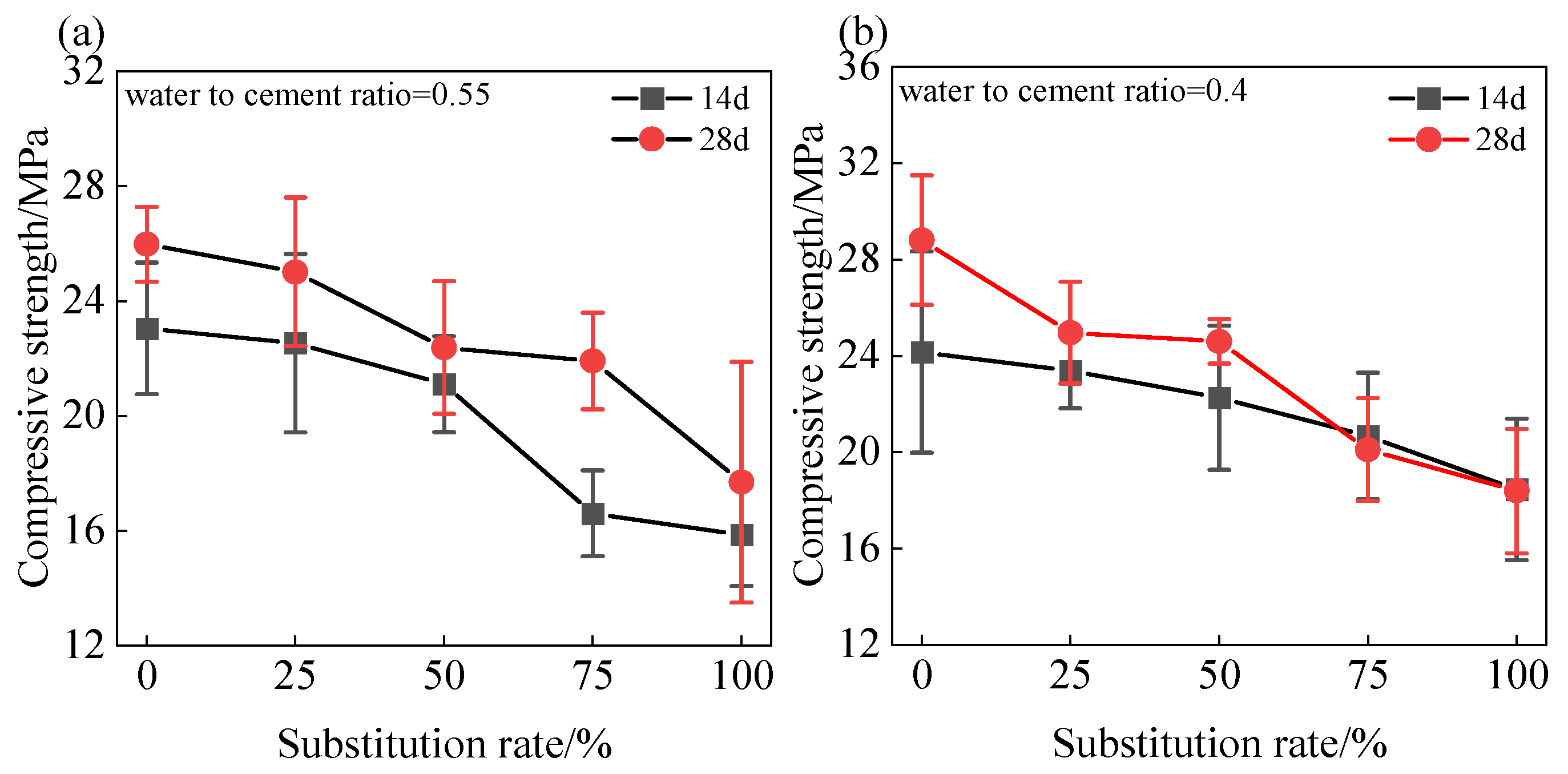
3.3. Compressive Strength
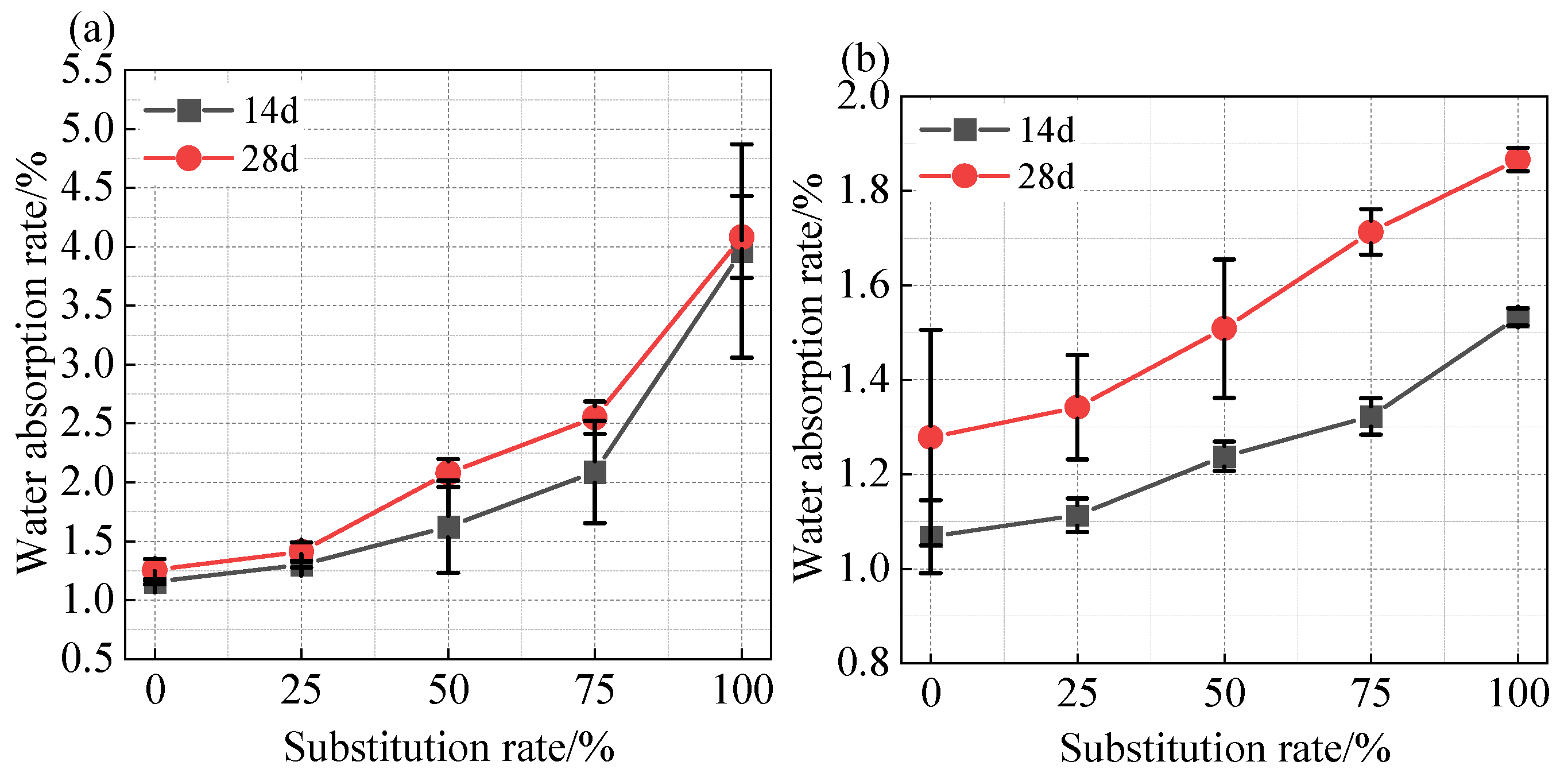
3.4. Water Absorption Rate
3.5. Microscopic Characterization
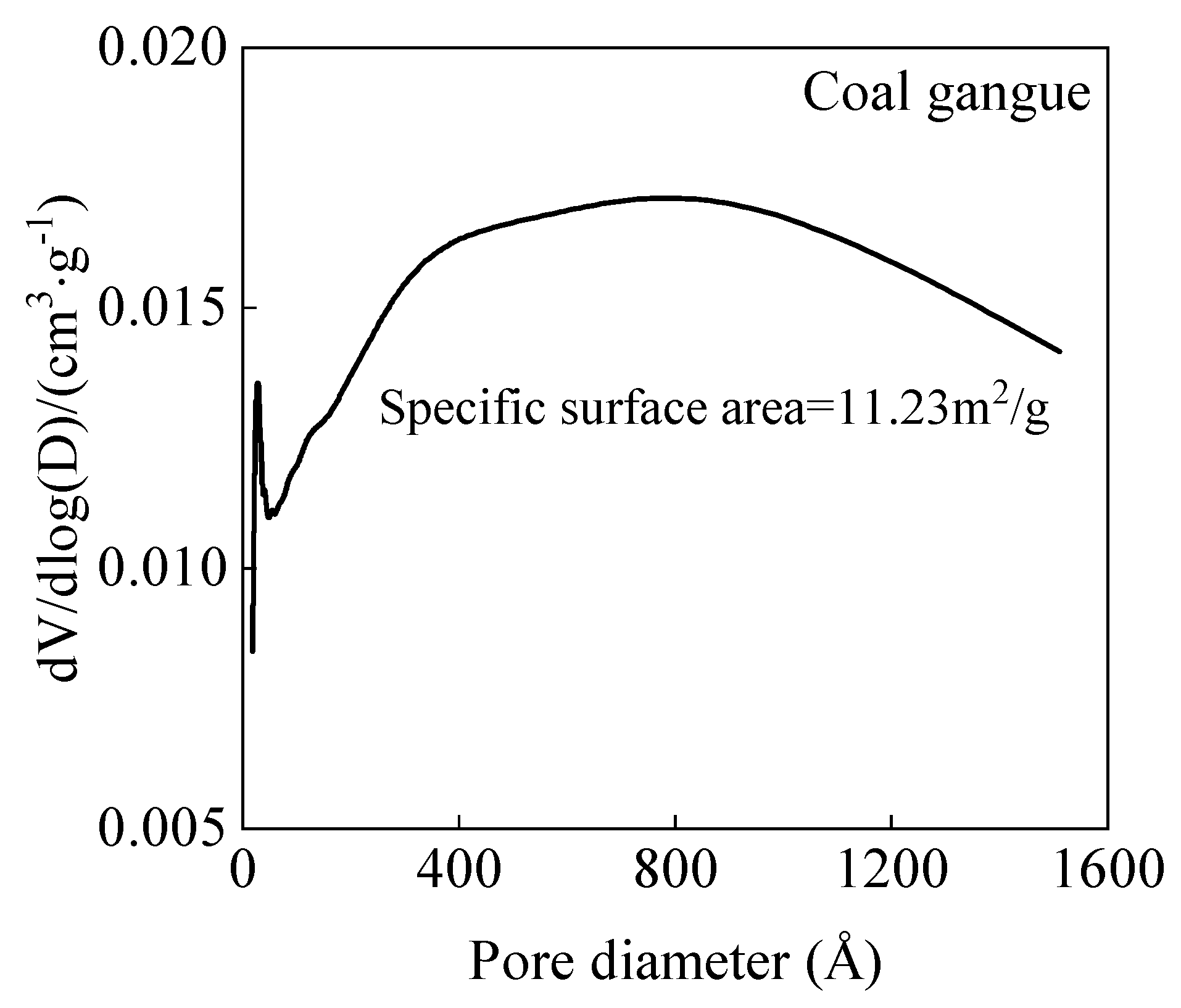
3.5.1. BET
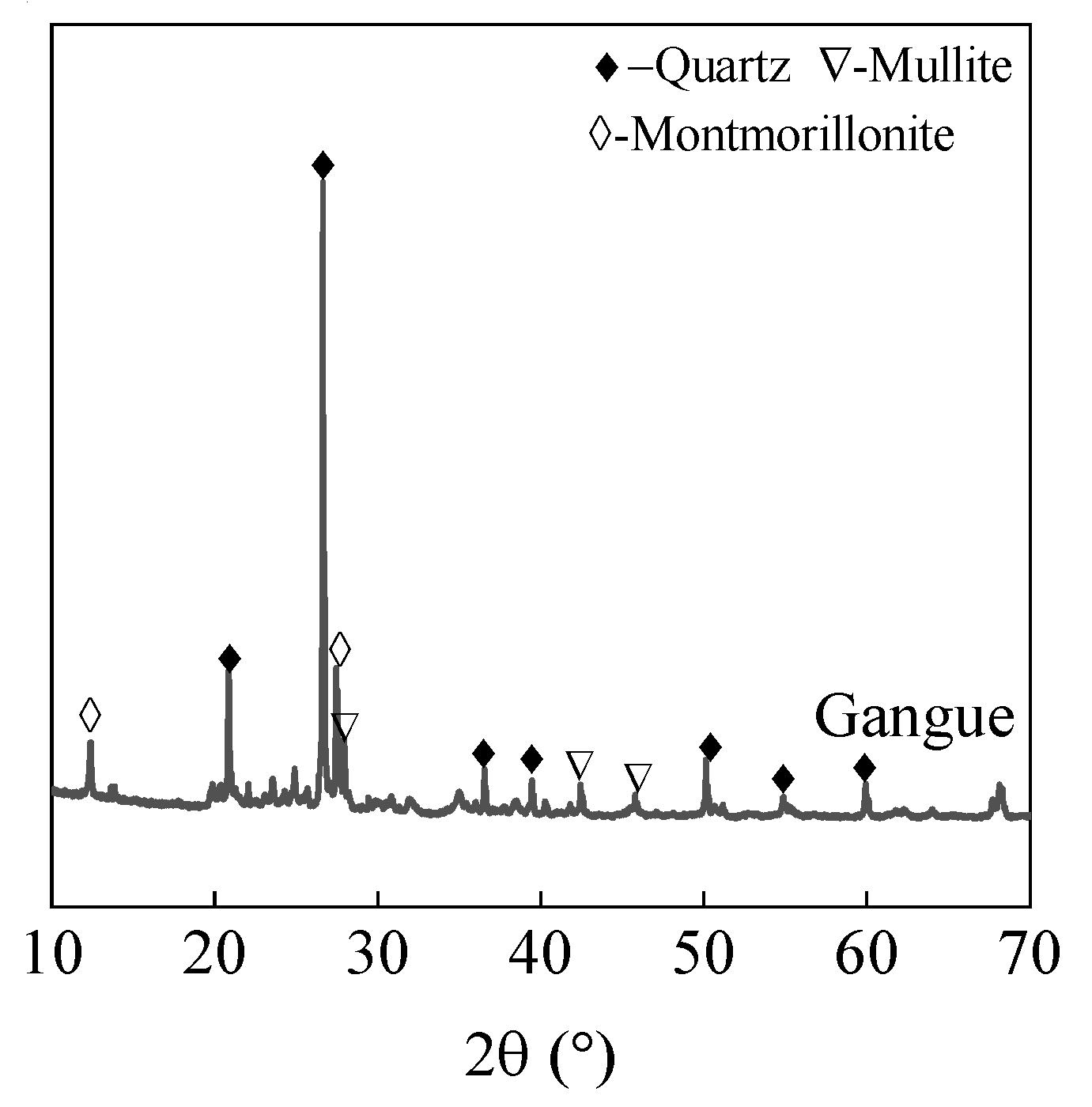
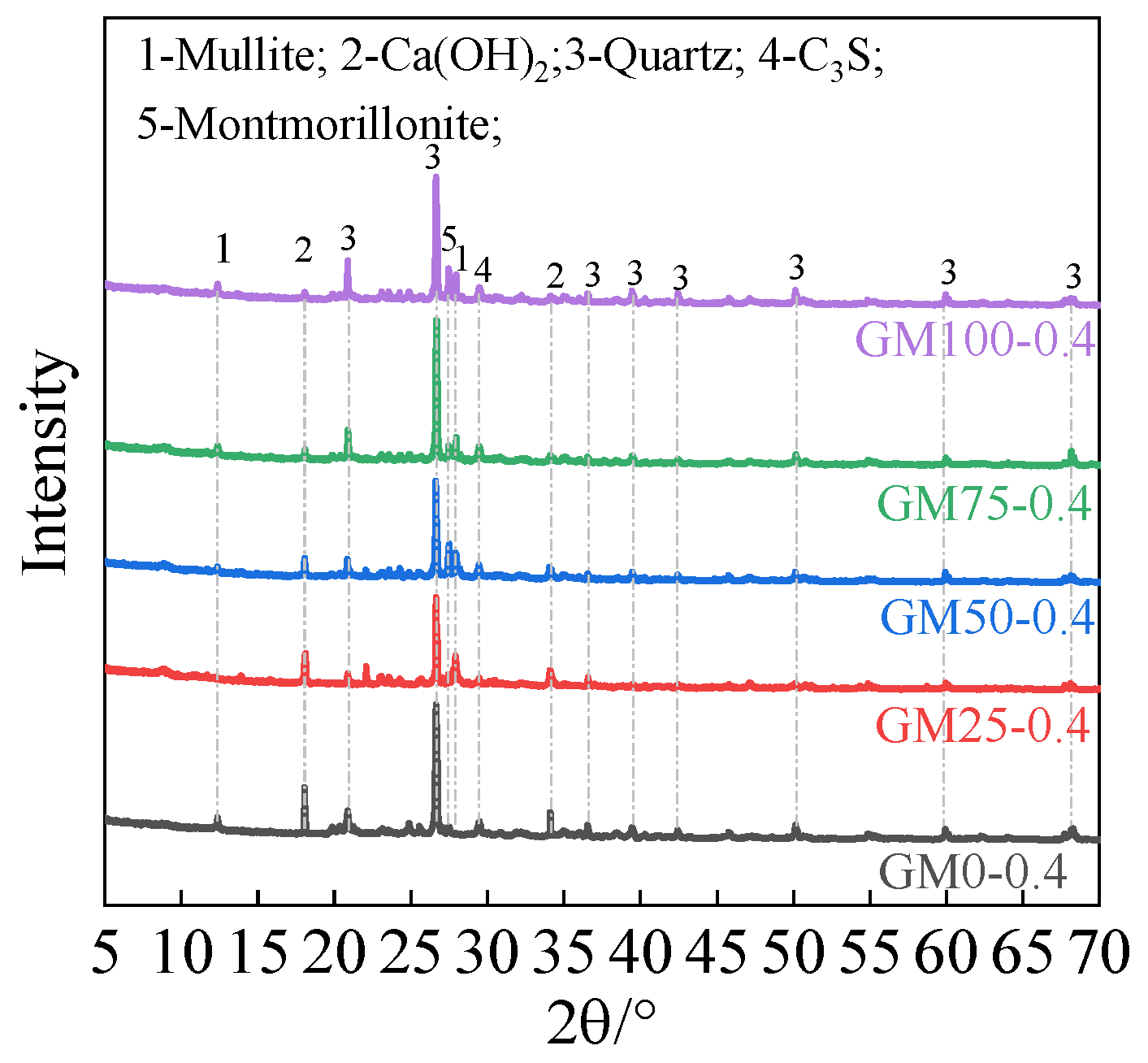
3.5.2. XRD
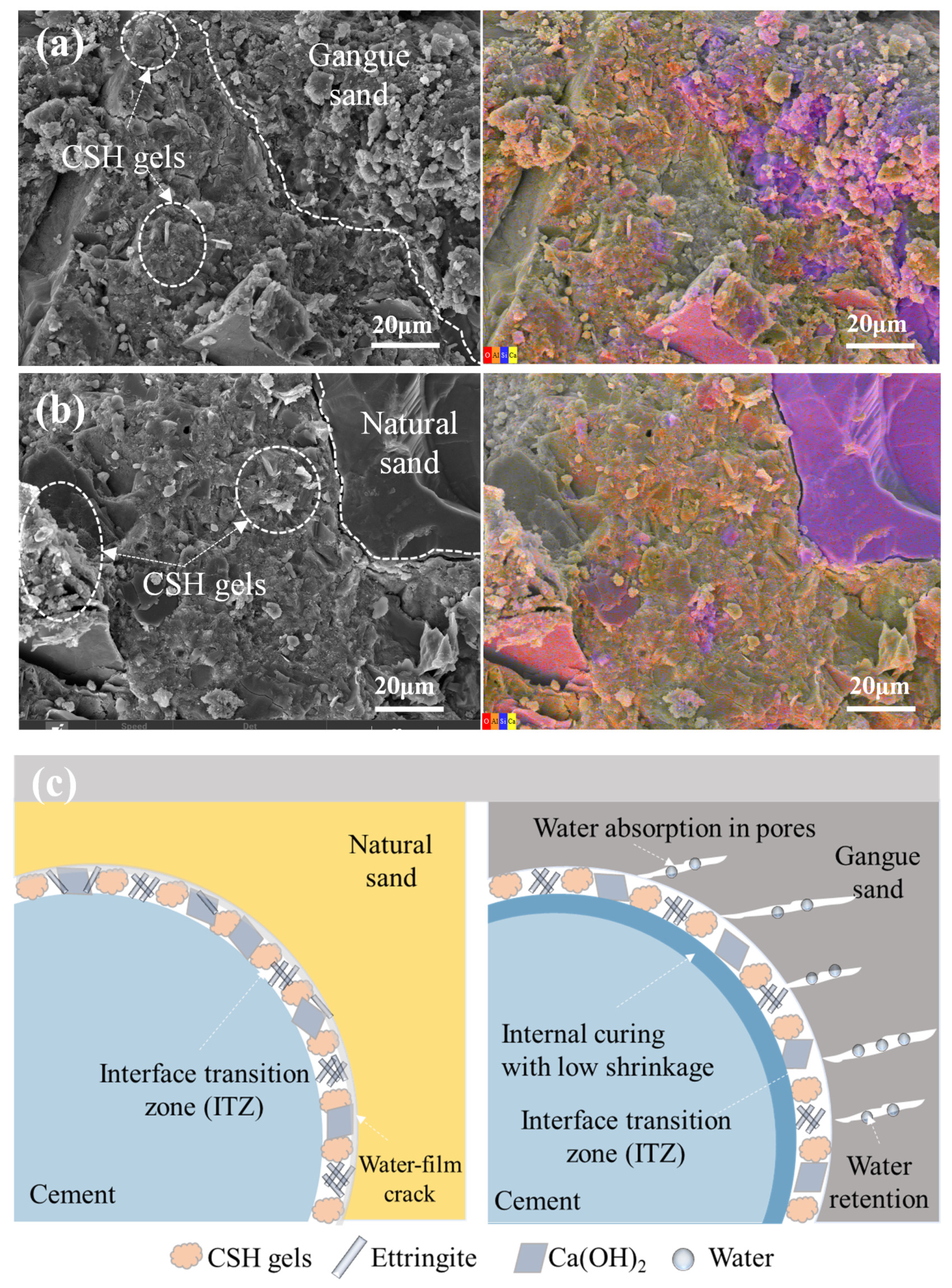
3.5.3. Macro-Micro Interface Analysis
3.6. Environment Assessment
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Coal gangue sand, characterized by a porous structure, demonstrated significant effects on shotcrete mortar performance. At a 0.55 water–cement ratio with 100% replacement, the mortar exhibited 30% increased porosity, 40% decreased compressive strength, and 57% shortened setting time. Despite these changes, the mortar surface maintained integrity after 28-day water immersion, indicating basic durability.
- (2)
- Optimal performance was achieved at 0.4 water–cement ratio with 50% coal gangue sand replacement, meeting M20 grade requirements with a setting time under 12 min and 28-day compressive strength exceeding 23 MPa. Notably, this mix design reduced environmental impact by 70% compared to conventional natural sand mortar at equivalent strength levels.
- (3)
- Microstructural analysis revealed that coal gangue sand’s water absorption provided beneficial internal curing effects during cement hydration. Although pore size and volume increased by 20% and 30%, respectively, the improved interface transition zone and progressive cement hydration effectively compensated for the initial strength reduction, ensuring stable long-term performance.
