Drug Repurposing for COVID-19 Treatment by Integrating Network Pharmacology and Transcriptomics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Genes Related to COVID-19
2.2. Drug–Target Relationship Modules
2.3. Network-Based Proximity between Drugs and COVID-19
2.4. Biological Enrichment Analysis of COVID-19 Related Genes on the Drug-Induced Expression Profiles
2.5. GSEA Analysis of Repurposing Drugs in Specific Cell-Types
2.6. Network-Based Prediction of Drug Combinations
3. Results
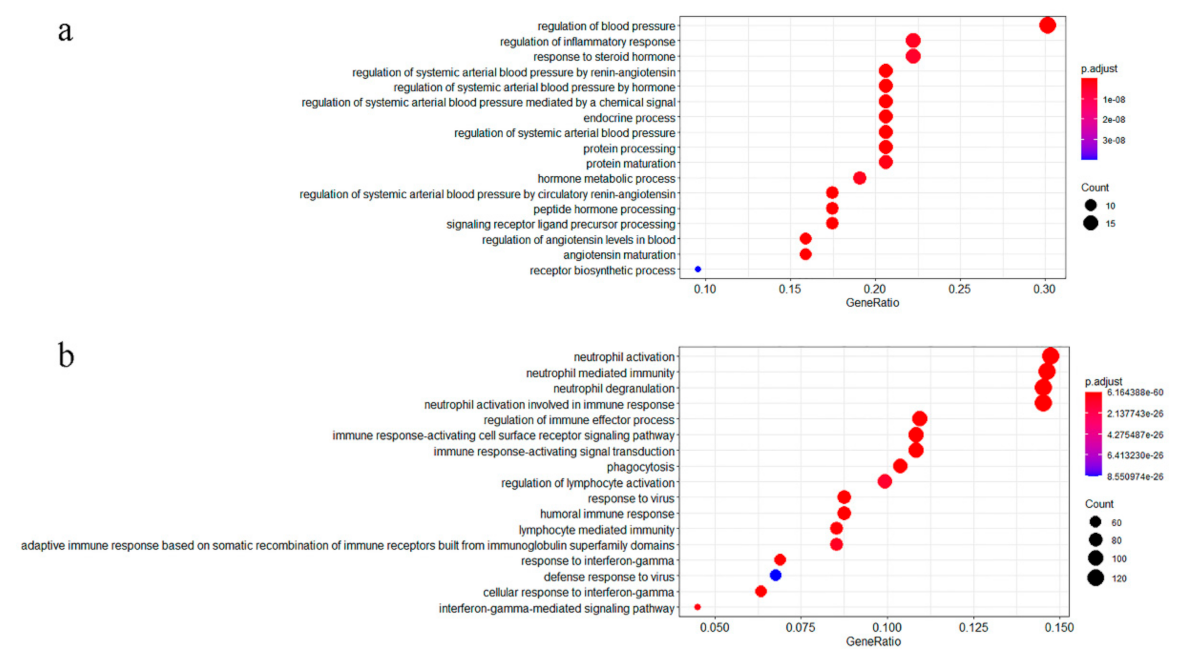
3.1. GO Enrichment Analysis of COVID-19 Related Genes
3.2. Network-Based Proximity Scores between Drug–Target Modules and COVID-19 Related Genes
3.3. GSEA Analysis of COVID-19 Related Genes in Drug-Induced Signatures
3.4. Repurposing Drugs Sensitivity in Specific Cell Type
3.5. Identification of Synergistic Drug Combinations
4. Discussion
- Nicardipine
- Promethazine
- Orantinib and Tipifarnib
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jin, Y.; Yang, H.; Ji, W.; Wu, W.; Chen, S.; Zhang, W.; Duan, G. Virology, Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Control of COVID-19. Viruses 2020, 12, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19)—World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019 (accessed on 14 January 2021).
