Lyophilization of Nanocapsules: Instability Sources, Formulation and Process Parameters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
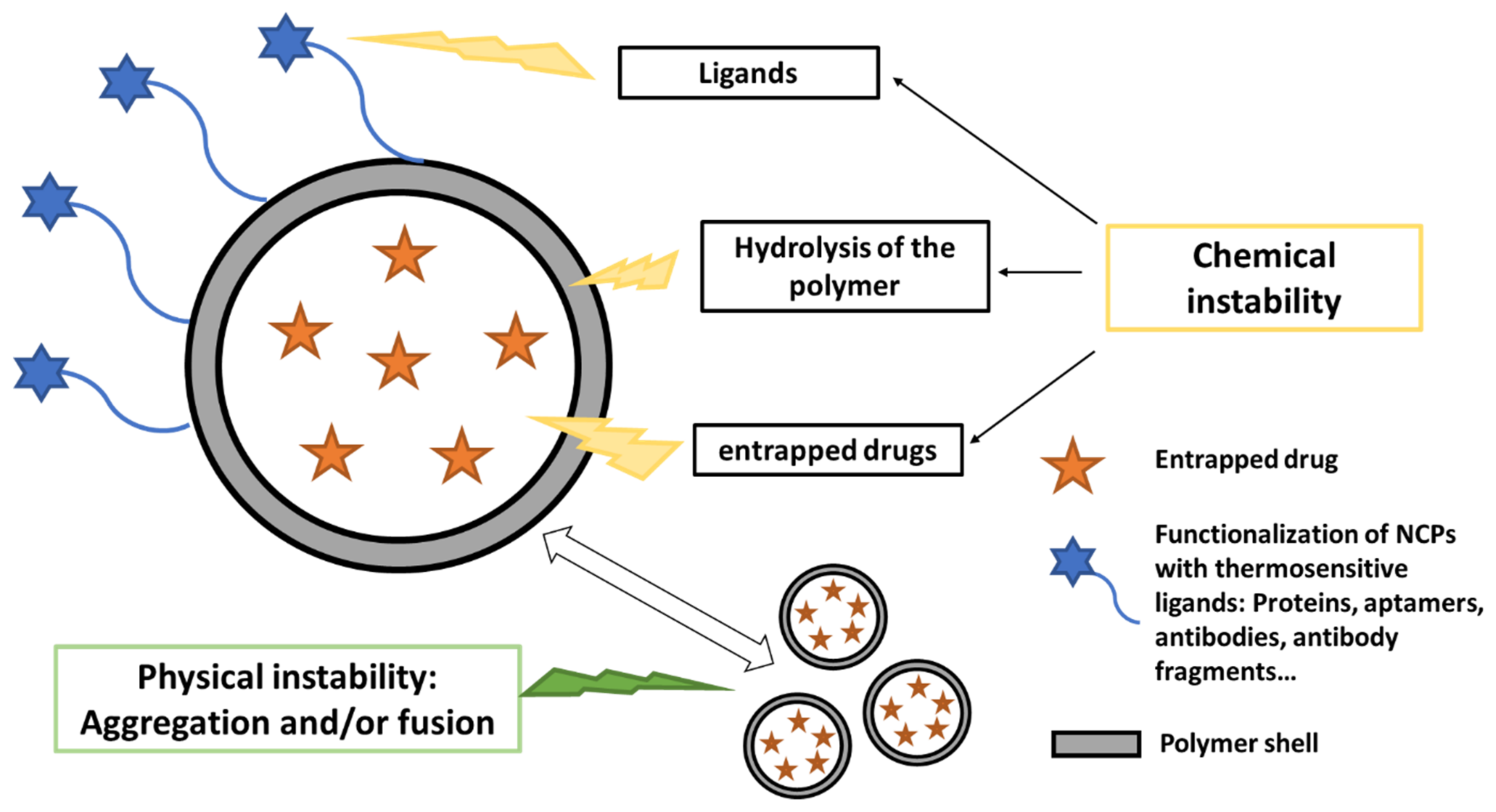
2. Instability of Nanocapsules in Aqueous Media
2.1. Physical Instability
2.2. Chemical Instability
3. How to Improve the Stability and Storage of Nanocapsules?
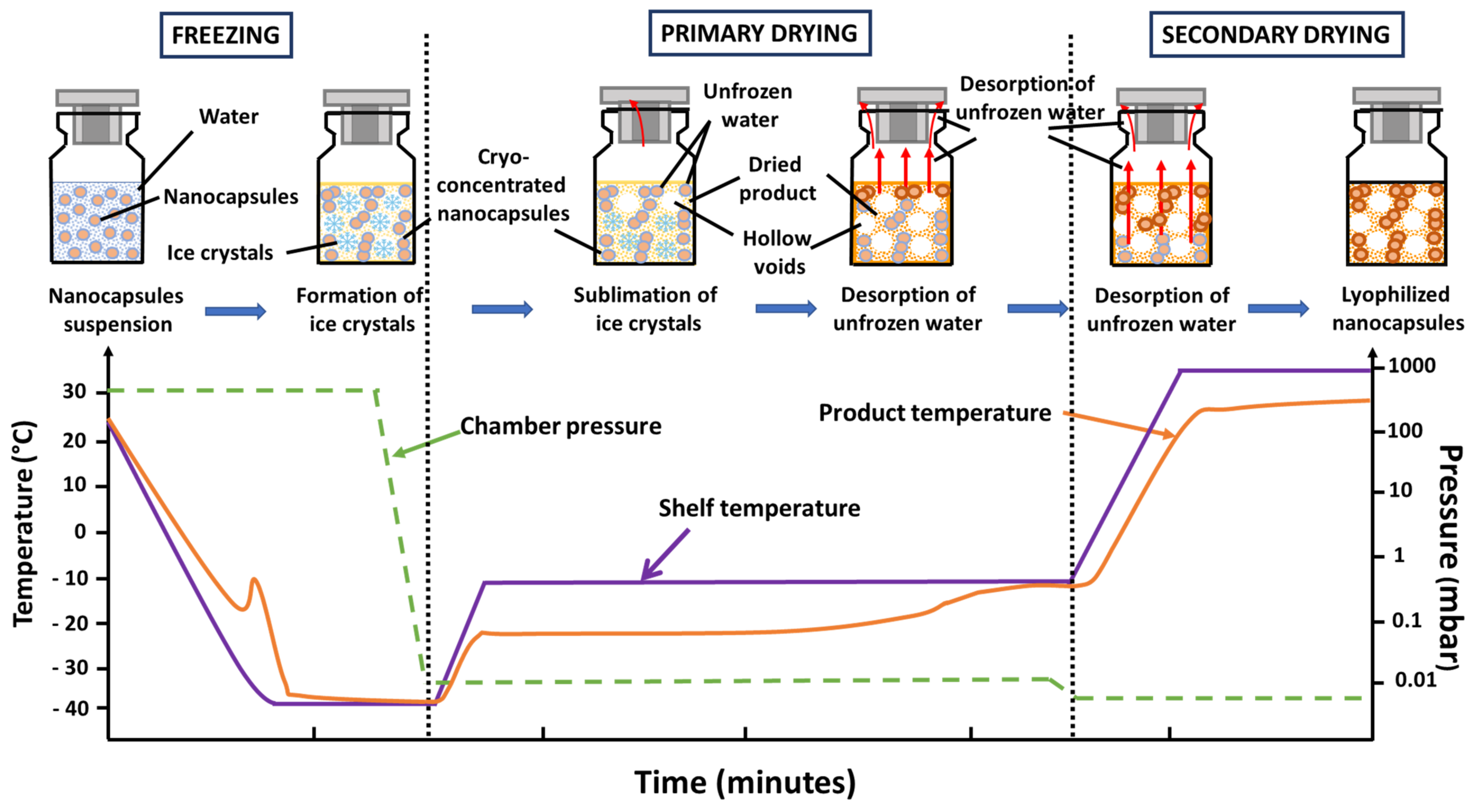
3.1. Freezing
3.2. Primary Drying
3.3. Secondary Drying
4. Freeze Drying Nanocapsules
4.1. Formulation
4.1.1. Protectant
4.1.2. Nanocapsule Stabilizers
4.1.3. Core and Encapsulated Drug
4.2. Freeze Drying Process
4.3. Storage Stability
5. Characterization Methods
5.1. Morphological Observations
5.1.1. Macroscopic Aspect
5.1.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
5.1.3. Environmental Scanning Electron Microscopy
5.1.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
5.1.5. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
5.1.6. Freeze Drying Microscopy
5.2. Reconstitution Time
5.3. Particle Size and Polydispersity Index
5.4. Zeta Potential
5.5. Activity of Encapsulated Substances and/or Functionalized Ligands
5.6. Residual Moisture Content and Study of Water Sorption Isotherms
5.7. Differential Scanning Calorimetry
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mozafari, M.R. Nanomaterials and Nanosystems for Biomedical Applications; Springer Science & Business Media: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; ISBN 978-1-4020-6289-6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Li, J.; Morozov, K.I.; Wu, Z.; Xu, T.; Rozen, I.; Leshansky, A.M.; Li, L.; Wang, J. Highly Efficient Freestyle Magnetic Nanoswimmer. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 5092–5098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, K.; Zhang, Y.; Bao, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Xin, C.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z. Biosafety of Micro/Nanomotors towards Medical Application. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 3441–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulte, J.W.M.; Modo, M. Nanoparticles in Biomedical Imaging: Emerging Technologies and Applications; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2007; ISBN 978-0-387-72027-2. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.T.-W.; Martino, U.; Khan, R.; Bazzar, M.; Southern, P.; Tuncel, D.; Al-Jamal, K.T. Engineering Red-Emitting Multi-Functional Nanocapsules for Magnetic Tumour Targeting and Imaging. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 2590–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nankali, E.; Shaabanzadeh, M.; Torbati, M.B. Fluorescent Tamoxifen-Encapsulated Nanocapsules Functionalized with Folic Acid for Enhanced Drug Delivery toward Breast Cancer Cell Line MCF-7 and Cancer Cell Imaging. Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2020, 393, 1211–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potara, M.; Nagy-Simon, T.; Focsan, M.; Licarete, E.; Soritau, O.; Vulpoi, A.; Astilean, S. Folate-Targeted Pluronic-Chitosan Nanocapsules Loaded with IR780 for near-Infrared Fluorescence Imaging and Photothermal-Photodynamic Therapy of Ovarian Cancer. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 203, 111755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Garcia-Gabilondo, M.; Rosell, A.; Roig, A. MRI/Photoluminescence Dual-Modal Imaging Magnetic PLGA Nanocapsules for Theranostics. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mao, J.; Li, Y.; Cai, Q.; Tang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, C.; Xu, Y.; Zeng, B.; Luo, W.; Kuo, S.; et al. Tumor Microenvironment-Activated Self-Charge-Generable Metallosupramolecular Polymer Nanocapsules for Photoacoustic Imaging-Guided Targeted Synergistic Photothermal-Chemotherapy. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 405, 126690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunay, M.S.; Ozer, A.Y.; Chalon, S. Drug Delivery Systems for Imaging and Therapy of Parkinson’s Disease. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2016, 14, 376–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillman, A.J.; Bridges, N.N. Nanoparticle Sensors for Biological Medicine; Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL): Richland, WA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, X.; Engwer, C.; Desai, S.; Vila-Sanjurjo, C.; Goycoolea, F.M. An Investigation of the Interactions between an E-Coli Bacterial Quorum Sensing Biosensor and Chitosan-Based Nanocapsules. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 149, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, W.; Gu, Z. Enzyme Nanocapsules for Glucose Sensing and Insulin Delivery. In Biocatalysis and Nanotechnology; Grunwald, P., Ed.; Pan Stanford Series on Biocatalysis; Jenny Stanford Publishing: Singapore, 2017; Volume 3, pp. 561–593. ISBN 978-1-315-19660-2. [Google Scholar]
