Invasion of Emerald Ash Borer Agrilus planipennis and Ash Dieback Pathogen Hymenoscyphus fraxineus in Ukraine—A Concerted Action
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
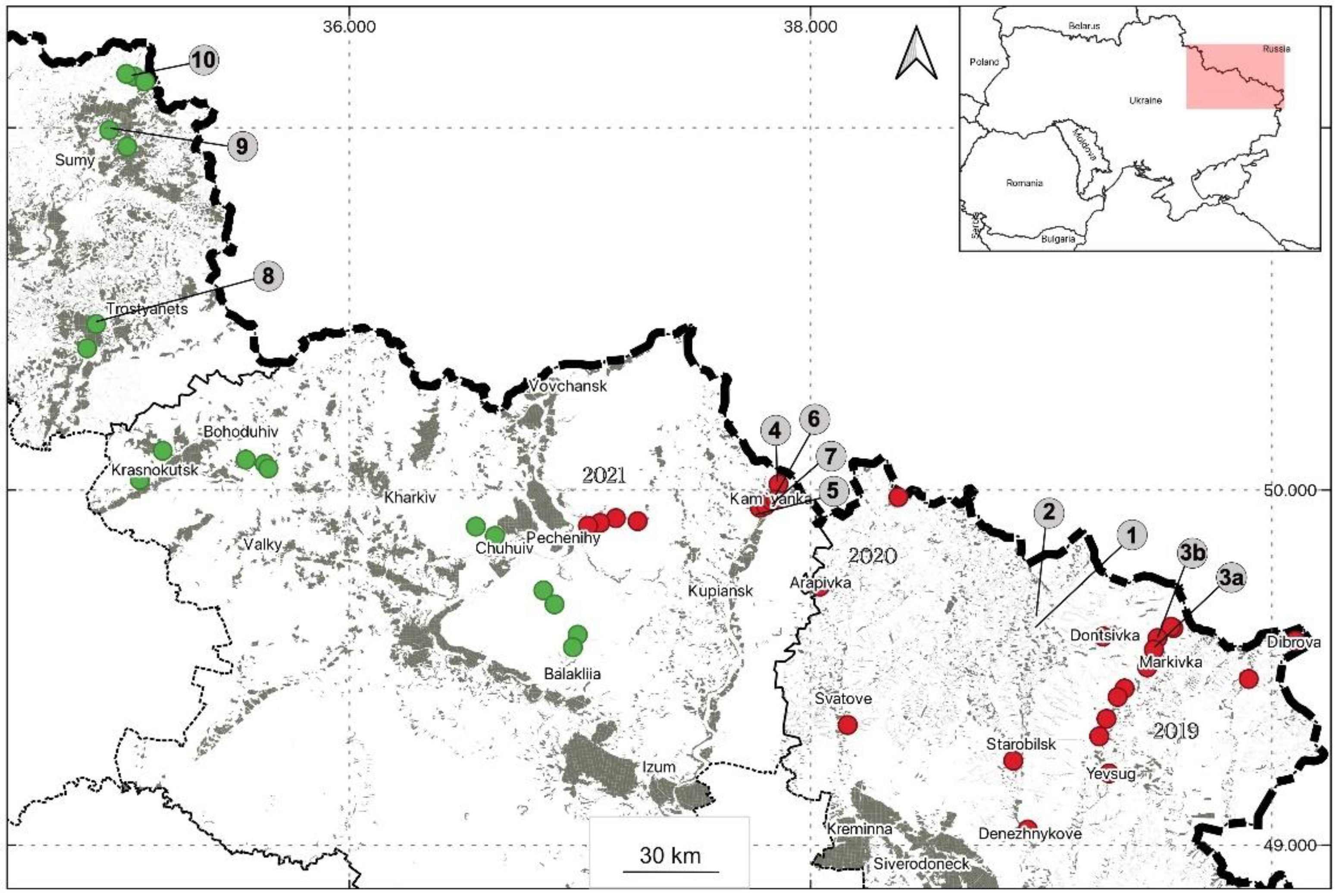
- Invasion of EAB to Ukraine occurred 2–3 years previously to its first records in 2019, and is currently expanding both in terms of newly infested trees and invaded geographic area.
- Fraxinus excelsior (in interior of forest stands) is more resistant to EAB than F. pennsylvanica (in field shelterbelts).
- Fraxinus excelsior is more susceptible to ADB than F. pennsylvanica.
- Infection by ADB is likely to predispose F. excelsior to infestation by EAB.
- Ash trees infected by ADB are predisposed for the colonization by ash bark beetles Hylesinus spp.