- Li, G.; De Clercq, E. Therapeutic Options for the 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-NCoV). Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 149–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Zhou, M.; Dong, X.; Qu, J.; Gong, F.; Han, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Y.; et al. Epidemiological and Clinical Characteristics of 99 Cases of 2019 Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A Descriptive Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, W.; Shi, X.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, B.; Liu, J.; Wang, D.; Liu, C.; Meng, Y.; Cui, L.; et al. Early Antiviral Treatment Contributes to Alleviate the Severity and Improve the Prognosis of Patients with Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19). J. Intern. Med. 2020, 288, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Du, G.; Du, R.; Zhao, J.; Jin, Y.; Fu, S.; Gao, L.; Cheng, Z.; Lu, Q.; et al. Remdesivir in Adults with Severe COVID-19: A Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Multicentre Trial. Lancet 2020, 395, 1569–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Home—ClinicalTrials.Gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed on 11 March 2021).
- Warren, T.K.; Jordan, R.; Lo, M.K.; Ray, A.S.; Mackman, R.L.; Soloveva, V.; Siegel, D.; Perron, M.; Bannister, R.; Hui, H.C.; et al. Therapeutic Efficacy of the Small Molecule GS-5734 against Ebola Virus in Rhesus Monkeys. Nature 2016, 531, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinner, C.D.; Gottlieb, R.L.; Criner, G.J.; Arribas Lopez, J.R.; Cattelan, A.M.; Soriano Viladomiu, A.; Ogbuagu, O.; Malhotra, P.; Mullane, K.M.; Castagna, A.; et al. Effect of Remdesivir vs. Standard Care on Clinical Status at 11 Days in Patients with Moderate COVID-19: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2020, 324, 1048–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.; Peto, R.; Abdool Karim, Q.; Alejandria, M.; Henao Restrepo, A.M.; Hernandez Garcia, C.; Kieny, M.P.; Malekzadeh, R.; Murthy, S.; Preziosi, M.-P.; et al. Repurposed Antiviral Drugs for COVID-19; Interim WHO SOLIDARITY Trial Results. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, J.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Kuang, W.; Peng, J.; Chen, L.; Zeng, J. A Network Integration Approach for Drug-Target Interaction Prediction and Computational Drug Repositioning from Heterogeneous Information. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Desai, R.J.; Handy, D.E.; Wang, R.; Schneeweiss, S.; Barabási, A.-L.; Loscalzo, J. Network-Based Approach to Prediction and Population-Based Validation of in Silico Drug Repurposing. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, Y.-F.; Chien, C.-S.; Yarmishyn, A.A.; Lin, Y.-Y.; Luo, Y.-H.; Lin, Y.-T.; Lai, W.-Y.; Yang, D.-M.; Chou, S.-J.; Yang, Y.-P.; et al. A Review of SARS-CoV-2 and the Ongoing Clinical Trials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, D.E.; Jang, G.M.; Bouhaddou, M.; Xu, J.; Obernier, K.; White, K.M.; O’Meara, M.J.; Rezelj, V.V.; Guo, J.Z.; Swaney, D.L.; et al. A SARS-CoV-2 Protein Interaction Map Reveals Targets for Drug-Repurposing. Nature 2020, 583, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Lee, S.; Lee, I. NGSEA: Network-Based Gene Set Enrichment Analysis for Interpreting Gene Expression Phenotypes with Functional Gene Sets. Mol. Cells 2019, 42, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, A.Z.; Ramsey, S.A. A Computational Systems Biology Approach for Identifying Candidate Drugs for Repositioning for Cardiovascular Disease. Interdiscip. Sci. Comput. Life Sci. 2018, 10, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guney, E.; Menche, J.; Vidal, M.; Barabasi, A.-L. Network-Based in Silico Drug Efficacy Screening. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iorio, F.; Bosotti, R.; Scacheri, E.; Belcastro, V.; Mithbaokar, P.; Ferriero, R.; Murino, L.; Tagliaferri, R.; Brunetti-Pierri, N.; Isacchi, A.; et al. Discovery of Drug Mode of Action and Drug Repositioning from Transcriptional Responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14621–14626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vásquez-Bochm, L.X.; Velázquez-Paniagua, M.; Castro-Vázquez, S.S.; Guerrero-Rodríguez, S.L.; Mondragon-Peralta, A.; De La Fuente-Granada, M.; Pérez-Tapia, S.M.; González-Arenas, A.; Velasco-Velázquez, M.A. Transcriptome-Based Identification of Lovastatin as a Breast Cancer Stem Cell-Targeting Drug. Pharmacol. Rep. 2019, 71, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Luo, H.; Xi, Z.; Rogaeva, E. Drug Repositioning for Diabetes Based on “Omics” Data Mining. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinnings, S.L.; Liu, N.; Buchmeier, N.; Tonge, P.J.; Xie, L.; Bourne, P.E. Drug Discovery Using Chemical Systems Biology: Repositioning the Safe Medicine Comtan to Treat Multi-Drug and Extensively Drug Resistant Tuberculosis. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2009, 5, e1000423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronaviridae—NCBI Datasets. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/datasets/coronavirus/genomes/ (accessed on 14 January 2021).
