Improved Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Uptake of Complexed Daidzein in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Apparatus
2.3. Standard Solutions, Calibration Curves, and Quality Control Samples
2.4. Sample Preparation
2.5. LC/MS/MS Analyses
2.6. Method Validation
2.7. Treatment Groups and Sample Collection
2.8. Pharmacokinetic Calculations
2.9. Statistical Analyses
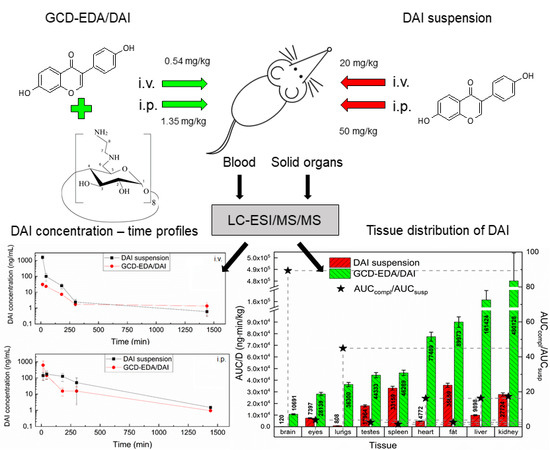
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Statement on Ethical Commitments
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clarkson, T.B. Soy, soy phytoestrogens and cardiovascular disease. J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 566S–569S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.M.; Yang, W.; Bosland, M.C. Soy isoflavones and prostate cancer: A review of molecular mechanisms. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 140, 116–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hua, F.; Li, C.-H.; Chen, X.-G.; Liu, X.-P. Daidzein exerts anticancer activity towards SKOV3 human ovarian cancer cells by inducing apoptosis and cell cycle arrest, and inhibiting the Raf/MEK/ERK cascade. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 3485–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.-S.; Qi, W.-T.; Guo, W.; Wang, C.-L.; Hu, Z.-B.; Li, A.-K. Genistein and daidzein induce apoptosis of colon cancer cells by inhibiting the accumulation of lipid droplets. Food Nutr. Res. 2018, 62, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Miao, H.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Huang, H. Daidzein induces apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer cells by restoring STK4/YAP1 signaling. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2017, 10, 15205–15212. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, C.; Namgung, H.; Lee, J.; Park, H.-C.; Ko, J.; Moon, H.; Ko, H.W.; Lee, H.J. Daidzein suppresses tumor necrosis factor-α induced migration and invasion by inhibiting hedgehog/gli1 signaling in human breast cancer cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 3759–3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wu, X.; Cao, Y.; Hou, Y.; Chen, H.; Wu, L.; Lu, L.; Zhu, W.; Gu, Y. Daidzein exerts anti-tumor activity against bladder cancer cells via inhibition of FGFR3 pathway. Neoplasma 2016, 63, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shim, S.H. 20S proteasome inhibitory activity of flavonoids isolated from Spatholobus suberectus. Phyther. Res. 2011, 25, 615–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujitaka, Y.; Shimoda, K.; Araki, M.; Doi, S.; Ono, T.; Hamada, H.; Hamada, H. Biotransformation of daidzein to diadzein-7-glucoside and its anti-allergic activity. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2017, 12, 1741–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, D.; Sarkar, S.; Bordoloi, J.; Wann, S.B.; Kalita, J.; Manna, P. Daidzein, its effects on impaired glucose and lipid metabolism and vascular inflammation associated with type 2 diabetes. BioFactors 2018, 44, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Mine, Y.; Tsao, R. Anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative activities of daidzein and its sulfonic acid ester derivatives. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 35, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roghani, M.; Vaez Mahdavi, M.-R.; Jalali-Nadoushan, M.-R.; Baluchnejadmojarad, T.; Naderi, G.; Roghani-Dehkordi, F.; Taghi Joghataei, M.; Kord, M. Chronic administration of daidzein, a soybean isoflavone, improves endothelial dysfunction and attenuates oxidative stress in streptozotocin- induced diabetic rats. Phyther. Res. 2013, 27, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitale, D.C.; Piazza, C.; Melilli, B.; Drago, F.; Salomone, S. Isoflavones: Estrogenic activity, biological effect and bioavailability. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2013, 38, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, C.D.; Lowik, C. Dose-dependent effects of phytoestrogens on bone. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 16, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Mao, Z.; Brinton, R.D. A select combination of clinically relevant phytoestrogens enhances estrogen receptor β-binding Selectivity and neuroprotective activities in vitro and in vivo. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 770–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, X.; Lee, S.-K.; Chun, O.K. Soy Isoflavones and Osteoporotic Bone Loss: A Review with an Emphasis on Modulation of Bone Remodeling. J. Med. Food 2016, 19, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasain, J.K.; Jones, K.; Brissie, N.; Moore, R.; Wyss, J.M.; Barnes, S. Identification of puerarin and its metabolites in rats by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 3708–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, Y.-H.; Kwon, S.-H.; Ma, S.-X.; Seo, J.-Y.; Lee, B.-R.; Kim, K.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, S.-Y.; Jang, C.-G. The memory-enhancing effects of 7,8,4′-trihydroxyisoflavone, a major metabolite of daidzein, are associated with activation of the cholinergic system and BDNF signaling pathway in mice. Brain Res. Bull. 2018, 142, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Tai, F.; Zhai, P.; Yuan, A.; Jia, R.; Zhang, X. Effect of daidzein on anxiety, social behavior and spatial learning in male Balb/cJ mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2010, 96, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfi, A.; Richard, M.; Gandolphe, C.; Scherman, D. Storage correction in cells of patients suffering from mucopolysaccharidoses types IIIA and VII after treatment with genistein and other isoflavones. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2010, 33, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloska, A.; Jakóbkiewicz-Banecka, J.; Narajczyk, M.; Banecka-Majkutewicz, Z.; Wȩgrzyn, G. Effects of flavonoids on glycosaminoglycan synthesis: Implications for substrate reduction therapy in Sanfilippo disease and other mucopolysaccharidoses. Metab. Brain Dis. 2011, 26, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Piotrowska, E.; Jakóbkiewicz-Banecka, J.; Barańska, S.; Tylki-Szymańska, A.; Czartoryska, B.; Wegrzyn, A.; Wegrzyn, G. Genistein-mediated inhibition of glycosaminoglycan synthesis as a basis for gene expression-targeted isoflavone therapy for mucopolysaccharidoses. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2006, 14, 846–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Piotrowska, E.; Jakóbkiewicz-Banecka, J.; Tylki-Szymanska, A.; Liberek, A.; Maryniak, A.; Malinowska, M.; Czartoryska, B.; Puk, E.; Kloska, A.; Liberek, T.; et al. Genistin-rich soy isoflavone extract in substrate reduction therapy for Sanfilippo syndrome: An open-label, pilot study in 10 pediatric patients. Curr. Ther. Res.-Clin. Exp. 2008, 69, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Piotrowska, E.; Jakóbkiewicz-Banecka, J.; Wȩgrzyn, G. Different amounts of isoflavones in various commercially available soy extracts in the light of gene expression-targeted isoflavone therapy. Phyther. Res. 2010, 24, S109–S113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskot, M.; Jakóbkiewicz-Banecka, J.; Kloska, A.; Smolińska, E.; Mozolewski, P.; Malinowska, M.; Rychłowski, M.; Banecki, B.; Wȩgrzyn, G.; Gabig-Cimińska, M. Modulation of expression of genes involved in glycosaminoglycan metabolism and lysosome biogenesis by flavonoids. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friso, A.; Tomanin, R.; Salvalaio, M.; Scarpa, M. Genistein reduces glycosaminoglycan levels in a mouse model of mucopolysaccharidosis type II. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 159, 1082–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- The European Union Clinical Trials. High Dose Genistein in Sanfilippo Syndrome. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr-search/trial/2013-001479-18/GB (accessed on 11 February 2020).
