Ultrasound-Responsive Smart Drug Delivery System of Lipid Coated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Lip-PFP-Dox-MSNPs
2.2.1. Preparation of Liposomes
2.2.2. Fabrication of MSNPs
2.2.3. Preparation of Dox-MSNPs
2.2.4. Preparation of PFP-Dox-MSNPs and Lipid Coating
2.3. Size and Surface Charge Measurement
2.4. Morphological Studies
2.5. Stability Studies of Lip-PFP-Dox-MSNPs
2.6. Ultrasound Triggered Drug Release
2.7. Measurement of Gas Produced by Vaporization
2.8. Cell Culture Experiments
2.8.1. In Vitro Cytotoxicity (MTT Assay)
2.8.2. Cellular Uptake Studies
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of MSNPs, Lip-MSNPs; Optimization and Characterization
3.2. Drug Loading and Preparation of Lip-PFP-Dox-MSNPs
3.3. Ultrasound Contrast Characterization and Stability of Carrier
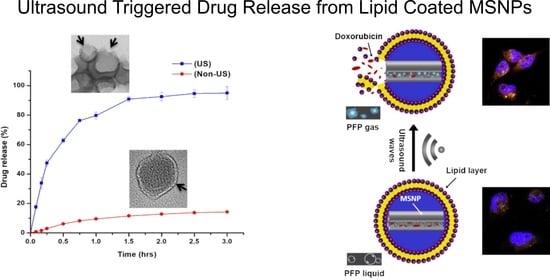
3.4. Ultrasound Triggered Drug Release
3.5. Cell Culture Experiments
3.6. Intracellular Drug Release and Cellular Uptake Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grigore, M. Organic and inorganic nano-systems used in cancer treatment. J. Med. Res. Health Educ. 2017, 1, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Baeza, A.; Ruiz-Molina, D.; Vallet-Regí, M. Recent advances in porous nanoparticles for drug delivery in antitumoral applications: Inorganic nanoparticles and nanoscale metal-organic frameworks. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2017, 14, 783–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Song, N.; Yang, Y.-W. Stimuli-responsive drug-delivery systems based on supramolecular nanovalves. Matter 2019, 1, 345–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Huang, P.; Chen, X. Stimuli-Responsive Programmed Specific Targeting in Nanomedicine. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 2991–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q.; Jia, J.; Niu, X.; Zheng, C.; Zhao, H.; Sun, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y. An oral drug delivery system with programmed drug release and imaging properties for orthotopic colon cancer therapy. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 15958–15970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, M.; Wang, X.; Toh, T.B.; Chow, E.K.-H. Applications of stimuli-responsive nanoscale drug delivery systems in translational research. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Du, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhai, G. Internal stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for drug delivery: Design strategies and applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 71, 1267–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roovers, S.; Deprez, J.; Priwitaningrum, D.; Lajoinie, G.; Rivron, N.; Declercq, H.; De Wever, O.; Stride, E.; Le Gac, S.; Versluis, M.; et al. Sonoprinting liposomes on tumor spheroids by microbubbles and ultrasound. J. Control. Release 2019, 316, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawak, M.; Mahmoud, G.; Dayyih, A.A.; Duse, L.; Pinnapireddy, S.R.; Engelhardt, K.; Awak, I.; Wölk, C.; König, A.M.; Brüßler, J. Magnetic resonance activatable thermosensitive liposomes for controlled doxorubicin delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 115, 111116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, D.; Guo, Z. Endogenous stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for drug delivery. Chem. Lett. 2016, 45, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roovers, S.; Segers, T.; Lajoinie, G.; Deprez, J.; Versluis, M.; De Smedt, S.C.; Lentacker, I. The Role of Ultrasound-Driven Microbubble Dynamics in Drug Delivery: From Microbubble Fundamentals to Clinical Translation. Langmuir 2019, 35, 10173–10191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, A.; Chattaraj, R.; Blum, N.T.; Goodwin, A.P. Understanding acoustic cavitation initiation by porous nanoparticles: Toward nanoscale agents for ultrasound imaging and therapy. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 5962–5972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Cock, I.; Zagato, E.; Braeckmans, K.; Luan, Y.; de Jong, N.; De Smedt, S.C.; Lentacker, I. Ultrasound and microbubble mediated drug delivery: Acoustic pressure as determinant for uptake via membrane pores or endocytosis. J. Control. Release 2015, 197, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Şen, T.; Tüfekçioğlu, O.; Koza, Y. Mechanical index. Anatol. J. Cardiol. 