Vitamin E TPGS-Poloxamer Nanoparticles Entrapping a Novel PI3Kα Inhibitor Potentiate Its Activity against Breast Cancer Cell Lines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of R19-Loaded NPs
2.3. Particle Size and Zeta Potential Measurements
2.4. Drug Loading Efficiency Determination
2.5. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Imaging
2.6. Characterization by Fourier Transform-Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
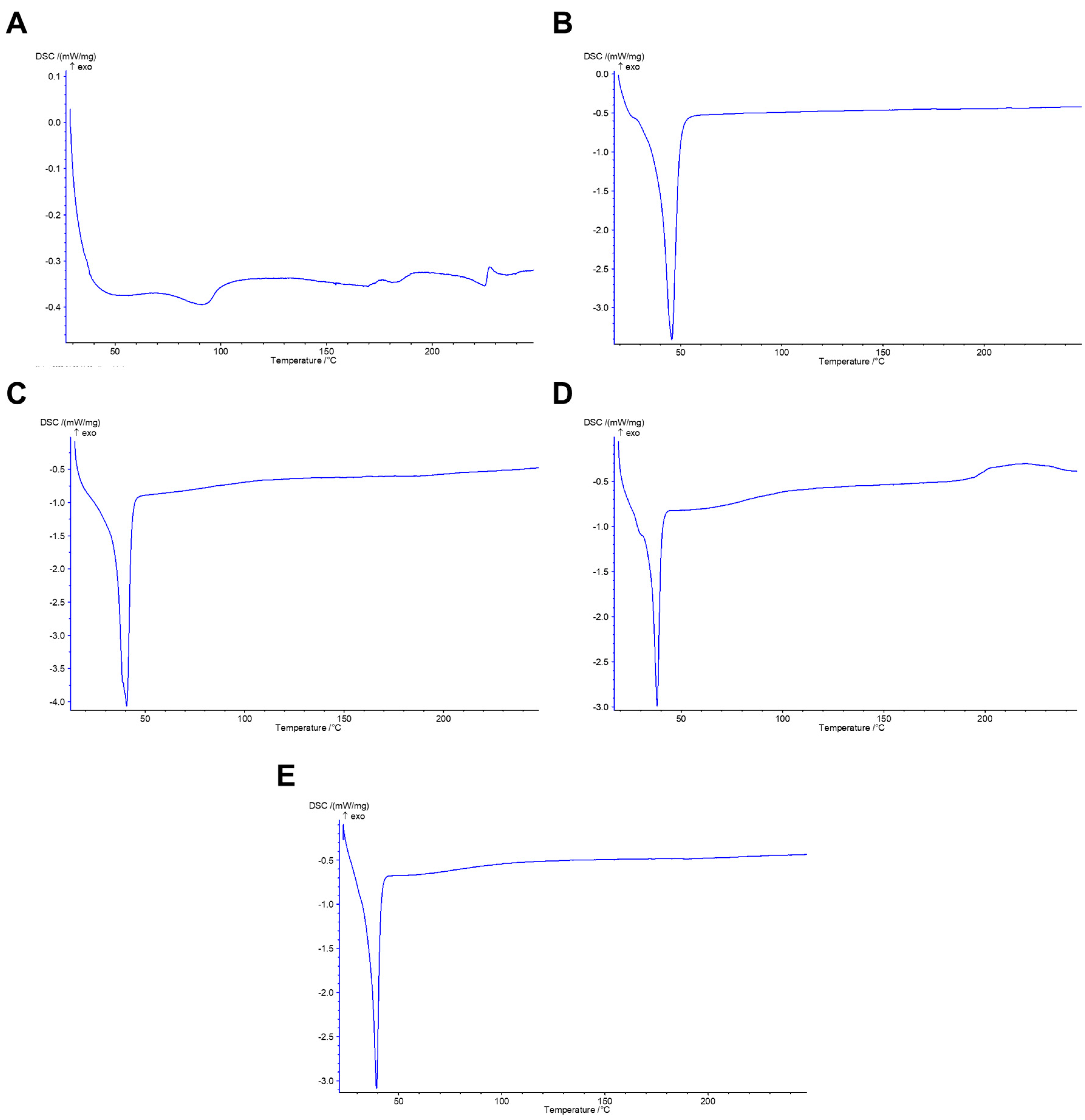
2.7. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.8. Colloidal Stability of R19-Loaded NPs
2.9. In Vitro Release of R19 from R19-Loaded NPs
