Chronic Administration of 7,8-DHF Lessens the Depression-like Behavior of Juvenile Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Treated Rats at Their Adult Age
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
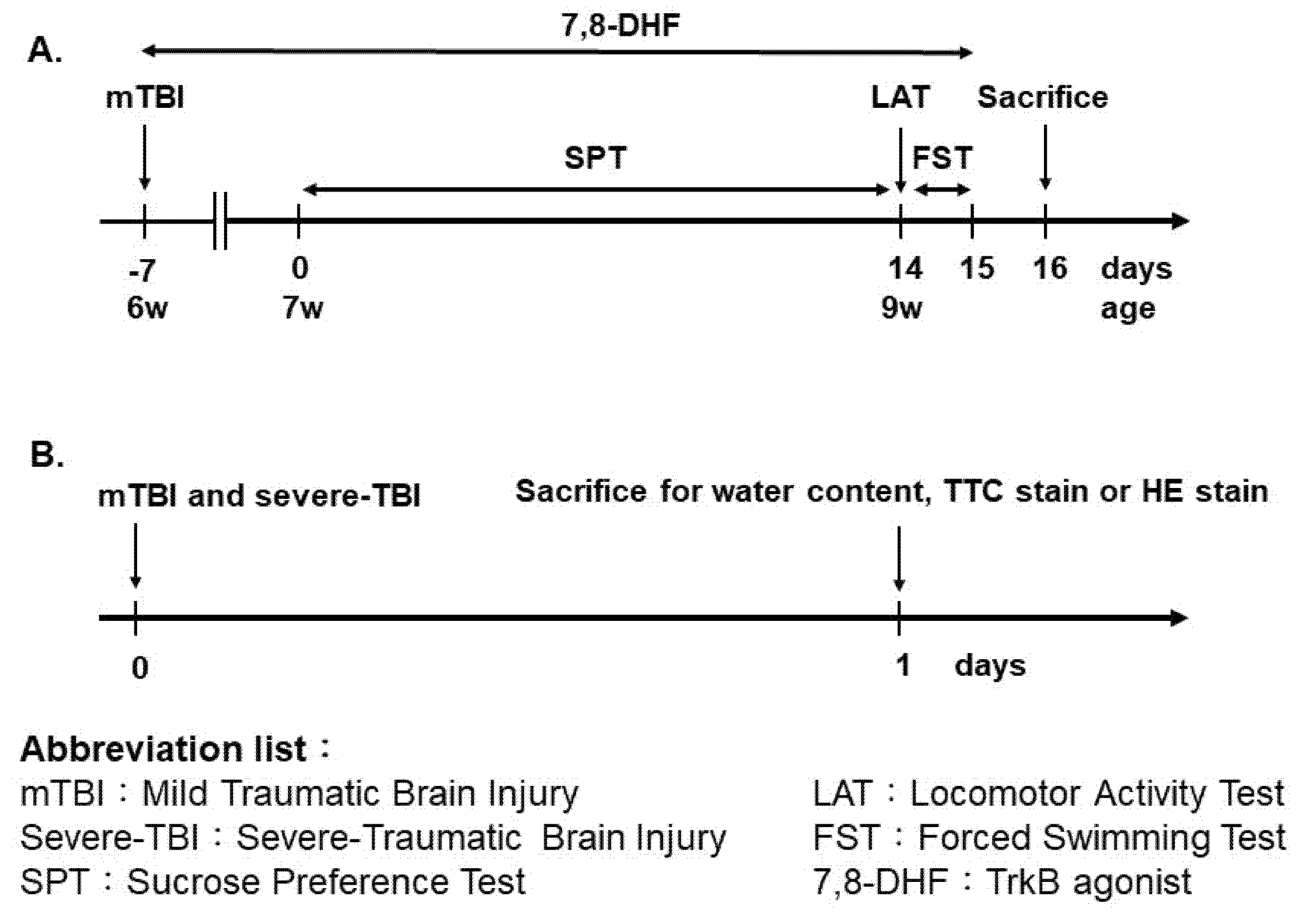
2.2. The Juvenile Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Model
2.3. Brain Damage Measurement
- a.
- 2,3,5,-triphenyltetrazolium chloride monohydrate stain (TTC stain)
- b.
