LC-MS/MS Method for the Quantification of PARP Inhibitors Olaparib, Rucaparib and Niraparib in Human Plasma and Dried Blood Spot: Development, Validation and Clinical Validation for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring
Abstract
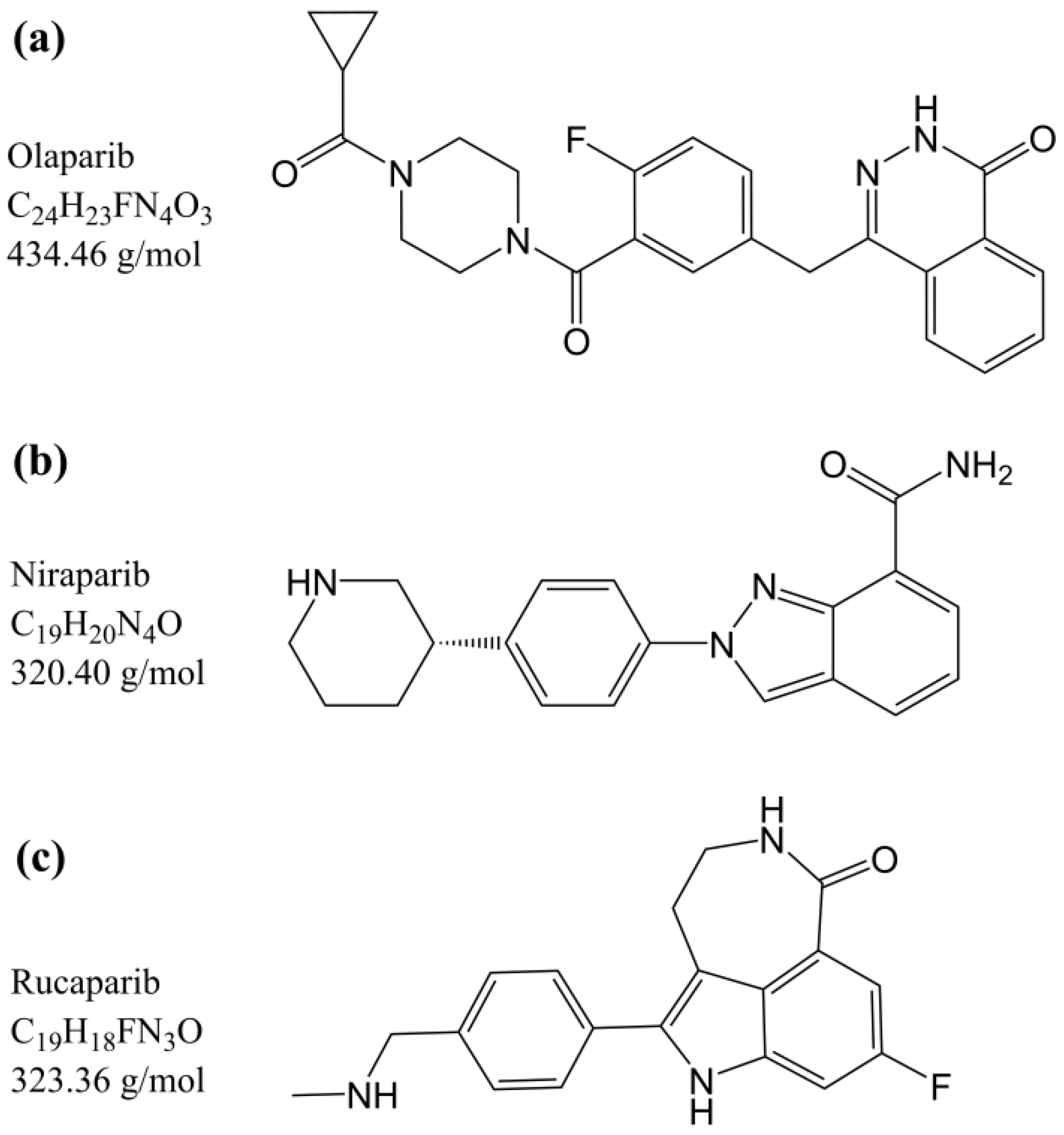
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Used
2.2. Stock and Working Solutions
2.3. Human Plasma Sample Preparation
2.4. DBS Sample Preparation
2.5. Chromatographic and Mass Spectrometric Conditions
2.6. Validation of the Method in Human Plasma
2.6.1. Linearity
2.6.2. Accuracy and Precision
2.6.3. Recovery and Matrix Effect
2.6.4. Selectivity and Sensitivity
2.6.5. Dilution Integrity and Stability
2.7. Validation of the Method in DBS
2.7.1. Hematocrit Effect
2.7.2. Recovery and Matrix Effect
2.7.3. Carryover and Stability
2.8. Clinical Validation
2.9. Incurred Sample Reanalysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Development and Optimization of the LC-MS/MS Method
3.2. Validation of the Method in Human Plasma
3.2.1. Linearity
3.2.2. Accuracy and Precision
3.2.3. Recovery and Matrix Effect
3.2.4. Selectivity and Sensitivity
3.2.5. Dilution Integrity and Stability
3.3. Validation of the Method in DBS
3.3.1. Linearity
3.3.2. Accuracy and Precision
3.3.3. Hematocrit Effect
3.3.4. Recovery and Matrix Effect
3.3.5. Selectivity and Sensitivity
3.3.6. Carryover and Stability
3.4. Clinical Validation
3.5. Incurred Sample Reanalysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Groenland, S.L.; Mathijssen, R.H.J.; Beijnen, J.H.; Huitema, A.D.R.; Steeghs, N. Individualized dosing of oral targeted therapies in oncology is crucial in the era of precision medicine. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 75, 1309–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller-Schoell, A.; Groenland, S.L.; Scherf-Clavel, O.; van Dyk, M.; Huisinga, W.; Michelet, R.; Jaehde, U.; Steeghs, N.; Huitema, A.D.R.; Kloft, C. Therapeutic drug monitoring of oral targeted antineoplastic drugs. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 77, 441–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruin, M.A.C.; Sonke, G.S.; Beijnen, J.H.; Huitema, A.D.R. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of PARP Inhibitors in Oncology. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2022, 61, 1649–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Center for Drug Evaluation and Research Multi Disciplinary Review, Olaparib (Capsules) 2014 (Application Number 206162Orig1s000). Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2014/206162Orig1s000MedR.pdf (accessed on 4 May 2022).
- US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Center for Drug Evaluation and Research Multi Disciplinary Review, Olaparib (Tablets) 2016 (Application Number 208558Orig1s000). Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2017/208558Orig1s000MultidisciplineR.pdf (accessed on 4 May 2022).
- US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Center for Drug Evaluation and Research Multi Disciplinary Review, Rucaparib 2016 (Application Number 209115Orig1s000). Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2016/209115Orig1s000MultiDisciplineR.pdf (accessed on 4 May 2022).
