Reduction-Hypersensitive Podophyllotoxin Prodrug Self-Assembled Nanoparticles for Cancer Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
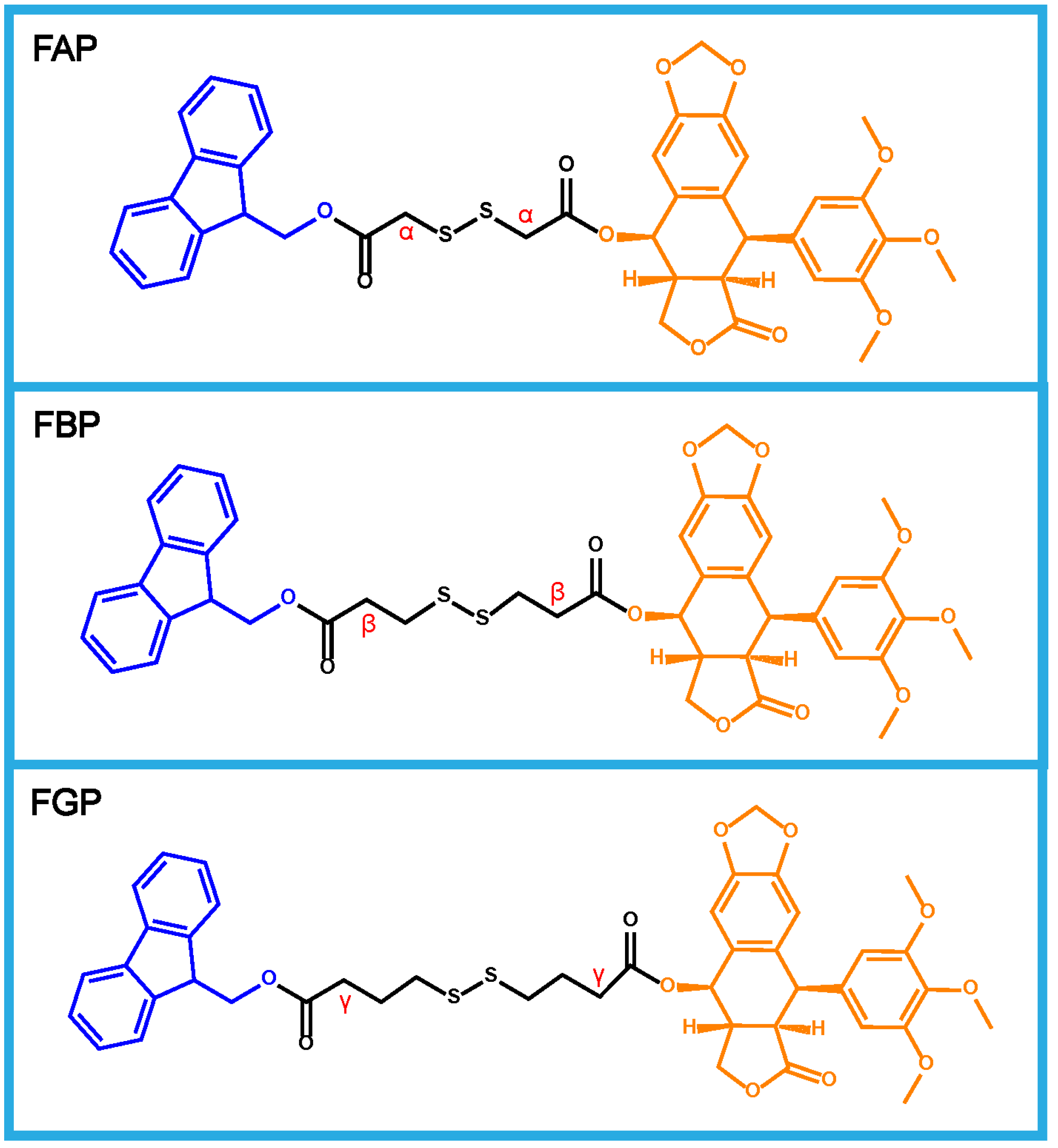
2.2. Synthesis of Prodrugs
2.3. Preparation and Characterization of Prodrug NPs
2.4. Molecular Docking Simulation
2.5. Colloid Stability
2.6. In Vitro Reduction-Responsive Release
2.7. Cell Culture
2.8. Cellular Uptake
2.9. Cytotoxicity
2.10. Animal Studies
2.11. Pharmacokinetics Studies
2.12. Biodistribution
2.13. Maximum Tolerated Dose and Hemolysis Test
2.14. In Vivo Antitumor Activity
2.15. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Design and Synthesis of Prodrugs
3.2. Preparation and Characterization of Prodrug NPs
3.3. Molecular Docking Simulation
3.4. Colloid Stability
3.5. In Vitro Reduction-Responsive Release
3.6. Cellular Uptake
3.7. Cytotoxicity
3.8. Pharmacokinetics Studies
3.9. Biodistribution
3.10. Maximum Tolerated Dose and Hemolysis Test
3.11. In Vivo Antitumor Efficacy
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giaquinto, A.N.; Miller, K.D.; Tossas, K.Y.; Winn, R.A.; Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.L. Cancer statistics for African American/Black People 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 202–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Fan, T.; An, J.; Choi, W.; Duo, Y.; Ge, Y.; Zhang, B.; Nie, G.; Xie, N.; Zheng, T.; et al. Emerging combination strategies with phototherapy in cancer nanomedicine. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 8065–8087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, Z.; Rahim, M.A.; Jan, N.; Shah, H.; Rawas-Qalaji, M.; Khan, S.; Sohail, M.; Thu, H.E.; Ramli, N.A.; Sarfraz, R.M.; et al. Cell membrane cloaked nanomedicines for bio-imaging and immunotherapy of cancer: Improved pharmacokinetics, cell internalization and anticancer efficacy. J. Control. Release 2021, 335, 130–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldoghachi, A.F.; Aldoghachi, A.F.; Breyne, K.; Ling, K.H.; Cheah, P.S. Recent Advances in the Therapeutic Strategies of Glioblastoma Multiforme. Neuroscience 2022, 491, 240–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Lin, L.; Guo, Z.; Chen, J.; Maruyama, A.; Tian, H.; Chen, X. In situ vaccination and gene-mediated PD-L1 blockade for enhanced tumor immunotherapy. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 1770–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, W.; Chu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, N. A review on nano-based drug delivery system for cancer chemoimmunotherapy. Nano-Micro Lett. 2020, 12, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Zhou, Z.G.; Xiong, W.; Chen, J.S.; Shen, J.L.; Li, R.T.; Ye, R.R. Tumor microenvironment triggered local oxygen generation and photosensitizer release from manganese dioxide mineralized albumin-ICG nanocomplex to amplify photodynamic immunotherapy efficacy. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 3948–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behranvand, N.; Nasri, F.; Zolfaghari Emameh, R.; Khani, P.; Hosseini, A.; Garssen, J.; Falak, R. Chemotherapy: A double-edged sword in cancer treatment. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2022, 71, 507–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.Y.; Jia, K.Y.; Sun, K.; Zhang, L.M.; Wang, Z.F. Smart responsive nanoplatform via in situ forming disulfiram-copper ion chelation complex for cancer combination chemotherapy. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 415, 128947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Zeng, W.; Wang, C.