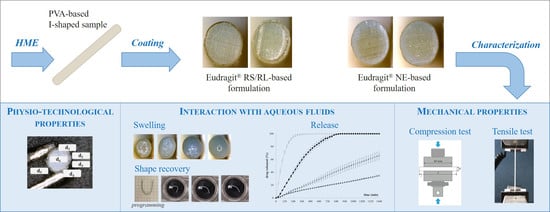
Expandable Drug Delivery Systems Based on Shape Memory Polymers: Impact of Film Coating on Mechanical Properties and Release and Recovery Performance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of PVA-Based Formulations
2.2.2. Hot Melt Extrusion
2.2.3. Film-Coating
2.2.4. Characterization
Weight Gain and Coating Thickness
Thermal Properties
Mechanical Properties
Swelling
- ₋ timm for uncoated samples = 10 min, 30 min, 1 h, 2 h, 4 h, and 6 h;
- ₋ timm for samples coated with Eudragit® RS/RL = 10 min, 30 min, 1 h, 4 h, and 6 h;
- ₋ timm for samples coated with Eudragit® NE = 10 min, 30 min, 1 h, 4 h, 6 h, 10 h, and 24 h.
Release
Shape Memory Effect
3. Results
3.1. Coating of the Expandable Prototypes
3.2. Thermal Analysis
3.3. Release Tests
3.4. Swelling Behavior
3.5. Mechanical Tests
3.6. Shape Memory Effect
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bardonnet, P.; Faivre, V.; Pugh, W.; Piffaretti, J.; Falson, F. Gastroretentive dosage forms: Overview and special case of Helicobacter pylori. J. Control. Release 2006, 111, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.; Tripathi, P.; Bhardwaj, P.; Maho, A. Recent advances in gastro retentive drug delivery systems and its application on treatment of H. Pylori infections. J. Anal. Pharm. Res. 2018, 7, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, C.M.; Bettencourt, C.; Rossi, A.; Buttini, F.; Barata, P. Overview on gastroretentive drug delivery systems for improving drug bioavailability. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 510, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melocchi, A.; Uboldi, M.; Cerea, M.; Foppoli, A.; Maroni, A.; Moutaharrik, S.; Palugan, L.; Zema, L.; Gazzaniga, A. Shape memory materials and 4D printing in pharmaceutics. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 173, 216–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrettos, N.-N.; Roberts, C.J.; Zhu, Z. Gastroretentive Technologies in Tandem with Controlled-Release Strategies: A Potent Answer to Oral Drug Bioavailability and Patient Compliance Implications. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klausner, E.A.; Lavy, E.; Friedman, M.; Hoffman, A. Expandable gastroretentive dosage forms. J. Control. Release 2003, 90, 143–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Kaushik, D. An overview on various approaches and recent patents on gastroretentive drug delivery systems. Recent Pat. Drug Deliv. Formul. 2018, 12, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palugan, L.; Cerea, M.; Cirilli, M.; Moutaharrik, S.; Maroni, A.; Zema, L.; Melocchi, A.; Uboldi, M.; Filippin, I.; Foppoli, A.; et al. Intravesical drug delivery approaches for improved therapy of urinary bladder diseases. Int. J. Pharm. X 2021, 3, 100100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroni, A.; Melocchi, A.; Zema, L.; Foppoli, A.; Gazzaniga, A. Retentive drug delivery systems based on shape memory materials. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altreuter, D.H.; Kirtane, A.R.; Grant, T.; Kruger, C.; Traverso, G.; Bellinger, A.M. Changing the pill: Developments toward the promise of an ultra-long-acting gastroretentive dosage form. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 1189–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellinger, A.M.; Jafari, M.; Grant, T.M.; Zhang, S.; Slater, H.C.; Wenger, E.A.; Mo, S.; Lee, Y.-A.L.; Mazdiyasni, H.; Kogan, L.; et al. Oral, ultra–long-lasting drug delivery: Application toward malaria elimination goals. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 365ra157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kirillova, A.; Ionov, L. Shape-changing polymers for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 1597–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirtane, A.R.; Abouzid, O.; Minahan, D.; Bensel, T.; Hill, A.L.; Selinger, C.; Bershteyn, A.; Craig, M.; Mo, S.S.; Mazdiyasni, H.; et al. Development of an oral once-weekly drug delivery system for HIV antiretroviral therapy. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, W.; Liu, L.; Zhang, F.; Leng, J.; Liu, Y. Shape memory polymers and their composites in biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 97, 864–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behl, M.; Lendlein, A. Shape-memory polymers. Mater. Today 2007, 10, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gall, K.; Yakacki, C.M.; Liu, Y.; Shandas, R.; Willett, N.; Anseth, K.S. Thermomechanics of the shape memory effect in polymers for biomedical applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2005, 73A, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melocchi, A.; Inverardi, N.; Uboldi, M.; Baldi, F.; Maroni, A.; Pandini, S.; Briatico-Vangosa, F.; Zema, L.; Gazzaniga, A. Retentive device for intravesical drug delivery based on water-induced shape memory response of poly(vinyl alcohol): Design concept and 4D printing feasibility. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 559, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melocchi, A.; Uboldi, M.; Inverardi, N.; Briatico-Vangosa, F.; Baldi, F.; Pandini, S.; Scalet, G.; Auricchio, F.; Cerea, M.; Foppoli, A.; et al. Expandable drug delivery system for gastric retention based on shape memory polymers: Development via 4D printing and extrusion. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 571, 118700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandari, S.; Nyavanandi, D.; Dumpa, N.; Repka, M.A. Coupling hot melt extrusion and fused deposition modeling: Critical properties for successful performance. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 172, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casati, F.; Melocchi, A.; Moutaharrik, S.; Uboldi, M.; Foppoli, A.; Maroni, A.; Zema, L.; Neut, C.; Siepmann, F.; Siepmann, J.; et al. Injection molded capsules for colon delivery combining time-controlled and enzyme-triggered approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallakunta, V.R.; Sarabu, S.; Bandari, S.; Tiwari, R.; Patil, H.; Repka, M.A. An update on the contribution of hot-melt extrusion technology to novel drug delivery in the twenty-first century: Part I. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melocchi, A.; Uboldi, M.; Parietti, F.; Cerea, M.; Foppoli, A.; Palugan, L.; Gazzaniga, A.; Maroni, A.; Zema, L. Lego-Inspired Capsular Devices for the Development of Personalized Dietary Supplements: Proof of Concept with Multimodal Release of Caffeine. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 109, 1990–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melocchi, A.; Uboldi, M.; Cerea, M.; Foppoli, A.; Maroni, A.; Moutaharrik, S.; Palugan, L.; Zema, L.; Gazzaniga, A. A Graphical Review on the Escalation of Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) 3D Printing in the Pharmaceutical Field. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 109, 2943–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melocchi, A.; Uboldi, M.; Briatico-Vangosa, F.; Moutaharrik, S.; Cerea, M.; Foppoli, A.; Maroni, A.; Palugan, L.; Zema, L.; Gazzaniga, A. The Chronotopic™ System for Pulsatile and Colonic Delivery of Active Molecules in the Era of Precision Medicine: Feasibility by 3D Printing via Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM). Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parulski, C.; Jennotte, O.; Lechanteur, A.; Evrard, B. Challenges of fused deposition modeling 3D printing in pharmaceutical applications: Where are we now? Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 175, 113810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarabu, S.; Bandari, S.; Kallakunta, V.R.; Tiwari, R.; Patil, H.; A Repka, M. An update on the contribution of hot-melt extrusion technology to novel drug delivery in the twenty-first century: Part II. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 567–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simões, M.F.; Pinto, R.M.A.; Simões, S. Hot-Melt Extrusion: A Roadmap for Product Development. AAPS PharmSciTech 2021, 22, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, T.; Hann, S.Y.; Chiesa, I.; Cui, H.; Celikkin, N.; Micalizzi, S.; Barbetta, A.; Costantini, M.; Esworthy, T.; Zhang, L.G.; et al. 4D printing in biomedical applications: Emerging trends and technologies. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 7608–7632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, P.; Li, H.; Gong, J.; Fan, Z.; Smith, A.T.; Shen, K.; Khalfalla, T.O.; Huang, H.; Qian, X.; McCutcheon, J.R.; et al. 4D printing of polymers: Techniques, materials, and prospects. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2022, 126, 101506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Morde, R.S.; Mariani, S.; La Mattina, A.A.; Vignali, E.; Yang, C.; Barillaro, G.; Lee, H. 4D Printing of a bioinspired microneedle array with backward-facing barbs for enhanced tissue adhesion. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1909197. [Google Scholar]