- US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Center for Drug Evaluation and Research Multi Disciplinary Review, Niraparib 2016 (Application Number 208447Orig1s000). Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2017/208447orig1s000multidiscipliner.pdf (accessed on 4 May 2022).
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), Lynparza Capsules, Public Assessment Report; Procedure Number EMEA/H/C/003726/0000; EMA: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), Lynparza Tablets, Public Assessment Report; Procedure Number EMEA/H/C/003726/X/0016/G; EMA: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), Rubraca Public Assessment Report; Procedure Number EMEA/H/C/004272/0000; EMA: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), Zejula Public Assessment Report; Procedure Number EMEA/H/C/004249/0000; EMA: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Curtin, N.J.; Szabo, C. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibition: Past, present and future. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 711–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schettini, F.; Giudici, F.; Bernocchi, O.; Sirico, M.; Corona, S.P.; Giuliano, M.; Locci, M.; Paris, I.; Scambia, G.; De Placido, S.; et al. Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors in solid tumours: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 149, 134–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pressiat, C.; Huynh, H.-H.; Plé, A.; Sauvageon, H.; Madelaine, I.; Chougnet, C.; Le Maignan, C.; Mourah, S.; Goldwirt, L. Development and Validation of a Simultaneous Quantification Method of Ruxolitinib, Vismodegib, Olaparib, and Pazopanib in Human Plasma Using Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Ther. Drug Monit. 2018, 40, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolibois, J.; Schmitt, A.; Royer, B. A simple and fast LC-MS/MS method for the routine measurement of cabozantinib, olaparib, palbociclib, pazopanib, sorafenib, sunitinib and its main active metabolite in human plasma. J. Chromatogr. B 2019, 1132, 121844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruin, M.A.C.; de Vries, N.; Lucas, L.; Rosing, H.; Huitema, A.D.R.; Beijnen, J.H. Development and validation of an integrated LC-MS/MS assay for therapeutic drug monitoring of five PARP-inhibitors. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2020, 1138, 121925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krens, S.D.; van der Meulen, E.; Jansman, F.G.A.; Burger, D.M.; van Erp, N.P. Quantification of cobimetinib, cabozantinib, dabrafenib, niraparib, olaparib, vemurafenib, regorafenib and its metabolite regorafenib M2 in human plasma by UPLC-MS/MS. Biomed. Chromatogr. BMC 2020, 34, e4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaparib FDA Prescribing Information. Revised May 2020. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/208558s014lbl.pdf (accessed on 31 August 2022).