- Bechnak, L.; El Kurdi, R.; Patra, D. Fluorescence Sensing of Nucleic Acid by Curcumin Encapsulated Poly(Ethylene Oxide)-Block-Poly(Propylene Oxide)-Block-Poly(Ethylene Oxide) Based Nanocapsules. J. Fluoresc. 2020, 30, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiji, M.M. Polymeric Gene Delivery: Principles and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; ISBN 978-0-203-50047-7. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Wang, M.; Guan, S.; Huang, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, X.; Jiang, X.; Luo, Q.; Xu, J.; Liu, J. Cucurbit[8]Uril-Based Supramolecular Polymer Nanocapsules as an Effective SiRNA Delivery Platform for Gene Therapy. Polym. Chem. 2019, 10, 5659–5664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resnier, P.; Galopin, N.; Sibiril, Y.; Clavreul, A.; Cayon, J.; Briganti, A.; Legras, P.; Vessieres, A.; Montier, T.; Jaouen, G.; et al. Efficient Ferrocifen Anticancer Drug and Bcl-2 Gene Therapy Using Lipid Nanocapsules on Human Melanoma Xenograft in Mouse. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 126, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resnier, P.; LeQuinio, P.; Lautram, N.; Andre, E.; Gaillard, C.; Bastiat, G.; Benoit, J.-P.; Passirani, C. Efficient In Vitro Gene Therapy with PEG SiRNA Lipid Nanocapsules for Passive Targeting Strategy in Melanoma. Biotechnol. J. 2014, 9, 1389–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gaspar, V.M.; Sousa, F.; Queiroz, J.A.; Correia, I.J. Formulation of Chitosan-TPP-PDNA Nanocapsules for Gene Therapy Applications. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 015101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthikeyan, K.; Jain, A.; Cring, M.; Searby, C.; Sheffield, V.C. Positively Charged TPGS-Chiotsan Nanocapsules as a Non-Viral Vector for Glaucoma Gene Therapy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 2896. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Yang, M.; Zhao, N.; Xu, F.-J. Rattle-Structured Rough Nanocapsules with in-Situ-Formed Reil Gold Nanorod Cores for Complementary Gene/Chemo/Photothermal Therapy. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 5646–5656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasimi, P.; Haidari, M. Medical Use of Nanoparticles: Drug Delivery and Diagnosis Diseases. Int. J. Green Nanotechnol. 2013, 1, 194308921350697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, K.; Zimmer, A.; Kreuter, J. Acrylic Nanoparticles for Ocular Drug Delivery. STP Pharma Sci. 1997, 7, 445–451. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Guy, R.H. Applications of Nanoparticles in Topical Drug Delivery and in Cosmetics. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2009, 19, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leyva-Gomez, G.; Pinon-Segundo, E.; Mendoza-Munoz, N.; Zambrano-Zaragoza, M.L.; Mendoza-Elvira, S.; Quintanar-Guerrero, D. Approaches in Polymeric Nanoparticles for Vaginal Drug Delivery: A Review of the State of the Art. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhunchu, S.; Rojsitthisak, P. Biopolymeric Alginate-Chitosan Nanoparticles as Drug Delivery Carriers for Cancer Therapy. Pharmazie 2014, 69, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos Chaves, P.; Ourique, A.F.; Frank, L.A.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Guterres, S.S.; Beck, R.C.R. Carvedilol-Loaded Nanocapsules: Mucoadhesive Properties and Permeability across the Sublingual Mucosa. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 114, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, U.; Chauhan, S.; Nagaich, U.; Jain, N. Current Advances in Chitosan Nanoparticles Based Drug Delivery and Targeting. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 9, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo, P.; RemunanLopez, C.; VilaJato, J.L.; Alonso, M.J. Development of Positively Charged Colloidal Drug Carriers: Chitosan Coated Polyester Nanocapsules and Submicron-Emulsions. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1997, 275, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vauthier, C.; Labarre, D.; Ponchel, G. Design Aspects of Poly(Alkylcyanoacrylate) Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. J. Drug Target. 2007, 15, 641–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonte, P.; Reis, S.; Sarmento, B. Facts and Evidences on the Lyophilization of Polymeric Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. J. Control. Release 2016, 225, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudshinge, S.R.; Deore, A.B.; Patil, S.; Bhalgat, C.M. Nanoparticles: Emerging Carriers for Drug Delivery. Saudi Pharm. J. 2011, 19, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Legrand, P.; Barratt, G.; Mosqueira, V.; Fessi, H.; Devissaguet, J.P. Polymeric Nanocapsules as Drug Delivery Systems. A Review. STP Pharma Sci. 1999, 9, 411–418. [Google Scholar]