- Uboldi, M.; Melocchi, A.; Moutaharrik, S.; Palugan, L.; Cerea, M.; Foppoli, A.; Maroni, A.; Gazzaniga, A.; Zema, L. Administration strategies and smart devices for drug release in specific sites of the upper GI tract. J. Control. Release 2022, 348, 537–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, J.P.; Kirk, T.B.; Xu, J.; Ma, D.; Xue, W. Three-dimensional printing of shape memory hydrogels with internal structure for drug delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 84, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inverardi, N.; Scalet, G.; Melocchi, A.; Uboldi, M.; Maroni, A.; Zema, L.; Gazzaniga, A.; Auricchio, F.; Briatico-Vangosa, F.; Baldi, F.; et al. Experimental and computational analysis of a pharmaceutical-grade shape memory polymer applied to the development of gastroretentive drug delivery systems. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 124, 104814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uboldi, M.; Melocchi, A.; Moutaharrik, S.; Cerea, M.; Gazzaniga, A.; Zema, L. Dataset on a Small-Scale Film-Coating Process Developed for Self-Expanding 4D Printed Drug Delivery Devices. Coatings 2021, 11, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirtane, A.R.; Hua, T.; Hayward, A.; Bajpayee, A.; Wahane, A.; Lopes, A.; Bensel, T.; Ma, L.; Stanczyk, F.Z.; Brooks, S.; et al. A once-a-month oral contraceptive. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaay2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, M.; Vishwanath, K.; Eweje, F.; Roxhed, N.; Grant, T.; Castaneda, M.; Steiger, C.; Mazdiyasni, H.; Bensel, T.; Minahan, D.; et al. A gastric resident drug delivery system for prolonged gram-level dosing of tuberculosis treatment. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaau6267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verma, M.; Chu, J.N.; Salama, J.A.; Faiz, M.T.; Gwynne, F.E.D.; Lopes, A.; Hess, K.; Soares, V.; Steiger, C.; McManus, R.; et al. Development of a long-acting direct-acting antiviral system for hepatitis c virus treatment in a swine model. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, S-1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allopurinol. Available online: https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00437 (accessed on 25 October 2022).
- Kulkarni, R.V.; Mutalik, S.; Hiremath, D. Effect of plasticizers on the permeability and mechanical properties of Eudragit® films for transdermal application. Indian. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 64, 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Thakral, S.; Thakral, N.K.; Majumdar, D.K. Eudragit®: A technology evaluation. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajdik, J.; Pintye-Hódi, K.; Regdon, G., Jr.; Fazekas, P.; Szabó-Révész, P.; ErÞs, I. The effect of storage on the behaviour of Eudragit® NE free film. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2003, 73, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baert, L.; Remon, J. Water vapour permeation of aqueous based ethylacrylate methylmethacrylate copolymer films. Int. J. Pharm. 1993, 99, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semdé, R.; Karim, A.; Devleeschouwer, M.J.; Moës, A. Jtudies of pectin HM/Eudragit® RL/Eudragit® NE film-coating formulations intended for colonic drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 197, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caramella, C.; Ferrari, F.; Bonferoni, M.C.; Gazzaniga, A.; E Sangalli, M.; Conte, U.; Valserra, M.D.B.D.; Feletti, F. Swelling-restricted minimatrices for controlled release of drugs. Preliminary in-vivo studies. Boll. Chim. Farm. 1989, 128, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Colombo, P.; Conte, U.; Gazzaniga, A.; Maggi, L.; Sangalli, M.; Peppas, N.; Lamanna, A. Drug release modulation by physical restrictions of matrix swelling. Int. J. Pharm. 