- Brain edema
2.4. Locomotor Activity Test (LAT)
2.5. Sucrose Preference Test (SPT)
2.6. Forced Swim Test (FST)
2.7. Western Blot
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. The mTBI-J Treatment Does Not Induce Severe Cerebral Damage in Juvenile Rats
3.2. The Mild Juvenile TBI Treated Animals Showed an Increase in Depression-like Behavior in Adulthood
3.3. Determination of the BDNF and TrkB Expression in the Dorsal Hippocampus and Ventral Hippocampus of mTBI-J Treated Animals
3.4. To Evaluate the Possible Therapeutic Effect of 7,8-DHF on the mTBI-J Induced Depression-like Behavior
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khellaf, A.; Khan, D.Z.; Helmy, A. Recent advances in traumatic brain injury. J. Neurol. 2019, 266, 2878–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maas, A.I.R.; Menon, D.K.; Adelson, P.D.; Andelic, N.; Bell, M.J.; Belli, A.; Bragge, P.; Brazinova, A.; Büki, A.; Chesnut, R.M.; et al. Traumatic brain injury: Integrated approaches to improve prevention, clinical care, and research. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 987–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Popernack, M.L.; Gray, N.; Reuter-Rice, K. Moderate-to-severe traumatic brain injury in children: Complications and rehabilitation strategies. J. Pediatr. Health Care 2015, 29, e1–e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, P.; Li, R.; Schwebel, D.C.; Zhu, M.; Hu, G. Traumatic brain injury mortality among u.S. Children and adolescents ages 0–19 years, 1999–2017. J. Saf. Res. 2020, 72, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, D.K.; Schwab, K.; Wright, D.W.; Maas, A.I. Demographics and Clinical Assessment Working Group of the International and Interagency Initiative toward Common Data Elements for Research on Traumatic Brain Injury and Psychological Health. Position statement: Definition of traumatic brain injury. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2010, 91, 1637–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuehn, B. Traumatic brain injuries among youth. JAMA 2019, 321, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, I.L.; Li, C.Y.; Chu, D.C.; Chien, L.C. An epidemiological analysis of head injuries in taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williams, W.H.; Chitsabesan, P.; Fazel, S.; McMillan, T.; Hughes, N.; Parsonage, M.; Tonks, J. Traumatic brain injury: A potential cause of violent crime? Lancet Psychiatry 2018, 5, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCauley, S.R.; Wilde, E.A.; Anderson, V.A.; Bedell, G.; Beers, S.R.; Campbell, T.F.; Chapman, S.B.; Ewing-Cobbs, L.; Gerring, J.P.; Gioia, G.A.; et al. Recommendations for the use of common outcome measures in pediatric traumatic brain injury research. J. Neurotrauma 2012, 29, 678–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tramontana, M.G.; Prokop, J.W.; Williamson, E.; Duffie, T.; LaFever, H. Traumatic brain injury-related attention deficits in children: A controlled treatment trial with lisdexamfetamine dimesylate (vyvanse). Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosin, D.M.; Sniezek, J.E.; Waxweiler, R.J. Trends in death associated with traumatic brain injury, 1979 through 1992. Success and failure. JAMA 1995, 273, 1778–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cernak, I. Animal models of head trauma. NeuroRx 2005, 2, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ng, S.Y.; Lee, A.Y.W. Traumatic brain injuries: Pathophysiology and potential therapeutic targets. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2019, 13, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postolache, T.T.; Wadhawan, A.; Can, A.; Lowry, C.A.; Woodbury, M.; Makkar, H.; Hoisington, A.J.; Scott, A.J.; Potocki, E.; Benros, M.E.; et al. Inflammation in traumatic brain injury. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2020, 74, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayir, A.; Kafali, M.E.; Ak, A.; Sahin, M.; Karagozoglu, E.; Gul, M.; Karabulut, K. Effects of hypertonic saline, haes and dimethylsulphoxide on free oxygen radicals in haemorrhagic shock oxygen radicals in haemorrhagic shock. Ulus. Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2003, 9, 154–159. [Google Scholar]