- Santos-Magalhães, N.S.; Mosqueira, V.C.F. Nanotechnology Applied to the Treatment of Malaria. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 560–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Couvreur, P.; Barratt, G.; Fattal, E.; Vauthier, C. Nanocapsule Technology: A Review. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 2002, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Gigliobianco, M.R.; Censi, R.; Di Martino, P. Polymeric Nanocapsules as Nanotechnological Alternative for Drug Delivery System: Current Status, Challenges and Opportunities. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, L. Freeze-Drying/Lyophilization of Pharmaceutical and Biological Products; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; ISBN 978-1-4398-2576-1. [Google Scholar]
- Nosworthy, N.J.; McKenzie, D.R.; Bilek, M.M. A New Surface for Immobilizing and Maintaining the Function of Enzymes in a Freeze-Dried State. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 2577–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelwahed, W.; Degobert, G.; Fessi, H. Investigation of Nanocapsules Stabilization by Amorphous Excipients during Freeze-Drying and Storage. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2006, 63, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hester, S.; Ferenz, K.B.; Eitner, S.; Langer, K. Development of a Lyophilization Process for Long-Term Storage of Albumin-Based Perfluorodecalin-Filled Artificial Oxygen Carriers. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Shepherd, D.; Sun, J.; Ouellette, D.; Grant, K.L.; Tang, X.; Pikal, M.J. Mechanism of Protein Stabilization by Sugars during Freeze-Drying and Storage: Native Structure Preservation, Specific Interaction, and/or Immobilization in a Glassy Matrix? J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 94, 1427–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzatti, G.K.; Netz, P.A.; Fiel, L.A.; Pohlmann, A.R. Colloidal Dispersion Stability: Kinetic Modeling of Agglomeration and Aggregation. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2014, 26, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelwahed, W.; Degobert, G.; Fessi, H. A Pilot Study of Freeze Drying of Poly(Epsilon-Caprolactone) Nanocapsules Stabilized by Poly(Vinyl Alcohol): Formulation and Process Optimization. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 309, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chacón, M.; Molpeceres, J.; Berges, L.; Guzmán, M.; Aberturas, M.R. Stability and Freeze-Drying of Cyclosporine Loaded Poly(d,l Lactide–Glycolide) Carriers. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 1999, 8, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffin Pohlmann, A.; Weiss, V.; Mertins, O.; Pesce da Silveira, N.; Stanisçuaski Guterres, S. Spray-Dried Indomethacin-Loaded Polyester Nanocapsules and Nanospheres: Development, Stability Evaluation and Nanostructure Models. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 16, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa Lobato, K.B.; Paese, K.; Forgearini, J.C.; Guterres, S.S.; Jablonski, A.; de Oliviera Rios, A. Characterisation and Stability Evaluation of Bixin Nanocapsules. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 3906–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, J.; Watanabe, W. Physical and Chemical Stability of Drug Nanoparticles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 456–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belbella, A.; Vauthier, C.; Fessi, H.; Devissaguet, J.-P.; Puisieux, F. In Vitro Degradation of Nanospheres from Poly(D,L-Lactides) of Different Molecular Weights and Polydispersities. Int. J. Pharm. 