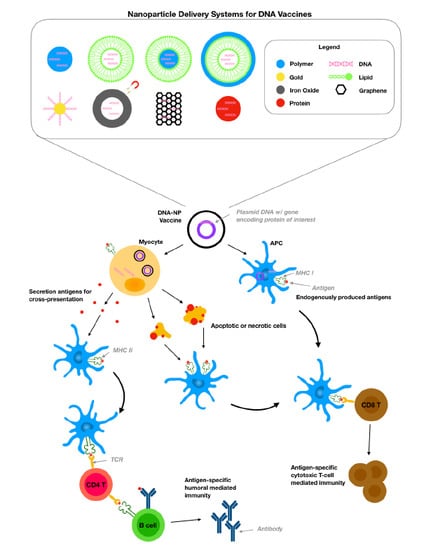
Engineered Nanodelivery Systems to Improve DNA Vaccine Technologies
Abstract
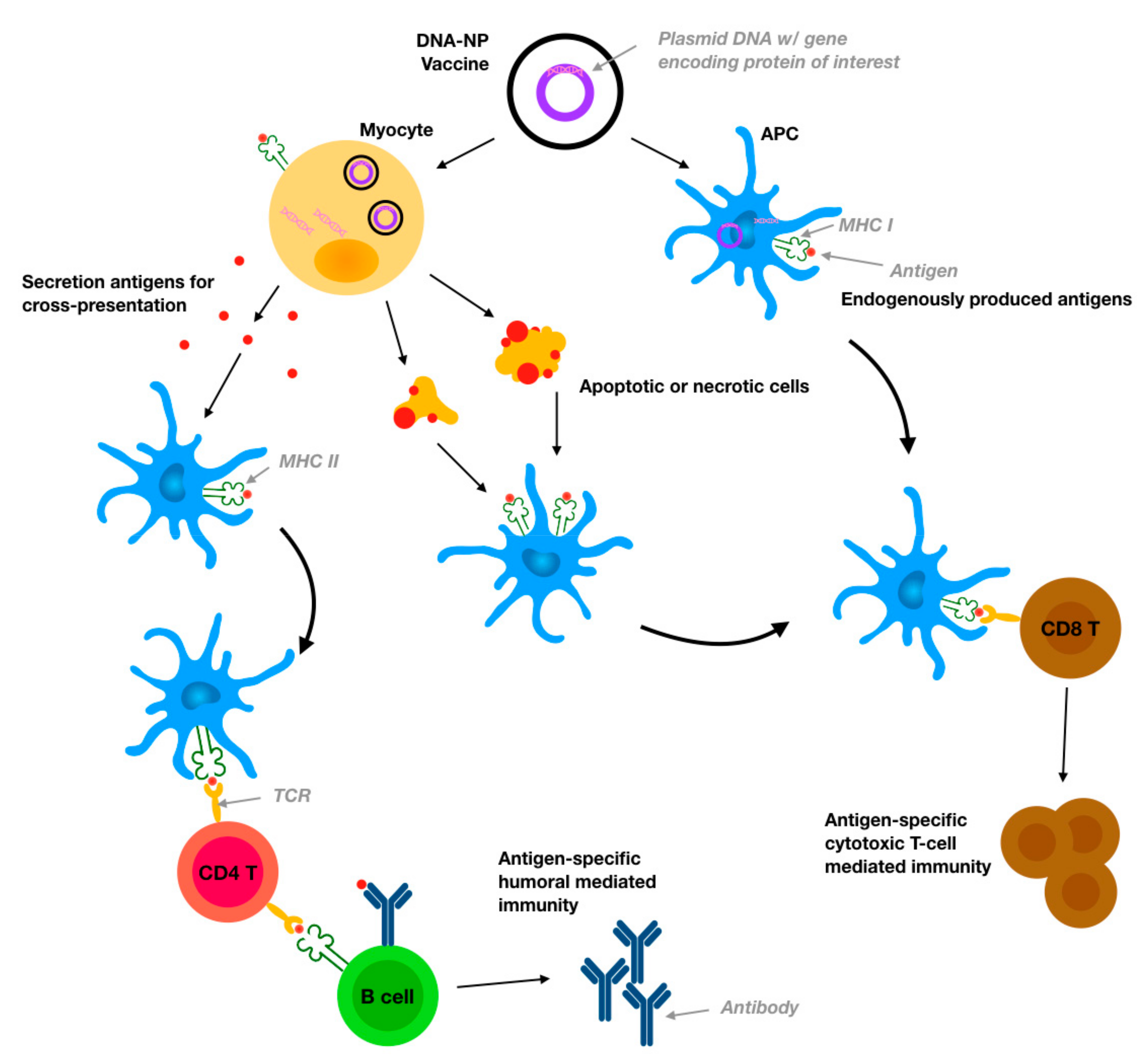
:1. Introduction
2. Challenges Associated with DNA Vaccines
3. Methods to Address Challenges of DNA Vaccine Delivery
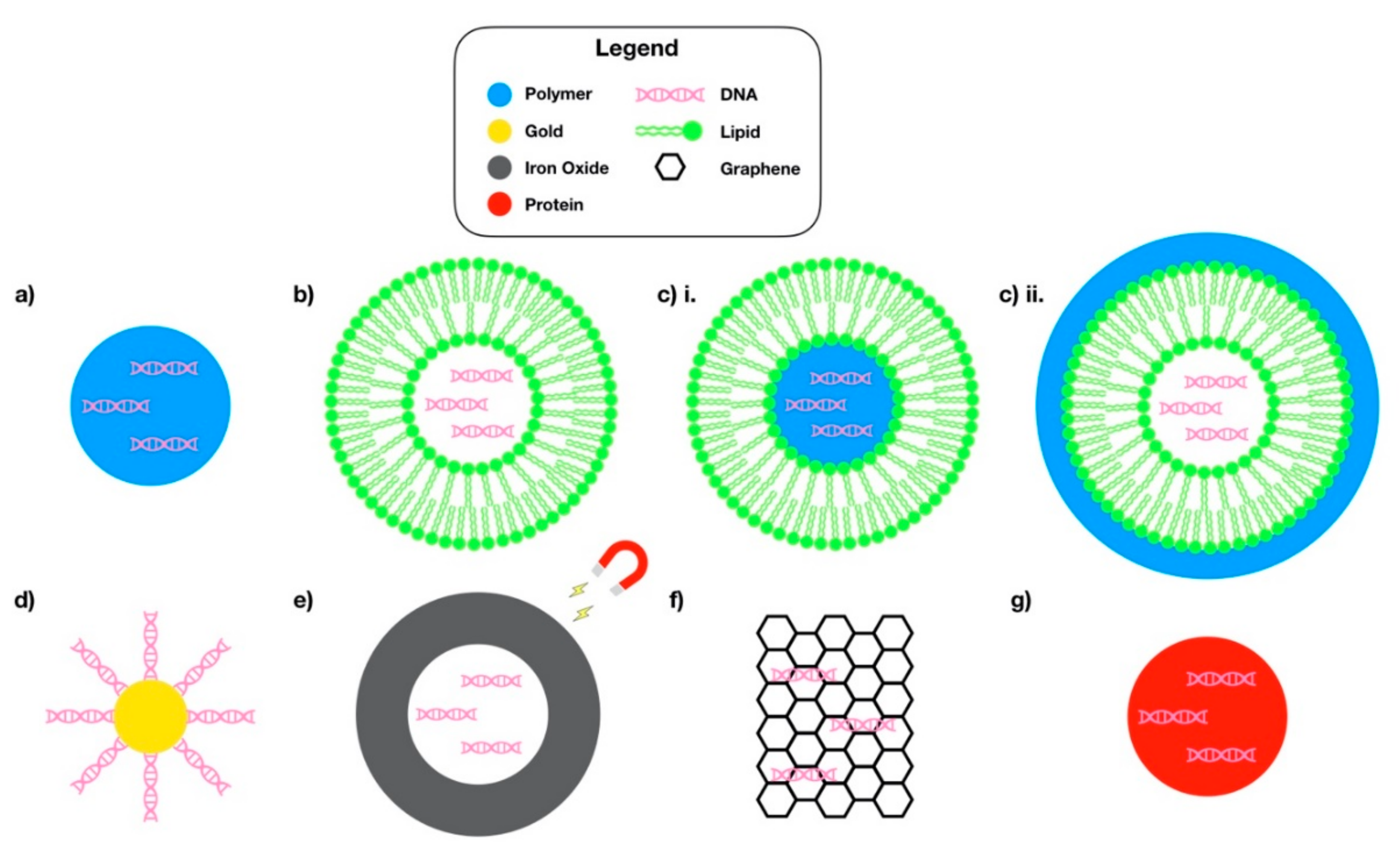
4. Nanotechnologies to Tackle Delivery Challenges of DNA Vaccine
4.1. Polymer Nanoparticles.
4.2. Lipid Nanoparticles
4.3. Hybrid Lipid-Polymer Nanoparticles
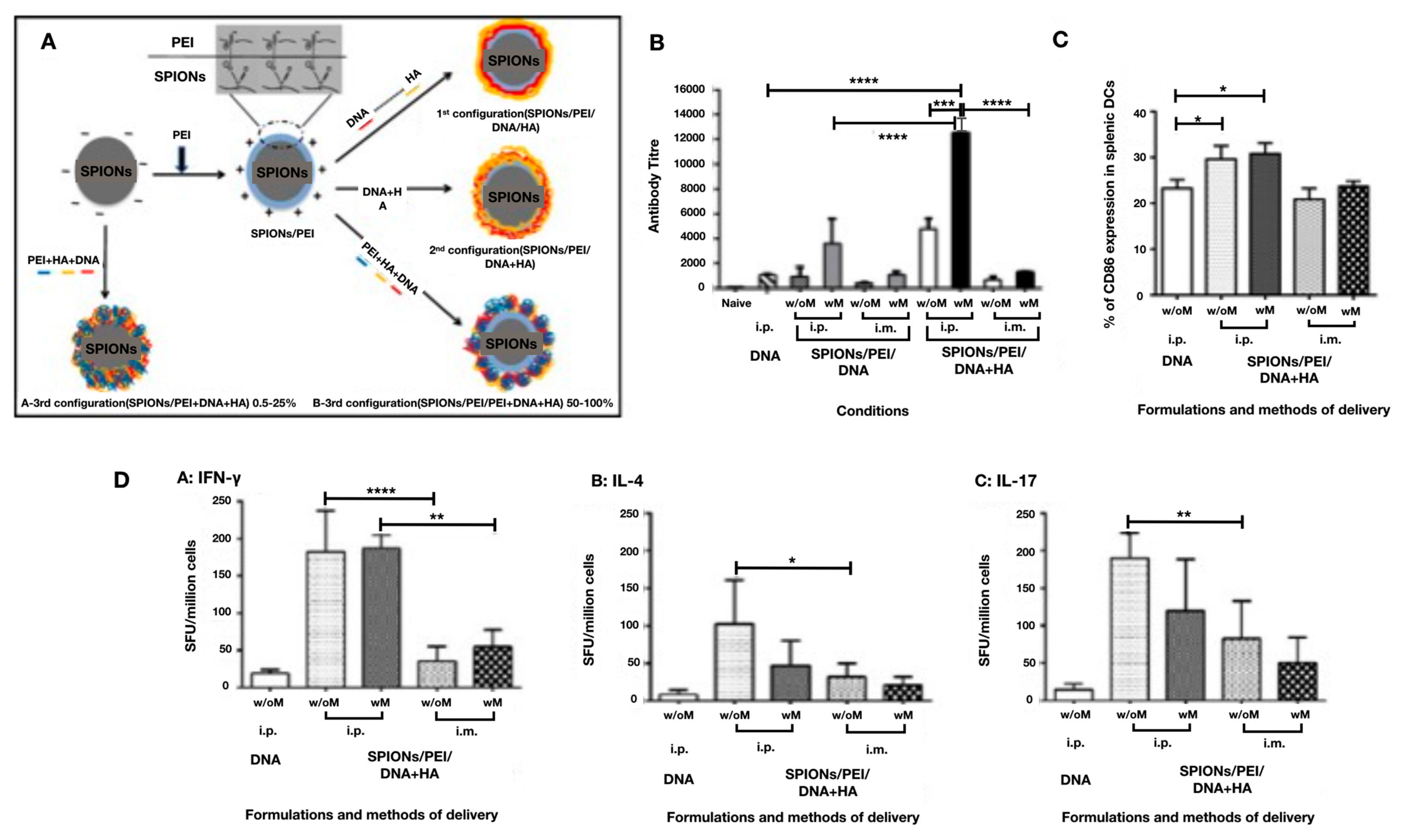
4.4. Inorganic Nanoparticles
4.5. Virus-Like Particles
4.6. Protein-Based Nanoparticles
5. Clinical Trials on DNA Vaccine Technology
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Plotkin, S. History of vaccination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 12283–12287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kutzler, M.A.; Weiner, D.B. DNA vaccines: Ready for prime time? Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plotkin, S.A. Vaccines: Past, present and future. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karch, C.P.; Burkhard, P. Vaccine technologies: From whole organisms to rationally designed protein assemblies. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 120, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Hong, Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, C. Polymers for DNA vaccine delivery. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 3, 108–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobernik, D.; Bros, M. DNA vaccines—how far from clinical use? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suschak, J.J.; Williams, J.A.; Schmaljohn, C.S. Advancements in DNA vaccine vectors, non-mechanical delivery methods, and molecular adjuvants to increase immunogenicity. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2017, 13, 2837–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Putnam, D. Polymers for gene delivery across length scales. Nat. Mater. 2006, 5, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexis, F.; Pridgen, E.; Molnar, L.K.; Farokhzad, O.C. Factors affecting the clearance and biodistribution of polymeric nanoparticles. Mol. Pharm. 2008, 5, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibraheem, D.; Elaissari, A.; Fessi, H. Gene therapy and DNA delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 459, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambricht, L.; Lopes, A.; Kos, S.; Sersa, G.; Préat, V.; Vandermeulen, G. Clinical potential of electroporation for gene therapy and DNA vaccine delivery. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sardesai, N.Y.; Weiner, D.B. Electroporation delivery of DNA vaccines: Prospects for success. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2011, 23, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ravi, A.D.; Sadhna, D.; Nagpaal, D.; Chawla, L. Needle free injection technology: A complete insight. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2015, 5, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kale, T.R.; Momin, M. Needle free injection technology-An overview. Innov. Pharm. 2014, 5, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goudy, K.S.; Wang, B.; Tisch, R. Gene gun-mediated DNA vaccination enhances antigen-specific immunotherapy at a late preclinical stage of type 1 diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 129, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jinturkar, K.A.; Rathi, M.N.; Misra, A. Gene delivery using physical methods. In Challenges in Delivery of Therapeutic Genomics and Proteomics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 83–126. [Google Scholar]
- Lukashev, A.; Zamyatnin, A. Viral vectors for gene therapy: Current state and clinical perspectives. Biochemistry 2016, 81, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.A.A.; He, N.; Li, Z.; Ali, Z.; Zhang, L. Nanoparticles for DNA vaccine delivery. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2014, 10, 2332–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCluskie, M.J.; Millan, C.L.B.; Gramzinski, R.A.; Robinson, H.L.; Santoro, J.C.; Fuller, J.T.; Widera, G.; Haynes, J.R.; Purcell, R.H.; Davis, H.L. Route and method of delivery of DNA vaccine influence immune responses in mice and non-human primates. Mol. Med. 1999, 5, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Nguyen, M.T. Recent advances of vaccine adjuvants for infectious diseases. Immune Netw. 2015, 15, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramamoorth, M.; Narvekar, A. Non viral vectors in gene therapy-an overview. