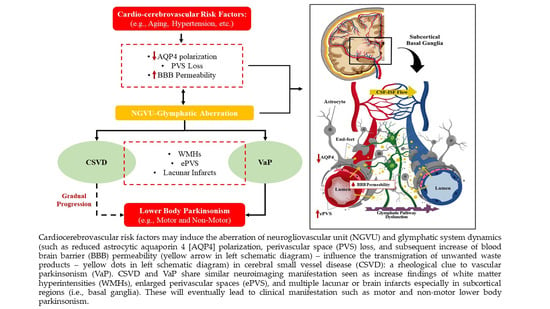
Aberrant Neurogliovascular Unit Dynamics in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: A Rheological Clue to Vascular Parkinsonism
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Literature Search Strategy
2. Overview of the Neurogliovascular Unit
2.1. Neurogliovascular Unit: Structure, Function, and Metabolic Coupling
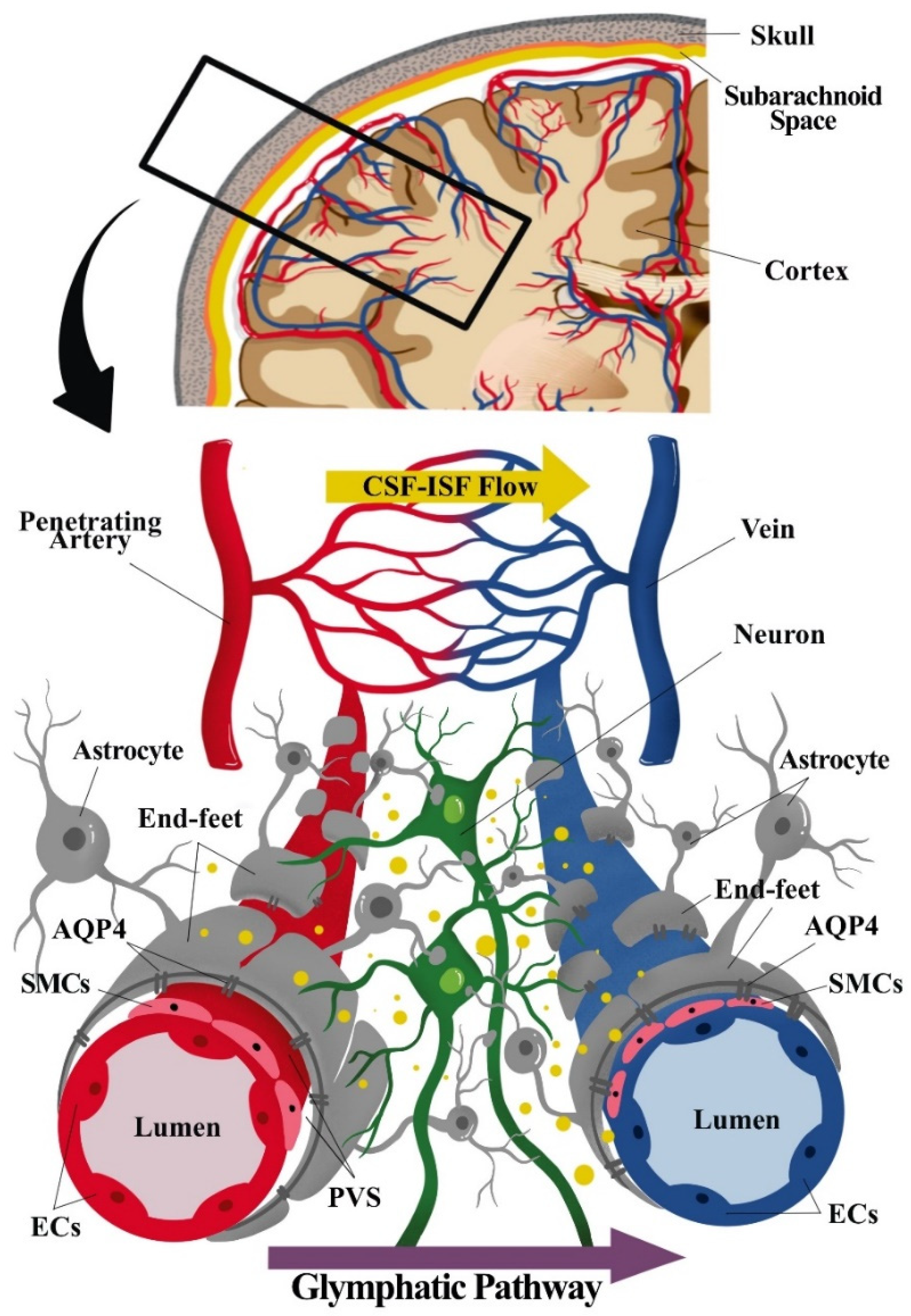
2.2. The Glymphatic System and NGVU
3. Parkinsonism and Vascular Parkinsonism
3.1. Parkinsonism: Characteristic and Classification
3.2. Vascular Parkinsonism (VaP)
VaP Pathomechanism
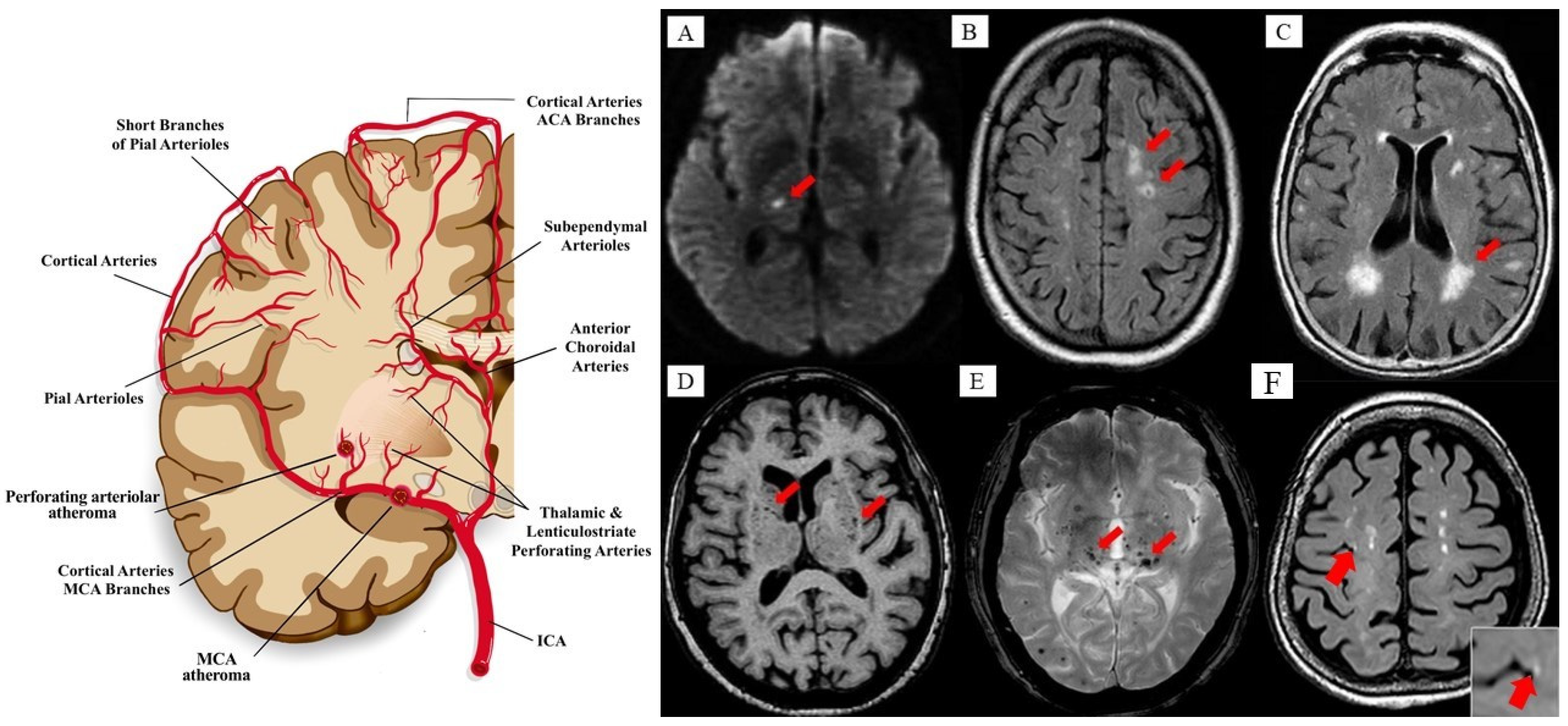
4. Cerebral Small Vessel Disease (CSVD)
4.1. Clinical Features of CSVD
4.2. Emerging Pathomechanism of CSVD
5. CSVD and VaP: Clinicopathological Correlates
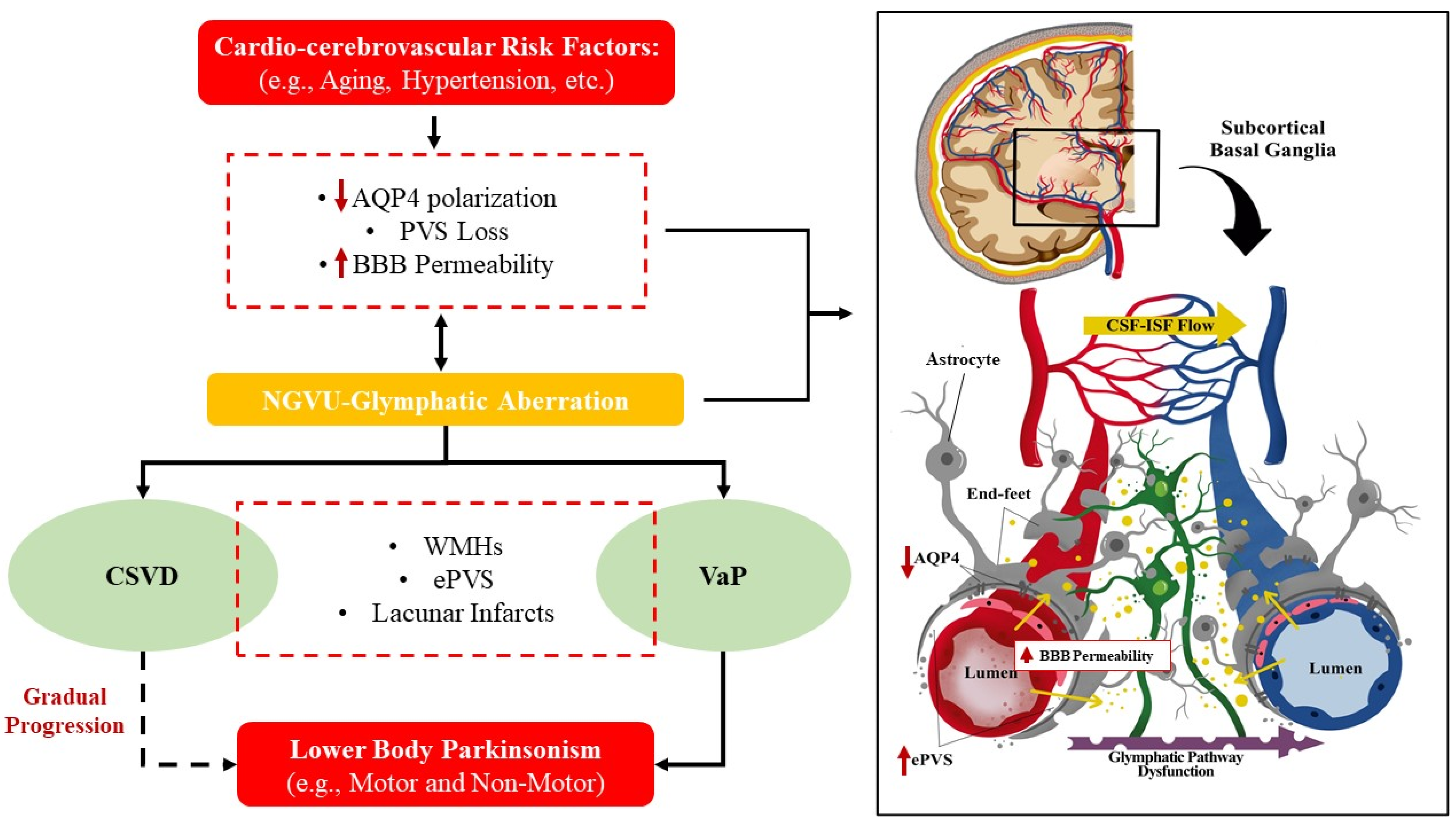
6. CSVD and VaP: The Clue in the Aberrant NGVU Dynamics
Potential Pharmaceutics, Prophylaxis, Prevention, and Therapy for CSVD and VaP
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Verkhratsky, A.; Nedergaard, M. Physiology of astroglia. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 239–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, M.D.; Zhao, Z.; Montagne, A.; Nelson, A.R.; Zlokovic, B.V. Blood-brain barrier: From physiology to disease and back. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 21–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louveau, A.; Herz, J.; Alme, M.N.; Salvador, A.F.; Dong, M.Q.; Viar, K.E.; Herod, S.G.; Knopp, J.; Setliff, J.C.; Lupi, A.L.; et al. CNS lymphatic drainage and neuroinflammation are regulated by meningeal lymphatic vasculature. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 1380–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lammie, A.G. Small vessel disease. In Cerebrovascular Diseases; Kalimo, H., Ed.; ISN Neuropath Press: Basel, Switzerland, 2005; pp. 85–91. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, E.E. Clinical presentations and epidemiology of vascular dementia. Clin. Sci. 2017, 131, 1059–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handley, A.; Medcalf, P.; Hellier, K.; Dutta, D. Movement disorders after stroke. Age Ageing 2009, 38, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thanvi, B.; Lo, N.; Robinson, T. Vascular parkinsonism—An important cause of parkinsonism in older people. Age Ageing 2005, 34, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, D.; Kuruvilla, A. Vascular parkinsonism: What makes it different? Postgrad. Med. J. 2011, 87, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korczyn, A.D. Vascular parkinsonism—Characteristics, pathogenesis, and treatment. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2015, 11, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zonta, M.; Angulo, M.C.; Gobbo, S.; Rosengarten, B.; Hossmann, K.A.; Pozzan, T.; Carmignoto, G. Neuron-to-astrocyte signaling is central to the dynamic control of brain microcirculation. Nat. Neurosci. 2003, 6, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabria, K.; Chakravarthy, V.S. Low-dimensional models of “neuro-glio-vascular unit” for describing neural dynamics under normal and energy-starved conditions. Front. Neurol. 2016, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jessen, K.R. Glial cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 36, 1861–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, F.A.; Carvalho, L.R.; Grinberg, L.T.; Farfel, J.M.; Ferretti, R.E.; Leite, R.E.; Filho, W.J.; Lent, R.; Herculano-Houzel, S. Equal numbers of neuronal and nonneuronal cells make the human brain an isometrically scaled-up primate brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 2009, 513, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, N.; Rönnbäck, L.; Hansson, E. Astrocyte–endothelial interactions at the blood–brain barrier. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barres, B.A. The mystery and magic of glia: A perspective on their roles in health and disease. Neuron 2008, 60, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Navarrete, M.; Perea, G.; de Sevilla, D.F.; Gómez-Gonzalo, M.; Núñez, A.; Martín, E.D.; Araque, A. Astrocytes mediate in vivo cholinergic-induced synaptic plasticity. PLoS Biol. 2012, 10, e1001259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cabezas, R.; Avila, M.F.; Torrente, D.; El-Bachá, R.S.; Morales, L.; Gonzalez, J.; Barreto, G.E. Astrocyte’s role in Parkinson: A double-edged sword. In Neurodegenerative Diseases; IntechOpen Access Publisher: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Araque, A.; Carmignoto, G.; Haydon, P.; Oliet, S.; Robitaille, R.; Volterra, A. Gliotransmitters Travel in Time and Space. Neuron 2014, 81, 728–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abbott, N.; Patabendige, A.; Dolman, D.; Yusof, S.; Begley, D. Structure and function of the blood–brain barrier. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 37, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler, R.C.; Roman, R.J.; Harder, D.R. Astrocytes and the regulation of cerebral blood flow. Trends Neurosci. 2009, 32, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perea, G.; Navarrete, M.; Araque, A. Tripartite synapses: Astrocytes process and control synaptic information. Trends Neurosci. 2009, 32, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haydon, P.G.; Carmignoto, G. Astrocyte control of synaptic transmission and neurovascular coupling. Physiol. Rev. 2006, 86, 1009–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nilsson, H.; Aalkjaer, C. Vasomotion: Mechanisms and Physiological Importance. Mol. Interv. 2003, 3, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iadecola, C. Neurovascular regulation in the normal brain and in Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2004, 5, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benveniste, H.; Liu, X.; Koundal, S.; Sanggaard, S.; Lee, H.; Wardlaw, J. The glymphatic system and waste clearance with brain aging: A review. Gerontology 2019, 65, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivoriunas, A.; Verkhratsky, A. Astrocyte-derived extracellular vesicles mediate intercellular communications of the neurogliovascular unit. Neural Regen. Res. 2021, 16, 1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalkara, T.; Alarcon-Martinez, L. Cerebral microvascular pericytes and neurogliovascular signaling in health and disease. Brain Res. 2015, 1623, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attwell, D.; Buchan, A.M.; Charpak, S.; Lauritzen, M.; MacVicar, B.A.; Newman, E.A. Glial and neuronal control of brain blood flow. Nature 2010, 468, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bosetti, F. Arachidonic acid metabolism in brain physiology and pathology: Lessons from genetically altered mouse models. J. Neurochem. 