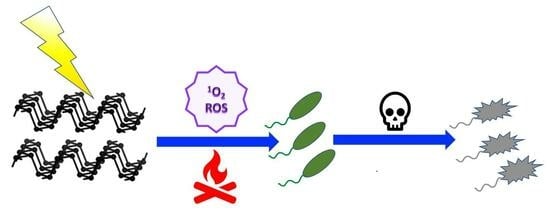
Innovative Phosphorene Nanoplatform for Light Antimicrobial Therapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Antimicrobial Phototherapy
2.1. Basic Mechanisms
2.2. Antimicrobial PDT Activity
- -
- Positive charge for high-affinity binding to negatively charged bacterial cell membranes;
- -
- Low molecular weight or a structure that facilitates penetration through the biofilm matrix;
- -
- High 1O2 quantum yield;
- -
- High photostability;
- -
- No dark toxicity and/or mutagenicity towards host eukaryotic cells in the “therapeutic window” where microorganisms can be killed without damaging the surrounding cells.
2.3. Antimicrobial PTT Activity
3. Structure and Properties of bP and bP-NPs
3.1. Physical, Mechanical, and Chemical Features of bP and Phosphorene (bP-NPs)
3.2. Preparation of bP and bP-NPs
- (1)
- Mechanical cleavage, also known as the “Scotch-tape” method, involves the sequential peeling off of layers from bulk bP using adhesive tape. After the process is complete, the material is transferred to a substrate (Si/SiO2) and cleaned. Although this technique can produce high-quality phosphorene, the yield is typically low, and contamination caused by adhesive residue cannot be ignored [43];
- (2)
- In electrochemical exfoliation, consisting of anodic oxidation and cationic intercalation, a voltage is applied to bulk bP, serving as an electrode in an electrolyte solution, causing a structural deformation of the layered bP and yielding 2D nanoflakes [50];
- (3)
- Sonication-assisted liquid phase exfoliation is a reliable method for producing high quantities of bP-NPs. This method consists of three steps: immersion in a solvent, ultrasonication, and purification [69].
4. Antimicrobial Photoactivity of bP
4.1. Mechanisms of bP Photoactivity
4.2. Bare bP-NPs
4.3. bP-NPs-Based Hybrid Materials
4.3.1. Metals
4.3.2. Hydrogels
4.3.3. Antimicrobial Compounds
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Global AMR R&D Hub; WHO. Incentivising the Development of New Antibacterial Treatments; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Talebi Bezmin Abadi, A.; Rizvanov, A.A.; Haertlé, T.; Blatt, N.L. World Health Organization Report: Current Crisis of Antibiotic Resistance. BioNanoScience 2019, 9, 778–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, J.M.A.; Webber, M.A.; Baylay, A.J.; Ogbolu, D.O.; Piddock, L.J.V. Molecular Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancuso, G.; Midiri, A.; Gerace, E.; Biondo, C. Bacterial Antibiotic Resistance: The Most Critical Pathogens. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, C.W.; Mah, T.-F. Molecular Mechanisms of Biofilm-Based Antibiotic Resistance and Tolerance in Pathogenic Bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 276–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cieplik, F.; Deng, D.; Crielaard, W.; Buchalla, W.; Hellwig, E.; Al-Ahmad, A.; Maisch, T. Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy—What We Know and What We Don’t. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 44, 571–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maisch, T. Photoantimicrobials—An Update. Transl. Biophotonics 2020, 2, e201900033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, J.H.; Rodrigues, J.A.; Pimenta, S.; Dong, T.; Yang, Z. Photodynamic Therapy Review: Principles, Photosensitizers, Applications, and Future Directions. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, Z.L.; Kuriakose, S.; Cheeseman, S.; Dickey, M.D.; Genzer, J.; Christofferson, A.J.; Crawford, R.J.; McConville, C.F.; Chapman, J.; Truong, V.K.; et al. Antipathogenic Properties and Applications of Low-Dimensional Materials. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, A.; Mathew, S.; Radoor, S.; Kim, J.T.; Rhim, J.-W.; Siengchin, S. Recent Advances in Two-Dimensional Nanomaterials: Properties, Antimicrobial, and Drug Delivery Application of Nanocomposites. Mater. Today Chem. 2023, 30, 101492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, F.; Liu, X.; Xia, T. Black Phosphorus for Fighting Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria: What Is Known and What Is Missing. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 721, 137740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favron, A.; Gaufrès, E.; Fossard, F.; Phaneuf-L’Heureux, A.-L.; Tang, N.Y.-W.; Lévesque, P.L.; Loiseau, A.; Leonelli, R.; Francoeur, S.; Martel, R. Photooxidation and Quantum Confinement Effects in Exfoliated Black Phosphorus. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 826–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Jian, Y.; Wu, W.; Lv, R. Black Phosphorus Nanosheet with High Thermal Conversion Efficiency for Photodynamic/Photothermal/Immunotherapy. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 4940–4948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, X.; Shao, W.; Chen, S.; Xie, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Xie, Y. Ultrathin Black Phosphorus Nanosheets for Efficient Singlet Oxygen Generation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 11376–11382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, C.; Li, L.; Hu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y. Antibacterial Black Phosphorus Nanosheets for Biomedical Applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 7069–7093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naskar, A.; Kim, K. Black Phosphorus Nanomaterials as Multi-Potent and Emerging Platforms against Bacterial Infections. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 137, 103800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashef, N.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Hamblin, M.R. Advances in Antimicrobial Photodynamic Inactivation at the Nanoscale. Nanophotonics 2017, 6, 853–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cieplik, F.; Tabenski, L.; Buchalla, W.; Maisch, T. Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy for Inactivation of Biofilms Formed by Oral Key Pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Hamblin, M.R. Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy to Control Clinically Relevant Biofilm Infections. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delcanale, P.; Abbruzzetti, S.; Viappiani, C. Photodynamic Treatment of Pathogens. Riv. Nuovo Cim. 2022, 45, 407–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Laguna, V.; Gilaberte, Y.; Millán-Lou, M.I.; Agut, M.; Nonell, S.; Rezusta, A.; Hamblin, M.R. A Combination of Photodynamic Therapy and Antimicrobial Compounds to Treat Skin and Mucosal Infections: A Systematic Review. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2019, 18, 1020–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nonell, S. Oxygen (and Lack Thereof) in Photodynamic Therapy. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2023, 41, 103440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, W.F.; Melendez, A.J. INTRODUCTION. Clin. Exp. Pharma Physio 2006, 33, 480–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Sherwood, M.E.; Murray, C.K.; Vrahas, M.S.; Hooper, D.C.; Hamblin, M.R.; Dai, T. Antimicrobial Blue Light Inactivation of Candida Albicans: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Virulence 2016, 7, 536–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Chen, J.; Amin, R.; Lu, M.; Bhayana, B.; Zhao, J.; Murray, C.K.; Hamblin, M.R.; Hooper, D.C.; et al. Antimicrobial Blue Light Inactivation of Gram-Negative Pathogens in Biofilms: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 213, 1380–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, T.; Gupta, A.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Yin, R.; Murray, C.K.; Vrahas, M.S.; Sherwood, M.E.; Tegos, G.P.; Hamblin, M.R. Blue Light Rescues Mice from Potentially Fatal Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Burn Infection: Efficacy, Safety, and Mechanism of Action. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamblin, M.R.; Viveiros, J.; Yang, C.; Ahmadi, A.; Ganz, R.A.; Tolkoff, M.J. Helicobacter Pylori Accumulates Photoactive Porphyrins and Is Killed by Visible Light. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 2822–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morici, P.; Battisti, A.; Tortora, G.; Menciassi, A.; Checcucci, G.; Ghetti, F.; Sgarbossa, A. The In Vitro Photoinactivation of Helicobacter Pylori by a Novel LED-Based Device. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battisti, A.; Morici, P.; Sgarbossa, A. Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy of Porphyrins in Helicobacter Pylori Biofilms. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, J.; Hoenes, K.; Vatter, P.; Hessling, M. Antimicrobial Effect of Visible Light—Photoinactivation of Legionella Rubrilucens by Irradiation at 450, 470, and 620 Nm. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ferrer-Espada, R.; Baglo, Y.; Goh, X.S.; Held, K.D.; Grad, Y.H.; Gu, Y.; Gelfand, J.A.; Dai, T. Photoinactivation of Neisseria Gonorrhoeae: A Paradigm-Changing Approach for Combating Antibiotic-Resistant Gonococcal Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 220, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fyrestam, J.; Bjurshammar, N.; Paulsson, E.; Johannsen, A.; Östman, C. Determination of Porphyrins in Oral Bacteria by Liquid Chromatography Electrospray Ionization Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 7013–7023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, A.; Sasaki, H.; Toyama, T.; Araki, M.; Fujioka, J.; Tsukiyama, K.; Hamada, N.; Yoshino, F. Antimicrobial Effect of Blue Light Using Porphyromonas Gingivalis Pigment. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biener, G.; Masson-Meyers, D.S.; Bumah, V.V.; Hussey, G.; Stoneman, M.R.; Enwemeka, C.S.; Raicu, V. Blue/Violet Laser Inactivates Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus by Altering Its Transmembrane Potential. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2017, 170, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, E.; Faustino, M.A.; Neves, M.G.; Cunha, A.; Tome, J.; Almeida, A. An Insight on Bacterial Cellular Targets of Photodynamic Inactivation. Future Med. Chem. 2014, 6, 141–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzyżek, P.; Grande, R.; Migdał, P.; Paluch, E.; Gościniak, G. Biofilm Formation as a Complex Result of Virulence and Adaptive Responses of Helicobacter Pylori. Pathogens 2020, 9, 1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, K.; Reddy, S.; Barathe, P.; Shriram, V.; Anand, U.; Proćków, J.; Kumar, V. Combating Drug-Resistant Bacteria Using Photothermally Active Nanomaterials: A Perspective Review. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 747019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dediu, V.; Ghitman, J.; Gradisteanu Pircalabioru, G.; Chan, K.H.; Iliescu, F.S.; Iliescu, C. Trends in Photothermal Nanostructures for Antimicrobial Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, R.; Jin, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, J. Black Phosphorus Quantum Dots: Synthesis, Properties, Functionalized Modification and Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 6795–6823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Lai, C.; Zeng, G.; Huang, D.; Qin, L.; Zhang, M.; Cheng, M.; Liu, X.; Yi, H.; Zhou, C.; et al. Black Phosphorus, a Rising Star 2D Nanomaterial in the Post-Graphene Era: Synthesis, Properties, Modifications, and Photocatalysis Applications. Small 2019, 15, 1804565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahamed, M.I.; Shakeel, N.; Anwar, N. Structure and Fundamental Properties of Black Phosphorus; Inamuddin, Boddula, R., Asiri, A.M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 139–156. [Google Scholar]
- Fukuoka, S.; Taen, T.; Osada, T. Electronic Structure and the Properties of Phosphorene and Few-Layer Black Phosphorus. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2015, 84, 121004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Neal, A.T.; Zhu, Z.; Luo, Z.; Xu, X.; Tománek, D.; Ye, P.D. Phosphorene: An Unexplored 2D Semiconductor with a High Hole Mobility. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 4033–4041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Lin, X.; Xu, Z.; Chu, D. Recent Developments in Black Phosphorus Transistors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 8760–8775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, L.; Chen, C.; Smith, S.C. Phosphorene: Fabrication, Properties, and Applications. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 2794–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pica, M.; D’Amato, R. Chemistry of Phosphorene: Synthesis, Functionalization and Biomedical Applications in an Update Review. Inorganics 2020, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jones, A.M.; Seyler, K.L.; Tran, V.; Jia, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, H.; Yang, L.; Xu, X.; Xia, F. Highly Anisotropic and Robust Excitons in Monolayer Black Phosphorus. Nat. Nanotech. 2015, 10, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, V.; Neugebauer, P.; Mounkachi, O.; Lahbabi, S.; El Fatimy, A. Phosphorene—An Emerging Two-Dimensional Material: Recent Advances in Synthesis, Functionalization, and Applications. 2D Mater. 2022, 9, 032001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozhukil Valappil, M.; Alwarappan, S.; Pillai, V.K. Phosphorene Quantum Dots: Synthesis, Properties and Catalytic Applications. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 1037–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Hui, K.S.; Hui, K.N. 2D Black Phosphorus: From Preparation to Applications for Electrochemical Energy Storage. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1700491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Song, J.; Yang, H. Emerging Low-Dimensional Black Phosphorus: From Physical-Optical Properties to Biomedical Applications. Sci. China Chem. 2023, 66, 406–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.-W. Electronic Properties of Phosphorene/Graphene and Phosphorene/Hexagonal Boron Nitride Heterostructures. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 13929–13936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peruzzini, M.; Bini, R.; Bolognesi, M.; Caporali, M.; Ceppatelli, M.; Cicogna, F.; Coiai, S.; Heun, S.; Ienco, A.; Benito, I.I.; et al. A Perspective on Recent Advances in Phosphorene Functionalization and Its Applications in Devices. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 2019, 1476–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, A.; Wang, M.; Zhu, X.; Rodin, A.S.; Su, H.; Castro Neto, A.H. Phosphorene: From Theory to Applications. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Q.; Gu, S.; Sun, Z.; Chu, P.K.; Yu, X. The Electrical, Thermal, and Thermoelectric Properties of Black Phosphorus. APL Mater. 2020, 8, 120903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torbatian, Z.; Asgari, R. Optical Absorption Properties of Few-Layer Phosphorene. Phys. Rev. B 2018, 98, 205407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molas, M.R.; Macewicz, Ł.; Wieloszyńska, A.; Jakóbczyk, P.; Wysmołek, A.; Bogdanowicz, R.; Jasinski, J.B. Photoluminescence as a Probe of Phosphorene Properties. npj 2d Mater. Appl. 2021, 5, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.-W.; Park, H.S. Negative Poisson’s Ratio in Single-Layer Black Phosphorus. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzi, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, X.-F. Mechanical Properties and Applications of 2D Black Phosphorus. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 128, 230903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Druenen, M.; Davitt, F.; Collins, T.; Glynn, C.; O’Dwyer, C.; Holmes, J.D.; Collins, G. Evaluating the Surface Chemistry of Black Phosphorus during Ambient Degradation. Langmuir 2019, 35, 2172–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Druenen, M. Degradation of Black Phosphorus and Strategies to Enhance Its Ambient Lifetime. Adv. Mater. Inter. 2020, 7, 2001102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abellán, G.; Wild, S.; Lloret, V.; Scheuschner, N.; Gillen, R.; Mundloch, U.; Maultzsch, J.; Varela, M.; Hauke, F.; Hirsch, A. Fundamental Insights into the Degradation and Stabilization of Thin Layer Black Phosphorus. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 10432–10440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wan, Y.; Xie, H.; Mu, Y.; Du, P.; Wang, D.; Wu, X.; Ji, H.; Wan, L. Degradation Chemistry and Stabilization of Exfoliated Few-Layer Black Phosphorus in Water. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 7561–7567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Chen, Q.; Tong, Y.; Wang, J. Light-Induced Ambient Degradation of Few-Layer Black Phosphorus: Mechanism and Protection. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 11437–11441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walia, S.; Sabri, Y.; Ahmed, T.; Field, M.R.; Ramanathan, R.; Arash, A.; Bhargava, S.K.; Sriram, S.; Bhaskaran, M.; Bansal, V.; et al. Defining the Role of Humidity in the Ambient Degradation of Few-Layer Black Phosphorus. 2D Mater. 2016, 4, 015025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Singh, Y.; Cho, S.-Y.; Sasikala, S.P.; Koo, S.H.; Narayan, R.; Jung, H.-T.; Jung, Y.; Kim, S.O. Ambient Stabilization of Few Layer Phosphorene via Noncovalent Functionalization with Surfactants: Systematic 2D NMR Characterization in Aqueous Dispersion. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 2786–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.B.; Hagaman, D.; Ji, H.-F. Growth of 2D Black Phosphorus Film from Chemical Vapor Deposition. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 215602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Hammoumi, M.; Chaudhary, V.; Neugebauer, P.; El Fatimy, A. Chemical Vapor Deposition: A Potential Tool for Wafer Scale Growth of Two-Dimensional Layered Materials. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2022, 55, 473001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; He, X.; She, L.; Sun, J.; Jiang, R.; Xu, H.; Shi, F.; Lei, Z.; Liu, Z.-H. Solvothermal-Assisted Liquid-Phase Exfoliation of Large Size and High Quality Black Phosphorus. J. Mater. 2018, 4, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, T.K.; Datta, A. Disentangling the Liquid Phase Exfoliation of Two-Dimensional Materials: An “In Silico ” Perspective. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 22157–22179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Weng, S.; Niu, R.; Zhen, W.; Xu, F.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, C. Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)-Assisted Exfoliation of van Der Waals Materials. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 38774–38781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Liu, L.; Huang, W.; Wu, K. Polyvinylpyrrolidone-Assisted Solvent Exfoliation of Black Phosphorus Nanosheets and Electrochemical Sensing of p-Nitrophenol. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1167, 338594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Xie, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Liang, W.; Huang, W.; Kang, J.; Cheng, F.; Kang, L.; et al. From Phosphorus to Phosphorene: Applications in Disease Theranostics. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 446, 214110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, M.; Ren, W.X.; Jeong, T.; Won, M.; Park, G.Y.; Sang, D.K.; Liu, L.-P.; Zhang, H.; Kim, J.S. Omnipotent Phosphorene: A next-Generation, Two-Dimensional Nanoplatform for Multidisciplinary Biomedical Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 5588–5601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatullo, M.; Genovese, F.; Aiello, E.; Amantea, M.; Makeeva, I.; Zavan, B.; Rengo, S.; Fortunato, L. Phosphorene Is the New Graphene in Biomedical Applications. Materials 2019, 12, 2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, M.; Anderson, G.; Zhao, R.; Alruqi, A.; Mroczkowska, J.E.; Sumanasekera, G.; Jasinski, J.B. Recent Advances in Synthesis, Properties, and Applications of Phosphorene. npj 2d Mater. Appl. 2017, 1, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Gaihre, B.; George, M.N.; Li, Y.; Tilton, M.; Yaszemski, M.J.; Lu, L. 2D Phosphorene Nanosheets, Quantum Dots, Nanoribbons: Synthesis and Biomedical Applications. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 2768–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Sando, S.; Cui, T. Biosensor Based on Layer by Layer Deposited Phosphorene Nanoparticles for Liver Cancer Detection. In Proceedings of the ASME 2017 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Tampa, FL, USA, 3–9 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Mei, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, A.; Tang, L.; Gao, H.; Wang, W. Black Phosphorus, an Emerging Versatile Nanoplatform for Cancer Immunotherapy. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Su, C.; Yang, B.; Fei, X.; Li, Y.; Hou, Y.; Zhao, H.; Guo, Y.; Zhuang, Z.; et al. Biodegradable Black Phosphorus-Based Nanomaterials in Biomedicine: Theranostic Applications. CMC 2019, 26, 1788–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boddula, R.; Inamuddin, M.; Asiri, A. Black Phosphorus; EPUB3 with Adobe DRM; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; Available online: https://www.ibs.it/black-phosphorus-ebook-inglese-vari/e/9783030295554 (accessed on 27 October 2023).
- Choi, J.R.; Yong, K.W.; Choi, J.Y.; Nilghaz, A.; Lin, Y.; Xu, J.; Lu, X. Black Phosphorus and Its Biomedical Applications. Theranostics 2018, 8, 1005–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Dong, A.; Wang, B.; Zhang, H. Current Advances in Black Phosphorus-Based Drug Delivery Systems for Cancer Therapy. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2003033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, H.; Yan, C.; Liu, Y.; Hong, S.; Tao, H.; Robertson, A.W.; Wang, Z.; Pádua, A.A.H. New Solvent-Stabilized Few-Layer Black Phosphorus for Antibacterial Applications. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 12543–12553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, Z.L.; Kuriakose, S.; Cheeseman, S.; Mayes, E.L.H.; Murali, A.; Oo, Z.Y.; Ahmed, T.; Tran, N.; Boyce, K.; Chapman, J.; et al. Broad-Spectrum Solvent-Free Layered Black Phosphorus as a Rapid Action Antimicrobial. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 17340–17352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, Z.L.; Cheeseman, S.; Huang, L.Z.Y.; Penman, R.; Ahmed, T.; Bryant, S.J.; Bryant, G.; Christofferson, A.J.; Orrell-Trigg, R.; Dekiwadia, C.; et al. Illuminating the Biochemical Interaction of Antimicrobial Few-Layer Black Phosphorus with Microbial Cells Using Synchrotron Macro-ATR-FTIR. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 7527–7539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virgo, E.P.; Haidari, H.; Shaw, Z.L.; Huang, L.Z.Y.; Kennewell, T.L.; Smith, L.; Ahmed, T.; Bryant, S.J.; Howarth, G.S.; Walia, S.; et al. Layered Black Phosphorus Nanoflakes Reduce Bacterial Burden and Enhance Healing of Murine Infected Wounds. Adv. Ther. 2023, 6, 2300235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Zhang, M.; Yu, S.; Wu, Q.; Ma, K.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, C.; Wang, F. Silver-Laden Black Phosphorus Nanosheets for an Efficient In Vivo Antimicrobial Application. Small 2020, 16, 1905938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wu, L.; Wang, H.; Zhou, W.; Liu, H.; Cui, H.; Li, P.; Chu, P.K.; Yu, X.