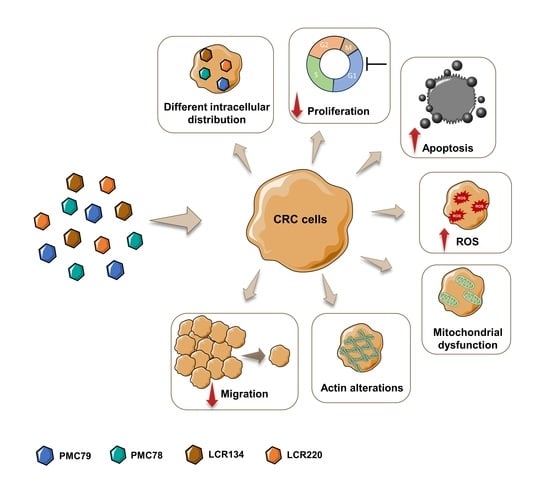
New Ruthenium-Cyclopentadienyl Complexes Affect Colorectal Cancer Hallmarks Showing High Therapeutic Potential
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
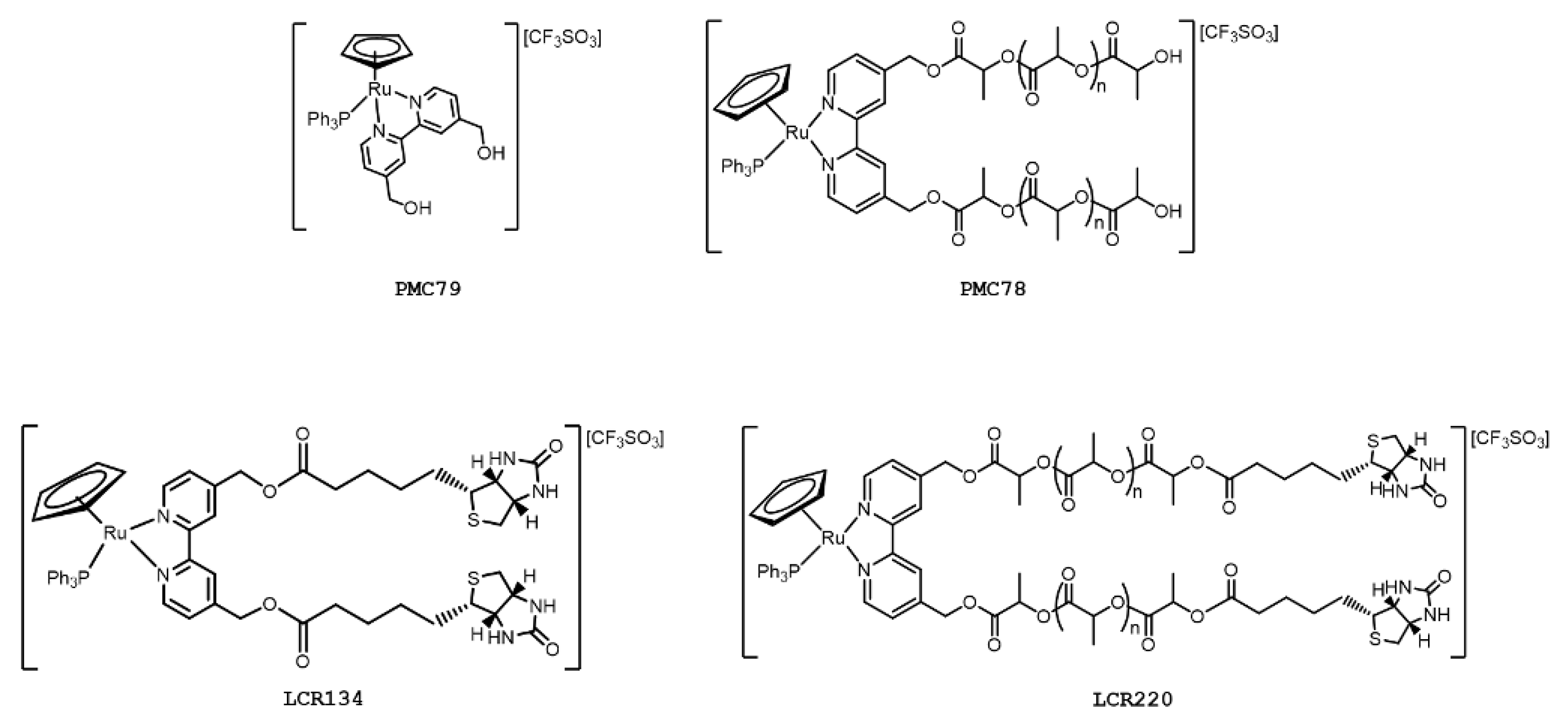
2.1. Compounds under Study
2.2. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