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chuncai, Z.; Guijian, L.; Dun, W.; Ting, F.; Ruwei, W.; Xiang, F. Mobility Behavior and Environmental Implications of Trace Elements Associated with Coal Gangue: A Case Study at the Huainan Coalfield in China. Chemosphere 2014, 95, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabłońska, B.; Kityk, A.V.; Busch, M.; Huber, P. The Structural and Surface Properties of Natural and Modified Coal Gangue. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 190, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; Chu, Y.; Liu, K.; Sun, D. Research Progress of Resourceful and Efficient Utilization of Coal Gangue in the Field of Building Materials. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 99, 111526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Xia, J.; Xia, Z.; Chen, M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y. Study on the Mechanical Behavior and Micro-Mechanism of Concrete with Coal Gangue Fine and Coarse Aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 338, 127626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caneda-Martínez, L.; Sánchez, J.; Medina, C.; Isabel Sánchez de Rojas, M.; Torres, J.; Frías, M. Reuse of Coal Mining Waste to Lengthen the Service Life of Cementitious Matrices. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 99, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sun, W.; Yang, Z. Numerical Simulation of the Dynamic Change Law of Spontaneous Combustion of Coal Gangue Mountains. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 37201–37211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, H.; Gao, S. Utilization of Coal Gangue Sand in Structural Concrete as Fine Aggregate towards Sustainable Production. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 417, 135264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Jiu, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, S.; Chen, C.; Jia, R. Modification of Low-Quality Calcined Coal Gangue and Its Effect on Mechanical Properties and Microstructure. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 458, 139433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Zhu, H.; Wu, C.; Chen, H.; Sun, J.; Liu, J. Study on Compressive Strength and Durability of Alkali-Activated Coal Gangue-Slag Concrete and Its Mechanism. Powder Technol. 2020, 368, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Jiang, W.; Yang, S.; Wang, W. A Sustainable Low-Carbon Pervious Concrete Using Modified Coal Gangue Aggregates Based on ITZ Enhancement. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 377, 134310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Qiao, J.; Jia, R.; Wei, P.; Li, Y.; Ke, G. The Influence of Carbon Imperfections on the Physicochemical Characteristics of Coal Gangue Aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 409, 133965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wen, Q.; Gao, S.; Tang, J. Comparative Study on Mechanical and Environmental Properties of Coal Gangue Sand Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 400, 132646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, H.; Tang, J.; Gao, S. Mechanical and Environmental Performance of Structural Concrete with Coal Gangue Fine Aggregate. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 84, 108488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ould Ouali, M.; Poorsolhjouy, P.; Placidi, L.; Misra, A. Evaluation of the Effects of Stress Concentrations on Plates Using Granular Micromechanics. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 290, 123227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Lei, T.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Bai, J. Study on Frost Resistance and Deterioration Law of Manufactured Sand Coal Gangue Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 470, 140544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Guo, X.; Yao, X.; Han, R.; Li, L.; Zhang, M. Using Chinese Coal Gangue as an Ecological Aggregate and Its Modification: A Review. Materials 2022, 15, 4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, R.P.; Cavalaro, S.H.P.; Segura, I.; Figueiredo, A.D.; Pérez, J. Early Age Hydration of Cement Pastes with Alkaline and Alkali-Free Accelerators for Sprayed Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 111, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Zhao, J.; Huang, G.; Liu, W.V. Influence of Water-to-Binder Ratios on the Performance of Limestone Calcined Clay Cement-Based Paste for Mining Applications. Green Smart Min. Eng. 2024, 1, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Xu, Y. Environmentally Friendly Utilization of Coal Gangue as Aggregates for Shotcrete Used in the Construction of Coal Mine Tunnel. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2021, 15, e00751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Guo, B.; Zheng, T.; Li, J.; Su, L.; Li, Z. Mechanical Properties and Microscopic Characteristics of Nano-SiO2 Modified Coal Gangue Shotcrete. Ceram. Int. 2025, 51, 7427–7436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, J.J.; Megat Johari, M.A.; Mazloom, M. Effect of Admixtures on the Setting Times of High-Strength Concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2000, 22, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Ji, Y.; Li, J.; Hou, Z.; Dong, Z. Improving Strength of Calcinated Coal Gangue Geopolymer Mortars via Increasing Calcium Content. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 166, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Chen, C.; Song, W.; Hou, W. High-Capacity Utilization of Coal Gangue as Supplementary Cementitious Material, Geopolymer, and Aggregate: A Review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 435, 136857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa, M.E.; Villagrán Zaccardi, Y.A.; Zega, C.J. A Critical Review of the Resulting Effective Water-to-Cement Ratio of Fine Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 313, 125536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skalny, J.; Phillips, J.C.; Cahn, D.S. Low Water to Cement Ratio Concretes. Cem. Concr. Res. 1973, 3, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, F.; Mörtel, H.; Rudert, V. Dense Packing