-F. Synergistic Antibacterial Activity of Black Phosphorus Nanosheets Modified with Titanium Aminobenzenesulfanato Complexes. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 1202–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, İ.; Küçükkeçeci, H.; Sevgi, F.; Metin, Ö.; Hatay Patir, I. Photothermal Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Activity of Black Phosphorus/Gold Nanocomposites against Pathogenic Bacteria. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 26822–26831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naskar, A.; Lee, S.; Kim, K. Au–ZnO Conjugated Black Phosphorus as a Near-Infrared Light-Triggering and Recurrence-Suppressing Nanoantibiotic Platform against Staphylococcus Aureus. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Xiang, Y.; Liu, X.; Cui, Z.; Yang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhu, S.; Zheng, Y.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Wu, S. Repeatable Photodynamic Therapy with Triggered Signaling Pathways of Fibroblast Cell Proliferation and Differentiation To Promote Bacteria-Accompanied Wound Healing. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 1747–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Q.; Sun, T.; Su, W.; Jing, X.; Ye, B.; Su, Y.; Zeng, L.; Qu, Y.; Yang, X.; Wu, Y.; et al. Bioinspired Multifunctional Black Phosphorus Hydrogel with Antibacterial and Antioxidant Properties: A Stepwise Countermeasure for Diabetic Skin Wound Healing. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 11, 2102791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Chang, L.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Huang, S.; Chen, Z.; Ren, X.; Mei, X. Tea Polyphenol Modified, Photothermal Responsive and ROS Generative Black Phosphorus Quantum Dots as Nanoplatforms for Promoting MRSA Infected Wounds Healing in Diabetic Rats. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, T.; Zhang, M.; Han, B.; Xia, T.; Ni, S.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Tian, X. Thermosensitive Black Phosphorus Hydrogel Loaded with Silver Sulfadiazine Promotes Skin Wound Healing. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, A.; Wang, C.; Mo, W.; Li, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Zhang, Y. Photon-Responsive Antibacterial Nanoplatform for Synergistic Photothermal-/Pharmaco-Therapy of Skin Infection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Li, H.; Deng, H.; Fang, W.; Huang, X.; Qiao, J.; Tong, Y. Near Infrared Light-Responsive and Drug-Loaded Black Phosphorus Nanosheets for Antibacterial Applications. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 214, 112433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Liu, T.; Feng, X.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, C.; Quan, G.; Cai, J.; et al. A Perfect Pair: Stabilized Black Phosphorous Nanosheets Engineering with Antimicrobial Peptides for Robust Multidrug Resistant Bacteria Eradication (Adv. Healthcare Mater. 10/2022). Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2022, 11, 2270053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; An, D.; Jin, Y.; Feng, D.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Miao, W. Mannan-Functionalized Black Phosphorus Nanosheets Mediate the Targeted Elimination of Intracellular Bacteria via Combined Phototherapy. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 88, 104929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Properties | bP ÷ bP-NPs | |
|---|---|---|
| Band gap (eV) | 0.3 ÷ 2 | |
| Band type | Direct | |
| Charge mobility (cm2/Vs) | 1000 ÷ 600 | |
| Seebeck coefficients (μV/K at 300 K) | 413/300 ÷ 50 | |
| Thermal conductivity (W/mK) | ZZ | AC |
| ~18 | 12 | |
| Elongation at break (%) | 27 | 30 |
| Young’s modulus (GPa) | ~100 | ~25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Passaglia, E.; Sgarbossa, A. Innovative Phosphorene Nanoplatform for Light Antimicrobial Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2748. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15122748
Passaglia E, Sgarbossa A. Innovative Phosphorene Nanoplatform for Light Antimicrobial Therapy. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(12):2748. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15122748
Chicago/Turabian StylePassaglia, Elisa, and Antonella Sgarbossa. 2023. "Innovative Phosphorene Nanoplatform for Light Antimicrobial Therapy" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 12: 2748. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15122748
APA StylePassaglia, E., & Sgarbossa, A. (2023). Innovative Phosphorene Nanoplatform for Light Antimicrobial Therapy. Pharmaceutics, 15(12), 2748. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15122748