In Vitro Nephrotoxicity and Permeation of Vancomycin Hydrochloride Loaded Liposomes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials
3. Methods
3.1. Preparation of VHCL Loaded Liposomes
3.2. Characterization of Liposomes
Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) Measurements
3.3. Zeta Potential Measurements
3.3.1. Examination of Vesicle Morphology with Cryo-TEM
3.3.2. Determination of Loading Efficiency of VHCL into Liposomes by HPLC
3.3.3. Determination of Encapsulation Efficiency of VHCL into Liposomes by HPLC
3.3.4. In Vitro Release of VHCL from VHCL-Loaded Liposomes
3.3.5. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay
3.3.6. Permeation Assay
3.3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
4.1. Characterization of Liposomes
4.2. In Vitro Release of VHCL from Liposomes
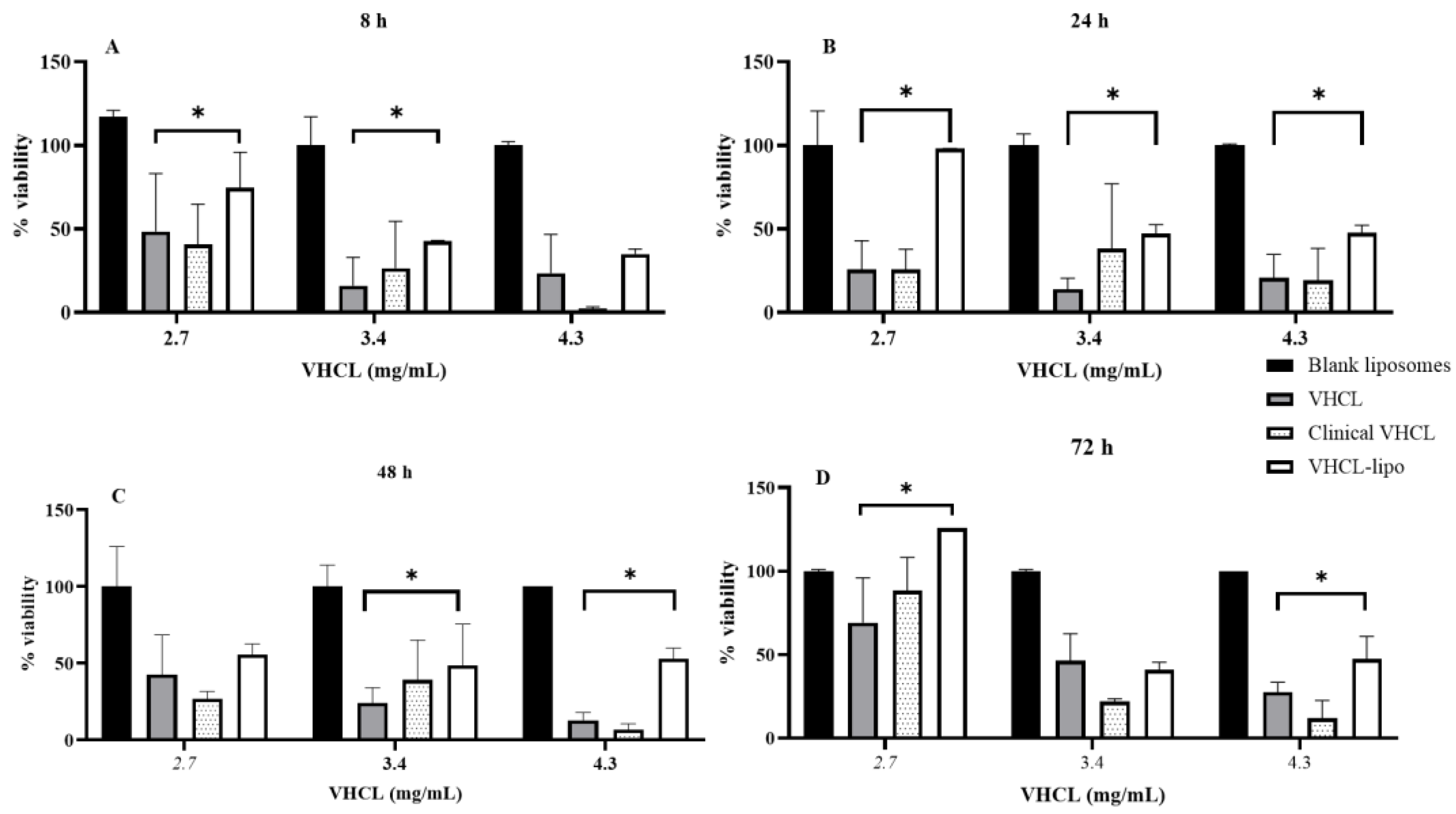
4.3. Cytotoxicity Assay
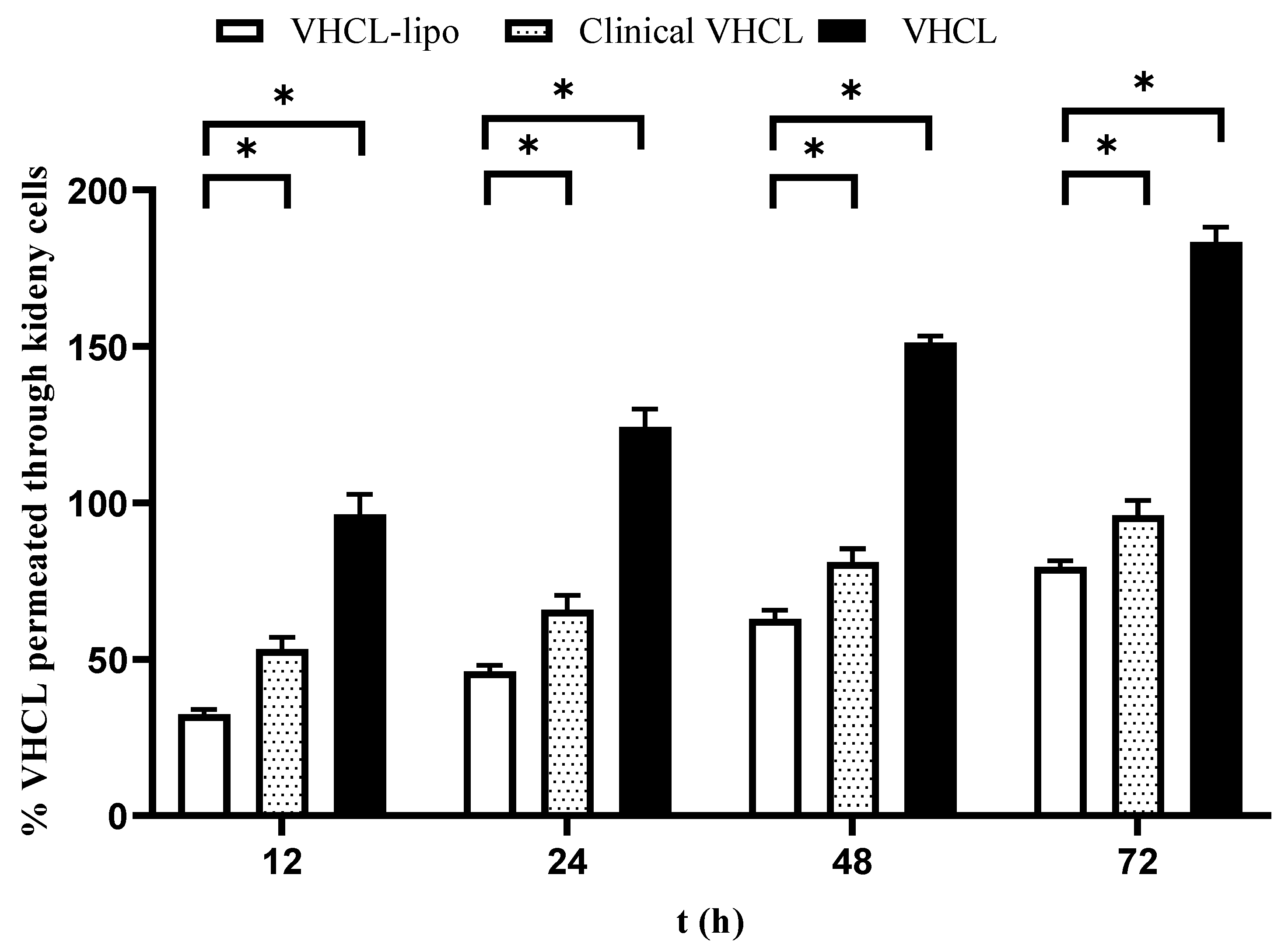
4.4. Permeation Assay
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| VHCL | vancomycin hydrochloride |
| VHCL-lipo | PEGylated vancomycin hydrochloride |
| MVV | Multivesicular vesicles |
| MDCK | Madin–Darby Canine Kidney cells |
| BeWo | BeWo is a cell line exhibiting epithelial morphology that was isolated from the placenta of a patient with choriocarcinoma |
| NRK-52E | Rat Kidney epithelial cells |
| TEER | Trans Epithelial Electrical Resistance |
| CDC | Center for Disease Control and Prevention |
| LCMS/MS | Triple-quad Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry |
| Kim-1 | Kidney Injury molecule-1 |
| GD | Gestational Day |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| PBS | Phosphate buffer saline pH 7.4 |
| ATCC | American-Type Culture Collection |
| TEM | Transmission electron Micrography |
| PDI | Polydispersity Index |
| PEG | Polyethylene glycol |
| PEG-DSPE 2000 | (1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N- [maleimide (polyethylene glycol)-2000]) |
| HPLC | High-pressure liquid chromatography |
| CCD | Charge-Coupled Device |
| ACD | Air Conditioning Disconnect |
References
- Pascual, M.J.; Macias, R.I.; Garcia-Del-Pozo, J.; Serrano, M.A.; Marin, J.J. Enhanced efficiency of the placental barrier to cisplatin through binding to glycocholic acid. Anticancer Res. 2001, 21, 2703–2707. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mean Age of Mothers is on the Rise: United States, 2000–2014. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/products/databriefs/db232.htm (accessed on 19 April 2022).