- Wilk, A.J.; Rustagi, A.; Zhao, N.Q.; Roque, J.; Martinez-Colon, G.J.; McKechnie, J.L.; Ivison, G.T.; Ranganath, T.; Vergara, R.; Hollis, T.; et al. A Single-Cell Atlas of the Peripheral Immune Response in Patients with Severe COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1070–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.Y. ClusterProfiler: An R Package for Comparing Biological Themes among Gene Clusters. Omics J. Integr. Biol. 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Guo, A.C.; Lo, E.J.; Marcu, A.; Grant, J.R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.; Sayeeda, Z.; et al. DrugBank 5.0: A Major Update to the DrugBank Database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D1074–D1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SuperTarget. Available online: http://insilico.charite.de/supertarget/index.php?site=drugs (accessed on 14 January 2021).
- Rodchenkov, I.; Babur, O.; Luna, A.; Aksoy, B.A.; Wong, J.V.; Fong, D.; Franz, M.; Siper, M.C.; Cheung, M.; Wrana, M.; et al. Pathway Commons 2019 Update: Integration, Analysis and Exploration of Pathway Data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D489–D497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misselbeck, K.; Parolo, S.; Lorenzini, F.; Savoca, V.; Leonardelli, L.; Bora, P.; Morine, M.J.; Mione, M.C.; Domenici, E.; Priami, C. A Network-Based Approach to Identify Deregulated Pathways and Drug Effects in Metabolic Syndrome. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Yuan, M.; Xin, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, J. Screening Novel Drug Candidates for Alzheimer’s Disease by an Integrated Network and Transcriptome Analysis. Bioinformatics 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis: A Knowledge-Based Approach for Interpreting Genome-Wide Expression Profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Narayan, R.; Corsello, S.M.; Peck, D.D.; Natoli, T.E.; Lu, X.; Gould, J.; Davis, J.F.; Tubelli, A.A.; Asiedu, J.K.; et al. A Next Generation Connectivity Map: L1000 Platform and the First 1,000,000 Profiles. Cell 2017, 171, 1437–1452.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.W.; Zhang, D.; Tian, R.H.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.S.; Cao, J.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zan, T.; Gao, L.; et al. The Underlying Changes and Predicting Role of Peripheral Blood Inflammatory Cells in Severe COVID-19 Patients: A Sentinel? Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 508, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Yang, L.; Liu, R.; Liu, F.; Wu, K.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Zhu, C. Prominent Changes in Blood Coagulation of Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2020, 58, 1116–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laing, A.G.; Lorenc, A.; del Barrio, I.D.M.; Das, A.; Fish, M.; Monin, L.; Munoz-Ruiz, M.; McKenzie, D.R.; Hayday, T.S.; Francos-Quijorna, I.; et al. A Dynamic COVID-19 Immune Signature Includes Associations with Poor Prognosis. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1623–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuart, T.; Butler, A.; Hoffman, P.; Hafemeister, C.; Papalexi, E.; Mauck, W.M.; Hao, Y.; Stoeckius, M.; Smibert, P.; Satija, R. Comprehensive Integration of Single-Cell Data. Cell 2019, 177, 1888–1902.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Vilar, S.; Tatonetti, N.P. High-Throughput Methods for Combinatorial Drug Discovery. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 205rv1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, F.; Kovacs, I.A.; Barabasi, A.L. Network-Based Prediction of Drug Combinations. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menche, J.; Sharma, A.; Kitsak, M.; Ghiassian, S.D.; Vidal, M.; Loscalzo, J.; Barabasi, A.L. Disease Networks. Uncovering Disease-Disease Relationships through the Incomplete Interactome. Science 2015, 347, 1257601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, J.; Xiao, G.; Zhang, J.; He, X.; Ou, M.; Bi, J.; Yang, R.; Di, W.