- Niraparib FDA Prescribing Information. Revised April 2020. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/208447s015s017lbledt.pdf (accessed on 31 August 2022).
- Rucaparib FDA Prescribing Information. Revised May 2020. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2020/209115s004lbl.pdf (accessed on 31 August 2022).
- Talazoparib FDA Prescribing Information. Revised October 2018. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2018/211651s000lbl.pdf (accessed on 31 August 2022).
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP), Talzenna Public Assessment Report; Procedure Number EMEA/H/C/004674/0000; EMA: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Center for Drug Evaluation and Research Multi Disciplinary Review, Talazoparib 2018 (Application Number 211651Orig1s000). Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2018/211651Orig1s000MultidisciplineR.pdf (accessed on 31 August 2022).
- Orleni, M.; Canil, G.; Posocco, B.; Gagno, S.; Toffoli, G. Bioanalytical Methods for Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase Inhibitor Quantification: A Review for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. Ther. Drug Monit. 2023, 43, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, P.C.; Boss, D.S.; Yap, T.A.; Tutt, A.; Wu, P.; Mergui-Roelvink, M.; Mortimer, P.; Swaisland, H.; Lau, A.; O’Connor, M.J.; et al. Inhibition of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase in tumors from BRCA mutation carriers. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, S.K.; Schelman, W.R.; Wilding, G.; Moreno, V.; Baird, R.D.; Miranda, S.; Hylands, L.; Riisnaes, R.; Forster, M.; Omlin, A.; et al. The poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor niraparib (MK4827) in BRCA mutation carriers and patients with sporadic cancer: A phase 1 dose-escalation trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 882–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swisher, E.M.; Lin, K.K.; Oza, A.M.; Scott, C.L.; Giordano, H.; Sun, J.; Konecny, G.E.; Coleman, R.L.; Tinker, A.V.; O’Malley, D.M.; et al. Rucaparib in relapsed, platinum-sensitive high-grade ovarian carcinoma (ARIEL2 Part 1): An international, multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Li, J.; Learoyd, M.; Bui, K.; Berges, A.; Milenkova, T.; Al-Huniti, N.; Tomkinson, H.; Xu, H. Efficacy and Safety Exposure-Response Analyses of Olaparib Capsule and Tablet Formulations in Oncology Patients. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 105, 1492–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Mirza, M.R.; Gilbert, L.; Fabbro, M.; Tinker, A.V.; Wang, X.; Redondo, A.; Berek, J.S.; Woelber, L.; et al. The exposure-response relationship of niraparib in patients with gBRCAmut and non-gBRCAmut: Results from the ENGOT-OV16/NOVA Trial. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, v331–v332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verheijen, R.B.; Yu, H.; Schellens, J.H.M.; Beijnen, J.H.; Steeghs, N.; Huitema, A.D.R. Practical Recommendations for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Kinase Inhibitors in Oncology. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 102, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, M.V.; Raymundo, S.; de Oliveira, V.; Staudt, D.E.; Gössling, G.; Peteffi, G.P.; Biazús, J.V.; Cavalheiro, J.A.; Tre-Hardy, M.; Capron, A.; et al. Ultra-high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometric method for the determination of tamoxifen, N -desmethyltamoxifen, 4-hydroxytamoxifen and endoxifen in dried blood spots—Development, validation and clinical application during breast cancer adjuvant therapy. Talanta 2015, 132, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poetto, A.S.; Posocco, B.; Gagno, S.; Orleni, M.; Zanchetta, M.; Iacuzzi, V.; Canil, G.; Buzzo, M.; Montico, M.; Guardascione, M.; et al. A new dried blood spot LC-MS/MS method for therapeutic drug monitoring of palbociclib, ribociclib, and letrozole in patients with cancer. J. Chromatogr. B 2021, 1185, 122985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braal, C.L.; Lam, M.H.; Rienks, T.; van Tilborg, C.J.; Heuts, W.; Heijns, J.B.; Bos, M.E.M.M.; Mathijssen, R.H.J.; de Bruijn, P.; Koolen, S.L.W. Quantification of ribociclib in dried blood spots by LC–MS/MS: Method development and clinical validation. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 201, 114118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nuland, M.; Rosing, H.; Schellens, J.H.M.; Beijnen, J.H. Bioanalytical LC–MS/MS validation of therapeutic drug monitoring assays in oncology. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2020, 34, e4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, R.A.; Alffenaar, J.-W.C.; Botma, R.; Greijdanus, B.; Touw, D.J.; Uges, D.R.; Kosterink, J.G. What is the right blood hematocrit preparation procedure for standards and quality control samples for dried blood spot analysis? Bioanalysis 2015, 7, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency (EMA); Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP). Guideline on Bioanalytical Method Validation. 2011. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/guideline-bioanalytical-method-validation_en.pdf (accessed on 12 August 2022).
- US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Center for Drug Evaluation and Research Bioanalytical Method Validation Guidance for Industry. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/files/drugs/published/Bioanalytical-Method-Validation-Guidance-for-Industry.pdf (accessed on 12 August 2022).
- Almeida, A.M.; Castel-Branco, M.M.; Falcão, A.C. Linear regression for calibration lines revisited: Weighting schemes for bioanalytical methods. J. Chromatogr. B 2002, 774, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capiau, S.; Veenhof, H.; Koster, R.A.; Bergqvist, Y.; Boettcher, M.; Halmingh, O.; Keevil, B.G.; Koch, B.C.P.; Linden, R.; Pistos, C.; et al. Official International Association for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring and Clinical Toxicology Guideline: Development and Validation of Dried Blood Spot–Based Methods for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. Ther. Drug Monit. 2019, 41, 409–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matuszewski, B.K.; Constanzer, M.L.; Chavez-Eng, C.M. Strategies for the Assessment of Matrix Effect in Quantitative Bioanalytical Methods Based on HPLC−MS/MS. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 3019–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- TD2010IDCR; Identification Criteria for Qualitative Assays Incorporating Column Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry. WADA Laboratory Committee: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2010.
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Center for Veterinary Medicine, Guidance for Industry. Mass Spectrometry for Confirmation of the Identity of Animal Drug Resides. 2003. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/cvm-gfi-118-mass-spectrometry-confirmation-identity-animal-drug-residues (accessed on 12 August 2022).
- Sparidans, R.W.; Martens, I.; Valkenburg-van Iersel, L.B.J.; den Hartigh, J.; Schellens, J.H.M.; Beijnen, J.H. Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometric assay for the PARP-1 inhibitor olaparib in combination with the nitrogen mustard melphalan in human plasma. J. Chromatogr. B 2011, 879, 1851–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijenhuis, C.M.; Lucas, L.; Rosing, H.; Schellens, J.H.M.; Beijnen, J.H. Development and validation of a high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry assay quantifying olaparib in human plasma. J. Chromatogr. B 2013, 940, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparidans, R.W.; Durmus, S.; Schinkel, A.H.; Schellens, J.H.M.; Beijnen, J.H. Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometric assay for the PARP inhibitor rucaparib in plasma. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 88, 626–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Andel, L.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, S.; Kansra, V.; Agarwal, S.; Hughes, L.; Tibben, M.M.; Gebretensae, A.; Rosing, H.; Schellens, J.H.M.; et al. Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry assay for the quantification of niraparib and its metabolite M1 in human plasma and urine. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1040, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthelette, K.D.; Swann, T. Increased Retention of Polar Analytes Using CORTECS T3 Columns. Available online: https://www.waters.com/webassets/cms/library/docs/720005946en.pdf (accessed on 23 August 2022).