- Audus, K.L. Controlling drug delivery across the placenta. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 1999, 8, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pregnancy and Lactation Labeling (Drugs) Final Rule. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/labeling-information-drug-products/pregnancy-and-lactation-labeling-drugs-final-rule#:~:text=The%20PLLR%20removes%20pregnancy%20letter,the%20new%20PLLR%20labeling%20requirements (accessed on 19 April 2022).
- Keelan, J.A.; Leong, J.W.; Ho, D.; Iyer, K.S. Therapeutic and safety considerations of nanoparticle-mediated drug delivery in pregnancy. Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 2229–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tüzel-Kox, S.N.; Patel, H.M.; Kox, W.J. Uptake of drug-carrier liposomes by placenta: Transplacental delivery of drugs and nutrients. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1995, 274, 104–109. [Google Scholar]
- Rennert, O.M.M. Drug-induced somatic alterations. Clin. Obstet. Gynecol. 1975, 18, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzago, M.M.; Bortolotti, A.; Stellari, F.F.; Diomede, L.; Algeri, M.; Efrati, S.; Salmona, M.; Bonati, M. Placental transfer of valproic acid after liposome encapsulation during in vitro human placenta perfusion. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1996, 277, 79–86. [Google Scholar]
- Refuerzo, J.S.; Alexander, J.F.; Leonard, F.; Leon, M.; Longo, M.; Godin, B. Liposomes: A nanoscale drug carrying system to prevent indomethacin passage to the fetus in a pregnant mouse model. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 212, 508.e501–508.e507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajoria, R.; Sooranna, S.; Chatterjee, R. Effect of lipid composition of cationic SUV liposomes on materno-fetal transfer of warfarin across the perfused human term placenta. Placenta 2013, 34, 1216–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippone, E.; Kraft, W.; Farber, J. The Nephrotoxicity of Vancomycin. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 102, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mergenhagen, K.A.; Borton, A.R. Vancomycin Nephrotoxicity: A Review. J. Pharm. Pract. 2014, 27, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elyasi, S.; Khalili, H.; Dashti-Khavidaki, S.; Mohammadpour, A. Vancomycin-induced nephrotoxicity: Mechanism, incidence, risk factors and special populations. A literature review. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 68, 1243–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, M.D.; Pais, G.M.; Chang, J.; Hlukhenka, K.; Avedissian, S.N.; Gulati, A.; Prozialeck, W.C.; Lamar, P.C.; Zhang, Z.; Scheetz, M.H.; et al. Evaluation of Fetal and Maternal Vancomycin-Induced Kidney Injury during Pregnancy in a Rat Model. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e00761-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourget, P.; Fernandez, H.; Delouis, C.; Ribou, F. Transplacental passage of vancomycin during the second trimester of pregnancy. Obstet. Gynecol. 1991, 78, 908–911. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reyes, M.P.; Ostrea, E.M., Jr.; Cabinian, A.E.; Schmitt, C.; Rintelmann, W. Vancomycin during pregnancy: Does it cause hearing loss or nephrotoxicity in the infant? Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1989, 161, 977–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laiprasert, J.; Klein, K.; Mueller, B.A.; Pearlman, M.D. Transplacental passage of vancomycin in noninfected term pregnant women. Obstet. Gynecol. 2007, 109, 1105–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, R.A.; Gries, C.L.; Buening, M.K. Developmental Toxicology Studies of Vancomycin Hydrochloride Administered Intravenously to Rats and Rabbits1. Toxicol. Sci. 1994, 23, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcanti, I.M.; Pontes-Neto, J.G.; Kocerginsky, P.O.; Bezerra-Neto, A.M.; Lima, J.L.; Lira-Nogueira, M.C.; Maciel, M.A.; Neves, R.P.; Pimentel, M.F.; Santos-Magalhães, N.S. Antimicrobial activity of β-lapachone encapsulated into liposomes against meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Cryptococcus neoformans clinical strains. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2015, 3, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pumerantz, A.; Muppidi, K.; Agnihotri, S.; Guerra, C.; Venketaraman, V.; Wang, J.; Betageri, G. Preparation of liposomal vancomycin and intracellular killing of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2011, 37, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, J.; Gao, J.; Chen, S.; Huang, G. Chitosan coated vancomycin hydrochloride liposomes: Characterizations and evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 495, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, F.; Gao, J.; Wang, L.; Huang, G. Liposomes for systematic delivery of vancomycin hydrochloride to decrease nephrotoxicity: Characterization and evaluation. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 10, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, W.; Hair, D.; Xu, J.; Wu, C.; Han, C.C. Light scattering studies of stereocomplex formation of stereoregular poly(methyl methacrylate) in solutions. Eur. Polym. J. 2005, 41, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, M.D.; O’Donnell, J.N.; Venkatesan, N.; Chang, J.; Nguyen, H.; Rhodes, N.J.; Pais, G.; Chapman, R.L.; Griffin, B.; Scheetz, M.H. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Method for Rich Pharmacokinetic Sampling Schemes in Translational Rat Toxicity Models with Vancomycin. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2017, 10, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eloy, J.O.; Claro de Souza, M.; Petrilli, R.; Barcellos, J.P.; Lee, R.J.; Marchetti, J.M. Liposomes as carriers of hydrophilic small molecule drugs: Strategies to enhance encapsulation and delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 123, 345–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cullis, R.P.; Hope, M.J.; Bally, M.B.; Madden, T.D.; Janoff, A.S. Preparation and Optimization of Liposomes. In Liposomes from Biophysics to Therapeutics; Ostro, M.J., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1987; p. 39. [Google Scholar]
- Akbarzadeh, A.; Rezaei-Sadabady, R.; Davaran, S.; Joo, S.W.; Zarghami, N.; Hanifehpour, Y.; Samiei, M.; Kouhi, M.; Nejati-Koshki, K. Liposome: Classification, preparation, and applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- FDA Access Data on VANCOMYCIN Injection, for Intravenous Use. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2019/211962s000lbl.pdf (accessed on 19 April 2022).



| Type of Liposomes | Percentage Loading | Percentage Encapsulation |
|---|---|---|
| Non-PEGylated liposomes prepared by thin-film hydration followed by freeze–thaw | 29 ± 2.44 | 15.5 ± 0.9 |
| Non-PEGylated liposomes prepared by reverse-phase evaporation | 32 ± 1.76 | 28.5 ± 1 |
| PEGylated liposomes prepared by thin-film hydration followed by freeze–thaw | 40 ± 2.98 | 62 ± 0.8 |
| PEGylated liposomes prepared by reverse-phase evaporation | 24 ± 2.86 | 16.9 ± 0.92 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Papp, N.; Panicker, J.; Rubino, J.; Pais, G.; Czechowicz, A.; Prozialeck, W.C.; Griffin, B.; Weissig, V.; Scheetz, M.; Joshi, M.D. In Vitro Nephrotoxicity and Permeation of Vancomycin Hydrochloride Loaded Liposomes. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14061153
Papp N, Panicker J, Rubino J, Pais G, Czechowicz A, Prozialeck WC, Griffin B, Weissig V, Scheetz M, Joshi MD. In Vitro Nephrotoxicity and Permeation of Vancomycin Hydrochloride Loaded Liposomes. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(6):1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14061153
Chicago/Turabian StylePapp, Nicole, Jeffin Panicker, John Rubino, Gwendolyn Pais, Alexander Czechowicz, Walter C. Prozialeck, Brooke Griffin, Volkmar Weissig, Marc Scheetz, and Medha D. Joshi. 2022. "In Vitro Nephrotoxicity and Permeation of Vancomycin Hydrochloride Loaded Liposomes" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 6: 1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14061153
APA StylePapp, N., Panicker, J., Rubino, J., Pais, G., Czechowicz, A., Prozialeck, W. C., Griffin, B., Weissig, V., Scheetz, M., & Joshi, M. D. (2022). In Vitro Nephrotoxicity and Permeation of Vancomycin Hydrochloride Loaded Liposomes. Pharmaceutics, 14(6), 1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14061153