2.10. Cell Viability Assays
2.11. Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Assay
2.12. Cellular Uptake of NR-Labeled NPs
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of R19-Loaded NPs
3.2. Stability of R19-Loaded NPs
3.3. In Vitro Release of R19 from R19-Loaded NPs
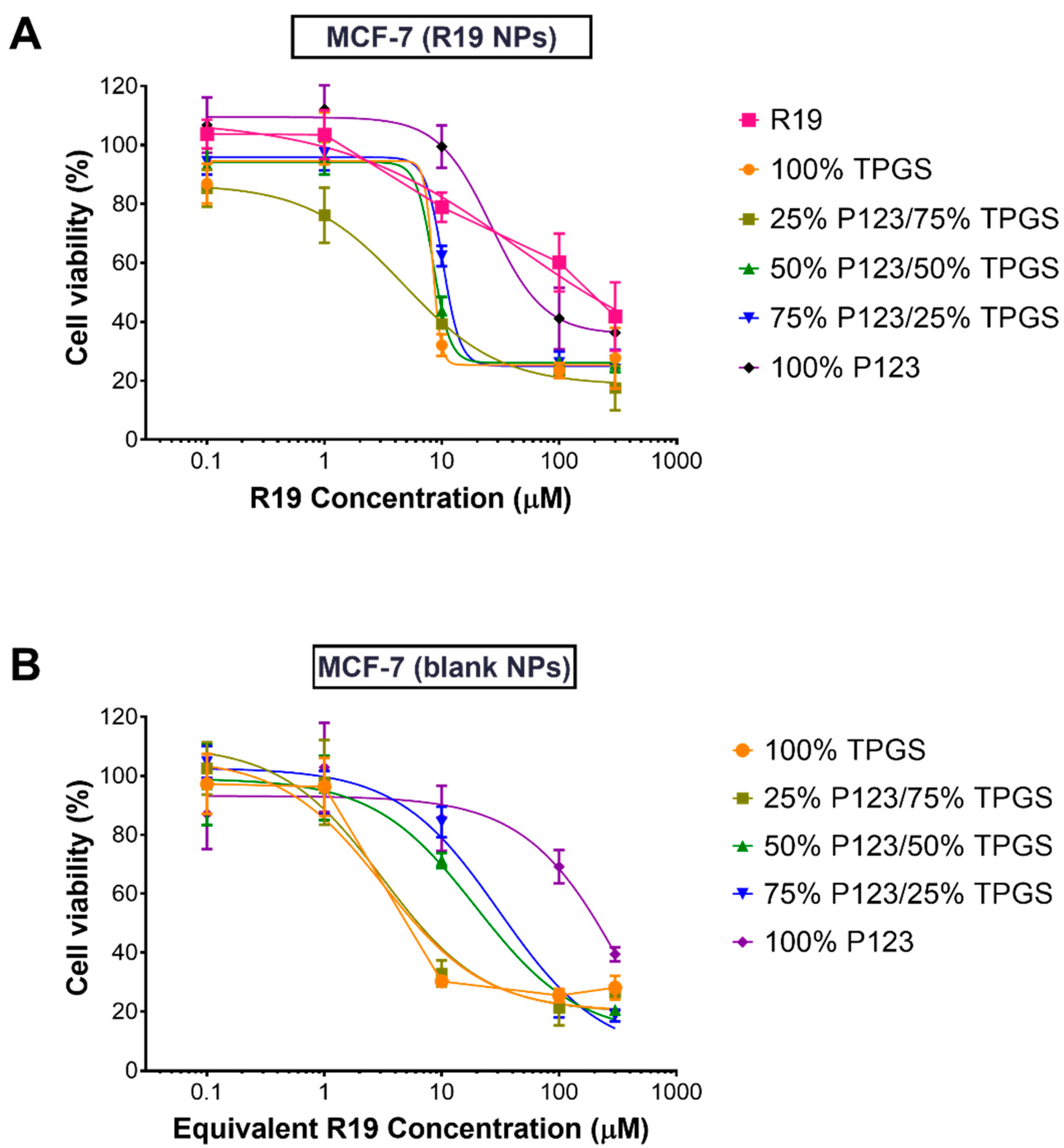
3.4. Cell Viability Assays
3.5. Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Assay of R19-Treated Cells
3.6. Cellular Uptake of NR-Labeled NPs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Cancer Fact Sheet. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer (accessed on 14 July 2022).