- Anthonymuthu, T.S.; Kenny, E.M.; Bayır, H. Therapies targeting lipid peroxidation in traumatic brain injury. Brain Res. 2016, 1640, 57–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Korley, F.K.; Diaz-Arrastia, R.; Wu, A.H.; Yue, J.K.; Manley, G.T.; Sair, H.I.; Van Eyk, J.; Everett, A.D.; Okonkwo, D.O.; Valadka, A.B.; et al. Circulating brain-derived neurotrophic factor has diagnostic and prognostic value in traumatic brain injury. J. Neurotrauma 2016, 33, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, K.T.; Wang, Y.W.; Wo, Y.Y.; Yang, Y.L. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase-mediated il-1-induced cortical neuron damage during traumatic brain injury. Neurosci. Lett. 2005, 386, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.T.; Wang, Y.W.; Yang, J.T.; Yang, Y.L.; Chen, H.I. Effect of interleukin-1 on traumatic brain injury-induced damage to hippocampal neurons. J. Neurotrauma 2005, 22, 885–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.T.; Wu, C.Y.; Cheng, N.C.; Wo, Y.Y.; Yang, J.T.; Yen, H.H.; Yang, Y.L. Inhibition of the na+ -k+ -2cl- -cotransporter in choroid plexus attenuates traumatic brain injury-induced brain edema and neuronal damage. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 548, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.T.; Cheng, N.C.; Wu, C.Y.; Yang, Y.L. Nkcc1-mediated traumatic brain injury-induced brain edema and neuron death via raf/mek/mapk cascade. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 36, 917–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, R.M.; Kochanek, P.M.; Simard, J.M. Pathophysiology and treatment of cerebral edema in traumatic brain injury. Neuropharmacology 2019, 145, 230–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, N.D.; Haroon, E.; Xu, X.; Woolwine, B.J.; Li, Z.; Felger, J.C. Inflammation negatively correlates with amygdala-ventromedial prefrontal functional connectivity in association with anxiety in patients with depression: Preliminary results. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 73, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sydnor, V.J.; Bouix, S.; Pasternak, O.; Hartl, E.; Levin-Gleba, L.; Reid, B.; Tripodis, Y.; Guenette, J.P.; Kaufmann, D.; Makris, N.; et al. Mild traumatic brain injury impacts associations between limbic system microstructure and post-traumatic stress disorder symptomatology. Neuroimage Clin. 2020, 26, 102190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shen, M.; Sun, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Jin, X.; Xu, J.; Ding, L.; Sun, X. Aminoguanidine reverses cognitive deficits and activation of camp/creb/bdnf pathway in mouse hippocampus after traumatic brain injury (tbi). Brain Inj. 2018, 32, 1858–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffman, A.N.; Paode, P.R.; May, H.G.; Ortiz, J.B.; Kemmou, S.; Lifshitz, J.; Conrad, C.D.; Currier Thomas, T. Early and persistent dendritic hypertrophy in the basolateral amygdala following experimental diffuse traumatic brain injury. J. Neurotrauma 2017, 34, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stein, M.B.; Jain, S.; Giacino, J.T.; Levin, H.; Dikmen, S.; Nelson, L.D.; Vassar, M.J.; Okonkwo, D.O.; Diaz-Arrastia, R.; Robertson, C.S.; et al. Risk of posttraumatic stress disorder and major depression in civilian patients after mild traumatic brain injury: A track-tbi study. JAMA Psychiatry 2019, 76, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papp, M.; Willner, P.; Muscat, R. An animal model of anhedonia: Attenuation of sucrose consumption and place preference conditioning by chronic unpredictable mild stress. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1991, 104, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, J.W.; Duman, R.S. Il-1β is an essential mediator of the antineurogenic and anhedonic effects of stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 105, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Willner, P.; Towell, A.; Sampson, D.; Sophokleous, S.; Muscat, R. Reduction of sucrose preference by chronic unpredictable mild stress, and its restoration by a tricyclic antidepressant. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1987, 93, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fann, J.R.; Bombardier, C.H.; Vannoy, S.; Dyer, J.; Ludman, E.; Dikmen, S.; Marshall, K.; Barber, J.; Temkin, N. Telephone and in-person cognitive behavioral therapy for major depression after traumatic brain injury: A randomized controlled trial. J. Neurotrauma 2015, 32, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bryant, R. Post-traumatic stress disorder vs traumatic brain injury. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2011, 13, 251–262. [Google Scholar]
