Antiviral Mechanism of Virucidal Sialic Acid Modified Cyclodextrin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells, Virus and Chemicals
2.2. Chemical Synthesis and Characterization
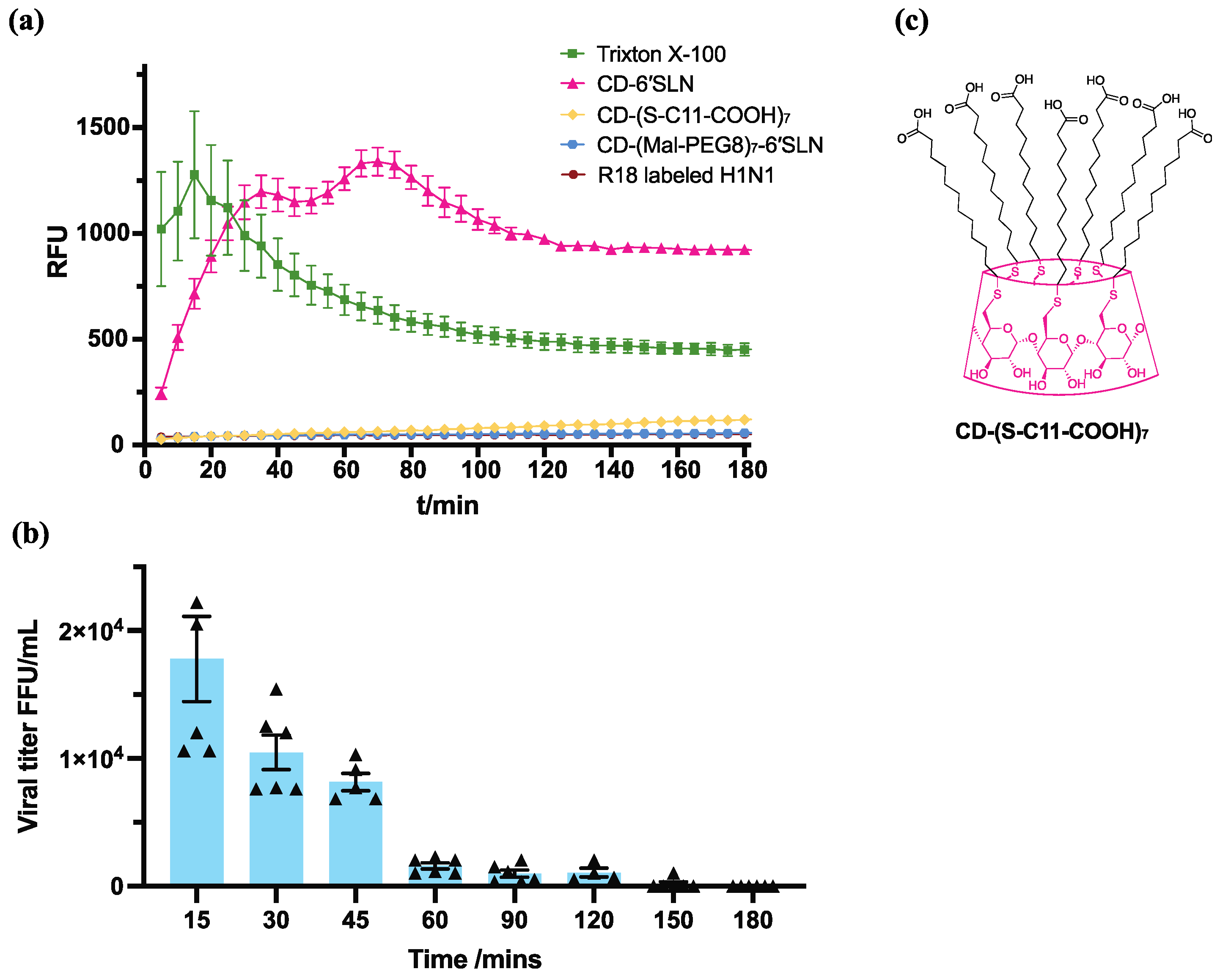
2.2.1. CD-(S-C11-COOH)7
2.2.2. CD-6′SLN
2.2.3. CD-(Mal-PEG8)7-6′SLN
2.3. H1N1 Inhibition Assay
2.4. Biolayer Interferometry
2.5. Neuraminidase Inhibition Assay
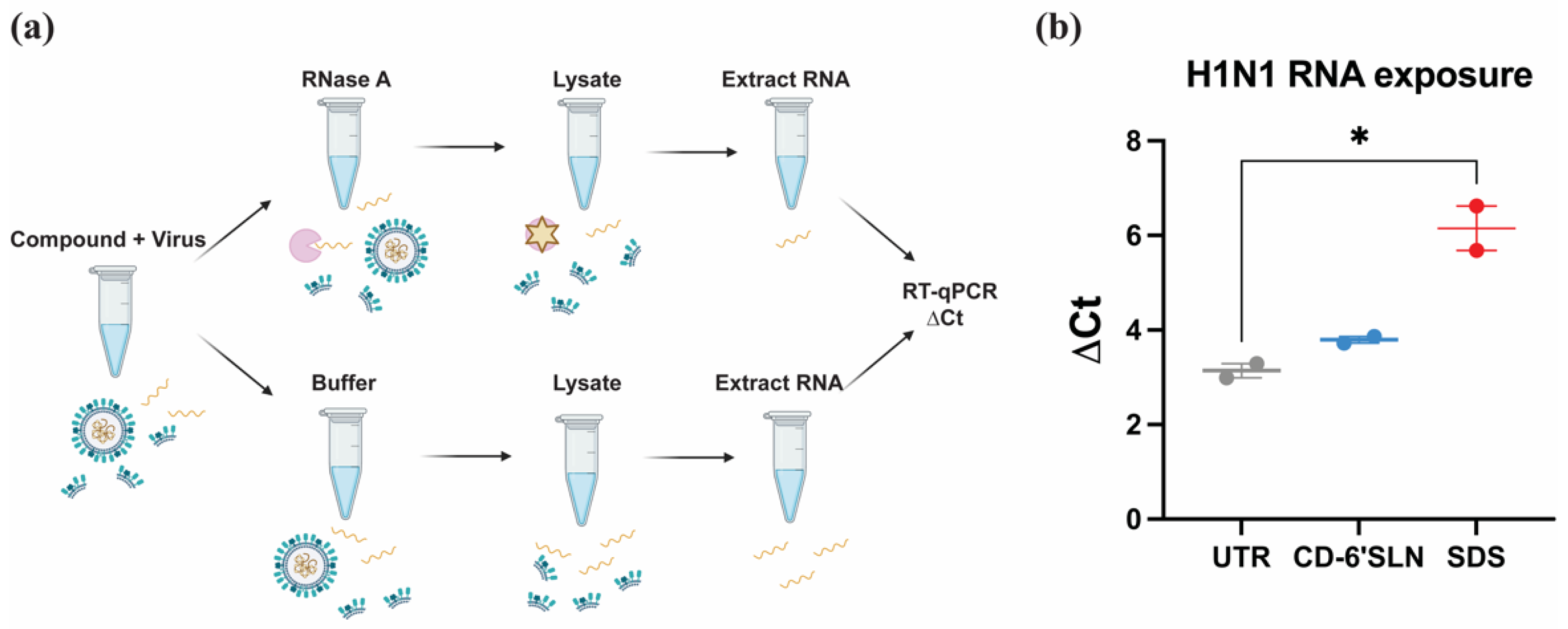
2.6. RNA Exposure Assay
2.7. R18-Labeled H1N1 Preparation
2.8. R18 Release Assay
2.9. H1N1 Virucidal Assay
3. Results
3.1. CD-6′SLN Inhibits H1N1 Virus Primarily through an Extracellular Mechanism
- (i)
- cell pretreatment: CD-6′SLN preincubation with the cells 1 h before cell inoculation with the virus;
- (ii)
- virus pretreatment: CD-6′SLN addition to the virus inoculum 1 h before addition to the cells;
- (iii)
- cotreatment: simultaneous addition of CD-6′SLN and of the viral inoculum to the cells;
- (iv)
- post-treatment: CD-6′SLN addition after viral attachment.
