Canis Familiaris Papillomavirus Type 26: A Novel Papillomavirus of Dogs and the First Canine Papillomavirus within the Omegapapillomavirus Genus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
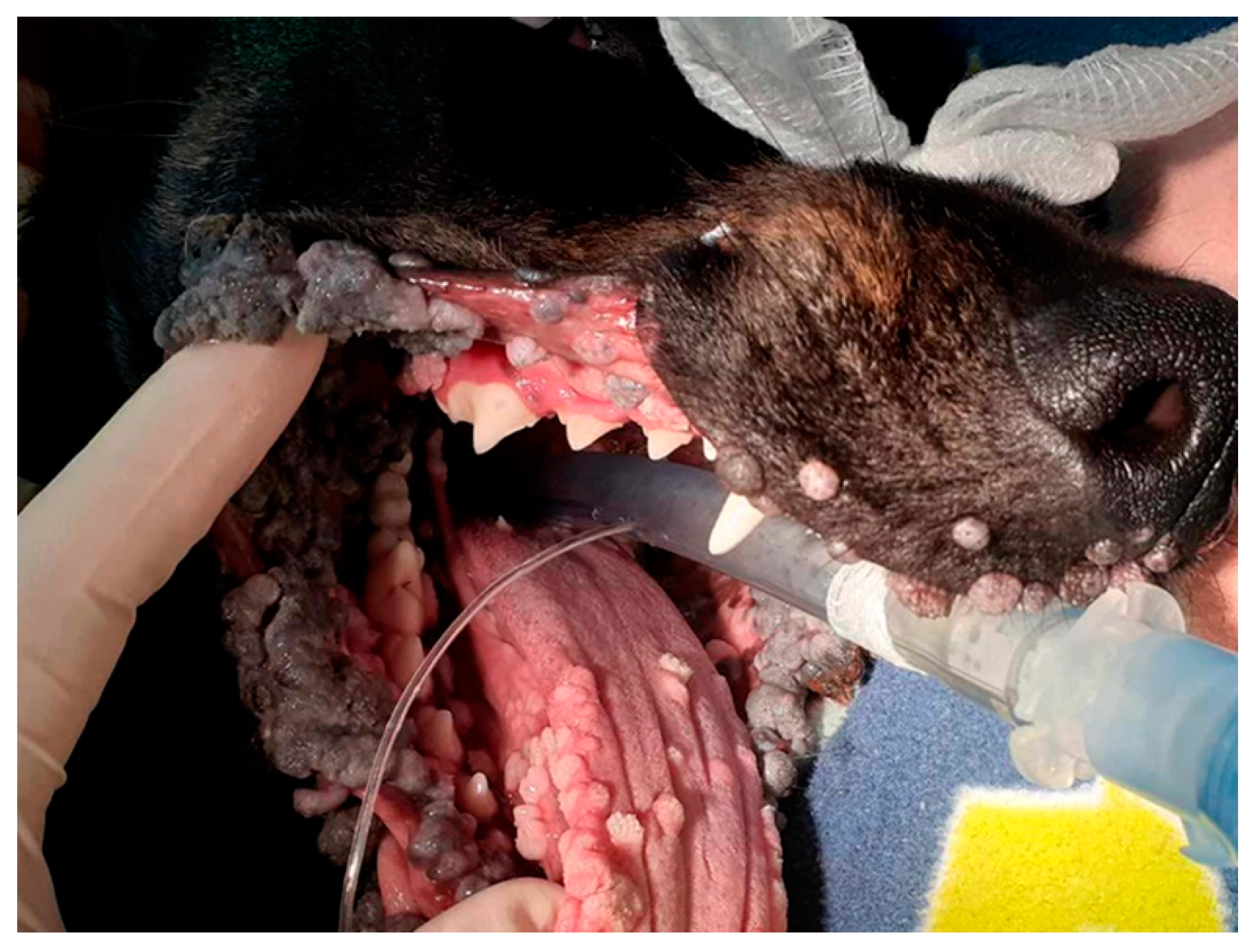
2.1. Initial Case Summary, Sample Collection, PCR, and DNA Sequencing
2.2. Complete Genome Sequencing of the Novel PV
2.3. DNA and Protein Sequence Analysis
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Detection of CPV26 in Other Canine Papillomas and Squamous Cell Carcinomas
3. Results
3.1. Histology and Initial PCR and DNA Sequencing
3.2. CPV26 Complete Gene Sequence
3.3. Open Reading Frame Organization of CPV26 Genes
3.4. Phylogenetic Analysis of CPV26
3.5. CPV26 Sequence Similarity to Other Papillomaviruses
3.6. Detection of CPV26 in Other Canine Lesions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Doorbar, J.; Quint, W.; Banks, L.; Bravo, I.G.; Stoler, M.; Broker, T.R.; Stanley, M.A. The biology and life-cycle of human papillomaviruses. Vaccine 2012, 30 (Suppl. S5), F55–F70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, C.E.; Zollinger, S.; Tobler, K.; Ackermann, M.; Favrot, C. Clinically healthy skin of dogs is a potential reservoir for canine papillomaviruses. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 707–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munday, J.S.; Knight, C.G.; Luff, J.A. Papillomaviral skin diseases of humans, dogs, cats and horses: A comparative review. Part 1: Papillomavirus biology and hyperplastic lesions. Vet. J. 2022, 288, 105897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munday, J.S.; Knight, C.G.; Luff, J.A. Papillomaviral skin diseases of humans, dogs, cats and horses: A comparative review. Part 2: Pre-neoplastic and neoplastic diseases. Vet. J. 2022, 288, 105898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, A.P.; Coyner, K.S.; Trimmer, A.M.; Tater, K.; Rishniw, M. Canine pedal papilloma identification and management: A retrospective series of 44 cases. Vet. Dermatol. 2021, 32, 509-e141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, H.E.; Weese, J.S.; Stull, J.W. Canine oral papillomavirus outbreak at a dog daycare facility. Can. Vet. J. 2017, 58, 747–749. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Munday, J.S.; Thomson, N.A.; Luff, J.A. Papillomaviruses in dogs and cats. Vet. J. 2017, 225, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sancak, A.; Favrot, C.; Geisseler, M.D.; Muller, M.; Lange, C.E. Antibody titres against canine papillomavirus 1 peak around clinical regression in naturally occurring oral papillomatosis. Vet. Dermatol. 2015, 26, 57-e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regalado Ibarra, A.M.; Legendre, L.; Munday, J.S. Malignant transformation of a canine papillomavirus type 1-induced persistent oral papilloma in a 3-year-old dog. J. Vet. Dent. 2018, 35, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luff, J.A.; Affolter, V.K.; Yeargan, B.; Moore, P.F. Detection of six novel papillomavirus sequences within canine pigmented plaques. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2012, 24, 576–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munday, J.S.; Orbell, G.; Robinson, L. Detection of a novel papillomaviral sequence in viral plaques confined to the pinna of a dog. Vet. Dermatol. 2023, 34, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munday, J.S.; Lam, A.T.H.; Sakai, M. Extensive progressive pigmented viral plaques in a Chihuahua dog. Vet. Dermatol. 