2.3. Compounds Dilution and Storage
2.4. Cell Viability Analysis Using Sulforhodamine B Assay
2.5. Intracellular Distribution Measured Using Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry
2.6. Colony Formation Assay
2.7. Proliferation Assessment Using Carboxyfluorescein Diacetate Succinimidyl Ester Labeling
2.8. Cell Cycle Analysis Using Flow Cytometry
2.9. Detection of DNA Strand Breaks Using Terminal Transferase dUTP Nick End Labeling Assay
2.10. Cell Death Evaluation Using Annexin V/Propidium Iodide Assay
2.11. Determination of Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species Using Dihydroethidium Assay
2.12. Analysis of Mitochondrial Mass and Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Alterations Using Flow Cytometry
2.13. Evaluation of Alterations in F-Actin Cytoskeleton Using Phalloidin Staining
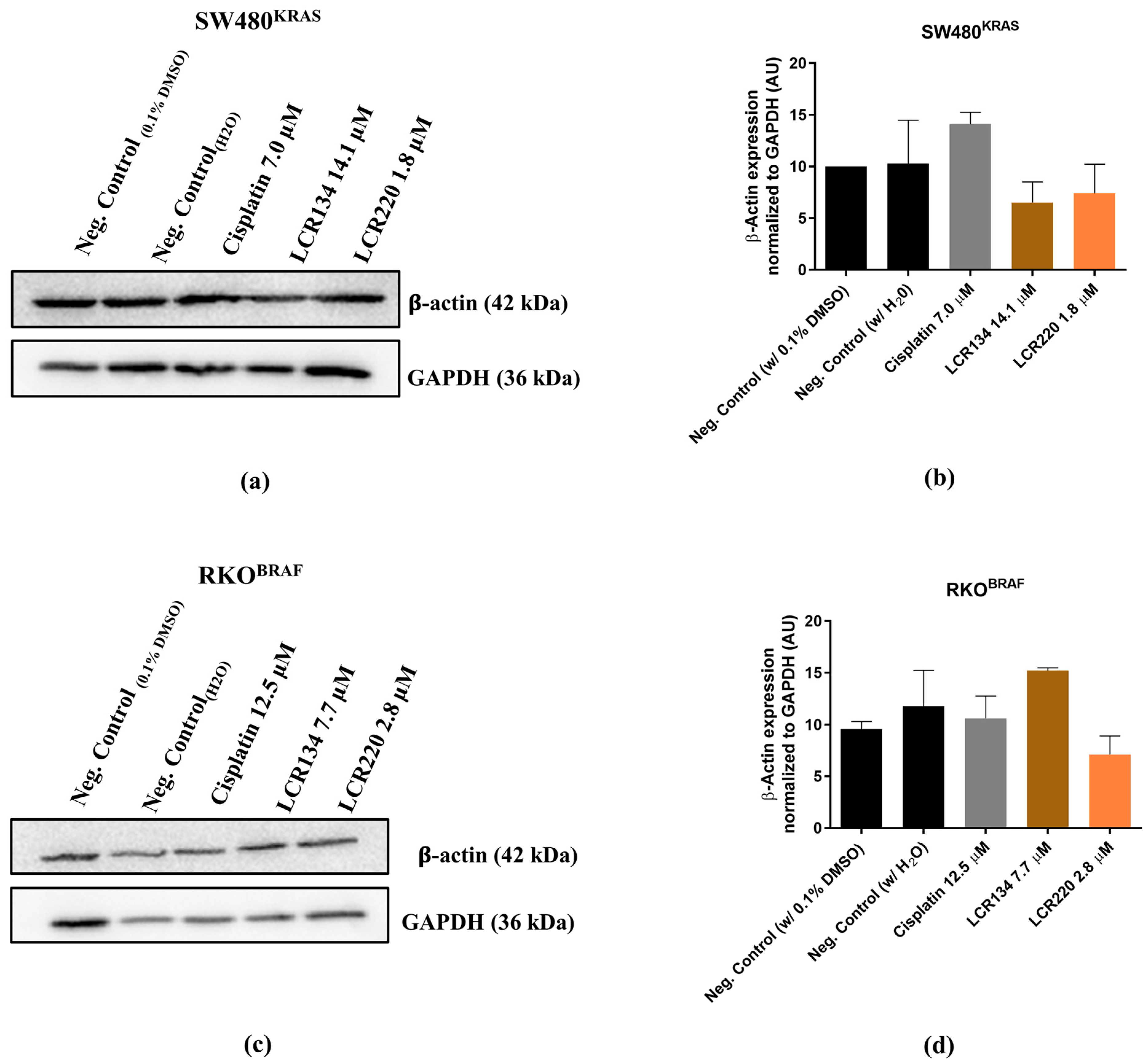
2.14. Western Blot Analysis