- Blakey, S.M.; Wagner, H.R.; Naylor, J.; Brancu, M.; Lane, I.; Sallee, M.; Kimbrel, N.A.; Workgroup, V.A.M.-A.M.; Elbogen, E.B. Chronic pain, tbi, and ptsd in military veterans: A link to suicidal ideation and violent impulses? J. Pain 2018, 19, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, L.A. Neuropsychological and neuroimaging findings in traumatic brain injury and post-traumatic stress disorder. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2011, 13, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yi, J.H.; Cho, S.Y.; Jeon, S.J.; Jung, J.W.; Park, M.S.; Kim, D.H.; Ryu, J.H. Early immature neuronal death is partially involved in memory impairment induced by cerebral ischemia. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 308, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazwi, N.L.; Izzy, S.; Tan, C.O.; Martinez, S.; Glenn, M.B.; Giacino, J.T.; Wu, O.; Zafonte, R.; Edlow, B.L. Traumatic microbleeds in the hippocampus and corpus callosum predict duration of posttraumatic amnesia. J. Head Trauma Rehabil. 2019, 34, E10–E18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peruzzaro, S.T.; Andrews, M.M.M.; Al-Gharaibeh, A.; Pupiec, O.; Resk, M.; Story, D.; Maiti, P.; Rossignol, J.; Dunbar, G.L. Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells genetically engineered to overexpress interleukin-10 promotes alternative inflammatory response in rat model of traumatic brain injury. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, A.; Deveci, E. Evaluation of pecam-1 and p38 mapk expressions in cerebellum tissue of rats treated with caffeic acid phenethyl ester: A biochemical and immunohistochemical study. Folia Morphol. (Warsz) 2018, 78, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrade, P.; Banuelos-Cabrera, I.; Lapinlampi, N.; Paananen, T.; Ciszek, R.; Ndode-Ekane, X.E.; Pitkanen, A. Acute non-convulsive status epilepticus after experimental traumatic brain injury in rats. J. Neurotrauma 2018, 36, 1890–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, H.-T.; Chiu, W.-T.; Yang, D.-Y.; Tsai, S.-H. The epidemiology and utilization of medical resources on mild head injury in taipei city. J. Emerg. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 18, 61–70. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, J.M.; Read, C.A. Psychiatric comorbidity following traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj. 2007, 21, 1321–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schachar, R.J.; Park, L.S.; Dennis, M. Mental health implications of traumatic brain injury (tbi) in children and youth. J. Can. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2015, 24, 100–108. [Google Scholar]
- Seel, R.T.; Kreutzer, J.S.; Rosenthal, M.; Hammond, F.M.; Corrigan, J.D.; Black, K. Depression after traumatic brain injury: A national institute on disability and rehabilitation research model systems multicenter investigation. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2003, 84, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razzoli, M.; Domenici, E.; Carboni, L.; Rantamaki, T.; Lindholm, J.; Castren, E.; Arban, R. A role for bdnf/trkb signaling in behavioral and physiological consequences of social defeat stress. Genes Brain Behav. 2011, 10, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, M.C.; Hung, Y.H.; Ho, P.Y.; Yang, Y.L.; Lu, K.T. Neonatal glucocorticoid treatment increased depression-like behaviour in adult rats. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 17, 1995–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bodnar, C.N.; Morganti, J.M.; Bachstetter, A.D. Depression following a traumatic brain injury: Uncovering cytokine dysregulation as a pathogenic mechanism. Neural Regen. Res. 2018, 13, 1693–1704. [Google Scholar]
- Minichiello, L. Trkb signalling pathways in ltp and learning. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 850–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schafe, G.E.; Swank, M.W.; Rodrigues, S.M.; Debiec, J.; Doyère, V. Phosphorylation of erk/map kinase is required for long-term potentiation in anatomically restricted regions of the lateral amygdala in vivo. Learn. Mem. 2008, 15, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Phillips, C. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor, depression, and physical activity: Making the neuroplastic connection. Neural. Plast 2017, 2017, 7260130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhong, J.; Zou, B.; Fang, L.; Chen, J.; Deng, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, X.; Qu, Z.; Lei, Y.; et al. Meta-analyses of comparative efficacy of antidepressant medications on peripheral bdnf concentration in patients with depression. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silverberg, N.D.; Panenka, W.J. Antidepressants for depression after concussion and traumatic brain injury are still best practice. BMC Psychiatry 2019, 19, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Polyakova, M.; Schroeter, M.L.; Elzinga, B.M.; Holiga, S.; Schoenknecht, P.; de Kloet, E.R.; Molendijk, M.L. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and antidepressive effect of electroconvulsive therapy: Systematic review and meta-analyses of the preclinical and clinical literature. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141564. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.W.; Zhang, S.F.; Li, Z.H.; Han, F. 7,8-dihydroxyflavone reverses the depressive symptoms in mouse chronic mild stress. Neurosci. Lett. 2016, 635, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, R.; Noble, E.; Tyagi, E.; Zhuang, Y.; Ying, Z.; Gomez-Pinilla, F. Flavonoid derivative 7,8-dhf attenuates tbi pathology via trkb activation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1852, 862–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, S.J.; Kang, K.A.; Piao, M.J.; Ryu, Y.S.; Fernando, P.; Zhen, A.X.; Hyun, Y.J.; Ahn, M.J.; Kang, H.K.; Hyun, J.W. 7,8-dihydroxyflavone protects high glucose-damaged neuronal cells against oxidative stress. Biomol. Ther. (Seoul) 2018, 27, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Schroeder, J.P.; Chan, C.B.; Song, M.; Yu, S.P.; Weinshenker, D.; Ye, K. 7,8-dihydroxyflavone prevents synaptic loss and memory deficits in a mouse model of alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychopharmacology 2014, 39, 638–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Girgis, F.; Pace, J.; Sweet, J.; Miller, J.P. Hippocampal neurophysiologic changes after mild traumatic brain injury and potential neuromodulation treatment approaches. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulyaeva, N.V. Functional neurochemistry of the ventral and dorsal hippocampus: Stress, depression, dementia and remote hippocampal damage. Neurochem. Res. 2019, 44, 1306–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marmarou, A.; Foda, M.A.; van den Brink, W.; Campbell, J.; Kita, H.; Demetriadou, K. A new model of diffuse brain injury in rats. Part i: Pathophysiology and biomechanics. J. Neurosurg. 1994, 80, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hehar, H.; Yeates, K.; Kolb, B.; Esser, M.J.; Mychasiuk, R. Impulsivity and concussion in juvenile rats: Examining molecular and structural aspects of the frontostriatal pathway. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baskaya, M.K.; Dogan, A.; Temiz, C.; Dempsey, R.J. Application of 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride staining to evaluate injury volume after controlled cortical impact brain injury: Role of brain edema in evolution of injury volume. J. Neurotrauma 2000, 17, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.-C.; Hsu, Y.-C.; Wang, C.-C.; Hu, C.-Y.; Chio, C.-C.; Kuo, J.-R. Early electroacupuncture treatment ameliorates neuroinflammation in rats with traumatic brain injury. BMC Complementary Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, B.S.; Wang, C.C.; Chang, M.H.; Chio, C.C. Evaluation of traumatic brain injury by optical technique. BMC Neurol. 2015, 15, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keep, R.F.; Hua, Y.; Xi, G. Brain water content. A misunderstood measurement? Transl. Stroke Res. 2012, 3, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yankelevitch-Yahav, R.; Franko, M.; Huly, A.; Doron, R. The forced swim test as a model of depressive-like behavior. J. Vis. Exp. 2015, 97, 52587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, J.R.; Cheng, Y.H.; Chen, Y.S.; Chio, C.C.; Gean, P.W. Involvement of extracellular signal regulated kinases in traumatic brain injury-induced depression in rodents. J. Neurotrauma 2013, 30, 1223–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jones, N.C.; Cardamone, L.; Williams, J.P.; Salzberg, M.R.; Myers, D.; O’Brien, T.J. Experimental traumatic brain injury induces a pervasive hyperanxious phenotype in rats. J. Neurotrauma 2008, 25, 1367–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Gao, X.; Dong, W.; Chen, J. The role of 7, 8-dihydroxyflavone in preventing dendrite degeneration in cortex after moderate traumatic brain injury. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 1884–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.