2007, 102, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, X.; Gebremedhin, D.; Falck, J.R.; Harder, D.R.; Koehler, R.C. Interaction of mechanisms involving epoxyeicosatrienoic acids, adenosine receptors, and metabotropic glutamate receptors in neurovascular coupling in rat whisker barrel cortex. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2008, 28, 111–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, G.R.; Choi, H.B.; Rungta, R.L.; Ellis-Davies, G.C.; MacVicar, B.A. Brain metabolism dictates the polarity of astrocyte control over arterioles. Nature 2008, 456, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, W.; McConnell, E.; Pare, J.F.; Xu, Q.; Chen, M.; Peng, W.; Lovatt, D.; Han, X.; Smith, Y.; Nedergaard, M. Glutamate-dependent neuroglial calcium signaling differs between young and adult brain. Science 2013, 339, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Filosa, J.A.; Bonev, A.D.; Straub, S.V.; Meredith, A.L.; Wilkerson, M.K.; Aldrich, R.W.; Nelson, M.T. Local potassium signaling couple’s neuronal activity to vasodilation in the brain. Nat. Neurosci. 2006, 9, 1397–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastide, M.; Ouk, T.; Plaisier, F.; Petrault, O.; Stolc, S.; Bordet, R. Neurogliovascular unit after cerebral ischemia: Is the vascular wall a pharmacological target. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2007, 32, S36–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atochin, D.; Huang, P.L. Role of endothelial nitric oxide in cerebrovascular regulation. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2011, 12, 1334–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecrux, C.; Toussay, X.; Kocharyan, A.; Fernandes, P.; Neupane, S.; Lévesque, M.; Plaisier, F.; Shmuel, A.; Cauli, B.; Hamel, E. Pyramidal neurons are “neurogenic hubs” in the neurovascular coupling response to whisker stimulation. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 9836–9847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duchemin, S.; Boily, M.; Sadekova, N.; Girouard, H. The complex contribution of NOS interneurons in the physiology of cerebrovascular regulation. Front. Neural Circuits 2012, 6, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, L.; Kang, H.; Xu, Q.; Chen, M.J.; Liao, Y.; Thiyagarajan, M.; O’Donnell, J.; Christensen, D.J.; Nicholson, C.; Iliff, J.J.; et al. Sleep drives metabolite clearance from the adult brain. Science 2013, 342, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nielsen, S.; Nagelhus, E.A.; Amiry-Moghaddam, M.; Bourque, C.; Agre, P.; Ottersen, O.P. Specialized membrane domains for water transport in glial cells: High-resolution immunogold cytochemistry of aquaporin-4 in rat brain. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nedergaard, M. Garbage truck of the brain. Science 2013, 340, 1529–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, Q.; Ineichen, B.V.; Detmar, M.; Proulx, S.T. Outflow of cerebrospinal fluid is predominantly through lymphatic vessels and is reduced in aged mice. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iliff, J.J.; Wang, M.; Liao, Y.; Plogg, B.A.; Peng, W.; Gundersen, G.A.; Benveniste, H.; Vates, G.E.; Deane, R.; Goldman, S.A.; et al. A paravascular pathway facilitates CSF flow through the brain parenchyma and the clearance of interstitial solutes, including amyloid β. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 147ra111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jessen, N.A.; Munk, A.S.F.; Lundgaard, I.; Nedergaard, M. The glymphatic system: A beginner’s guide. Neurochem. Res. 2015, 40, 2583–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mestre, H.; Kostrikov, S.; Mehta, R.I.; Nedergaard, M. Perivascular spaces, glymphatic dysfunction, and small vessel disease. Clin. Sci. 2017, 131, 2257–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xue, Y.; Liu, N.; Zhang, M.; Ren, X.; Tang, J.; Fu, J. Concomitant enlargement of perivascular spaces and decrease in glymphatic transport in an animal model of cerebral small vessel disease. Brain Res. Bull. 2020, 161, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plog, B.A.; Dashnaw, M.L.; Hitomi, E.; Peng, W.; Liao, Y.; Lou, N.; Deane, R.; Nedergaard, M. Biomarkers of traumatic injury are transported from brain to blood via the glymphatic system. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, W.; Achariyar, T.M.; Li, B.; Liao, Y.; Mestre, H.; Hitomi, E.; Regan, S.; Kasper, T.; Peng, S.; Ding, F.; et al. Suppression of glymphatic fluid transport in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2016, 93, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, A.J.; Verkman, A.S. The “glymphatic” mechanism for solute clearance in Alzheimer’s disease: Game changer or unproven speculation? FASEB J. 2018, 32, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fournier, A.P.; Gauberti, M.; Quenault, A.; Vivien, D.; Macrez, R.; Docagne, F. Reduced spinal cord parenchymal cerebrospinal fluid circulation in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2019, 39, 1258–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaberel, T.; Gakuba, C.; Goulay, R.; De Lizarrondo, S.M.; Hanouz, J.L.; Emery, E.; Touze, E.; Vivien, D.; Gauberti, M. Impaired glymphatic perfusion after strokes revealed by contrast-enhanced MRI: A new target for fibrinolysis? Stroke 2014, 45, 3092–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schain, A.J.; Melo-Carrillo, A.; Strassman, A.M.; Burstein, R. Cortical spreading depression closes paravascular space and impairs glymphatic flow: Implications for migraine headache. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 2904–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iliff, J.J.; Chen, M.J.; Plog, B.A.; Zeppenfeld, D.M.; Soltero, M.; Yang, L.; Singh, I.; Deane, R.; Nedergaard, M. Impairment of glymphatic pathway function promotes tau pathology after traumatic brain injury. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 16180–16193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, M.; Yang, L.; Sun, G.; Qi, S.; Li, B. Mechanism of depression as a risk factor in the development of Alzheimer’s disease: The function of AQP4 and the glymphatic system. Psychopharmacology 2017, 234, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duker, A.P.; Espay, A.J. Parkinsonism associated with striatal perivascular space dilation. Neurology 2007, 68, 1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, S.H.; Nichols III, F.T.; Espay, A.J.; Duker, A.P.; Morgan, J.C.; Sethi, K.D. Dilated Virchow–Robin spaces and parkinsonism. Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 589–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Lyoo, C.H.; Chung, T.S. Parkinsonism and Dementia Associated with Giant Virchow-Robin Spaces. J. Mov. Disord. 2015, 8, 106–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Hong, I.K.; Ahn, T.B. Dilated Virchow-Robin space and dopamine transporter imaging in the striatum of patients with Parkinsonism. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 42, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Conforti, R.; Sardaro, A.; Negro, A.; Caiazzo, G.; Paccone, A.; De Micco, R.; Cirillo, S.; Tessitore, A. Dilated Virchow-Robin space and Parkinson’s disease: A case report of combined MRI and diffusion tensor imaging. Radiol. Case Rep. 2018, 13, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Y.; Hu, W.; Gan, J.; Song, L.; Wu, N.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Z. Exploring the association between Cerebral small-vessel diseases and motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. Brain Behav. 2019, 9, e01219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, Y.W.; Shin, N.Y.; Chung, S.J.; Kim, J.; Lim, S.M.; Lee, P.H.; Lee, S.K.; Ahn, K.J. Magnetic Resonance Imaging–Visible Perivascular Spaces in Basal Ganglia Predict Cognitive Decline in Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2019, 34, 1672–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, K.; Sugiura, M.; Nishimura, Y.; Sakura, H. The effect of small vessel disease on motor and cognitive function in Parkinson’s disease. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2019, 182, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Li, W.J.; Huang, X.S. Alpha-synuclein levels in patients with multiple system atrophy: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Neurosci. 2018, 128, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnetti, L.; Paciotti, S.; Farotti, L.; Bellomo, G.; Sepe, F.N.; Eusebi, P. Parkinson’s and Lewy body dementia CSF biomarkers. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 495, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanouilidou, E.; Elenis, D.; Papasilekas, T.; Stranjalis, G.; Gerozissis, K.; Ioannou, P.C.; Vekrellis, K. Assessment of α-synuclein secretion in mouse and human brain parenchyma. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundaram, S.; Hughes, R.L.; Peterson, E.; Müller-Oehring, E.M.; Brontë-Stewart, H.M.; Poston, K.L.; Faerman, A.; Bhowmick, C.; Schulte, T. Establishing a framework for neuropathological correlates and glymphatic system functioning in Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 103, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winikates, J.; Jankovic, J. Clinical correlates of vascular parkinsonism. Arch. Neurol. 1999, 56, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tysnes, O.B.; Storstein, A. Epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neural Transm. 2017, 124, 901–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorsey, E.; Sherer, T.; Okun, M.S.; Bloem, B.R. The emerging evidence of the Parkinson pandemic. J. Parkinson Dis. 2018, 8, S3–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolters, E.C.; Braak, H. Parkinson’s disease: Premotor clinico-pathological correlations. Parkinson Dis. Relat. Disord. 2006, 70, 309–319. [Google Scholar]
- Sulzer, D. Multiple hit hypotheses for dopamine neuron loss in Parkinson’s disease. Trends Neurosci. 2007, 30, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savica, R.; Carlin, J.M.; Grossardt, B.R.; Bower, J.H.; Ahlskog, J.E.; Maraganore, D.M.; Bharucha, A.E.; Rocca, W.A. Medical records documentation of constipation preceding Parkinson disease: A case-control study. Neurology 2009, 73, 1752–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cersosimo, M.G.; Benarroch, E.E. Pathological correlates of gastrointestinal dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2012, 46, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, J.; Sethi, K.D. Differential diagnosis. In Handbook of Parkinson’s Disease; Informa Healthcare Inc.: London, UK, 2007; pp. 29–47. [Google Scholar]
- Dickson, D.W. Neuropathology of Parkinson disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2018, 46, S30–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletti, G.; Fera, F.; Condino, F.; Auteri, W.; Gallo, O.; Pugliese, P.; Arabia, G.; Morgante, L.; Barone, P.; Zappia, M.; et al. MR imaging of middle cerebellar peduncle width: Differentiation of multiple system atrophy from Parkinson disease. Radiology 2006, 239, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quattrone, A.; Nicoletti, G.; Messina, D.; Fera, F.; Condino, F.; Pugliese, P.; Lanza, P.; Barone, P.; Morgante, L.; Zappia, M.; et al. MR imaging index for differentiation of progressive supranuclear palsy from Parkinson disease and the Parkinson variant of multiple system atrophy. Radiology 2008, 246, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, M.; Arabia, G.; Salsone, M.; Novellino, F.; Giofrè, L.; Paletta, R.; Messina, D.; Nicoletti, G.; Condino, F.; Gallo, O.; et al. Accuracy of magnetic resonance parkinsonism index for differentiation of progressive supranuclear palsy from probable or possible Parkinson disease. Mov. Disord. 2011, 26, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostile, G.; Nicoletti, A.; Cicero, C.E.; Cavallaro, T.; Bruno, E.; Dibilio, V.; Luca, A.; Sciacca, G.; Raciti, L.; Contrafatto, D.; et al. Magnetic resonance parkinsonism index in progressive supranuclear palsy and vascular parkinsonism. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 37, 591–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Critchley, M. Arteriosclerotic parkinsonism. Brain 1929, 52, 23–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fitzgerald, P.M.; Jankovic, J. Lower body parkinsonism: Evidence for vascular etiology. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 1989, 4, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zijlmans, J.C.; Daniel, S.E.; Hughes, A.J.; Révész, T.; Lees, A.J. Clinicopathological investigation of vascular parkinsonism, including clinical criteria for diagnosis. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2004, 19, 630–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, P.G.; Lees, A.J.; Bacellar, A.; Zijlmans, J.; Katzenschlager, R.; Silveira-Moriyama, L. The clinical features of pathologically confirmed vascular parkinsonism. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2012, 83, 1027–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirkiran, M.; Bozdemir, H.; Sarica, Y. Vascular parkinsonism: A distinct, heterogeneous clinical entity. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2001, 104, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rektor, I.; Bohnen, N.I.; Korczyn, A.D.; Gryb, V.; Kumar, H.; Kramberger, M.G.; de Leeuw, F.E.; Pirtošek, Z.; Rektorová, I.; Schlesinger, I.; et al. An updated diagnostic approach to subtype definition of vascular parkinsonism–Recommendations from an expert working group. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2018, 49, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.K.; Lin, S.; Mok, V.C. Neuroimaging in vascular parkinsonism. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2019, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kalra, S.; Grosset, D.G.; Benamer, H.T. Differentiating vascular parkinsonism from idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review. Mov. Disord. 2010, 25, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rektor, I.; Rektorová, I.; Kubová, D. Vascular parkinsonism—An update. J. Neurol. Sci. 2006, 248, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampello, L.; Alvano, A.; Battaglia, G.; Raffaele, R.; Vecchio, I.; Malaguarnera, M. Different clinical and evolutional patterns in late idiopathic and vascular parkinsonism. J. Neurol. 2005, 252, 1045–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanouchi, H.; Nagura, H. Neurological signs and frontal white matter lesions in vascular parkinsonism: A clinicopathologic study. Stroke 1997, 28, 965–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadley, A.J.; van Zanten, J.J.V.; Aldred, S. The interactions of oxidative stress and inflammation with vascular dysfunction in ageing: The vascular health triad. Age 2013, 35, 705–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, G.A.; Bjerke, M.; Wallin, A. Multimodal markers of inflammation in the subcortical ischemic vascular disease type of vascular cognitive impairment. Stroke 2014, 45, 1531–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, J. Cerebral hypoperfusion and cognitive impairment: The pathogenic role of vascular oxidative stress. Int. J. Neurosci. 2012, 122, 494–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Gong, C.X. From chronic cerebral hypoperfusion to Alzheimer-like brain pathology and neurodegeneration. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 35, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.L.; Wang, L.H.; Yang, T.; Sun, J.Y.; Mao, L.L.; Yang, M.F.; Yuan, H.; Colvin, R.A.; Yang, X.Y. Lymphatic drainage system of the brain: A novel target for intervention of neurological diseases. Prog. Neurobiol. 2018, 163, 118–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, K.N.; Sanggaard, S.; Mestre, H.; Lee, H.; Kostrikov, S.; Xavier, A.L.; Gjedde, A.; Benveniste, H.; Nedergaard, M. Impaired glymphatic transport in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 6365–6377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cuadrado-Godia, E.; Dwivedi, P.; Sharma, S.; Santiago, A.O.; Gonzalez, J.R.; Balcells, M.; Laird, J.; Turk, M.; Suri, H.S.; Nicolaides, A.; et al. Cerebral small vessel disease: A review focusing on pathophysiology, biomarkers, and machine learning strategies. J. Stroke 2018, 20, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yang, Y.; Reis, C.; Tao, T.; Li, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.H. Cerebral small vessel disease. Cell Transplant. 2018, 27, 1711–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardlaw, J.M.; Smith, C.; Dichgans, M. Small vessel disease: Mechanisms and clinical implications. Lancet Neurol. 2019, 18, 684–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostile, G.; Nicoletti, A.; Zappia, M. Vascular Parkinsonism: Still looking for a diagnosis. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwanenburg, J.J.; van Osch, M.J. Targeting cerebral small vessel disease with MRI. Stroke 2017, 48, 3175–3182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardlaw, J.M.; Smith, E.E.; Biessels, G.J.; Cordonnier, C.; Fazekas, F.; Frayne, R.; Lindley, R.I.; O’Brien, J.T.; Barkhof, F.; Benavente, O.R.; et al. Standards for reporting vascular changes on neuroimaging (STRIVE v1): Neuroimaging standards for research into small vessel disease and its contribution to ageing and neurodegeneration. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 822–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Veluw, S.J.; Shih, A.Y.; Smith, E.E.; Chen, C.; Schneider, J.A.; Wardlaw, J.M.; Greenberg, S.M.; Biessels, G.J. Detection, risk factors, and functional consequences of cerebral microinfarcts. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 730–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debette, S.; Schilling, S.; Duperron, M.G.; Larsson, S.C.; Markus, H.S. Clinical significance of magnetic resonance imaging markers of vascular brain injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Georgakis, M.K.; Duering, M.; Wardlaw, J.M.; Dichgans, M. WMH and long-term outcomes in ischemic stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurology 2019, 92, e1298–e1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mustapha, M.; Nassir, C.M.N.C.M.; Aminuddin, N.; Safri, A.A.; Ghazali, M.M. Cerebral Small Vessel Disease (CSVD)–lessons from the animal models. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takasugi, J.; Miwa, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Okazaki, S.; Todo, K.; Sasaki, T.; Sakaguchi, M.; Mochizuki, H. Cortical cerebral microinfarcts on 3T magnetic resonance imaging in patients with carotid artery stenosis. Stroke 2019, 50, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leary, M.C.; Saver, J.L. Annual incidence of first silent stroke in the United States: A preliminary estimate. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2003, 16, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruso, P.; Signori, R.; Moretti, R. Small vessel disease to subcortical dementia: A dynamic model, which interfaces aging, cholinergic dysregulation and the neurovascular unit. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2019, 15, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.E.; Saposnik, G.; Biessels, G.J.; Doubal, F.N.; Fornage, M.; Gorelick, P.B.; Greenberg, S.M.; Higashida, R.T.; Kasner, S.E.; Seshadri, S.; et al. Prevention of stroke in patients with silent cerebrovascular disease: A scientific statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2017, 48, e44–e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuladhar, A.M.; van Norden, A.G.; de Laat, K.F.; Zwiers, M.P.; van Dijk, E.J.; Norris, D.G.; de Leeuw, F.E. White matter integrity in small vessel disease is related to cognition. NeuroImage Clin. 2015, 7, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arba, F.; Quinn, T.; Hankey, G.; Lees, K.; Wardlaw, J.; Ali, M.; Inzitari, D. Enlarged perivascular spaces and cognitive impairment after stroke and transient ischemic attack. Int. J. Stroke 2016, 13, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Knopman, D.S.; Penman, A.D.; Catellier, D.J.; Coker, L.H.; Shibata, D.K.; Sharrett, A.R.; Mosley, T.H. Vascular risk factors and longitudinal changes on brain MRI: The ARIC study. Neurology 2011, 76, 1879–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dijk, E.J.; Prins, N.D.; Vrooman, H.A.; Hofman, A.; Koudstaal, P.J.; Breteler, M.M. Progression of cerebral small vessel disease in relation to risk factors and cognitive consequences: Rotterdam Scan study. Stroke 2008, 39, 2712–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wright, C.B.; Dong, C.; Perez, E.J.; De Rosa, J.; Yoshita, M.; Rundek, T.; DeCarli, C.; Gutierrez, J.; Elkind, M.S.; Sacco, R.L. Subclinical cerebrovascular disease increases the risk of incident stroke and mortality: The northern manhattan study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e004069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gutierrez, J.; Rundek, T.; Ekind, M.S.V.; Sacco, R.L.; Wright, C.B. Perivascular spaces are associated with atherosclerosis: An insight from the Northern Manhattan Study. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2013, 34, 1711–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sudre, C.H.; Smith, L.; Atkinson, D.; Chaturvedi, N.; Ourselin, S.; Barkhof, F.; Hughes, A.D.; Jäger, H.R.; Cardoso, M.J. Cardiovascular risk factors and white matter hyperintensities: Difference in susceptibility in south Asians compared with Europeans. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e010533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hilal, S.; Mok, V.; Youn, Y.C.; Wong, A.; Ikram, M.K.; Chen, C.L.H. Prevalence, risk factors and consequences of cerebral small vessel diseases: Data from three Asian countries. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2017, 88, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Fang, F.; Cui, M.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Kong, X.; Tian, W.; Fan, M.; Yuan, Z.; Chen, J.; et al. Incidental findings on brain MRI among Chinese at the age of 55–65 years: The Taizhou Imaging Study. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yakushiji, Y.; Charidimou, A.; Hara, M.; Noguchi, T.; Nishihara, M.; Eriguchi, M.; Nanri, Y.; Nishiyama, M.; Werring, D.J.; Hara, H. Topography and associations of perivascular spaces in healthy adults: The Kashima scan study. Neurology 2014, 83, 2116–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnan, G.A.; Norrving, B.; Bamford, J.M.; Bogousslavsky, J. Classification of subcortical infarcts. In Subcortical Stroke; Oxford University Press Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Asdaghi, N.; Jeerakathil, T.; Hameed, B.; Saini, M.; McCombe, J.A.; Shuaib, A.; Emery, D.; Butcher, K. Oxfordshire community stroke project classification poorly differentiates small cortical and subcortical infarcts. Stroke 2011, 42, 2143–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loos, C.M.; Staals, J.; Wardlaw, J.M.; van Oostenbrugge, R.J. Cavitation of deep lacunar infarcts in patients with first-ever lacunar stroke: A 2-year follow-up study with MR. Stroke 2012, 43, 2245–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, A.S.; Regenhardt, R.W.; Vernooij, M.W.; Blacker, D.; Charidimou, A.; Viswanathan, A. Asymptomatic cerebral small vessel disease: Insights from population-based studies. J. Stroke 2019, 21, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levit, A.; Hachinski, V.; Whitehead, S.N. Neurovascular unit dysregulation, white matter disease, and executive dysfunction: The shared triad of vascular cognitive impairment and Alzheimer disease. Geroscience 2020, 42, 445–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Holst, H.M.; van Uden, I.W.; Tuladhar, A.M.; de Laat, K.F.; van Norden, A.G.; Norris, D.G.; Van Dijk, E.J.; Esselink, R.A.; Platel, B.; de Leeuw, F.E. Cerebral small vessel disease and incident parkinsonism: The RUN DMC study. Neurology 2015, 85, 1569–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hatate, J.; Miwa, K.; Matsumoto, M.; Sasaki, T.; Yagita, Y.; Sakaguchi, M.; Kitagawa, K.; Mochizuki, H. Association between cerebral small vessel diseases and mild parkinsonian signs in the elderly with vascular risk factors. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2016, 26, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Direk, N.; Perez, H.S.; Akoudad, S.; Verhaaren, B.F.; Niessen, W.J.; Hofman, A.; Vernooij, M.W.; Ikram, M.A.; Tiemeier, H. Markers of cerebral small vessel disease and severity of depression in the general population. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2016, 253, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rensma, S.P.; van Sloten, T.T.; Launer, L.J.; Stehouwer, C.D. Cerebral small vessel disease and risk of incident stroke, dementia and depression, and all-cause mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2018, 90, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iadecola, C. The neurovascular unit coming of age: A journey through neurovascular coupling in health and disease. Neuron 2017, 96, 17–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chojdak-Łukasiewicz, J.; Dziadkowiak, E.; Zimny, A.; Paradowski, B. Cerebral small vessel disease: A review. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2021, 30, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, W.R.; Moody, D.M.; Challa, V.R.; Thore, C.R.; Anstrom, J.A. Venous collagenosis and arteriolar tortuosity in leukoaraiosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2002, 203, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, W.R.; Moody, D.M.; Challa, V.R.; Thore, C.R.; Anstrom, J.A. Apoptosis in leukoaraiosis lesions. J. Neurol. Sci. 2002, 203, 169–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, F.J.; Chen, Y.; He, W.B.; Cai, Z.H. Prevalence of white matter hyperintensities increase with age. Neural Regen. Res. 2018, 13, 2141–2146. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Low, A.; Mak, E.; Rowe, J.B.; Markus, H.S.; O’Brien, J.T. Inflammation, and cerebral small vessel disease: A systematic review. Ageing Res. Rev. 2019, 53, 100916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Huang, Y.; Cai, W.; Chen, X.; Men, X.; Lu, T.; Wu, A.; Lu, Z. Age-related cerebral small vessel disease and inflammaging. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harper, J.W.; Elledge, S.J. The DNA damage response: Ten years after. Mol. Cell. 2007, 28, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciccia, A.; Elledge, S.J. The DNA damage response: Making it safe to play with knives. Mol. Cell. 2010, 40, 179–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hashimoto, M.; Tsugawa, T.; Kawagishi, H.; Asai, A.; Sugimoto, M. Loss of HuR leads to senescence-like cytokine induction in rodent fibroblasts by activating NF-kappaB. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1840, 3079–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, S.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, S.; Khanabdali, R.; Kalionis, B.; Wu, J.; Wan, W.; Tai, X. An update on inflamm-aging: Mechanisms, prevention, and treatment. J. Immunol. Res. 2016, 2016, 8426874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.; Shah, P.P.; Nativio, R.; Berger, S.L. Epigenetic mechanisms of longevity and aging. Cell 2016, 166, 822–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ermolaeva, M.; Neri, F.; Ori, A.; Rudolph, K.L. Cellular and epigenetic drivers of stem cell ageing. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 594–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Qu, J.; Liu, G.H.; Belmonte, J.C.I. The ageing epigenome and its rejuvenation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Yan, Y. Emerging role of immunity in cerebral small vessel disease. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jann, K.; Shao, X.; Ma, S.J.; Cen, S.Y.; D’Orazio, L.; Barisano, G.; Yan, L.; Casey, M.; Lamas, J.; Staffaroni, A.M.; et al. Evaluation of Cerebral Blood Flow Measured by 3D PCASL as Biomarker of Vascular Cognitive Impairment and Dementia (VCID) in a Cohort of Elderly Latinx Subjects at Risk of Small Vessel Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.E.; Wong, S.M.; van de Haar, H.J.; Staals, J.; Jansen, J.F.; Jeukens, C.R.; Hofman, P.A.; van Oostenbrugge, R.J.; Backes, W.H. Blood-brain barrier leakage is more widespread in patients with cerebral small vessel disease. Neurology 2017, 88, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naraoka, M.; Matsuda, N.; Shimamura, N.; Asano, K.; Ohkuma, H. the role of arterioles and the microcirculation in the development of vasospasm after aneurysmal SAH. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wardlaw, J.M. Update on cerebral small vessel disease: A dynamic whole-brain disease. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2016, 1, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, L.; Ma, L.; Wu, H.; He, X.; Zhu, M.; Wang, L.; Mei, F. Case Report of a pathologically confirmed vascular parkinsonism with early cognitive impairment and Behavioral disturbance. BMC Neurol. 2021, 21, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.J.; Daniel, S.E.; Kilford, L.; Lees, A.J. Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: A clinico-pathological study of 100 cases. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1992, 55, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zijlmans, J.C.M.; Thijssen, H.O.M.; Vogels, O.J.M.; Kremer, H.M.P.; Poels, P.J.E.; Schoonderwaldt, H.C.; Merx, J.L.; Van’t Hof, M.A.; Thien, T.; Horstink, M.W.I.M. MRI in patients with suspected vascular parkinsonism. Neurology 1995, 45, 2183–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dunet, V.; Deverdun, J.; Charroud, C.; Le Bars, E.; Molino, F.; De Champfleur, S.M.; Maury, F.; Charif, M.; Ayrignac, X.; Labauge, P.; et al. MRI volumetric morphometry in vascular parkinsonism. J. Neurol. 2017, 264, 1511–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swallow, D.M.A.; Counsell, C.E.; Murray, A.D. POMD02 Degree and clinical correlates of cerebral small vessel vascular disease in incident parkinsonian patients. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2010, 81, e57–e58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salsone, M.; Caligiuri, M.E.; Vescio, V.; Arabia, G.; Cherubini, A.; Nicoletti, G.; Morelli, M.; Quattrone, A.; Vescio, B.; Nisticò, R.; et al. Microstructural changes of normal-appearing white matter in vascular parkinsonism. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2019, 63, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yin, W.; Yu, X.; Zhu, X.; Qian, Y.; Sun, Z. Altered Brain Function in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease Patients with Gait Disorders: A Resting-State Functional MRI Study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baezner, H.; Blahak, C.; Poggesi, A.; Pantoni, L.; Inzitari, D.; Chabriat, H.; Erkinjuntti, T.; Fazekas, F.; Ferro, J.M.; Langhorne, P.; et al. Association of gait and balance disorders with age-related white matter changes: The LADIS study. Neurology 2008, 70, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, M.E.; Senjem, M.L.; Petersen, R.C.; Hollman, J.H.; Preboske, G.M.; Weigand, S.D.; Knopman, D.S.; Ferman, T.J.; Dickson, D.W.; Jack, C.R. Functional impact of white matter hyperintensities in cognitively normal elderly subjects. Arch. Neurol. 2010, 67, 1379–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uehara, T.; Tabuchi, M.; Mori, E. Risk factors for silent cerebral infarcts in subcortical white matter and basal ganglia. Stroke 1999, 30, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.C.; Park, S.J.; Ki, H.K.; Gwon, H.C.; Chung, C.S.; Byun, H.S.; Shin, K.J.; Shin, M.H.; Lee, W.R. Prevalence and risk factors of silent cerebral infarction in apparently normal adults. Hypertension 2000, 36, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Wan, H.; Zhang, M.; Liu, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Ma, H.; Pan, Y.; Feng, T.; Wang, Y. Cerebral small vessel disease may worsen motor function, cognition, and mood in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2021, 83, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vizcarra, J.A.; Lang, A.E.; Sethi, K.D.; Espay, A.J. Vascular Parkinsonism: Deconstructing a Syndrome. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 886–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Troili, F.; Cipollini, V.; Moci, M.; Morena, E.; Palotai, M.; Rinaldi, V.; Romano, C.; Ristori, G.; Giubilei, F.; Salvetti, M.; et al. Perivascular Unit: This Must Be the Place. The Anatomical Crossroad between the Immune, Vascular and Nervous System. Front. Neuroanat. 2020, 14, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Swieten, J.C.; van Den Hout, J.H.W.; van Ketel, B.A.; Hijdra, A.; Wokke, J.H.; van Gijn, J. Periventricular lesions in the white matter on magnetic resonance imaging in the elderly: A morphometric correlation with arteriolosclerosis and dilated perivascular spaces. Brain 1991, 114, 761–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vital, C.; Julien, J.; Mascalchi, M.; Cosottini, M.; Salvi, F. Expanding lacunae causing triventricular hydrocephalus [3](multiple letters). J. Neurosurg. 2000, 93, 155–156. [Google Scholar]