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; et al. Renin-Angiotensin System Inhibitors Improve the Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients with Hypertension. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 757–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woelfel, R.; Corman, V.M.; Guggemos, W.; Seilmaier, M.; Zange, S.; Mueller, M.A.; Niemeyer, D.; Jones, T.C.; Vollmar, P.; Rothe, C.; et al. Virological Assessment of Hospitalized Patients with COVID-2019. Nature 2020, 581, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stancioiu, F.; Papadakis, G.Z.; Kteniadakis, S.; Izotov, B.N.; Coleman, M.D.; Spandidos, D.A.; Tsatsakis, A. A Dissection of SARSCoV2 with Clinical Implications (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 46, 489–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraz, W.R.; Gomes, R.A.; S Novaes, A.L.; Goulart Trossini, G.H. Ligand and Structure-Based Virtual Screening Applied to the SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease: An in Silico Repurposing Study. Future Med. Chem. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrell, R.P.; Frankel, S.R.; Miller, W.H.; Scheinberg, D.A.; Itri, L.M.; Hittelman, W.N.; Vyas, R.; Andreeff, M.; Tafuri, A.; Jakubowski, A.; et al. Differentiation Therapy of Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia with Tretinoin (All-Trans-Retinoic Acid). N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 324, 1385–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riva, L.; Yuan, S.; Yin, X.; Martin-Sancho, L.; Matsunaga, N.; Pache, L.; Burgstaller-Muehlbacher, S.; De Jesus, P.D.; Teriete, P.; Hull, M.V.; et al. Discovery of SARS-CoV-2 Antiviral Drugs through Large-Scale Compound Repurposing. Nature 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Wilde, A.H.; Pham, U.; Posthuma, C.C.; Snijder, E.J. Cyclophilins and Cyclophilin Inhibitors in Nidovirus Replication. Virology 2018, 522, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glowacka, P.; Rudnicka, L.; Warszawik-Hendzel, O.; Sikora, M.; Goldust, M.; Gajda, P.; Stochmal, A.; Blicharz, L.; Rakowska, A.; Olszewska, M. The Antiviral Properties of Cyclosporine. Focus on Coronavirus, Hepatitis C Virus, Influenza Virus, and Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infections. Biology 2020, 9, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unal, G.; Turan, B.; Balcioglu, Y.H. Immunopharmacological Management of COVID-19: Potential Therapeutic Role of Valproic Acid. Med. Hypotheses 2020, 143, 109891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markham, A. Fostamatinib: First Global Approval. Drugs 2018, 78, 959–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alimova, M.; Sidhom, E.H.; Satyam, A.; Dvela-Levitt, M.; Melanson, M.; Chamberlain, B.T.; Alper, S.L.; Santos, J.; Gutierrez, J.; Subramanian, A.; et al. A High Content Screen for Mucin-1-Reducing Compounds Identifies Fostamatinib as a Candidate for Rapid Repurposing for Acute Lung Injury during the COVID-19 Pandemic. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risner, K.H.; Tieu, K.V.; Wang, Y.; Bakovic, A.; Alem, F.; Bhalla, N.; Nathan, S.; Conway, D.E.; Macklin, P.; Narayanan, A. Maraviroc Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Multiplication and s-Protein Mediated Cell Fusion in Cell Culture. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.J.; Qin, J.J.; Cheng, X.; Shen, L.; Zhao, Y.C.; Yuan, Y.; Lei, F.; Chen, M.M.; Yang, H.; Bai, L.; et al. In-Hospital Use of Statins Is Associated with a Reduced Risk of Mortality among Individuals with COVID-19. Cell Metab. 2020, 32, 176–187.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Nava, G.; Trelles-Garcia, D.P.; Yanez-Bello, M.A.; Chung, C.W.; Trelles-Garcia, V.P.; Friedman, H.J. Atorvastatin Associated with Decreased Hazard for Death in COVID-19 Patients Admitted to an ICU: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barh, D.; Tiwari, S.; Weener, M.E.; Azevedo, V.; Góes-Neto, A.; Gromiha, M.M.; Ghosh, P. Multi-Omics-Based Identification of SARS-CoV-2 Infection Biology and Candidate Drugs against COVID-19. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 126, 104051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorkin, E.M.; Clissold, S.P. Nicardipine. A Review of Its Pharmacodynamic and Pharmacokinetic Properties, and Therapeutic Efficacy, in the Treatment of Angina Pectoris, Hypertension and Related Cardiovascular Disorders. Drugs 1987, 33, 296–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solaimanzadeh, I. Acetazolamide, Nifedipine and Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors: Rationale for Their Utilization as Adjunctive Countermeasures in the Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Cureus 2020, 12, e7343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solaimanzadeh, I. Nifedipine and Amlodipine Are Associated with Improved Mortality and Decreased Risk for Intubation and Mechanical Ventilation in Elderly Patients Hospitalized for COVID-19. Cureus 2020, 12, e8069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southard, B.T.; Al Khalili, Y. Promethazine; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, M.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Wen, Y.; Xu, G.; Zhao, J.; Cheng, L.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, F.; et al. Single-Cell Landscape of Bronchoalveolar Immune Cells in Patients with COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 842–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, M.; Shiina, S.; Nakachi, K.; Mitsunaga, S.; Shimizu, S.; Kojima, Y.; Ueno, H.; Morizane, C.; Kondo, S.; Sakamoto, Y.; et al. Phase I Study on the Safety, Pharmacokinetic Profile, and Efficacy of the Combination of TSU-68, an Oral Antiangiogenic Agent, and S-1 in Patients with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Investig. New Drugs 2014, 32, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gilardi, M.; Wang, Z.; Proietto, M.; Chillà, A.; Calleja-Valera, J.L.; Goto, Y.; Vanoni, M.; Janes, M.R.; Mikulski, Z.; Gualberto, A.; et al. Tipifarnib as a Precision Therapy for HRAS-Mutant Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2020, 19, 1784–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciliberto, G.; Mancini, R.; Paggi, M.G. Drug Repurposing against COVID-19: Focus on Anticancer Agents. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vatansev, H.; Kadiyoran, C.; Cumhur Cure, M.; Cure, E. COVID-19 Infection Can Cause Chemotherapy Resistance Development in Patients with Breast Cancer and Tamoxifen May Cause Susceptibility to COVID-19 Infection. Med. Hypotheses 2020, 143, 110091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stelzig, K.E.; Canepa-Escaro, F.; Schiliro, M.; Berdnikovs, S.; Prakash, Y.S.; Chiarella, S.E. Estrogen Regulates the Expression of SARS-CoV-2 Receptor ACE2 in Differentiated Airway Epithelial Cells. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2020, 318, L1280–L1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaduganathan, M.; Vardeny, O.; Michel, T.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Solomon, S.D. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Inhibitors in Patients with Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1653–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- South, A.M.; Tomlinson, L.; Edmonston, D.; Hiremath, S.; Sparks, M.A. Controversies of Renin-Angiotensin System Inhibition during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.; McAuley, D.F.; Brown, M.; Sanchez, E.; Tattersall, R.S.; Manson, J.J. COVID-19: Consider Cytokine Storm Syndromes and Immunosuppression. Lancet 2020, 395, 1033–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, D.; Zhou, F.; Xu, F. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): Cytokine Storms, Hyper-Inflammatory Phenotypes, and Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Genes Dis. 2020, 7, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazgan, B.; Yazgan, Y.; Ovey, I.S.; Naziroglu, M. Raloxifene and Tamoxifen Reduce PARP Activity, Cytokine and Oxidative Stress Levels in the Brain and Blood of Ovariectomized Rats. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2016, 60, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayan, M.; Zinger, H.; Kalush, F.; Mor, G.; Amir-Zaltzman, Y.; Kohen, F.; Sthoeger, Z.; Mozes, E. The Beneficial Effects of Treatment with Tamoxifen and Anti-Oestradiol Antibody on Experimental Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Are Associated with Cytokine Modulations. Immunology 1997, 90, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchiya, S.; Yamabe, M.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Kobayashi, Y.; Konno, T.; Tada, K. Establishment and Characterization of a Human Acute Monocytic Leukemia Cell Line (THP-1). Int. J. Cancer 1980, 26, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiersinga, W.J.; Rhodes, A.; Cheng, A.C.; Peacock, S.J.; Prescott, H.C. Pathophysiology, Transmission, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review. JAMA 2020, 324, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| DrugBank ID | Z-Score | Drug Name | Structure | Pharmacodynamics | Reported Studies of COVID-19 (PMID) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DB12010 | −8.75 | Fostamatinib | 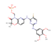 | immunosuppressive agents | 32637960 |
| DB12695 | −6.64 | Phenethyl-isothiocyanate |  | anti-carcinogenic agents | 33131530 |
| DB01069 | −5.65 | Promethazine |  | anti-allergic agents | NA 1 |
| DB00641 | −5.49 | Simvastatin | 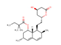 | anti-cholesteremic agents | 32626922 |
| DB00675 | −4.75 | Tamoxifen | 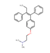 | anti-estrogen | 32663742 |
| DB01076 | −4.74 | Atorvastatin |  | immunosuppressive agents | 32664990 32817953 |
| DB11672 | −3.65 | Curcumin |  | antiviral agents | 32430996 32442323 |
| DB00755 | −3.37 | Tretinoin |  | anti-neoplastic agents | 32707573 |
| DB01234 | −3.21 | Dexamethasone |  | antiviral agents | 327065533 2620554 |
| DB00608 | −3.14 | Chloroquine |  | antiviral agents | 32145363 32147496 |
| DB00313 | −2.90 | Valproic acid |  | anti-convulsant | 32498007 |
| DB01016 | −2.82 | Glibenclamide |  | antiviral agents | 32787684 |
| DB00622 | −2.75 | Nicardipine |  | anti-hypertensive | NA |
| DB01115 | −2.68 | Nifedipine |  | anti-hypertensive | 32226695 32411566 |
| DB00091 | −2.65 | Cyclosporine |  | immunosuppressive agents | 32376422 32487139 |
| DB02709 | −5.63 | Resveratrol |  | analgesics | 32412158 32764275 |
| DB12072 | −2.54 | Orantinib |  | anti-cancer agents | NA |
| DB04960 | −2.40 | Tipifarnib |  | anti-cancer agents | NA |
| Drug Name | B Cells | CD14+ Monocytes Cells | CD16+ Monocytes Cells | Dendritic Cells | NK Cells | CD4+ T Cells | CD8+ T Cells |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chloroquine | NA 1 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Nicardipine | Significant 2 | Significant | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Simvastatin | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Tamoxifen | Significant | Significant | NA | Significant | NA | NA | NA |
| Promethazine | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Nifedipine | Significant | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Resveratrol | Significant | NA | NA | Significant | NA | NA | NA |
| Tipifarnib | Significant | Significant | NA | Significant | NA | NA | NA |
| Orantinib | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Tretinoin | Significant | Significant | Significant | Significant | NA | NA | NA |
| Atorvastatin | Significant | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Dexamethasone | Significant | Significant | Significant | Significant | NA | NA | NA |
| Curcumin | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Fostamatinib | Significant | Significant | NA | Significant | NA | NA | NA |