1996, 129, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobo, D.; Robinson, K.J.; Islam, J.; Thurecht, K.J.; Corrie, S.R. Nanoparticle-Based Medicines: A Review of FDA-Approved Materials and Clinical Trials to Date. Pharm. Res. 2016, 33, 2373–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, H.M.; Sohn, M.; Al-Ghananeem, A.; De Luca, P.P. Materials for Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms: Molecular Pharmaceutics and Controlled Release Drug Delivery Aspects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdelwahed, W.; Degobert, G.; Stainmesse, S.; Fessi, H. Freeze-Drying of Nanoparticles: Formulation, Process and Storage Considerations. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2006, 58, 1688–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guinebretière, S.; Briançon, S.; Fessi, H.; Teodorescu, V.S.; Blanchin, M.G. Nanocapsules of Biodegradable Polymers: Preparation and Characterization by Direct High Resolution Electron Microscopy. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2002, 21, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauchetier, E.; Deniau, M.; Fessi, H.; Astier, A.; Paul, M. Atovaquone-Loaded Nanocapsules: Influence of the Nature of the Polymer on Their In Vitro Characteristics. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 250, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moinard-Chécot, D.; Chevalier, Y.; Briançon, S.; Beney, L.; Fessi, H. Mechanism of Nanocapsules Formation by the Emulsion–Diffusion Process. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 317, 458–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamekhi, F.; Tamjid, E.; Khajeh, K. Development of Chitosan Coated Calcium-Alginate Nanocapsules for Oral Delivery of Liraglutide to Diabetic Patients. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, S.; Sun, C.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, C. Hollow and Degradable Polyelectrolyte Nanocapsules for Protein Drug Delivery. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damgé, C.; Aprahamian, M.; Humbert, W.; Pinget, M. Ileal Uptake of Polyalkylcyanoacrylate Nanocapsules in the Rat. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2000, 52, 1049–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomcebo Thwala, L.; Pan Delgado, D.; Leone, K.; Marigo, I.; Benetti, F.; Chenlo, M.; Alvarez, C.; Tovar, S.; Dieguez, C.; Stefania Csaba, N.; et al. Protamine Nanocapsules as Carriers for Oral Peptide Delivery. J. Control. Release 2018, 291, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanità, G.; Carrese, B.; Lamberti, A. Nanoparticle Surface Functionalization: How to Improve Biocompatibility and Cellular Internalization. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikal, M.J. Freeze-Drying of Proteins. In Formulation and Delivery of Proteins and Peptides; ACS Symposium Series; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1994; Volume 567, pp. 120–133. ISBN 978-0-8412-2959-4. [Google Scholar]
- Manning, M.C.; Chou, D.K.; Murphy, B.M.; Payne, R.W.; Katayama, D.S. Stability of Protein Pharmaceuticals: An Update. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 544–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banga, A.K. Therapeutic Peptides and Proteins: Formulation, Processing, and Delivery Systems, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-1-4665-6607-1. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, C.R.; Bassani, V.L.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Michalowski, C.B.; Petrovick, P.R.; Guterres, S.S. Preparation and Characterization of Spray-Dried Polymeric Nanocapsules. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2000, 26, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenmaker, L.; Witzigmann, D.; Kulkarni, J.A.; Verbeke, R.; Kersten, G.; Jiskoot, W.; Crommelin, D.J.A. MRNA-Lipid Nanoparticle COVID-19 Vaccines: Structure and Stability. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 601, 120586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grau, S.; Ferrández, O.; Martín-García, E.; Maldonado, R. Reconstituted MRNA Covid-19 Vaccines May Maintain Stability after Continuous Movement. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crommelin, D.J.A.; Anchordoquy, T.J.; Volkin, D.B.; Jiskoot, W.; Mastrobattista, E. Addressing the Cold Reality of MRNA Vaccine Stability. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 110, 997–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewa-Tagne, P.; Briançon, S.; Fessi, H. Preparation of Redispersible Dry Nanocapsules by Means of Spray-Drying: Development and Characterisation. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 30, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, R.F.; Motta, M.H.; Härter, A.P.G.; Flores, F.C.; Beck, R.C.R.; Schaffazick, S.R.; de Bona da Silva, C. Spray-Dried Powders Improve the Controlled Release of Antifungal Tioconazole-Loaded Polymeric Nanocapsules Compared to with Lyophilized Products. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 59, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, F.; Vatanara, A.; Park, E.; Na, D. Drying Technologies for the Stability and Bioavailability of Biopharmaceuticals. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, M.E.; Lamprecht, A. Spray Freeze Drying as an Alternative Technique for Lyophilization of Polymeric and Lipid-Based Nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 516, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishwarya, S.P.; Anandharamakrishnan, C.; Stapley, A.G.F. Spray-Freeze-Drying: A Novel Process for the Drying of Foods and Bioproducts. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 41, 161–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Ma, C.; Sun, M.; Guo, C.; Shen, J.; Wang, J.; Nie, F.; Gao, B. Preparation and Characterization of Nano Amitriptyline Hydrochloride Particles by Spray Freeze Drying. Nanomedicine 2019, 14, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Tran, T.; Teo, J.; Hadinoto, K. Dry Powder Aerosols of Curcumin-Chitosan Nanoparticle Complex Prepared by Spray Freeze Drying and Their Antimicrobial Efficacy against Common Respiratory Bacterial Pathogens. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 504, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guterres, S.; Weiss, V.; Freitas, L.; Pohlmann, A. Influence of Benzyl Benzoate as Oil Core on the Physicochemical Properties of Spray-Dried Powders from Polymeric Nanocapsules Containing Indomethacin. Drug Deliv. 2000, 7, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grenha, A.; Seijo, B.; Remunan-Lopez, C. Microencapsulated Chitosan Nanoparticles for Lung Protein Delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 25, 427–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewa-Tagne, P.; Degobert, G.; Briançon, S.; Bordes, C.; Gauvrit, J.-Y.; Lanteri, P.; Fessi, H. Spray-Drying Nanocapsules in Presence of Colloidal Silica as Drying Auxiliary Agent: Formulation and Process Variables Optimization Using Experimental Designs. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 650–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umerska, A.; Mugheirbi, N.; Kasprzak, A.; Saulnier, P.; Tajber, L. Carbohydrate-Based Trojan Microparticles as Carriers for Pulmonary Delivery of Lipid Nanocapsules Using Dry Powder Inhalation. Powder Technol. 2020, 364, 507–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanning, S.; Süverkrüp, R.; Lamprecht, A. Pharmaceutical Spray Freeze Drying. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 488, 136–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwegman, J.J.; Nieblas, R. Thermal Characterization as Part of an Empirical Process for Developing Optimized Formulations and Lyophilization Cycles; McCrone: Chicago, IL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Khattab, W.M.; Zein El-Dein, E.E.; El-Gizawy, S.A. Formulation of Lyophilized Oily-Core Poly-Ɛ-Caprolactone Nanocapsules to Improve Oral Bioavailability of Olmesartan Medoxomil. Drug Devel. and Ind. Pharm. 2020, 46, 795–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khayata, N.; Abdelwahed, W.; Chehna, M.F.; Charcosset, C.; Fessi, H. Stability Study and Lyophilization of Vitamin E-Loaded Nanocapsules Prepared by Membrane Contactor. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 439, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crecente-Campo, J.; Lorenzo-Abalde, S.; Mora, A.; Marzoa, J.; Csaba, N.; Blanco, J.; González-Fernández, Á.; Alonso, M.J. Bilayer Polymeric Nanocapsules: A Formulation Approach for a Thermostable and Adjuvanted E. Coli Antigen Vaccine. J. Control. Release 2018, 286, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, M.V.; Esteban, H.; Brea, J.; Loza, M.I.; Torres, D.; Alonso, M.J. Intracellular Delivery of Docetaxel Using Freeze-Dried Polysaccharide Nanocapsules. J. Microencapsul. 2013, 30, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyarzun-Ampuero, F.A.; Rivera-Rodríguez, G.R.; Alonso, M.J.; Torres, D. Hyaluronan Nanocapsules as a New Vehicle for Intracellular Drug Delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 49, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bexiga, N.M.; Bloise, A.C.; Alencar, A.M.; Stephano, M.A. Freeze-Drying of Ovalbumin-Loaded Carboxymethyl Chitosan Nanocapsules: Impact of Freezing and Annealing Procedures on Physicochemical Properties of the Formulation during Dried Storage. Dry. Technol. 