3.2. CD-6′SLN Binds to HA but Not NA
3.3. CD-6′SLN Does Not Release Viral Genome
3.4. CD-6′SLN Affects Viral Envelope
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iuliano, A.D.; Roguski, K.M.; Chang, H.H.; Muscatello, D.J.; Palekar, R.; Tempia, S.; Cohen, C.; Gran, J.M.; Schanzer, D.; Cowling, B.J.; et al. Estimates of global seasonal influenza-associated respiratory mortality: A modelling study. Lancet 2018, 391, 1285–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Świerczyńska, M.; Mirowska-Guzel, D.M.; Pindelska, E. Antiviral Drugs in Influenza. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samson, M.; Pizzorno, M.A.; Abed, Y.; Boivin, G. Influenza virus resistance to neuraminidase inhibitors. Antivir. Res. 2013, 98, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omoto, S.; Speranzini, V.; Hashimoto, T.; Noshi, T.; Yamaguchi, H.; Kawai, M.; Kawaguchi, K.; Uehara, T.; Shishido, T.; Naito, A.; et al. Characterization of influenza virus variants induced by treatment with the endonuclease inhibitor baloxavir marboxil. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, F.G.; Sugaya, N.; Hirotsu, N.; Lee, N.; De Jong, M.D.; Hurt, A.C.; Ishida, T.; Sekino, H.; Yamada, K.; Portsmouth, S.; et al. Baloxavir Marboxil for Uncomplicated Influenza in Adults and Adolescents. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantaleo, G.; Correia, B.; Fenwick, C.; Joo, V.S.; Perez, L. Antibodies to combat viral infections: Development strategies and progress. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 676–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, M.; Umemura, S.; Sugiyama, N.; Kuwano, N.; Koizumi, A.; Sawada, T.; Yanase, M.; Takaha, T.; Kadokawa, J.I.; Usui, T.; et al. Synthesis of multivalent sialyllactosamine-carrying glyco-nanoparticles with high affinity to the human influenza virus hemagglutinin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 153, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamabe, M.; Kaihatsu, K.; Ebara, Y. Sialyllactose-Modified Three-Way Junction DNA as Binding Inhibitor of Influenza Virus Hemagglutinin. Bioconjugate Chem. 2018, 29, 1490–1494. [Google Scholar]
- Stadtmueller, M.N.; Bhatia, S.; Kiran, P.; Hilsch, M.; Reiter-Scherer, V.; Adam, L.; Parshad, B.; Budt, M.; Klenk, S.; Sellrie, K.; et al. Evaluation of Multivalent Sialylated Polyglycerols for Resistance Induction in and Broad Antiviral Activity against Influenza A Viruses. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 12774–12789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.-J.; Na, D.H.; Kwak, J.H.; Douaisi, M.; Zhang, F.; Park, E.J.; Park, J.-H.; Youn, H.; Song, C.-S.; Kane, R.S.; et al. Nanostructured glycan architecture is important in the inhibition of influenza A virus infection. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 12, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasting, C.; Schalley, C.A.; Weber, M.; Seitz, O.; Hecht, S.; Koksch, B.; Dernedde, J.; Graf, C.; Knapp, E.-W.; Haag, R. Multivalency as a Chemical Organization and Action Principle. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 10472–10498. [Google Scholar]
- Pieters, R.J. Maximising multivalency effects in protein–carbohydrate interactions. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009, 7, 2013–2025. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kocabiyik, O.; Cagno, V.; Silva, P.J.; Zhu, Y.; Sedano, L.; Bhide, Y.; Mettier, J.; Medaglia, C.; Da Costa, B.; Constant, S.; et al. Non-Toxic Virucidal Macromolecules Show High Efficacy Against Influenza Virus Ex Vivo and In Vivo. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2001012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.C.; Choudhary, M.; Mourya, A.; Khatri, D.K.; Singh, P.K.; Madan, J.; Singh, H. Acute and Subacute Toxicity Assessment of Andrographolide-2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin Complex via Oral and Inhalation Route of Administration in Sprague-Dawley Rats. Sci. World J. 2022, 2022, 6224107. [Google Scholar]
- Olivier, P.; Verwaerde, F.; Hedges, A.R. Subchronic Toxicity of Orally Administered Beta-Cyclodextrin in Rats. J. Am. Coll. Toxicol. 1991, 10, 407–419. [Google Scholar]
- Furuike, T.; Sadamoto, R.; Niikura, K.; Monde, K.; Sakairi, N.; Nishimura, S.-I. Chemical and enzymatic synthesis of glycocluster having seven sialyl lewis X arrays using β-cyclodextrin as a key scaffold material. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 1737–1742. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, G.N.; Paulson, J.C. Receptor determinants of human and animal influenza virus isolates: Differences in receptor specificity of the H3 hemagglutinin based on species of origin. Virology 1983, 127, 361–373. [Google Scholar]
- Stevens, J.; Blixt, O.; Glaser, L.; Taubenberger, J.K.; Palese, P.; Paulson, J.C.; Wilson, I.A. Glycan Microarray Analysis of the Hemagglutinins from Modern and Pandemic Influenza Viruses Reveals Different Receptor Specificities. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 355, 1143–1155. [Google Scholar]
