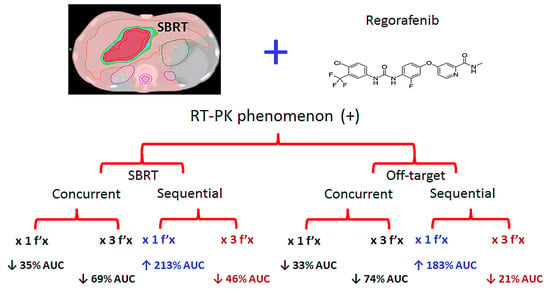
Effect of Synchronous Versus Sequential Regimens on the Pharmacokinetics and Biodistribution of Regorafenib with Irradiation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
Reagents
2.2. In Vivo Study
2.2.1. Animals and Sample Preparation
2.2.2. Irradiation Technique
2.2.3. Drug Delivery with RT under Different Time Schedules and Doses
2.2.4. Sample Preparation
2.2.5. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Ultraviolet (HPLC–UV)
2.2.6. Regorafenib Plasma Extraction
2.2.7. Calibration Curves
2.2.8. Accuracy and Precision Evaluation
2.2.9. Organ Distribution
2.2.10. Organ Samples
2.2.11. Hepatic and Renal Functions
2.2.12. Pharmacokinetics and Data Analysis
2.3. In Vitro Study
2.3.1. Cell Viability Assay
2.3.2. Morphological Observation
2.3.3. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.3.4. Apoptosis Assay
2.3.5. Colony Formation Assays
2.4. Calculations and Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Results of Pharmacokinetics for Regorafenib with or without Radiotherapy
3.1.1. Optimization of HPLC–UV Conditions
3.1.2. Method of Validation of Linearity, Recovery, Precision, Accuracy and Stability
3.1.3. Both RT2Gy and RT9Gy Modulated the Area under the Concentration Versus Time Curve (AUC) of Regorafenib in the Plasma of Freely Moving Rats
3.1.4. Organ Distributions under Different Regimens of RT and Regorafenib
3.1.5. Liver and Renal Functions in Different Regimens of RT and Regorafenib
3.2. In Vitro Study
3.2.1. Cell Viability Analysis
3.2.2. Morphological Changes
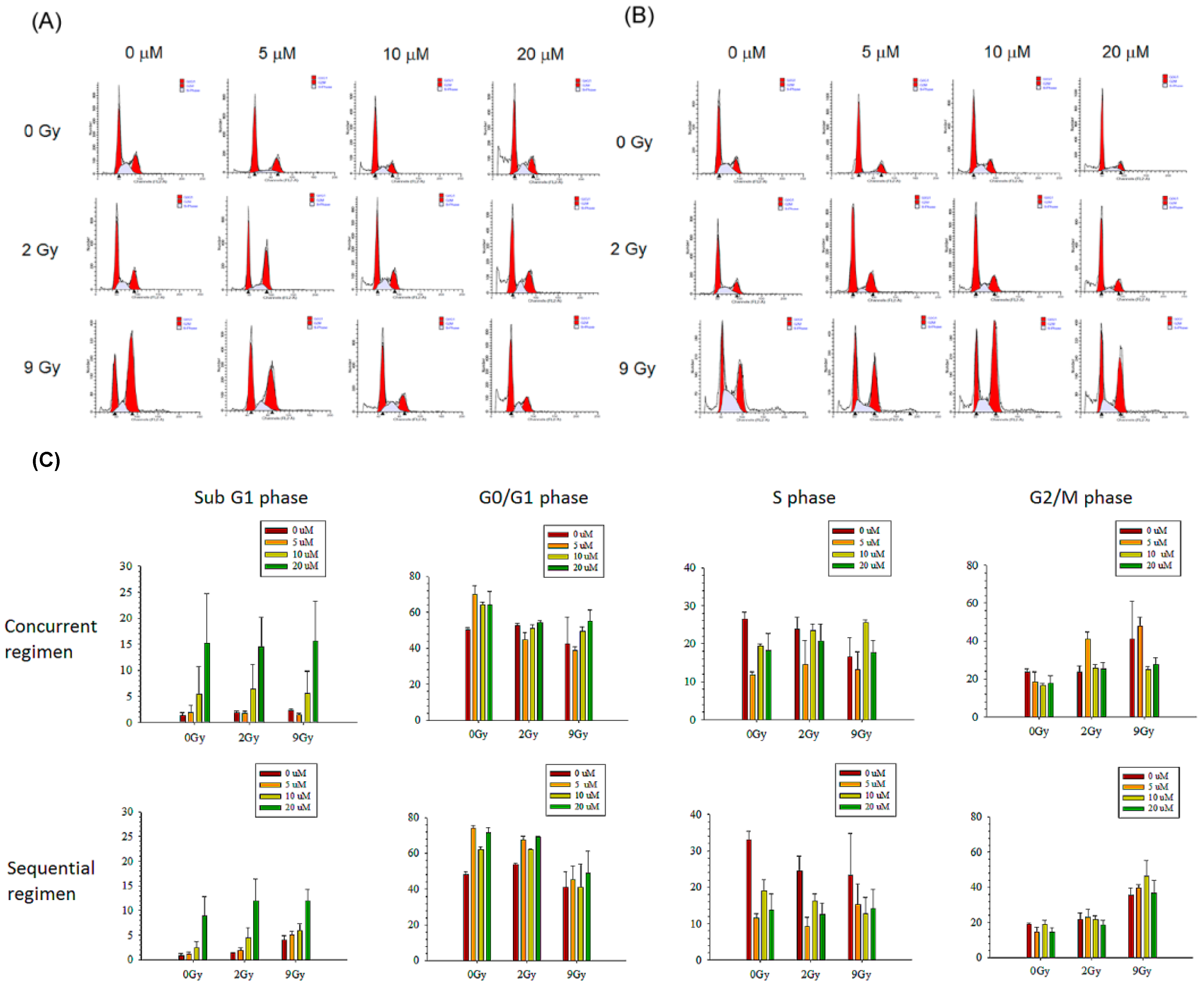
3.2.3. Cell Cycle Analysis
3.2.4. Apoptosis Analysis
3.2.5. Colony Formation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kulik, L.; El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 477–491.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Ricci, S.; Mazzaferro, V.; Hilgard, P.; Gane, E.; Blanc, J.F.; de Oliveira, A.C.; Santoro, A.; Raoul, J.L.; Forner, A.; et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.L.; Kang, Y.K.; Chen, Z.; Tsao, C.J.; Qin, S.; Kim, J.S.; Luo, R.; Feng, J.; Ye, S.; Yang, T.S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Decaens, T.; Raoul, J.L.; Boucher, E.; Kudo, M.; Chang, C.; Kang, Y.K.; Assenat, E.; Lim, H.Y.; Boige, V.; et al. Brivanib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma who were intolerant to sorafenib or for whom sorafenib failed: Results from the randomized phase III BRISK-PS study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3509–3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.X.; Kudo, M.; Assenat, E.; Cattan, S.; Kang, Y.K.; Lim, H.Y.; Poon, R.T.; Blanc, J.F.; Vogel, A.; Chen, C.L.; et al. Effect of everolimus on survival in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma after failure of sorafenib: The EVOLVE-1 randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2014, 312, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.X.; Park, J.O.; Ryoo, B.Y.; Yen, C.J.; Poon, R.; Pastorelli, D.; Blanc, J.F.; Chung, H.C.; Baron, A.D.; Pfiffer, T.E.; et al. Ramucirumab versus placebo as second-line treatment in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma following first-line therapy with sorafenib (REACH): A randomised, double-blind, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 859–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruix, J.; Qin, S.; Merle, P.; Granito, A.; Huang, Y.H.; Bodoky, G.; Pracht, M.; Yokosuka, O.; Rosmorduc, O.; Breder, V.; et al. Regorafenib for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who progressed on sorafenib treatment (RESORCE): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Potters, L.; Kavanagh, B.; Galvin, J.M.; Hevezi, J.M.; Janjan, N.A.; Larson, D.A.; Mehta, M.P.; Ryu, S.; Steinberg, M.; Timmerman, R.; et al. American Society for Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology (ASTRO) and American College of Radiology (ACR) practice guideline for the performance of stereotactic body radiation therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 76, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.W.; Lin, L.C.; Kuo, Y.C.; Liang, J.A.; Kuo, C.C.; Chiou, J.F. Phase 2 study of combined sorafenib and radiation therapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2014, 88, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.H.; Chen, Y.J.; Tsai, T.H.; Wang, L.Y.; Tai, H.C.; Huang, H.L.; Huang, Y.C. Robust combination of liver stereotactic body radiotherapy modulates pharmacokinetics of sorafenib toward preferable parameters. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brade, A.M.; Ng, S.; Brierley, J.; Kim, J.; Dinniwell, R.; Ringash, J.; Wong, R.R.; Cho, C.; Knox, J.; Dawson, L.A. Phase 1 Trial of Sorafenib and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 94, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goody, R.B.; Brade, A.M.; Wang, L.; Craig, T.; Brierley, J.; Dinniwell, R.; Wong, R.K.S.; Cho, C.; Kim, J.; Kassam, Z.; et al. Phase I trial of radiation therapy and sorafenib in unresectable liver metastases. Radiother. Oncol. 2017, 123, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.H.; Lin, S.C.; Shueng, P.W.; Kuo, D.Y. Recall radiation dermatitis by sorafenib following stereotactic body radiation therapy. Oncotargets Ther. 2014, 7, 1111–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tian, S.; Nissenblatt, M.; Goyal, S. Regorafenib-induced transverse myelopathy after stereotactic body radiation therapy. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2014, 5, E128–E131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberto, M.; Falcone, R.; Mazzuca, F.; Archibugi, L.; Castaldi, N.; Botticelli, A.; Osti, M.F.; Marchetti, P. The role of stereotactic body radiation therapy in oligometastatic colorectal cancer: Clinical case report of a long-responder patient treated with regorafenib beyond progression. Medicine (Baltimore) 2017, 96, e9023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.H.; Hsieh, Y.J.; Liu, C.Y.; Tai, H.C.; Huang, Y.C.; Shueng, P.W.; Wu, L.J.; Wang, L.Y.; Tsai, T.H.; Chen, Y.J. Abdominal irradiation modulates 5-Fluorouracil pharmacokinetics. J. Transl. Med. 2010, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsieh, C.H.; Hou, M.L.; Chiang, M.H.; Tai, H.C.; Tien, H.J.; Wang, L.Y.; Tsai, T.H.; Chen, Y.J. Head and neck irradiation modulates pharmacokinetics of 5-fluorouracil and cisplatin. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reagan-Shaw, S.; Nihal, M.; Ahmad, N. Dose translation from animal to human studies revisited. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 659–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilhelm, S.M.; Dumas, J.; Adnane, L.; Lynch, M.; Carter, C.A.; Schutz, G.; Thierauch, K.H.; Zopf, D. Regorafenib (BAY 73-4506): A new oral multikinase inhibitor of angiogenic, stromal and oncogenic receptor tyrosine kinases with potent preclinical antitumor activity. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustin, H.G.; Koh, G.Y.; Thurston, G.; Alitalo, K. Control of vascular morphogenesis and homeostasis through the angiopoietin-Tie system. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.S.; Merle, P.; Granito, A.; Huang, Y.H.; Bodoky, G.; Pracht, M.; Yokosuka, O.; Rosmorduc, O.; Gerolami, R.; Caparello, C.; et al. Outcomes of sequential treatment with sorafenib followed by regorafenib for HCC: Additional analyses from the phase III RESORCE trial. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fondevila, F.; Mendez-Blanco, C.; Fernandez-Palanca, P.; Gonzalez-Gallego, J.; Mauriz, J.L. Anti-tumoral activity of single and combined regorafenib treatments in preclinical models of liver and gastrointestinal cancers. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, J.C.; Chou, C.H.; Kuo, M.L.; Hsieh, C.Y. Radiation-enhanced hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion with MMP-9 expression through PI3K/Akt/NF-kappaB signal transduction pathway. Oncogene 2006, 25, 7009–7018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, Y.; Shen, X.; He, M.; Wu, Z.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, S.; Cui, J.; Zeng, Z. Activation of the JNK-c-Jun pathway in response to irradiation facilitates Fas ligand secretion in hepatoma cells and increases hepatocyte injury. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, J.J.; Pan, P.J.; Hsu, F.T. Regorafenib induces extrinsic and intrinsic apoptosis through inhibition of ERK/NF-kappaB activation in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 1036–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bergers, G.; Hanahan, D. Modes of resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy. Nat. Rev. 2008, 8, 592–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mancuso, M.R.; Davis, R.; Norberg, S.M.; O’Brien, S.; Sennino, B.; Nakahara, T.; Yao, V.J.; Inai, T.; Brooks, P.; Freimark, B.; et al. Rapid vascular regrowth in tumors after reversal of VEGF inhibition. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 2610–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wachsberger, P.; Burd, R.; Dicker, A.P. Tumor response to ionizing radiation combined with antiangiogenesis or vascular targeting agents: Exploring mechanisms of interaction. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 1957–1971. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Karin, M. Ionizing radiation and short wavelength UV activate NF-kappaB through two distinct mechanisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 13012–13017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuo, M.T.; Liu, Z.; Wei, Y.; Lin-Lee, Y.C.; Tatebe, S.; Mills, G.B.; Unate, H. Induction of human MDR1 gene expression by 2-acetylaminofluorene is mediated by effectors of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway that activate NF-kappaB signaling. Oncogene 2002, 21, 1945–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eyries, M.; Collins, T.; Khachigian, L.M. Modulation of growth factor gene expression in vascular cells by oxidative stress. Endothel. J. Endothel. Cell Res. 2004, 11, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, M.; Griffith, J.; Panneerselvam, J.; Babu, A.; Mani, J.; Herman, T.; Ramesh, R.; Munshi, A. Regorafenib sensitizes human breast cancer cells to radiation by inhibiting multiple kinases and inducing DNA damage. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatto, L.; Nannini, M.; Saponara, M.; Di Scioscio, V.; Beltramo, G.; Frezza, G.P.; Ercolani, G.; Pinna, A.D.; Astolfi, A.; Urbini, M.; et al. Radiotherapy in the management of gist: State of the art and new potential scenarios. Clin. Sarcoma Res. 2017, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carr, B.I.; Cavallini, A.; Lippolis, C.; D’Alessandro, R.; Messa, C.; Refolo, M.G.; Tafaro, A. Fluoro-Sorafenib (Regorafenib) effects on hepatoma cells: Growth inhibition, quiescence, and recovery. J. Cell. Physiol. 2013, 228, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsieh, C.H.; Jeng, K.S.; Lin, C.C.; Chen, C.K.; Liu, C.Y.; Lin, C.P.; Tai, H.C.; Wang, C.H.; Shueng, P.W.; Chen, Y.J. Combination of sorafenib and intensity modulated radiotherapy for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Drug Investig. 2009, 29, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.D.; Liu, J.; Ren, Z.G.; Gu, K.; Zhou, Z.H.; Li, W.T.; Chen, Z.; Xu, Z.Y.; Liu, L.M.; Jiang, G.L. Maintenance of Sorafenib following combined therapy of three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy/intensity-modulated radiation therapy and transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in patients with locally advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A phase I/II study. Radiat. Oncol. 