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, L.; Zhu, X.; Ke, Y.; He, X.; Kuang, Y.; Huang, Q. A step-by-step multiple stimuli-responsive metal-phenolic network prodrug nanoparticles for chemotherapy. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 1205–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarvarian, P.; Samadi, P.; Gholipour, E.; Shams Asenjan, K.; Hojjat-Farsangi, M.; Motavalli, R.; Motavalli Khiavi, F.; Yousefi, M. Application of emerging plant-derived nanoparticles as a novel approach for nano-drug delivery systems. Immunol. Investig. 2022, 51, 1039–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, X.; Jiang, X.; Li, Y.; Han, W.; Rodriguez, M.; Xu, Z.; Lin, W. Sequential Treatment of Bioresponsive Nanoparticles Elicits Antiangiogenesis and Apoptosis and Synergizes with a CD40 Agonist for Antitumor Immunity. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 765–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, S.; Gu, K.; Guo, Z.; Huang, X.; Wang, M.; Amin, H.M.; Zhu, W.; Shi, P. GSH-Activated NIR Fluorescent Prodrug for Podophyllotoxin Delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 29496–29504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Ernsting, M.J.; Undzys, E.; Li, S.D. A highly tumor-targeted nanoparticle of podophyllotoxin penetrated tumor core and regressed multidrug resistant tumors. Biomaterials 2015, 52, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, R.; Xuan, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, W.; Ma, P.; Ju, B.; Zhen, Y.; Zhang, S. Cationic Nanoparticulate System for Codelivery of MicroRNA-424 and Podophyllotoxin as a Multimodal Anticancer Therapy. Mol. Pharm. 2022, 19, 2092–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, W.; Xuan, Y.; Zhen, Y.; Ju, B.; Guo, S.; Zhang, S. Self-Assembly of Podophyllotoxin-Loaded Lipid Bilayer Nanoparticles for Highly Effective Chemotherapy and Immunotherapy via Downregulation of Programmed Cell Death Ligand 1 Production. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 3943–3954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Lv, S.; Zhang, D.; Deng, M.; Zhang, X.; Tang, Z.; Chen, X. A polypeptide based podophyllotoxin conjugate for the treatment of multi drug resistant breast cancer with enhanced efficiency and minimal toxicity. Acta Biomater. 2018, 73, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, Z.; Gohar, U.F.; Jamshed, I.; Mushtaq, A.; Mukhtar, H.; Zia-Ui-Haq, M.; Toma, S.I.; Manea, R.; Moga, M.; Popovici, B. Podophyllotoxin: History, Recent Advances and Future Prospects. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.S.; Li, X.Y.; Lu, Y.; Hou, M.L.; Xu, Z.G.; Li, B.S. A thiol-responsive and self-immolative podophyllotoxin prodrug for cancer therapy. Tetrahedron. Lett. 2021, 71, 153044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Liu, F.; Tao, B.; Sun, S. GSH-responsive anti-mitotic cell penetrating peptide-linked podophyllotoxin conjugate for improving water solubility and targeted synergistic drug delivery. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Szeitz, A.; Klassen, T.; Li, S.D. Selective targeting and therapy of metastatic and multidrug resistant tumors using a long circulating podophyllotoxin nanoparticle. Biomaterials 2017, 137, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Chen, Q.; He, Z.; Luo, C.; Sun, J. Smart transformable nanomedicines for cancer therapy. Biomaterials 2021, 271, 120737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, X.; Li, S.; Sun, B.; Chen, Q.; Sun, J.; He, Z.; Luo, C. Ferroptosis-driven nanotherapeutics for cancer treatment. J. Control. Release 2020, 319, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.; Sun, J.; Liu, D.; Sun, B.; Miao, L.; Musetti, S.; Li, J.; Han, X.; Du, Y.; Li, L.; et al. Self-Assembled Redox Dual-Responsive Prodrug-Nanosystem Formed by Single Thioether-Bridged Paclitaxel-Fatty Acid Conjugate for Cancer Chemotherapy. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 5401–5408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, R.H.; Liu, Z.N.; Liu, T.; Yuan, P.Y.; Bai, Y.K.; Chen, X. Redox-responsive micelles integrating catalytic nanomedicine and selective chemotherapy for effective tumor treatment. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 3076–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, C.; Wei, T.; Gayet, O.; Loncle, C.; Borge, L.; Dusetti, N.; Ma, X.; Marson, D.; Laurini, E. Dendrimeric nanosystem consistently circumvents heterogeneous drug response and resistance in pancreatic cancer. Exploration 2021, 1, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Han, Y.; Sun, Q.; Li, Z. Harnessing anti-tumor and tumor-tropism functions of macrophages via nanotechnology for tumor immunotherapy. Exploration 2022, 2, 20210166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, P.H.L.; Tran, T.T.D. Nano-sized Solid Dispersions for Improving the Bioavailability of Poorly Water-soluble Drugs. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2020, 26, 4917–4924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karole, A.; Parvez, S.; Thakur, R.S.; Mudavath, S.L. Effervescent based nano-gas carrier enhanced the bioavailability of poorly aqueous soluble drug: A comprehensive mechanistic understanding. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 69, 103167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Chandrawanshi, N.; Jain, V. Surfactant-Based Anhydrous Nano Carrier System for Poorly Aqueous Soluble Anti-Cancer Drugs. In Handbook of Research on Advancements in Cancer Therapeutics; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2021; pp. 413–432. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.S.; Renner, F.; Azizighannad, S.; Mitra, S. Direct incorporation of nano graphene oxide (nGO) into hydrophobic drug crystals for enhanced aqueous dissolution. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 189, 110827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Huang, F.; Li, B.; Miao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y. Dual-light triggered metabolizable nano-micelles for selective tumor-targeted photodynamic/hyperthermia therapy. Acta Biomater. 2021, 119, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, F.; Zafar, H.; Zhang, S.L.; Kamal, Z.; Su, J.; Yuan, W.E.; Qiu, M.F. Recent Advances in Cell Membrane-Derived Biomimetic Nanotechnology for Cancer Immunotherapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2002081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.Y.; Cheng, Q.; Ye, J.J.; Zhang, M.K.; Zhang, C.; Gao, F.; Ding, X.L.; Feng, J.; Zhang, X.Z. Establishment of Facile Nanomedicine Construction Methodology to Comprehensively Overcome Hurdles across Tumor-Specific Nano-Delivery. Adv. Func. Mater. 2020, 30, 2002239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirtane, A.R.; Verma, M.; Karandikar, P.; Furin, J.; Langer, R.; Traverso, G. Nanotechnology approaches for global infectious diseases. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oroojalian, F.; Charbgoo, F.; Hashemi, M.; Amani, A.; Yazdian-Robati, R.