PET Imaging of the Neurotensin Targeting Peptide NOTA-NT-20.3 Using Cobalt-55, Copper-64 and Gallium-68
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Radiolabeling of NOTA-NT-20.3
2.3. In Vitro Studies
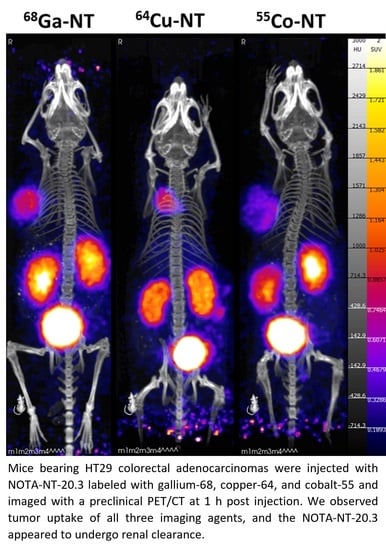
2.4. In Vivo Experiments
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results/Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maschauer, S.; Prante, O. Radiopharmaceuticals for imaging and endoradiotherapy of neurotensin receptor-positive tumors. J. Labelled. Comp. Radiopharm. 2018, 61, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitabgi, P. Targeting neurotensin receptors with agonists and antagonists for therapeutic purposes. Curr. Opin. Drug Discov. Devel. 2002, 5, 764–776. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Evers, B.M. Neurotensin and growth of normal and neoplastic tissues. Peptides 2006, 27, 2424–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Yang, W.; Cui, H.; Xu, M.; Yi, L. Oncogenic role of neurotensin and neurotensin receptors in various cancers. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2017, 44, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reubi, J.C.; Waser, B.; Friess, H.; Buchler, M.; Laissue, J. Neurotensin receptors: A new marker for human ductal pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Gut 1998, 42, 546–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, H.; Yoon, J.H.; Yoo, Y.S.; Kang, M.J. Validation of Neurotensin Receptor 1 as a Therapeutic Target for Gastric Cancer. Mol. Cells 2018, 41, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souaze, F.; Dupouy, S.; Viardot-Foucault, V.; Bruyneel, E.; Attoub, S.; Gespach, C.; Gompel, A.; Forgez, P. Expression of neurotensin and NT1 receptor in human breast cancer: A potential role in tumor progression. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 6243–6249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokko, K.P.; Hadden, M.K.; Orwig, K.S.; Mazella, J.; Dix, T.A. In vitro analysis of stable, receptor-selective neurotensin[8-13] analogues. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 4141–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Previti, S.; Vivancos, M.; Remond, E.; Beaulieu, S.; Longpre, J.M.; Ballet, S.; Sarret, P.; Cavelier, F. Insightful Backbone Modifications Preventing Proteolytic Degradation of Neurotensin Analogs Improve NTS1-Induced Protective Hypothermia. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Garayoa, E.; Blauenstein, P.; Bruehlmeier, M.; Blanc, A.; Iterbeke, K.; Conrath, P.; Tourwe, D.; Schubiger, P.A. Preclinical evaluation of a new, stabilized neurotensin(8--13) pseudopeptide radiolabeled with (99m)tc. J. Nucl. Med. 2002, 43, 374–383. [Google Scholar]
- de Visser, M.; Janssen, P.J.; Srinivasan, A.; Reubi, J.C.; Waser, B.; Erion, J.L.; Schmidt, M.A.; Krenning, E.P.; de Jong, M. Stabilised 111In-labelled DTPA- and DOTA-conjugated neurotensin analogues for imaging and therapy of exocrine pancreatic cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2003, 30, 1134–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Minnix, M.; Allen, R.; Bading, J.; Chea, J.; Wong, P.; Bowles, N.; Poku, E.; Shively, J.E. Preclinical PET Imaging of NTSR-1-Positive Tumors with (64)Cu- and (68)Ga-DOTA-Neurotensin Analogs and Therapy with an (225)Ac-DOTA-Neurotensin Analog. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2021, 36, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maschauer, S.; Ruckdeschel, T.; Tripal, P.; Haubner, R.; Einsiedel, J.; Hubner, H.; Gmeiner, P.; Kuwert, T.; Prante, O. In vivo monitoring of the antiangiogenic effect of neurotensin receptor-mediated radiotherapy by small-animal positron emission tomography: A pilot study. Pharmaceuticals 2014, 7, 464–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshoukr, F.; Rosant, C.; Maes, V.; Abdelhak, J.; Raguin, O.; Burg, S.; Sarda, L.; Barbet, J.; Tourwe, D.; Pelaprat, D.; et al. Novel neurotensin analogues for radioisotope targeting to neurotensin receptor-positive tumors. Bioconjug Chem. 2009, 20, 1602–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshoukr, F.; Prignon, A.; Brans, L.; Jallane, A.; Mendes, S.; Talbot, J.N.; Tourwe, D.; Barbet, J.; Gruaz-Guyon, A. Novel DOTA-neurotensin analogues for 111In scintigraphy and 68Ga PET imaging of neurotensin receptor-positive tumors. Bioconjug Chem. 2011, 22, 1374–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yordanova, A.; Eppard, E.; Kurpig, S.; Bundschuh, R.A.; Schonberger, S.; Gonzalez-Carmona, M.; Feldmann, G.; Ahmadzadehfar, H.; Essler, M. Theranostics in nuclear medicine practice. Onco Targets Ther. 2017, 10, 4821–4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwekkeboom, D.J.; de Herder, W.W.; Kam, B.L.; van Eijck, C.H.; van Essen, M.; Kooij, P.P.; Feelders, R.A.; van Aken, M.O.; Krenning, E.P. Treatment with the radiolabeled somatostatin analog [177 Lu-DOTA 0,Tyr3]octreotate: Toxicity, efficacy, and survival. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 2124–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strosberg, J.; El-Haddad, G.; Wolin, E.; Hendifar, A.; Yao, J.; Chasen, B.; Mittra, E.; Kunz, P.L.; Kulke, M.H.; Jacene, H.; et al. Phase 3 Trial of (177)Lu-Dotatate for Midgut Neuroendocrine Tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, C.; Rousseau, J.; Ramogida, C.F.; Celler, A.; Rahmim, A.; Uribe, C.F. Implications of physics, chemistry and biology for dosimetry calculations using theranostic pairs. Theranostics 2022, 12, 232–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, T.L.; Baun, C.; Olsen, B.B.; Dam, J.H.; Thisgaard, H. Improving Contrast and Detectability: Imaging with [(55)Co]Co-DOTATATE in Comparison with [(64)Cu]Cu-DOTATATE and [(68)Ga]Ga-DOTATATE. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 61, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thisgaard, H.; Olsen, B.B.; Dam, J.H.; Bollen, P.; Mollenhauer, J.; Hoilund-Carlsen, P.F. Evaluation of cobalt-labeled octreotide analogs for molecular imaging and auger electron-based radionuclide therapy. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 1311–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Edwards, W.B.; Xu, B.; Akers, W.; Cheney, P.P.; Liang, K.; Rogers, B.E.; Anderson, C.J.; Achilefu, S. Agonist-antagonist dilemma in molecular imaging: Evaluation of a monomolecular multimodal imaging agent for the somatostatin receptor. Bioconjug Chem. 2008, 19, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fani, M.; Braun, F.; Waser, B.; Beetschen, K.; Cescato, R.; Erchegyi, J.; Rivier, J.E.; Weber, W.A.; Maecke, H.R.; Reubi, J.C. Unexpected sensitivity of sst2 antagonists to N-terminal radiometal modifications. J. Nucl. Med. 2012, 53, 1481–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radford, L.L.; Fernandez, S.; Beacham, R.; El Sayed, R.; Farkas, R.; Benesova, M.; Muller, C.; Lapi, S.E. New (55)Co-labeled Albumin-Binding Folate Derivatives as Potential PET Agents for Folate Receptor Imaging. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdovinos, H.F.; Hernandez, R.; Graves, S.; Ellison, P.A.; Barnhart, T.E.; Theuer, C.P.; Engle, J.W.; Cai, W.; Nickles, R.J. Cyclotron production and radiochemical separation of (55)Co and (58m)Co from (54)Fe, (58)Ni and (57)Fe targets. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2017, 130, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, D.W.; Shefer, R.E.; Klinkowstein, R.E.; Bass, L.A.; Margeneau, W.H.; Cutler, C.S.; Anderson, C.J.; Welch, M.J. Efficient production of high specific activity 64Cu using a biomedical cyclotron. Nucl. Med. Biol. 1997, 24, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudin, H.; Pelaprat, D.; Rostene, W.; Pickel, V.M.; Beaudet, A. Correlative ultrastructural distribution of neurotensin receptor proteins and binding sites in the rat substantia nigra. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 8473–8484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, A.; Facca, V.J.; Cai, Z.; Reilly, R.M. Auger electrons for cancer therapy—A review. EJNMMI Radiopharm. Chem. 2019, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrissou, M.B.; Pichard, A.; Tee, B.; Kibedi, T.; Poty, S.; Pouget, J.P. Targeted Radionuclide Therapy Using Auger Electron Emitters: The Quest for the Right Vector and the Right Radionuclide. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjaergaard, K.; Sandahl, T.D.; Frisch, K.; Vase, K.H.; Keiding, S.; Vilstrup, H.; Ott, P.; Gormsen, L.C.; Munk, O.L. Intravenous and oral copper kinetics, biodistribution and dosimetry in healthy humans studied by [(64)Cu]copper PET/CT. EJNMMI Radiopharm, Chem 2020, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalafatakis, K.; Triantafyllou, K. Contribution of neurotensin in the immune and neuroendocrine modulation of normal and abnormal enteric function. Regul. Pept. 2011, 170, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maschauer, S.; Einsiedel, J.; Hubner, H.; Gmeiner, P.; Prante, O. (18)F- and (68)Ga-Labeled Neurotensin Peptides for PET Imaging of Neurotensin Receptor 1. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 6480–6492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastren, T.; Marquez, B.V.; Sultan, D.E.; Bollinger, E.; Eisenbeis, P.; Voller, T.; Lapi, S.E. Cyclotron Production of High-Specific Activity 55Co and In Vivo Evaluation of the Stability of 55Co Metal-Chelate-Peptide Complexes. Mol. Imaging 2015, 14, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Isotope | Half-Life | Positron Branching Ratio | Mean Positron Energy | Principal Photons (keV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ga-68 | 67.7 min | 89% | 829 keV | 511 (178%), 1077 (3%) |
| Cu-64 | 12.7 h | 17.5% | 278 keV | 511 (35.2 %), 1346 (0.5%) |
| Co-55 | 17.5 h | 76% | 570 keV | 511 (152%), 931 (75%) |
| Isotope | 1 h PBS | 1 h Serum | 4 h PBS | 4 h Serum | 24 h PBS | 24 h Serum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [68Ga]Ga-NOTA-NT-20.3 | >95% | >95% | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| [64Cu]Cu-NOTA-NT-20.3 | >95% | >95% | >95% | >95% | >95% | >95% |
| [55Co]Co-NOTA-NT-20.3 | N/A | N/A | >95% | >95% | >95% | >95% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Houson, H.A.; Tekin, V.; Lin, W.; Aluicio-Sarduy, E.; Engle, J.W.; Lapi, S.E. PET Imaging of the Neurotensin Targeting Peptide NOTA-NT-20.3 Using Cobalt-55, Copper-64 and Gallium-68. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2724. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14122724
Houson HA, Tekin V, Lin W, Aluicio-Sarduy E, Engle JW, Lapi SE. PET Imaging of the Neurotensin Targeting Peptide NOTA-NT-20.3 Using Cobalt-55, Copper-64 and Gallium-68. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(12):2724. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14122724
Chicago/Turabian StyleHouson, Hailey A., Volkan Tekin, Wilson Lin, Eduardo Aluicio-Sarduy, Jonathan W. Engle, and Suzanne E. Lapi. 2022. "PET Imaging of the Neurotensin Targeting Peptide NOTA-NT-20.3 Using Cobalt-55, Copper-64 and Gallium-68" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 12: 2724. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14122724
APA StyleHouson, H. A., Tekin, V., Lin, W., Aluicio-Sarduy, E., Engle, J. W., & Lapi, S. E. (2022). PET Imaging of the Neurotensin Targeting Peptide NOTA-NT-20.3 Using Cobalt-55, Copper-64 and Gallium-68. Pharmaceutics, 14(12), 2724. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14122724