The Therapeutic Effect of Human Serum Albumin Dimer-Doxorubicin Complex against Human Pancreatic Tumors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Expression and Purification of HSA-m and HSA-d
2.3. Cells and Animals
2.4. Preparation of HSA-DOX
2.5. Quantification of DOX Loaded to HSA
2.6. In Vitro Release Profile of DOX from HSA-m-DOX or HSA-d-DOX
2.7. In Vitro Antitumor Activity of HSA-DOX
2.8. Quantification of Intracellular DOX
2.9. Pharmacokinetic Analysis of HSA-DOX
2.10. In Vivo Antitumor Activity and Side Effects of HSA-DOX
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation of HSA-d-DOX
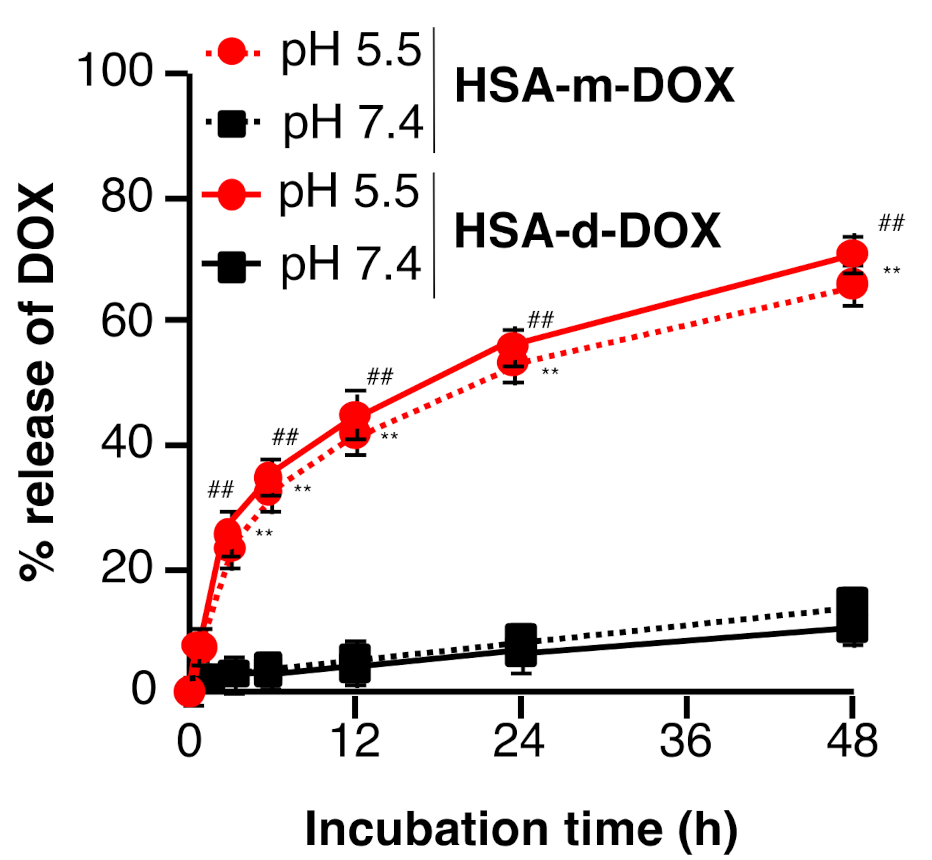
3.2. In Vitro Release Profile of DOX from HSA-m-DOX or HSA-d-DOX
3.3. In Vitro Antitumor Activity of HSA-d-DOX against Human Pancreatic Tumor Cells
3.4. Biodistribution of HSA-d-DOX
3.5. In Vivo Antitumor Activity of HSA-d-DOX
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matsumura, Y. Cancer stromal targeting therapy to overcome the pitfall of EPR effect. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2020, 154–155, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, E.; Iioka, H.; Saito, K. Tumor-homing peptide and its utility for advanced cancer medicine. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 2118–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, R.H.; Carter, S.K. Adriamycin. A new anticancer drug with significant clinical activity. Ann. Intern. Med. 1974, 80, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Bryan, R.M.; Luce, J.K.; Talley, R.W.; Gottlieb, J.A.; Baker, L.H.; Bonadonna, G. Phase II evaluation of adriamycin in human neoplasia. Cancer 1973, 32, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Safra, T.; Muggia, F.; Jeffers, S.; Tsao-Wei, D.D.; Groshen, S.; Lyass, O.; Henderson, R.; Berry, G.; Gabizon, A. Pegylated liposomal doxorubicin (doxil): Reduced clinical cardiotoxicity in patients reaching or exceeding cumulative doses of 500 mg/m2. Ann. Oncol. 2000, 11, 1029–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyass, O.; Uziely, B.; Ben-Yosef, R.; Tzemach, D.; Heshing, N.I.; Lotem, M.; Brufman, G.; Gabizon, A. Correlation of toxicity with pharmacokinetics of pegylated liposomal doxorubicin (Doxil) in metastatic breast carcinoma. Cancer 2000, 89, 1037–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, Y.; Hamaguchi, T.; Ura, T.; Muro, K.; Yamada, Y.; Shimada, Y.; Shirao, K.; Okusaka, T.; Ueno, H.; Ikeda, M.; et al. Phase I clinical trial and pharmacokinetic evaluation of NK911, a micelle-encapsulated doxorubicin. Br. J. Cancer 2004, 91, 1775–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratz, F. DOXO-EMCH (INNO-206): The first albumin-binding prodrug of doxorubicin to enter clinical trials. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2007, 16, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graeser, R.; Esser, N.; Unger, H.; Fichtner, I.; Zhu, A.; Unger, C.; Kratz, F. INNO-206, the (6-maleimidocaproyl hydrazone derivative of doxorubicin), shows superior antitumor efficacy compared to doxorubicin in different tumor xenograft models and in an orthotopic pancreas carcinoma model. Investig. New Drugs 2009, 28, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kratz, F.; Warnecke, A. Finding the optimal balance: Challenges of improving conventional cancer chemotherapy using suitable combinations with nano-sized drug delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2012, 164, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Sun, J.; Zhang, W.; Sui, X.; Yan, Z.; He, Z. Nanoparticle Albumin—Bound (NAB) Technology is a Promising Method for Anti-Cancer Drug Delivery. Recent Patents Anti-Cancer Drug Discov. 2009, 4, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaly, N.; Xiao, Z.; Valencia, P.M.; Radovic-Moreno, A.F.; Farokhzad, O.C. Targeted polymeric therapeutic nanoparticles: Design, development and clinical translation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2971–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, L.M.; Poudel, K.; Ou, W.; Phung, C.D.; Nguyen, H.T.; Nguyen, B.L.; Karmacharya, P.; Pandit, M.; Chang, J.-H.; Jeong, J.-H.; et al. Combination chemotherapeutic and immune-therapeutic anticancer approach via anti-PD-L1 antibody conjugated albumin nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 605, 120816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Ng, T.S.C.; Wang, S.J.; Prytyskach, M.; Rodell, C.B.; Mikula, H.; Kohler, R.H.; Garlin, M.A.; Lauffenburger, D.A.; Parangi, S.; et al. Therapeutically reprogrammed nutrient signalling enhances nanoparticulate albumin bound drug uptake and efficacy in KRAS-mutant cancer. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 830–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushita, S.; Chuang, V.T.G.; Kanazawa, M.; Tanase, S.; Kawai, K.; Maruyama, T.; Suenaga, A.; Otagiri, M. Recombinant Human Serum Albumin Dimer has High Blood Circulation Activity and Low Vascular Permeability in Comparison with Native Human Serum Albumin. Pharm. Res. 2006, 23, 882–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kinoshita, R.; Ishima, Y.; Ikeda, M.; Kragh-Hansen, U.; Fang, J.; Nakamura, H.; Chuang, V.T.G.; Tanaka, R.; Maeda, H.; Kodama, A.; et al. S-Nitrosated human serum albumin dimer as novel nano-EPR enhancer applied to macromolecular anti-tumor drugs such as micelles and liposomes. J. Control. Release 2015, 217, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinoshita, R.; Ishima, Y.; Chuang, V.T.G.; Nakamura, H.; Fang, J.; Watanabe, H.; Shimizu, T.; Okuhira, K.; Ishida, T.; Maeda, H.; et al. Improved anticancer effects of albumin-bound paclitaxel nanoparticle via augmentation of EPR effect and albumin-protein interactions using S-nitrosated human serum albumin dimer. Biomater. 2017, 140, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishima, Y.; Maruyama, T.; Otagiri, M.; Ishida, T. Drug Delivery System for Refractory Cancer Therapy via an Endogenous Albumin Transport System. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 68, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, N.; Trieu, V.; Damascelli, B.; Soon-Shiong, P. SPARC Expression Correlates with Tumor Response to Albumin-Bound Paclitaxel in Head and Neck Cancer Patients. Transl. Oncol. 