2022, 33, 252–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokking, L.B.; Ehrhart, E.J.; Lichtensteiger, C.A.; Campbell, K.L. Pigmented epidermal plaques in three dogs. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2004, 40, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luff, J.; Rowland, P.; Mader, M.; Orr, C.; Yuan, H. Two canine papillomaviruses associated with metastatic squamous cell carcinoma in two related Basenji dogs. Vet. Pathol. 2016, 53, 1160–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munday, J.S.; Dunowska, M.; Laurie, R.E.; Hills, S. Genomic characterisation of canine papillomavirus type 17, a possible rare cause of canine oral squamous cell carcinoma. Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 182, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luff, J.; Mader, M.; Rowland, P.; Britton, M.; Fass, J.; Yuan, H. Viral genome integration of canine papillomavirus 16. Papillomavirus Res. 2019, 7, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, H.U.; Burk, R.D.; Chen, Z.; van Doorslaer, K.; Hausen, H.; de Villiers, E.M. Classification of papillomaviruses (PVs) based on 189 PV types and proposal of taxonomic amendments. Virology 2010, 401, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rector, A.; Van Ranst, M. Animal papillomaviruses. Virology 2013, 445, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munday, J.S.; Gedye, K.; Knox, M.A.; Robinson, L.; Lin, X. Genomic characterization of Canis familiaris papillomavirus type 25, a novel papillomavirus associated with a viral plaque from the pinna of a dog. Animals 2023, 13, 1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, C.E.; Jennings, S.H.; Diallo, A.; Lyons, J. Canine papillomavirus types 1 and 2 in classical papillomas: High abundance, different morphological associations and frequent co-infections. Vet. J. 2019, 250, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maglennon, G.A.; McIntosh, P.; Doorbar, J. Persistence of viral DNA in the epithelial basal layer suggests a model for papillomavirus latency following immune regression. Virology 2011, 414, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doorbar, J. The E4 protein; structure, function and patterns of expression. Virology 2013, 445, 80–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vande Pol, S.B.; Klingelhutz, A.J. Papillomavirus E6 oncoproteins. Virology 2013, 445, 115–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longworth, M.S.; Laimins, L.A. Pathogenesis of human papillomaviruses in differentiating epithelia. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2004, 68, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munday, J.S.; Hardcastle, M.R.; Sim, M. Detection of a putative novel papillomavirus type within a large exophytic papilloma on the fetlock of a horse. Pathogens 2020, 9, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munday, J.S.; Kiupel, M.; French, A.F.; Howe, L.; Squires, R.A. Detection of papillomaviral sequences in feline Bowenoid in situ carcinoma using consensus primers. Vet. Dermatol. 2007, 18, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Misawa, K.; Kuma, K.; Miyata, T. MAFFT: A novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 3059–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenwyk, J.L.; Buida, T.J., 3rd; Li, Y.; Shen, X.X.; Rokas, A. ClipKIT: A multiple sequence alignment trimming software for accurate phylogenomic inference. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3001007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefort, V.; Longueville, J.E.; Gascuel, O. SMS: Smart Model Selection in PhyML. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 2422–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anisimova, M.; Gascuel, O. Approximate likelihood-ratio test for branches: A fast, accurate, and powerful alternative. Syst. Biol. 2006, 55, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, B.; Gao, S.; Lercher, M.J.; Hu, S.; Chen, W.H. Evolview v3: A webserver for visualization, annotation, and management of phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W270–W275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Zou, N.; Lin, B.Y.; Chow, L.T.; Harper, J.W. Interaction between cyclin-dependent kinases and human papillomavirus replication-initiation protein E1 is required for efficient viral replication. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Doorslaer, K.; Rector, A.; Jenson, A.B.; Sundberg, J.P.; Van Ranst, M.; Ghim, S.J. Complete genomic characterization of a murine papillomavirus isolated from papillomatous lesions of a European harvest mouse (Micromys minutus). J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 1484–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Net, J.L.; Orth, G.; Sundberg, J.P.; Cassonnet, P.; Poisson, L.; Masson, M.T.; George, C.; Longeart, L. Multiple pigmented cutaneous papules associated with a novel canine papillomavirus in an immunosuppressed dog. Vet. Pathol. 1997, 34, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Yang, S.; Shan, T.; Hou, R.; Liu, Z.; Li, W.; Guo, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, P.; Wang, X.; et al. Virome comparisons in wild-diseased and healthy captive giant pandas. Microbiome 2017, 5, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smeele, Z.E.; Burns, J.M.; Van Doorsaler, K.; Fontenele, R.S.; Waits, K.; Stainton, D.; Shero, M.R.; Beltran, R.S.; Kirkham, A.L.; Berngartt, R.; et al. Diverse papillomaviruses identified in Weddell seals. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, H.; Rector, A.; Bertelsen, M.F.; Leifsson, P.S.; Van Ranst, M. Novel papillomavirus isolated from the oral mucosa of a polar bear does not cluster with other papillomaviruses of carnivores. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 129, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Long, T.; Wong, P.Y.; Ho, W.C.S.; Burk, R.D.; Chan, P.K.S. Non-human primate papillomaviruses share similar evolutionary histories and niche adaptation as the human counterparts. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, J.J.; Finarelli, J.A.; Zehr, S.; Hsu, J.; Nedbal, M.A. Molecular phylogeny of the carnivora (mammalia): Assessing the impact of increased sampling on resolving enigmatic relationships. Syst. Biol. 2005, 54, 317–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, J.A.; Hauton, C.; Bennett, K.A.; Hall, A.J. Phocid seal leptin: Tertiary structure and hydrophobic receptor binding site preservation during distinct leptin gene evolution. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman, A.; Munger, K. The papillomavirus E7 proteins. Virology 2013, 445, 138–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paver, E.C.; Currie, A.M.; Gupta, R.; Dahlstrom, J.E. Human papilloma virus related squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck: Diagnosis, clinical implications and detection of HPV. Pathology 2020, 52, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munday, J.S.; Aberdein, D. Loss of retinoblastoma protein, but not p53, is associated with the presence of papillomaviral DNA in feline viral plaques, Bowenoid in situ carcinomas, and squamous cell carcinomas. Vet. Pathol. 