- Lavery, C.; Hendriksz, C.J.; Jones, S.A. Mortality in patients with Sanfilippo syndrome. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2017, 12, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nan, G.; Shi, J.; Huang, Y.; Sun, J.; Lv, J.; Yang, G.; Li, Y. Dissociation Constants and Solubilities of Daidzein and Genistein in Different Solvents. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2014, 59, 1304–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amawi, H.; Ashby, C.R., Jr.; Tiwari, A.K. Cancer chemoprevention through dietary flavonoids: What’s limiting? Chin. J. Cancer 2017, 36, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Setchell, K.D.R.; Faughnan, M.S.; Avades, T.; Zimmer-Nechemias, L.; Brown, N.M.; Wolfe, B.E.; Brashear, W.T.; Desai, P.; Oldfield, M.F.; Botting, N.P.; et al. Comparing the pharmacokinetics of daidzein and genistein with the use of 13C-labeled tracers in premenopausal women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Setchell, K.D.R.; Brown, N.M.; Desai, P.; Zimmer-Nechemias, L.; Wolfe, B.E.; Brashear, W.T.; Kirschner, A.S.; Cassidy, A.; Heubi, J.E. Bioavailability of pure isoflavones in healthy humans and analysis of commercial soy isoflavone supplements. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 1362S–1375S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fairley, B.; Botting, N.P.; Cassidy, A. The synthesis of daidzein sulfates. Tetrahedron 2003, 59, 5407–5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakubo, A.; Koga, K.; Isobe, M.; Fushimi, T.; Saitoh, T.; Ohshima, Y.; Tsukamoto, Y. First finding of Daidzein 7-O-phosphate and Genistein 7-O-phosphate that are hydrolyzed by sulfatase. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 8801–8805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needs, P.W.; Williamson, G. Syntheses of daidzein-7-yl β-d-glucopyranosiduronic acid and daidzein-4′,7-yl di-β-d-glucopyranosiduronic acid. Carbohydr. Res. 2001, 330, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Gaudio, P.; Russo, P.; Rodriguez Dorado, R.; Sansone, F.; Mencherini, T.; Gasparri, F.; Aquino, R.P. Submicrometric hypromellose acetate succinate particles as carrier for soy isoflavones extract with improved skin penetration performance. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 165, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Gaudio, P.; Sansone, F.; Mencherini, T.; De Cicco, F.; Russo, P.; Aquino, R.P. Nanospray Drying as a Novel Tool to Improve Technological Properties of Soy Isoflavone Extracts. Planta Med. 2017, 83, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, T.; Gu, L. TPGS emulsified zein nanoparticles enhanced oral bioavailability of daidzin: In vitro characteristics and in vivo performance. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 2062–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.-H.; Hu, S.C.; Lee, C.-W.; Yeh, A.-C.; Tseng, C.-H.; Yen, F.-L. Design of acid-responsive polymeric nanoparticles for 7, 3′, 4′-trihydroxyisoflavone topical administration. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 1615–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumara, N.R.R.; Madhusudhan, B. Evaluation of anticancer efficacy of daidzein-loaded poly(D, L) lactic acid nanoparticles. J. Bionanosci. 2011, 5, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, Y.; Su, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ding, L.; Yan, X.; Zhao, D.; Shao, N.; Ye, X.; Cheng, Y. Inclusion complexes of isoflavones with two commercially available dendrimers: Solubility, stability, structures, release behaviors, cytotoxicity, and anti-oxidant activities. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 421, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Xie, J.; Zhou, W.; Shi, W. Temperature sensitivity and drug encapsulation of star-shaped amphiphilic block copolymer based on dendritic poly(ether-amide). J. Biomed. Mater. Res.-Part. A 2009, 89, 988–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panizzon, G.P.; Bueno, F.G.; Ueda-Nakamura, T.; Nakamura, C.V.; Filho, B.P.D. Preparation of spray-dried soy isoflavone-loaded gelatin microspheres for enhancement of dissolution: Formulation, characterization and in vitro evaluation. Pharmaceutics 2014, 6, 599–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ge, Y.-B.; Chen, D.-W.; Xie, L.-P.; Zhang, R. Optimized preparation of daidzein-loaded chitosan microspheres and in vivo evaluation after intramuscular injection in rats. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 338, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daruházi, Á.E.; Kiss, T.; Vecsernyés, M.; Szente, L.; Szoke, T.; Lemberkovics, T. Investigation of transport of genistein, daidzein and their inclusion complexes prepared with different cyclodextrins on Caco-2 cell line. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2013, 84, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yuan, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, W.; Wang, X. Studies on the inclusion complexes of daidzein with β-cyclodextrin and derivatives. Molecules 2017, 22, 2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rungrotmongkol, T.; Chakcharoensap, T.; Pongsawasdi, P.; Kungwan, N.; Wolschann, P. The inclusion complexation of daidzein with β-cyclodextrin and 2,6-dimethyl-β-cyclodextrin: A theoretical and experimental study. Monatshefte fur Chemie 2018, 149, 1739–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.-H.; Su, L.-N.; Pang, Y.-H.; Guo, Y.-F.; Wang, F.; Liao, X.-L.; Yang, B.; Wand, F.; Liao, X.-L.; Yang, B. Preparation, Characterization and Water Solubility of Inclusion Complexes of Daidzein with Amino-Modified β-Cyclodextrins. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2017, 45, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumić, B.; Jablan, J.; Cinčić, D.; Zovko Končić, M.; Jug, M. Cyclodextrin encapsulation of daidzein and genistein by grinding: Implication on the glycosaminoglycan accumulation in mucopolysaccharidosis type II and III fibroblasts. J. Microencapsul. 2018, 35, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiński, K.; Kujdowicz, M.; Kajta, M.; Nowakowska, M.; Szczubiałka, K. Enhanced delivery of daidzein into fibroblasts and neuronal cells with cationic derivatives of gamma-cyclodextrin for the control of cellular glycosaminoglycans. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 91, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA-Biopharmaceutics-2001 Guidance for Industry: Bioanalytical Method Validation. 2001.
