Molecular Mechanisms Underlying the Anti-Inflammatory Properties of (R)-(-)-Carvone: Potential Roles of JNK1, Nrf2 and NF-κB
Abstract
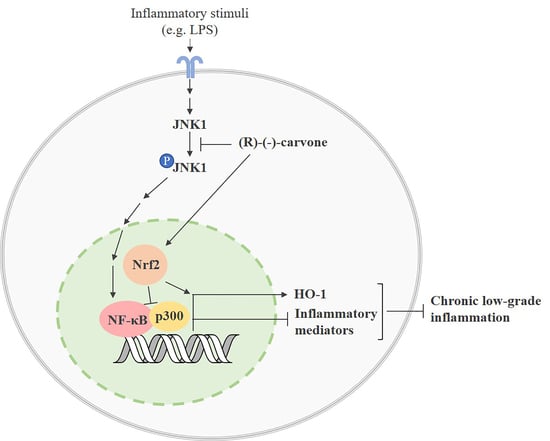
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Treatments
2.2. Preparation of Cell Extracts
2.3. Western Blot
2.4. Immunocytochemistry
2.5. SIRT1 Activity Assay
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1.(R)-(-)-Carvone Inhibits LPS-Induced Phosphorylation of JNK1, but Not That of Other JNK Isoforms, p38 and ERK1/2
3.2.(R)-(-)-Carvone Does Not Interfere with the Canonical Activation Pathway and Nuclear Translocation of NF-κB
3.3. (R)-(-)-Carvone Inhibits IκB-α Resynthesis
3.4. (R)-(-)-Carvone Tends to Decrease LPS-Induced Acetylation of NF-κB/p65 at Lys310 Independently of SIRT1 Activity and Expression
3.5. (R)-(-)-Carvone Promotes Nrf2 Nuclear Translocation and the Expression of its Target Gene, Heme Oxygenase-1
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Azab, A.; Nassar, A.; Azab, A. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Natural Products. Molecules 2016, 21, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Cássia da Silveira e Sá, R.; Andrade, L.; de Sousa, D. A Review on Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Monoterpenes. Molecules 2013, 18, 1227–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miguel, M.G. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Essential Oils: A Short Review. Molecules 2010, 15, 9252–9287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mendes, A.F.; Cruz, M.T.; Gualillo, O. Editorial: The Physiology of Inflammation—The Final Common Pathway to Disease. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furman, D.; Campisi, J.; Verdin, E.; Carrera-Bastos, P.; Targ, S.; Franceschi, C.; Ferrucci, L.; Gilroy, D.W.; Fasano, A.; Miller, G.W.; et al. Chronic Inflammation in the Etiology of Disease across the Life Span. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1822–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Deng, H.; Cui, H.; Fang, J.; Zuo, Z.; Deng, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L. Inflammatory Responses and Inflammation-Associated Diseases in Organs. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7204–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rufino, A.T.; Ribeiro, M.; Judas, F.; Salgueiro, L.; Lopes, M.C.; Cavaleiro, C.; Mendes, A.F. Anti-Inflammatory and Chondroprotective Activity of (+)-α-Pinene: Structural and Enantiomeric Selectivity. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rufino, A.T.; Ribeiro, M.; Sousa, C.; Judas, F.; Salgueiro, L.; Cavaleiro, C.; Mendes, A.F. Evaluation of the Anti-Inflammatory, Anti-Catabolic and pro-Anabolic Effects of E-Caryophyllene, Myrcene and Limonene in a Cell Model of Osteoarthritis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 750, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rufino, A.T.; Ferreira, I.; Judas, F.; Salgueiro, L.; Lopes, M.C.; Cavaleiro, C.; Mendes, A.F. Differential Effects of the Essential Oils of Lavandula Luisieri and Eryngium Duriaei Subsp. Juresianum in Cell Models of Two Chronic Inflammatory Diseases. Pharm. Biol. 2015, 53, 1220–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sousa, C.; Leitão, A.J.; Neves, B.M.; Judas, F.; Cavaleiro, C.; Mendes, A.F. Standardised Comparison of Limonene-Derived Monoterpenes Identifies Structural Determinants of Anti-Inflammatory Activity. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, C.; Neves, B.M.; Leitão, A.J.; Mendes, A.F. Elucidation of the Mechanism Underlying the Anti-Inflammatory Properties of (S)-(+)-Carvone Identifies a Novel Class of Sirtuin-1 Activators in a Murine Macrophage Cell Line. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, C.; Ribeiro, M.; Rufino, A.T.; Leitão, A.J.; Mendes, A.F. Assessment of Cell Line Competence for Studies of Pharmacological GPR30 Modulation. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. 2017, 37, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur, J.S.C.; Ley, S.C. Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases in Innate Immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulero, M.C.; Huxford, T.; Ghosh, G. NF-ΚB, IκB, and IKK: Integral Components of Immune System Signaling. In Structural Immunology; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 207–226. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, J.P.; Carmody, R.J. NF-ΚB and the Transcriptional Control of Inflammation. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2018, 335, 41–84. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Tang, E.; Guan, K.; Wang, C.-Y. IKKβ Plays an Essential Role in the Phosphorylation of RelA/P65 on Serine 536 Induced by Lipopolysaccharide. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 5630–5635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sakurai, H.; Chiba, H.; Miyoshi, H.; Sugita, T.; Toriumi, W. IκB Kinases Phosphorylate NF-ΚB P65 Subunit on Serine 536 in the Transactivation Domain. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 30353–30356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, B.; Yang, X.-D.; Lamb, A.; Chen, L.-F. Posttranslational Modifications of NF-ΚB: Another Layer of Regulation for NF-ΚB Signaling Pathway. Cell. Signal. 2010, 22, 1282–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, J.D.; Ryseck, R.-P.; Attar, R.M.; Dambach, D.; Bravo, R. Functional Redundancy of the Nuclear Factor ΚB Inhibitors IκBα and IκBβ. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 188, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.F.; Mu, Y.; Greene, W.C. Acetylation of RelA at Discrete Sites Regulates Distinct Nuclear Functions of NF-KappaB. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 6539–6548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yeung, F.; Hoberg, J.E.; Ramsey, C.S.; Keller, M.D.; Jones, D.R.; Frye, R.A.; Mayo, M.W. Modulation of NF-ΚB-Dependent Transcription and Cell Survival by the SIRT1 Deacetylase. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 2369–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wardyn, J.D.; Ponsford, A.H.; Sanderson, C.M. Dissecting Molecular Cross-Talk between Nrf2 and NF-ΚB Response Pathways. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2015, 43, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Kenney, P.; Lam, L. Anethofuran, Carvone, and Limonene: Potential Cancer Chemoprotective Agents from Dill Weed Oil and Caraway Oil. Planta Med. 1992, 58, 338–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talalay, P.; De Long, M.J.; Prochaska, H.J. Identification of a Common Chemical Signal Regulating the Induction of Enzymes That Protect against Chemical Carcinogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 8261–8265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hambleton, J.; Weinstein, S.L.; Lem, L.; DeFranco, A.L. Activation of C-Jun N-Terminal Kinase in Bacterial Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Macrophages. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 2774–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meng, Q.; Xia, Y. C-Jun, at the Crossroad of the Signaling Network. Protein Cell 2011, 2, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin, M.U.; Wesche, H. Summary and Comparison of the Signaling Mechanisms of the Toll/Interleukin-1 Receptor Family. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Cell Res. 2002, 1592, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guha, M.; Mackman, N. LPS Induction of Gene Expression in Human Monocytes. Cell. Signal. 2001, 13, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolter, S.; Doerrie, A.; Weber, A.; Schneider, H.; Hoffmann, E.; von der Ohe, J.; Bakiri, L.; Wagner, E.F.; Resch, K.; Kracht, M. C-Jun Controls Histone Modifications, NF-ΚB Recruitment, and RNA Polymerase II Function To Activate the Ccl2 Gene. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 4407–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marques, F.M.; Figueira, M.M.; Schmitt, E.F.P.; Kondratyuk, T.P.; Endringer, D.C.; Scherer, R.; Fronza, M. In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Terpenes via Suppression of Superoxide and Nitric Oxide Generation and the NF-ΚB Signalling Pathway. Inflammopharmacology 2019, 27, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, A.F.; Caramona, M.M.; Carvalho, A.P.; Lopes, M.C. Differential Roles of Hydrogen Peroxide and Superoxide in Mediating IL-1-Induced NF-?B Activation and INOS Expression in Bovine Articular Chondrocytes. J. Cell. Biochem. 2003, 88, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreira Mendes, A.; Caramona, M.M.; Carvalho, A.P.; Lopes, M.C. Hydrogen Peroxide Mediates Interleukin-1β-Induced AP-1 Activation in Articular Chondrocytes: Implications for the Regulation of INOS Expression. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2003, 19, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaestel, M.; Kotlyarov, A.; Kracht, M. Targeting Innate Immunity Protein Kinase Signalling in Inflammation. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 480–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, N.-H. Naturally Occurring NF-KB Inhibitors. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2006, 6, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobasheri, A. Intersection of Inflammation and Herbal Medicine in the Treatment of Osteoarthritis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2012, 14, 604–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, Z.-M.; Guan, P.; Luo, L.-F.; Qin, L.-Y.; Wang, N.; Zhao, Y.-S.; Ji, E.-S. Resveratrol Protects against CIH-Induced Myocardial Injury by Targeting Nrf2 and Blocking NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Life Sci. 2020, 245, 117362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, C.; Mendes, A.F. Monoterpenes as Sirtuin-1 Activators: Therapeutic Potential in Aging and Related Diseases. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.A.; Oriquat, G.A.; Abbas, M.M.; Al-Najjar, B.O.; Kandil, Y.I. Hypolipidaemic and Insulin Secretagogue Activities of (R)-(−)-Carvone. Malaysian J. Med. Sci. 2020, 27, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.M.; Kandil, Y.İ.; Abbas, M.A. R-(-)-Carvone Attenuated Doxorubicin Induced Cardiotoxicity In Vivo and Potentiated Its Anticancer Toxicity In Vitro. Balkan Med. J. 2020, 37, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro-Filho, J.; da Silva Brandi, J.; Ferreira Costa, H.; Carla de Paula Medeiros, K.; Alves Leite, J.; Pergentino de Sousa, D.; Regina Piuvezam, M. Carvone Enantiomers Differentially Modulate IgE-Mediated Airway Inflammation in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.M.U.; Luo, L.; Namani, A.; Wang, X.J.; Tang, X. Nrf2 Signaling Pathway: Pivotal Roles in Inflammation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.-C.; Hung, L.-F.; Wu, W.-L.; Chang, D.-M.; Huang, C.-Y.; Lai, J.-H.; Ho, L.-J. Chondroprotective Effects and Mechanisms of Resveratrol in Advanced Glycation End Products-Stimulated Chondrocytes. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010, 12, R167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Lin, J.; Sun, K.; Guo, J.; Yao, X.; Wang, G.; Hou, L.; Xu, J.; Guo, J.; Guo, F. Deferoxamine Alleviates Osteoarthritis by Inhibiting Chondrocyte Ferroptosis and Activating the Nrf2 Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 791376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Luo, J.; Jing, X.; Guo, J.; Yao, X.; Hao, X.; Ye, Y.; Liang, S.; Lin, J.; Wang, G.; et al. Astaxanthin Protects against Osteoarthritis via Nrf2: A Guardian of Cartilage Homeostasis. Aging 2019, 11, 10513–10531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zeng, Y. Curcumin Reduces Inflammation in Knee Osteoarthritis Rats through Blocking TLR4 /MyD88/NF-κB Signal Pathway. Drug Dev. Res. 2019, 80, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Jia, J.; Jin, X.; Tong, W.; Tian, H. Resveratrol Ameliorates Inflammatory Damage and Protects against Osteoarthritis in a Rat Model of Osteoarthritis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 17, 1493–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.