2015, 15, 334–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirsi, S.R.; Borden, M.A. State-of-the-art materials for ultrasound-triggered drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 72, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, H.; Lee, H.; Kim, K.; Kim, H. Effect of high intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) in conjunction with a nanomedicines-microbubble complex for enhanced drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2017, 266, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bing, C.; Patel, P.; Staruch, R.M.; Shaikh, S.; Nofiele, J.; Wodzak Staruch, M.; Chopra, R. Longer heating duration increases localized doxorubicin deposition and therapeutic index in Vx2 tumors using MR-HIFU mild hyperthermia and thermosensitive liposomal doxorubicin. Int. J. Hypertherm. 2019, 36, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Entzian, K.; Aigner, A. Drug Delivery by Ultrasound-Responsive Nanocarriers for Cancer Treatment. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.Y.; Tariq, I.; Ali, S.; Amin, M.U.; Engelhardt, K.; Pinnapireddy, S.R.; Duse, L.; Schäfer, J.; Bakowsky, U. Targeted ErbB3 cancer therapy: A synergistic approach to effectively combat cancer. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 575, 118961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paris, J.L.; Baeza, A.; Vallet-Regí, M. Overcoming the stability, toxicity, and biodegradation challenges of tumor stimuli-responsive inorganic nanoparticles for delivery of cancer therapeutics. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 1095–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, Q.; Liu, Z. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for stimuli-responsive controlled drug delivery: Advances, challenges, and outlook. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Cheng, C.-A.; Lee, B.-Y.; Clemens, D.L.; Huang, W.-Y.; Horwitz, M.A.; Zink, J.I. Facile strategy enabling both high loading and high release amounts of the water-insoluble drug Clofazimine using mesoporous silica nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 31870–31881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Lin, C.-Y.; Kang, S.-T.; Chang, Y.-C.; Zheng, H.; Yang, C.-M.; Yeh, C.-K. Superhydrophobic silica nanoparticles as ultrasound contrast agents. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 36, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, J.L.; Cabañas, M.V.; Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Polymer-grafted mesoporous silica nanoparticles as ultrasound-responsive drug carriers. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 11023–11033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paris, J.L.; Vallet-Regí, M. Ultrasound-activated nanomaterials for therapeutics. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2020, 93, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tariq, I.; Pinnapireddy, S.R.; Duse, L.; Ali, M.Y.; Ali, S.; Amin, M.U.; Goergen, N.; Jedelská, J.; Schäfer, J.; Bakowsky, U. Lipodendriplexes: A promising nanocarrier for enhanced gene delivery with minimal cytotoxicity. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 135, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Amin, M.U.; Ali, M.Y.; Tariq, I.; Pinnapireddy, S.R.; Duse, L.; Goergen, N.; Wölk, C.; Hause, G.; Jedelská, J.; et al. Wavelength dependent photo-cytotoxicity to ovarian carcinoma cells using temoporfin loaded tetraether liposomes as efficient drug delivery system. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 150, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattni, B.S.; Chupin, V.V.; Torchilin, V.P. New developments in liposomal drug delivery. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 10938–10966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cauda, V.; Engelke, H.; Sauer, A.; Arcizet, D.; Rädler, J.; Bein, T. Colchicine-loaded lipid bilayer-coated 50 nm mesoporous nanoparticles efficiently induce microtubule depolymerization upon cell uptake. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 2484–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.U.; Ali, S.; Ali, M.Y.; Tariq, I.; Nasrullah, U.; Pinnapreddy, S.R.; Wölk, C.; Bakowsky, U.; Brüßler, J. Enhanced Efficacy and Drug Delivery with Lipid Coated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles in Cancer Therapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2021, 165, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Xia, H. Ultrasound reversible response nanocarrier based on sodium alginate modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klibanov, A.L.; Shevchenko, T.I.; Raju, B.I.; Seip, R.; Chin, C.T. Ultrasound-triggered release of materials entrapped in microbubble-liposome constructs: A tool for targeted drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2010, 148, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Endreas, W.; Brüßler, J.; Vornicescu, D.; Keusgen, M.; Bakowsky, U.; Steinmetzer, T. Thrombin-Inhibiting Anticoagulant Liposomes: Development and Characterization. ChemMedChem 2016, 11, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, G.; Jedelská, J.; Omar, S.M.; Strehlow, B.; Schneider, M.; Bakowsky, U. Stabilized tetraether lipids based particles guided prophyrins photodynamic therapy. Drug Deliv. 2018, 25, 1526–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamada, H.; Urata, C.; Higashitamori, S.; Aoyama, Y.; Yamauchi, Y.; Kuroda, K. Critical roles of cationic surfactants in the preparation of colloidal mesostructured silica nanoparticles: Control of mesostructure, particle size, and dispersion. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 3491–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Gao, L.; Wang, L.; Shi, L.; Wei, E.; Zhou, B.; Zhou, L.; Ge, B. Polydopamine and peptide decorated doxorubicin-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a targeted drug delivery system for bladder cancer therapy. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dengler, E.C.; Liu, J.; Kerwin, A.; Torres, S.; Olcott, C.M.; Bowman, B.N.; Armijo, L.; Gentry, K.; Wilkerson, J.; Wallace, J.; et al. Mesoporous silica-supported lipid bilayers (protocells) for DNA cargo delivery to the spinal cord. J. Control. Release 2013, 168, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, S.L.; Hamilton, A.J.; Pozharski, E.; Nagaraj, A.; Klegerman, M.E.; McPherson, D.D.; MacDonald, R.C. Physical correlates of the ultrasonic reflectivity of lipid dispersions suitable as diagnostic contrast agents. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2002, 28, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, A.; Chattaraj, R.; Blum, N.T.; Shi, D.; Kumar, K.; Goodwin, A.P. Phospholipid capped mesoporous nanoparticles for targeted high intensity focused ultrasound ablation. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1700514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Situ, A.; Kang, Y.; Villabroza, K.R.; Liao, Y.; Chang, C.H.; Donahue, T.; Nel, A.E.; Meng, H. Irinotecan delivery by lipid-coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles shows improved efficacy and safety over liposomes for pancreatic cancer. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 2702–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Li, F.; Guo, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Gan, Y. Biofunctionalized polymer-lipid supported mesoporous silica nanoparticles for release of chemotherapeutics in multidrug resistant cancer cells. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 3650–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Huang, J.; Wang, X.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Sun, Z.; Zou, H.; Sun, D.; et al. The eradication of breast cancer cells and stem cells by 8-hydroxyquinoline-loaded hyaluronan modified mesoporous silica nanoparticle-supported lipid bilayers containing docetaxel. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 7662–7673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durfee, P.N.; Lin, Y.-S.; Dunphy, D.R.; Muñiz, A.E.J.; Butler, K.S.; Humphrey, K.R.; Lokke, A.J.; Agola, J.O.; Chou, S.S.; Chen, I.-M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticle-supported lipid bilayers (protocells) for active targeting and delivery to individual leukemia cells. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 8325–8345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.-A.; Chen, W.; Zhang, L.; Wu, H.H.; Zink, J.I. A responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticle platform for magnetic resonance imaging-guided high-intensity focused ultrasound-stimulated cargo delivery with controllable location, time, and dose. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 17670–17684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Pan, Y.; Cheng, R.; Sheng, L.; Wu, W.; Pan, G.; Feng, Q.; Cui, W. Doxorubicin-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticle composite nanofibers for long-term adjustments of tumor apoptosis. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 245101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, K.; Long, G.F.; Liu, M.Y.; Du, Z.X.; Liang, Z.