2009, 2, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seno, T.; Harada, H.; Kohno, S.; Teraoka, M.; Inoue, A.; Ohnishi, T. Downregulation of SPARC expression inhibits cell migration and invasion in malignant gliomas. Int. J. Oncol. 2009, 34, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishima, Y.; Chen, D.; Fang, J.; Maeda, H.; Minomo, A.; Kragh-Hansen, U.; Kai, T.; Maruyama, T.; Otagiri, M. S-Nitrosated Human Serum Albumin Dimer is not only a Novel Anti-Tumor Drug but also a Potentiator for Anti-Tumor Drugs with Augmented EPR Effects. Bioconjugate Chem. 2012, 23, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.F. Removal of Fatty Acids from Serum Albumin by Charcoal Treatment. J. Biol. Chem. 1967, 242, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishima, Y.; Sawa, T.; Kragh-Hansen, U.; Miyamoto, Y.; Matsushita, S.; Akaike, T.; Otagiri, M. S-Nitrosylation of Human Variant Albumin Liprizzi (R410C) Confers Potent Antibacterial and Cytoprotective Properties. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 320, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matsushita, S.; Isima, Y.; Chuang, V.T.G.; Watanabe, H.; Tanase, S.; Maruyama, T.; Otagiri, M. Functional Analysis of Recombinant Human Serum Albumin Domains for Pharmaceutical Applications. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 1924–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.H.; Byeon, H.J.; Choi, J.S.; Thao, L.; Kim, I.; Lee, E.S.; Shin, B.S.; Lee, K.C.; Youn, Y.S. Inhalable self-assembled albumin nanoparticles for treating drug-resistant lung cancer. J. Control. Release 2015, 197, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichimizu, S.; Watanabe, H.; Maeda, H.; Hamasaki, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Chuang, V.T.G.; Kinoshita, R.; Nishida, K.; Tanaka, R.; Enoki, Y.; et al. Design and tuning of a cell-penetrating albumin derivative as a versatile nanovehicle for intracellular drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2018, 277, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Wang, J.; Lu, Q.; Xia, G.; Zhang, Y.; Song, L.; Fang, Y. Novel synthesizing method of pH-dependent doxorubicin-loaded anti-CD22-labelled drug delivery nanosystem. Drug. Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 5123–5133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, L.; Bae, Y.H. Cancer nanomedicines targeting tumor extracellular pH. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 99, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chatterjee, M.; Ben-Josef, E.; Robb, R.; Vedaie, M.; Seum, S.; Thirumoorthy, K.; Palanichamy, K.; Harbrecht, M.; Chakravarti, A.; Williams, T.M. Caveolae-Mediated Endocytosis Is Critical for Albumin Cellular Uptake and Response to Albumin-Bound Chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 5925–5937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iwao, Y.; Anraku, M.; Yamasaki, K.; Kragh-Hansen, U.; Kawai, K.; Maruyama, T.; Otagiri, M. Oxidation of Arg-410 promotes the elimination of human serum albumin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Proteins Proteom. 