- Dolan, J.W. 2002-5. Peak Tailing and Resolution. Available online: https://lctsbible.com/2002/05/01/peak-tailing-and-resolution/ (accessed on 17 April 2023).
- Snyder, L.R.; Kirkland, J.J.; Dolan, J.W. Introduction to Modern Liquid Chromatography; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-0-470-50818-3. [Google Scholar]
- Ralston, P.B.; Strein, T.G. A Study of Deproteinization Methods for Subsequent Serum Analysis with Capillary Electrophoresis. Microchem. J. 1997, 55, 270–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polson, C.; Sarkar, P.; Incledon, B.; Raguvaran, V.; Grant, R. Optimization of protein precipitation based upon effectiveness of protein removal and ionization effect in liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2003, 785, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfiglio, R.; King, R.C.; Olah, T.V.; Merkle, K. The effects of sample preparation methods on the variability of the electrospray ionization response for model drug compounds. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 1999, 13, 1175–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kesel, P.M.; Capiau, S.; Lambert, W.E.; Stove, C.P. Current strategies for coping with the hematocrit problem in dried blood spot analysis. Bioanalysis 2014, 6, 1871–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacuzzi, V.; Posocco, B.; Zanchetta, M.; Gagno, S.; Poetto, A.S.; Guardascione, M.; Toffoli, G. Dried Blood Spot Technique Applied in Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Anticancer Drugs: A Review on Conversion Methods to Correlate Plasma and Dried Blood Spot Concentrations. Pharm. Res. 2021, 38, 759–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.; Watkins, S.; Nash, E.; Isaacson, J.; Etter, J.; Beltman, J.; Fan, R.; Shen, L.; Mutlib, A.; Kemeny, V.; et al. Evaluation of absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of [14C]-rucaparib, a poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Investig. New Drugs 2020, 38, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited. Report on the Deliberation Results; Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency: Tokyo, Japan, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Berezhkovskiy, L.M.; Zhang, X.; Cheong, J. A Convenient Method to Measure Blood–Plasma Concentration Ratio Using Routine Plasma Collection in In Vivo Pharmacokinetic Studies. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 5293–5298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Concentration Level | Concentration (ng/mL) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Olaparib | Rucaparib | Niraparib | |
| H | 140 | 100 | 60 |
| G | 280 | 200 | 120 |
| F | 700 | 500 | 300 |
| E | 1400 | 1000 | 600 |
| D | 2800 | 2000 | 1200 |
| C | 4200 | 3000 | 1800 |
| B | 5600 | 4000 | 2400 |
| A | 7000 | 5000 | 3000 |
| QC L | 357 | 255 | 153 |
| QC M | 2380 | 1700 | 1020 |
| QC H | 5950 | 4250 | 2550 |
| Analyte | Nominal Concentration (ng/mL) | Within-Run (n = 5) | Between-Run (n = 15) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Concentration (ng/mL) | CV% | Acc% | Mean Concentration (ng/mL) | CV% | Acc% | ||
| rucaparib | 100 | 87 | 6 | 87 | 96 | 8 | 96 |
| 255 | 250 | 7 | 98 | 259 | 7 | 101 | |
| 1700 | 1708 | 7 | 100 | 1732 | 4 | 102 | |
| 4250 | 4190 | 5 | 99 | 4289 | 4 | 101 | |
