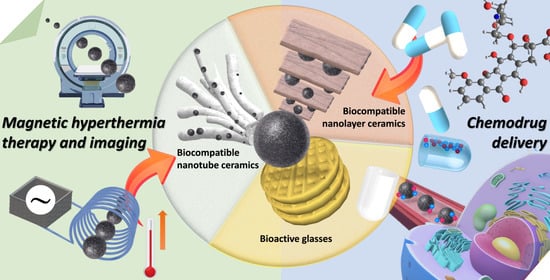
Iron-Based Ceramic Composite Nanomaterials for Magnetic Fluid Hyperthermia and Drug Delivery
Abstract
Share and Cite
Chan, M.-H.; Li, C.-H.; Chang, Y.-C.; Hsiao, M. Iron-Based Ceramic Composite Nanomaterials for Magnetic Fluid Hyperthermia and Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2584. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14122584
Chan M-H, Li C-H, Chang Y-C, Hsiao M. Iron-Based Ceramic Composite Nanomaterials for Magnetic Fluid Hyperthermia and Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(12):2584. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14122584
Chicago/Turabian StyleChan, Ming-Hsien, Chien-Hsiu Li, Yu-Chan Chang, and Michael Hsiao. 2022. "Iron-Based Ceramic Composite Nanomaterials for Magnetic Fluid Hyperthermia and Drug Delivery" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 12: 2584. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14122584
APA StyleChan, M.-H., Li, C.-H., Chang, Y.-C., & Hsiao, M. (2022). Iron-Based Ceramic Composite Nanomaterials for Magnetic Fluid Hyperthermia and Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics, 14(12), 2584. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14122584