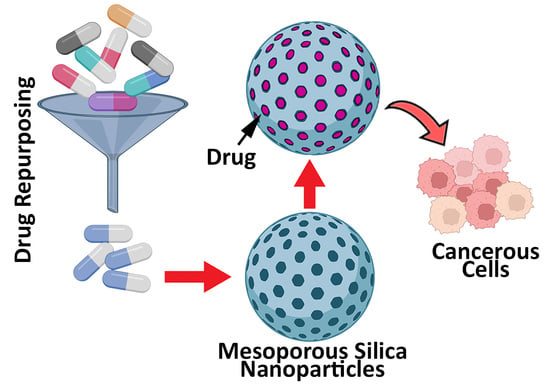
Application of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles in Cancer Therapy and Delivery of Repurposed Anthelmintics for Cancer Therapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Biomedical Applications of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles
2.1. Cancer/Tumor Therapy
2.1.1. MSNs for Photodynamic (PDT) and Sonodynamic (SDT) Therapies
2.1.2. MSNs for Chemotherapy
2.1.3. MSN Application in Radiotherapy
2.1.4. MSN Application in Immunotherapy
2.1.5. MSN Application in Gene Therapy
3. Anthelmintics for Drug Repurposing
3.1. Applications of MSNs for the Delivery of Anthelmintic Drugs for Cancer Therapy
3.1.1. Albendazole
3.1.2. Thiabendazole
3.1.3. Fenbendazole
3.1.4. Niclosamide
3.1.5. Avermectins
Ivermectin
Abamectin (Avermectin B1)
4. Toxicity of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles
4.1. Toxicity to the Respiratory System
4.2. Toxicity to the Nervous System
4.2.1. Brain
4.2.2. Eye
4.3. Toxicity to the Digestive System
4.3.1. Liver
4.3.2. Gastrointestinal Tract
4.4. Toxicity to the Circulatory System
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alavi, S.E.; Muflih Al Harthi, S.; Ebrahimi Shahmabadi, H.; Akbarzadeh, A. Cisplatin-loaded polybutylcyanoacrylate nanoparticles with improved properties as an anticancer agent. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alavi, S.E.; Shahmabadi, H.E. GLP-1 peptide analogs for targeting pancreatic beta cells. Drug Discov. Today 2021, 26, 1936–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Movahedi, F.; Ebrahimi Shahmabadi, H.; Alavi, S.E.; Koohi Moftakhari Esfahani, M. Release modeling and comparison of nanoarchaeosomal, nanoliposomal and pegylated nanoliposomal carriers for paclitaxel. Tumor Biol. 2014, 35, 8665–8672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koohi Moftakhari Esfahani, M.; Alavi, S.E.; Movahedi, F.; Alavi, F.; Akbarzadeh, A. Cytotoxicity of liposomal Paclitaxel in breast cancer cell line mcf-7. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2013, 28, 358–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darge, H.F.; Hanurry, E.Y.; Birhan, Y.S.; Mekonnen, T.W.; Andrgie, A.T.; Chou, H.-Y.; Lai, J.-Y.; Tsai, H.-C. Multifunctional drug-loaded micelles encapsulated in thermo-sensitive hydrogel for in vivo local cancer treatment: Synergistic effects of anti-vascular and immuno-chemotherapy. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 406, 126879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi Shahmabadi, H.; Movahedi, F.; Koohi Moftakhari Esfahani, M.; Alavi, S.E.; Eslamifar, A.; Mohammadi Anaraki, G.; Akbarzadeh, A. Efficacy of Cisplatin-loaded polybutyl cyanoacrylate nanoparticles on the glioblastoma. Tumor Biol. 2014, 35, 4799–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaferi, M.; Koohi Moftakhari Esfahani, M.; Raza, A.; Al Harthi, S.; Ebrahimi Shahmabadi, H.; Alavi, S.E. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles: Synthesis methods and their therapeutic use-recent advances. J. Drug Target. 2021, 29, 131–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahikkala, A.; Pereira, S.A.; Figueiredo, P.; Passos, M.L.; Araujo, A.R.; Saraiva, M.L.M.; Santos, H.A. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted and stimuli-responsive delivery of chemotherapeutics: A review. Adv. Biosyst. 2018, 2, 1800020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koohi Moftakhari Esfahani, M.; Alavi, S.E.; Shahbazian, S.; Ebrahimi Shahmabadi, H. Drug delivery of cisplatin to breast cancer by polybutylcyanoacrylate nanoparticles. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2018, 37, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seljak, K.B.; Kocbek, P.; Gašperlin, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as delivery carriers: An overview of drug loading techniques. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 59, 101906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Li, K.; Wang, J.; Zhou, S. Selective hydrogenation of phenol to cyclohexanone over Pd nanoparticles encaged hollow mesoporous silica catalytic nanoreactors. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2021, 610, 117961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regí, M. Our contributions to applications of mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Acta Biomaterialia 2022, 137, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Li, T.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Z. Fluorescent carbon dots embedded in mesoporous silica nanospheres: A simple platform for Cr(VI) detection in environmental water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.-F.; Zou, R.; Chen, G.-F.; Liu, B.-M.; Zhang, Y.; Jiao, J.; Wong, K.-L.; Wang, J. Large-Pore Mesoporous-Silica-Assisted synthesis of high-performance ZnGa2O4:Cr3+/Sn4+@MSNs multifunctional nanoplatform with optimized optical probe mass ratio and superior residual pore volume for improved bioimaging and drug delivery. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 130021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regi, M.; Rámila, A.; Del Real, R.; Pérez-Pariente, J. A new property of MCM-41: Drug delivery system. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Li, L.; Chen, D. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles: Synthesis, biocompatibility and drug delivery. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1504–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, R.; Aiyer, S.; Chauhan, D.S.; Srivastava, R.; Selvaraj, K. Bioresponsive carbon nano-gated multifunctional mesoporous silica for cancer theranostics. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 4537–4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempen, P.J.; Greasley, S.; Parker, K.A.; Campbell, J.L.; Chang, H.-Y.; Jones, J.R.; Sinclair, R.; Gambhir, S.S.; Jokerst, J.V. Theranostic mesoporous silica nanoparticles biodegrade after pro-survival drug delivery and ultrasound/magnetic resonance imaging of stem cells. Theranostics 2015, 5, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kresge, A.C.; Leonowicz, M.; Roth, W.J.; Vartuli, J.; Beck, J. Ordered mesoporous molecular sieves synthesized by a liquid-crystal template mechanism. Nature 1992, 359, 710–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slowing, I.I.; Trewyn, B.G.; Lin, V.S.-Y. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for intracellular delivery of membrane-impermeable proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 8845–8849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhou, B.; Du, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ai, Y.; Xia, Z.; Zhao, G. Folic acid (FA)-conjugated mesoporous silica nanoparticles combined with MRP-1 siRNA improves the suppressive effects of myricetin on non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 125, 109561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slowing, I.I.; Vivero-Escoto, J.L.; Wu, C.-W.; Lin, V.S.-Y. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as controlled release drug delivery and gene transfection carriers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1278–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenholm, J.M.; Sahlgren, C.; Lindén, M. Towards multifunctional, targeted drug delivery systems using mesoporous silica nanoparticles–opportunities & challenges. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 1870–1883. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Tambe, P.; Paknikar, K.M.; Gajbhiye, V. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as cutting-edge theranostics: Advancement from merely a carrier to tailor-made smart delivery platform. J. Control. Release 2018, 287, 35–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paris, J.L.; Colilla, M.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Tuning mesoporous silica dissolution in physiological environments: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 8761–8771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1902634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastegari, E.; Hsiao, Y.-J.; Lai, W.-Y.; Lai, Y.-H.; Yang, T.-C.; Chen, S.-J.; Huang, P.-I.; Chiou, S.-H.; Mou, C.-Y.; Chien, Y. An update on mesoporous silica nanoparticle applications in nanomedicine. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Tang, K.; Hou, Y.; Yu, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y. Ultralow-intensity near infrared light synchronously activated collaborative chemo/photothermal/photodynamic therapy. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abaza, S.F.; Elbialy, N.S.; Mohamed, N. Incorporating silver nanoshell-coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles improves physicochemical and antimicrobial properties of chitosan films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 189, 792–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, M.J.; Lee, S.-W. Antibacterial toxicity of mesoporous silica nanoparticles with functional decoration of specific organic moieties. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 630, 127612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, A.; Kamato, D.; Sime, F.; Roberts, J.; Popat, A.; Falconer, J.; Kumeria, T. Influence of PEGylated porous silicon nanoparticles on permeation and efflux of an orally administered antibiotic. Mater. Today Adv. 2022, 13, 100210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, X.; Yang, B.; Li, J.; Xu, L.; Liu, H.; Li, S.; Xu, J.; Yang, M.; Wei, M. Evaluation of biomimetically synthesized mesoporous silica nanoparticles as drug carriers: Structure, wettability, degradation, biocompatibility and brain distribution. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 94, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Lian, D.; Ma, H.; Gao, N.; Zhao, L.; Luan, P.; Zeng, X. New advances in gated materials of mesoporous silica for drug controlled release. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 3696–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Wang, H.; Zhang, M.; Cheng, W.; Li, Z.; Nie, J.; Liu, G.; Lian, D.; Xie, Z.; Huang, L. Self-controlled release of Oxaliplatin prodrug from d-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (TPGS) functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles for cancer therapy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 525, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Liu, G.; Tao, W.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, X.; He, F.; Pan, J.; Mei, L.; Pan, G. A drug-self-gated mesoporous antitumor nanoplatform based on pH-sensitive dynamic covalent bond. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1605985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi, S.E.; Cabot, P.J.; Yap, G.Y.; Moyle, P.M. Optimized methods for the production and bioconjugation of site-specific, alkyne-modified glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogs to azide-modified delivery platforms using copper-catalyzed alkyne–azide cycloaddition. Bioconjugate Chem. 2020, 31, 1820–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alavi, S.E.; Cabot, P.J.; Raza, A.; Moyle, P.M. Developing GLP-1 conjugated self-assembling nanofibers using copper-catalyzed alkyne–azide cycloaddition and evaluation of their biological activity. Bioconjugate Chem. 2021, 32, 810–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alavi, S.E.; Cabot, P.J.; Moyle, P.M. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and strategies to improve their efficiency. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 2278–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, Y.; Alavi, S.E.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Heidarinasab, A. Improving lithium carbonate therapeutics by pegylated liposomal technology: An in vivo study. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2016, 25, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi, S.E.; Raza, A.; Esfahani, M.K.M.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Abdollahi, S.H.; Shahmabadi, H.E. Carboplatin niosomal nanoplatform for potentiated chemotherapy. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.; Nie, J.; Gao, N.; Liu, G.; Tao, W.; Xiao, X.; Jiang, L.; Liu, Z.; Zeng, X.; Mei, L. A multifunctional nanoplatform against multidrug resistant cancer: Merging the best of targeted chemo/gene/photothermal therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1704135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wei, H.; Shan, X.; Wang, X.; Ou, M.; Liu, Q.; Gao, N.; Chen, H.; Mei, L. Charge-reversal biodegradable MSNs for tumor synergetic chemo/photothermal and visualized therapy. J. Control. Release 2021, 338, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrasa, M.; Asadollahi, M.A.; Ghaedi, K.; Salehi, H.; Arpanaei, A. Electrospun aligned PLGA and PLGA/gelatin nanofibers embedded with silica nanoparticles for tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 79, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Jin, R.; Chen, L.; Dang, M.; Cao, H.; Dong, Y.; Cai, B.; Bai, G.; Gooding, J.J. Injectable hydrogel with MSNs/microRNA-21-5p delivery enables both immunomodification and enhanced angiogenesis for myocardial infarction therapy in pigs. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabd6740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Xu, H.; Sun, S.; Guo, P.; Wang, Y.; Qian, C.; Zhong, Y.; Yang, D. Wound therapy via a photo-responsively antibacterial nano-graphene quantum dots conjugate. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2020, 210, 111978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dineshkumar, S.; Raj, A.; Srivastava, A.; Mukherjee, S.; Pasha, S.S.; Kachwal, V.; Fageria, L.; Chowdhury, R.; Laskar, I.R. Facile incorporation of “aggregation-induced emission”-active conjugated polymer into mesoporous silica hollow nanospheres: Synthesis, characterization, photophysical studies, and application in bioimaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 31270–31282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Tao, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wan, S.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, G.; Wang, J. YSA-conjugated mesoporous silica nanoparticles effectively target EphA2-overexpressing breast cancer cells. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2018, 81, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.-A.; Chen, W.; Zhang, L.; Wu, H.H.; Zink, J.I. A responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticle platform for magnetic resonance imaging-guided high-intensity focused ultrasound-stimulated cargo delivery with controllable location, time, and dose. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 17670–17684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argentati, C.; Morena, F.; Fontana, C.; Tortorella, I.; Emiliani, C.; Latterini, L.; Zampini, G.; Martino, S. Functionalized silica star-shaped nanoparticles and human mesenchymal stem cells: An in vitro model. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, M.M.; Ramya, A.N.; Vijayan, V.M.; Nair, J.B.; Bastian, B.T.; Pillai, R.K.; Therakathinal, S.T.; Maiti, K.K. Targeted Theranostic Nano Vehicle Endorsed with Self-Destruction and Immunostimulatory Features to Circumvent Drug Resistance and Wipe-Out Tumor Reinitiating Cancer Stem Cells. Small 2020, 16, 2003309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, J.K.; Tsai, C.P.; Chung, T.H.; Hung, Y.; Yao, M.; Liu, H.M.; Mou, C.Y.; Yang, C.S.; Chen, Y.C.; Huang, D.M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a delivery system of gadolinium for effective human stem cell tracking. Small 2008, 4, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Wang, J.; Yang, S.; Lu, Q.; Li, P.; Li, N. Rod-shape MSN@ MoS2 nanoplatform for FL/MSOT/CT imaging-guided photothermal and photodynamic therapy. Theranostics 2019, 9, 3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koohi Moftakhari Esfahani, M.; Alavi, S.E.; Cabot, P.J.; Islam, N.; Izake, E.L. PEGylated Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles (MCM-41): A Promising Carrier for the Targeted Delivery of Fenbendazole into Prostrate Cancer Cells. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargrove, D.; Lu, X. Neutron-Activatable Nanoparticles for Intraperitoneal Radiation Therapy. In Cancer Nanotechnology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 379–389. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, P.-H.; Wang, M.-L.; Chang, J.-H.; Yarmishyn, A.A.; Nhi Nguyen, P.N.; Chen, W.; Chien, Y.; Huo, T.-I.; Mou, C.-Y.; Chiou, S.-H. Dual delivery of HNF4α and cisplatin by mesoporous silica nanoparticles inhibits cancer pluripotency and tumorigenicity in hepatoma-derived CD133-expressing stem cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 19808–19818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, J.; Goßl, D.e.; Ustyanovska, N.; Xiong, M.; Hauser, D.; Zhuzhgova, O.; Hocevar, S.; Taskoparan, B.l.; Poller, L.; Datz, S. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as pH-responsive carrier for the immune-activating drug resiquimod enhance the local immune response in mice. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 4450–4466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiran, A.R.; Kumari, G.K.; Krishnamurthy, P.T. Carbon nanotubes in drug delivery: Focus on anticancer therapies. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 59, 101892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.R.; Ferris, D.P.; Lee, J.-H.; Choi, E.; Cho, M.H.; Kim, E.S.; Stoddart, J.F.; Shin, J.-S.; Cheon, J.; Zink, J.I. Noninvasive remote-controlled release of drug molecules in vitro using magnetic actuation of mechanized nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 10623–10625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Li, H.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, M.; Li, M.; Gong, T.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, X. pH-sensitive polymeric micelles for targeted delivery to inflamed joints. J. Control. Release 2017, 246, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Liong, M.; Zink, J.I.; Tamanoi, F. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a delivery system for hydrophobic anticancer drugs. Small 2007, 3, 1341–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Liang, S.; Long, M.; Xu, H. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as potential carriers for enhanced drug solubility of paclitaxel. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 78, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babaei, M.; Abnous, K.; Taghdisi, S.M.; Taghavi, S.; Sh Saljooghi, A.; Ramezani, M.; Alibolandi, M. Targeted rod-shaped mesoporous silica nanoparticles for the co-delivery of camptothecin and survivin shRNA in to colon adenocarcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 156, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Fu, M.; Yang, X.; Jia, G.; Shi, X.; Ji, J.; Liu, X.; Zhai, G. Paclitaxel and quercetin co-loaded functional mesoporous silica nanoparticles overcoming multidrug resistance in breast cancer. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 196, 111284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhavsar, D.B.; Patel, V.; Sawant, K.K. Design and characterization of dual responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles for breast cancer targeted therapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 152, 105428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Li, L.; Zhou, S.; Qiu, L.; Qian, Z.; Liu, X.; Cao, X.; Zhang, H. TPGS functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles for anticancer drug delivery to overcome multidrug resistance. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 84, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitran, R.A.; Berger, D.; Munteanu, C.; Matei, C. Evaluation of different mesoporous silica supports for energy storage in shape-stabilized phase change materials with dual thermal responses. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 15177–15184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sábio, R.M.; Meneguin, A.B.; Ribeiro, T.C.; Silva, R.R.; Chorilli, M. New insights towards mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a technological platform for chemotherapeutic drugs delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 564, 379–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolmans, D.E.; Fukumura, D.; Jain, R.K. Photodynamic therapy for cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konan, Y.N.; Gurny, R.; Allémann, E. State of the art in the delivery of photosensitizers for photodynamic therapy. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2002, 66, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucky, S.S.; Soo, K.C.; Zhang, Y. Nanoparticles in photodynamic therapy. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 1990–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y. Mesoporous silica-based nanoplatforms for the delivery of photodynamic therapy agents. J. Pharm. Investig. 2018, 48, 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, J.; Ma, Z.; Wang, D.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Le, L.; Kang, A.; Hu, P.; She, L.; Yang, F. Magnetic and pH dual-responsive mesoporous silica nanocomposites for effective and low-toxic photodynamic therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, G.; Zhang, Q.; He, S.; Liu, Y. Curcumin-loaded PEGylated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for effective photodynamic therapy. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 24624–24630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Qian, X.; Chen, Y.; Yu, L.; Lin, H.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, J. Metalloporphyrin-encapsulated biodegradable nanosystems for highly efficient magnetic resonance imaging-guided sonodynamic cancer therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, Y. Micro/nanoparticle-augmented sonodynamic therapy (SDT): Breaking the depth shallow of photoactivation. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 8097–8129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Han, J.; Yu, L.; Qian, X.; Xing, H.; Lin, H.; Wu, M.; Yang, T.; Chen, Y. Synergistic sonodynamic/chemotherapeutic suppression of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeted biodegradable mesoporous nanosonosensitizers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1800145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Yao, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, M.; Zhou, L.; Zhong, G.; Zheng, Y.; Li, N.; Zhai, Z.; Yang, S. Therapeutic effect of doxorubicin-chlorin E6-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles combined with ultrasound on triple-negative breast cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, Y.-J.; Wu, C.-H.; Jin, Q.-f.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chiang, P.-H.; Wu, N.; Fan, C.-H.; Yang, C.-M.; Yeh, C.-K. Superhydrophobic drug-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles capped with β-cyclodextrin for ultrasound image-guided combined antivascular and chemo-sonodynamic therapy. Biomaterials 2020, 232, 119723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepagan, V.; You, D.G.; Um, W.; Ko, H.; Kwon, S.; Choi, K.Y.; Yi, G.-R.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, D.S.; Kim, K. Long-circulating Au-TiO2 nanocomposite as a sonosensitizer for ROS-mediated eradication of cancer. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 6257–6264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulrazzak, F.H.; Hussein, F.H.; Alkaim, A.F.; Ivanova, I.; Emeline, A.V.; Bahnemannd, D.W. Sonochemical/hydration—Dehydration synthesis of Pt—TiO2 NPs/decorated carbon nanotubes with enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen production activity. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2016, 15, 1347–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, N.; Cui, H.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Song, X.; Ding, L.; Tian, J. Highly efficient photocatalytic activity of Ag3PO4/Ag/ZnS (en) 0.5 photocatalysts through Z-scheme photocatalytic mechanism. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 18392–18399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, J.H.; You, D.G.; Kim, S.; Um, W.; Jeon, J.; Kim, C.H.; Joo, H.; Yi, G.R.; Park, J.H. Cavitation-Inducible Mesoporous Silica–Titania Nanoparticles for Cancer Sonotheranostics. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2020, 9, 2000877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Tao, L.; Li, H.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, S.; Xue, J.; Zhang, X. Hollow mesoporous carbon modified with cRGD peptide nanoplatform for targeted drug delivery and chemo-photothermal therapy of prostatic carcinoma. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 570, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Shi, L.; Long, R.; Ren, G.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y. A carboxymethyl lentinan layer by layer self-assembly system as a promising drug chemotherapeutic platform. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 261, 117847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Meng, S.; Li, H.; Yang, Q.; Xu, Z.; Chen, X.; Sun, Z.; Jiang, B.; Li, C. Nanoplatform based on GSH-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles for cancer therapy and mitochondrial targeted imaging. Microchim. Acta 2021, 188, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, T.; Li, J.; Xu, N.; Cai, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, S. Au Catalyzing Control Release NO in vivo and Tumor Growth-Inhibiting Effect in Chemo-Photothermal Combination Therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, L.; Shi, L.; Yuan, Y.; Fu, D.; Ye, Z.; Li, Q.; Deng, Y.; Liu, X.; Lv, Q. A sequentially responsive nanosystem breaches cascaded bio-barriers and suppresses P-glycoprotein function for reversing cancer drug resistance. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 54343–54355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; He, X.; Shi, K.; Yuan, L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Ming, Y.; Yi, C.; Qian, Z. Injectable Thermosensitive Hydrogel Containing Erlotinib-Loaded Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as a Localized Drug Delivery System for NSCLC Therapy. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2001442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Lin, J.; Li, C.; Huang, P.; Hou, W.; Zhang, C.; Liu, J.; Huang, S.; Luo, Y.; Fan, W. Dual-stimuli responsive nanotheranostics for multimodal imaging guided trimodal synergistic therapy. Small 2017, 13, 1602580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.X.; Zhang, D.; Hu, X.; Peng, R.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Tan, W. Multicolor Two-photon Nanosystem for Multiplexed Intracellular Imaging and Targeted Cancer Therapy. Angew. Chem. 2021, 133, 12677–12684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickens, E.; Ahmed, S. Principles of cancer treatment by chemotherapy. Surgery (Oxford) 2018, 36, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, P.D.; Verma, S.; Robertson, A.P.; Martin, R.J. Adapting techniques for calcium imaging in muscles of adult Brugia malayi. Invertebr. Neurosci. 2020, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laudisi, F.; Marônek, M.; Di Grazia, A.; Monteleone, G.; Stolfi, C. Repositioning of anthelmintic drugs for the treatment of cancers of the digestive system. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alavi, S.E.; Ebrahimi Shahmabadi, H. Anthelmintics for drug repurposing: Opportunities and challenges. Saudi Pharm. J. 2021, 29, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, G.; Wang, S.; He, Y.; Han, S.; Du, C.; Li, S.; Fan, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, J. Platelet-membrane-camouflaged bismuth sulfide nanorods for synergistic radio-photothermal therapy against cancer. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 3450–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Shao, Y.; Chang, C.; Zhu, Y. Efficient active oxygen free radical generated in tumor cell by loading-(HCONH2)·H2O2 delivery nanosystem with soft-X-ray radiotherapy. Materials 2018, 11, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallares, R.M.; Agbo, P.; Liu, X.; An, D.D.; Gauny, S.S.; Zeltmann, S.E.; Minor, A.M.; Abergel, R.J. Engineering mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted alpha therapy against breast cancer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 40078–40084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mingos, D.M.P. The discovery of the elements in the periodic table. Period. Table I 2019, 181, 1–57. [Google Scholar]
- Paden, M.H.L. Development of a Simplified Soft-Donor Technique for Trivalent Actinide-Lanthanide Separations; The University of Manchester (United Kingdom): Manchester, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.D.; Nguyen, H.T.; Chen, H.; Cox, P.B.; Wang, L.; Nagata, K.; Hao, Z.; Wang, A.; Li, Z.; Xie, J. X-ray induced photodynamic therapy: A combination of radiotherapy and photodynamic therapy. Theranostics 2016, 6, 2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Wang, X.; Jiang, Z.; Yu, X.; Liu, X.; Mao, R.; Chen, X.; Li, W. Codoping enhanced radioluminescence of nanoscintillators for X-ray-activated synergistic cancer therapy and prognosis using metabolomics. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 10419–10433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, D.; Cha, B.G.; Cho, Y.; Min, J.; Park, E.-B.; Kang, S.-J.; Kim, J. Extra-large pore mesoporous silica nanoparticles for directing in vivo M2 macrophage polarization by delivering IL-4. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 2747–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, B.G.; Jeong, J.H.; Kim, J. Extra-large pore mesoporous silica nanoparticles enabling co-delivery of high amounts of protein antigen and toll-like receptor 9 agonist for enhanced cancer vaccine efficacy. ACS Cent. Sci. 2018, 4, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.Y.; Kim, M.K.; Nguyen, T.L.; Kim, J. Hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles with extra-large mesopores for enhanced cancer vaccine. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 34658–34666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Nam, J.; Hong, H.; Xu, Y.; Moon, J.J. Positron emission tomography-guided photodynamic therapy with biodegradable mesoporous silica nanoparticles for personalized cancer immunotherapy. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 12148–12161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noureddine, A.; Maestas-Olguin, A.; Saada, E.A.; LaBauve, A.E.; Agola, J.O.; Baty, K.E.; Howard, T.; Sabo, J.K.; Espinoza, C.R.S.; Doudna, J.A. Engineering of monosized lipid-coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for CRISPR delivery. Acta Biomater. 2020, 114, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, D.; Lu, M.-M.; Zhao, Y.-W.; Zhang, F.; Tan, Y.-F.; Zheng, X.; Pan, Y.; Xiao, X.-A.; Wang, Z.; Dong, W.-F. The shape effect of magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles on endocytosis, biocompatibility and biodistribution. Acta Biomater. 2017, 49, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, M.; Chen, Y.; Tu, J.; Liufu, C.; Yu, J.; Yuan, Z.; Gong, X.; Chen, Z. Ultrasound responsive magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticle-loaded microbubbles for efficient gene delivery. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 2904–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Lemus, E.; Martínez-García, M. Pathway-based drug-repurposing schemes in cancer: The role of translational bioinformatics. Front. Oncol. 2021, 10, 605680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armando, R.G.; Mengual Gómez, D.L.; Gomez, D.E. New drugs are not enough-drug repositioning in oncology: An update. Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 56, 651–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashburn, T.T.; Thor, K.B. Drug repositioning: Identifying and developing new uses for existing drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Fierro, A.; Dueñas-González, A. Drug repurposing for cancer therapy, easier said than done. In Seminars in Cancer Biology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 123–131. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Z.-J.; Luo, X.; Zhang, W.; Peng, F.; Cui, B.; Wu, S.-J.; Zheng, F.-M.; Xu, J.; Xu, L.-Z.; Long, Z.-J. Flubendazole, FDA-approved anthelmintic, targets breast cancer stem-like cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 6326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerini, A.E.; Triggiani, L.; Maddalo, M.; Bonù, M.L.; Frassine, F.; Baiguini, A.; Alghisi, A.; Tomasini, D.; Borghetti, P.; Pasinetti, N. Mebendazole as a candidate for drug repurposing in oncology: An extensive review of current literature. Cancers 2019, 11, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, E.J.; Löbenberg, R.; de Araujo, G.L.B.; Bou-Chacra, N.A. Niclosamide repositioning for treating cancer: Challenges and nano-based drug delivery opportunities. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2019, 141, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, D.-S.; Lee, E.-S.; Adunyah, S.E. The antitumor potentials of benzimidazole anthelmintics as repurposing drugs. Immune Netw. 2020, 20, e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakran, M.; Li, L.; Müller, R.H. Overcoming the challenge of poor drug solubility. Pharm. Eng. 2012, 32, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, H.; Urata, C.; Aoyama, Y.; Osada, S.; Yamauchi, Y.; Kuroda, K. Preparation of colloidal mesoporous silica nanoparticles with different diameters and their unique degradation behavior in static aqueous systems. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 1462–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, I.R.; Ferris, D.P.; Frasconi, M.; Malin, D.; Strekalova, E.; Yilmaz, M.D.; Ambrogio, M.W.; Algaradah, M.M.; Hong, M.P.; Chen, X. Esterase-and pH-responsive poly (β-amino ester)-capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 7178–7183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, C.; Mastrotto, F.; Taresco, V.; Tchoryk, A.; Quaglia, F.; Stolnik, S.; Alexander, C. Enhanced uptake in 2D-and 3D-lung cancer cell models of redox responsive PEGylated nanoparticles with sensitivity to reducing extra-and intracellular environments. J. Control. Release 2018, 277, 126–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokbulut, C.; McKellar, Q.A. Anthelmintic drugs used in equine species. Vet. Parasitol. 2018, 261, 27–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Andrade Picanço, G.; de Lima, N.F.; Fraga, C.M.; da Costa, T.L.; Isac, E.; Ambrosio, J.; Castillo, R.; Vinaud, M.C. A benzimidazole derivative (RCB15) in vitro induces the alternative energetic metabolism and glycolysis in Taenia crassiceps cysticerci. Acta Trop. 2017, 176, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dababat, A.; Pariyar, S.; Nicol, J.; Erginbas Orakci, G.; Goll, M.; Watrin, C.; Duveiller, E.; Braun, H.; Cabrera, J.; Sikora, R. Influence of thiabendazole seed treatment on the integrated control of Heterodera filipjevi on six wheat genotypes with different levels of genetic resistance under controlled conditions. Nematropica 2014, 44, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Lekdumrongsak, T.; Tiawsirisup, S.; Banlunara, W.; Prapasawat, F.; Pussayanawin, M.; Prommatha, N.; Suttiyaporn, S. Efficacy of Fenbendazole against Ascaridia Spp. in Large Macaws. Thai J. Vet. Med. 2014, 44, 231. [Google Scholar]
- Thakare, R.; Kaul, G.; Shukla, M.; Kesharwani, P.; Srinivas, N.; Dasgupta, A.; Chopra, S. Repurposing nonantibiotic drugs as antibacterials. In Drug Discovery Targeting Drug-Resistant Bacteria; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 105–138. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, M.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Z. Antibiotic ivermectin preferentially targets renal cancer through inducing mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative damage. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 492, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Puinean, A.M.; Williamson, M.S.; Smelt, C.L.; Millar, N.S.; Wu, Y. Mutations on M3 helix of Plutella xylostella glutamate-gated chloride channel confer unequal resistance to abamectin by two different mechanisms. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 86, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaferi, M.; Zahra, W.; Akbarzadeh, A.; Shahmabadi, H.E.; Alavi, S.E. Enhancing the efficacy of albendazole for liver cancer treatment using mesoporous silica nanoparticles: An in vitro study. EXCLI J. 2022, 21, 236–249. [Google Scholar]
- Ang, C.W.; Tan, L.; Qu, Z.; West, N.P.; Cooper, M.A.; Popat, A.; Blaskovich, M.A. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles improve oral delivery of antitubercular bicyclic nitroimidazoles. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Z.-A.; Zhang, L.; Guo, M.; Liu, Y.; Huo, Q. Synthesis of mesoporous silica nanoparticles via controlled hydrolysis and condensation of silicon alkoxide. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 3823–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, R.; Nayak, U.Y.; Raichur, A.M.; Garg, S. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles: A comprehensive review on synthesis and recent advances. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barczak, M. Template removal from mesoporous silicas using different methods as a tool for adjusting their properties. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 4182–4191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cychosz, K.A.; Thommes, M. Progress in the physisorption characterization of nanoporous gas storage materials. Engineering 2018, 4, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Castillo, D.J.; de la Cruz Hernández, E.N.; Frías Márquez, D.M.; Tilley, R.D.; Gloag, L.; Owen, P.Q.; López González, R.; Alvarez Lemus, M.A. Albendazole Release from Silica-Chitosan Nanospheres. In Vitro Study on Cervix Cancer Cell Lines. Polymers 2021, 13, 1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adrover, M.E.; Pedernera, M.; Bonne, M.; Lebeau, B.; Bucalá, V.; Gallo, L. Synthesis and characterization of mesoporous SBA-15 and SBA-16 as carriers to improve albendazole dissolution rate. Saudi Pharm. J. 2020, 28, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koohi Moftakhari Esfahani, M.; Islam, N.; Cabot, P.J.; Izake, E.L. Development of Thiabendazole-Loaded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Cancer Therapy. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patsula, V.; Moskvin, M.; Dutz, S.; Horák, D. Size-dependent magnetic properties of iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2016, 88, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koohi Moftakhari Esfahani, M.; Alavi, S.E.; Cabot, P.J.; Islam, N.; Izake, E.L. β-Lactoglobulin-Modified Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: A Promising Carrier for the Targeted Delivery of Fenbendazole into Prostate Cancer Cells. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardhi, V.; Chavan, R.B.; Thipparaboina, R.; Thatikonda, S.; Naidu, V.; Shastri, N.R. Preparation, characterization, and cytotoxicity studies of niclosamide loaded mesoporous drug delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 528, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Saber Batiha, G.; Alqahtani, A.; Ilesanmi, O.B.; Saati, A.A.; El-Mleeh, A.; Hetta, H.F.; Magdy Beshbishy, A. Avermectin derivatives, pharmacokinetics, therapeutic and toxic dosages, mechanism of action, and their biological effects. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.; Wen, H.; Zhou, H.; Hao, L.; Chen, H.; Zhou, X. Coordination bonding-based polydopamine-modified mesoporous silica for sustained avermectin release. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 105, 110073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.-Z.; Xu, S.-A.; Wen, L.-X.; Liu, F.; Liu, A.-Q.; Wang, Q.; Sun, H.-Y.; Yu, W.; Chen, J.-F. Controlled release of avermectin from porous hollow silica nanoparticles: Influence of shell thickness on loading efficiency, UV-shielding property and release. J. Control. Release 2006, 111, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wang, W.; Dong, H.; Tang, R.; Yang, J.; Niu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Jiang, N.; Cao, Y. Fabrication of smart stimuli-responsive mesoporous organosilica nano-vehicles for targeted pesticide delivery. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 122075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Chen, W.; Shen, Y.; Chen, Q.; Yang, J.; Zhang, M.; Yang, W.; Yuan, S. Fabrication of abamectin-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles by emulsion-solvent evaporation to improve photolysis stability and extend insecticidal activity. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 345705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cui, H.; Sun, C.; Zhao, X.; Cui, B. Construction and evaluation of controlled-release delivery system of Abamectin using porous silica nanoparticles as carriers. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugadoss, S.; Lison, D.; Godderis, L.; Van Den Brule, S.; Mast, J.; Brassinne, F.; Sebaihi, N.; Hoet, P.H. Toxicology of silica nanoparticles: An update. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 2967–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Li, P.; Zhao, R.; Zhao, L.; Liu, J.; Peng, S.; Fu, X.; Wang, X.; Luo, R.; Wang, R. Silica nanoparticles: Biomedical applications and toxicity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 151, 113053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-R.; Lee, S.-Y.; Lee, E.J.; Park, S.H.; Seong, N.-w.; Seo, H.-S.; Shin, S.-S.; Kim, S.-J.; Meang, E.-H.; Park, M.-K. Toxicity of colloidal silica nanoparticles administered orally for 90 days in rats. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 67. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Kim, M.-S.; Lee, D.; Kwon, T.K.; Khang, D.; Yun, H.-S.; Kim, S.-H. The comparative immunotoxicity of mesoporous silica nanoparticles and colloidal silica nanoparticles in mice. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 147. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.-H.; Gu, L.; Von Maltzahn, G.; Ruoslahti, E.; Bhatia, S.N.; Sailor, M.J. Biodegradable luminescent porous silicon nanoparticles for in vivo applications. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Nie, J.; Xu, L.; Liang, C.; Peng, Y.; Liu, G.; Wang, T.; Mei, L.; Huang, L.; Zeng, X. pH-sensitive delivery vehicle based on folic acid-conjugated polydopamine-modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 18462–18473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Wu, D.; Yin, X.; Jin, X.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, S.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y. Intracellular pH-responsive and rituximab-conjugated mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery to lymphoma B cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hozayen, W.G.; Mahmoud, A.M.; Desouky, E.M.; El-Nahass, E.-S.; Soliman, H.A.; Farghali, A.A. Cardiac and pulmonary toxicity of mesoporous silica nanoparticles is associated with excessive ROS production and redox imbalance in Wistar rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 2527–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Kovochich, M.; Brant, J.; Hotze, M.; Sempf, J.; Oberley, T.; Sioutas, C.; Yeh, J.I.; Wiesner, M.R.; Nel, A.E. Comparison of the abilities of ambient and manufactured nanoparticles to induce cellular toxicity according to an oxidative stress paradigm. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 1794–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacCuaig, W.M.; Samykutty, A.; Foote, J.; Luo, W.; Filatenkov, A.; Li, M.; Houchen, C.; Grizzle, W.E.; McNally, L.R. Toxicity Assessment of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles upon Intravenous Injection in Mice: Implications for Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Xie, L.; Fang, C.-J.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.-J.; Zhen, X.-Y.; Yan, C.-H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Peng, S. Implications for blood-brain-barrier permeability, in vitro oxidative stress and neurotoxicity potential induced by mesoporous silica nanoparticles: Effects of surface modification. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 2800–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.Y.; Li, X.; Sun, M.Z.; Wang, Y.P.; Wu, M.; Zhang, C.Y.; Wang, Y.N.; Liu, B.; Zhang, Y.S.; Zhao, X. An assessment of the impact of SiO2 nanoparticles of different sizes on the rest/wake behavior and the developmental profile of zebrafish larvae. Small 2013, 9, 3161–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izak-Nau, E.; Kenesei, K.; Murali, K.; Voetz, M.; Eiden, S.; Puntes, V.F.; Duschl, A.; Madarász, E. Interaction of differently functionalized fluorescent silica nanoparticles with neural stem-and tissue-type cells. Nanotoxicology 2014, 8, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, S.; Manivasagam, G.; Kumar, P.; Ambasta, R.K. Cellular Toxicity of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle in SHSY5Y and BM-MNCs Cell. Pharm. Nanotechnol. 2018, 6, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhu, S.; Hu, X.; Sun, D.; Yang, J.; Yang, C.; Wu, W.; Li, Y.; Gu, X.; Li, M. Toxicity and mechanism of mesoporous silica nanoparticles in eyes. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 13637–13653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Jeong, H.; Hong, J.; Chang, M.; Kim, M.; Chuck, R.S.; Lee, J.K.; Park, C.-Y. The effect of silica nanoparticles on human corneal epithelial cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Luan, J.; Chen, W.; Fan, J.; Nan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Meng, G.; Ju, D. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles induced hepatotoxicity via NLRP3 inflammasome activation and caspase-1-dependent pyroptosis. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 9141–9152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Yang, M.; Cheng, M.; Fan, L.; Wang, X.; Xu, T.; Wang, B.; Chen, W. Associations between urinary phthalate metabolite concentrations and markers of liver injury in the US adult population. Environ. Int. 2021, 155, 106608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhavsar, D.; Patel, V.; Sawant, K. Systematic investigation of in vitro and in vivo safety, toxicity and degradation of mesoporous silica nanoparticles synthesized using commercial sodium silicate. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 284, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.M.; Desouky, E.M.; Hozayen, W.G.; Bin-Jumah, M.; El-Nahass, E.-S.; Soliman, H.A.; Farghali, A.A. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles trigger liver and kidney injury and fibrosis via altering TLR4/NF-κB, JAK2/STAT3 and Nrf2/HO-1 signaling in rats. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, N.; Guo, C.; Dai, X.; Wang, C.; Gong, L.; Yu, L.; Peng, C.; Li, Y. Forsythiae Fructuse water extract attenuates liver fibrosis via TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB and TGF-β/smads signaling pathways. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 262, 113275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehrke, H.; Frühmesser, A.; Pelka, J.; Esselen, M.; Hecht, L.L.; Blank, H.; Schuchmann, H.P.; Gerthsen, D.; Marquardt, C.; Diabaté, S. In vitro toxicity of amorphous silica nanoparticles in human colon carcinoma cells. Nanotoxicology 2012, 7, 274–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.-D.; Zhang, X.-D.; Yang, X.-S.; Huang, Z.-L.; Wei, X.; Yang, X.-F.; Liao, W.-Z. Subacute toxicity of mesoporous silica nanoparticles to the intestinal tract and the underlying mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 409, 124502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabellos, J.; Gimeno-Benito, I.; Catalán, J.; Lindberg, H.K.; Vales, G.; Fernandez-Rosas, E.; Ghemis, R.; Jensen, K.A.; Atluri, R.; Vázquez-Campos, S. Short-term oral administration of non-porous and mesoporous silica did not induce local or systemic toxicity in mice. Nanotoxicology 2020, 14, 1324–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, R.; Jin, J.; Zhu, Y.Z. Short-term oral administration of mesoporous silica nanoparticles potentially induced colon inflammation in rats through alteration of gut microbiota. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lin, Y.-S.; Haynes, C.L. On-chip evaluation of shear stress effect on cytotoxicity of mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Analytical chemistry 2011, 83, 8377–8382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlando, A.; Cazzaniga, E.; Tringali, M.; Gullo, F.; Becchetti, A.; Minniti, S.; Taraballi, F.; Tasciotti, E.; Re, F. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles trigger mitophagy in endothelial cells and perturb neuronal network activity in a size-and time-dependent manner. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salve, R.; Kumar, P.; Ngamcherdtrakul, W.; Gajbhiye, V.; Yantasee, W. Stimuli-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles: A custom-tailored next generation approach in cargo delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 124, 112084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benezra, M.; Penate-Medina, O.; Zanzonico, P.B.; Schaer, D.; Ow, H.; Burns, A.; DeStanchina, E.; Longo, V.; Herz, E.; Iyer, S.; et al. Multimodal silica nanoparticles are effective cancer-targeted probes in a model of human melanoma. J. Clin. Invest. 2011, 121, 2768–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharlamov, A. Plasmonic Photothermal Therapy of Atherosclerosis and Preparation of Target Lesion in Patients with Arterial Remodeling: Subanalysis of Nanom-Fim Trial. Atherosclerosis 2019, 287, e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharlamov, A.N.; Tyurnina, A.E.; Veselova, V.S.; Kovtun, O.P.; Shur, V.Y.; Gabinsky, J.L. Silica–gold nanoparticles for atheroprotective management of plaques: Results of the NANOM-FIM trial. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 8003–8015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharlamov, A.N.; Feinstein, J.A.; Cramer, J.A.; Boothroyd, J.A.; Shishkina, E.V.; Shur, V. Plasmonic photothermal therapy of atherosclerosis with nanoparticles: Long-term outcomes and safety in NANOM-FIM trial. Future Cardiol. 2017, 13, 345–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Name | Chemical Structure | Class | Mode of Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Albendazole |  | Benzimidazoles | Impairment of the polymerization of β-tubulin and α-tubulin [122]. |
| Thiabendazole |  | Benzimidazoles | Most likely influencing the helminth-specific mitochondrial enzyme fumarate reductase and by which inhibiting the citric acid cycle and mitochondrial respiration, resulting in helminth’s death [123]. |
| Fenbendazole |  | Benzimidazoles | Binding to nematode β-tubulin and preventing microtubule formation [124]. |
| Niclosamide |  | Salicylanilides | Inhibiting the glucose uptake; therefore, uncoupling energy-generating oxidative phosphorylation in intestinal worms; thus, making the worms hungry for ATP [125]. |
| Ivermectin |  | Macrocyclic lactones | Binding and activating chloride ion channels in nematodes [126]. |
| Abamectin |  | Macrocyclic lactones | Activating glutamate-gated chloride channels and modulating other Cys-loop ion channels [127]. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koohi Moftakhari Esfahani, M.; Alavi, S.E.; Cabot, P.J.; Islam, N.; Izake, E.L. Application of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles in Cancer Therapy and Delivery of Repurposed Anthelmintics for Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14081579
Koohi Moftakhari Esfahani M, Alavi SE, Cabot PJ, Islam N, Izake EL. Application of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles in Cancer Therapy and Delivery of Repurposed Anthelmintics for Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(8):1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14081579
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoohi Moftakhari Esfahani, Maedeh, Seyed Ebrahim Alavi, Peter J. Cabot, Nazrul Islam, and Emad L. Izake. 2022. "Application of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles in Cancer Therapy and Delivery of Repurposed Anthelmintics for Cancer Therapy" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 8: 1579. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14081579