| Valproic-acid | Significant | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Glibenclamide | Significant | Significant | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Phenethyl Isothiocyanate | Significant | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Cyclosporin | Significant | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Drug A | Drug B | Drug A Common. Name | Drug B Common.Name | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DB01069 | DB12072 | Promethazine | Orantinib | 0.76 | −2.58 | −2.53 |
| DB12072 | DB00313 | Orantinib | Valproic acid | 0.67 | −2.53 | −2.99 |
| DB12072 | DB00755 | Orantinib | Tretinoin | 0.66 | −2.53 | −2.44 |
| DB00755 | DB12010 | Tretinoin | Fostamatinib | 0.66 | −2.44 | −3.68 |
| DB00622 | DB12072 | Nicardipine | Orantinib | 0.60 | −2.81 | −2.53 |
| DB01115 | DB12072 | Nifedipine | Orantinib | 0.57 | −2.71 | −2.53 |
| DB12072 | DB01234 | Orantinib | Dexamethasone | 0.54 | −2.53 | −3.40 |
| DB01069 | DB04960 | Promethazine | Tipifarnib | 0.49 | −2.58 | −2.35 |
| DB12695 | DB00091 | Phenethyl Isothiocyanate | Cyclosporine | 0.43 | −3.22 | −2.67 |
| DB04960 | DB12695 | Tipifarnib | Phenethyl Isothiocyanate | 0.43 | −2.35 | −3.22 |
| DB00675 | DB12072 | Tamoxifen | Orantinib | 0.42 | −3.40 | −2.53 |
| DB01069 | DB12010 | Promethazine | Fostamatinib | 0.42 | −2.58 | −3.68 |
| DB12072 | DB01016 | Orantinib | Glyburide | 0.40 | −2.53 | −2.90 |
| DB00641 | DB12072 | Simvastatin | Orantinib | 0.39 | −4.37 | −2.53 |
| DB12072 | DB00091 | Orantinib | Cyclosporine | 0.37 | −2.53 | −2.67 |
| DB02709 | DB12072 | Resveratrol | Orantinib | 0.37 | −3.91 | −2.53 |
| DB12072 | DB01076 | Orantinib | Atorvastatin | 0.37 | −2.53 | −4.23 |
| DB01069 | DB01076 | Promethazine | Atorvastatin | 0.37 | −2.58 | −4.23 |
| DB01069 | DB12695 | Promethazine | Phenethyl Isothiocyanate | 0.34 | −2.58 | −3.22 |
| DB00608 | DB12072 | Chloroquine | Orantinib | 0.34 | −3.31 | −2.53 |
| DB01069 | DB02709 | Promethazine | Resveratrol | 0.33 | −2.58 | −3.91 |
| DB12072 | DB12695 | Orantinib | Phenethyl Isothiocyanate | 0.30 | −2.53 | −3.22 |
| DB01069 | DB11672 | Promethazine | Curcumin | 0.26 | −2.58 | −2.81 |
| DB01016 | DB12695 | Glyburide | Phenethyl Isothiocyanate | 0.18 | −2.90 | −3.22 |
| DB12010 | DB12695 | Fostamatinib | Phenethyl Isothiocyanate | 0.17 | −3.68 | −3.22 |
| DB00622 | DB12695 | Nicardipine | Phenethyl Isothiocyanate | 0.16 | −2.81 | −3.22 |
| DB04960 | DB00755 | Tipifarnib | Tretinoin | 0.14 | −2.35 | −2.44 |
| DB01076 | DB12695 | Atorvastatin | Phenethyl Isothiocyanate | 0.11 | −4.23 | −3.22 |
| DB11672 | DB12695 | Curcumin | Phenethyl Isothiocyanate | 0.06 | −2.81 | −3.22 |
| DB00608 | DB11672 | Chloroquine | Curcumin | 0.04 | −3.31 | −2.81 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, D.-Y.; Liu, J.-C.; Liang, S.; Meng, X.-H.; Greenbaum, J.; Xiao, H.-M.; Tan, L.-J.; Deng, H.-W. Drug Repurposing for COVID-19 Treatment by Integrating Network Pharmacology and Transcriptomics. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13040545
Liu D-Y, Liu J-C, Liang S, Meng X-H, Greenbaum J, Xiao H-M, Tan L-J, Deng H-W. Drug Repurposing for COVID-19 Treatment by Integrating Network Pharmacology and Transcriptomics. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(4):545. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13040545
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Dan-Yang, Jia-Chen Liu, Shuang Liang, Xiang-He Meng, Jonathan Greenbaum, Hong-Mei Xiao, Li-Jun Tan, and Hong-Wen Deng. 2021. "Drug Repurposing for COVID-19 Treatment by Integrating Network Pharmacology and Transcriptomics" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 4: 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13040545
APA StyleLiu, D.-Y., Liu, J.-C., Liang, S., Meng, X.-H., Greenbaum, J., Xiao, H.-M., Tan, L.-J., & Deng, H.-W. (2021). Drug Repurposing for COVID-19 Treatment by Integrating Network Pharmacology and Transcriptomics. Pharmaceutics, 13(4), 545. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13040545