2.15. Cellular Motility Assessment Using Wound Healing Assay
2.16. Proteomic Study
2.17. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
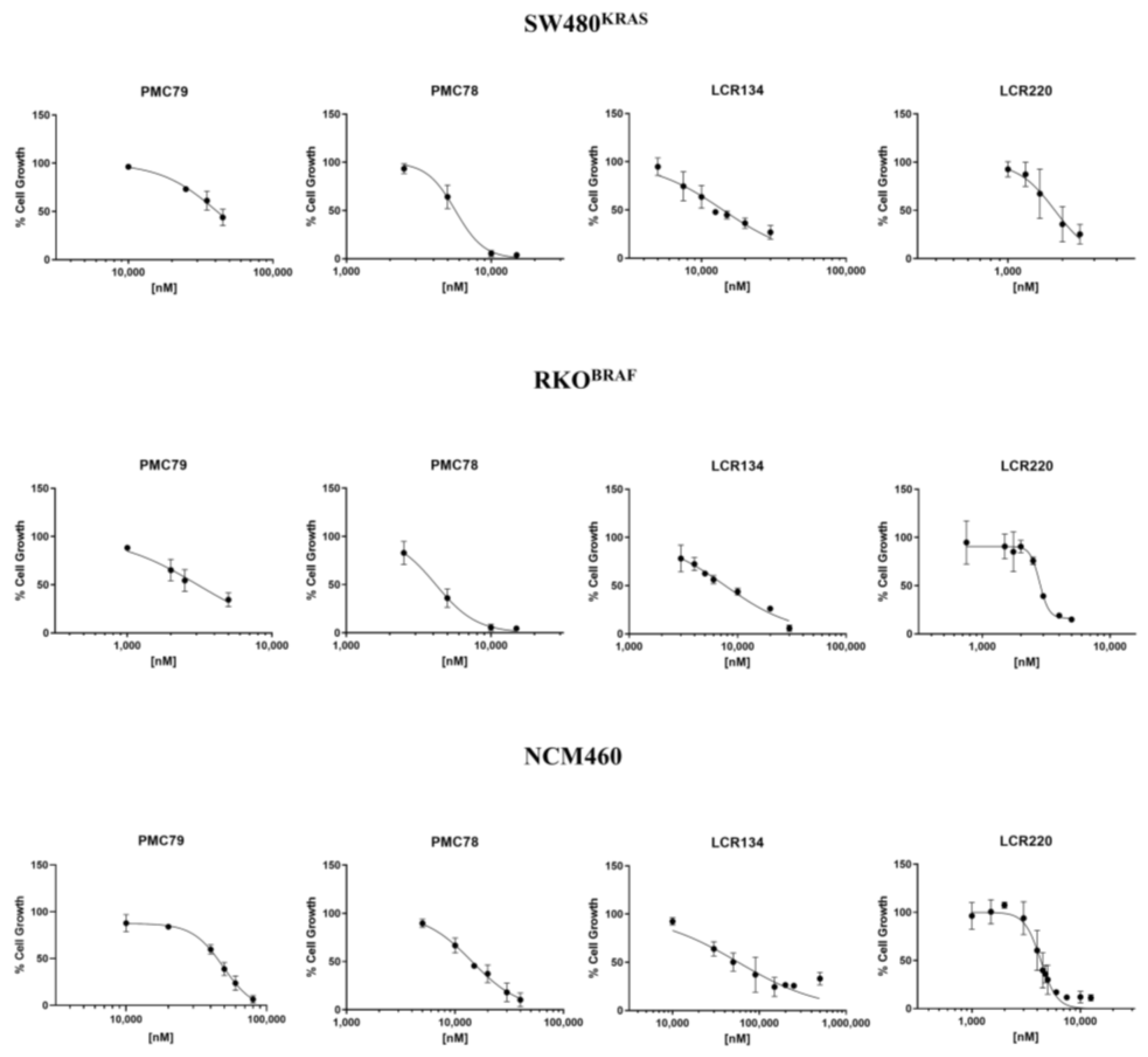
3.1. Ru Compounds Decrease Cell Growth of CRC Cells at Low Doses
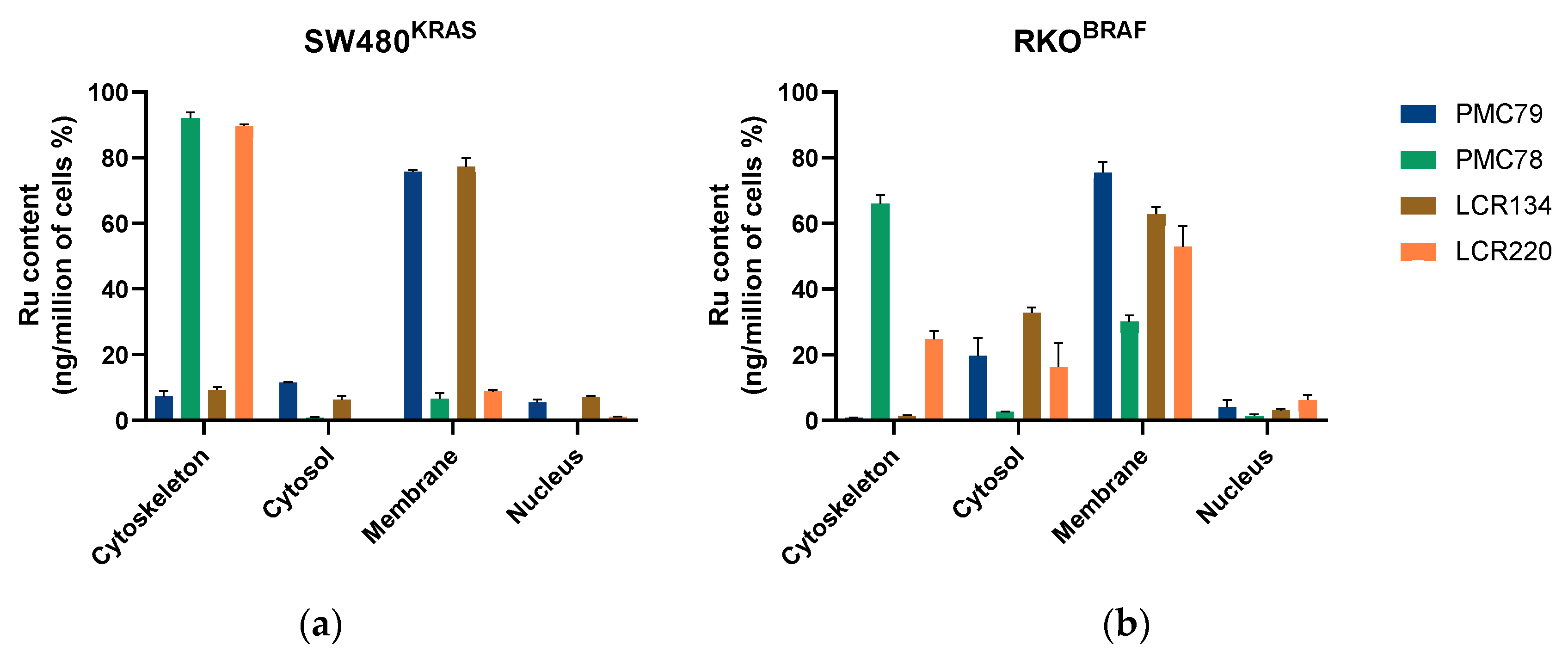
3.2. Ru Compounds Are Differently Distributed in CRC Cells