- Inventory and mapping of surviving F. excelsior, affected by both ADB and EAB, is necessary to acquire genetic resources for the work on strategic, long-term restoration of devastated areas, thereby tackling a possible invasion of EAB to the EU.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baranchikov, Y.; Mozolevskaya, E.; Yurchenko, G.; Kenis, M. Occurrence of the emerald ash borer, Agrilus planipennis in Russia and its potential impact on European forestry. EPPO Bull. 2008, 38, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herms, D.A.; McCullough, D.G. Emerald ash borer invasion of North America: History, biology, ecology, impacts, and management. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2014, 59, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drogvalenko, A.N.; Orlova-Bienkowskaja, M.J.; Bienkowski, A.O. Record of the emerald ash borer (Agrilus planipennis) in Ukraine is confirmed. Insects 2019, 10, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meshkova, V.L. Emerald ash borer-newly arriving to our territories. Lisoviy Visn. 2019, 6, 8–11. (In Ukrainian) [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, R.A.J.; Bauer, L.S.; Poland, T.M.; Windell, K.N. Flight performance of Agrilus planipennis (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) on a flight mill and in free flight. J. Insect Behav. 2010, 23, 128–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gninenko, Y.I.; Klyukin, M.S.; Khegay, I.V. Distribution speed of emerald ash borer in Russia. In Emerald Ash Borer—Distribution and Protection Measures in the USA and Russia; Gninenko, Y.I., Ed.; VNIILM: Pushkino, Russia, 2016; pp. 57–62. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Short, M.T.; Chase, K.D.; Feeley, T.E.; Kees, A.M.; Wittman, J.T.; Aukema, B.H. Rail transport as a vector of emerald ash borer. Agric. For. Entomol. 2020, 22, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selikhovkin, A.V.; Musolin, D.L.; Popovichev, B.G.; Merkuryev, S.A.; Volkovitsh, M.G.; Vasaitis, R. Invasive Populations of the Emerald Ash Borer Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire, 1888 (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) in Saint Petersburg, Russia: A Hitchhiker? Insects 2022, 13, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasaitis, R.; Enderle, R. Dieback of European Ash (Fraxinus spp.)–Consequences and Guidelines for Sustainable Management; Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences: Uppsala, Sweden, 2017; p. 320. Available online: http://www.slu.se/globalassets/ew/org/inst/mykopat/forskning/stenlid/dieback-of-european-ash.pdf (accessed on 31 August 2021).
- Menkis, A.; Bakys, R.; Åslund, M.S.; Davydenko, K.; Elfstrand, M.; Stenlid, J.; Vasaitis, R. Identifying Fraxinus excelsior tolerant to ash dieback: Visual field monitoring versus a molecular marker. For. Pathol. 2019, 50, e12572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Enderle, R.; Stenlid, J.; Vasaitis, R. An overview of ash (Fraxinus spp.) and ash dieback disease in Europe. CAB Rev. 2019, 14, 025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKinney, L.V.; Nielsen, L.R.; Collinge, D.B.; Thomsen, I.M.; Hansen, J.K.; Kjær, E.D. The ash dieback crisis: Genetic variation in resistance can prove a long-term solution. Plant Pathol. 2014, 63, 485–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semizer-Cuming, D.; Krutovsky, K.V.; Baranchikov, Y.N.; Kjӕr, E.D.; Williams, S.G. Saving the world’s ash forests calls for international cooperation now. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 3, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlova-Bienkowskaja, M.J.; Drogvalenko, A.N.; Zabaluev, I.A.; Sazhnev, A.S.; Peregudova, E.Y.; Mazurov, S.G.; Komarov, E.V.; Struchaev, V.V.; Martynov, V.V.; Nikulina, T.V.; et al. Current range of Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire, an alien pest of ash trees, in European Russia and Ukraine. Ann. For. Sci. 2020, 77, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranchikov, Y.N.; Seraya, L.G.; Grinash, M.N. All European ash species are susceptible to emerald ash borer Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire (Coleoptera: Buprestidae)–A Far Eastern invader. Sib. For. J. 2014, 6, 80–85, (In Russian with English summary). [Google Scholar]
- Musolin, D.L.; Selikhovkin, A.V.; Shabunin, D.A.; Zviagintsev, V.B.; Baranchikov, Y.N. Between ash Dieback and Emerald Ash Borer: Two Asian Invaders in Russia and the Future of Ash in Europe. Baltic For. 2017, 23, 316–333. Available online: https://www.balticforestry.mi.lt/bf/PDF_Articles/2017-23%5B1%5D/Baltic%20Forestry%202017.1_316-333.pdf (accessed on 31 August 2021).