-S.; Lee, H.-J.; Jeon, Y.-D.; Han, Y.-H.; Kee, J.-Y.; Kim, H.-J.; Shin, H.-J.; Kang, J.; Lee, B.S.; Kim, S.-H.; et al. Alpha-Pinene Exhibits Anti-Inflammatory Activity Through the Suppression of MAPKs and the NF-ΚB Pathway in Mouse Peritoneal Macrophages. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2015, 43, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somensi, N.; Rabelo, T.K.; Guimarães, A.G.; Quintans-Junior, L.J.; de Souza Araújo, A.A.; Moreira, J.C.F.; Gelain, D.P. Carvacrol Suppresses LPS-Induced pro-Inflammatory Activation in RAW 264.7 Macrophages through ERK1/2 and NF-KB Pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 75, 105743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Protein | Source | Clonality | Dilution | Supplier | Catalogue/Lot Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| phospho-p44/42 MAPK (ERK1/2) (Thr202/Tyr204) | rabbit | polyclonal | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling Technology, Inc., Danvers, MA, USA | 9101/27 |
| p44/42 MAPK (ERK1/2) | rabbit | polyclonal | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. | 9102/26 |
| phospho-p38 MAPK (Thr180/Tyr182) | rabbit | polyclonal | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. | 9211/ 21 |
| p38 MAPK | rabbit | polyclonal | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. | 9212/17 |
| phospho-SAPK/JNK (Thr183/Tyr185) | rabbit | monoclonal | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. | 4668/11 |
| SAPK/JNK | rabbit | polyclonal | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. | 9252/17 |
| phospho-IκB-α (Ser32/36) | mouse | monoclonal | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. | 9246/14 |
| IκB-α | rabbit | polyclonal | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling Technology, Inc., Danvers, MA, USA | 9242/9 |
| NF-κB p65 (D14E12) XP(R) | rabbit | monoclonal | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. | 8242/4 |
| phospho- NF-κB p65 (Ser536) | rabbit | monoclonal | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. | 3033/14 |
| acetyl-NF-κB p65 (Lys310) | rabbit | polyclonal | 1:750 | Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. | 3045/2 |
| Sirtuin-1 | rabbit | polyclonal | 1:1000 | Sigma-Aldrich Co. | 07-131/2736563 |
| Nrf2 (C-20) | rabbit | polyclonal | 1:500 | Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Dallas, TX, USA | sc-722/A1612 |
| Heme oxygenase-1 | mouse | monoclonal | 1:1000 | Invitrogen, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA | MA 1-112/TK2665301 |
| β-tubulin I | mouse | monoclonal | 1:20,000 | Sigma-Aldrich Co. | T7816/052M4835 |
| lamin B1 | rabbit | polyclonal | 1:1000 | Abcam, Cambridge, UK | ab16048/ GR48958-1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sousa, C.; Neves, B.M.; Leitão, A.J.; Mendes, A.F. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying the Anti-Inflammatory Properties of (R)-(-)-Carvone: Potential Roles of JNK1, Nrf2 and NF-κB. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15010249
Sousa C, Neves BM, Leitão AJ, Mendes AF. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying the Anti-Inflammatory Properties of (R)-(-)-Carvone: Potential Roles of JNK1, Nrf2 and NF-κB. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(1):249. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15010249
Chicago/Turabian StyleSousa, Cátia, Bruno Miguel Neves, Alcino Jorge Leitão, and Alexandrina Ferreira Mendes. 2023. "Molecular Mechanisms Underlying the Anti-Inflammatory Properties of (R)-(-)-Carvone: Potential Roles of JNK1, Nrf2 and NF-κB" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 1: 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15010249
APA StyleSousa, C., Neves, B. M., Leitão, A. J., & Mendes, A. F. (2023). Molecular Mechanisms Underlying the Anti-Inflammatory Properties of (R)-(-)-Carvone: Potential Roles of JNK1, Nrf2 and NF-κB. Pharmaceutics, 15(1), 249. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15010249