1990, 63, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzaniga, A.; Sangalli, M.; Conte, U.; Caramella, C.; Colombo, P.; La Manna, A. On the release mechanism from coated swellable minimatrices. Int. J. Pharm. 1993, 91, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, S.-F.; Hsieh, C.-M.; Chen, Y.-C.; Wang, Y.-C.; Ho, H.-O.; Sheu, M.-T. Characterizations of Plasticized Polymeric Film Coatings for Preparing Multiple-Unit Floating Drug Delivery Systems (muFDDSs) with Controlled-Release Characteristics. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, F.; Shahabi, M.; Afrasiabi, H. Comparison of physicomechanical properties of films prepared from organic solutions and aqueous dispersion of Eudragit RL. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 19, 100–106. [Google Scholar]












| Coating Formulation | Spray Rate (mL/min) | Nebulized Air Pressure (bar) | Pattern Pressure (bar) | Drying Air Temperature (°C) | Drying Air Flow (m3/h) | Sample Rotation Speed (rpm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eudragit® RS/RL ethanolic solution | 7 | 0.75 | 1 | 40 | 50 | 2.3 |
| Eudragit® NE aqueous suspension | 2.1 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 60 | 65 | 1.5 |
| Coating Formulation | Coating Process Time (min) | Code | |
|---|---|---|---|
PVA-based samples | None | 0 | uncoated |
Eudragit® RS/RL-based coating | 4 | R4 | |
| 8 | R8 | ||
| 16 | R16 | ||
Eudragit® NE-based coating | 4 | N4 | |
| 8 | N8 | ||
| 16 | N16 |
| (a) | Code | Thickness, µm (CV) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position | ||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| R4 | 107.8 (4.7) | 110.1 (5.6) | 113.6 (5.7) | 117.2 (5.4) | 116.7 (6.4) | |
| R8 | 173.5 (2.1) | 171.4 (2.1) | 175.2 (1.3) | 178.6 (4.3) | 174.3 (4.9) | |
| R16 | 443.3 (6.8) | 455.8 (1.4) | 449.0 (4.1) | 450.8 (4.9) | 428.5 (3.8) | |
| (b) | Code | Thickness, µm (CV) | ||||
| Position | ||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| N4 | 55.2 (16.3) | 56.8 (12.3) | 56.1 (12.0) | 54.2 (15.6) | 53.6 (14.8) | |
| N8 | 75.6 (5.3) | 86.5 (7.9) | 86.1 (7.7) | 83.9 (4.1) | 88.1 (8.0) | |
| N16 | 132.7 (4.6) | 140.0 (1.6) | 144.4 (3.7) | 143.2 (2.9) | 142.6 (3.2) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uboldi, M.; Pasini, C.; Pandini, S.; Baldi, F.; Briatico-Vangosa, F.; Inverardi, N.; Maroni, A.; Moutaharrik, S.; Melocchi, A.; Gazzaniga, A.; et al. Expandable Drug Delivery Systems Based on Shape Memory Polymers: Impact of Film Coating on Mechanical Properties and Release and Recovery Performance. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2814. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14122814
Uboldi M, Pasini C, Pandini S, Baldi F, Briatico-Vangosa F, Inverardi N, Maroni A, Moutaharrik S, Melocchi A, Gazzaniga A, et al. Expandable Drug Delivery Systems Based on Shape Memory Polymers: Impact of Film Coating on Mechanical Properties and Release and Recovery Performance. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(12):2814. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14122814
Chicago/Turabian StyleUboldi, Marco, Chiara Pasini, Stefano Pandini, Francesco Baldi, Francesco Briatico-Vangosa, Nicoletta Inverardi, Alessandra Maroni, Saliha Moutaharrik, Alice Melocchi, Andrea Gazzaniga, and et al. 2022. "Expandable Drug Delivery Systems Based on Shape Memory Polymers: Impact of Film Coating on Mechanical Properties and Release and Recovery Performance" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 12: 2814. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14122814
APA StyleUboldi, M., Pasini, C., Pandini, S., Baldi, F., Briatico-Vangosa, F., Inverardi, N., Maroni, A., Moutaharrik, S., Melocchi, A., Gazzaniga, A., & Zema, L. (2022). Expandable Drug Delivery Systems Based on Shape Memory Polymers: Impact of Film Coating on Mechanical Properties and Release and Recovery Performance. Pharmaceutics, 14(12), 2814. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14122814