2018, 36, 400–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejrapha, P.; Min, S.-G.; Surassmo, S.; Choi, M.-J. Physicothermal Properties of Freeze-Dried Fish Oil Nanocapsules Frozen under Different Conditions. Dry. Technol. 2010, 28, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozdag, S.; Dillen, K.; Vandervoort, J.; Ludwig, A. The Effect of Freeze-Drying with Different Cryoprotectants and Gamma-Irradiation Sterilization on the Characteristics of Ciprofloxacin HCl-Loaded Poly(D,L-Lactide-Glycolide) Nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 57, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saez, A.; Guzmán, M.; Molpeceres, J.; Aberturas, M.R. Freeze-Drying of Polycaprolactone and Poly(d,l-Lactic-Glycolic) Nanoparticles Induce Minor Particle Size Changes Affecting the Oral Pharmacokinetics of Loaded Drugs. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2000, 50, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonte, P.; Soares, S.; Sousa, F.; Costa, A.; Seabra, V.; Reis, S.; Sarmento, B. Stability Study Perspective of the Effect of Freeze-Drying Using Cryoprotectants on the Structure of Insulin Loaded into PLGA Nanoparticles. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 3753–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Akers, M.; Jain, M.; Guo, J.; Distler, A.; Swift, R.; Wadhwa, M.-V.S.; Jameel, F.; Patro, S.; Freund, E. Mechanistic Studies of Glass Vial Breakage for Frozen Formulations. I. Vial Breakage Caused by Crystallizable Excipient Mannitol. PDA J. Pharm. Sci. Technol. 2007, 61, 441–451. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, G.; Akers, M.; Jain, M.; Guo, J.; Distler, A.; Swift, R.; Wadhwa, M.-V.S.; Jameel, F.; Patro, S.; Freund, E. Mechanistic Studies of Glass Vial Breakage for Frozen Formulations. II. Vial Breakage Caused by Amorphous Protein Formulations. PDA J. Pharm. Sci. Technol. 2007, 61, 452–460. [Google Scholar]
- Date, P.V.; Samad, A.; Devarajan, P.V. Freeze Thaw: A Simple Approach for Prediction of Optimal Cryoprotectant for Freeze Drying. AAPS PharmSciTech 2010, 11, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, D. Stability of Nanosuspensions in Drug Delivery. J. Control. Release 2013, 172, 1126–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürsoy, A.; Eroǧlu, L.; Ulutin, S.; Taşyürek, M.; Fessi, H.; Puisieux, F.; Devissaguet, J.-P. Evaluation of Indomethacin Nanocapsules for Their Physical Stability and Inhibitory Activity on Inflammation and Platelet Aggregation. Int. J. Pharm. 1989, 52, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Pikal, M.J. Design of Freeze-Drying Processes for Pharmaceuticals: Practical Advice. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chasteigner, S.de.; Cavé, G.; Fessi, H.; Devissaguet, J.-P.; Puisieux, F. Freeze-Drying of Itraconazole-Loaded Nanosphere Suspensions: A Feasibility Study. Drug Dev. Res. 1996, 38, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinidis, A.K.; Kuu, W.; Otten, L.; Nail, S.L.; Sever, R.R. Controlled Nucleation in Freeze-drying: Effects on Pore Size in the Dried Product Layer, Mass Transfer Resistance, and Primary Drying Rate. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 3453–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.J.; Briançon, S.; Andrieu, J.; Min, S.G.; Fessi, H. Effect of Freeze-Drying Process Conditions on the Stability of Nanoparticles. Dry. Technol. 2004, 22, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, N.-O.; Lee, M.K.; Lee, J. Mechanism of Freeze-Drying Drug Nanosuspensions. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 437, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.K.; Kim, M.Y.; Kim, S.; Lee, J. Cryoprotectants for Freeze Drying of Drug Nano-Suspensions: Effect of Freezing Rate. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 98, 4808–4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Z.; Hsu, C.-H.; Mumper, R.J. Physical Characterization and Macrophage Cell Uptake of Mannan-Coated Nanoparticles. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2003, 29, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
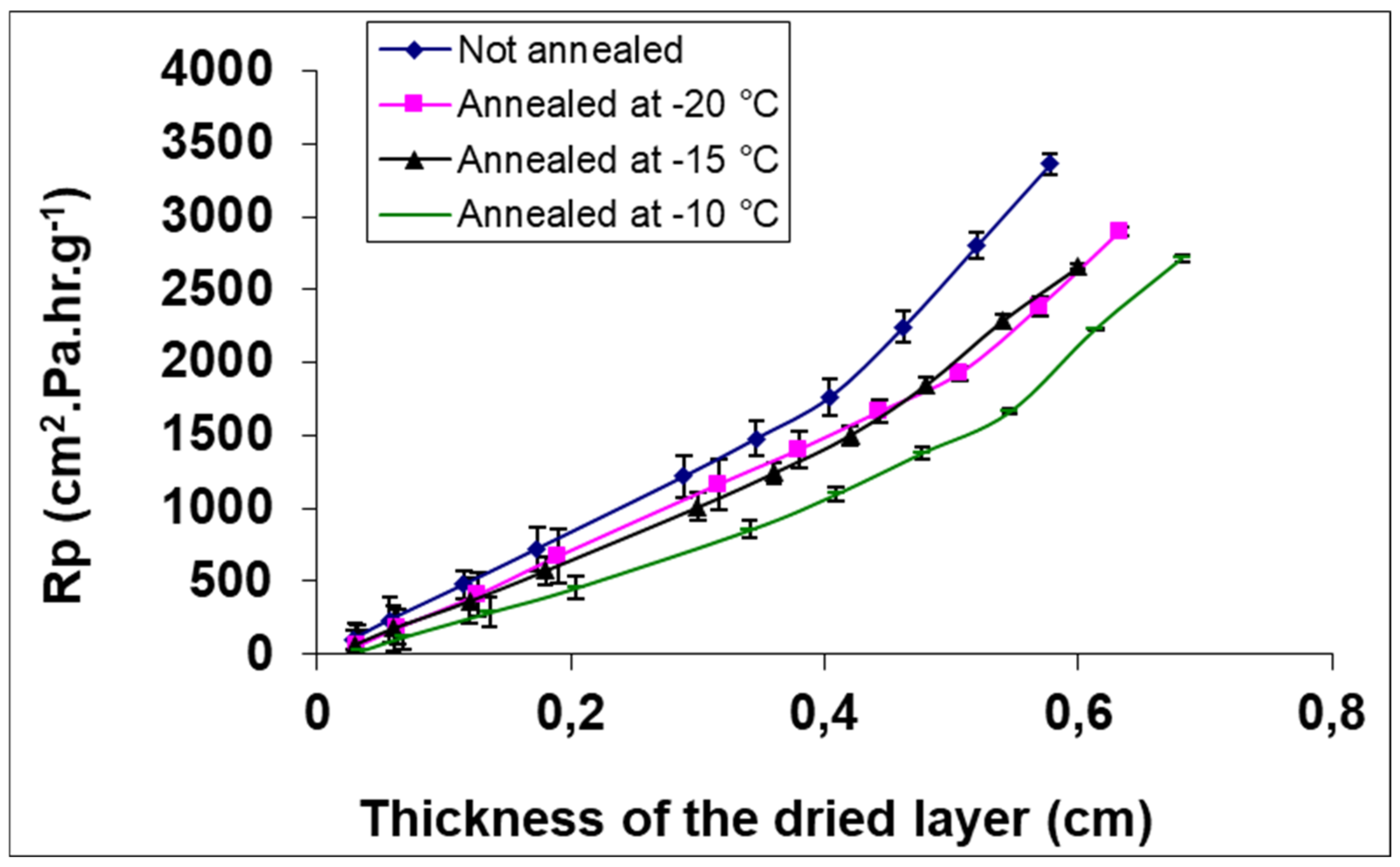