| niraparib | 60 | 61 | 2 | 101 | 60 | 3 | 101 |
| 153 | 155 | 5 | 101 | 156 | 3 | 102 | |
| 1020 | 1043 | 2 | 102 | 1044 | 2 | 102 | |
| 2460 | 2442 | 2 | 96 | 2460 | 3 | 96 | |
| olaparib | 140 | 139 | 3 | 99 | 143 | 4 | 102 |
| 357 | 356 | 2 | 100 | 358 | 3 | 100 | |
| 2380 | 2361 | 3 | 99 | 2386 | 3 | 100 | |
| 5950 | 5802 | 3 | 98 | 5810 | 3 | 98 | |
| Analyte | Nominal Concentration (ng/mL) | %Rec (n = 5) | CV% | ISN-MF (n = 7) | CV% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rucaparib | 255 | 101 | 8 | 1.02 | 4 |
| 1700 | 98 | 3 | - | - | |
| 4250 | 99 | 2 | 0.98 | 2 | |
| niraparib | 153 | 98 | 2 | 1.06 | 2 |
| 1020 | 99 | 1 | - | - | |
| 2460 | 98 | 3 | 0.97 | 2 | |
| olaparib | 357 | 101 | 2 | 0.94 | 1 |
| 2380 | 103 | 3 | - | - | |
| 5950 | 103 | 3 | 0.96 | 2 |
| Analyte | Nominal Concentration (ng/mL) | 5 h at RT (n = 3) | 5 Days in Autosampler Conditions (Final Extract at 15 °C, Dark) (n = 3) | 6 Freeze–Thaw Cycles (n = 3) | 194 Days at −80 °C (n = 3) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Concentration (ng/mL) | CV% | Acc% | Mean Concentration (ng/mL) | CV% | Acc% | Mean Concentration (ng/mL) | CV% | Acc% | Mean Concentration (ng/mL) | CV% | Acc% | ||
| rucaparib | 255 | 254 | 5 | 100 | 259 | 6 | 102 | 270 | 4 | 106 | 251 | 6 | 98 |
| 4250 | 4325 | 7 | 102 | 4321 | 1 | 102 | 4432 | 1 | 104 | 4273 | 3 | 101 | |
| niraparib | 153 | 159 | 4 | 104 | 155 | 3 | 101 | 153 | 3 | 100 | 151 | 4 | 99 |
| 2550 | 2477 | 2 | 97 | 2406 | 1 | 94 | 2458 | 2 | 96 | 2388 | 1 | 94 | |
| olaparib | 357 | 347 | 3 | 97 | 335 | 1 | 94 | 377 | 2 | 106 | 357 | 1 | 100 |
| 5950 | 5846 | 2 | 98 | 5549 | 1 | 93 | 6077 | 2 | 102 | 5860 | 1 | 98 | |
| Analyte | Nominal Concentration (ng/mL) | Within-Run (n = 5) | Between-Run (n = 15) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Concentration (ng/mL) | CV% | Acc% | Mean Concentration (ng/mL) | CV% | Acc% | ||
| rucaparib | 100 | 95 | 6 | 95 | 96 | 5 | 96 |
| 255 | 255 | 3 | 100 | 258 | 3 | 101 | |
| 1700 | 1784 | 3 | 105 | 1761 | 3 | 104 | |
| 4250 | 4402 | 4 | 104 | 4353 | 5 | 102 | |
| niraparib | 60 | 60 | 3 | 101 | 59 | 4 | 98 |
| 153 | 149 | 2 | 98 | 149 | 3 | 97 | |
| 1020 | 1026 | 3 | 101 | 1009 | 3 | 99 | |
| 2460 | 2483 | 3 | 97 | 2418 | 3 | 95 | |
| olaparib | 140 | 132 | 2 | 94 | 140 | 5 | 100 |
| 357 | 338 | 2 | 95 | 350 | 4 | 98 | |
| 2380 | 2373 | 2 | 100 | 2376 | 3 | 100 | |
| 5950 | 5859 | 1 | 98 | 5918 | 3 | 99 | |
| Analyte | Nominal Concentration (ng/mL) | 29% Hct (n = 3) | 45% Hct (n = 3) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Concentration (ng/mL) | CV% | Acc% | Mean Concentration (ng/mL) | CV% | Acc% | ||
| rucaparib | 100 | 108 | 9 | 108 | 102 | 2 | 102 |
| 255 | 291 | 3 | 114 | 259 | 7 | 101 | |
| 1700 | 1917 | 3 | 113 | 1791 | 5 | 105 | |
| 4250 | 4797 | 4 | 113 | 4617 | 3 | 109 | |
| niraparib | 60 | 63 | 4 | 105 | 57 | 6 | 96 |
| 153 | 176 | 4 | 115 | 150 | 9 | 98 | |
| 1020 | 1143 | 2 | 112 | 1060 | 3 | 104 | |
| 2460 | 2894 | 4 | 113 | 2641 | 1 | 104 | |
| olaparib | 140 | 156 | 6 | 112 | 150 | 3 | 107 |
| 357 | 376 | 3 | 105 | 366 | 2 | 103 | |
| 2380 | 2497 | 3 | 105 | 2283 | 1 | 96 | |
| 5950 | 6473 | 5 | 109 | 5734 | 4 | 96 | |
| Analyte | Nominal Concentration (ng/mL) | %Rec (n = 24) | CV% | ISN-MF (n = 24) | CV% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rucaparib | 255 | 66 | 8 | 1.17 | 5 |