- Rallis, K.S.; Lai Yau, T.H.; Sideris, M. Chemoradiotherapy in cancer treatment: Rationale and clinical applications. Anticancer Res. 2021, 41, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirrmacher, V. From chemotherapy to biological therapy: A review of novel concepts to reduce the side effects of systemic cancer treatment (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 54, 407–419. [Google Scholar]
- Kannaiyan, R.; Mahadevan, D. A comprehensive review of protein kinase inhibitors for cancer therapy. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2018, 18, 1249–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrs, M.; Korabecny, J.; Jun, D.; Hodny, Z.; Bartek, J.; Kuca, K. Phosphatidylinositol 3-inase (PI3K) and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related kinase (PIKK) inhibitors: Importance of the morpholine ring. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 41–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Kwok-Shing Ng, P.; Kucherlapati, M.; Chen, F.; Liu, Y.; Tsang, Y.H.; de Velasco, G.; Jeong, K.J.; Akbani, R.; Hadjipanayis, A.; et al. A Pan-cancer proteogenomic atlas of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway alterations. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 820–832.e823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.S.; Cui, W. Proliferation, survival and metabolism: The role of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signalling in pluripotency and cell fate determination. Development 2016, 143, 3050–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamadneh, L.; Bahader, M.; Abuarqoub, R.; AlWahsh, M.; Alhusban, A.; Hikmat, S. PI3K/AKT and MAPK1 molecular changes preceding matrix metallopeptidases overexpression during tamoxifen-resistance development are correlated to poor prognosis in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer 2021, 28, 1358–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbah, D.A.; Haroon, R.A.; Bardaweel, S.K.; Hajjo, R.; Sweidan, K. N-phenyl-6-chloro-4-hydroxy-2-quinolone-3-carboxamides: Molecular docking, synthesis, and biological investigation as anticancer agents. Molecules 2020, 26, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Su, T.; Shi, Q.; Feng, Y.; Tao, Z.; Huang, Q.; Li, L.; Hu, L.; Li, S.; Tan, H.; et al. Co-administration of iRGD enhances tumor-targeted delivery and anti-tumor effects of paclitaxel-loaded PLGA nanoparticles for colorectal cancer treatment. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 8543–8560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Wang, K.; Oppong-Gyebi, A.; Hu, J. Application of nanotechnology in cancer diagnosis and therapy—A mini-review. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 17, 2964–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunoqrot, S.; Hamed, R.; Abdel-Halim, H.; Tarawneh, O. Synergistic interplay of medicinal chemistry and formulation strategies in nanotechnology—From drug discovery to nanocarrier design and development. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 1451–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagliardi, A.; Giuliano, E.; Venkateswararao, E.; Fresta, M.; Bulotta, S.; Awasthi, V.; Cosco, D. Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles for drug delivery to solid tumors. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 601626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamaly, N.; Yameen, B.; Wu, J.; Farokhzad, O.C. Degradable controlled-release polymers and polymeric nanoparticles: Mechanisms of controlling drug release. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 2602–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, H.; Jun, F.; Maeda, H. Development of next-generation macromolecular drugs based on the EPR effect: Challenges and pitfalls. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2015, 12, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunoqrot, S.; Alsadi, A.; Tarawneh, O.; Hamed, R. Polymer type and molecular weight dictate the encapsulation efficiency and release of Quercetin from polymeric micelles. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2017, 295, 2051–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, A.; Singh, K.; Bahadur, A.; Marangoni, G.; Bahadur, P. Interaction and solubilization of some phenolic antioxidants in Pluronic® micelles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 86, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Du, J.; Duan, Y.; Zang, Y.n.; Zhang, H.; Yang, C.; Cao, F.; Zhai, G. Curcumin loaded mixed micelles composed of Pluronic P123 and F68: Preparation, optimization and in vitro characterization. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 97, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Nguyen, T.H.; Dang, L.H.; Vu-Quang, H.; Tran, N.Q. Folate-conjugated chitosan-pluronic P123 nanogels: Synthesis and characterizations towards dual drug delivery. J. Nanomater. 2019, 2019, 1067821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, H.; Chen, L.; Sui, X.; Wu, B.; Zou, S.; Li, A.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, D.; Cai, S.; et al. Enhanced delivery of sorafenib with anti-GPC3 antibody-conjugated TPGS-b-PCL/Pluronic P123 polymeric nanoparticles for targeted therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 91, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, T.; Gu, L. TPGS emulsified zein nanoparticles enhanced oral bioavailability of daidzin: In vitro characteristics and in vivo performance. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 2062–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaonkar, R.; Ganguly, S.; Dewanjee, S.; Sinha, S.; Gupta, A.; Ganguly, S.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Debnath, C. Garcinol loaded vitamin E TPGS emulsified PLGA nanoparticles: Preparation, physicochemical characterization, in vitro and in vivo studies. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 530–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.; Tao, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, G.; Wang, T.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, X.; Mei, L. Docetaxel (DTX)-loaded polydopamine-modified TPGS-PLA nanoparticles as a targeted drug delivery system for the treatment of liver cancer. Acta Biomater. 2016, 30, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Tao, W.; Chen, Y.; Chang, D.; Wang, T.; Zhang, X.; Mei, L.; Zeng, X.; Huang, L. Doxorubicin-loaded star-shaped copolymer PLGA-vitamin E TPGS nanoparticles for lung cancer therapy. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2015, 26, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, L.; Feng, S.S. PLGA/TPGS nanoparticles for controlled release of paclitaxel: Effects of the emulsifier and drug loading ratio. Pharm. Res. 2003, 20, 1864–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunoqrot, S.; Orainee, B.; Alqudah, D.A.; Daoud, F.; Alshaer, W. Curcumin-tannic acid-poloxamer nanoassemblies enhance curcumin’s uptake and bioactivity against cancer cells in vitro. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 610, 121255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunoqrot, S.; Al-Shalabi, E.; Al-Bakri, A.G.; Zalloum, H.; Abu-Irmaileh, B.; Ibrahim, L.H.; Zeno, H. Coffee bean polyphenols can form biocompatible template-free antioxidant nanoparticles with various sizes and distinct colors. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 2767–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.Z.; Riviere, K.; Marroum, P. In vivo bioequivalence and in vitro similarity factor (f2) for dissolution profile comparisons of extended release formulations: How and when do they match? Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 1144–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivandzade, F.; Bhalerao, A.; Cucullo, L. Analysis of the Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Using the Cationic JC-1 Dye as a Sensitive Fluorescent Probe. Bio-Protocol 2019, 9, e3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyane, D.; Raval, N.; Maheshwari, R.; Tambe, V.; Kalia, K.; Tekade, R.K. Employment of enhanced permeability and retention effect (EPR): Nanoparticle-based precision tools for targeting of therapeutic and diagnostic agent in cancer. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 98, 1252–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez Rivas, C.J.; Tarhini, M.; Badri, W.; Miladi, K.; Greige-Gerges, H.; Nazari, Q.A.; Galindo Rodríguez, S.A.; Román, R.Á.; Fessi, H.; Elaissari, A. Nanoprecipitation process: From encapsulation to drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 532, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danaei, M.; Dehghankhold, M.; Ataei, S.; Hasanzadeh Davarani, F.; Javanmard, R.; Dokhani, A.; Khorasani, S.; Mozafari, M.R. Impact of particle size and polydispersity index on the clinical applications of lipidic nanocarrier systems. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraris, S.; Cazzola, M.; Peretti, V.; Stella, B.; Spriano, S. Zeta potential measurements on solid surfaces for in vitro biomaterials testing: Surface charge, reactivity upon contact with fluids and protein absorption. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2018, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khare, V.; Sakarchi, W.A.; Gupta, P.N.; Curtis, A.D.M.; Hoskins, C. Synthesis and characterization of TPGS–gemcitabine prodrug micelles for pancreatic cancer therapy. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 60126–60137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehvari, K.; Lin, K.-S.; Hammouda, B. Small-angle neutron scattering studies of microenvironmental and structural changes of Pluronic micelles upon encapsulation of paclitaxel. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 71, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.-L.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.-Z. FTIR spectroscopic study on effects of temperature and polymer composition on the structural properties of PEO−PPO−PEO block copolymer micelles. Langmuir 2002, 18, 5370–5374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.; Feng, S.S. A novel controlled release formulation for the anticancer drug paclitaxel (Taxol®): PLGA nanoparticles containing vitamin E TPGS. J. Control. Release 2003, 86, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, F.; Jing, B.; Qiu, H. Lyotropic liquid-crystalline phases formed by pluronic p123 in ethylammonium nitrate. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 6578–6584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.; Feng, S.S. Vitamin E TPGS used as emulsifier in the solvent evaporation/extraction technique for fabrication of polymeric nanospheres for controlled release of paclitaxel (Taxol®). J. Control. Release 2002, 80, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.A.; Xinyu, H.; Jabeen, A.; Ahsan, A.; Seidu, T.A.; Kutoka, P.T.; Wang, B. Enhanced cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of vorinostat through encapsulation in TPGS-modified liposomes. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 199, 111523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jindal, N.; Mehta, S.K. Nevirapine loaded Poloxamer 407/Pluronic P123 mixed micelles: Optimization of formulation and in vitro evaluation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 129, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Cai, X.; Du, H.; Zhai, G. Novel in situ gel systems based on P123/TPGS mixed micelles and gellan gum for ophthalmic delivery of curcumin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 128, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Zheng, R.; Zhang, S.; Wang, S.; Chen, R.; Sun, K.; Zeng, H.; Zhou, J.; Wei, W. Global patterns of breast cancer incidence and mortality: A population-based cancer registry data analysis from 2000 to 2020. Cancer Commun. 2021, 41, 1183–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neophytou, C.M.; Constantinou, C.; Papageorgis, P.; Constantinou, A.I. D-alpha-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol succinate (TPGS) induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis selectively in Survivin-overexpressing breast cancer cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 89, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Moreno, C.; Jimenez-Del-Rio, M.; Sierra-Garcia, L.; Lopez-Osorio, B.; Velez-Pardo, C. Vitamin E synthetic derivate-TPGS-selectively induces apoptosis in Jurkat T cells via oxidative stress signaling pathways: Implications for acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Apoptosis 2016, 21, 1019–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.