Temperature-Dependent Soil Organic Carbon Turnover in Taiwan’s Forests Revealed by Stable Carbon Isotope Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site Description
2.2. Total Organic Carbon, Total Nitrogen, and Stable Isotope Composition
2.3. Bulk Density and SOC Inventory
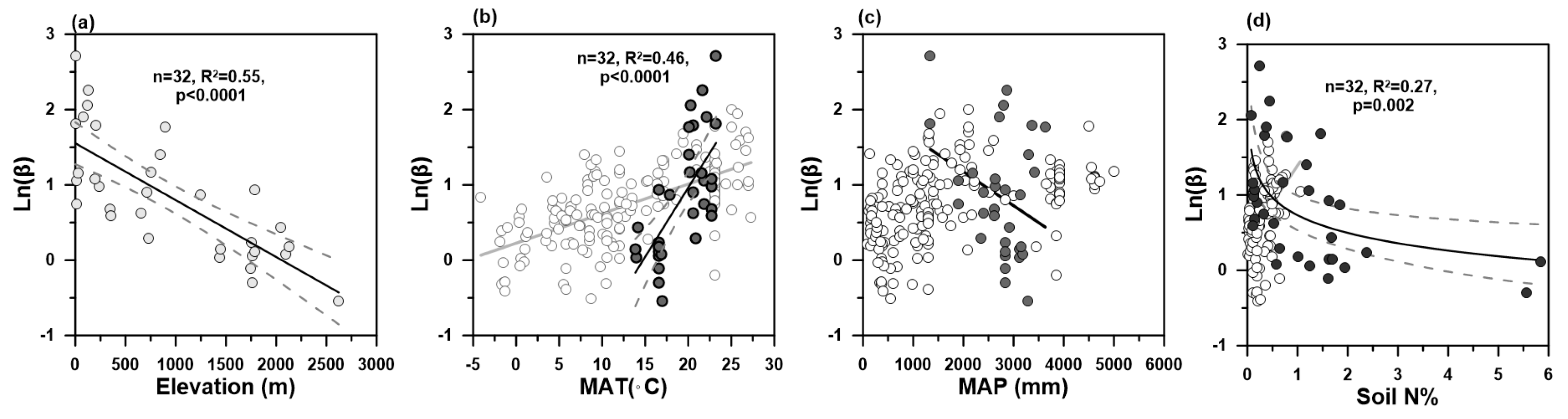
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Elevational Gradient of Soil Organic Carbon Stocks
3.2. Soil Organic Carbon Turnover Rates Using β Proxy
3.3. Climate and Nutrient Dependences of β
3.4. Implications for Climate Change
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SOC | Soil Organic Carbon |
| MAT | Mean Annual Temperature |
| MAP | Mean Annual Precipitation |
References
- Batjes, N.H. Total carbon and nitrogen in the soils of the world. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2014, 65, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharlemann, J.P.; Tanner, E.V.; Hiederer, R.; Kapos, V. Global soil carbon: Understanding and managing the largest terrestrial carbon pool. Carbon Manag. 2014, 5, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowther, T.W.; Todd-Brown, K.E.; Rowe, C.W.; Wieder, W.R.; Carey, J.C.; Machmuller, M.B.; Snoek, B.; Fang, S.; Zhou, G.; Allison, S.D. Quantifying global soil carbon losses in response to warming. Nature 2016, 540, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.B.; Lajtha, K.; Crow, S.E.; Hugelius, G.; Kramer, M.G.; Piñeiro, G. The ecology of soil carbon: Pools, vulnerabilities, and biotic and abiotic controls. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2017, 48, 419–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond-Lamberty, B.; Bailey, V.L.; Chen, M.; Gough, C.M.; Vargas, R. Globally rising soil heterotrophic respiration over recent decades. Nature 2018, 560, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulman, B.N.; Phillips, R.P.; Oishi, A.C.; Shevliakova, E.; Pacala, S.W. Microbe-driven