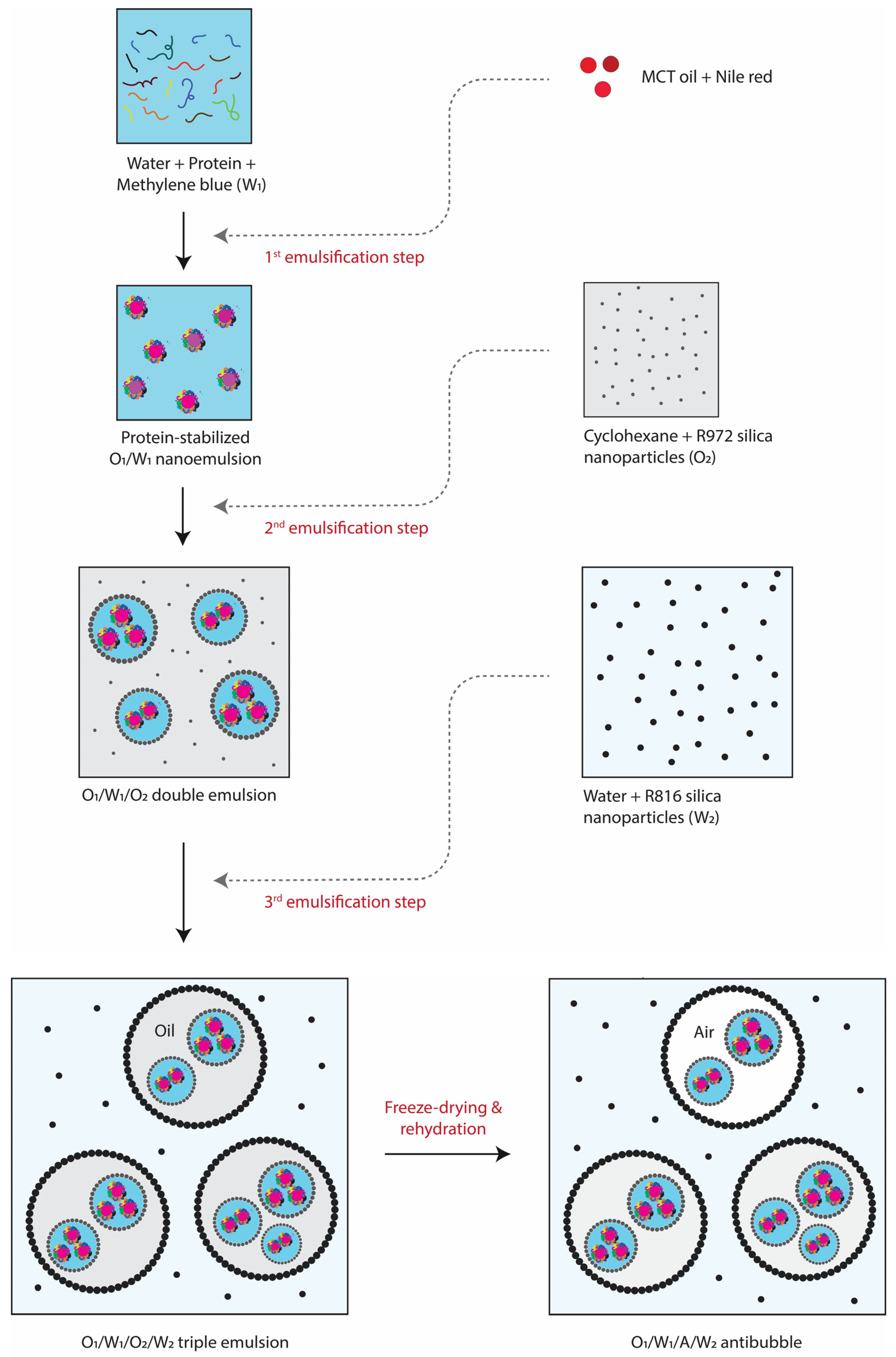
1. Introduction
Antibubbles, constituting a newly developed encapsulate for drug delivery applications, have gained scientific attention due to their unique structure, that is, a gaseous layer surrounding inner aqueous droplets (i.e., water-in-air-in-water, W
1/A/W
2) [
1]. The gaseous layer protects the drug-containing inner droplets by minimizing interaction with the external environment. However, the water–air interfaces must be sufficiently stable to allow antibubbles to be used as drug delivery systems. Nanoparticle-stabilized antibubbles offer enhanced stability and are preferred over surfactant-based antibubbles. They are produced when a Pickering double emulsion (W
1/O/W
2) is freeze-dried and then rehydrated [
2]. The middle layer of the double emulsion is always a volatile oil that sublimates along with the inner and outer water phases during freeze-drying. However, upon rehydration, the inner and outer water phases regain water, whereas the middle air layer (previously an oil layer) remains intact. To ensure the preservation of the structure during lyophilization, it is essential to introduce a cryoprotective element (often a carbohydrate) into both the inner and outer water phases, thereby preventing structural collapse. To attain a complete delivery of the drug from the cores of the encapsulates, the nanoparticles at both the W/A and A/W interfaces must be dislocated. This will subsequently release the drug from the inner cores into the surrounding environment. The nature of potential triggers for drug release can vary based on the type of nanoparticles stabilizing the interface and the specific location where drug release is needed. Antibubbles are unique in the sense that drug release can be initiated through the displacement of interfacially adsorbed nanoparticles by site-specific triggers. For instance, gastric delivery can be obtained via the acid-dependent dissolution of the interfacial particles [
2]. Several other mechanisms can be employed as a specific trigger (e.g., ultrasounds [
3], temperature [
4], or bile salts [
5]) at a specific site (e.g., mouth, stomach, intestine, or colon), causing the nanoparticles at the interface to dissolve or dislocate, releasing the gas shell and ultimately the inner drug-containing cores.
Up till now, only double-emulsion templated antibubbles have been prepared (e.g., described in the above paragraph), which are effective for encapsulating water-soluble drugs. However, in many cases, drugs are lipophilic, or a lipophilic drug must be delivered together with a hydrophilic drug. Hence, there is a necessity to develop antibubbles capable of encapsulating lipophilic substances as well. In this context, we introduce novel triple-emulsion templated antibubbles (O/W
1/A/W
2), enabling the simultaneous encapsulation of both hydrophilic and lipophilic drugs. The proof-of-concept formation and stability of this novel structure were tested through the loading of lipophilic and hydrophilic dyes (i.e., Nile red and methylene blue, respectively) in a primary oil-in-water (O
1/W