- Searles, J.A.; Carpenter, J.F.; Randolph, T.W. Annealing to Optimize the Primary Drying Rate, Reduce Freezing-Induced Drying Rate Heterogeneity, and Determine Tg′ in Pharmaceutical Lyophilization. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 90, 872–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelwahed, W.; Degobert, G.; Fessi, H. Freeze-Drying of Nanocapsules: Impact of Annealing on the Drying Process. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 324, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelwahed, W. Lyophilisation Des Nanovecteurs de Type : Nanocapsules, Nanospheres et Nanoémulsion. Etude Fondementale de La Formulation et Du Procédé de Lyophilisation. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Claude Bernard Lyon 1, Villeurbanne, France, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Pikal, M.J.; Shah, S. The Collapse Temperature in Freeze Drying: Dependence on Measurement Methodology and Rate of Water Removal from the Glassy Phase. Int. J. Pharm. 1990, 62, 165–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severo, M.G.; Zeferino, A.S.; Soccol, C.R. 21—Development of a Rabies Vaccine in Cell Culture for Veterinary Use in the Lyophilized Form. In Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Thomaz-Soccol, V., Pandey, A., Resende, R.R., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 523–560. ISBN 978-0-444-63660-7. [Google Scholar]
- Schaffazick, S.R.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Dalla-Costa, T.; Guterres, S.S. Freeze-Drying Polymeric Colloidal Suspensions: Nanocapsules, Nanospheres and Nanodispersion. A Comparative Study. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2003, 56, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacasi, G.R.R.; Campmany, A.C.C.; Gras, M.A.E.; García, M.E.; López, M.L.G. Freeze Drying Optimization of Polymeric Nanoparticles for Ocular Flurbiprofen Delivery: Effect of Protectant Agents and Critical Process Parameters on Long-Term Stability. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2017, 43, 637–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemoine, D.; Francois, C.; Kedzierewicz, F.; Preat, V.; Hoffman, M.; Maincent, P. Stability Study of Nanoparticles of Poly(ɛ-Caprolactone), Poly(d,l-Lactide) and Poly(d,l-Lactide-Co-Glycolide). Biomaterials 1996, 17, 2191–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, L.S.; Laurencin, C.T. Biodegradable Polymers as Biomaterials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 762–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Ruan, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Bi, D. Studies on Glass Transition Temperature of Chitosan with Four Techniques. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 93, 1553–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lappe, S.; Mulac, D.; Langer, K. Polymeric Nanoparticles—Influence of the Glass Transition Temperature on Drug Release. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 517, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzer, M.; Vogel, V.; Mäntele, W.; Schwartz, D.; Haase, W.; Langer, K. Physico-Chemical Characterisation of PLGA Nanoparticles after Freeze-Drying and Storage. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 72, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Chen, G.; Fan, J.; Liu, J.; Xu, X.; Zhang, S. Moisture Sorption Characteristics of Freeze-Dried Human Platelets. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2011, 12, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahl, V.; Khinast, J.; Paudel, A. Lyophilized Protein Powders: A Review of Analytical Tools for Root Cause Analysis of Lot-to-Lot Variability. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 82, 468–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remmele, R.L.; Krishnan, S.; Callahan, W.J. Development of Stable Lyophilized Protein Drug Products. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2012, 13, 471–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raval, N.; Maheshwari, R.; Kalyane, D.; Youngren-Ortiz, S.R.; Chougule, M.B.; Tekade, R.K. Chapter 10—Importance of Physicochemical Characterization of Nanoparticles in Pharmaceutical Product Development. In Basic Fundamentals of Drug Delivery; Tekade, R.K., Ed.; Advances in Pharmaceutical Product Development and Research; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 369–400. ISBN 978-0-12-817909-3. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, R. Progress in Nanoparticles Characterization: Sizing and Zeta Potential Measurement. Particuology 2008, 6, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, N.A.; Polli, G.P. The Lyophilization of Pharmaceuticals: A Literature Review. PDA J. Pharm. Sci. Technol. 1984, 38, 48–60. [Google Scholar]