-X.; Tsiakaras, P. Nitrogen doped ordered mesoporous carbon: Synthesis and active sites for electrocatalysis of oxygen reduction reaction. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 165, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, R.; Oda, Y.; Utoguchi, N.; Maruyama, K. Progress in the development of ultrasound-mediated gene delivery systems utilizing nano- and microbubbles. J. Control. Release 2011, 149, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Hu, H.; Li, T.Y.; Johri, A.M.; Li, X.; Wang, J. Stable Encapsulated Air Nanobubbles in Water. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2015, 54, 14291–14294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levenback, B.J.; Sehgal, C.M.; Wood, A.K. Modeling of thermal effects in antivascular ultrasound therapy. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2012, 131, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.Y.; Byun, K.-T.; Kwak, H.-Y. Temperature and pressure fields due to collapsing bubble under ultrasound. Chem. Eng. J. 2007, 132, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, D.; Zong, S.; Yang, L.; Zhong, Y.; Cui, Y. pH and thermo dual-stimuli-responsive drug carrier based on mesoporous silica nanoparticles encapsulated in a copolymer-lipid bilayer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 10895–10903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaban, V.V.; Prezhdo, O.V. Water boiling inside carbon nanotubes: Toward efficient drug release. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 5647–5655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brüßler, J.; Strehlow, B.; Becker, A.; Schubert, R.; Schümmelfeder, J.; Nimsky, C.; Bakowsky, U. Nanoscaled ultrasound contrast agents for enhanced sonothrombolysis. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 172, 728–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasternak, M.M.; Strohm, E.M.; Berndl, E.S.; Kolios, M.C. Properties of cells through life and death—An acoustic microscopy investigation. Cell Cycle 2015, 14, 2891–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, J.; Howard, C.B.; Mahler, S.M.; Thurecht, K.J.; Huang, L.; Xu, Z.P. Enhanced delivery of siRNA to triple negative breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo through functionalizing lipid-coated calcium phosphate nanoparticles with dual target ligands. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 4258–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.; Amin, M.U.; Tariq, I.; Sohail, M.F.; Ali, M.Y.; Preis, E.; Ambreen, G.; Pinnapireddy, S.R.; Jedelská, J.; Schäfer, J. Lipoparticles for Synergistic Chemo-Photodynamic Therapy to Ovarian Carcinoma Cells: In vitro and in vivo Assessments. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Particle Size ± SD (nm) | PDI | Zeta Potential ± SD (mV) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSNPs | 118 ± 20 | 0.159 | +34 ± 5 | Before washing |
| −17 ± 4 | After washing | |||
| Liposomes | 126 ± 12 | 0.177 | +18 ± 4 | |
| Lip-MSNPs | 130 ± 10 | 0.242 | +8 ± 3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amin, M.U.; Ali, S.; Tariq, I.; Ali, M.Y.; Pinnapreddy, S.R.; Preis, E.; Wölk, C.; Harvey, R.D.; Hause, G.; Brüßler, J.; et al. Ultrasound-Responsive Smart Drug Delivery System of Lipid Coated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13091396
Amin MU, Ali S, Tariq I, Ali MY, Pinnapreddy SR, Preis E, Wölk C, Harvey RD, Hause G, Brüßler J, et al. Ultrasound-Responsive Smart Drug Delivery System of Lipid Coated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13(9):1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13091396
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmin, Muhammad Umair, Sajid Ali, Imran Tariq, Muhammad Yasir Ali, Shashank Reddy Pinnapreddy, Eduard Preis, Christian Wölk, Richard D. Harvey, Gerd Hause, Jana Brüßler, and et al. 2021. "Ultrasound-Responsive Smart Drug Delivery System of Lipid Coated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles" Pharmaceutics 13, no. 9: 1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13091396
APA StyleAmin, M. U., Ali, S., Tariq, I., Ali, M. Y., Pinnapreddy, S. R., Preis, E., Wölk, C., Harvey, R. D., Hause, G., Brüßler, J., & Bakowsky, U. (2021). Ultrasound-Responsive Smart Drug Delivery System of Lipid Coated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics, 13(9), 1396. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13091396