1) nano-emulsion. The rest of the procedure was similar to the preparation of double-emulsion templated antibubbles as reported previously [
5], i.e., the primary O
1/W
1 emulsion was used to create the O
1/W
1/O
2 (double) and O
1/W
1/O
2/W
2 (triple) emulsions. The latter was freeze-dried, and then rehydrated to get O
1/W
1/A/W
2 antibubbles.
A crucial factor when creating such antibubbles is employing a suitable stabilization mechanism for the primary O
1/W
1 emulsion. Principally, a surfactant capable of generating a nano-sized emulsion while having minimal interactions with other interfaces within the antibubble structure (usually stabilized by silica nanoparticles) is a viable choice to contemplate. Low-molecular-weight surfactants (like Tween 20) are fundamentally unsuitable due to their widely acknowledged ability to modify the wettability of solid particles, leading to their displacement from the interface [
6]. Conversely, employing silica particles in W
1 (similar to W
2) is also unfavorable, given the challenges in achieving a nano-emulsion. Therefore, we opted to use proteins to stabilize the O
1/W
1 primary emulsion given their established ability to generate stable nano-emulsion systems [
7]. Whey protein, a highly utilized animal protein, has sparked concerns regarding its allergenic potential, prompting a shift towards more user-friendly plant-based proteins. This transition is reinforced by the sustainability benefits associated with plant proteins, as well as their compatibility with vegetarian, vegan, and diverse dietary preferences dictated by culture and religion [
8]. Consequently, the current study investigates the stabilization of the primary emulsion using whey protein as well as two plant proteins, namely soy and pea. The entrapment of hydrophilic and lipophilic components in different antibubble variants, and the overall integrity of the antibubble structure (during an extended rehydration period), were assessed to identify the optimal choice for stabilizing triple-emulsion-based antibubbles.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The hydrophobized fumed silica particles, AEROSIL
® R972 and AEROSIL
® R816, were kindly provided by Evonik (Dubai, United Arab Emirates). The AEROSIL
® R972 silica particles, being the most hydrophobic, were employed to stabilize the W/O emulsion. The less hydrophobic AEROSIL
® R816 silica particles, which can easily be dispersed in the water phase, were used to stabilize the O/W emulsion. Both types of silica particles were utilized in emulsification without any pre-treatment. The median diameter of both types of silica particles was typically around 200 nm [
2]. Whey protein isolate (WPI, 92% purity), soy protein isolate (SPI, 90% purity), and pea protein isolate (PPI, 80% purity) were supplied by Myprotein (Manchester, UK). Cyclohexane (≥99.5%) was purchased from Honeywell (Charlotte, NC, USA). Medium-chain triglyceride (MCT) oil was provided by NOW
® Sports (Bloomingdale, IL, United States). Maltodextrin (dextrose equivalent: 16.5–19.5), methylene blue (≥95%), Nile red, and Tween
® 20 were provided by Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA).
