Optimization of In Vivo Electroporation Conditions and Delivery of DNA Vaccine Encoding SARS-CoV-2 RBD Using the Determined Protocol
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plasmids
2.2. Animals
2.3. Selection of Optimal Parameters for EP
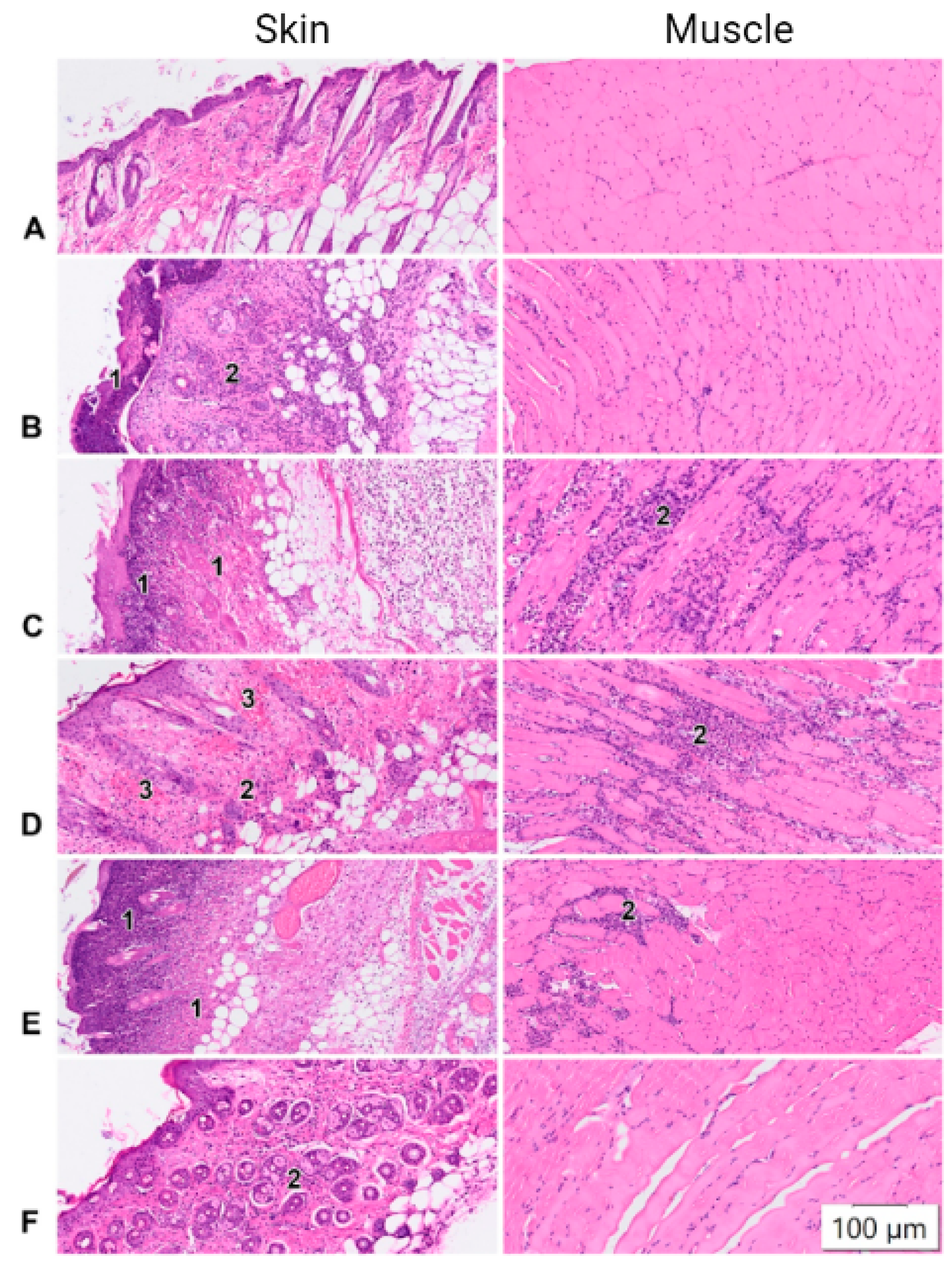
2.4. Histological Studies
2.5. DNA Immunization of Mice
2.6. ELISA Analysis
2.7. Virus Neutralization
2.8. Isolation of Splenocytes
2.9. IFN-γ ELISpot Analysis
2.10. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Optimization of In Vivo EP Conditions
3.2. Humoral Immune Response in Mice
3.3. Analysis of the T Cell Immune Response
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chavda, V.P.; Pandya, R.; Apostol Poulos, V. DNA vaccines for SARS-CoV-2: Towards third-generation vaccination era. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2021, 20, 1549–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Marc, G.P.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S.A.; Rouphael, N.; Creech, C.B.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momin, T.; Kansagra, K.; Patel, H.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, B.; Patel, J.; Mittal, R.; Sanmukhani, J.; Maithal, K.; Dey, A.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of a DNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine (ZyCoV-D): Results of an open-label, non-randomized phase I part of phase I/II clinical study by intradermal route in healthy subjects in India. eClinicalMedicine 2021, 38, 101020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallapaty, S. India’s DNA COVID vaccine is a world first—More are coming. Nature 2021, 597, 161–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Petrovsky, N. Molecular mechanisms for enhanced DNA vaccine immunogenicity. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2015, 15, 313–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braathen, R.; Cecilie, H.; Spång, L.; Hinke, D.M.; Blazevski, J.; Bobic, S.; Fossum, E.; Bogen, B. A DNA Vaccine That Encodes an Antigen-Presenting Cell-Specific Heterodimeric Protein Protects against Cancer and Influenza. Mol. Therapy. Methods Clin. Dev. 2020, 17, 378–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Wu, Y.; Kim, Y.B.; Oh, Y.-K. Advances in vaccine delivery systems against viral infectious diseases. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2021, 11, 1401–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazhan, S.; Antonets, D.; Starostina, E.; Ilyicheva, T.; Kaplina, O.; Marchenko, V.; Durymanov, A.; Oreshkova, S.; Karpenko, L.I. In silico design of influenza a virus artificial epitope-based T-cell antigens and the evaluation of their immunogenicity in mice. Vaccines 2020, 8, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpenko, L.I.; Bazhan, S.I.; Eroshkin, A.M.; Antonets, D.V.; Chikaev, A.N.; Ilyichev, A.A. Artificial Epitope-Based Immunogens in HIV-Vaccine Design (Chapter 12). In Advances in HIV and AIDS Control; Okware, S.I., Ed.; Uganda Christian University: Mukono, Kamaala, 2018; pp. 205–225. ISBN 978-1-78984-603-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanke, T. Conserved immunogens in prime-boost strategies for the next-generation HIV-1 vaccines. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2014, 14, 601–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sardesai, N.Y.; Weiner, D.B. Electroporation delivery of DNA vaccines: Prospects for success. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2011, 23, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, C.; Sun, J.; Hayashi, H.; Suzuki, A.; Sakaguchi, Y.; Miyazaki, H.; Nishikawa, T.; Nakagami, H.; Yamashita, K.; Kaneda, Y. Stable Immune Response Induced by Intradermal DNA Vaccination by a Novel Needleless Pyro-Drive Jet Injector. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 21, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Conforti, A.; Marra, E.; Palombo, F.; Roscilli, G.; Ravà, M.; Fumagalli, V.; Muzi, A.; Maffei, M.; Luberto, L.; Lione, L.; et al. COVID-eVax, an electroporated DNA vaccine candidate encoding the SARS-CoV-2 RBD, elicits protective responses in animal models. Mol. Ther. 2022, 30, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peletta, A.; Prompetchara, E.; Tharakhet, K.; Kaewpang, P.; Buranapraditkun, S.; Techawiwattanaboon, T.; Jbilou, T.; Krangvichian, P.; Sirivichayakul, S.; Manopwisedjaroen, S.; et al. DNA Vaccine Administered by Cationic Lipoplexes or by In Vivo Electroporation Induces Comparable Antibody Responses against SARS-CoV-2 in Mice. Vaccines 2021, 9, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallengärd, D.; Bråve, A.; Isaguliants, M.; Blomberg, P.; Enger, J.; Stout, R.; King, A.; Wahren, B. A combination of intradermal jet-injection and electroporation overcomes in vivodose restriction of DNA vaccines. Genet. Vaccines Ther. 2012, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petkov, S.P.; Heuts, F.; Krotova, O.A.; Kilpelainen, A.; Engström, G.; Starodubova, E.S.; Isaguliants, M.G. Evaluation of immunogen delivery by DNA immunization using non-invasive bioluminescence imaging. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2013, 9, 2228–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Modjarrad, K.; Roberts, C.C.; Mills, K.T.; Castellano, A.R.; Paolino, K.; Muthumani, K.; Reuschel, E.L.; Robb, M.L.; Racine, T.; Oh, M.-D.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of an anti-Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus DNA vaccine: A phase 1, open-label, single-arm, dose-escalation trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andrade, V.M.; Christensen-Quick, A.; Agnes, J.; Tur, J.; Reed, C.; Kalia, R.; Marrero, I.; Elwood, D.; Schultheis, K.; Purwar, M.; et al. INO-4800 DNA vaccine induces neutralizing antibodies and T cell activity against global SARS-CoV-2 variants. NPJ Vaccines 2021, 6, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebas, P.; Yang, S.; Boyer, J.D.; Reuschel, E.L.; Patel, A.; Christensen-Quick, A.; Andrade, V.M.; Morrow, M.P.; Kraynyak, K.; Agnes, J.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of INO-4800 DNA vaccine against SARS-CoV-2: A preliminary report of an open-label, Phase 1 clinical trial. eClinicalMedicine 2020, 31, 100689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraynyak, K.A.; Blackwood, E.; Agnes, J.; Tebas, P.; Giffear, M.; Amante, D.; Reuschel, E.L.; Purwar, M.; Christensen-Quick, A.; Liu, N.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 DNA Vaccine INO-4800 Induces Durable Immune Responses Capable of Being Boosted in a Phase 1 Open-Label Trial. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 225, 1923–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, K.E.; Humeau, L.M. Electroporation-enhanced delivery of nucleic acid vaccines. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2015, 14, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramot, Y.; Caselli, G.; Aurisicchio, L.; Andreini, I.; Marra, E.; Luberto, L.; Stoppoloni, D.; Pacello, M.L.; Monetini, L.; Nyska, A. Toxicity and Local Tolerance of COVID- eVax, a Plasmid DNA Vaccine for SARS-CoV-2, Delivered by Electroporation. Toxicol. Pathol. 