-H.; Hung, T.-H.; Chen, C.-C.; Ke, C.-H.; Lee, C.-Y.; Wang, P.-Y.; Chen, S.-F. Post-injury treatment with 7, 8-dihydroxyflavone, a trkb receptor agonist, protects against experimental traumatic brain injury via pi3k/akt signaling. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Gao, X.; Zhao, S.; Hu, W.; Chen, J. The small-molecule trkb agonist 7, 8-dihydroxyflavone decreases hippocampal newborn neuron death after traumatic brain injury. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2015, 74, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, W.T.; Kuo, C.Y.; Hung, C.C.; Chen, M. The effect of the taiwan motorcycle helmet use law on head injuries. Am. J. Public Health 2000, 90, 793–796. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Pu, H.; Zhang, H.; Wei, Z.; Jiang, X.; Xu, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Liu, J.; Meng, H.; et al. Inhibition of na(+)-k(+)-2cl(-) cotransporter attenuates blood-brain-barrier disruption in a mouse model of traumatic brain injury. Neurochem. Int. 2017, 111, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, J.O.; Gladwin, M.T.; Ahluwalia, A.; Benjamin, N.; Bryan, N.S.; Butler, A.; Cabrales, P.; Fago, A.; Feelisch, M.; Ford, P.C. Nitrate and nitrite in biology, nutrition and therapeutics. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2009, 5, 865–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokina, E.; Reutov, V.; Senilova, Y.E.; Khodorov, B.; Pinelis, V. Changes in atp content in cerebellar granule cells during hyperstimulation of glutamate receptors: Possible role of no and nitrite ions. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2007, 143, 442–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodorov, B.; Storozhevykh, T.; Surin, A.; Yuryavichyus, A.; Sorokina, E.; Borodin, A.; Vinskaya, N.; Khaspekov, L.; Pinelis, V. The leading role of mitochondrial depolarization in the mechanism of glutamate-induced disruptions in Ca2+ homeostasis. Neurosci. Behav. Physiol. 2002, 32, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reutov, V.; Sorokina, E.; Sukmansky, O. Cycles of nitric oxide (no), superoxide radical anion (• O2−) and hydrogen sulfur/sulfur dioxide (H2S/SO2) in mammals. Curr. Res. Biopolym. 2020, 2, 112. [Google Scholar]
- Samosudova, N.; Reutov, V. Ultrastructural changes in the frog brain in the presence of high concentrations of glutamate and an no-generating compound. Biophysics 2018, 63, 402–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reutov, V.; Samosudova, N.; Sorokina, E. A model of glutamate neurotoxicity and mechanisms of the development of the typical pathological process. Biophysics 2019, 64, 233–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokina, E.; Semenova, Z.B.; Averianova, N.; Karaseva, O.; Arsenieva, E.; Luk’yanov, V.; Reutov, V.; Asanov, A.Y.; Roshal, L.; Pinelis, V. Polymorphism of the apoe gene and markers of brain damage in the outcomes of severe traumatic brain injury in children. Neurosci. Behav. Physiol. 2021, 51, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reutov, V.P.S.E.G.; Samosudova, N.V.; Okhotin, V.E. Pathogenesis of neurological and mental disorders in patients with covid-19: Possible role of reactive nitrogen and oxygen species. Int. J. Psychiatry 2021, 6, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Sorokina, E.G.; Semenova, Z.B.; Reutov, V.P.; Arsenieva, E.N.; Karaseva, O.V.; Fisenko, A.P.; Roshal, L.M.; Pinelis, V.G. Brain biomarkers in children after mild and severe traumatic brain injury. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2021, 131, 103–107. [Google Scholar]
- Mete, A.Ö.; Koçak, K.; Saracaloglu, A.; Demiryürek, S.; Altınbaş, Ö.; Demiryürek, A.T. Effects of antiviral drug therapy on dynamic thiol/disulphide homeostasis and nitric oxide levels in covid-19 patients. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 907, 174306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silver, J.M.; McAllister, T.W.; Arciniegas, D.B. Textbook of Traumatic Brain Injury; American Psychiatric Pub: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Cherian, L.; Hlatky, R.; Robertson, C.S. Nitric oxide in traumatic brain injury. Brain Pathol. 2004, 14, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipton, S.A.; Choi, Y.B.; Pan, Z.H.; Lei, S.Z.; Chen, H.S.; Sucher, N.J.; Loscalzo, J.; Singel, D.J.; Stamler, J.S. A redox-based mechanism for the neuroprotective and neurodestructive effects of nitric oxide and related nitroso-compounds. Nature 1993, 364, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.R.