Response of Soil Enzyme and Plant Stoichiometry to Root Interactions: Insights from Mixed Plantings of Moso Bamboo
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
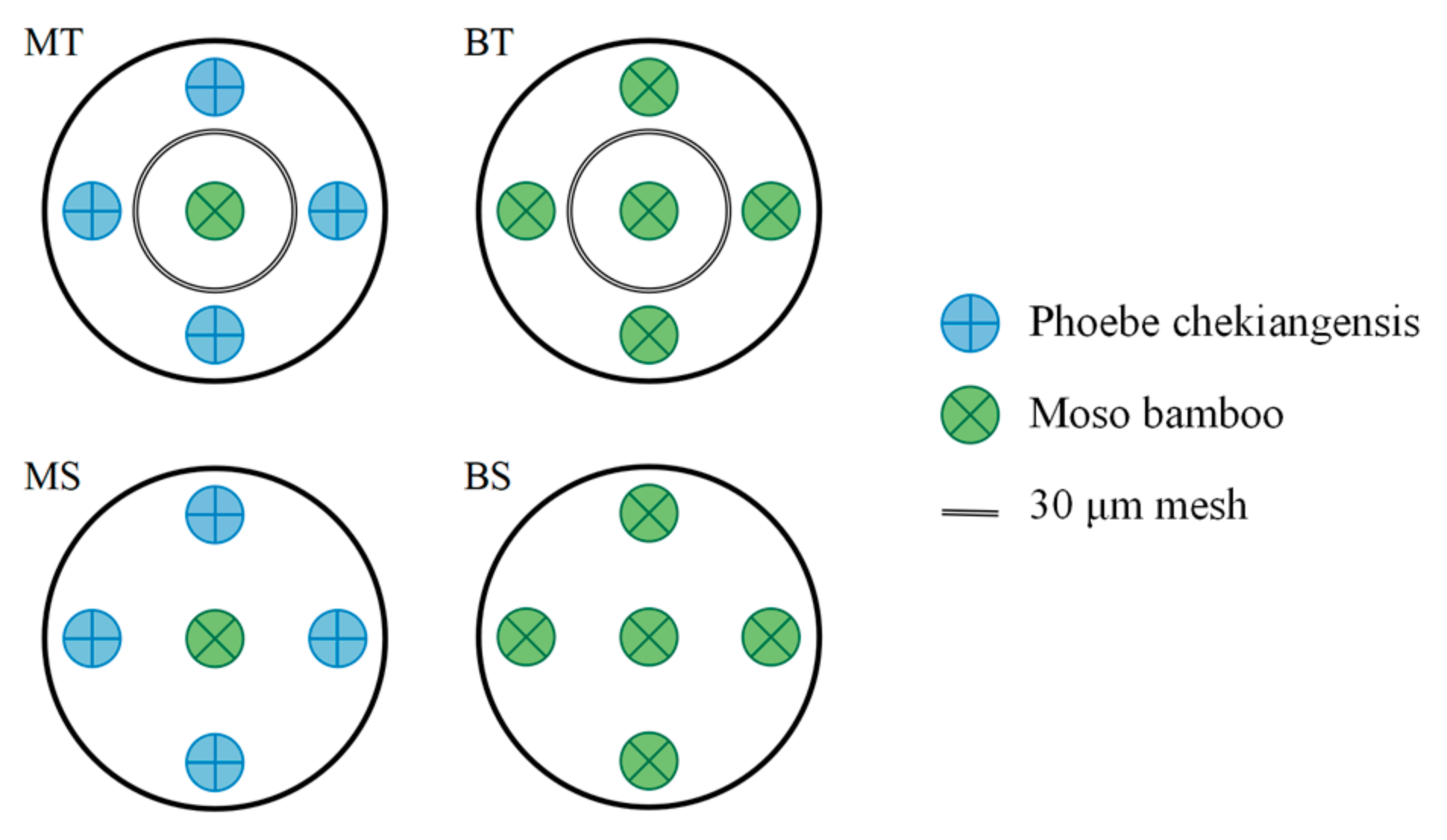
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Analysis of Soil Biotic and Abiotic Indicators
2.5. Calculation of Microbial Metabolic Limitation and CUE
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
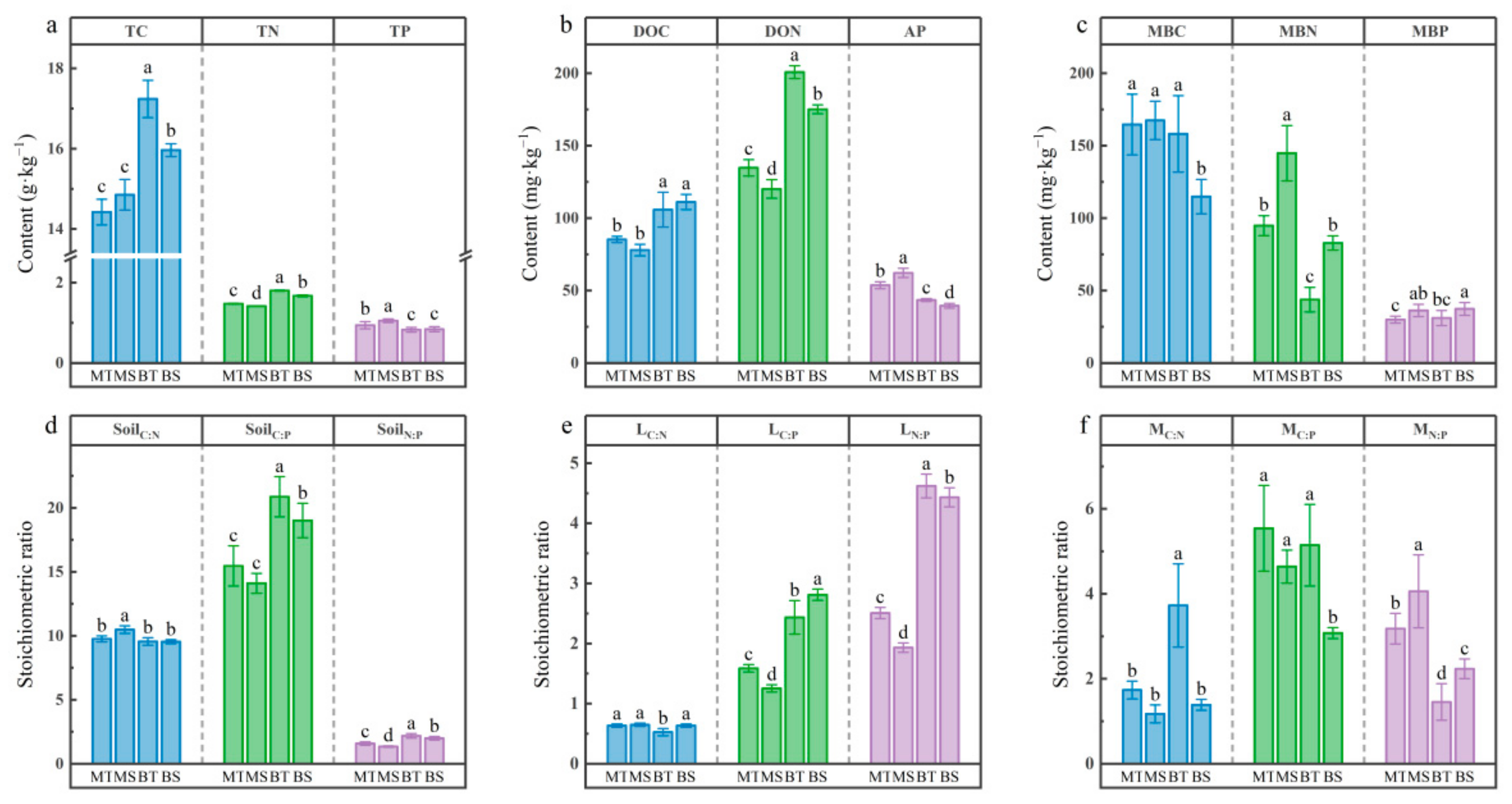
3.1. Soil Chemistry and Microbial Biomass
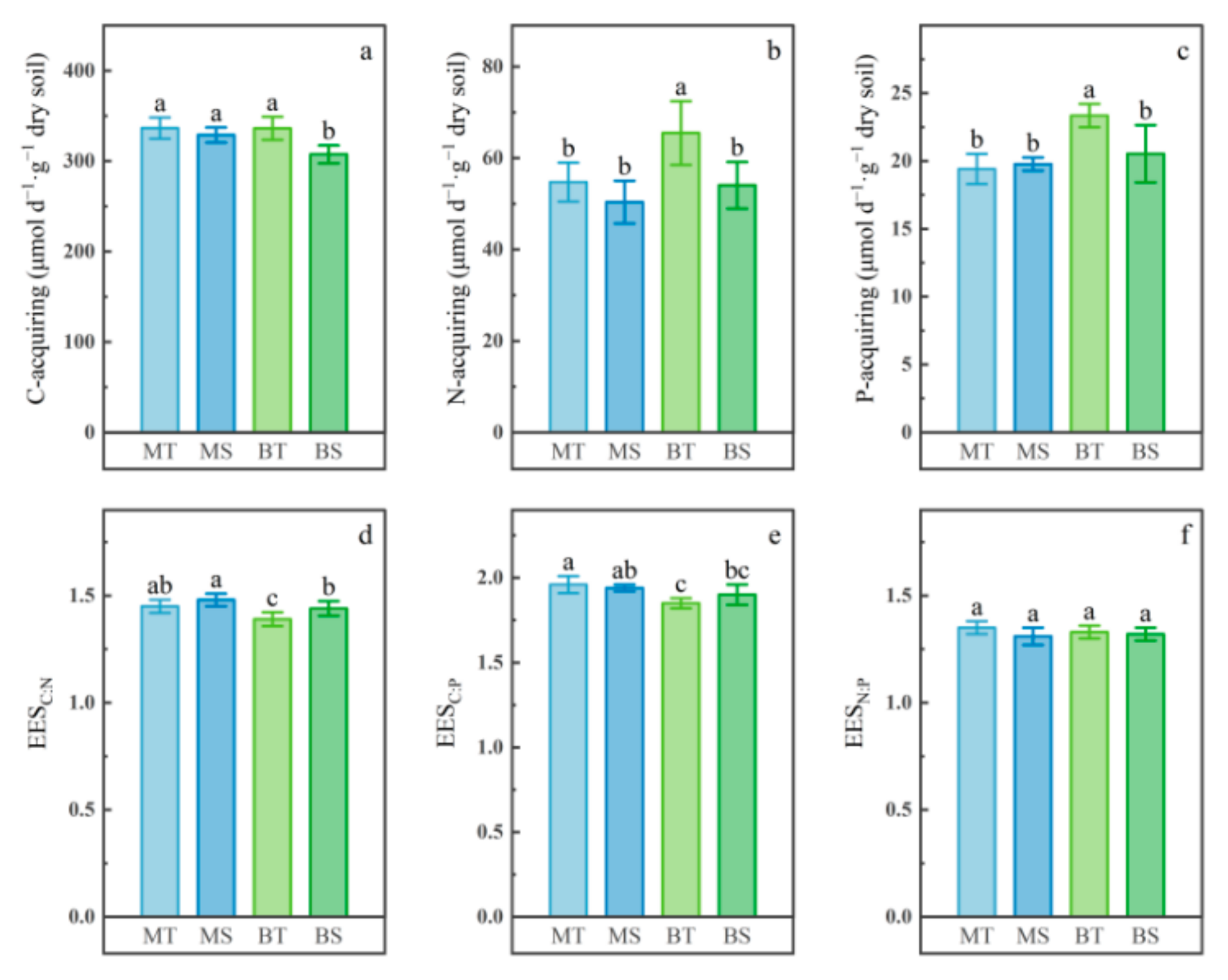
3.2. Soil Enzyme Activities and Stoichiometric Ratios
3.3. Plant Nutrient Content and Stoichiometry
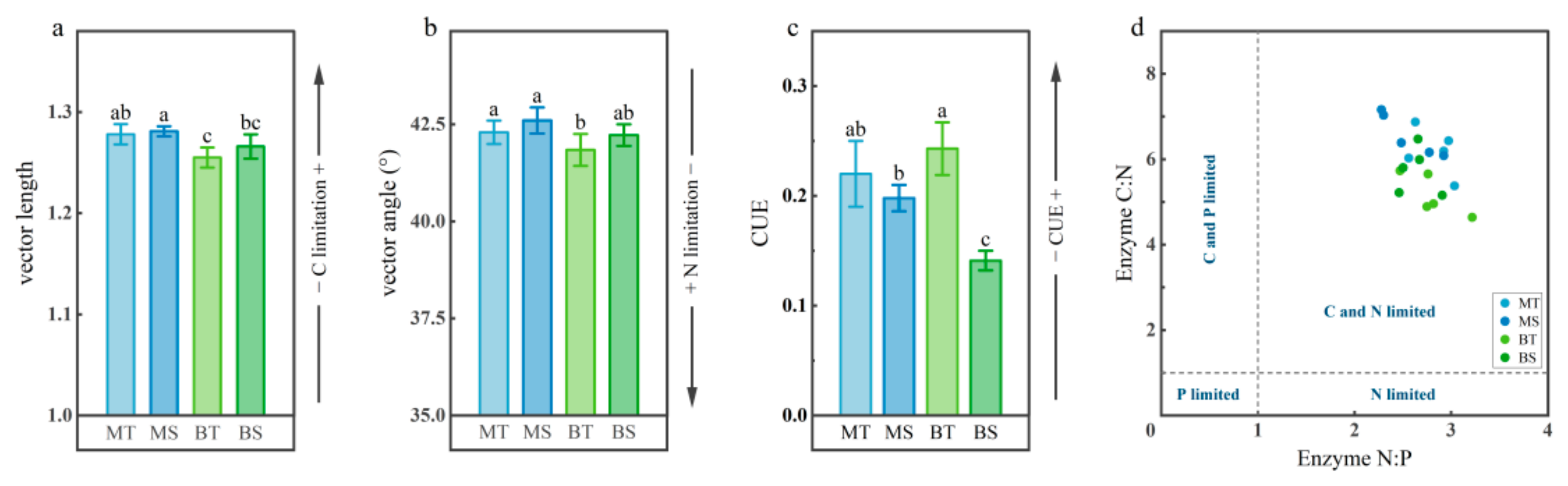
3.4. Microbial Metabolic Limitation and Carbon Use Efficiency
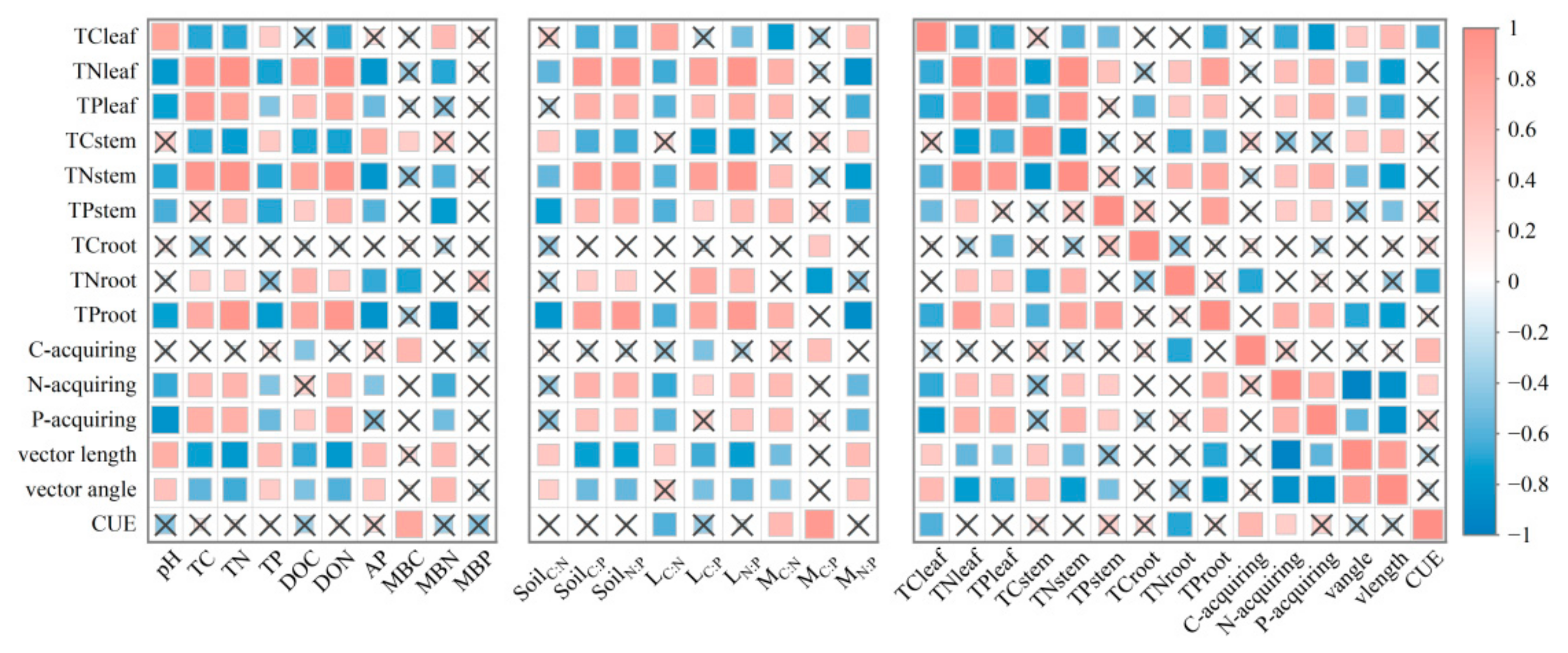
3.5. Relationship Between Soil Enzyme Activity and Chemical Properties
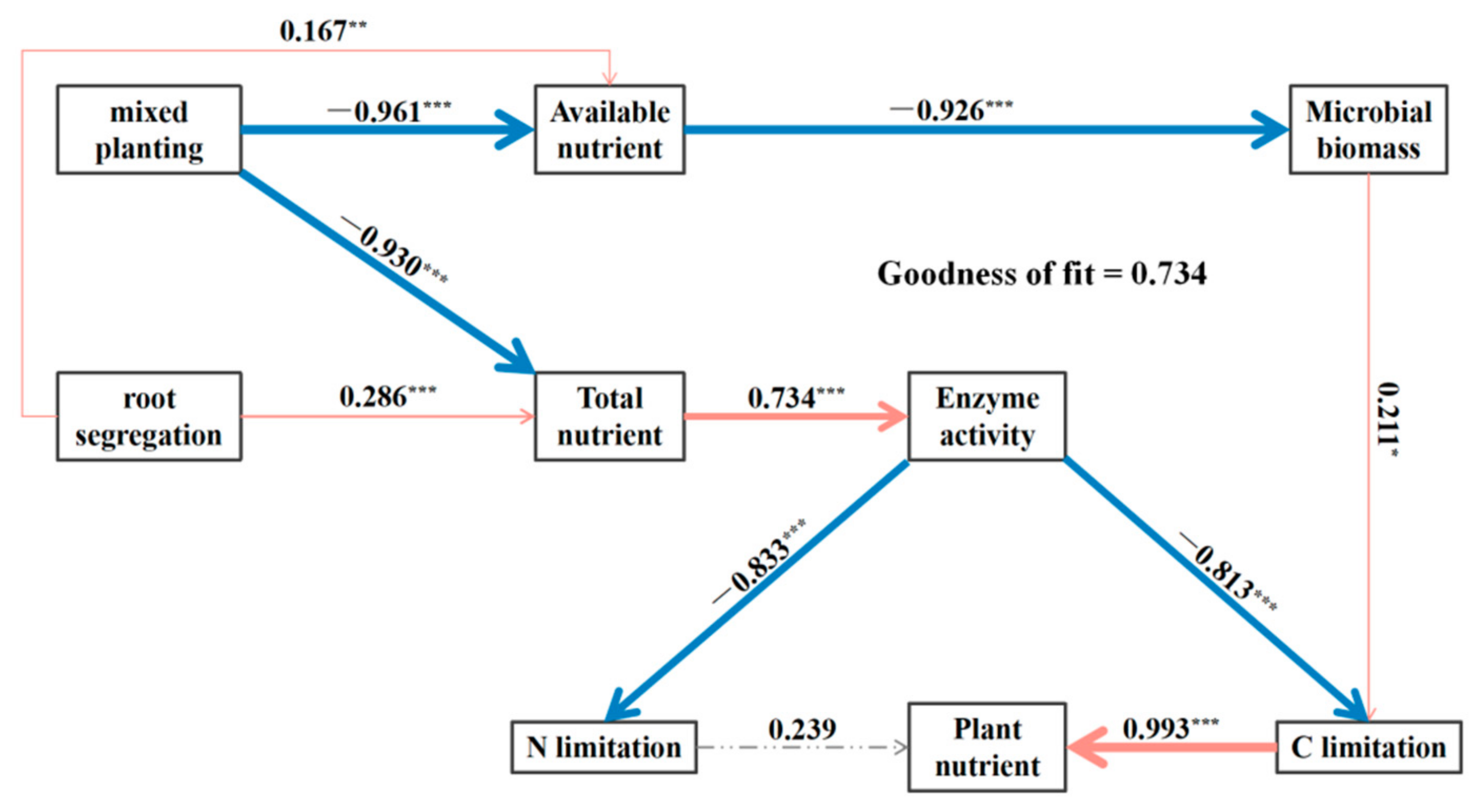
3.6. Drivers of Soil Microbial and Plant Indicators
4. Discussion
4.1. Factors Influencing Soil Chemistry, Microbial Biomass, and Enzyme Activity
4.2. Factors Influencing Microbial Metabolic Limitation and CUE
4.3. Factors Driving Plant Nutrient Distribution Strategies
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, S.; Cui, L.; Xu, J.; Liu, M.; Wang, W.; Xia, A.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xu, X.; Cui, X. A Global Synthesis of Plant-Plant Interaction Investigations: Current Knowledge and Future Directions. Plant Soil 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Fang, L.; Guo, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Zhang, X. Ecoenzymatic Stoichiometry and Microbial Nutrient Limitation in Rhizosphere Soil in the Arid Area of the Northern Loess Plateau, China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 116, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ju, W.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, Y.; Beiyuan, J.; Fan, Q.; Wei, S.; Li, S.; et al. Microbial Metabolic Limitation of Rhizosphere under Heavy Metal Stress: Evidence from Soil Ecoenzymatic Stoichiometry. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 300, 118978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Moorhead, D.L.; Wang, X.; Xu, M.; Wang, X.; Wei, X.; Zhu, Z.; Ge, T.; Peng, S.; Zhu, B.; et al. Decreasing Microbial Phosphorus Limitation Increases Soil Carbon Release. Geoderma 2022, 419, 115868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, S.D.; Wallenstein, M.D.; Bradford, M.A. Soil-Carbon Response to Warming Dependent on Microbial Physiology. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Hill, B.H.; Follstad Shah, J.J. Ecoenzymatic Stoichiometry of Microbial Organic Nutrient Acquisition in Soil and Sediment. Nature 2009, 462, 795–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyakov, Y.; Xu, X. Competition between Roots and Microorganisms for Nitrogen: Mechanisms and Ecological Relevance. New Phytol. 2013, 198, 656–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, T.; Keiblinger, K.M.; Schmid, E.; Sterflinger-Gleixner, K.; Ellersdorfer, G.; Roschitzki, B.; Richter, A.; Eberl, L.; Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S.; Riedel, K. Who Is Who in Litter Decomposition? Metaproteomics Reveals Major Microbial Players and Their Biogeochemical Functions. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1749–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapia-Torres, Y.; Elser, J.J.; Souza, V.; García-Oliva, F. Ecoenzymatic Stoichiometry at the Extremes: How Microbes Cope in an Ultra-Oligotrophic Desert Soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 87, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moorhead, D.L.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Hill, B.H.; Weintraub, M.N. Vector Analysis of Ecoenzyme Activities Reveal Constraints on Coupled C, N and P Dynamics. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 93, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, D.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, W.; Xiao, K.; Wang, K. Nitrogen Addition Aggravates Microbial Carbon Limitation: Evidence from Ecoenzymatic Stoichiometry. Geoderma 2018, 329, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Cheng, X.; Liu, G. Increased Soil Organic Carbon Response to Fertilization Is Associated with Increasing Microbial Carbon Use Efficiency: Data Synthesis. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 171, 108731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Turner, B.L.; Talbot, J.M.; Waring, B.G.; Powers, J.S.; Kuske, C.R.; Moorhead, D.L.; Shah, J.J.F. Stoichiometry of Microbial Carbon Use Efficiency in Soils. Ecol. Monogr. 2016, 86, 172–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Peng, C.; Huang, C.; Wang, K.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Hai, X.; Shangguan, Z. Drivers of Soil Microbial Metabolic Limitation Changes along a Vegetation Restoration Gradient on the Loess Plateau, China. Geoderma 2019, 353, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosinger, C.; Rousk, J.; Sandén, H. Can Enzymatic Stoichiometry Be Used to Determine Growth-Limiting Nutrients for Microorganisms?