2010, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.Y.; Wang, Y.C.; Wu, T.H.; Lee, C.F.; Wu, T.J.; Chou, H.S.; Tsang, N.M.; Chan, K.M.; Lee, W.C. Efficacy of External Beam Radiation-Based Treatment plus Locoregional Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Associated with Portal Vein Tumor Thrombosis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 6017406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, N.A.; Richel, D.J.; Verhoeff, J.J.; Stalpers, L.J. Bowel perforation after radiotherapy in a patient receiving sorafenib. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 2405–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollom, E.L.; Deng, L.; Pai, R.K.; Brown, J.M.; Giaccia, A.; Loo, B.W., Jr.; Shultz, D.B.; Le, Q.T.; Koong, A.C.; Chang, D.T. Gastrointestinal Toxicities With Combined Antiangiogenic and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 92, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, T.H.; Chen, Y.J.; Hou, M.L.; Wang, L.Y.; Tai, H.C.; Hsieh, C.H. Pelvic irradiation modulates the pharmacokinetics of cisplatin in the plasma and lymphatic system. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2015, 7, 375–384. [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh, C.H.; Liu, C.Y.; Hsieh, Y.J.; Tai, H.C.; Wang, L.Y.; Tsai, T.H.; Chen, Y.J. Matrix metalloproteinase-8 mediates the unfavorable systemic impact of local irradiation on pharmacokinetics of anti-cancer drug 5-Fluorouracil. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alongi, F.; Giaj-Levra, N.; Fiorentino, A.; Mazzola, R.; Fersino, S.; Ricchetti, F.; Ruggieri, R. Low-dose bath with volumetric modulated arc therapy in breast cancer: “Much ado about nothing?”. Tumori 2016, 102, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeiner, P.S.; Kinzig, M.; Dive, I.; Maurer, G.D.; Filipski, K.; Harter, P.N.; Senft, C.; Bahr, O.; Hattingen, E.; Steinbach, J.P.; et al. Regorafenib CSF Penetration, Efficacy, and MRI Patterns in Recurrent Malignant Glioma Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demetri, G.D.; Reichardt, P.; Kang, Y.K.; Blay, J.Y.; Rutkowski, P.; Gelderblom, H.; Hohenberger, P.; Leahy, M.; von Mehren, M.; Joensuu, H.; et al. Efficacy and safety of regorafenib for advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumours after failure of imatinib and sunitinib (GRID): An international, multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2013, 381, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grothey, A.; Van Cutsem, E.; Sobrero, A.; Siena, S.; Falcone, A.; Ychou, M.; Humblet, Y.; Bouche, O.; Mineur, L.; Barone, C.; et al. Regorafenib monotherapy for previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer (CORRECT): An international, multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2013, 381, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouverneur, A.; Claraz, P.; Rousset, M.; Arnaud, M.; Fourrier-Reglat, A.; Pariente, A.; Aparicio, T.; Miremont-Salame, G.; Noize, P. Comparative Safety of Targeted Therapies for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer between Elderly and Younger Patients: A Study Using the International Pharmacovigilance Database. Target. Oncol. 