2021, 49, 1255–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosati, M.; Agarwal, M.; Hu, X.; Devasundaram, S.; Stellas, D.; Chowdhury, B.; Bear, J.; Burns, R.; Donohue, D.; Pessaint, L.; et al. Control of SARS-CoV-2 infection after Spike DNA or Spike DNA+Protein co-immunization in rhesus macaques. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Patel, A.; Tursi, N.J.; Zhu, X.; Muthumani, K.; Kulp, D.W.; Weiner, D.B. Harnessing Recent Advances in Synthetic DNA and Electroporation Technologies for Rapid Vaccine Development Against COVID-19 and Other Emerging Infectious Diseases. Front. Med. Technol. 2020, 2, 571030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krotova, O.; Starodubova, E.; Petkov, S.; Kostic, L.; Agapkina, J.; Hallengärd, D.; Viklund, A.; Latyshev, O.; Gelius, E.; Dillenbeck, T.; et al. Consensus HIV-1 FSU-A Integrase Gene Variants Electroporated into Mice Induce Polyfunctional Antigen-Specific CD4+ and CD8+ T Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Latanova, A.A.; Petkov, S.; Kilpelainen, A.; Jansons, J.; Latyshev, O.E.; Kuzmenko, Y.V.; Hinkula, J.; Abakumov, M.A.; Valuev-Elliston, V.T.; Gomelsky, M.; et al. Codon optimization and improved delivery/immunization regimen enhance the immune response against wild-type and drug-resistant HIV-1 reverse transcriptase, preserving its Th2-polarity. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leroy, L.-A.; Donald, A.M.; Kandlur, A.; Bose, D.; Xiao, P.; Gagnon, J.; Villinger, F.; Chebloune, Y. Cytokine Adjuvants IL-7 and IL-15 Improve Humoral Responses of a SHIV LentiDNA Vaccine in Animal Models. Vaccines 2022, 10, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgoyakova, M.B.; Karpenko, L.I.; Rudometov, A.P.; Volosnikova, E.A.; Merkuleva, I.A.; Starostina, E.V.; Zadorozhny, A.M.; Isaeva, A.A.; Nesmeyanova, V.S.; Shanshin, D.V.; et al. Self-Assembled Particles Combining SARS-CoV-2 RBD Protein and RBD DNA Vaccine Induce Synergistic Enhancement of the Humoral Response in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merkuleva, I.A.; Shcherbakov, D.N.; Borgoyakova, M.B.; Shanshin, D.V.; Rudometov, A.P.; Karpenko, L.I.; Belenkaya, S.V.; Isaeva, A.A.; Nesmeyanova, V.S.; Kazachinskaia, V.I.; et al. Comparative Immunogenicity of the Recombinant Receptor-Binding Domain of Protein S SARS-CoV-2 Obtained in Prokaryotic and Mammalian Expression System. Vaccines 2022, 10, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A simple method of estimating fifty per cent endpoints. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpenko, L.I.; Rudometov, A.P.; Sharabrin, S.V.; Shcherbakov, D.N.; Borgoyakova, M.B.; Bazhan, S.I.; Volosnikova, E.A.; Rudometova, N.B.; Orlova, L.A.; Pyshnaya, I.A.; et al. Delivery of mRNA Vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 Using a Polyglucin: Spermidine-Conjugate. Vaccines 2021, 9, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemayehu, A.; Demissie, A.; Yusuf, M.; Lencha, A.G.; Oljira, L. Covid-19 Vaccine Acceptance and Determinant Factors among General Public in East Africa: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Health Serv. Res. Manag. Epidemiol. 2022, 9, 23333928221106269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgoyakova, M.B.; Karpenko, L.I.; Rudometov, A.P.; Shanshin, D.V.; Isaeva, A.A.; Nesmeyanova, V.S.; Volkova, N.V.; Belenkaya, S.V.; Murashkin, D.E.; Shcherbakov, D.N.; et al. Immunogenic Properties of the DNA Construct Encoding the Receptor-Binding Domain of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein. Mol. Biol. 2021, 55, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.L.; Bou-Gharios, G.; Partridge, T.A. Non-viral gene delivery in skeletal muscle: A protein factory. Gene Ther. 2003, 10, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hickling, J.K.; Jones, K.R.; Friede, M.; Zehrung, D.; Chen, D.; Kristensen, D. Intradermal delivery of vaccines: Potential benefits and current challenges. Bull. World Health Organ. 