turnover offsets mineral-mediated storage of soil carbon under elevated CO2. Nat. Clim. Change 2014, 4, 1099–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, E.A.; Janssens, I.A. Temperature sensitivity of soil carbon decomposition and feedbacks to climate change. Nature 2006, 440, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalhais, N.; Forkel, M.; Khomik, M.; Bellarby, J.; Jung, M.; Migliavacca, M.; Saatchi, S.; Santoro, M.; Thurner, M.; Weber, U. Global covariation of carbon turnover times with climate in terrestrial ecosystems. Nature 2014, 514, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giardina, C.P.; Ryan, M.G. Evidence that decomposition rates of organic carbon in mineral soil do not vary with temperature. Nature 2000, 404, 858–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acton, P.; Fox, J.; Campbell, E.; Rowe, H.; Wilkinson, M. Carbon isotopes for estimating soil decomposition and physical mixing in well-drained forest soils. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2013, 118, 1532–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Houlton, B.Z.; Liu, D.; Hou, J.; Cheng, W.; Bai, E. Stable isotopic constraints on global soil organic carbon turnover. Biogeosciences 2018, 15, 987–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, R.G.; Galy, A.; Hovius, N.; Chen, M.-C.; Horng, M.-J.; Chen, H. Tropical-cyclone-driven erosion of the terrestrial biosphere from mountains. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 759–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, S.J.; Hilton, R.G.; Selvaraj, K.; Dai, M.; Zehetner, F.; Huang, J.C.; Hsu, S.C.; Sparkes, R.; Liu, J.T.; Lee, T.Y.; et al. Preservation of terrestrial organic carbon in marine sediments offshore Taiwan: Mountain building and atmospheric carbon dioxide sequestration. Earth Surf. Dyn. 2014, 2, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadson, S.J.; Hovius, N.; Chen, H.; Dade, W.B.; Hsieh, M.