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Ramezani, M.; Hamblin, M.R. Recent advances in nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems for the kidney. J. Control. Release 2020, 321, 442–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alphandéry, E. Nano-therapies for glioblastoma treatment. Cancers 2020, 12, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gu, X.; Gao, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, L.; Peng, H.; He, Y.; Liu, Y.; Feng, N. Nano-delivery systems focused on tumor microenvironment regulation and biomimetic strategies for treatment of breast cancer metastasis. J. Control. Release 2021, 333, 374–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Qiu, Q.; Liao, R.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; He, Z.; Zhang, S.; Luo, C. Modularly engineered prodrug-nanoassemblies for cancer therapy: Nonpharmacological moiety dominating delivery fates. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 980–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, C.; Zhou, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, S.; Wang, S.; Sun, B.; He, Z. Investigating the crucial roles of aliphatic tails in disulfide bond-linked docetaxel prodrug nanoassemblies. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 16, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Ma, X.B.; Yang, Q.C.; Yang, L.L.; Yang, S.C.; Liang, M.Y.; Xu, Z.G.; Sun, Z.J. Microenvironment-Responsive Prodrug-Induced Pyroptosis Boosts Cancer Immunotherapy. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2101840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, X.Z.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Wang, C.; Sun, J.; He, Z.G.; Luo, C.; Zhang, S.W. Emerging Prodrug-Engineered nanomedicines for synergistic Chemo-Phototherapy. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 442, 136383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zou, H.; Mu, J.Q.; Yu, N.; Xu, Y.; Liu, G.H.; Liang, X.J.; Guo, S.T. Acid-sensitive PEGylated cabazitaxel prodrugs for antitumor therapy. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 1751–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Hu, J.J.; Dai, J.; Lou, X.; Zhao, Z.; Xia, F.; Tang, B.Z. Self-Guiding Polymeric Prodrug Micelles with Two Aggregation-Induced Emission Photosensitizers for Enhanced Chemo-Photodynamic Therapy. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 3026–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Luo, C.; Yu, H.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Q.; Yang, W.; Wang, M.; Kan, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; et al. Disulfide bond-driven oxidation-and reduction-responsive prodrug nanoassemblies for cancer therapy. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 3643–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; Qiu, Q.; Liao, R.; Zhang, S.; Luo, C. Reduction-Hypersensitive Podophyllotoxin Prodrug Self-Assembled Nanoparticles for Cancer Treatment. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 784. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030784
Wang X, Wang Y, Yu J, Qiu Q, Liao R, Zhang S, Luo C. Reduction-Hypersensitive Podophyllotoxin Prodrug Self-Assembled Nanoparticles for Cancer Treatment. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(3):784. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030784
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xinhui, Yuequan Wang, Jiaxin Yu, Qian Qiu, Rui Liao, Shenwu Zhang, and Cong Luo. 2023. "Reduction-Hypersensitive Podophyllotoxin Prodrug Self-Assembled Nanoparticles for Cancer Treatment" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 3: 784. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030784
APA StyleWang, X., Wang, Y., Yu, J., Qiu, Q., Liao, R., Zhang, S., & Luo, C. (2023). Reduction-Hypersensitive Podophyllotoxin Prodrug Self-Assembled Nanoparticles for Cancer Treatment. Pharmaceutics, 15(3), 784. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030784