- Sauter, N.K.; Hanson, J.E.; Glick, G.D.; Brown, J.H.; Crowther, R.L.; Park, S.J.; Skehel, J.J.; Wiley, D.C. Binding of influenza virus hemagglutinin to analogs of its cell-surface receptor, sialic acid: Analysis by proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and x-ray crystallography. Biochemistry 1992, 31, 9609–9621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, N.; Solforosi, L.; Clementi, N.; De Marco, D.; Clementi, M.; Burioni, R. A potential role for monoclonal antibodies in prophylactic and therapeutic treatment of influenza. Antivir. Res. 2011, 92, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, J.N.; McKimm-Breschkin, J.L.; Caldwell, J.B.; Kortt, A.A.; Colman, P.M. The structure of the complex between influenza virus neuraminidase and sialic acid, the viral receptor. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 1992, 14, 327–332. [Google Scholar]
- de Vries, E.; Du, W.; Guo, H.; de Haan, C.A.M. Influenza a Virus Hemagglutinin–Neuraminidase–Receptor Balance: Preserving Virus Motility. Trends Microbiol. 2020, 28, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matrosovich, M.N.; Matrosovich, T.Y.; Gray, T.; Roberts, N.A.; Klenk, H.-D. Neuraminidase Is Important for the Initiation of Influenza Virus Infection in Human Airway Epithelium. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 12665–12667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAuley, J.L.; Gilbertson, B.; Trifkovic, S.; Brown, L.E.; McKimm-Breschkin, J.L. Influenza Virus Neuraminidase Structure and Functions. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.T.; Cagno, V.; Janeček, M.; Ortiz, D.; Gasilova, N.; Piret, J.; Gasbarri, M.; Constant, D.A.; Han, Y.; Vuković, L.; et al. Modified cyclodextrins as broad-spectrum antivirals. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaax9318. [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra, D.; De Boer, T.; Klappe, K.; Wilschut, J. Fluorescence method for measuring the kinetics of fusion between biological membranes. Biochemistry 1984, 23, 5675–5681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colpitts, C.C.; Schang, L.M. A Small Molecule Inhibits Virion Attachment to Heparan Sulfate- or Sialic Acid-Containing Glycans. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 7806–7817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, M.D.; Warren, S.; Hughes, C.; Lewis, P.; Zhang, F. Human genetic risk of treatment with antiviral nucleoside analog drugs that induce lethal mutagenesis: The special case of molnupiravir. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2022, 63, 37–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassine, I.H.; Ben M’Hadheb, M.; Menéndez-Arias, L. Lethal Mutagenesis of RNA Viruses and Approved Drugs with Antiviral Mutagenic Activity. Viruses 2022, 14, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, D.H. Teratogenicity risk of antiretroviral therapy in pregnancy. Curr. HIV/AIDS Rep. 2007, 4, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matrosovich, M.; Klenk, H.-D. Natural and synthetic sialic acid-containing inhibitors of influenza virus receptor binding. Rev. Med. Virol. 2003, 13, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, D.H.; Marcelletti, J.R.; Pope, L.E.; Khalil, M.H.; Katz, L.R.; McFadden, R. n-Docosanol: Broad Spectrum Anti-Viral Activity against Lipid-enveloped Viruses. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1994, 724, 472–488. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pope, L.E.; Marcelletti, J.F.; Katz, L.R.; Katz, D.H. Anti-herpes simplex virus activity of n-docosanol correlates with intracellular metabolic conversion of the drug. J. Lipid Res. 1996, 37, 2167–2178. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pope, L.E.; Marcelletti, J.F.; Katz, L.R.; Lin, J.Y.; Katz, D.H.; Parish, M.L.; Spear, P.G. The anti-herpes simplex virus activity of n-docosanol includes inhibition of the viral entry process. Antivir. Res. 1998, 40, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Sysoev, A.A.; Silva, P.H.J.; Batista, M.; Stellacci, F. Antiviral Mechanism of Virucidal Sialic Acid Modified Cyclodextrin. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15020582
Zhu Y, Sysoev AA, Silva PHJ, Batista M, Stellacci F. Antiviral Mechanism of Virucidal Sialic Acid Modified Cyclodextrin. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(2):582. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15020582
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yong, Andrey A. Sysoev, Paulo H. Jacob Silva, Marine Batista, and Francesco Stellacci. 2023. "Antiviral Mechanism of Virucidal Sialic Acid Modified Cyclodextrin" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 2: 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15020582
APA StyleZhu, Y., Sysoev, A. A., Silva, P. H. J., Batista, M., & Stellacci, F. (2023). Antiviral Mechanism of Virucidal Sialic Acid Modified Cyclodextrin. Pharmaceutics, 15(2), 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15020582