-L.; Willett, S.D.; Hu, J.-C.; Horng, M.-J.; Chen, M.-C.; Stark, C.P. Links between erosion, runoff variability and seismicity in the Taiwan orogen. Nature 2003, 426, 648–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilton, R.G.; Galy, A.; Hovius, N.; Horng, M.-J.; Chen, H. The isotopic composition of particulate organic carbon in mountain rivers of Taiwan. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 3164–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.-W.; Ding, X.; Liu, J.T.; Li, D.; Lee, T.-Y.; Zheng, X.; Zheng, Z.; Xu, M.N.; Dai, M.; Kao, S.-J. Isotopic evidence for the influence of typhoons and submarine canyons on the sourcing and transport behavior of biospheric organic carbon to the deep sea. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2017, 465, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galy, V.; Peucker-Ehrenbrink, B.; Eglinton, T. Global carbon export from the terrestrial biosphere controlled by erosion. Nature 2015, 521, 204–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.-W.; Hilton, R.G.; Chang, Y.-P.; Yang, R.J.; Ding, X.; Zheng, X.; Lee, T.-Y.; Lu, H.-J.; Lu, J.-T.; Lin, Y.-S.; et al. Climate-regulation of organic carbon export in erosive mountain settings: A case study from Taiwan since the last glacial maximum. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2024, 334, 108687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horan, K.; Hilton, R.G.; Selby, D.; Ottley, C.J.; Gröcke, D.R.; Hicks, M.; Burton, K.W. Mountain glaciation drives rapid oxidation of rock-bound organic carbon. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1701107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Gorman, P.A.; Allan, R.P.; Byrne, M.P.; Previdi, M. Energetic constraints on precipitation under climate change. Surv. Geophys. 