of Cement Pastes and Resulting Consequences on Mortar Properties. Cem. Concr. Res. 1997, 27, 1481–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, M.; Liao, L.; Lv, G. Environmental Hazards and Comprehensive Utilization of Solid Waste Coal Gangue. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2024, 34, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyl, D.; Ghasemzadeh, F.; Pour-Ghaz, M. Modeling Water Absorption in Concrete and Mortar with Distributed Damage. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 125, 438–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Wang, Q.; Qu, L.; Li, X.; Xu, S. Study of Water Absorption and Corrosion Resistance of the Mortar with Waste Marble Powder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 345, 128235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Tu, A.; Chen, C.; Lehman, D.E. Mechanical Properties, Durability, and Life-Cycle Assessment of Concrete Building Blocks Incorporating Recycled Concrete Aggregates. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 199, 136–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dacić, A.; Mester-Szabó, E.; Fenyvesi, O.; Szalay, Z. Life Cycle Assessment of Concrete Incorporating All Concrete Recycling Products. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 21, e03910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, F.; Devlin, G.; McDonnell, K. Miscanthus Production and Processing in Ireland: An Analysis of Energy Requirements and Environmental Impacts. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 23, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Chemical Composition | Na2O | MgO | Al2O3 | SiO2 | P2O5 | SO3 | K2O | CaO | TiO2 | Fe2O3 | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Natural sand | 0.2 | 0.6 | 7.5 | 86.7 | - | 0.3 | 1.7 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 1.8 | 0.5 |
| Coal gangue sand | 1.3 | 0.8 | 24.3 | 63.0 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 3.8 | 1.2 | 0.9 | 4.1 | 0.2 |
| J85-type accelerator | 10.7 | 1.3 | 36.9 | 34.4 | 0.2 | 1.3 | 1.9 | 6.4 | 1.1 | 4.8 | 1.0 |
| NO. | Cement (g) | Water (g) | Natural Sand (g) | Coal Gangue Sand (g) | Accelerating Agent (g) | Water Reducer (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GM0-0.55 | 900 | 495 | 2700 | 0 | 47.7 | 6 |
| GM25-0.55 | 900 | 495 | 2025 | 675 | 47.7 | 8 |
| GM50-0.55 | 900 | 495 | 1350 | 1350 | 47.7 | 10 |
| GM75-0.55 | 900 | 495 | 675 | 2025 | 47.7 | 12 |
| GM100-0.55 | 900 | 495 | 0 | 2700 | 47.7 | 15 |
| GM0-0.4 | 900 | 360 | 2700 | 0 | 47.7 | 30 |
| GM25-0.4 | 900 | 360 | 2025 | 675 | 47.7 | 32 |
| GM50-0.4 | 900 | 360 | 1350 | 1350 | 47.7 | 35 |
| GM75-0.4 | 900 | 360 | 675 | 2025 | 47.7 | 45 |
| GM100-0.4 | 900 | 360 | 0 | 2700 | 47.7 | 60 |
| Classification | Materials | Cement (kg/kg) | Natural Sand (kg/kg) | Coal Gangue Sand (kg/kg) | GWP/AP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Greenhouse gases | CO2 | 8.85 × 10−1 | 2.34 × 10−3 | 1.31 × 10−2 | 1 |
| CH4 | 5.80 × 10−4 | 3.70 × 10−6 | 2.34 × 10−5 | 27 | |
| N2O | 2.22 × 10−5 | 3.81 × 10−8 | 5.06 × 10−5 | 298 | |
| Acidified gas | SO2 | 1.05 × 10−3 | 9.49 × 10−6 | 6.55 × 10−5 | 1 |