- Wardlaw, J.M.; Doubal, F.; Armitage, P.; Chappell, F.; Carpenter, T.; Muñoz Maniega, S.; Farrall, A.; Sudlow, C.; Dennis, M.; Dhillon, B. Lacunar stroke is associated with diffuse blood–brain barrier dysfunction. Ann. Neurol. Off. J. Am. Neurol. Assoc. Child Neurol. Soc. 2009, 65, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouhl, R.P.; van Oostenbrugge, R.J.; Theunissen, R.O.; Knottnerus, I.L.; Staals, J.; Henskens, L.H.; Kroon, A.A.; de Leeuw, P.W.; Lodder, J.; Tervaert, J.W.C.; et al. Autoantibodies against oxidized low-density lipoprotein in cerebral small vessel disease. Stroke 2010, 41, 2687–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maggi, P.; Macri, S.M.C.; Gaitán, M.I.; Leibovitch, E.; Wholer, J.E.; Knight, H.L.; Ellis, M.; Wu, T.; Silva, A.C.; Massacesi, L.; et al. The formation of inflammatory demyelinated lesions in cerebral white matter. Ann. Neurol. 2014, 76, 594–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaria, R.N. Small vessel disease and Alzheimer’s dementia: Pathological considerations. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2002, 13 (Suppl. 2), 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thore, C.R.; Anstrom, J.A.; Moody, D.M.; Challa, V.R.; Marion, M.C.; Brown, W.R. Morphometric analysis of arteriolar tortuosity in human cerebral white matter of preterm, young, and aged subjects. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2007, 66, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkes, C.A.; Härtig, W.; Kacza, J.; Schliebs, R.; Weller, R.O.; Nicoll, J.A.; Carare, R.O. Perivascular drainage of solutes is impaired in the ageing mouse brain and in the presence of cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Acta Neuropathol. 2011, 121, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbel-Ornath, M.; Hudry, E.; Eikermann-Haerter, K.; Hou, S.; Gregory, J.; Zhao, L.; Betensky, R.; Frosch, M.; Greenberg, S.; Bacskai, B. Interstitial fluid drainage is impaired in ischemic stroke and Alzheimer’s disease mouse models. Acta Neuropathol. 2013, 126, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weller, R.O.; Hawkes, C.A.; Kalaria, R.N.; Werring, D.J.; Carare, R.O. White matter changes in dementia: Role of impaired drainage of interstitial fluid. Brain Pathol. 2015, 25, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadaczek, P.; Yamashita, Y.; Mirek, H.; Tamas, L.; Bohn, M.C.; Noble, C.; Park, J.W.; Bankiewicz, K. The “perivascular pump” driven by arterial pulsation is a powerful mechanism for the distribution of therapeutic molecules within the brain. Mol. Ther. 2006, 14, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Iliff, J.J.; Yang, L.; Yang, J.; Chen, X.; Chen, M.J.; Giese, R.N.; Wang, B.; Shi, X.; Nedergaard, M. ‘Hit & Run’ model of closed-skull traumatic brain injury (TBI) reveals complex patterns of post-traumatic AQP4 dysregulation. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2013, 33, 834–845. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kress, B.T.; Iliff, J.J.; Xia, M.; Wang, M.; Wei, H.S.; Zeppenfeld, D.; Xie, L.; Kang, H.; Xu, Q.; Liew, J.A.; et al. Impairment of paravascular clearance pathways in the aging brain. Ann. Neurol. 2014, 76, 845–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantoni, L. Cerebral small vessel disease: From pathogenesis and clinical characteristics to therapeutic challenges. Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnell, H.L.; Kersch, C.N.; Woltjer, R.L.; Neuwelt, E.A. The translational significance of the neurovascular unit. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Montgolfier, O.; Pinçon, A.; Pouliot, P.; Gillis, M.A.; Bishop, J.; Sled, J.G.; Villeneuve, L.; Ferland, G.; Lévy, B.I.; Lesage, F.; et al. High systolic blood pressure induces cerebral microvascular endothelial dysfunction, neurovascular unit damage, and cognitive decline in mice. Hypertension 2019, 73, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armulik, A.; Genové, G.; Mäe, M.; Nisancioglu, M.H.; Wallgard, E.; Niaudet, C.; He, L.; Norlin, J.; Lindblom, P.; Strittmatter, K.; et al. Pericytes regulate the blood–brain barrier. Nature 2010, 468, 557–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferland-McCollough, D.; Slater, S.; Richard, J.; Reni, C.; Mangialardi, G. Pericytes, an overlooked player in vascular pathobiology. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 171, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safar, M.E.; Asmar, R.; Benetos, A.; Blacher, J.; Boutouyrie, P.; Lacolley, P.; Laurent, S.; London, G.; Pannier, B.; Protogerou, A.; et al. Interaction between hypertension and arterial stiffness: An expert reappraisal. Hypertension 2018, 72, 796–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greter, M.; Heppner, F.L.; Lemos, M.P.; Odermatt, B.M.; Goebels, N.; Laufer, T.; Noelle, R.J.; Becher, B. Dendritic cells permit immune invasion of the CNS in an animal model of multiple sclerosis. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelhardt, B.; Carare, R.O.; Bechmann, I.; Flügel, A.; Laman, J.D.; Weller, R.O. Vascular, glial, and lymphatic immune gateways of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 132, 317–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawakami, N.; Lassmann, S.; Li, Z.; Odoardi, F.; Ritter, T.; Ziemssen, T.; Klinkert, W.E.; Ellwart, J.W.; Bradl, M.; Krivacic, K.; et al. The activation status of neuroantigen-specific T cells in the target organ determines the clinical outcome of autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, S.; Dinh, T.T. Progressive postnatal dilation of brain ventricles in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Brain Res. 1986, 370, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koundal, S.; Liu, X.; Sanggaard, S.; Mortensen, K.; Wardlaw, J.; Nedergaard, M.; Benveniste, H.; Lee, H. Brain morphometry and longitudinal relaxation time of spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRs) in early and intermediate stages of hypertension investigated by 3D VFA-SPGR MRI. Neuroscience 2019, 404, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepehrband, F.; Cabeen, R.P.; Choupan, J.; Barisano, G.; Law, M.; Toga, A.W.