—A Critical Assessment in Two Subtropical Soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 128, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo, Y.; Bell, C.; Koyama, A.; Canarini, A.; Boot, C.M.; Wallenstein, M.; Pendall, E. Plant Traits, Stoichiometry and Microbes as Drivers of Decomposition in the Rhizosphere in a Temperate Grassland. J. Ecol. 2017, 105, 1750–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, G. Regulation of Soil C–N–P Stoichiometry by Intercropping Mitigates Microbial Resource Limitations and Contributes to Maize Productivity. Plant Soil 2023, 498, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaway, R.M. The Detection of Neighbors by Plants. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2002, 17, 104–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, B.; Shi, W.; Wang, H.; Lin, F. 15N Labeling Technology Reveals Enhancement of Nitrogen Uptake and Transfer by Root Interaction in Cotton/Soybean Intercropping. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 6307–6316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te, X.; Din, A.M.U.; Cui, K.; Raza, M.A.; Fraz Ali, M.; Xiao, J. Inter-Specific Root Interactions and Water Use Efficiency of Maize/Soybean Relay Strip Intercropping. Field Crops Res. 2023, 291, 108793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Guo, L.; Ramakrishnan, M.; Fei, Z.; Vinod, K.K.; Ding, Y.; Jiao, C.; Gao, Z.; Zha, R.; Wang, C.; et al. Rapid Growth of Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis): Cellular Roadmaps, Transcriptome Dynamics, and Environmental Factors. Plant Cell 2022, 34, 3577–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, H.; Chen, J.; Wu, Q.; Niu, L.; Li, Y.; Liang, C.; Shen, Y.; Xu, Q. Intensive Management Decreases Soil Aggregation and Changes the Abundance and Community Compositions of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi in Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens) Forests. For. Ecol. Manag. 2017, 400, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Gao, H.; Xue, X.; Ren, J.; Chen, X.; Niu, B. Variation of Sugar Compounds in Phoebe Chekiangensis Seeds during Natural Desiccation. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0299669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, B.; Yang, Z. Effects of Precious Tree Introduction into Moso Bamboo Forests on Soil Carbon and Nitrogen Pools. Forests 2022, 13, 1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, A.; Lv, J. Spatial Patterns of Bamboo Expansion across Scales: How Does Moso Bamboo Interact. with Competing Trees? Landsc. Ecol. 2023, 38, 3925–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Bi, R.; Xu, X.; Shen, H.; Zhang, Q.; Xiong, Z. General Patterns of Soil Nutrient Stoichiometry, Microbial