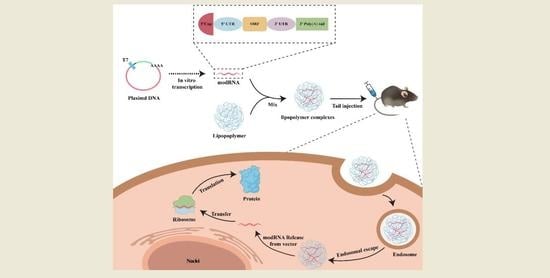
Safe and Effective Delivery of mRNA Using Modified PEI-Based Lipopolymers
Abstract
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Ai, X.; Remant-Bahadur, K.C.; Dick, T.A.; Yan, B.; Lu, T.; Zhou, X.; Luo, R.; Liu, M.; et al. Safe and Effective Delivery of mRNA Using Modified PEI-Based Lipopolymers. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15020410
Wang H, Liu X, Ai X, Remant-Bahadur KC, Dick TA, Yan B, Lu T, Zhou X, Luo R, Liu M, et al. Safe and Effective Delivery of mRNA Using Modified PEI-Based Lipopolymers. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(2):410. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15020410
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Huijing, Xin Liu, Xuefeng Ai, K. C. Remant-Bahadur, Teo A. Dick, Bingqian Yan, Tingting Lu, Xingliang Zhou, Runjiao Luo, Minglu Liu, and et al. 2023. "Safe and Effective Delivery of mRNA Using Modified PEI-Based Lipopolymers" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 2: 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15020410
APA StyleWang, H., Liu, X., Ai, X., Remant-Bahadur, K. C., Dick, T. A., Yan, B., Lu, T., Zhou, X., Luo, R., Liu, M., Wang, X., Li, K., Wang, W., Uludag, H., & Fu, W. (2023). Safe and Effective Delivery of mRNA Using Modified PEI-Based Lipopolymers. Pharmaceutics, 15(2), 410. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15020410