| NOx | 1.79 × 10−3 | 1.52 × 10−6 | 5.06 × 10−5 | 0.7 | |
| NH3 | 1.02 × 10−8 | 7.24 × 10−9 | 5.37 × 10−7 | 1.88 |
| Classification | Cement (kg/kg) | Natural Sand (kg/kg) | Coal Gangue Sand (kg/kg) | Weight Coefficient (RMB/kg-CO2eq) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GWP | 9.07 × 10−1 | 2.45 × 10−3 | 2.88 × 10−2 | 5.53 × 10−2 |
| AP | 2.30 × 10−3 | 1.06 × 10−5 | 1.02 × 10−4 | 6.57 × 10−1 |
| NO. | ||
|---|---|---|
| GM0-0.4 | 1.30 × 10−2 | 4.52 × 10−4 |
| GM25-0.4 | 1.33 × 10−2 | 5.33 × 10−4 |
| GM50-0.4 | 1.36 × 10−2 | 5.53 × 10−4 |
| GM75-0.4 | 1.39 × 10−2 | 6.91 × 10−4 |
| GM100-0.4 | 1.42 × 10−2 | 7.70 × 10−4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, Y. Influence and Mechanism of Coal Gangue Sand on the Properties and Microstructure of Shotcrete Mortar. Materials 2025, 18, 1940. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18091940
Cui Y. Influence and Mechanism of Coal Gangue Sand on the Properties and Microstructure of Shotcrete Mortar. Materials. 2025; 18(9):1940. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18091940
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Yong. 2025. "Influence and Mechanism of Coal Gangue Sand on the Properties and Microstructure of Shotcrete Mortar" Materials 18, no. 9: 1940. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18091940
APA StyleCui, Y. (2025). Influence and Mechanism of Coal Gangue Sand on the Properties and Microstructure of Shotcrete Mortar. Materials, 18(9), 1940. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18091940