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Perivascular space fluid contributes to diffusion tensor imaging changes in white matter. NeuroImage 2019, 197, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Küppers, E.; Gleiser, C.; Brito, V.; Wachter, B.; Pauly, T.; Hirt, B.; Grissmer, S. AQP4 expression in striatal primary cultures is regulated by dopamine–implications for proliferation of astrocytes. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 2173–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, B.; Sun, H.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, M.; Ding, J.; Fang, F.; Fan, Y.; Hu, G. Aquaporin-4 deficiency diminishes the differential degeneration of midbrain dopaminergic neurons in experimental Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2016, 614, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.M.; Cheung, M.S.; Gibbs, R.G.; Bhakoo, K.K. MRI detection of endothelial cell inflammation using targeted superparamagnetic particles of iron oxide (SPIO). Clin. Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, E.E.; Markus, H.S. New treatment approaches to modify the course of cerebral small vessel diseases. Stroke 2020, 51, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Otano, J.; Gaig, C.; Muxi, A.; Lomeña, F.; Compta, Y.; Buongiorno, M.T.; Martí, M.J.; Tolosa, E.; Valldeoriola, F. 123I-MIBG cardiac uptake, smell identification and 123I-FP-CIT SPECT in the differential diagnosis between vascular parkinsonism and Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2014, 20, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bath, P.M.; Wardlaw, J.M. Pharmacological treatment and prevention of cerebral small vessel disease: A review of potential interventions. Int. J. Stroke 2015, 10, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Cui, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, S.; Jia, Q.; Chai, Q.; Gong, G.; Zhang, H.; et al. Assessing the effectiveness of statin therapy for alleviating cerebral small vessel disease progression in people ≥ 75 years of age. BMC Geriatr. 2020, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, I.S.; Choue, R. Obesity, inflammation and diet. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2013, 16, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, N.; Sen, P. The senescent cell epigenome. Aging 2018, 10, 3590–3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cecco, M.; Ito, T.; Petrashen, A.P.; Elias, A.E.; Skvir, N.J.; Criscione, S.W.; Caligiana, A.; Brocculi, G.; Adney, E.M.; Boeke, J.D.; et al. L1 drives IFN in senescent cells and promotes age-associated inflammation. Nature 2019, 566, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, D.J.; Childs, B.G.; Durik, M.; Wijers, M.E.; Sieben, C.J.; Zhong, J.; Saltness, R.A.; Jeganathan, K.B.; Verzosa, G.C.; Pezeshki, A.; et al. Naturally occurring p16(Ink4a)-positive cells shorten healthy lifespan. Nature 2016, 530, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grosse, L.; Wagner, N.; Emelyanov, A.; Molina, C.; Lacas-Gervais, S.; Wagner, K.D.; Bulavin, D.V. Defined p16(high) senescent cell types are indispensable for mouse healthspan. Cell Metab. 2020, 32, 87–99.e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Chiang, H.H.; Luo, H.; Zheng, Z.; Qiao, Q.; Wang, L.; Tan, M.; Ohkubo, R.; Mu, W.C.; Zhao, S.; et al. An acetylation switch of the NLRP3 inflammasome regulates agingassociated chronic inflammation and insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2020, 31, 580–591.e585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondo, W.G.; Chan, L.L.; Levy, J.K. Vascular parkinsonism: Clinical correlates predicting motor improvement after lumbar puncture. Mov. Disord. 2002, 17, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espay, A.J.; Narayan, R.K.; Duker, A.P.; Barrett, E.T.; de Courten-Myers, G. Lower-body parkinsonism: Reconsidering the threshold for external lumbar drainage. Nat. Clin. Pract. Neurol. 2008, 4, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiguchi, I.; Ishii, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Kawasaki, T.; Yagi, H.; Shiino, A.; Shirakashi, Y.; Kawamoto, Y. Shunt-responsive parkinsonism and reversible white matter lesions in patients with idiopathic NPH. J. Neurol. 2008, 255, 1392–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisell, M.; Tullberg, M.; Hellström, P.; Edsbagge, M.; Högfeldt, M.; Wikkelsö, C. Shunt surgery in patients with hydrocephalus and white matter changes. J. Neurosurg. 2011, 114, 1432–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Risk Factors | Clinical Syndromes | Pathology | Neuroimaging Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Body Parkinsonism: Motor
| CSVD
|
|
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Che Mohd Nassir, C.M.N.; Damodaran, T.; Yusof, S.R.; Norazit, A.; Chilla, G.; Huen, I.; K. N., B.P.; Mohamed Ibrahim, N.; Mustapha, M. Aberrant Neurogliovascular Unit Dynamics in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: A Rheological Clue to Vascular Parkinsonism. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1207. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13081207
Che Mohd Nassir CMN, Damodaran T, Yusof SR, Norazit A, Chilla G, Huen I, K. N. BP, Mohamed Ibrahim N, Mustapha M. Aberrant Neurogliovascular Unit Dynamics in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: A Rheological Clue to Vascular Parkinsonism. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(8):1207. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13081207
Chicago/Turabian StyleChe Mohd Nassir, Che Mohd Nasril, Thenmoly Damodaran, Siti R. Yusof, Anwar Norazit, Geetha Chilla, Isaac Huen, Bhanu Prakash K. N., Norlinah Mohamed Ibrahim, and Muzaimi Mustapha. 2021. "Aberrant Neurogliovascular Unit Dynamics in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: A Rheological Clue to Vascular Parkinsonism" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 8: 1207. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13081207
APA StyleChe Mohd Nassir, C. M. N., Damodaran, T., Yusof, S. R., Norazit, A., Chilla, G., Huen, I., K. N., B. P., Mohamed Ibrahim, N., & Mustapha, M. (2021). Aberrant Neurogliovascular Unit Dynamics in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: A Rheological Clue to Vascular Parkinsonism. Pharmaceutics, 13(8), 1207. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13081207