The Role of Transmission Electron Microscopy in the Early Development of Mesoporous Materials for Tissue Regeneration and Drug Delivery Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
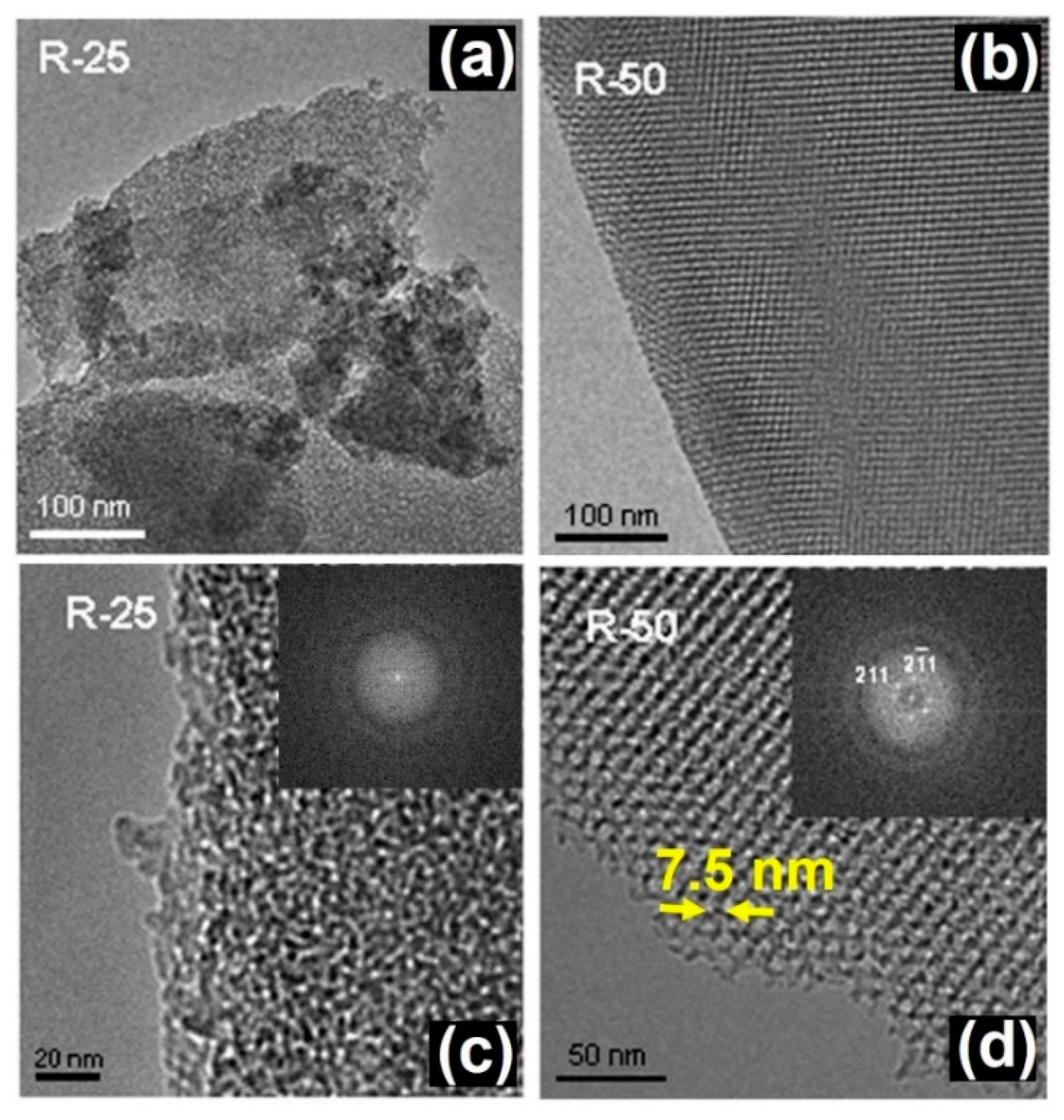
3. Results
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Manzano Garcia, M.; Colilla, M. Biomedical Applications of Mesoporous Ceramics: Drug Delivery, Smart Materials and Bone Tissue Engineering; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; ISBN 9780367380601. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Shi, J. Chemistry of Mesoporous Organosilica in Nanotechnology: Molecularly Organic–Inorganic Hybridization into Frameworks. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 3235–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argauer, R.J.; Landolt, G.R. Crystalline Zeolite Zsm-5 and Method of Preparing the Same. U.S. Patent 3702886, 14 November 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa, T.; Shimizu, T.; Kuroda, K.; Kato, C. The preparation of alkyltrimethylammonium-kanemite complexes and their conversion to microporous materials. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1990, 63, 988–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inagaki, S.; Fukushima, Y.; Kuroda, K. Synthesis of highly ordered mesoporous materials from a layered polysilicate. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1993, 8, 680–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresge, C.T.; Leonowicz, M.E.; Roth, W.J.; Vartuli, J.C.; Beck, J.S. Ordered mesoporous molecular sieves synthesized by a liquid-crystal template mechanism. Nature 1992, 359, 710–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, J.S.; Vartuli, J.C.; Roth, W.J.; Leonowicz, M.E.; Kresge, C.T.; Schmitt, K.D.; Chu, C.T.W.; Olson, D.H.; Sheppard, E.W.; McCullen, S.B.; et al. A new family of mesoporous molecular sieves prepared with liquid crystal templates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 10834–10843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derouane, E.G. (Ed.) Catalysts for Fine Chemical Synthesis: Microporous and Mesoporous Solid Catalysts; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; Volume 4, ISBN 978047 1490548. [Google Scholar]
- Zu, L.; Zhang, W.; Qu, L.; Liu, L.; Li, W.; Liu, A.Y.; Li, W. Mesoporous Materials for Electrochemical Energy Storage and Conversion. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2002152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Rámila, A.; del Real, R.P.; Pérez-Pariente, J. A New Property of MCM-41: Drug Delivery System. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Colilla, M.; González, B. Medical applications of organic–inorganic hybrid materials within the field of silica-based bioceramics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 596–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bass, J.D.; Grosso, D.; Boissiere, C.; Belamie, E.; Coradin, T.; Sanchez, C. Stability of Mesoporous Oxide and Mixed Metal Oxide Materials under Biologically Relevant Conditions. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 4349–4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, A.; Colilla, M.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Vallet-Regí, M. Incorporation of Phosphorus into Mesostructured Silicas: A Novel Approach to Reduce the SiO2 Leaching in Water. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 4135–4145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba, I.; Colilla, M.; Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. In vitro stability of SBA-15 under physiological conditions. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2010, 132, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza, A.; Guisasola, E.; Ruiz-Hernández, E.; Vallet-Regí, M. Magnetically triggered multidrug release by hybrid mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeza, A.; Guisasola, E.; Torres-Pardo, A.; González-Calbet, J.M.; Melen, G.J.; Ramirez, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Hybrid enzyme-polymeric capsules/mesoporous silica nanodevice for in situ cytotoxic agent generation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 4625–4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paris, J.L.; Cabañas, M.V.; Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Polymer-grafted mesoporous silica nanoparticles as ultrasound-responsive drug carriers. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 11023–11033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Villegas, M.R.; Baeza, A.; Usategui, A.; Ortiz-Romero, P.L.; Pablos, J.L.; Vallet-Regí, M. Collagenase nanocapsules: An approach to fibrosis treatment. Acta Biomater. 2018, 74, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora-Raimundo, P.; Lozano, D.; Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Nanoparticles to knockdown osteoporosis-related gene and promote osteogenic marker expression for osteoporosis treatment. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 5451–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paris, J.L.; de la Torre, P.; Cabañas, M.V.; Manzano, M.; Flores, A.I.; Vallet-Regí, M. Vectorization of ultrasound-responsive nanoparticles in placental mesenchymal stem cells for cancer therapy. Acta Biomater. 2019, 83, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, J.L.; Lafuente, N.; Cabañas, V.; Román, J.; Peña, J.; Vallet-Regí, M. Fabrication of a nanoparticle-containing 3d porous bone scaffold with proangiogenic and antibacterial properties. Acta Biomater. 2019, 86, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heras, C.; Sanchez-Salcedo, S.; Lozano, D.; Peña, J.; Esbrit, P.; Vallet-Regí, M.; Salinas, A. Osteostatin potentiates the bioactivity of mesoporous glass scaffolds containing Zn2+ ions in human mesenchymal stem cell cultures. Acta Biomater. 2019, 89, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, V.M.; Álvarez, E.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Baeza, A.; Serrano-López, J.; Vallet-Regí, M. Bacteria as nanoparticles carrier for enhancing penetration in a tumoral matrix model. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 7, 1901942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Carmona, M.; Colilla, M.; Ruiz-González, M.L.; González-Calbet, J.M.; Vallet-Regí, M. High resolution transmission electron microscopy: A key tool to understand drug release from mesoporous matrices. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 225, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Huo, Q.; Feng, J.; Chmelka, B.F.; Stucky, G.D. Nonionic Triblock and Star Diblock Copolymer and Oligomeric Surfactant Syntheses of Highly Ordered, Hydrothermally Stable. Mesoporous Silica Struct. 1998, 120, 6024–6036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Jun, S.; Ryoo, R. Improvement of Hydrothermal Stability of Mesoporous Silica Using Salts: Reinvestigation for Time-Dependent Effects. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 6200–6205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Ryoo, R. Synthesis of MCM-48 single crystals. Chem. Commun. 1998, 2, 259–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, M.; Jaroniec, M.; Sayari, A. Adsorption Study of Surface and Structural Properties of MCM-41 Materials of Different Pore Sizes. J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, M.; Jaroniec, M.; Sayari, A. Application of Large Pore MCM-41 Molecular Sieves to Improve Pore Size Analysis Using Nitrogen Adsorption Measurements. Langmuir 1997, 13, 6267–6273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, M.; Jaroniec, M.; Ryoo, R.; Joo, S.H. Characterization of MCM-48 Silicas with Tailored Pore Sizes Synthesized via a Highly Efficient Procedure. Chem. Mater. 2000, 12, 1414–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.M.; Terasaki, O.; Gai, P.L.; Zhou, W.; González-Calbet, J.M. Structural Elucidation of Microporous and Mesoporous Catalysts and Molecular Sieves by High-Resolution Electron Microscopy. Acc. Chem. Res. 2001, 34, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcos, D.; López-Noriega, A.; Ruiz-Hernández, E.; Ruiz, L.; González-Calbet, J.M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Synthesis of Mesoporous Microparticles for Biomedical Application. Key Eng. Mater. 