- EMA. Guideline on Bioanalytical Method Validation Guideline on Bioanalytical Method Validation Table of Contents; EMA: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Wang, H.J.; Murphy, P.A.; Cook, L.; Hendrich, S. Daidzein is a more bioavailable soymilk isoflavone than is genistein in adult women. J. Nutr. 1994, 124, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karr, S.C.; Lampe, J.W.; Hutchins, A.M.; Slavin, J.L. Urinary isoflavonoid excretion in humans is dose dependent at low to moderate levels of soy-protein consumption. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 66, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wakai, K.; Egami, I.; Kato, K.; Kawamura, T.; Tamakoshi, A.; Nakayama, T.; Wada, M.; Ohno, Y. Dietary intake and sources of isoflavones among Japanese. Nutr. Cancer 1999, 33, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Compound | Transition | CE (V) | DP (V) | FP (V) | EP (V) | CXP (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DAI | 255.1⟶199.1 | 50 | 60 | 300 | 10 | 10 |
| IS | 271.1⟶215.2 | 45 | 70 | 200 | 10 | 10 |
| Parameters | DAI in Suspension | GCD-EDA/DAI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| i.v. (20 mg/kg) | i.p. (50 mg/kg) | i.v. (0.54 mg/kg) | i.p. (1.35 mg/kg) | |
| (ng/mL) | 6162 | - | 63.11 | - |
| AUC0⟶t (ng·min/mL) | 94,667 | 66,703 | 18,348 | 37,790 |
| t0.5 (min) | 230 | 204.7 | 379.5 | 300.4 |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | - | 173.1 | - | 614.7 |
| tmax (min) | - | 45 | - | 15 |
| MRT (min) | 257.3 | 217.7 | 299.4 | 126.5 |
| Vss (L/kg) * Vd/F (L/kg) | 6.2 | * 220 | 38.6 | * 15.3 |
| Cl (mL/min/kg) * Cl/F (mL/min/kg) | 210.8 | * 774.6 | 84.1 | * 35.3 |
| F (%) | 28.2 | 82.4 | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwiecień, A.; Ruda-Kucerova, J.; Kamiński, K.; Babinska, Z.; Popiołek, I.; Szczubiałka, K.; Nowakowska, M.; Walczak, M. Improved Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Uptake of Complexed Daidzein in Rats. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12020162
Kwiecień A, Ruda-Kucerova J, Kamiński K, Babinska Z, Popiołek I, Szczubiałka K, Nowakowska M, Walczak M. Improved Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Uptake of Complexed Daidzein in Rats. Pharmaceutics. 2020; 12(2):162. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12020162
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwiecień, Anna, Jana Ruda-Kucerova, Kamil Kamiński, Zuzana Babinska, Iwona Popiołek, Krzysztof Szczubiałka, Maria Nowakowska, and Maria Walczak. 2020. "Improved Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Uptake of Complexed Daidzein in Rats" Pharmaceutics 12, no. 2: 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12020162
APA StyleKwiecień, A., Ruda-Kucerova, J., Kamiński, K., Babinska, Z., Popiołek, I., Szczubiałka, K., Nowakowska, M., & Walczak, M. (2020). Improved Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Uptake of Complexed Daidzein in Rats. Pharmaceutics, 12(2), 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics12020162