| 1700 | 68 | 8 | 1.14 | 6 | |
| 4250 | 66 | 4 | 1.14 | 5 | |
| niraparib | 153 | 56 | 10 | 1.36 | 7 |
| 1020 | 56 | 6 | 1.38 | 8 | |
| 2460 | 57 | 5 | 1.35 | 8 | |
| olaparib | 357 | 93 | 7 | 1.06 | 7 |
| 2380 | 94 | 6 | 1.03 | 8 | |
| 5950 | 92 | 6 | 1.02 | 7 |
| Analyte | Nominal Concentration (ng/mL) | 14 Days in Autosampler Conditions (Final Extract at 15 °C, Dark) (n = 3) | 219 Days in Desiccator Conditions (20 °C, Humidity < 35%) (n = 3) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Concentration (ng/mL) | CV% | Acc% | Mean Concentration (ng/mL) | CV% | Acc% | ||
| rucaparib | 255 | 257 | 2 | 101 | 252 | 1 | 99 |
| 4250 | 4336 | 5 | 102 | 4018 | 4 | 95 | |
| niraparib | 153 | 147 | 5 | 96 | 141 | 1 | 92 |
| 2550 | 2330 | 1 | 91 | 2301 | 3 | 90 | |
| olaparib | 357 | 356 | 6 | 100 | 368 | 1 | 103 |
| 5950 | 5964 | 3 | 100 | 6104 | 1 | 103 | |
| Analyte | CF | Passing–Bablok Regression | Lin’s CCC | Bland–Altman Analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slope (95% CI) | Intercept (95% CI) * | Cusum Test | Bias (95% CI) * | SD * | Spearman Correlation | |||
| rucaparib | 1.427 | 0.90 (0.73–1.17) | 92 (−284–385) | p > 0.05 | 0.935 | −16 (−129–97) | 212 | rS = −0.2399 (p = 0.37) |
| niraparib | 1.440 | 1.02 (0.95–1.07) | −5 (−31–15) | p > 0.05 | 0.960 | 0 (−22–22) | 71 | rS = −0.0991 (p = 0.53) |
| olaparib | 0.718 | 1.00 (0.97–1.03) | 1 (−34–30) | p > 0.05 | 0.995 | −1 (−30–28) | 104 | rS = 0.0489 (p = 0.73) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Canil, G.; Orleni, M.; Posocco, B.; Gagno, S.; Bignucolo, A.; Montico, M.; Roncato, R.; Corsetti, S.; Bartoletti, M.; Toffoli, G. LC-MS/MS Method for the Quantification of PARP Inhibitors Olaparib, Rucaparib and Niraparib in Human Plasma and Dried Blood Spot: Development, Validation and Clinical Validation for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1524. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15051524
Canil G, Orleni M, Posocco B, Gagno S, Bignucolo A, Montico M, Roncato R, Corsetti S, Bartoletti M, Toffoli G. LC-MS/MS Method for the Quantification of PARP Inhibitors Olaparib, Rucaparib and Niraparib in Human Plasma and Dried Blood Spot: Development, Validation and Clinical Validation for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(5):1524. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15051524
Chicago/Turabian StyleCanil, Giovanni, Marco Orleni, Bianca Posocco, Sara Gagno, Alessia Bignucolo, Marcella Montico, Rossana Roncato, Serena Corsetti, Michele Bartoletti, and Giuseppe Toffoli. 2023. "LC-MS/MS Method for the Quantification of PARP Inhibitors Olaparib, Rucaparib and Niraparib in Human Plasma and Dried Blood Spot: Development, Validation and Clinical Validation for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 5: 1524. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15051524
APA StyleCanil, G., Orleni, M., Posocco, B., Gagno, S., Bignucolo, A., Montico, M., Roncato, R., Corsetti, S., Bartoletti, M., & Toffoli, G. (2023). LC-MS/MS Method for the Quantification of PARP Inhibitors Olaparib, Rucaparib and Niraparib in Human Plasma and Dried Blood Spot: Development, Validation and Clinical Validation for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. Pharmaceutics, 15(5), 1524. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15051524