- Capozzi, L.C.; Trout, B.L.; Pisano, R. From Batch to Continuous: Freeze-Drying of Suspended Vials for Pharmaceuticals in Unit-Doses. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 1635–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.P.; Hsu, C.C. Determination of Residual Moisture in Lyophilized Protein Pharmaceuticals Using a Rapid and Non-Invasive Method: Near Infrared Spectroscopy. PDA J. Pharm. Sci. Technol. 2002, 56, 196–205. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, N.S.; Edge, M. Fundamentals of Polymer Degradation and Stabilization; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992; ISBN 978-1-85166-773-4. [Google Scholar]
- Leys, L.; Vanbillemont, B.; Bockstal, P.J.V.; Lammens, J.; Nuytten, G.; Corver, J.; Vervaet, C.; Beer, T.D. A Primary Drying Model-Based Comparison of Conventional Batch Freeze-Drying to Continuous Spin-Freeze-Drying for Unit Doses. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 157, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Composition Polymer Shell/Oily Core | Nanocapsule Diameter (nm) | Membrane Thickness (nm) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCL/Miglyol® 812 | 520 | 1.5–2 | [52] |
| PCL65/BB | 228 ± 16.1 | 20.9 | [53] |
| PCL100/BB | 241.7 ± 32.5 | 22.2 | |
| PLGA/BB | 228.8 ± 9.8 | 20.9 | |
| PLA/BB | 236.6 ± 13.2 | 21.8 | |
| PCL80/Miglyol® 812 | 457 ± 5 | 35 | [54] |
| Drying Procedure | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Freeze drying |
|
|
| Spray drying |
|
|
| Spray freeze drying |
|
|
| Process Parameters | Formulation before FD | Characterization of Lyophilized NCPs | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stages | Temperature | Pressure | Thermal Characterization | ||
| Freezing | Cooling temp. | Atmospheric pressure | TP < Teu, Tg’ |
| |
| Cooling rate | |||||
| Duration * | |||||
| Annealing * | Heating rate | TP > Tg’ | |||
| Annealing temperature | |||||
| Duration * | |||||
| Cooling rate | |||||
| Primary drying (sublimation) | Duration * | Reduced pressure | TP < 2–5 °C of Tc or Tg’ | ||
| Heating rate | |||||
| Sublimation temp. | |||||
| Secondary drying (desorption) | Desoption temp. | Reduced pressure | TP < Tg # | ||
| Heating rate | |||||
| Duration * | |||||
| Encapsulated Drug | Conditions of Lyophilization Process | References | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polymer | Freezing | Primary Drying | Secondary Drying | |||
| PCL | Olmesartan Medoxomil | −40 °C overnight | Different drying phases for about 48h * | [81] | ||
| PCL | Vitamin E | −45 °C for 120 min | −20 °C for 480 min | +20 °C for 360 min | [82] | |
| Chitosan + dextran sulphate | IutA protein from Escherichia coli | −80 °C | −40 to −20 °C for 35 h | Gradually increase temperatures up to +20 °C | [83] | |
| Chitosan | Docetaxel | Quickly frozen in liquid nitrogen | −35 °C for 60 h | 24 h in high vacuum | [84] | |
| Hyaluronic acid | Docetaxel | −20 °C | −35 °C for 60 h 50 mTorr | 0 °C for 24 h | [85] | |
| 6-O-carboxymethyl chitosan | Ovalbumin | −50 °C for 30 min | −40 °C for 6 h | 20 °C for 4 h | [86] | |
| Isobutylcyanoacrylate | Iodized oil | Liquid nitrogen | −90 °C for 48 h under 10 mPa * | [57] | ||
| PCL | Fish oil | −30, −20 and −10 °C | −50 °C under 0.05 mbar * | [87] | ||
| Polymer | Encapsulated Substance | Protectants | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6-O-carboxymethyl chitosan | Ovalbumin | Mannitol, lactose | [86] |
| Chitosan | Docetaxel | Trehalose | [84] |
| PCL | no drug | Sucrose | [43] |
| PLGA | Cyclosporine | Glucose | [44] |
| PCL | no drug | PVP | [39] |
| PLGA | Ciprofloxacin HCl | Dextran | [89] |
| PLGA | Insulin | Fructose | [88] |
| PCL | Cyclosporin | Sorbitol | [90] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Degobert, G.; Aydin, D. Lyophilization of Nanocapsules: Instability Sources, Formulation and Process Parameters. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1112. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13081112
Degobert G, Aydin D. Lyophilization of Nanocapsules: Instability Sources, Formulation and Process Parameters. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(8):1112. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13081112
Chicago/Turabian StyleDegobert, Ghania, and Dunya Aydin. 2021. "Lyophilization of Nanocapsules: Instability Sources, Formulation and Process Parameters" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 8: 1112. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13081112
APA StyleDegobert, G., & Aydin, D. (2021). Lyophilization of Nanocapsules: Instability Sources, Formulation and Process Parameters. Pharmaceutics, 13(8), 1112. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13081112