2.2. Formation of Silica- or Protein-Stabilized O1/W1 Primary Emulsions
O1/W1 primary emulsions were fabricated using R816 silica nanoparticles (SNP) or proteins (WPI, SPI, or PPI). Briefly, 0.5% of SNP and 10% of maltodextrin were added to 15 mL of water and sonicated (Branson Digital Sonifier, SFX 550, Emerson, Brookfield, CT, USA) at 50% power for 1 min to disperse the nanoparticles in the aqueous phase. Then, MCT oil (containing 0.1% Nile red) was added to this mixture at a concentration of 5% of the aqueous phase. The coarse emulsion was prepared using T25 digital ULTRA-TURRAX® (IKA, Staufen, Germany) at 10,000 rpm for 1 min. Then, the coarse emulsion was subjected to a high-pressure homogenizer (APV 1000, APV SYSTEMS, Copenhagen, Denmark) at a pressure of 500 bar for three homogenization cycles. For the preparation of protein stabilized primary emulsions, each protein was solubilized in distilled water at a concentration of 2% (based on their purity levels). The protein solutions were stirred using a magnetic stirrer for 1 h at room temperature. For proper hydration, the protein solutions were kept in a refrigerator overnight at 4 °C. This was followed by centrifugation at 10,000 rpm at 4 °C for 30 min to remove any undissolved or suspended material from the protein mixtures. The supernatants were carefully collected from the top, leaving behind the sediments. Afterwards, MCT oil (containing 0.1% Nile red) was added to each protein suspension at a concentration of 5%. Similar to SNP-based emulsions, coarse emulsions were made using ULTRA-TURRAX® at 10,000 rpm for 1 min. The coarse emulsions were then subjected to high-pressure homogenization at 500 bar of pressure for three cycles to produce protein-stabilized nano-emulsions.
2.3. Determination of Drop Size Distribution of Primary Emulsions
The primary emulsions were characterized with respect to their droplet size distribution using a laser diffraction particle size analyzer (Malvern Mastersizer 3000, Malvern Panalytical Ltd., Malvern, UK). Refractive indices of 1.46 and 1.33 were used for MCT oil and aqueous phases, respectively. The emulsion samples were gradually added into the wet sample dispersion unit (Hydro EV) using a 3 mL bubble pipette until 10% obscuration level was reached. Each measurement cycle was run three times to record the droplet size distribution, and then the average median diameter and span value (a measure of droplet uniformity) were obtained.
2.4. Formation of O1/W1/O2 Double Emulsion
Protein-stabilized O1/W1 primary emulsions were further used to prepare O1/W1/O2 double-emulsion variants. Briefly, 5 mL of an O1/W1 nano-emulsion was acquired in a 15 mL plastic tube, to which methylene blue and maltodextrin were added at concentrations of 0.1% and 10%, respectively. The mixture was shaken on a vortex mixer until the added components (i.e., methylene blue and maltodextrin) were completely dissolved within the W1 phase of the nano-emulsion. A sample of cyclohexane (15 mL) containing 2.5% R972 hydrophobized fumed silica particles was acquired in another 50 mL plastic tube (denoted as O2 oil phase). This oil phase was sonicated (Branson Digital Sonifier, SFX 550, Emerson, Brookfield, CT, USA) at 50% power for 30 sec to disperse the silica particles. O1/W1 nano-emulsions were added to the cyclohexane and homogenized at 10,000 rpm for 1 min (T25 digital ULTRA-TURRAX®, IKA, Staufen, Germany) to obtain three different O1/W1/O2 emulsions. The only difference among all O1/W1/O2 emulsions was the inner O1/W1 nano-emulsions, which were stabilized with different proteins (denoted as O1/W1/O2—WPI, O1/W1/O2—SPI, and O1/W1/O2—PPI).