2008, 377, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slowing, I.; Trewyn, B.G.; Lin, V.S. Effect of surface functionalization of MCM-41-type mesoporous silica nanoparticles on the endocytosis by human cancer cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 14792–14793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, R.; Roy, I.; Ohulchanskyy, T.Y.; Goswami, L.N.; Bonoiu, A.C.; Bergey, E.J.; Tramposch, K.M.; Maitra, A.; Prasad, P.N. Covalently dye-linked, surface-controlled, and bioconjugated organically modified silica nanoparticles as targeted probes for optical imaging. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.J.; Fu, F.F.; Xu, K.B.; Zou, R.J.; Yang, J.M.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Xiao, Z.Y.; Hu, J.Q. Oleic acid-conjugated hollow mesoporous silica/CuS nanocomposites as a difunctional nanoplatform for targeted chemo-photothermal therapy of cancer cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 5358–5367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Balas, F.; Arcos, D. Mesoporous materials for drug delivery. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 7548–7558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gayam, S.R.; Wu, S.-P. Redox responsive Pd(II) templated rotaxane nanovalve capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles: A folic acid mediated biocompatible cancer-targeted drug delivery system. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 7009–7016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M.H.; Lin, H.M. Preparation and identification of multifunctional mesoporous silica nanoparticles for in vitro and in vivo dual-mode imaging, theranostics, and targeted tracking. Biomaterials 2015, 46, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.H.; Niu, Y.M.; Li, Y.; Gong, Y.X.; Shi, H.H.; Huo, Q.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Q.W. Stimuli-responsive delivery vehicles based on mesoporous silica nanoparticles: Recent advances and challenges. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 1339–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlipf, D.M.; Rankin, S.E.; Knutson, B.L. Selective external surface functionalization of large-pore silica materials capable of protein loading. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2017, 244, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talavera-Pech, W.A.; Esparza-Ruiz, A.; Quintana-Owen, P.A.; Vilchis-Nestor, R.; Carrera-Figueiras, C.; Avila-Ortega, A. Effects of different amounts of APTES on physicochemical and structural properties of amino-functionalized MCM-41-MSNs. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2016, 80, 697–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.L.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, C.S. Charge-Reversal APTES-Modified Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles with High Drug Loading and Release Controllability. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 17166–17175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabañas, M.V.; Lozano, D.; Torres-Pardo, A.; Sobrino, C.; González-Calbet, J.M.; Arcos, D.; Vallet-Regí, M. Features of aminopropyl modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Implications on the active targeting capability. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 220, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokubo, T.; Kushitani, H.; Sakka, S.; Kitsugi, T.; Yamamuro, T. Solutions able to reproduce in vivo surface-structure changes in bioactive glass-ceramic A-W. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1990, 24, 721–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Ruiz-González, L.; Doadrio, J.C.; González Calbet, J.M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Tissue regeneration: A new property of mesoporous materials. Solid State Sci. 2005, 7, 983–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Ruiz-González, L.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; González-Calbet, J.M. Revisiting silica based ordered mesoporous materials: Medical applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2006, 16, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.-B.; Nakanishi, K.; Kokubo, T.; Soga, N.; Ohtsuki, C.; Nakamura, T.; Kitsugi, T.; Yamamuro, T. Dependence of Apatite Formation on Silica Gel on Its Structure: Effect of Heat Treatment. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1995, 78, 1769–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regí, M. Ceramics for medical applications. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 2001, 2, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Ragel, C.; Salinas, A. Glasses with Medical Applications. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2003, 2003, 1029–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.M.; Clark, A.E.; Hench, L.L. Effect of Texture on the Rate of Hydroxyapatite Formation on Gel-Silica Surface. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1995, 78, 2463–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.M.; Hench, L.L. Mechanisms of hydroxyapatite formation on porous gel-silica substrates. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 1996, 7, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcos, D.; Greenspan, D.C.; Vallet-Regí, M. Influence of the Stabilization Temperature on Textural and Structural Features and Ion Release in SiO2−CaO−P2O5 Sol−Gel Glasses. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 1515–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bari, A.; Bloise, N.; Fiorilli, S.; Novajra, G.; Vallet-Regí, M.; Bruni, G.; Torres-Pardo, A.; González-Calbet, J.M.; Visai, L.; Vitale-Brovarone, C. Copper-containing mesoporous bioactive glass nanoparticles as multifunctional agent for bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2017, 55, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.Z.; Yan, X.X.; Zhou, X.F.; Zhou, L.; Wang, H.N.; Tang, H.W.; Yu, C. Mesoporous bioactive glasses for controlled drug release. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 109, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Yu, C.; Zhou, X.; Tang, J.; Zhao, D. Highly ordered mesoporous bioactive glasses with superior in vitro bone-forming bioactivities. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 5980–5984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Noriega, A.; Arcos, D.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Sakamoto, Y.; Terasaki, O.; Vallet-Regí, M. Ordered mesoporous bioactive glasses for bone tissue regeneration. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 3137–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Colilla, M. Structure and functionalization of mesoporous bioceramics for bone tissue regeneration and local drug delivery. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2012, 370, 1400–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, F.; Li, L.; Chen, D. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles: Synthesis, biocompatibility and drug delivery. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1504–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, D.; Gao, L.; Wang, J.; Shokouhimehr, M.; Liu, J.; Yu, Y.; Hackett, M.J.; So, P.; Zheng, B.; Yao, Z.; et al. A general strategy for site-directed enzyme immobilization by using NiO nanoparticle decorated mesoporous silica. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 7916–7921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Chang, J. Multifunctional mesoporous bioactive glasses for effective delivery of therapeutic ions and drug/growth factors. J. Control. Release 2014, 193, 282–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol-Taygun, M.; Zheng, K.; Boccaccini, A.R. Nanoscale bioactive glasses in medical applications. Int. J. Appl. Glass Sci. 2013, 4, 136–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Qiao, S.Z.; Hu, A.H.; Lu, G.Q. Magnetic nanocomposites with mesoporous structures: Synthesis and applications. Small 2011, 7, 425–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.; Trewyn, B.G.; Stellmaker, M.P.; Lin, V.S. Stimuli-responsive controlled-release delivery system based on mesoporous silica nanorods capped with magnetic nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 5038–5044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castanotto, D.; Rossi, J.J. The promises and pitfalls of RNA-interference-based therapeutics. Nature 2009, 457, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruiz-Hernández, E.; Baeza, A.; Vallet-Regí, M. Smart Drug Delivery through DNA/Magnetic Nanoparticle Gates. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Qiao, S.Z.; Jin, Y.G.; Yang, H.G.; Budihartono, S.; Stahr, F.; Yand, Z.F.; Wang, X.L.; Hao, Z.P.; Lu, G.Q. Fabrication and Size-Selective Bioseparation of Magnetic Silica Nanospheres with Highly Ordered Periodic Mesostructure. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2008, 18, 3203–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.R.; Kim, S.; Kang, D.H.; Lee, J.I.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, W.S.; Cho, D.H.; Lim, H.B.; Kim, J.; Hur, N.H. Highly Uniform Superparamagnetic Mesoporous Spheres with Submicrometer Scale and Their Uptake into Cells. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 6738–6742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Saavedra, F.; Ruiz-Hernández, E.; Boré, A.; Arcos, D.; Vallet-Regí, M.; Vilaboa, N. Magnetic mesoporous silica spheres for hyperthermia therapy. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 4522–4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knezevic, N.Z.; Ruiz-Hernández, E.; Hennink, W.E.; Vallet-Regí, M. Magnetic mesoporous silica-based core/shell nanoparticles for biomedical applications. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 9584–9593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boissiere, C.; Grosso, D.; Chaumonnot, A.; Nicole, L.; Sanchez, C. Aerosol route to functional nanostructured inorganic and hybrid porous materials. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 599–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Noriega, A.; Ruiz-Hernández, E.; Stevens, S.M.; Arcos, D.; Anderson, M.W.; Terasaki, O.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous Microspheres with Doubly Ordered Core−Shell Structure. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 18–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grün, M.; Lauer, I.; Unger, K.K. The synthesis of micrometer- and submicrometer-size spheres of ordered mesoporous oxide MCM-41. Adv. Mater. 1997, 9, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcos, D.; Fal-Miyar, V.; Ruiz-Hernández, E.; García-Hernández, M.; Ruiz-González, M.L.; González-Calbet, J.M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Supramolecular mechanisms in the synthesis of mesoporous magnetic nanospheres for hyperthermia. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karger, J.; Valiullin, R. Mass transfer in mesoporous materials: The benefit of microscopic diffusion measurement. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 4172–4197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasciotti, E.; Liu, X.; Bhavane, R.; Plant, K.; Leonard, A.D.; Price, B.K.; Cheng, M.M.; Decuzzi, P.; Tour, J.M.; Robertson, F.; et al. Mesoporous silicon particles as a multistage delivery system for imaging and therapeutic applications. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Gai, S.; Lin, J. Functionalized mesoporous silica materials for controlled drug delivery. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 3679–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. Ordered mesoporous materials for drug delivery. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 117, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trejo, C.G.; Lozano, D.; Manzano, M.; Doadrio, J.C.; Salinas, A.J.; Dapía, S.; Gómez-Barrena, E.; Vallet-Regí, M.; García-Honduvilla, N.; Buján, J.; et al. The osteoinductive properties of mesoporous silicate coated with osteostatin in a rabbit femur cavity defect model. Biomaterials 2010, 33, 8564–8573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Martinez, A.; Doadrio, A.L.; Pérez-Pariente, J.; Vallet-Regí, M. Release evaluation of drugs from ordered three-dimensional silica structures. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 26, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, J.; Rosenholm, J.; Areva, S.; Lindén, M. Influences of Material Characteristics on Ibuprofen Drug Loading and Release Profiles from Ordered Micro- and Mesoporous Silica Matrices. Chem. Mater. 2004, 16, 4160–4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, A.; Balas, F.; Colilla, M.; Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Functionalization degree of SBA-15 as key factor to modulate sodium alendronate dosage. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 116, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balas, F.; Manzano, M.; Horcajada, P.; Vallet-Regí, M. Confinement and Controlled Release of Bisphosphonates on Ordered Mesoporous Silica-Based Materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 8116–8117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Mourabit, S.; Guillot, M.; Toquer, G.; Cambedouzou, J.; Goettmann, F.; Grandjean, A. Stability of mesoporous silica under acidic conditions. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 10916–10924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Manzano, M.; González-Calbet, J.M.; Okunishi, E. Evidence of drug confinement into silica mesoporous matrices by STEM spherical aberration corrected microscopy. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 2956–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisasola, E.; Baeza, A.; Talelli, M.; Arcos, D.; Moros, M.; de la Fuente, J.M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Magnetic-Responsive Release Controlled by Hot Spot Effect. Langmuir 2015, 31, 12777–12782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Carmona, M.; Baeza, A.; Rodriguez-Milla, M.A.; García-Castro, J.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles grafted with a light-responsive protein shell for highly cytotoxic antitumoral therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 5746–5752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paris, J.L.; Mannaris, C.; Cabañas, M.V.; Carlisle, R.; Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M.; Coussios, C.C. Ultrasound-mediated cavitation-enhanced extravasation of mesoporous silica nanoparticles for controlled-release drug delivery. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 340, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, C.B.; Erdman, N. Low Voltage Electron Microscopy: Principles and Applications; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; ISBN 9781119971115. [Google Scholar]
- Egerton, R.F.; Li, P.; Malac, M. Radiation damage in the TEM and SEM. Micron 2004, 35, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crozier, P.A. Vibrational and valence aloof beam EELS: A potential tool for nondestructive characterization of nanoparticle surfaces. Ultramicroscopy 2017, 180, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Bilhorn, R. Performance of the DDD as a Direct Electron Detector for Low Dose Electron Microscopy. Microsc. Microanal. 2010, 16, 854–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henderson, R. Cryo-protection of protein crystals against radiation damage in electron and X-ray diffraction. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 1990, 241, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruiz-González, M.L.; Torres-Pardo, A.; González-Calbet, J.M. The Role of Transmission Electron Microscopy in the Early Development of Mesoporous Materials for Tissue Regeneration and Drug Delivery Applications. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2200. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13122200
Ruiz-González ML, Torres-Pardo A, González-Calbet JM. The Role of Transmission Electron Microscopy in the Early Development of Mesoporous Materials for Tissue Regeneration and Drug Delivery Applications. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(12):2200. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13122200
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuiz-González, María Luisa, Almudena Torres-Pardo, and José M. González-Calbet. 2021. "The Role of Transmission Electron Microscopy in the Early Development of Mesoporous Materials for Tissue Regeneration and Drug Delivery Applications" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 12: 2200. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13122200
APA StyleRuiz-González, M. L., Torres-Pardo, A., & González-Calbet, J. M. (2021). The Role of Transmission Electron Microscopy in the Early Development of Mesoporous Materials for Tissue Regeneration and Drug Delivery Applications. Pharmaceutics, 13(12), 2200. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13122200