2012, 33, 585–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinze, C.; Blenckner, T.; Martins, H.; Rusiecka, D.; Döscher, R.; Gehlen, M.; Gruber, N.; Holland, E.; Hov, Ø.; Joos, F. The quiet crossing of ocean tipping points. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2008478118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.W.; Torn, M.S.; Abiven, S.; Dittmar, T.; Guggenberger, G.; Janssens, I.A.; Kleber, M.; Kögel-Knabner, I.; Lehmann, J.; Manning, D.A. Persistence of soil organic matter as an ecosystem property. Nature 2011, 478, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Kleber, M. The contentious nature of soil organic matter. Nature 2015, 528, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bird, M.I.; Chivas, A.R.; Head, J. A latitudinal gradient in carbon turnover times in forest soils. Nature 1996, 381, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, J.S.; Schlesinger, W.H. Geographic and vertical patterns of stable carbon isotopes in tropical rain forest soils of Costa Rica. Geoderma 2002, 109, 141–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunn, M.; Spielvogel, S.; Sauer, T.; Oelmann, Y. Temperature and precipitation effects on δ 13 C depth profiles in SOM under temperate beech forests. Geoderma 2014, 235, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.E.; Fox, J.F.; Davis, C.M.; Rowe, H.D.; Thompson, N. Carbon and nitrogen isotopic measurements from southern Appalachian soils: Assessing soil carbon sequestration under climate and land-use variation. J. Environ. Eng. 2009, 135, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.-S. An Introduction to the Geology of Taiwan, Explanatory Text of the Geologic Map of Taiwan; Central Geological Survey: New Taipei City, Taiwan, 1988; pp. 151–152. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.-S.; Hseu, Z.-Y.; Tsai, C.-C. The Soils of Taiwan; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Soil Survey Staff. Keys to Soil Taxonomy, 10th ed.; USDA-Natural Resources Conservation Service: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Blake, G.R.; Hartage, K.H. Particle density. In Methods of Soil Analysis; Part 1: Physical Properties; Klute, A., Ed.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1986; pp. 377–381. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, C.-C.; Chen, Z.-S.; Hseu, Z.-Y.; Duh, C.-T.; Guo, H.-Y. Organic carbon storage and management strategies of the forest soils based on the forest soil survey database in Taiwan. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Evaluation and Sustainable Management of Soil Carbon Sequestration in Asian Countries, IPB International Conference Center, Bogor, Indonesia, 28–29 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Jeffrey, D. A note on the use of ignition loss as a means for the approximate estimation of soil bulk density. J. Ecol. 1970, 58, 297–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, A.; Bocock, K. Estimation of soil bulk-density from loss-on-ignition values. J. Appl. Ecol. 1981, 18, 919–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, M.; Chadwick, O. Climate-driven thresholds in reactive mineral retention of soil carbon at the global scale. Nat. Clim. Change 2018, 8, 1104–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, C.-C.; Tsai, C.-C.; Chen, Z.-S. Soil organic carbon stocks in relation to elevation gradients in volcanic ash soils of Taiwan. Geoderma 2013, 209, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garten, C.T., Jr.; Hanson, P.J. Measured forest soil C stocks and estimated turnover times along an elevation gradient. Geoderma 2006, 136, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.C.; Lin, K.C.; Huang, C.Y. Temporal and spatial patterns of remotely sensed litterfall in tropical and subtropical forests of Taiwan. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2016, 12, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedli, H.; Siegenthaler, U.; Rauber, D.; Oeschger, H. Measurements of concentration, 13C/12C and 18O/16O ratios of tropospheric carbon dioxide over Switzerland. Tellus B 1987, 39, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, K.; Guggenberger, G.; Zech, W. Isotopic fractionation of dissolved organic carbon in shallow forest soils as affected by sorption. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2001, 52, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Hui, D.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, G. Rates of litter decomposition in terrestrial ecosystems: Global patterns and controlling factors. J. Plant Ecol. 2008, 1, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuur, E.A. The effect of water on decomposition dynamics in mesic to wet Hawaiian montane forests. Ecosystems 2001, 4, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, B. Litter decomposition and organic matter turnover in northern forest soils. For. Ecol. Manag. 2000, 133, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fioretto, A.; Papa, S.; Pellegrino, A.; Fuggi, A. Decomposition dynamics of Myrtus communis and Quercus ilex leaf litter: Mass loss, microbial activity and quality change. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2007, 36, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.G.; Jia, B.; Lv, J.; Ma, Q.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Li, F.-m. Nitrogen fertilization decreases the decomposition of soil organic matter and plant residues in planted soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 112, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, H.; Blagodatskaya, E.; Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Kuzyakov, Y. Nitrogen fertilization increases rhizodeposit incorporation into microbial biomass and reduces soil organic matter losses. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2017, 53, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Ahlström, A.; Allison, S.D.; Batjes, N.H.; Brovkin, V.; Carvalhais, N.; Chappell, A.; Ciais, P.; Davidson, E.A.; Finzi, A. Toward more realistic projections of soil carbon dynamics by Earth system models. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2016, 30, 40–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
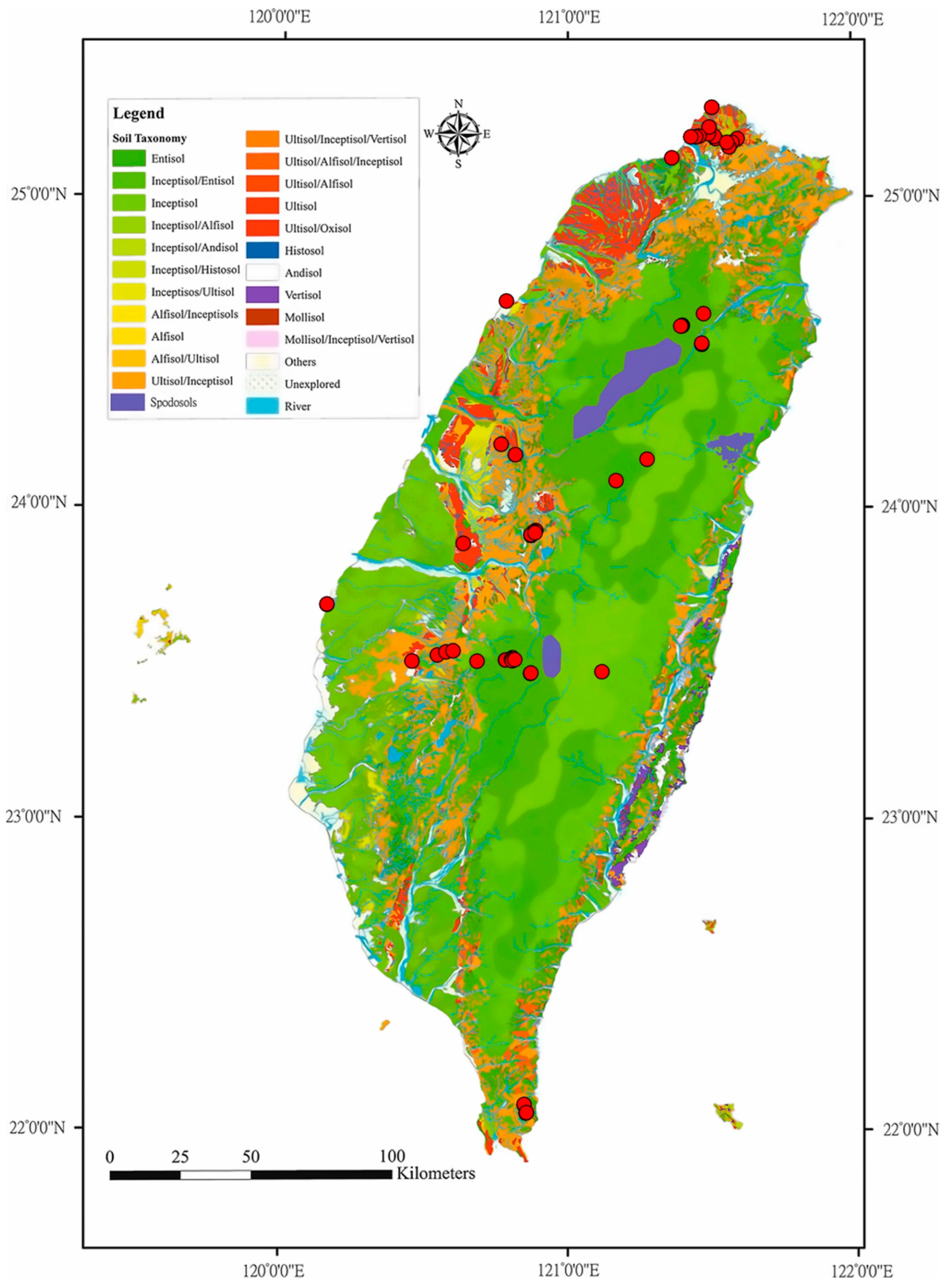
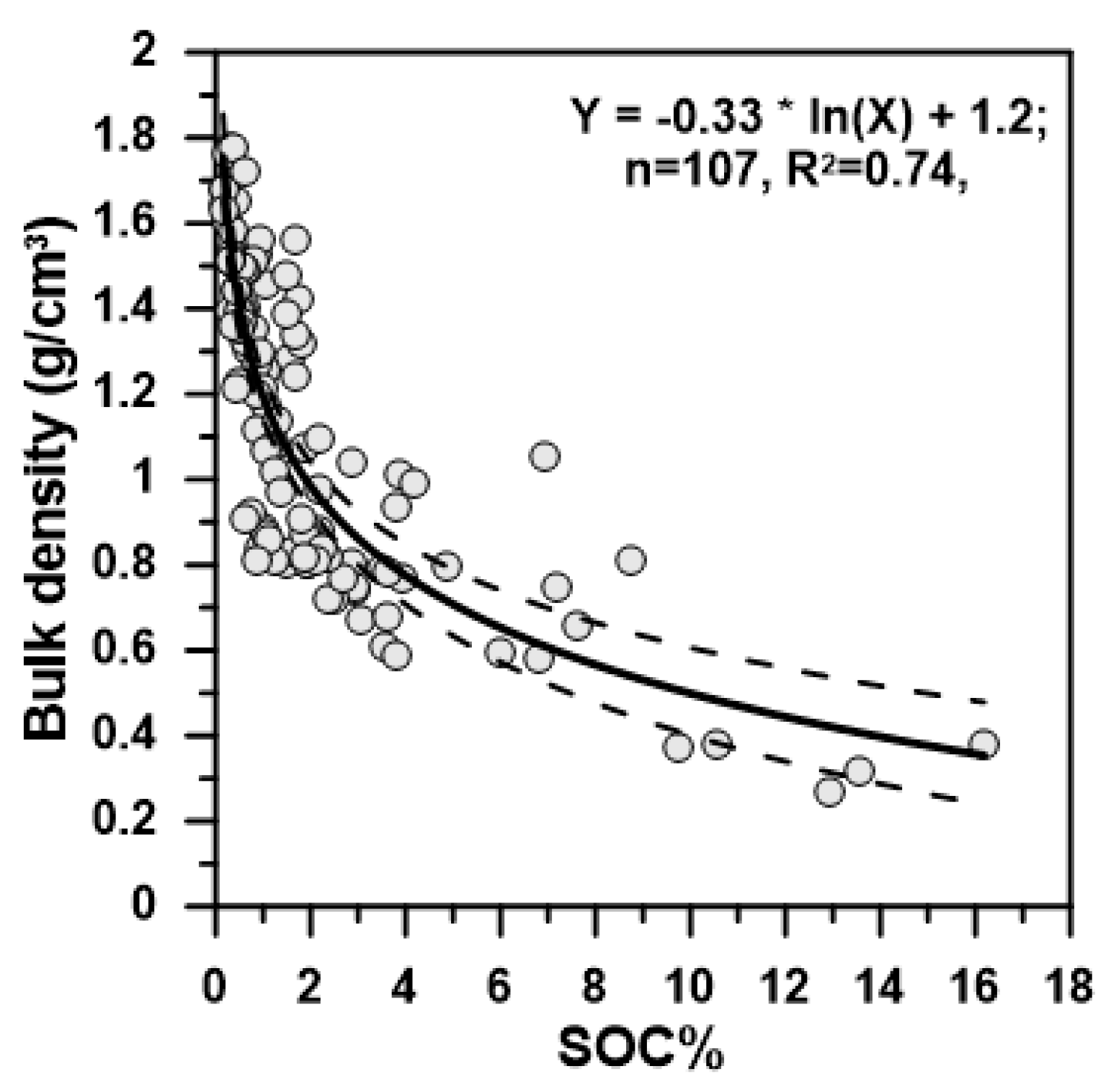
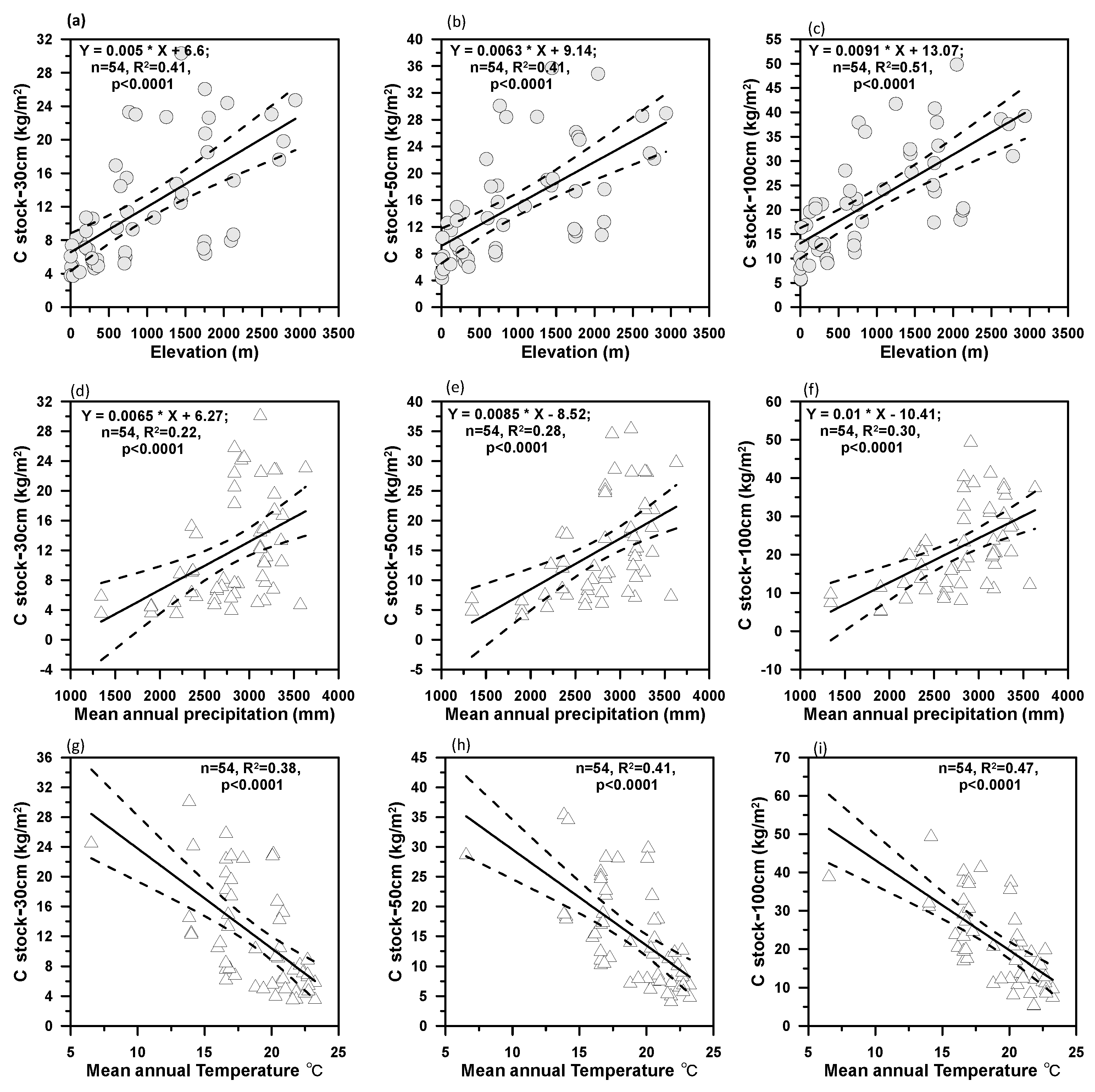
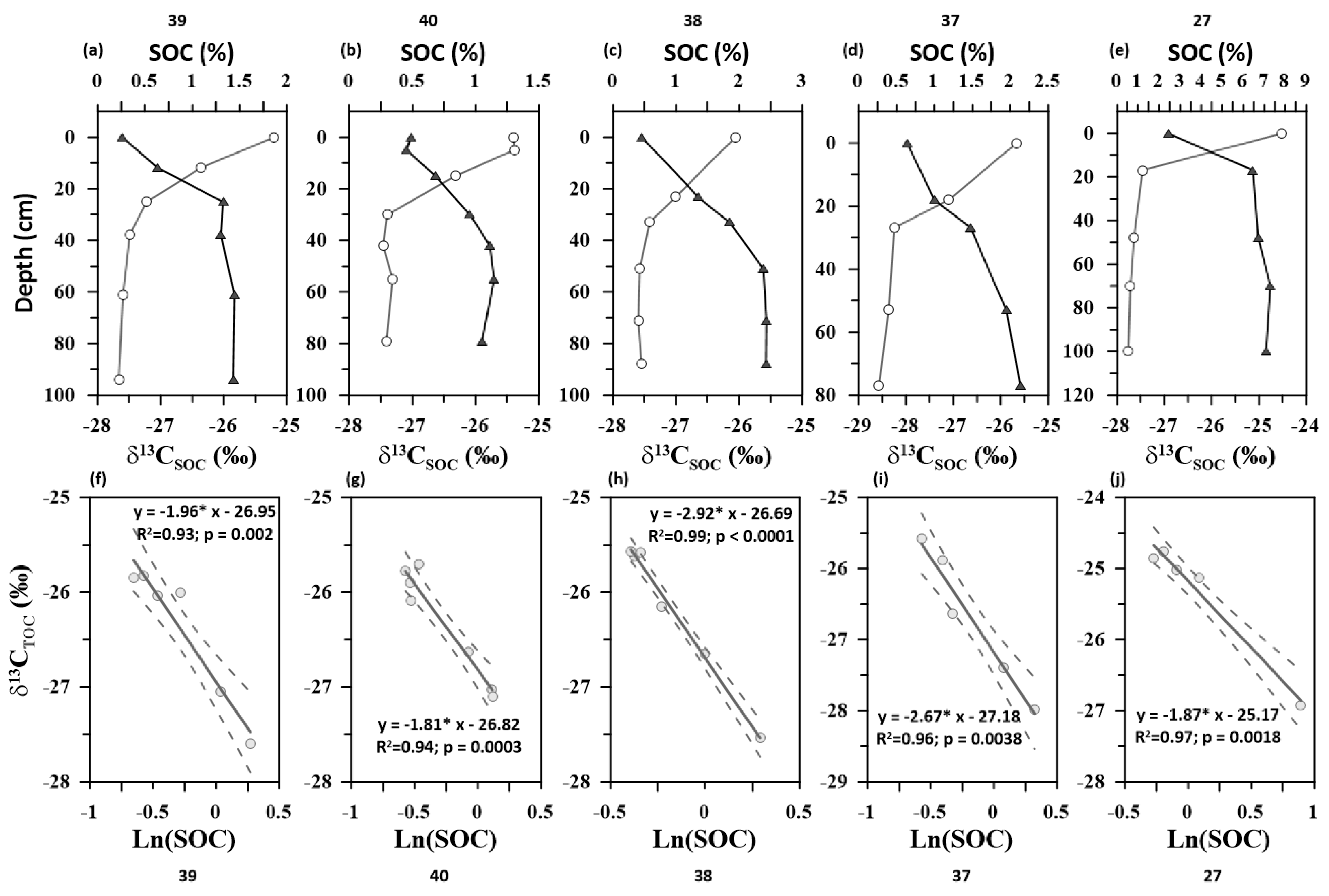
| Soil Profiles | Elevation (m) | MAP (mm) | MAT (°C) | ln(β) | R2 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KP4 | 201 | 3363 | 20.6 | 1.8 | 0.95 | 0.004 |
| KP5 | 127 | 2873 | 21.6 | 2.3 | 0.96 | 0.014 |
| KP6 | 78 | 2710 | 22.1 | 1.9 | 0.69 | 0.02 |
| 1 | 1748 | 2834 | 16.6 | −0.1 | 0.87 | 0.021 |
| 2 | 1753 | 2834 | 16.6 | 0.2 | 0.89 | 0.004 |
| 3 | 1759 | 2834 | 16.6 | −0.3 | 0.92 | 0.01 |
| 4 | 1758 | 2834 | 16.6 | 0.1 | 0.80 | 0.002 |
| 5 | 1786 | 2834 | 16.6 | 0.1 | 0.86 | 0.008 |
| 6 | 1786 | 2834 | 16.6 | 0.9 | 1 | 0.005 |
| 8 | 1249 | 3131 | 17.9 | 0.9 | 0.99 | <0.0001 |
| 9 | 1440 | 3122 | 14 | 0.3 | 0.97 | 0.018 |
| 11 | 1444 | 3123 | 13.8 | 0.2 | 0.96 | 0.004 |
| 14 | 899 | 3630 | 20.1 | 1.8 | 0.97 | <0.0001 |
| 15 | 757 | 3417 | 20.2 | 1.2 | 0.80 | 0.007 |
| 17 | 847 | 3300 | 20.1 | 1.4 | 0.82 | 0.095 |
| 20 | 8 | 1902 | 21.8 | 1.1 | 0.88 | 0.002 |
| 21 | 8 | 1902 | 21.8 | 0.7 | 0.93 | 0.008 |
| 22 | 0 | 1341 | 23.2 | 2.7 | 0.88 | 0.002 |
| 23 | 0 | 1341 | 23.2 | 1.8 | 0.56 | 0.087 |