2017, 12, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Parameter | AUC0-T | Cmax | Tmax | t½ | Cl | Vss | MRT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit | min mg/mL | mg/mL | min | min | mL/min/kg | mL/kg | min |
| Regorafenib 16 mg/kg × 1 d | 226.8 ± 122.7 | 1.45 ± 0.77 | 190 ± 68 | 942.3 ± 535.1 | 8.18 ± 3.06 | 12641.9 ± 6928.9 | 1483 ± 1066 |
| Regorafenib 16 mg/kg × 3d | 849.6 ± 317.3 a | 4.19 ± 1.53 | 90 ± 63 | 550 ± 146 | 4.21 ± 1.82 | 3604.5 ± 951.1 | 823 ± 341 |
| RT2 Gy × 1 f’x with regorafenib 16 mg/kg × 1d | 152.2 ± 143.5 | 0.92 ± 0.85 | 165 ± 59 | 409 ± 150 | 16.6 ± 7.21 | 21606.9 ± 20731.8 | 651 ± 215 |
| RT2 Gy × 1 f’x followed by regorafenib 16 mg/kg × 1 d | 641.8 ± 305.1 b,e | 3.63 ± 1.76 | 180 ± 63 | 346 ± 93 | 6.19 ± 0.35 | 3081.4 ± 773.1 | 553 ± 116 |
| RT2 Gy × 3 f’x with regorafenib 16 mg/kg × 3 d | 223.0 ± 134.0 d,j | 1.24 ± 0.79l | 125 ± 58 | 372 ± 152 | 23.20 ± 9.45 n | 12759.6 ± 8467.4 p | 584 ± 186 |
| RT2 Gy × 3 f’x followed by regorafenib 16 mg/kg × 3 d | 673.7 ± 224.1 c,f | 3.55 ± 1.08 | 100 ± 24 | 920 ± 956 | 8.56 ± 7.21 | 4156.0 ± 1959.9 | 1370 ± 1365 |
| RT9 Gy × 1 f’x with regorafenib 16 mg/kg × 1 d | 147.5 ± 187.0 | 0.83 ± 0.99 | 155 ± 84 | 654 ± 445 | 34.6 ± 25.3 | 30999.0 ± 34618.0 | 976.3 ± 639.4 |
| RT9 Gy × 1 f’x followed by regorafenib 16 mg/kg × 1 d | 711.4 ± 392.8 g,k | 4.32 ± 2.71 | 155 ± 29 | 608 ± 210 | 3.3 ± 4.3 | 2898.8 ± 4123.7 | 935.1 ± 320.9 |
| RT9 Gy × 3 f’x with regorafenib 16 mg/kg × 3 d | 260.0 ± 110.7 i | 1.39 ± 0.53 m | 98 ± 81 | 662 ± 598 | 19.0 ± 11.7 o | 11564.4 ± 3361.0 q | 983.1 ± 857.7 |
| RT9 Gy × 3 f’x followed by regorafenib 16 mg/kg × 3 d | 460.6 ± 220.5 h,j | 2.49 ± 1.49 | 110 ± 78 | 571 ± 323 | 11.4 ± 4.5 | 7960.3 ± 3023.5 r | 860.7 ± 467.9 |
| Organ (µg/g) | Heart | Liver | Spleen | Lung | Kidneys | Brain |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regorafenib 16 mg/kg × 1 d | 0.45 ± 0.31 | 1.46 ± 0.34 | 0.26 ± 0.10 | 0.47 ± 0.18 | 0.34 ± 0.19 | 0.03 ± 0.04 |
| Regorafenib 16 mg/kg × 3 d | 0.25 ± 0.10 | 1.45 ± 0.74 | 0.38 ± 0.22 | 1.12 ± 0.25 | 0.65 ± 0.25 | 0.01 ± 0.02 |
| RT2 Gy × 1 f’x with regorafenib 16 mg/kg × 1 d | 0.29 ± 0.17 | 1.10 ± 0.51 | 0.19 ± 0.07 | 0.29 ± 0.19 | 0.21 ± 0.11 | 0.02 ± 0.03 |
| RT2 Gy × 1 f’x followed by regorafenib 16 mg/kg × 1 d | 0.78 ± 0.27 a | 2.28 ± 0.75 d | 0.68 ± 0.30 g | 1.27 ± 0.64 l | 0.59 ± 0.27 | 0.08 ± 0.06 |
| RT2 Gy × 3 f’x with regorafenib 16 mg/kg × 3 d | 0.03 ± 0.03 b | 0.55 ± 0.27 e | 0.08 ± 0.06 h | 0.21 ± 0.09 m | 0.13 ± 0.06 r | 0.02 ± 0.05 |