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2015, 9, GE01–GE06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.N.; Green, J.J.; Chan, J.M.; Langer, R.; Anderson, D.G. Polymeric materials for gene delivery and DNA vaccination. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 847–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, S.T.; Swartz, M.A.; Hubbell, J.A. Targeting dendritic cells with biomaterials: Developing the next generation of vaccines. Trends Immunol. 2006, 27, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, S.T.; Van Der Vlies, A.J.; Simeoni, E.; Angeli, V.; Randolph, G.J.; O’Neil, C.P.; Lee, L.K.; Swartz, M.A.; Hubbell, J.A. Exploiting lymphatic transport and complement activation in nanoparticle vaccines. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alpar, H.O.; Somavarapu, S.; Atuah, K.; Bramwell, V. Biodegradable mucoadhesive particulates for nasal and pulmonary antigen and DNA delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 411–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Seth, A.; Wibowo, N.; Zhao, C.-X.; Mitter, N.; Yu, C.; Middelberg, A.P. Nanoparticle vaccines. Vaccine 2014, 32, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, S.J.; Ahn, M.H.; Lee, Y.W.; Pal, S.; Sangshetti, J.; Arote, R.B. Biodegradable Polymeric Nanocarrier-Based Immunotherapy in Hepatitis Vaccination. In Cutting-Edge Enabling Technologies for Regenerative Medicine; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 303–320. [Google Scholar]
- Shae, D.; Postma, A.; Wilson, J.T. Vaccine delivery: Where polymer chemistry meets immunology. Future Sci. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia-Fuentes, M.; Alonso, M.J. Chitosan-based drug nanocarriers: Where do we stand? J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschmann, M.D.; Merzouki, A.; Lavertu, M.; Thibault, M.; Jean, M.; Darras, V. Chitosans for delivery of nucleic acids. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1234–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.N.R. A review of chitin and chitosan applications. React. Funct. Polym. 2000, 46, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, E.C.; Jin, L.; Mori, A.; Muñoz-Wolf, N.; Oleszycka, E.; Moran, H.B.; Mansouri, S.; McEntee, C.P.; Lambe, E.; Agger, E.M. The vaccine adjuvant chitosan promotes cellular immunity via DNA sensor cGAS-STING-dependent induction of type I interferons. Immunity 2016, 44, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tahamtan, A.; Ghaemi, A.; Gorji, A.; Kalhor, H.R.; Sajadian, A.; Tabarraei, A.; Moradi, A.; Atyabi, F.; Kelishadi, M. Antitumor effect of therapeutic HPV DNA vaccines with chitosan-based nanodelivery systems. J. Biomed. Sci. 2014, 21, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, D.M.; Lampe, A.T.; Farris, E.; Williams, J.A.; Pannier, A.K. Chitosan nanoparticle delivery of Influenza A Virus DNA vaccine enhances antibody class switching and abrogates weight loss post IAV challenge. Am. Assoc. Immnol. 2017, 198, S1. [Google Scholar]
- Sawaengsak, C.; Mori, Y.; Yamanishi, K.; Srimanote, P.; Chaicumpa, W.; Mitrevej, A.; Sinchaipanid, N. Intranasal chitosan-DNA vaccines that protect across influenza virus subtypes. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 473, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, T.; Yue, Y.; Fan, X.; Dong, C.; Xu, W.; Xiong, S. M cell-targeting strategy facilitates mucosal immune response and enhances protection against CVB3-induced viral myocarditis elicited by chitosan-DNA vaccine. Vaccine 2014, 32, 4457–4465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shi, C.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Jin, Z.; Cui, S. Chitosan-coated poly (lactic-co-glycolic) acid nanoparticles as an efficient delivery system for Newcastle disease virus DNA vaccine. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 4609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Shi, C.; Guo, C.; Dai, C.; Chen, Q.; Jin, Z.; Zhao, Y. Preparation and efficacy of Newcastle disease virus DNA vaccine encapsulated in chitosan nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, K.; Han, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, L.; Yu, S.; Wang, X.; Jin, Z.; Wang, Y. Enhancing Mucosal Immune Response of Newcastle Disease Virus DNA Vaccine Using N-2-Hydroxypropyl Trimethylammonium Chloride Chitosan and N, O-Carboxymethyl Chitosan Nanoparticles as Delivery Carrier. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 15, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Li, S.; Li, W.; Yu, L.; Duan, X.; Han, J.; Wang, X.; Jin, Z. Quaternized chitosan nanoparticles loaded with the combined attenuated live vaccine against Newcastle disease and infectious bronchitis elicit immune response in chicken after intranasal administration. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 1574–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valero, Y.; Awad, E.; Buonocore, F.; Arizcun, M.; Esteban, M.Á.; Meseguer, J.; Chaves-Pozo, E.; Cuesta, A. An oral chitosan DNA vaccine against nodavirus improves transcription of cell-mediated cytotoxicity and interferon genes in the European sea bass juveniles gut and survival upon infection. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2016, 65, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Song, X.; Jing, J.; Zhao, K.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yue, B. Chitosan-DNA nanoparticles enhanced the immunogenicity of multivalent DNA vaccination on mice against Trueperella pyogenes infection. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Layek, B.; Lipp, L.; Singh, J. APC targeted micelle for enhanced intradermal delivery of hepatitis B DNA vaccine. J. Control. Release 2015, 207, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Zhao, H.; Li, M.; Yue, Y.; Xiong, S.; Xu, W. Intranasal vaccination with mannosylated chitosan formulated DNA vaccine enables robust IgA and cellular response induction in the lungs of mice and improves protection against pulmonary mycobacterial challenge. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueter, C.L.; Lee, C.K.; Wang, J.P.; Ostroff, G.R.; Specht, C.A.; Levitz, S.M. Spectrum and mechanisms of inflammasome activation by chitosan. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 5943–5951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Yin, Z.; Liu, N.; Yang, T.; Wang, J.; Bu, Z.; Wu, D. DNA–chitosan nanoparticles improve DNA vaccine-elicited immunity against Newcastle disease virus through shuttling chicken interleukin-2 gene. J. Microencapsul. 2010, 27, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebre, F.; Borchard, G.; Faneca, H.; Pedroso de Lima, M.; Borges, O. Intranasal administration of novel chitosan nanoparticle/DNA complexes induces antibody response to hepatitis B surface antigen in mice. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 472–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chereddy, K.K.; Vandermeulen, G.; Préat, V. PLGA based drug delivery systems: Promising carriers for wound healing activity. Wound Repair Regen. 2016, 24, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makadia, H.K.; Siegel, S.J. Poly lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) as biodegradable controlled drug delivery carrier. Polymers 2011, 3, 1377–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Li, W.; Huang, T.; Luo, X.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, C.; Dai, C.; Jin, Z.; Zhao, Y. Preparation and efficacy of Newcastle disease virus DNA vaccine encapsulated in PLGA nanoparticles. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Pan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lü, J.; Zhou, P.; Fang, Y.; Jiang, S. Intranasal delivery of cationic PLGA nano/microparticles-loaded FMDV DNA vaccine encoding IL-6 elicited protective immunity against FMDV challenge. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.P.; Ke, H.; Liang, Z.L.; Ma, J.Y.; Hao, L.; Liu, Z.X. Protective efficacy of cationic-PLGA microspheres loaded with DNA vaccine encoding the sip gene of Streptococcus agalactiae in tilapia. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 66, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bivas-Benita, M.; Lin, M.Y.; Bal, S.M.; van Meijgaarden, K.E.; Franken, K.L.; Friggen, A.H.; Junginger, H.E.; Borchard, G.; Klein, M.R.; Ottenhoff, T.H. Pulmonary delivery of DNA encoding Mycobacterium tuberculosis latency antigen Rv1733c associated to PLGA–PEI nanoparticles enhances T cell responses in a DNA prime/protein boost vaccination regimen in mice. Vaccine 2009, 27, 4010–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babaei, M.; Eshghi, H.; Abnous, K.; Rahimizadeh, M.; Ramezani, M. Promising gene delivery system based on polyethylenimine-modified silica nanoparticles. Cancer Gene Ther. 2017, 24, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayanathan, V.; Thomas, T.; Thomas, T. DNA nanoparticles and development of DNA delivery vehicles for gene therapy. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 14085–14094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Shen, G.; Zhu, J.; Tao, J. Polyethylenimine-based micro/nanoparticles as vaccine adjuvants. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 5443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Torrieri-Dramard, L.; Lambrecht, B.; Ferreira, H.L.; Van den Berg, T.; Klatzmann, D.; Bellier, B. Intranasal DNA vaccination induces potent mucosal and systemic immune responses and cross-protective immunity against influenza viruses. Mol. Ther. 2011, 19, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, Q.; Wu, M.; Fang, C.; Cheng, C.; Zhao, M.; Fang, W.; Chu, P.K.; Ping, Y.; Tang, G. Engineering nanoparticle-coated bacteria as oral DNA vaccines for cancer immunotherapy. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 2732–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Xu, B.; Xu, J.; Shou, D.; Liu, E.; Gao, J.; Liang, W.; Huang, Y. Microneedle-assisted dendritic cell-targeted nanoparticles for transcutaneous DNA immunization. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Xu, B.; Ji, Q.; Shou, D.; Sun, X.; Xu, J.; Gao, J.; Liang, W. A mannosylated cell-penetrating peptide-graft-polyethylenimine as a gene delivery vector. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 4236–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.W.; Lee, M.S.; Kim, K.R.; Lee, J.E.; Lee, K.; Park, J.S.; Matsumoto, Y.; Jo, D.G.; Lee, H.; Lee, D.S. Polyplex-releasing microneedles for enhanced cutaneous delivery of DNA vaccine. J. Control. Release 2014, 179, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, H.; Noh, J.Y.; Lee, D.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Song, C.S.; Kim, Y.C. Effective humoral immune response from a H1N1 DNA vaccine delivered to the skin by microneedles coated with PLGA-based cationic nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2017, 265, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suk, J.S.; Xu, Q.; Kim, N.; Hanes, J.; Ensign, L.M. PEGylation as a strategy for improving nanoparticle-based drug and gene delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 99, 28–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pack, D.W.; Hoffman, A.S.; Pun, S.; Stayton, P.S. Design and development of polymers for gene delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molino, N.M.; Neek, M.; Tucker, J.A.; Nelson, E.L.; Wang, S.-W. Display of DNA on nanoparticles for targeting antigen presenting cells. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ho, J.K.; White, P.J.; Pouton, C.W. Self-crosslinking lipopeptide/DNA/PEGylated particles: A new platform for DNA vaccination designed for assembly in aqueous solution. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2018, 12, 504–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shah, M.A.A.; Ali, Z.; Ahmad, R.; Qadri, I.; Fatima, K.; He, N. DNA mediated vaccines delivery through nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 15, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Shi, K.; Qu, Y.; Chu, B.; Qian, Z. Engineering nanoparticles for targeted delivery of nucleic acid therapeutics in tumor. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saade, F.; Petrovsky, N. Technologies for enhanced efficacy of DNA vaccines. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2012, 11, 189–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, R.; Karmali, P.P.; Pramanik, D.; Garu, A.; Venkata Mahidhar, Y.; Majeti, B.K.; Ramakrishna, S.; Srinivas, G.; Chaudhuri, A. Cationic amphiphile with shikimic acid headgroup shows more systemic promise than its mannosyl analogue as DNA vaccine carrier in dendritic cell based genetic immunization. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 1387–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garu, A.; Moku, G.; Gulla, S.K.; Chaudhuri, A. Genetic immunization with in vivo dendritic cell-targeting liposomal DNA vaccine carrier induces long-lasting antitumor immune response. Mol. Ther. 2016, 24, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carroll, T.D.; Jegaskanda, S.; Matzinger, S.R.; Fritts, L.; McChesney, M.B.; Kent, S.J.; Fairman, J.; Miller, C.J. A Lipid/DNA Adjuvant–Inactivated Influenza Virus Vaccine Protects Rhesus Macaques From Uncontrolled Virus Replication After Heterosubtypic Influenza A Virus Challenge. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, 856–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahale, N.; Thakkar, P.; Mali, R.; Walunj, D.; Chaudhari, S. Niosomes: Novel sustained release nonionic stable vesicular systems—an overview. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 183, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, X.; Wei, M.; He, S.; Yuan, W.E. Advances of Non-Ionic Surfactant Vesicles (Niosomes) and Their Application in Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jain, S.; Singh, P.; Mishra, V.; Vyas, S. Mannosylated niosomes as adjuvant–carrier system for oral genetic immunization against Hepatitis B. Immunol. Lett. 2005, 101, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyas, S.; Singh, R.; Jain, S.; Mishra, V.; Mahor, S.; Singh, P.; Gupta, P.; Rawat, A.; Dubey, P. Non-ionic surfactant based vesicles (niosomes) for non-invasive topical genetic immunization against hepatitis B. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 296, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamornpathomkul, B.; Niyomtham, N.; Yingyongnarongkul, B.E.; Prasitpuriprecha, C.; Rojanarata, T.; Ngawhirunpat, T.; Opanasopit, P. Cationic niosomes for enhanced skin immunization of plasmid DNA-encoding ovalbumin via hollow microneedles. AAPS Pharmscitech 2018, 19, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, R.; Garu, A.; Moku, G.; Agawane, S.B.; Chaudhuri, A. A long-lasting dendritic cell DNA vaccination system using lysinylated amphiphiles with mannose-mimicking head-groups. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 6220–6229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilboa, E. DC-based cancer vaccines. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garber, K. Alnylam launches era of RNAi drugs. Nat. Publ. Group 2018, 36, 777–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, J.A.; Cullis, P.R.; Van Der Meel, R. Lipid nanoparticles enabling gene therapies: From concepts to clinical utility. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2018, 28, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rezaee, M.; Oskuee, R.K.; Nassirli, H.; Malaekeh-Nikouei, B. Progress in the development of lipopolyplexes as efficient non-viral gene delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2016, 236, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Waters, A.K.; Kalyan, P.; Achrol, A.S.; Kesari, S.; Yenugonda, V.M. Lipid–polymer hybrid nanoparticles as a next-generation drug delivery platform: State of the art, emerging technologies, and perspectives. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Channarong, S.; Chaicumpa, W.; Sinchaipanid, N.; Mitrevej, A. Development and evaluation of chitosan-coated liposomes for oral DNA vaccine: The improvement of Peyer’s patch targeting using a polyplex-loaded liposomes. AAPS Pharmscitech 2011, 12, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Shan, H. Advances in mRNA vaccines for infectious diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 594. [Google Scholar]
- Pardi, N.; Hogan, M.J.; Porter, F.W.; Weissman, D. mRNA vaccines—A new era in vaccinology. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Islam, M.A.; Reesor, E.K.; Xu, Y.; Zope, H.R.; Zetter, B.R.; Shi, J. Biomaterials for mRNA delivery. Biomater. Sci. 2015, 3, 1519–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Riley, R.S.; June, C.H.; Langer, R.; Mitchell, M.J. Delivery technologies for cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 175–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Chen, C.; Wang, C.; Jiang, X. Functional nanomaterials can optimize the efficacy of vaccines. Small 2014, 10, 4505–4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.J.; Wu, M.S.; Barr, L.J.; Fuller, J.T.; Tussey, L.G.; Speller, S.; Culp, J.; Burkholder, J.K.; Swain, W.F.; Dixon, R.M. Induction of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells, T helper cells, and protective levels of antibody in humans by particle-mediated administration of a hepatitis B virus DNA vaccine. Vaccine 2000, 19, 764–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leutenegger, C.M.; Boretti, F.S.; Mislin, C.N.; Flynn, J.N.; Schroff, M.; Habel, A.; Junghans, C.; Koenig-Merediz, S.A.; Sigrist, B.; Aubert, A. Immunization of cats against feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV) infection by using minimalistic immunogenic defined gene expression vector vaccines expressing FIV gp140 alone or with feline interleukin-12 (IL-12), IL-16, or a CpG motif. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 10447–10457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dean, H.J.; Fuller, D.; Osorio, J.E. Powder and particle-mediated approaches for delivery of DNA and protein vaccines into the epidermis. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2003, 26, 373–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.; Klibanov, A.M. Conjugation to gold nanoparticles enhances polyethylenimine’s transfer of plasmid DNA into mammalian cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 9138–9143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salem, A.; Hung, C.-F.; Kim, T.W.; Wu, T.C.; Searson, P.; Leong, K. Multi-component nanorods for vaccination applications. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, X.; Ji, Y.; Zhao, Y. Surface-engineered gold nanorods: Promising DNA vaccine adjuvant for HIV-1 treatment. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 2003–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, X.; Yu, X.; Zha, X.; Fu, Q.; Liu, B.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Shan, Y. The effect of conjugation to gold nanoparticles on the ability of low molecular weight chitosan to transfer DNA vaccine. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulla, S.K.; Rao, B.R.; Moku, G.; Jinka, S.; Nimmu, N.V.; Khalid, S.; Patra, C.R.; Chaudhuri, A. In vivo targeting of DNA vaccines to dendritic cells using functionalized gold nanoparticles. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 773–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meka, R.R.; Mukherjee, S.; Patra, C.R.; Chaudhuri, A. Shikimoyl-ligand decorated gold nanoparticles for use in ex vivo engineered dendritic cell based DNA vaccination. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 7931–7943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draz, M.S.; Wang, Y.J.; Chen, F.F.; Xu, Y.; Shafiee, H. Electrically oscillating plasmonic nanoparticles for enhanced DNA vaccination against hepatitis C virus. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1604139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pirmoradi, F.N.; Pattekar, A.V.; Linn, F.; Recht, M.I.; Volkel, A.R.; Wang, Q.; Anderson, G.B.; Veiseh, M.; Kjono, S.; Peeters, E. A microarray MEMS device for biolistic delivery of vaccine and drug powders. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2015, 11, 1936–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iv, M.; Telischak, N.; Feng, D.; Holdsworth, S.J.; Yeom, K.W.; Daldrup-Link, H.E. Clinical applications of iron oxide nanoparticles for magnetic resonance imaging of brain tumors. Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 993–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, A.; Di Corato, R.; Kolosnjaj-Tabi, J.; Flaud, P.; Pellegrino, T.; Wilhelm, C. Duality of iron oxide nanoparticles in cancer therapy: Amplification of heating efficiency by magnetic hyperthermia and photothermal bimodal treatment. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 2436–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Qiao, R.; Tang, N.; Lu, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Xue, X.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, G. Active targeting theranostic iron oxide nanoparticles for MRI and magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound ablation of lung cancer. Biomaterials 2017, 127, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mok, H.; Zhang, M. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle-based delivery systems for biotherapeutics. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Deen, F.N.; Ho, J.; Selomulya, C.; Ma, C.; Coppel, R. Superparamagnetic nanoparticles for effective delivery of malaria DNA vaccine. Langmuir 2011, 27, 3703–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Deen, F.; Xiang, S.; Ma, C.; Wilson, K.; Coppel, R.; Selomulya, C.; Plebanski, M. Magnetic nanovectors for the development of DNA blood-stage malaria vaccines. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Al-Deen, F.N.; Ma, C.; Xiang, S.D.; Selomulya, C.; Plebanski, M.; Coppel, R.L. On the efficacy of malaria DNA vaccination with magnetic gene vectors. J. Control. Release 2013, 168, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcells, L.; Fornaguera, C.; Brugada-Vilà, P.; Guerra-Rebollo, M.; Meca-Cortés, Ó.; Martínez, G.; Rubio, N.; Blanco, J.; Santamaría, J.; Cascante, A. SPIONs’ Enhancer Effect on Cell Transfection: An Unexpected Advantage for an Improved Gene Delivery System. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 2728–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, A.; Qin, L.; Wang, W.; Zhu, R.; Yu, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, S. The use of layered double hydroxides as DNA vaccine delivery vector for enhancement of anti-melanoma immune response. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Deen, F.N.; Selomulya, C.; Williams, T. On designing stable magnetic vectors as carriers for malaria DNA vaccine. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 102, 492–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazayeri, S.D.; Ideris, A.; Zakaria, Z.; Shameli, K.; Moeini, H.; Omar, A.R. Cytotoxicity and immunological responses following oral vaccination of nanoencapsulated avian influenza virus H5 DNA vaccine with green synthesis silver nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.P.; Walker, T.L.; Liu, K.-l.; Cooper, H.M.; Lu, G.M.; Bartlett, P.F. Layered double hydroxide nanoparticles as cellular delivery vectors of supercoiled plasmid DNA. Int. J. Nanomed. 2007, 2, 163. [Google Scholar]
- Joyappa, D.H.; Kumar, C.A.; Banumathi, N.; Reddy, G.R.; Suryanarayana, V.V. Calcium phosphate nanoparticle prepared with foot and mouth disease virus P1-3CD gene construct protects mice and guinea pigs against the challenge virus. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 139, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, R.; Gao, B.; Wu, B.; Li, K.; Sun, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, S. The enhanced immune response of hepatitis B virus DNA vaccine using SiO2@ LDH nanoparticles as an adjuvant. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 466–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Rong, G.; Hao, Y.; Yu, L.; Kang, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Jin, Z.; Ren, Z.; Li, Z. IgA response and protection following nasal vaccination of chickens with Newcastle disease virus DNA vaccine nanoencapsulated with Ag@ SiO 2 hollow nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scheerlinck, J.-P.Y.; Greenwood, D.L. Virus-sized vaccine delivery systems. Drug Discov. Today 2008, 13, 882–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Li, S.; Yu, H.; Xia, N.; Modis, Y. Virus-like particle-based human vaccines: Quality assessment based on structural and functional properties. Trends Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 654–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuenmayor, J.; Gòdia, F.; Cervera, L. Production of virus-like particles for vaccines. New Biotechnol. 2017, 39, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, C.; Wagner, R. Virus-like particles—universal molecular toolboxes. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2007, 18, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcea, R.L.; Gissmann, L. Virus-like particles as vaccines and vessels for the delivery of small molecules. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2004, 15, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimchi-Sarfaty, C.; Arora, M.; Sandalon, Z.; Oppenheim, A.; Gottesman, M.M. High cloning capacity of in vitro packaged SV40 vectors with no SV40 virus sequences. Hum. Gene Ther. 2003, 14, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
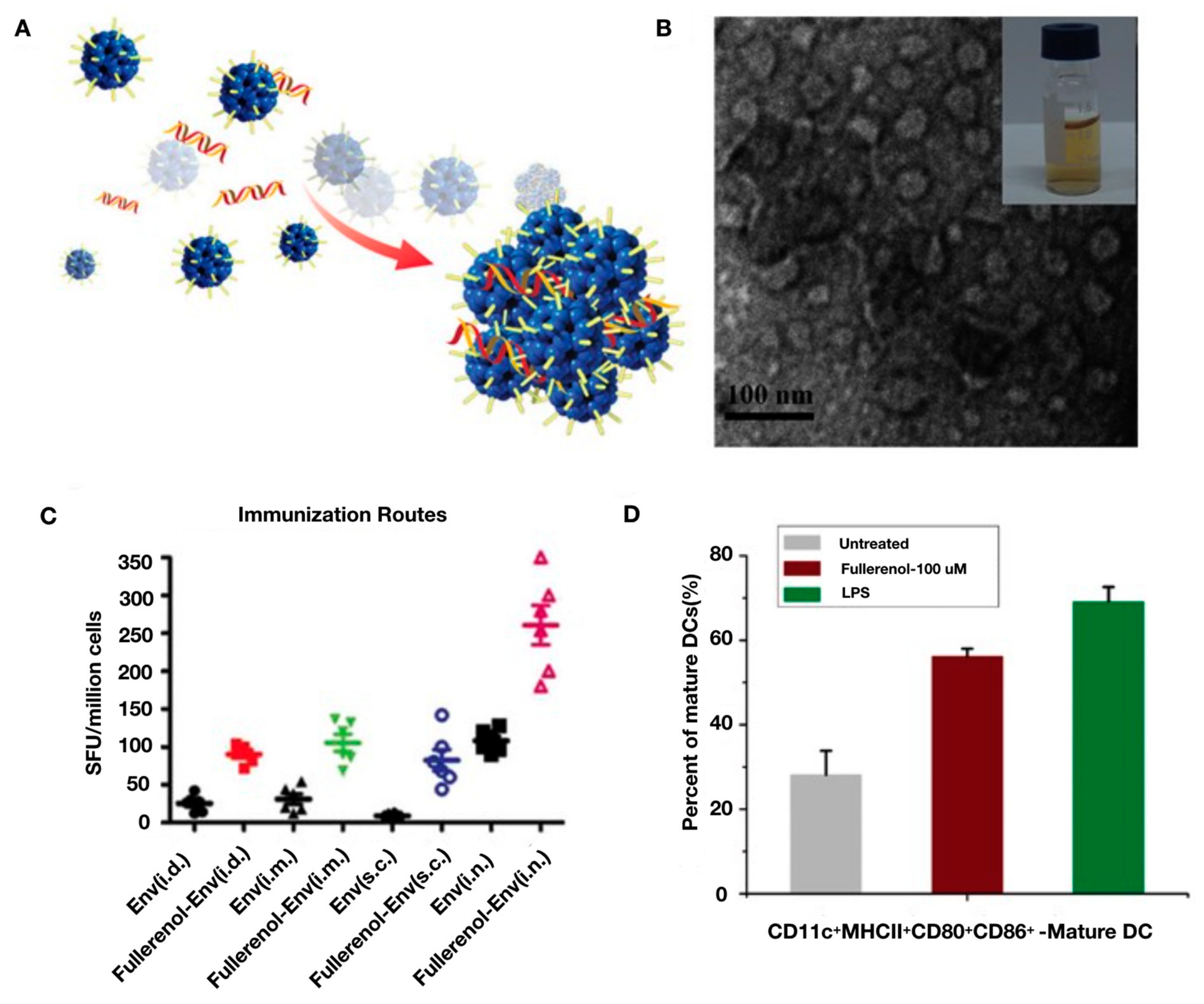