- Volkovitsh, M.G.; Bieńkowski, A.O.; Orlova-Bienkowskaja, M.J. Emerald ash borer approaches the borders of the European union and Kazakhstan and is confirmed to infest European ash. Forests 2021, 12, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davydenko, K.V.; Borysova, V.; Shcherbak, O.; Kryshtop, Y.; Meshkova, V. Situation and perspectives of European ash (Fraxinus spp.) in Ukraine: Focus on eastern border. Balt. For. 2019, 25, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshkova, V.; Samoday, V.; Davydenko, K. Ash dieback and contributing factors of forest weakening in provenance tests in the Sumy region. Cent. Eur. For. J. 2021, 67, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davydenko, K.; Vasaitis, R.; Stenlid, J.; Menkis, A. Fungi in foliage and shoots of Fraxinus excelsior in eastern Ukraine: A first report on Hymenoscyphus Pseudoalbidus. For. Path. 2013, 43, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucheryavenko, T.V.; Skrylnik, Y.E.; Davydenko, K.V.; Zinchenko, O.V.; Meshkova, V.L. The first data on the biological characteristics of Agrilus planipennis Fairmare, 1988 (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) in Ukraine. Ukrainian Entomol. J. 2020, 18, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlova-Bienkowskaja, M.J.; Bienkowski, A.O. The life cycle of the emerald ash borer Agrilus planipennis in European Russia and comparisons with its life cycles in Asia and North America. Agric. For. Entomol. 2016, 18, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshkova, V.L.; Kucheryavenko, T.V.; Skrylnik, Y.E.; Zinchenko, O.V.; Borysenko, A.I. Beginning of the spread of Agrilus planipennis Fairmaire (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) on the territory of Ukraine. Proc. St. Petersburg For. Tech. Acad. 2021, 236, 163–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, H.D.; Bartha, B.; Strasser, L.; Lemme, H. Development of ash dieback in south-eastern Germany and the increasing occurrence of secondary pathogens. Forests 2016, 7, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Plot | Fraxinus | Trees Monitored, no. (%) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| spp. | All | Year 2020 | Year 2021 | |||||||||
| ADB | EAB | Of those, ADB and EAB | Dead a | VisuallyHealthy | ADB | EAB | Of Those, ADB and EAB | Dead a | Visually Healthy | |||
| Luhansk region (LH) | ||||||||||||
| 1LH | F. pen.b | 38 | 1 (3) | 19 (50) | 0 | 12 (32) | 18 (47) | 2 (5) | 37 (97) | 1 (3) | 29 (76) | 0 |
| 2LH | F. pen. | 25 | 0 | 16 (64) | 0 | 7 (28) | 9 (36) | 1 (4) | 22 (88) | 0 | 14 (56) | 2 (8) |
| 3aLH | F. pen. | 25 | 0 | 21 (84) | 0 | 9 (36) | 4 (16) | 0 | 25 (100) | 0 | 17 (68) | 0 |
| All LH F. pen. | 88 | 1 (1) | 56 (64) | 0 | 28 (32) | 31 (35) | 3 (3.5) | 84 (95) | 1 (1) | 60 (68) | 2 (2) | |
| 3bLH, all LH F. ex. c | 16 | 4 (25) | 3 (19) | 2 (13) | 2 (13) | 11 (69) | 6 (38) | 7 (44) | 3 (19) | 7 (44) | 6 (38) | |
| χ2 test F. pen. vs. F. ex. d | *** | ** | n.s. | * | **** | **** | ** | n.s. | **** | |||
| Kharkiv region (KH, northwest from LH) | ||||||||||||
| 4KH | F. ex. | 60 | - | - | - | - | - | 15 (25) | 17 (28) | 9 (15) | 9 (15) | 37 (62) |
| 5KH | F. ex. | 55 | - | - | - | - | - | 18 (33) | 12 (22) | 6 (11) | 9 (16) | 31 (56) |
| 6KH | F. pen. | 52 | - | - | - | - | - | 7 (13) | 31 (60) | 4 (8) | 23 (44) | 18 (35) |
| 7KH | F. pen. | 45 | - | - | - | - | - | 3 (7) | 24 (53) | 2 (4) | 19 (42) | 20 (44) |