-Y.; Zeng, S.-Q.; Qin, Y.; Mu, Y.; Liu, H. Vitamin E-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol succinate decorated drug delivery system with synergistic antitumor effects to reverse drug resistance and immunosuppression. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 628, 127387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Du, X.; Wang, R.; Zhai, G. Progress in the study of D-α-tocopherol polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (TPGS) reversing multidrug resistance. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 205, 111914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tusskorn, O.; Khunluck, T.; Prawan, A.; Senggunprai, L.; Kukongviriyapan, V. Mitochondrial division inhibitor-1 potentiates cisplatin-induced apoptosis via the mitochondrial death pathway in cholangiocarcinoma cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 111, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| NP | R19 (mg) | Pluronic P123 (mg) | TPGS (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100% TPGS | 2 | 0 | 20 |
| 25% P123/75% TPGS | 2 | 5 | 15 |
| 50% P123/50% TPGS | 2 | 10 | 10 |
| 75% P123/25% TPGS | 2 | 15 | 5 |
| 100% P123 | 2 | 20 | 0 |
| NP | Particle Size * (nm) | PDI | Zeta Potential (mV) | DL% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100% TPGS | 108 ± 8 | 0.20 ± 0.06 | −1.7 ± 5.0 | 60 ± 6 |
| 25% P123/75% TPGS | 92 ± 7 | 0.20 ± 0.03 | −6.6 ± 19.6 | 57 ± 7 |
| 50% P123/50% TPGS | 111 ± 8 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | −5.4 ± 15.3 | 59 ± 10 |
| 75% P123/25% TPGS | 112 ± 8 | 0.15 ± 0.05 | 16.0 ± 2.9 | 59 ± 6 |
| 100% P123 | 100 ± 8 | 0.17 ± 0.02 | −10.5 ± 17.1 | 59 ± 7 |
| Sample 1 | Sample 2 | f2 |
|---|---|---|
| 100% P123 | 75% P123/25% TPGS | 71 |
| 50% P123/50% TPGS | 60 | |
| 25% P123/75% TPGS | 66 | |
| 100% TPGS | 88 | |
| 75% P123/25% TPGS | 50% P123/50% TPGS | 75 |
| 25% P123/75% TPGS | 84 | |
| 100% TPGS | 75 | |
| 50% P123/50% TPGS | 25% P123/75% TPGS | 78 |
| 100% TPGS | 62 | |
| 25% P123/75% TPGS | 100% TPGS | 69 |
| Treatment | IC50 (µM; Mean ± SEM *) | |
|---|---|---|
| MCF-7 | MDA-MB-231 | |
| R19 | 14.7 ± 5.3 | 17.0 ± 4.2 |
| 100% TPGS | 4.3 ± 1.9 | 1.8 ± 0.4 |
| 25% P123/75% TPGS | 4.7 ± 1.0 | 1.8 ± 0.7 |
| 50% P123/50% TPGS | 4.9 ± 1.1 | 3.5 ± 1.0 |
| 75% P123/25% TPGS | 12.3 ± 2.4 | 10.2 ± 3.2 |
| 100% P123 | 45.4 ± 18.6 | 37.5 ± 24.3 |
| Blank 100% TPGS | 3.2 ± 1.1 | 2.0 ± 0.8 |
| Blank 25% P123/75% TPGS | 3.1 ± 1.0 | 1.7 ± 0.3 |
| Blank 50% P123/50% TPGS | 19.5 ± 4.9 | 1.6 ± 0.4 |
| Blank 75% P123/25% TPGS | 31.0 ± 7.2 | 26.8 ± 5.8 |
| Blank 100% P123 | 415.1 ± 448.8 | 87.1 ± 52.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sunoqrot, S.; Aliyeh, S.; Abusulieh, S.; Sabbah, D. Vitamin E TPGS-Poloxamer Nanoparticles Entrapping a Novel PI3Kα Inhibitor Potentiate Its Activity against Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091977
Sunoqrot S, Aliyeh S, Abusulieh S, Sabbah D. Vitamin E TPGS-Poloxamer Nanoparticles Entrapping a Novel PI3Kα Inhibitor Potentiate Its Activity against Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Pharmaceutics. 2022; 14(9):1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091977
Chicago/Turabian StyleSunoqrot, Suhair, Sundos Aliyeh, Samah Abusulieh, and Dima Sabbah. 2022. "Vitamin E TPGS-Poloxamer Nanoparticles Entrapping a Novel PI3Kα Inhibitor Potentiate Its Activity against Breast Cancer Cell Lines" Pharmaceutics 14, no. 9: 1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091977
APA StyleSunoqrot, S., Aliyeh, S., Abusulieh, S., & Sabbah, D. (2022). Vitamin E TPGS-Poloxamer Nanoparticles Entrapping a Novel PI3Kα Inhibitor Potentiate Its Activity against Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Pharmaceutics, 14(9), 1977. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14091977