2.5. Determination of Drop Size Distribution of Double Emulsions
The double emulsions were analyzed for size and polydispersity through analysis of the images recorded using an optical microscope (Delphi-X observer, Euromex, Arnhem, The Netherlands) under bright-field and florescence modes. The sizes of around 500 double emulsion droplets were measured using ImageJ 1.53k software [
9]. The data were used to generate number-based size distribution curves for each double-emulsion variant using the frequency distribution function of GraphPad Prism 9 (GraphPad Software, Inc., Boston, MA, United States). Furthermore, the mean droplet size (D
d) and polydispersity index (PDI = [standard deviation/mean]
2) were also calculated for each data set.
2.6. Formation of O1/W1/O2/W2 Triple Emulsion
The double emulsions were used to produce O
1/W
1/O
2/W
2 triple emulsions. The aqueous phase (W
2) for dispersing the double emulsion consisted of distilled water containing 10% maltodextrin along with 0.5% R816 fumed silica particles. The aqueous phase was first sonicated at 50% power for 1 min to disperse the silica before making the triple emulsion. The triple emulsion was prepared by dispersing 5 mL of O
1/W
1/O
2 emulsion in 15 mL of W
2 phase via homogenization at 6000 rpm for 30 s. After following this procedure, we successfully prepared three distinct triple emulsions (denoted as O
1/W
1/O
2/W
2—WPI, O
1/W
1/O
2/W
2—SPI, and O
1/W
1/O
2/W
2—PPI). The optical microscopy and droplet size analyses of the triple emulsions were carried out as described in
Section 2.5.
2.7. Formation of Antibubbles
The triple emulsions were quickly frozen in −80 °C ultra-freezer (BINDER GmbH, Tuttlingen, Germany). Subsequently, the frozen triple emulsions were lyophilized using a freeze dryer (LyoAlfa 15, Telstar, Terrassa, Spain) at −80 °C and 0.01 mbar vacuum conditions for 48 h. Afterward, the three antibubble variants (i.e., O
1/W
1/A/W
2—WPI, O
1/W
1/A/W
2—SPI, and O
1/W
1/A/W
2—PPI) were obtained via rehydration of the freeze-dried material (0.1 g) in 10% maltodextrin solution (10 mL). The freeze-drying resulted in the replacement of O
2 oil phase of the original triple emulsion with an air phase (A) to produce antibubbles.
Figure 1 illustrates all the required steps involved in the formation of antibubbles. The optical microscopy and particle size analyses of the antibubbles were carried out as described in
Section 2.5. As a benchmark, the triple-emulsion-based antibubbles were compared with standard W
1/A/W
2 antibubbles in which the inner aqueous phase was not a nano-emulsion but consisted of just a 10% maltodextrin solution.
2.8. Entrapment Efficiency
2.8.1. Entrapment Efficiency of Lipophilic Component
The release of a lipophilic component, i.e., Nile red (NR), from the inner O
1 phase into the external O
2 phase during secondary emulsification step was quantified to calculate the entrapment efficiencies for the three O
1/W
1/O
2 double emulsions. However, as cyclohexane is volatile, the use of the double emulsions produced in
Section 2.4 could have resulted in an imprecise estimation of entrapment efficiency. Therefore, the entrapment of lipophilic components was estimated by preparing double emulsions using MCT oil in the internal and external oil phases, following the same procedure as described in
Section 2.4.
The light-pink-colored double emulsions were subjected to centrifugation (Centrifuge 5804 R, Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany) at 2000 rpm for 10 min. This resulted in a gentle separation of the oil layer (O
2) that appeared at the top of each double emulsion. The O
2 phase was then drawn using a 10 mL syringe, and this portion was then added to a 96-well microplate (MicroWell™, Thermo Scientific™, Loughborough, UK). The absorbance of all samples (Ab
s) was determined using a UV spectrophotometer (BioTek Epoch 2 microplate spectrophotometer, Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, United States) at a wavelength of 490 nm (
). This absorbance was compared with the absorbance obtained when the entire O
1 phase had leaked into the O
2 phase during the secondary emulsification step. This situation was mimicked by mixing O
1 phase directly into O
2 phase at the same O
1/O
2 ratio as that originally present in O
1/W
1/O
2 double emulsion. Subsequently, the absorbance of this O
1 and O
2 mixture (Ab
max) was determined at the same wavelength, and the entrapment of lipophilic component was calculated as follows:
where NR
s and NR
max are the NR concentrations (mg/mL) corresponding to Ab
s and Ab
max, respectively, which were obtained using a calibration curve obtained with known NR concentrations.