2012, 49, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petti, L.M.; Ricciardi, E.C.; Page, H.J.; Porter, K.A. Transforming signals resulting from sustained activation of the PDGFbeta receptor in mortal human fibroblasts. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 1172–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| ORF | ORF Location | Length (nt) | Length (aa) | Molecular Mass (kDa) | pI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E1 | 554–2428 | 1875 | 624 | 70.33 | 4.81 |
| E2 | 2493–3725 | 1233 | 410 | 46.15 | 9.08 |
| E4 | 2851–3498 | 648 | 215 | 23.72 | 8.91 |
| E6 | 1–423 | 423 | 140 | 16.61 | 7.66 |
| L1 | 5447–6961 | 1515 | 504 | 57.00 | 7.09 |
| L2 | 4003–5466 | 1464 | 487 | 51.21 | 6.85 |
| Papillomavirus | Host Species | Classification | L1 Similarity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ailuropoda melanoleuca papillomavirus 1 (NC_035201) | Giant Panda | Omegapapillomavirus | 72.2 |
| Leptonychotes weddellii papillomavirus 6 (NC_040818) | Weddel fur seal | Omegapapillomavirus | 70.0 |
| Arctocephalus gazella papillomavirus 2 (OR113680) | Antarctic fur seal | Omegapapillomavirus | 69.2 |
| Ursus maritimus Papillomavirus 1 (EF536349) | Polar Bear | Omegapapillomavirus | 69.0 |
| Hydrurga leptonyx papillomavirus 1 (OR113678) | Leopard seal | Omegapapillomavirus | 66.8 |
| Macaca mulata papillomavirus 1 (M60184) | Rhesus macaque | Alphapapillomavrius | 63.8 |
| Canine familiaris papillomavirus 1 (D55633) | Domestic dog | Lambdapapillomavirus | 61.6 |
| Canine familiaris papillomavirus 10 (JF800657) | Domestic dog | Chipapillomavirus | 61.6 |
| Canine familiaris papillomavirus 7 (FJ492742) | Domestic dog | Taupapillomavirus | 60.6 |
| Lesion | CPV1 Only | CPV2 Only | CPV6 Only | CPV6 and 26 | No CPV DNA | Total Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oral papilloma | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Oral SCC | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 21 | 21 |
| Cutaneous papilloma | 6 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 9 |
| Cutaneous SCC | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 6 |
| All lesions | 9 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 25 | 37 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Munday, J.S.; Bond, S.D.; Piripi, S.; Soulsby, S.J.; Knox, M.A. Canis Familiaris Papillomavirus Type 26: A Novel Papillomavirus of Dogs and the First Canine Papillomavirus within the Omegapapillomavirus Genus. Viruses 2024, 16, 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16040595
Munday JS, Bond SD, Piripi S, Soulsby SJ, Knox MA. Canis Familiaris Papillomavirus Type 26: A Novel Papillomavirus of Dogs and the First Canine Papillomavirus within the Omegapapillomavirus Genus. Viruses. 2024; 16(4):595. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16040595
Chicago/Turabian StyleMunday, John S., Sarah D. Bond, Susan Piripi, Susannah J. Soulsby, and Matthew A. Knox. 2024. "Canis Familiaris Papillomavirus Type 26: A Novel Papillomavirus of Dogs and the First Canine Papillomavirus within the Omegapapillomavirus Genus" Viruses 16, no. 4: 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16040595
APA StyleMunday, J. S., Bond, S. D., Piripi, S., Soulsby, S. J., & Knox, M. A. (2024). Canis Familiaris Papillomavirus Type 26: A Novel Papillomavirus of Dogs and the First Canine Papillomavirus within the Omegapapillomavirus Genus. Viruses, 16(4), 595. https://doi.org/10.3390/v16040595