Metabolic Limitation and Carbon Use Efficiency in Paddy and Vegetable Fields along a Climatic Transect of Eastern China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 378, 109322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Min, X.; Liu, G.; Li, P.; Xue, S. Effect of Plant–Plant Interactions and Drought Stress on the Response of Soil Nutrient Contents, Enzyme Activities and Microbial Metabolic Limitations. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 181, 104666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.-H.; Zhang, S.-Z.; Li, Y.-H.; Xia, Z.-C.; Yang, X.-F.; Meiners, S.J.; Wang, P. Plant Neighbor Detection and Allelochemical Response Are Driven by Root-Secreted Signaling Chemicals. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremner, J.M. Nitrogen-total. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part III. Chemical Methods; SSSA Book Series No. 5; Sparks, D.L., Page, A.L., Helmke, P.A., Loeppert, R.H., Eds.; American Society of Agronomy: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 1085–1121. [Google Scholar]
- Brookes, P.C.; Powlson, D.S.; Jenkinson, D.S. Measurement of Microbial Biomass Phosphorus in Soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1982, 14, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tietz, A.; Kirschner, A.; Langergraber, G.; Sleytr, K.; Haberl, R. Characterisation of Microbial Biocoenosis in Vertical Subsurface Flow Constructed Wetlands. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 380, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, E.D.; Brookes, P.C.; Jenkinson, D.S. An Extraction Method for Measuring Soil Microbial Biomass C. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1987, 19, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedin, L.O. Global Organization of Terrestrial Plant–Nutrient Interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 10849–10850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, R.; Xu, M.; Li, R.; Zhao, F.; Sheng, Q. Spatial Variability of Soil Microbial Biomass and Its Relationships with Edaphic, Vegetational and Climatic Factors in the Three-River Headwaters Region on Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2015, 95, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Duan, Y.; Huo, W.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, D.; Xu, M.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Wang, B.; Kuzyakov, Y.; et al. C:P Stoichiometric Imbalance between Soil and Microorganisms Drives Microbial Phosphorus Turnover in the Rhizosphere. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2022, 58, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Pan, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Deng, J.; Zhao, F.; Guo, Y.; Han, X.; Yang, G.; Feng, Y.; Ren, G.; et al. Resource Limitation and Modeled Microbial Metabolism along an Elevation Gradient. Catena 2021, 209, 105807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Mo, Q.; Tang, J.; Liu, W.; Batyrbek, M.; Liu, T.; Zhang, X.; Han, Q. Shaping the Succession Patterns of Different Soil Nutrients, Enzyme Stoichiometry, and Microbial Communities through Rotation Systems. Catena 2023, 236, 107740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Bing, H.; Chang, R.; Cui, Y.; Shen, G.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Fang, L. Microbial Metabolic Limitation Response to Experimental Warming along an Altitudinal Gradient in Alpine Grasslands, Eastern Tibetan Plateau. Catena 2022, 214, 106243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Shah, J.J.F. Ecoenzymatic Stoichiometry and Ecological Theory. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2012, 43, 313–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, M.J.; Mueller, K.E.; Olk, D.C.; Sawyer, J.E.; Six, J. Integrating Plant Litter Quality, Soil Organic Matter Stabilization, and the Carbon Saturation Concept. Glob. Change Biol. 2015, 21, 3200–3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Gu, J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Shan, C.; Shen, F. The Effects of Postfire Regeneration Patterns on Soil Microbial Metabolic Limitation Based on Eco-Enzyme Stoichiometry in the Boreal Forest of China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2024, 568, 122129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, F.; Zhong, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yang, C.; Gai, X. Bamboo—An Untapped Plant Resource for the Phytoremediation of Heavy Metal Contaminated Soils. Chemosphere 2019, 246, 125750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, C.; Jin, Y.; Sun, Z. Impacts of Thinning on Soil Carbon and Nutrients and Related Extracellular Enzymes in a Larch Plantation. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 450, 117523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, L.; Lin, W. Calla Lily Intercropping in Rubber Tree Plantations Changes the Nutrient Content, Microbial Abundance, and Enzyme Activity of Both Rhizosphere and Non-Rhizosphere Soil and Calla Lily Growth. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 132, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulis, V.; Kuehn, K.A.; Schoettle, L.N.; Leach, D.; Benstead, J.P.; Rosemond, A.D. Changes in Nutrient Stoichiometry, Elemental Homeostasis and Growth Rate of Aquatic Litter-Associated Fungi in Response to Inorganic Nutrient Supply. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2729–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanin, N.; Fromin, N.; Buatois, B.; Hättenschwiler, S. An Experimental Test of the Hypothesis of Non-homeostatic Consumer Stoichiometry in a Plant Litter–Microbe System. Ecol. Lett. 2013, 16, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Bai, E.; Wang, S.; Zong, S.; Liu, Z.; Fan, X.; Zhao, C.; Hagedorn, F. Three-dimensional Mapping of Carbon, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus in Soil Microbial Biomass and Their Stoichiometry at the Global Scale. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 6728–6740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Lauber, C.L.; Weintraub, M.N.; Ahmed, B.; Allison, S.D.; Crenshaw, C.; Contosta, A.R.; Cusack, D.; Frey, S.; Gallo, M.E.; et al. Stoichiometry of Soil Enzyme Activity at Global Scale. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, X.; Zhong, Z.; Zhang, X.; Bian, F.; Yang, C. Effects of Chicken Farming on Soil Organic Carbon Fractions and Fungal Communities in a Lei Bamboo (Phyllostachys Praecox) Forest in Subtropical China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2020, 479, 118603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spohn, M.; Pötsch, E.M.; Eichorst, S.A.; Woebken, D.; Wanek, W.; Richter, A. Soil Microbial Carbon Use Efficiency and Biomass Turnover in a Long-Term Fertilization Experiment in a Temperate Grassland. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 97, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, S.D.; Vitousek, P.M. Responses of Extracellular Enzymes to Simple and Complex Nutrient Inputs. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeler, B.L.; Hobbie, S.E.; Kellogg, L.E. Effects of Long-Term Nitrogen Addition on Microbial Enzyme Activity in Eight Forested and Grassland Sites: Implications for Litter and Soil Organic Matter Decomposition. Ecosystems 2008, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binkley, D.; Stape, J.L.; Bauerle, W.L.; Ryan, M.G. Explaining Growth of Individual Trees: Light Interception and Efficiency of Light Use by Eucalyptus at Four Sites in Brazil. For. Ecol. Manag. 2009, 259, 1704–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liang, C.; Shao, S.; Chen, J.; Qin, H.; Xu, Q. Linkages of Litter and Soil C:N:P Stoichiometry with Soil Microbial Resource Limitation and Community Structure in a Subtropical Broadleaf Forest Invaded by Moso Bamboo. Plant Soil 2021, 465, 473–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoni, S.; Taylor, P.; Richter, A.; Porporato, A.; Ågren, G.I. Environmental and Stoichiometric Controls on Microbial Carbon-use Efficiency in Soils. New Phytol. 