- Xu, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Ma, L.; Shao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, C. Morphologically virus-like fullerenol nanoparticles act as the dual-functional nanoadjuvant for HIV-1 vaccine. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 5928–5936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, S.M.; Doukas, J.; Hartikka, J.; Smith, L.; Rolland, A. Vaxfectin: A versatile adjuvant for plasmid DNA-and protein-based vaccines. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2010, 7, 1433–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, L.R.; Wloch, M.K.; Ye, M.; Reyes, L.R.; Boutsaboualoy, S.; Dunne, C.E.; Chaplin, J.A.; Rusalov, D.; Rolland, A.P.; Fisher, C.L. Phase 1 clinical trials of the safety and immunogenicity of adjuvanted plasmid DNA vaccines encoding influenza A virus H5 hemagglutinin. Vaccine 2010, 28, 2565–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.; Dai, S.; Jiao, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, B.; Zong, L. Mannosylated protamine as a novel DNA vaccine carrier for effective induction of anti-tumor immune responses. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 506, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, M.; Vermerris, W. Recent advances in nanomaterials for gene delivery—a review. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morán, M.C.; Rosell, N.; Ruano, G.; Busquets, M.A.; Vinardell, M.P. Gelatin-based nanoparticles as DNA delivery systems: Synthesis, physicochemical and biocompatible characterization. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 134, 156–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Mao, L.; Chen, W.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, W.; Zheng, W.; Zhao, Y.; Kong, D. A peptide-based nanofibrous hydrogel as a promising DNA nanovector for optimizing the efficacy of HIV vaccine. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 1439–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danko, J.R.; Kochel, T.; Teneza-Mora, N.; Luke, T.C.; Raviprakash, K.; Sun, P.; Simmons, M.; Moon, J.E.; De La Barrera, R.; Martinez, L.J. Safety and immunogenicity of a tetravalent dengue DNA vaccine administered with a cationic lipid-based adjuvant in a phase 1 clinical trial. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2018, 98, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiao, S.L.; Ganesan, A.P.; Rugo, H.S.; Coussens, L.M. Immune microenvironments in solid tumors: New targets for therapy. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 2559–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopes, A.; Vandermeulen, G.; Préat, V. Cancer DNA vaccines: Current preclinical and clinical developments and future perspectives. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnjatic, S.; Altorki, N.K.; Tang, D.N.; Tu, S.-M.; Kundra, V.; Ritter, G.; Old, L.J.; Logothetis, C.J.; Sharma, P. NY-ESO-1 DNA vaccine induces T-cell responses that are suppressed by regulatory T cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 2130–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anselmo, A.C.; Mitragotri, S. Nanoparticles in the clinic. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2016, 1, 10–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorritsma, S.; Gowans, E.; Grubor-Bauk, B.; Wijesundara, D. Delivery methods to increase cellular uptake and immunogenicity of DNA vaccines. Vaccine 2016, 34, 5488–5494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerdts, V.; Wilson, H.L.; Meurens, F.; van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk, S.; Wilson, D.; Walker, S.; Wheler, C.; Townsend, H.; Potter, A.A. Large animal models for vaccine development and testing. ILAR J. 2015, 56, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lim, M.; Badruddoza, A.Z.M.; Firdous, J.; Azad, M.; Mannan, A.; Al-Hilal, T.A.; Cho, C.-S.; Islam, M.A. Engineered Nanodelivery Systems to Improve DNA Vaccine Technologies. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12010030
Lim M, Badruddoza AZM, Firdous J, Azad M, Mannan A, Al-Hilal TA, Cho C-S, Islam MA. Engineered Nanodelivery Systems to Improve DNA Vaccine Technologies. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(1):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12010030
Chicago/Turabian StyleLim, Michael, Abu Zayed Md Badruddoza, Jannatul Firdous, Mohammad Azad, Adnan Mannan, Taslim Ahmed Al-Hilal, Chong-Su Cho, and Mohammad Ariful Islam. 2020. "Engineered Nanodelivery Systems to Improve DNA Vaccine Technologies" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 1: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12010030
APA StyleLim, M., Badruddoza, A. Z. M., Firdous, J., Azad, M., Mannan, A., Al-Hilal, T. A., Cho, C.-S., & Islam, M. A. (2020). Engineered Nanodelivery Systems to Improve DNA Vaccine Technologies. Pharmaceutics, 12(1), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12010030