| RT2 Gy × 3 f’x followed by regorafenib 16 mg/kg × 3 d | 0.29 ± 0.18 c | 1.68 ± 0.65 f | 0.41 ± 0.24 i | 0.99 ± 0.43 n | 0.73 ± 0.44 s | 0.03 ± 0.05 |
| RT9 Gy × 1 f’x with regorafenib 16 mg/kg × 1 d | 0.36 ± 0.33 | 1.01 ± 0.58 | 0.14 ± 0.07 | 0.17 ± 0.14 o | 0.18 ± 0.05 | 0.01 ± 0.02 |
| RT9 Gy × 1 f’x followed by regorafenib 16 mg/kg × 1 d | 0.87 ± 0.14 | 2.39 ± 1.20 | 0.68 ± 0.45 j | 1.01 ± 0.70 | 0.59 ± 0.34 | 0.06 ± 0.05 |
| RT9 Gy × 3 f’x with regorafenib 16 mg/kg × 3 d | 0.09 ± 0.07 | 0.70 ± 0.29 | 0.10 ± 0.08 k | 0.25 ± 0.18 p | 0.17 ± 0.12 t | 0.01 ± 0.02 |
| RT9 Gy × 3 f’x followed by regorafenib 16 mg/kg × 3 d | 0.17 ± 0.27 | 1.16 ± 1.12 | 0.23 ± 0.31 | 0.37 ± 0.23 q | 0.40 ± 0.43 | 0.04 ± 0.08 |
| Regorafenib (μM) | RT0 Gy | RT2 Gy | RT9 Gy | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | S | C | S | C | S | |||||||
| Huh-7 | Hep G2 | Huh-7 | Hep G2 | Huh-7 | Hep G2 | Huh-7 | Hep G2 | Huh-7 | Hep G2 | Huh-7 | Hep G2 | |
| IC50 | 6.56 | 9.87 | 12.8 | 17.68 | 6.38 | 10.5 | 12.07 | 18.89 | 6.36 | 8.43 | 15.23 | 16.81 |
| 0 | 100.0 ± 0.0, | 100.0 ± 0.0 | 100.0 ± 0.0 | 100.0 ± 0.0 | 100.1 ± 6.0 | 94.0 ± 16.2 | 87.0 ± 3.3 | 84.3 ± 2.2 | 103.9 ± 27.4 | 98.9 ± 20.8 | 85.7 ± 6.9 | 86.9 ± 6.9 |
| 5 | 60.9 ± 1.8 | 74.6 ± 2.4 | 72.6 ± 1.0 | 82.0 ± 1.9 | 59.8 ± 5.5 | 73.1 ± 11.7 | 59.5 ± 2.7 | 72.1 ± 1.7 | 62.3 ± 14.1 | 64.7 ± 11.3 | 60.2 ± 5.6 | 71.0 ± 5.3 |
| 10 | 35.1 ± 1.6 | 51.3 ± 3.1 | 55.2 ± 1.2 | 67.0 ± 1.3 | 33.9 ± 2.7 | 50.8 ± 7.0 | 46.0 ± 2.9 | 64.1 ± 1.3 | 34.3 ± 5.3 | 46.7 ± 8.9 | 47.6 ± 3.0 | 64.2 ± 4.3 |
| 20 | 15.4 ± 1.0 | 24.7 ± 1.2 | 41.4 ± 0.4 | 46.0 ± 3.4 | 14.4 ± 0.8 | 24.5 ± 2.5 | 36.3 ± 1.4 | 42.4 ± 0.8 | 14.1 ± 0.7 | 20.6 ± 1.5 | 41.1 ± 1.7 | 38.5 ± 1.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsai, T.-H.; Chen, Y.-J.; Wang, L.-Y.; Hsieh, C.-H. Effect of Synchronous Versus Sequential Regimens on the Pharmacokinetics and Biodistribution of Regorafenib with Irradiation. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13030386
Tsai T-H, Chen Y-J, Wang L-Y, Hsieh C-H. Effect of Synchronous Versus Sequential Regimens on the Pharmacokinetics and Biodistribution of Regorafenib with Irradiation. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(3):386. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13030386
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsai, Tung-Hu, Yu-Jen Chen, Li-Ying Wang, and Chen-Hsi Hsieh. 2021. "Effect of Synchronous Versus Sequential Regimens on the Pharmacokinetics and Biodistribution of Regorafenib with Irradiation" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 3: 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13030386
APA StyleTsai, T.-H., Chen, Y.-J., Wang, L.-Y., & Hsieh, C.-H. (2021). Effect of Synchronous Versus Sequential Regimens on the Pharmacokinetics and Biodistribution of Regorafenib with Irradiation. Pharmaceutics, 13(3), 386. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13030386