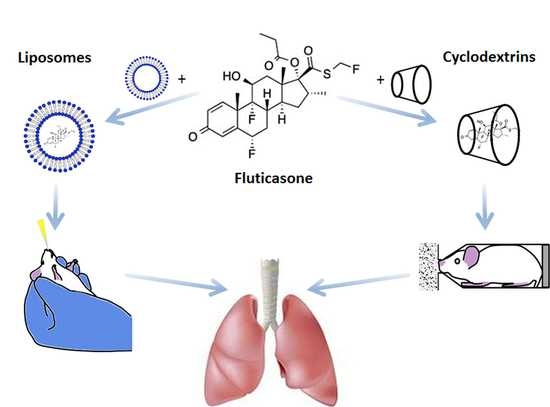
Pharmaceutical Benefits of Fluticasone Propionate Association to Delivery Systems: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation
Abstract
Share and Cite
Dogbe, M.G.; Mafilaza, A.Y.; Eleutério, C.V.; Cabral-Marques, H.; Simões, S.; Gaspar, M.M. Pharmaceutical Benefits of Fluticasone Propionate Association to Delivery Systems: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11100521
Dogbe MG, Mafilaza AY, Eleutério CV, Cabral-Marques H, Simões S, Gaspar MM. Pharmaceutical Benefits of Fluticasone Propionate Association to Delivery Systems: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(10):521. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11100521
Chicago/Turabian StyleDogbe, Marina G., Ambinintsoa Yattussia Mafilaza, Carla Vânia Eleutério, Helena Cabral-Marques, Sandra Simões, and Maria Manuela Gaspar. 2019. "Pharmaceutical Benefits of Fluticasone Propionate Association to Delivery Systems: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 10: 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11100521
APA StyleDogbe, M. G., Mafilaza, A. Y., Eleutério, C. V., Cabral-Marques, H., Simões, S., & Gaspar, M. M. (2019). Pharmaceutical Benefits of Fluticasone Propionate Association to Delivery Systems: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation. Pharmaceutics, 11(10), 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11100521