2006, 1764, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajou, K.; Watanabe, H.; Kragh-Hansen, U.; Maruyama, T.; Otagiri, M. The effect of glycation on the structure, function and biological fate of human serum albumin as revealed by recombinant mutants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 2003, 1623, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kratz, F.; Azab, S.; Zeisig, R.; Fichtner, I.; Warnecke, A. Evaluation of combination therapy schedules of doxorubicin and an acid-sensitive albumin-binding prodrug of doxorubicin in the MIA PaCa-2 pancreatic xenograft model. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 441, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Diameter (nm) | PDI | DOX/HSAs (Molar Ratio) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HSA-m-DOX | 3.98 ± 0.5 | 0.426 ± 0.01 | 4.08 ± 0.26 |
| HSA-d-DOX | 7.52 ± 0.7 | 0.297 ± 0.01 | 7.90± 0.46 |
| Treatment Groups | IC50 (DOX ng/mL) |
|---|---|
| HSA-m | - |
| HSA-d | - |
| HSA-m-DOX | 676.7 ± 52.4 |
| HSA-d-DOX | 454.2 ± 66.7 * |
| free-DOX | 62.21 ± 24.5 ** |
| WBC (×102/μL) | RBC (×104/μL) | HGB (g/dL) | PLT (×104/μL) | AST (IU/L) | ALT (IU/L) | BUN (mg/dL) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 24.3 ± 3.06 | 944.0 ± 32.5 | 114.4 ± 18.3 | 64.1 ± 12.4 | 19.6 ± 4.5 | 29.9 ± 3.2 | 78.8 ± 8.5 |
| INNO-206 | 20.5 ± 5.9 | 924.8 ± 47.8 | 106.5 ± 17.5 | 57.7 ± 11.1 | 16.6 ± 5.1 | 39.5 ± 4.4 | 78.3 ± 10.4 |
| HSA-m-DOX | 26.3 ± 8.3 | 934.8 ± 88.5 | 115.1 ± 13.2 | 62.8 ± 2.5 | 17.2 ± 5.1 | 33.7 ± 2.4 | 82.5 ± 19.3 |
| HSA-d-DOX | 17.8 ± 3.1 | 939.8 ± 79.0 | 102.6 ± 30.7 | 66.1 ± 7.5 | 20.4 ± 3.9 | 37.7 ± 2.6 | 78.8 ± 14.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kinoshita, R.; Ishima, Y.; Chuang, V.T.G.; Watanabe, H.; Shimizu, T.; Ando, H.; Okuhira, K.; Otagiri, M.; Ishida, T.; Maruyama, T. The Therapeutic Effect of Human Serum Albumin Dimer-Doxorubicin Complex against Human Pancreatic Tumors. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13081209
Kinoshita R, Ishima Y, Chuang VTG, Watanabe H, Shimizu T, Ando H, Okuhira K, Otagiri M, Ishida T, Maruyama T. The Therapeutic Effect of Human Serum Albumin Dimer-Doxorubicin Complex against Human Pancreatic Tumors. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(8):1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13081209
Chicago/Turabian StyleKinoshita, Ryo, Yu Ishima, Victor T. G. Chuang, Hiroshi Watanabe, Taro Shimizu, Hidenori Ando, Keiichiro Okuhira, Masaki Otagiri, Tatsuhiro Ishida, and Toru Maruyama. 2021. "The Therapeutic Effect of Human Serum Albumin Dimer-Doxorubicin Complex against Human Pancreatic Tumors" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 8: 1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13081209
APA StyleKinoshita, R., Ishima, Y., Chuang, V. T. G., Watanabe, H., Shimizu, T., Ando, H., Okuhira, K., Otagiri, M., Ishida, T., & Maruyama, T. (2021). The Therapeutic Effect of Human Serum Albumin Dimer-Doxorubicin Complex against Human Pancreatic Tumors. Pharmaceutics, 13(8), 1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13081209