| All KH F. pen. | 97 | - | - | - | - | - | 10 (10) | 55 (57) | 6 (6) | 42 (43) | 38 (39) | |
| All KH F. ex. | 115 | - | - | - | - | - | 33 (29) | 29 (25) | 15 (13) | 18 (16) | 68 (59) | |
| χ2 test F.pen. vs. F.ex. | ** | **** | n.s. | **** | ** | |||||||
| Sumy region (SU, northwest from KH) | ||||||||||||
| 8SU | F. ex. | 50 | - | - | - | - | - | 32 (64) | - | - | 31 (62) | 18 (36) |
| 9SU | F. ex. | 50 | - | - | - | - | - | 27 (54) | - | - | 19 (38) | 23 (46) |
| 10SU, all SU F. pen. | 25 | - | - | - | - | - | 8 (32) | - | - | 5 (20) | 17 (68) | |
| All SU F. ex. | 100 | - | - | - | - | - | 59 (59) | - | - | 50 (50) | 41 (41) | |
| χ2 test F.pen. vs. F.ex. | * | ** | * | |||||||||
| All plots (LH + KH + SU) | ||||||||||||
| All F. pen. | 210 | - | - | - | - | - | 21 (10) | 139 (66) | 7 (3) | 107 (51) | 57 (27) | |
| All F. ex. | 231 | - | - | - | - | - | 98 (42) | 36 (16) | 18 (8) | 75 (32) | 115 (50) | |
| χ2 test F.pen. vs. F.ex. | **** | **** | * | **** | **** | |||||||
| Plots infested by the emerald ash borer (LH + KH) | ||||||||||||
| LH + KH F. pen. | 185 | 13 (7) | 139 (75) | 7 (4) | 102 (55) | 40 (22) | ||||||
| LH + KH F. ex. | 131 | 39 (30) | 36 (27) | 18 (14) | 25 (19) | 74 (56) | ||||||
| χ2 test F.pen. vs. F.ex. | **** | **** | ** | **** | **** | |||||||
| Plot | Fraxinus spp. | Trees with ADB Symptoms, No. (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All (100%) | Colonized by Hylesinus spp. a | Dead (% of Colonized by Hylesinus spp.) | ||
| 4KH | F. excelsior | 15 | 4 (27) | 4 (100) |
| 5KH | F. excelsior | 18 | 7 (39) | 5 (71) |
| 6KH | F. pennsylvanica | 7 | 3 (43) | 1 (33) |
| 7KH | F. pennsylvanica | 3 | 1 (33) | 1 (100) |
| 8SU | F. excelsior | 32 | 31 (97) | 31 (100) |
| 9SU | F. excelsior | 27 | 22 (81) | 19 (86) |
| 10SU | F. pennsylvanica | 8 | 5 (63) | 5 (100) |
| All | F. excelsior | 92 | 64 (70) | 59 (92) |
| F. pennsylvanica | 18 | 9 (50) | 7 (78) | |
| χ2 test F. excelsior vs. F. pennsylvanicab | n.s. | * | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Davydenko, K.; Skrylnyk, Y.; Borysenko, O.; Menkis, A.; Vysotska, N.; Meshkova, V.; Olson, Å.; Elfstrand, M.; Vasaitis, R. Invasion of Emerald Ash Borer Agrilus planipennis and Ash Dieback Pathogen Hymenoscyphus fraxineus in Ukraine—A Concerted Action. Forests 2022, 13, 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13050789
Davydenko K, Skrylnyk Y, Borysenko O, Menkis A, Vysotska N, Meshkova V, Olson Å, Elfstrand M, Vasaitis R. Invasion of Emerald Ash Borer Agrilus planipennis and Ash Dieback Pathogen Hymenoscyphus fraxineus in Ukraine—A Concerted Action. Forests. 2022; 13(5):789. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13050789
Chicago/Turabian StyleDavydenko, Kateryna, Yuriy Skrylnyk, Oleksandr Borysenko, Audrius Menkis, Natalia Vysotska, Valentyna Meshkova, Åke Olson, Malin Elfstrand, and Rimvys Vasaitis. 2022. "Invasion of Emerald Ash Borer Agrilus planipennis and Ash Dieback Pathogen Hymenoscyphus fraxineus in Ukraine—A Concerted Action" Forests 13, no. 5: 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13050789
APA StyleDavydenko, K., Skrylnyk, Y., Borysenko, O., Menkis, A., Vysotska, N., Meshkova, V., Olson, Å., Elfstrand, M., & Vasaitis, R. (2022). Invasion of Emerald Ash Borer Agrilus planipennis and Ash Dieback Pathogen Hymenoscyphus fraxineus in Ukraine—A Concerted Action. Forests, 13(5), 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/f13050789