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, E.; Kim, M.; Park, M. Dorsal and ventral hippocampus differentiate in functional pathways and differentially associate with neurological disease-related genes during postnatal development. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gulyaeva, O.A.; Bakirov, A.B.; Chemikosova, T.S.; Averianov, S.V.; Arsenina, O.I.; Karimova, L.K. Dependence of dental status from the level of endogenous intoxication in chemical industry workers based on the oral fluid composition study. Stomatologiia (Mosk) 2019, 98, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.C.; Yao, W.; Hashimoto, K. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (bdnf)-trkb signaling in inflammation-related depression and potential therapeutic targets. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2016, 14, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Charney, D.S.; Manji, H.K. Life stress, genes, and depression: Multiple pathways lead to increased risk and new opportunities for intervention. Sci. STKE 2004, 2004, re5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McEwen, B.S. Protective and damaging effects of stress mediators: Central role of the brain. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2006, 8, 367–381. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Z. The relationships between stress, mental disorders, and epigenetic regulation of bdnf. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sagarkar, S.; Bhamburkar, T.; Shelkar, G.; Choudhary, A.; Kokare, D.M.; Sakharkar, A.J. Minimal traumatic brain injury causes persistent changes in DNA methylation at bdnf gene promoters in rat amygdala: A possible role in anxiety-like behaviors. Neurobiol. Dis. 2017, 106, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todkar, A.; Granholm, L.; Aljumah, M.; Nilsson, K.W.; Comasco, E.; Nylander, I. Hpa axis gene expression and DNA methylation profiles in rats exposed to early life stress, adult voluntary ethanol drinking and single housing. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2015, 8, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keller, J.; Gomez, R.; Williams, G.; Lembke, A.; Lazzeroni, L.; Murphy, G.M., Jr.; Schatzberg, A.F. Hpa axis in major depression: Cortisol, clinical symptomatology and genetic variation predict cognition. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Wong, M.L.; Licinio, J. Sequence variations of abcb1, slc6a2, slc6a3, slc6a4, creb1, crhr1 and ntrk2: Association with major depression and antidepressant response in mexican-americans. Mol. Psychiatry 2009, 14, 1105–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yohn, C.N.; Gergues, M.M.; Samuels, B.A. The role of 5-ht receptors in depression. Mol. Brain 2017, 10, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, S.-T.; Hung, H.-Y.; Ro, L.-S.; Liao, M.-F.; Amstislavskaya, T.G.; Tikhonova, M.A.; Yang, Y.-L.; Lu, K.-T. Chronic Administration of 7,8-DHF Lessens the Depression-like Behavior of Juvenile Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Treated Rats at Their Adult Age. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2169. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13122169
Yang S-T, Hung H-Y, Ro L-S, Liao M-F, Amstislavskaya TG, Tikhonova MA, Yang Y-L, Lu K-T. Chronic Administration of 7,8-DHF Lessens the Depression-like Behavior of Juvenile Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Treated Rats at Their Adult Age. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(12):2169. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13122169
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Shih-Te, Hsiu-Yi Hung, Long-Sun Ro, Ming-Feng Liao, Tamara G. Amstislavskaya, Maria A. Tikhonova, Yi-Ling Yang, and Kwok-Tung Lu. 2021. "Chronic Administration of 7,8-DHF Lessens the Depression-like Behavior of Juvenile Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Treated Rats at Their Adult Age" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 12: 2169. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13122169
APA StyleYang, S.-T., Hung, H.-Y., Ro, L.-S., Liao, M.-F., Amstislavskaya, T. G., Tikhonova, M. A., Yang, Y.-L., & Lu, K.-T. (2021). Chronic Administration of 7,8-DHF Lessens the Depression-like Behavior of Juvenile Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Treated Rats at Their Adult Age. Pharmaceutics, 13(12), 2169. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13122169