2012, 196, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zheng, M.; Mao, Q.; Xiao, K.; Wang, K.; Li, D. Cropland Conversion Changes the Status of Microbial Resource Limitation in Degraded Karst Soil. Geoderma 2019, 352, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicol, G.W.; Leininger, S.; Schleper, C.; Prosser, J.I. The Influence of Soil pH on the Diversity, Abundance and Transcriptional Activity of Ammonia Oxidizing Archaea and Bacteria. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 2966–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S.; Keiblinger, K.M.; Mooshammer, M.; Peñuelas, J.; Richter, A.; Sardans, J.; Wanek, W. The Application of Ecological Stoichiometry to Plant–Microbial–Soil Organic Matter Transformations. Ecol. Monogr. 2015, 85, 133–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, B.L. Vegetation Drives Soil Microbial Metabolic Limitation through Modifications of Soil Properties and Microbial Biomass during Desert Grassland-Shrubland State Anthropogenic Transition. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 202, 105609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Hu, J.; Peng, S.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Moorhead, D.L.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Xu, X.; Geyer, K.M.; Fang, L.; Smith, P.; et al. Limiting Resources Define the Global Pattern of Soil Microbial Carbon Use Efficiency. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2308176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.; Fu, R.; Nottingham, A.T.; Domeignoz-Horta, L.A.; Yang, X.; Du, H.; Wang, K.; Li, D. Tree Species Diversity Increases Soil Microbial Carbon Use Efficiency in a Subtropical Forest. Glob. Change Biol. 2023, 29, 7131–7144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Schimel, J.P.; Jastrow, J.D. The Importance of Anabolism in Microbial Control over Soil Carbon Storage. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, G.; Zhao, B.; Cong, N.; Zhu, J.; Zheng, Z.; Wu, W.; Duan, X. Excessive Climate Warming Exacerbates Nitrogen Limitation on Microbial Metabolism in an Alpine Meadow of the Tibetan Plateau: Evidence from Soil Ecoenzymatic Stoichiometry. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 930, 172731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.A.; Puissant, J.; Goodall, T.; Allison, S.D.; Griffiths, R.I. Soil Microbial Communities with Greater Investment in Resource Acquisition Have Lower Growth Yield. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 132, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Lu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Dijkstra, F.A. Carbon Efficiency for Nutrient Acquisition (CENA) by Plants: Role of Nutrient Availability and Microbial Symbionts. Plant Soil 2022, 476, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Cavagnaro, T.R.; Jiang, Y.; Keitel, C.; Dijkstra, F.A. Carbon Allocation to the Rhizosphere Is Affected by Drought and Nitrogen Addition. J. Ecol. 2021, 109, 3699–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.; Prentice, I.C.; Wright, I.J.; Wang, H.; Atkin, O.K.; Bloomfield, K.J.; Domingues, T.F.; Gleason, S.M.; Maire, V.; Onoda, Y.; et al. Leaf Nitrogen from the Perspective of Optimal Plant Function. J. Ecol. 2022, 110, 2585–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; He, N.; Liu, C.; Xu, L.; Chen, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Yu, G.; Sun, W.; Xiao, C.; et al. Variation and Evolution of C:N Ratio among Different Organs Enable Plants to Adapt to N-limited Environments. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2020, 26, 2534–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Shrestha, A.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, J.; Yu, F.; Wang, G. How Lignin Biosynthesis Responds to Nitrogen in Plants: A Scoping Review. Plant Biol. J. 2024, 26, 881–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ning, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, A.; Wu, Q.; Yu, Q.; Huang, K.; Bi, Y.; Du, X. Response of Soil Enzyme and Plant Stoichiometry to Root Interactions: Insights from Mixed Plantings of Moso Bamboo. Forests 2025, 16, 722. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16050722
Ning Y, Zhang J, Wang A, Wu Q, Yu Q, Huang K, Bi Y, Du X. Response of Soil Enzyme and Plant Stoichiometry to Root Interactions: Insights from Mixed Plantings of Moso Bamboo. Forests. 2025; 16(5):722. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16050722
Chicago/Turabian StyleNing, Yilin, Jie Zhang, Anke Wang, Qifeng Wu, Qunfang Yu, Kaiwen Huang, Yufang Bi, and Xuhua Du. 2025. "Response of Soil Enzyme and Plant Stoichiometry to Root Interactions: Insights from Mixed Plantings of Moso Bamboo" Forests 16, no. 5: 722. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16050722
APA StyleNing, Y., Zhang, J., Wang, A., Wu, Q., Yu, Q., Huang, K., Bi, Y., & Du, X. (2025). Response of Soil Enzyme and Plant Stoichiometry to Root Interactions: Insights from Mixed Plantings of Moso Bamboo. Forests, 16(5), 722. https://doi.org/10.3390/f16050722