2011, 89, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandermeulen, G.; Staes, E.; Vanderhaeghen, M.L.; Bureau, M.F.; Scherman, D.; Préat, V. Optimisation of intradermal DNA electrotransfer for immunisation. J. Control. Release 2007, 124, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.; Rajanathan, T.M.C.; Chandra, H.; Pericherla, H.P.R.; Kumar, S.; Choonia, H.S.; Bajpai, M.; Singh, A.K.; Sinha, A.; Saini, G.; et al. Immunogenic potential of DNA vaccine candidate, ZyCoV-D against SARS-CoV-2 in animal models. Vaccine 2021, 39, 4108–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.R.F.; Patel, A.; Ramos, S.; Elwood, D.; Zhu, X.; Yan, J.; Gary, E.N.; Walker, S.N.; Schultheis, K.; Purwar, M.; et al. Immunogenicity of a DNA vaccine candidate for COVID-19. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Protocol Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pulse mode | Exponential | Rectangular | |||
| Type of impulse | ± | ||||
| Voltage (V) | 40 | 30 | 50 | 12 | 6 |
| Current limit (mA) | 300 | 200 | 150 | 45 | 45 |
| Pulse time (ms) | 30 | 40 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Interval impulses (ms) | 1000 | 900 | 900 | 950 | 900 |
| Number of impulses | 3 | 3 | 5 | 3 | 3 |
| Injury | moderate infiltration | diffuse neutrophilic infiltration | neutrophilic-histiocytic infiltration | moderate infiltration | normal histological picture. |
| Level of GFP fluorescence | 66 | 97 | 158 | 85 | 71 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kisakov, D.N.; Kisakova, L.A.; Borgoyakova, M.B.; Starostina, E.V.; Taranov, O.S.; Ivleva, E.K.; Pyankov, O.V.; Zaykovskaya, A.V.; Shcherbakov, D.N.; Rudometov, A.P.; et al. Optimization of In Vivo Electroporation Conditions and Delivery of DNA Vaccine Encoding SARS-CoV-2 RBD Using the Determined Protocol. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2259. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14112259
Kisakov DN, Kisakova LA, Borgoyakova MB, Starostina EV, Taranov OS, Ivleva EK, Pyankov OV, Zaykovskaya AV, Shcherbakov DN, Rudometov AP, et al. Optimization of In Vivo Electroporation Conditions and Delivery of DNA Vaccine Encoding SARS-CoV-2 RBD Using the Determined Protocol. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(11):2259. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14112259
Chicago/Turabian StyleKisakov, Denis Nikolaevich, Lyubov Alexandrovna Kisakova, Maria Borisovna Borgoyakova, Ekaterina Vladimirovna Starostina, Oleg Svyatoslavovich Taranov, Elena Konstantinovna Ivleva, Oleg Viktorovich Pyankov, Anna Vladimirovna Zaykovskaya, Dmitry Nikolaevich Shcherbakov, Andrey Pavlovich Rudometov, and et al. 2022. "Optimization of In Vivo Electroporation Conditions and Delivery of DNA Vaccine Encoding SARS-CoV-2 RBD Using the Determined Protocol" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 11: 2259. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14112259
APA StyleKisakov, D. N., Kisakova, L. A., Borgoyakova, M. B., Starostina, E. V., Taranov, O. S., Ivleva, E. K., Pyankov, O. V., Zaykovskaya, A. V., Shcherbakov, D. N., Rudometov, A. P., Rudometova, N. B., Volkova, N. V., Gureev, V. N., Ilyichev, A. A., & Karpenko, L. I. (2022). Optimization of In Vivo Electroporation Conditions and Delivery of DNA Vaccine Encoding SARS-CoV-2 RBD Using the Determined Protocol. Pharmaceutics, 14(11), 2259. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14112259