2.8.2. Entrapment Efficiency of Hydrophilic Component
The release of a hydrophilic component, i.e., methylene blue (MB), from the inner W
1 phase into the outer W
2 phase was measured for all antibubble variants. Briefly, a small amount of antibubble powder (0.1 g) was extracted and added to 10 mL of water containing 10% maltodextrin. The mixture was allowed to rehydrate for 5 min. After shaking, 2 mL of the solution was collected in a microcentrifuge tube (Expell Secure, CAPP
®, Nordhausen, Germany) and centrifuged (MiPC 12, MiLab, Dubai, United Arab Emirates) at 3000 rpm for 5 min. The clear solution from the center of the microcentrifuge tube was collected with a 5 mL syringe and added to a 96-well microplate, and absorbance was determined using a UV spectrophotometer at 665 nm. The MB concentration (MB
s) was determined using a calibration curve obtained from known MB concentrations. The entrapment efficiency of each sample was calculated as follows:
and represent MB concentrations (mg/mL) in the sample and the maximum possible concentration of MB that can be released into the outer water phase, W2. To calculate the maximum possible release of methylene blue (i.e., MBmax), the antibubbles must be destroyed to release all the methylene blue in the external water phase. For this purpose, Tween 20 was added to the mixture at a concentration of 10%, followed by centrifugation of the mixture at 15,000 rpm for 5 min. Subsequently, the absorbance was recorded at the same wavelength.
2.9. Stability of Antibubbles
The stability of all antibubble variants was analyzed in terms of MB release from the cores over an extended period of time (i.e., 2 weeks). The freeze-dried antibubble powder (0.1 g) was rehydrated in 10 mL of 10% maltodextrin aqueous solution. An aliquot (2 mL) from each antibubbles sample was drawn at days 0, 1, 3, 7, 10, and 14 to quantify the release of MB in the W
2 phase at each storage interval. The procedure used for the measurement of MB
s and MB
max was similar to that described in
Section 2.8.2. The cumulative release of MB from each antibubble variant was expressed as follows:
2.10. Data Analysis
All the experiments and measurements were carried out in triplicate, and then the mean and standard deviation of each data set were calculated using Microsoft Excel 2019 (Microsoft, Redmond, WA, USA). Subsequently, the data were presented graphically by plotting the mean values using GraphPad Prism 9 (GraphPad Software, Inc., Boston, MA, United States). The standard deviation for each data set was represented using errors bars.
4. Conclusions
The purpose of this study was to develop triple-emulsion-based antibubbles capable of efficiently encapsulating both hydrophilic and lipophilic payloads, a feature not achievable with conventional double-emulsion-based antibubbles. Under specific process conditions, we successfully produced antibubble variants within the 23–25 μm size range, each featuring distinct cores containing hydrophilic and lipophilic payloads. The compartmentalized structures of these triple-emulsion-based antibubbles demonstrated substantial entrapment efficiencies for both lipophilic (ranging from 80% to 90%) and hydrophilic (ranging from 70% to 82%) components. This result suggests that antibubbles can serve as a promising option for fabricating multi-drug delivery systems and have the potential to perform better than other competitive drug delivery systems such as liposomes and multiple emulsions. For instance, liposomes exhibit the disadvantage of low encapsulation efficiencies for hydrophilic compounds, unless an active loading of drug is applied, but this only applies a limited range of drugs [
18,
19]. Moreover, lipophilic drugs may rapidly diffuse out of the liposome bilayer, leading to reduced drug retention and therapeutic efficacy [
20,
21,
22]. Compared to conventional multiple emulsions, antibubbles offer prolong payload stability, and they also provide triggered release capabilities, as mentioned in the Introduction section of this article. Because of these beneficial properties, the potential of triple-emulsion-based antibubbles as a drug delivery system justifies further in vitro and in vitro investigations conducted, e.g., through the co-delivery of multiple drugs such as daunorubicin (hydrophilic) and paclitaxel (lipophilic).