Sinonasal Stent Coated with Sustained-Release Varnish of Mometasone Furoate Inhibits Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Release from Macrophages: An In Vitro Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sustained-Release Varnish (SRV) Preparation
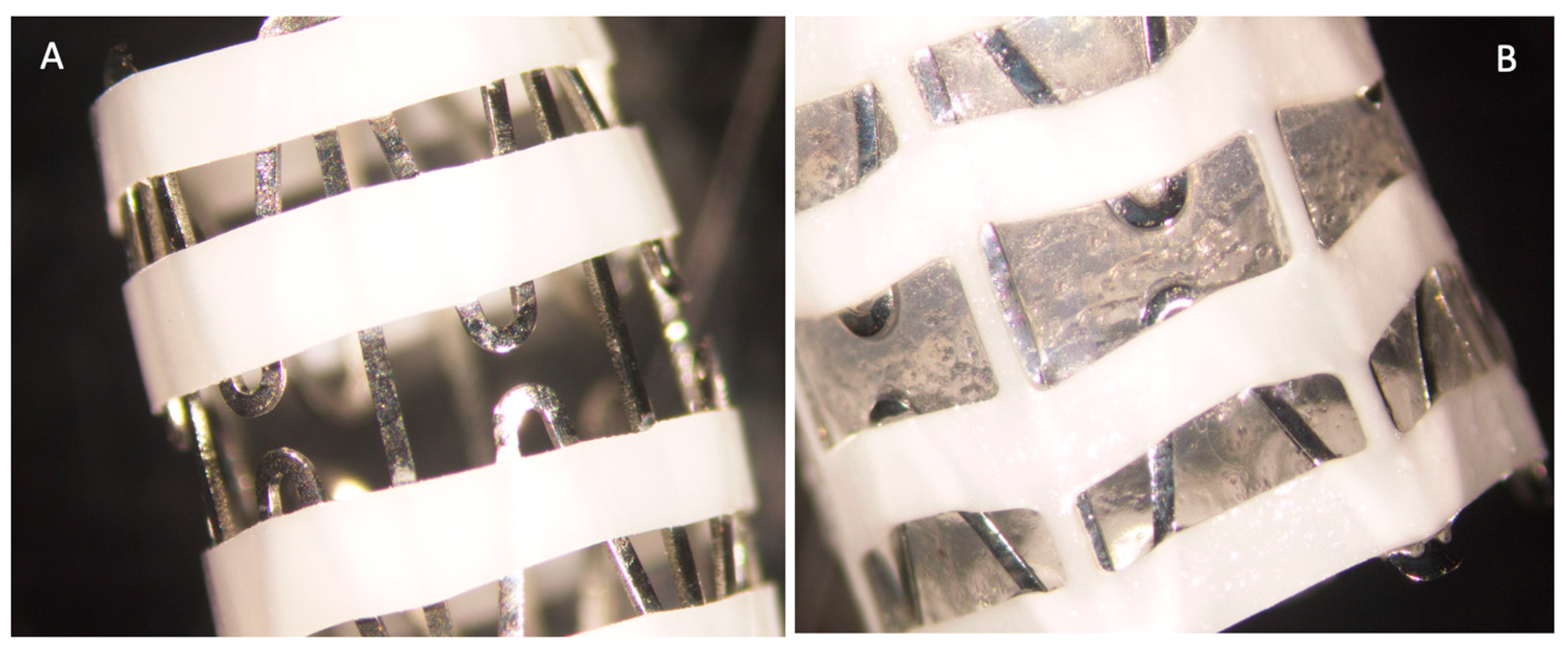
2.2. Coating of the Stents
2.3. Measuring the Biological Activity of MMF Using Different Cellular In Vitro Systems
2.3.1. RAW 264.7 Cell Cultures
2.3.2. A549 Lung Carcinoma Cells
2.3.3. PLB-985 Myeloid Leukemia Cells
2.4. Measuring the Biological Activity of the MMF Released from the Coated Stent
2.5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) of Cytokines
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Mometasone Furoate (MMF)
3.1.1. The Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Mometasone Furoate on PLB-985 Neutrophil-like Cells
3.1.2. The Inhibitory Effect of Mometasone Furoate on IL-1β-Induced GM-CSF Production in A549 Lung Carcinoma Cells
3.1.3. The Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Mometasone Furoate on RAW264.7 Macrophages
3.2. The Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Mometasone Furoate Released from SRV-MMF-Coated Sinonasal Stents
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Albu, S. Chronic Rhinosinusitis-An Update on Epidemiology, Pathogenesis and Management. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfeld, R.M.; Andes, D.; Bhattacharyya, N.; Cheung, D.; Eisenberg, S.; Ganiats, T.G.; Gelzer, A.; Hamilos, D.; Haydon, R.C., 3rd; Hudgins, P.A.; et al. Clinical practice guideline: Adult sinusitis. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2007, 137, S1–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fokkens, W.J.; Lund, V.J.; Hopkins, C.; Hellings, P.W.; Kern, R.; Reitsma, S.; Toppila-Salmi, S.; Bernal-Sprekelsen, M.; Mullol, J. Executive summary of EPOS 2020 including integrated care pathways. Rhinology 2020, 58, 82–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, J.W.; Zhao, J.F.; Li, X.L.; Liao, B.; Pan, L.; Zhu, K.Z.; Feng, Q.M.; Liu, J.X.; Yu, Z.E.; Song, J.; et al. Characterizing the Neutrophilic Inflammation in Chronic Rhinosinusitis With Nasal Polyps. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 793073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Zhou, B.; Wang, D.; Zang, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Cheng, L.; Li, J.; Wu, W.; et al. Comparison of Bioabsorbable Steroid-Eluting Sinus Stents Versus Nasopore After Endoscopic Sinus Surgery: A Multicenter, Randomized, Controlled, Single-Blinded Clinical Trial. Ear Nose Throat J. 2022, 101, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goshtasbi, K.; Abouzari, M.; Abiri, A.; Yasaka, T.; Sahyouni, R.; Bitner, B.; Tajudeen, B.A.; Kuan, E.C. Efficacy of steroid-eluting stents in management of chronic rhinosinusitis after endoscopic sinus surgery: Updated meta-analysis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2019, 9, 1443–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, A.; Ow, R.A.; Singh, A.; Weiss, R.L.; Han, J.K.; Gerencer, R.; Stolovitzky, J.P.; Stambaugh, J.W.; Raman, A. Safety and Effectiveness of a Bioabsorbable Steroid-Releasing Implant for the Paranasal Sinus Ostia: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 144, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, R.C.; Stolovitzky, J.P.; Silvers, S.L.; Singh, A.; Lee, J.T.; Yen, D.M.; Iloreta, A.M.C., Jr.; Langford, F.P.J.; Karanfilov, B.; Matheny, K.E.; et al. A phase 3 trial of mometasone furoate sinus implants for chronic sinusitis with recurrent nasal polyps. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2018, 8, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narwani, V.; Torabi, S.J.; Kasle, D.A.; Patel, R.A.; Lerner, M.Z.; Manes, R.P. Adverse Events Associated With Corticosteroid-Eluting Sinus Stents: A MAUDE Database Analysis. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2022, 166, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atri, C.; Guerfali, F.Z.; Laouini, D. Role of Human Macrophage Polarization in Inflammation during Infectious Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, A.; Schleimer, R.P.; Bleier, B.S. Mechanisms and pathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 149, 1491–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Li, Z.Y.; Jiang, W.X.; Liao, B.; Zhai, G.T.; Wang, N.; Zhen, Z.; Ruan, J.W.; Long, X.B.; Wang, H.; et al. The activation and function of IL-36γ in neutrophilic inflammation in chronic rhinosinusitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1646–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, W.; Liu, W.; Zhang, L.; Bai, J.; Fan, Y.; Xia, W.; Luo, Q.; Zheng, J.; Wang, H.; Li, Z.; et al. Increased neutrophilia in nasal polyps reduces the response to oral corticosteroid therapy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 129, 1522–1528.e1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bruaene, N.; Pérez-Novo, C.A.; Basinski, T.M.; Van Zele, T.; Holtappels, G.; De Ruyck, N.; Schmidt-Weber, C.; Akdis, C.; Van Cauwenberge, P.; Bachert, C.; et al. T-cell regulation in chronic paranasal sinus disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 121, 1435–1441.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kountakis, S.E.; Arango, P.; Bradley, D.; Wade, Z.K.; Borish, L. Molecular and cellular staging for the severity of chronic rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope 2004, 114, 1895–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, T.; Yoshikawa, M.; Asaka, D.; Okushi, T.; Matsuwaki, Y.; Otori, N.; Hama, T.; Moriyama, H. Mucosal eosinophilia and recurrence of nasal polyps— New classification of chronic rhinosinusitis. Rhinology 2011, 49, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitoma, H.; Horiuchi, T.; Tsukamoto, H.; Ueda, N. Molecular mechanisms of action of anti-TNF-α agents—Comparison among therapeutic TNF-α antagonists. Cytokine 2018, 101, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohori, J.; Ushikai, M.; Sun, D.; Nishimoto, K.; Sagara, Y.; Fukuiwa, T.; Matsune, S.; Kurono, Y. TNF-alpha upregulates VCAM-1 and NF-kappaB in fibroblasts from nasal polyps. Auris Nasus Larynx 2007, 34, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomassen, P.; Vandeplas, G.; Van Zele, T.; Cardell, L.O.; Arebro, J.; Olze, H.; Förster-Ruhrmann, U.; Kowalski, M.L.; Olszewska-Ziąber, A.; Holtappels, G.; et al. Inflammatory endotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis based on cluster analysis of biomarkers. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 1449–1456.e1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.K.; Kok, S.H.; Shun, C.T.; Hong, C.Y.; Wang, C.C.; Hsu, M.C.; Liu, C.M. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha stimulates the expression of C-C chemokine ligand 2 gene in fibroblasts from the human nasal polyp through the pathways of mitogen-activated protein kinase. Am. J. Rhinol. 2007, 21, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheller, J.; Ohnesorge, N.; Rose-John, S. Interleukin-6 trans-signalling in chronic inflammation and cancer. Scand. J. Immunol. 2006, 63, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, A.T.; Kato, A.; Zhang, N.; Conley, D.B.; Suh, L.; Tancowny, B.; Carter, D.; Carr, T.; Radtke, M.; Hulse, K.E.; et al. Evidence for altered activity of the IL-6 pathway in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 397–403.e310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bequignon, E.; Mangin, D.; Bécaud, J.; Pasquier, J.; Angely, C.; Bottier, M.; Escudier, E.; Isabey, D.; Filoche, M.; Louis, B.; et al. Pathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: Role of IL-6 in airway epithelial cell dysfunction. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, S.S.; Cheng, G. Role of interleukin 10 transcriptional regulation in inflammation and autoimmune disease. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 32, 23–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Han, R.; Kim, D.W.; Mo, J.H.; Jin, Y.; Rha, K.S.; Kim, Y.M. Role of Interleukin-10 on Nasal Polypogenesis in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okano, M.; Fujiwara, T.; Kariya, S.; Haruna, T.; Higaki, T.; Noyama, Y.; Makihara, S.; Kanai, K.; Nishizaki, K. Staphylococcal protein A-formulated immune complexes suppress enterotoxin-induced cellular responses in nasal polyps. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 343–350.e348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, M.; Golomb, G. New sustained release dosage form of chlorhexidine for dental use. I. Development and kinetics of release. J. Periodontal Res. 1982, 17, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tweedie, D.; Luo, W.; Short, R.G.; Brossi, A.; Holloway, H.W.; Li, Y.; Yu, Q.S.; Greig, N.H. A cellular model of inflammation for identifying TNF-alpha synthesis inhibitors. J. Neurosci. Methods 2009, 183, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagoshima, M.; Wilcke, T.; Ito, K.; Tsaprouni, L.; Barnes, P.J.; Punchard, N.; Adcock, I.M. Glucocorticoid-mediated transrepression is regulated by histone acetylation and DNA methylation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 429, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, R.; King, E.M.; Gong, W.; Rider, C.F.; Staples, K.J.; Holden, N.S.; Bergmann, M.W. Glucocorticoids inhibit IL-1beta-induced GM-CSF expression at multiple levels: Roles for the ERK pathway and repression by MKP-1. Biochem. J. 2010, 427, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedruzzi, E.; Fay, M.; Elbim, C.; Gaudry, M.; Gougerot-Pocidalo, M.A. Differentiation of PLB-985 myeloid cells into mature neutrophils, shown by degranulation of terminally differentiated compartments in response to N-formyl peptide and priming of superoxide anion production by granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Br. J. Haematol. 2002, 117, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sionov, R.V.; Assi, S.; Gershkovitz, M.; Sagiv, J.Y.; Polyansky, L.; Mishalian, I.; Fridlender, Z.G.; Granot, Z. Isolation and Characterization of Neutrophils with Anti-Tumor Properties. J. Vis. Exp. 2015, 100, e52933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volk, A.P.; Barber, B.M.; Goss, K.L.; Ruff, J.G.; Heise, C.K.; Hook, J.S.; Moreland, J.G. Priming of neutrophils and differentiated PLB-985 cells by pathophysiological concentrations of TNF-α is partially oxygen dependent. J. Innate Immun. 2011, 3, 298–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiomi, A.; Usui, T. Pivotal roles of GM-CSF in autoimmunity and inflammation. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 568543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Jimenez, D.; Kolb, J.P.; Cidlowski, J.A. Glucocorticoids as Regulators of Macrophage-Mediated Tissue Homeostasis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 669891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, D.; Friedman, M. Development of sustained-release devices for modulation of dental plaque biofilm and treatment of oral infectious diseases. Drug Dev. Res. 2000, 50, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldo Russomando, A.; Vogt Sionov, R.; Friedman, M.; Gati, I.; Eliashar, R.; Steinberg, D.; Gross, M. Sinonasal Stent Coated with Slow-Release Varnish of Chlorhexidine Has Sustained Protection against Bacterial Biofilm Growth in the Sinonasal Cavity: An In Vitro Study. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Succar, E.F.; Turner, J.H.; Chandra, R.K. Nasal saline irrigation: A clinical update. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2019, 9, S4–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grayson, J.W.; Harvey, R.J. Topical corticosteroid irrigations in chronic rhinosinusitis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2019, 9, S9–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, K.M.; Hoehle, L.P.; Caradonna, D.S.; Gray, S.T.; Sedaghat, A.R. Intranasal corticosteroids and saline: Usage and adherence in chronic rhinosinusitis patients. Laryngoscope 2020, 130, 852–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, D.W. The PROPEL™ steroid-releasing bioabsorbable implant to improve outcomes of sinus surgery. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2012, 6, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanjickal, D.G.; Lopina, S.T. Modeling of drug release from polymeric delivery systems--a review. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 2004, 21, 345–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerninski, R.; Finfter, O.; Nudelman, Z.; Tal, Y.; Kirmayer, D.; Friedman, M. Overnight use of oral appliance with sirolimus sustained-release varnish delivery system—A clinical note and an observational study. Quintessence Int. 2023, 54, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, D.; Friedman, M. Sustained-release drug delivery of antimicrobials in controlling of supragingival oral biofilms. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2017, 14, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, B.E.; Jakway, J.P.; Smith, S.R.; Siegel, M.I. Cytokine inhibition by a novel steroid, mometasone furoate. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 1991, 13, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackland, G.L.; Gutierrez Del Arroyo, A.; Yao, S.T.; Stephens, R.C.; Dyson, A.; Klein, N.J.; Singer, M.; Gourine, A.V. Low-molecular-weight polyethylene glycol improves survival in experimental sepsis. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 38, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siepmann, J.; Peppas, N.A. Mathematical modeling of controlled drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 48, 137–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, J.; Lee, K.; Kim, T.H. Current Perspective on Nasal Delivery Systems for Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cataldo Russomando, A.; Steinberg, D.; Gati, I.; Vogt Sionov, R.; Eliashar, R.; Friedman, M.; Gross, M. Sinonasal Stent Coated with Sustained-Release Varnish of Mometasone Furoate Inhibits Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Release from Macrophages: An In Vitro Study. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15031015
Cataldo Russomando A, Steinberg D, Gati I, Vogt Sionov R, Eliashar R, Friedman M, Gross M. Sinonasal Stent Coated with Sustained-Release Varnish of Mometasone Furoate Inhibits Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Release from Macrophages: An In Vitro Study. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(3):1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15031015
Chicago/Turabian StyleCataldo Russomando, Alessandra, Doron Steinberg, Irith Gati, Ronit Vogt Sionov, Ron Eliashar, Michael Friedman, and Menachem Gross. 2023. "Sinonasal Stent Coated with Sustained-Release Varnish of Mometasone Furoate Inhibits Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Release from Macrophages: An In Vitro Study" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 3: 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15031015
APA StyleCataldo Russomando, A., Steinberg, D., Gati, I., Vogt Sionov, R., Eliashar, R., Friedman, M., & Gross, M. (2023). Sinonasal Stent Coated with Sustained-Release Varnish of Mometasone Furoate Inhibits Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Release from Macrophages: An In Vitro Study. Pharmaceutics, 15(3), 1015. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15031015