| 24 | 730 | 2354 | 20.9 | 0.3 | 0.97 | <0.0001 |
| 25 | 715 | 2406 | 20.6 | 0.9 | 0.96 | 0.001 |
| 28 | 650 | 2404 | 20.6 | 0.6 | 0.97 | 0.002 |
| 30 | 2046 | 2911 | 14.2 | 0.4 | 0.97 | 0.002 |
| 35 | 2623 | 3281 | 17 | 0.1 | 0.82 | 0.005 |
| 37 | 234 | 2638 | 22.7 | 1 | 0.96 | 0.004 |
| 38 | 196 | 2638 | 22.7 | 1.1 | 0.99 | <0.0001 |
| 39 | 346 | 2609 | 22.7 | 0.7 | 0.93 | 0.002 |
| 40 | 356 | 2609 | 22.7 | 0.6 | 0.94 | <0.0001 |
| P1 | 30 | 2183 | 21.6 | 1.2 | 0.69 | 0.083 |
| P2 | 117 | 2799 | 20.3 | 2.1 | 0.98 | 0.012 |
| P6 | 2094 | 3179 | 16.9 | 0.1 | 0.63 | 0.019 |
| P8 | 2125 | 3148 | 16.6 | 0.2 | 0.64 | 0.057 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, L.-W.; Wu, M.; Li, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Huang, Z.; Lee, T.-Y.; Kao, S.-J. Temperature-Dependent Soil Organic Carbon Turnover in Taiwan’s Forests Revealed by Stable Carbon Isotope Analysis. Forests 2025, 16, 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16020342
Zheng L-W, Wu M, Li Q, Zheng Z, Huang Z, Lee T-Y, Kao S-J. Temperature-Dependent Soil Organic Carbon Turnover in Taiwan’s Forests Revealed by Stable Carbon Isotope Analysis. Forests. 2025; 16(2):342. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16020342
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Li-Wei, Meng Wu, Qianhui Li, Zhenzhen Zheng, Zhen Huang, Tsung-Yu Lee, and Shuh-Ji Kao. 2025. "Temperature-Dependent Soil Organic Carbon Turnover in Taiwan’s Forests Revealed by Stable Carbon Isotope Analysis" Forests 16, no. 2: 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16020342
APA StyleZheng, L.-W., Wu, M., Li, Q., Zheng, Z., Huang, Z., Lee, T.-Y., & Kao, S.-J. (2025). Temperature-Dependent Soil Organic Carbon Turnover in Taiwan’s Forests Revealed by Stable Carbon Isotope Analysis. Forests, 16(2), 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16020342