3.3. Ru Compounds Reduce the Clonogenic Potential of CRC Cells
3.4. Ru Compounds Inhibit Proliferation in CRC Cells
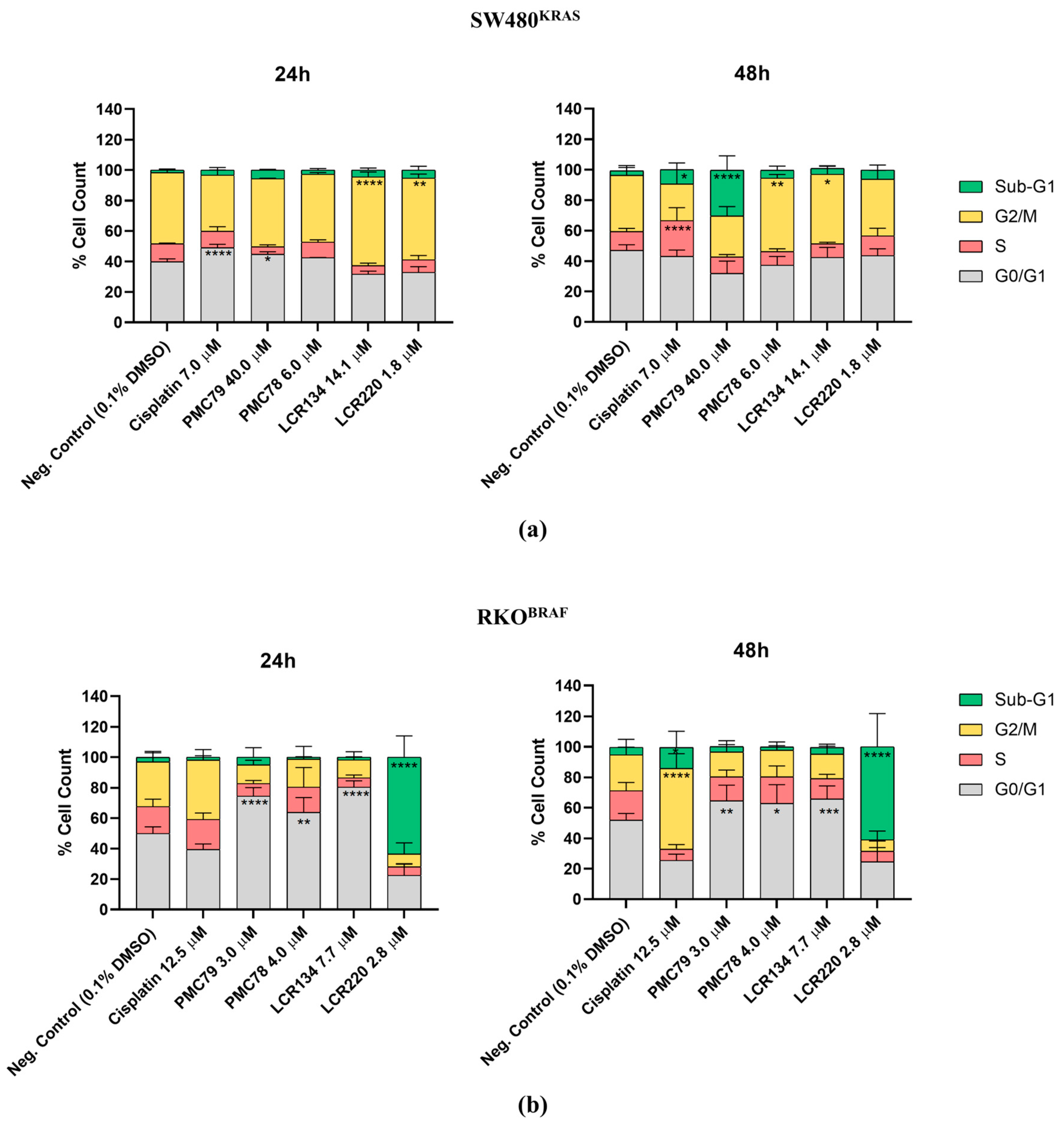
3.5. Ru Compounds Induce Cell Cycle Arrest in CRC Cells
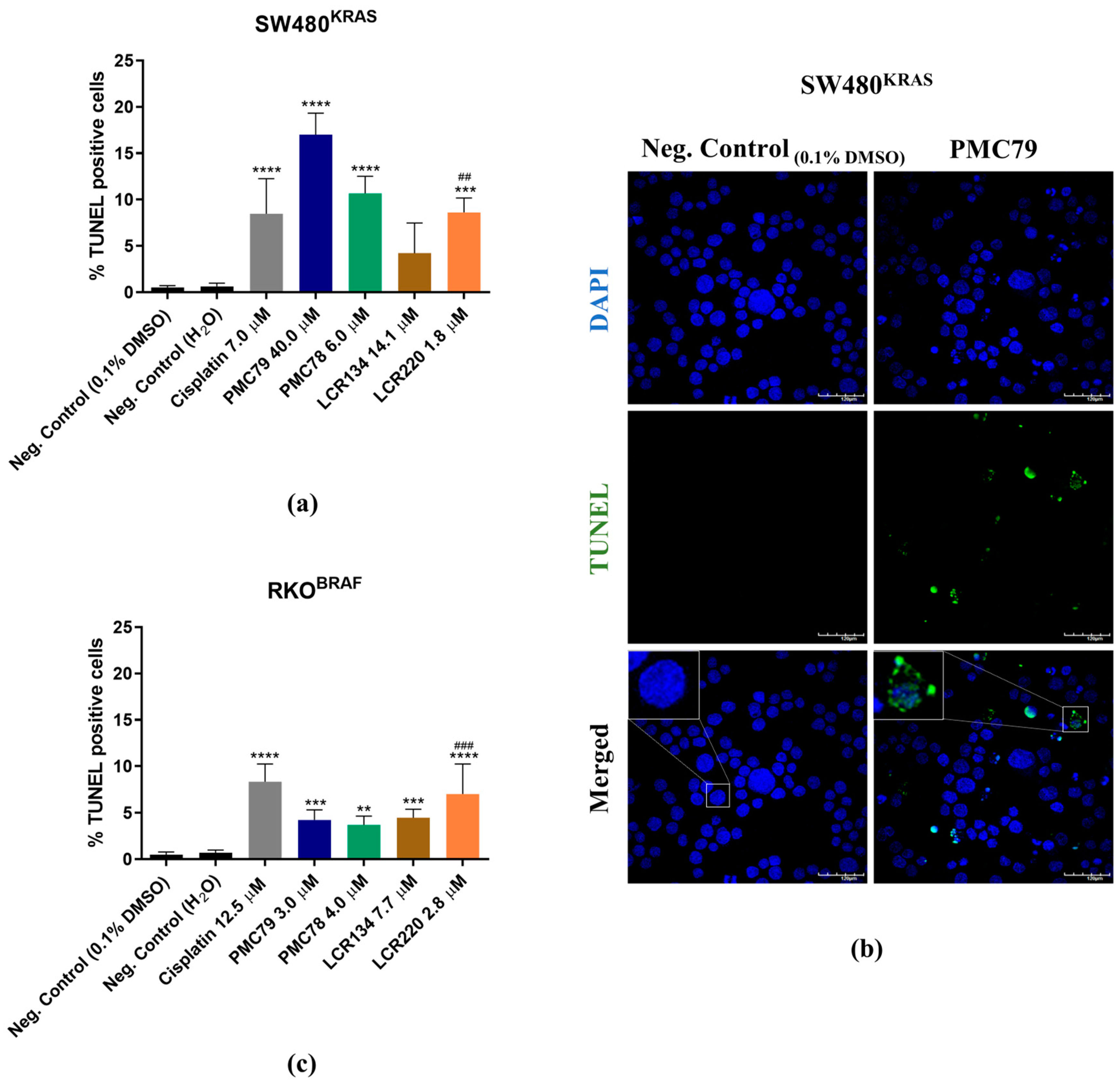
3.6. Ru Compounds Induce DNA Strand Breaks in CRC Cells
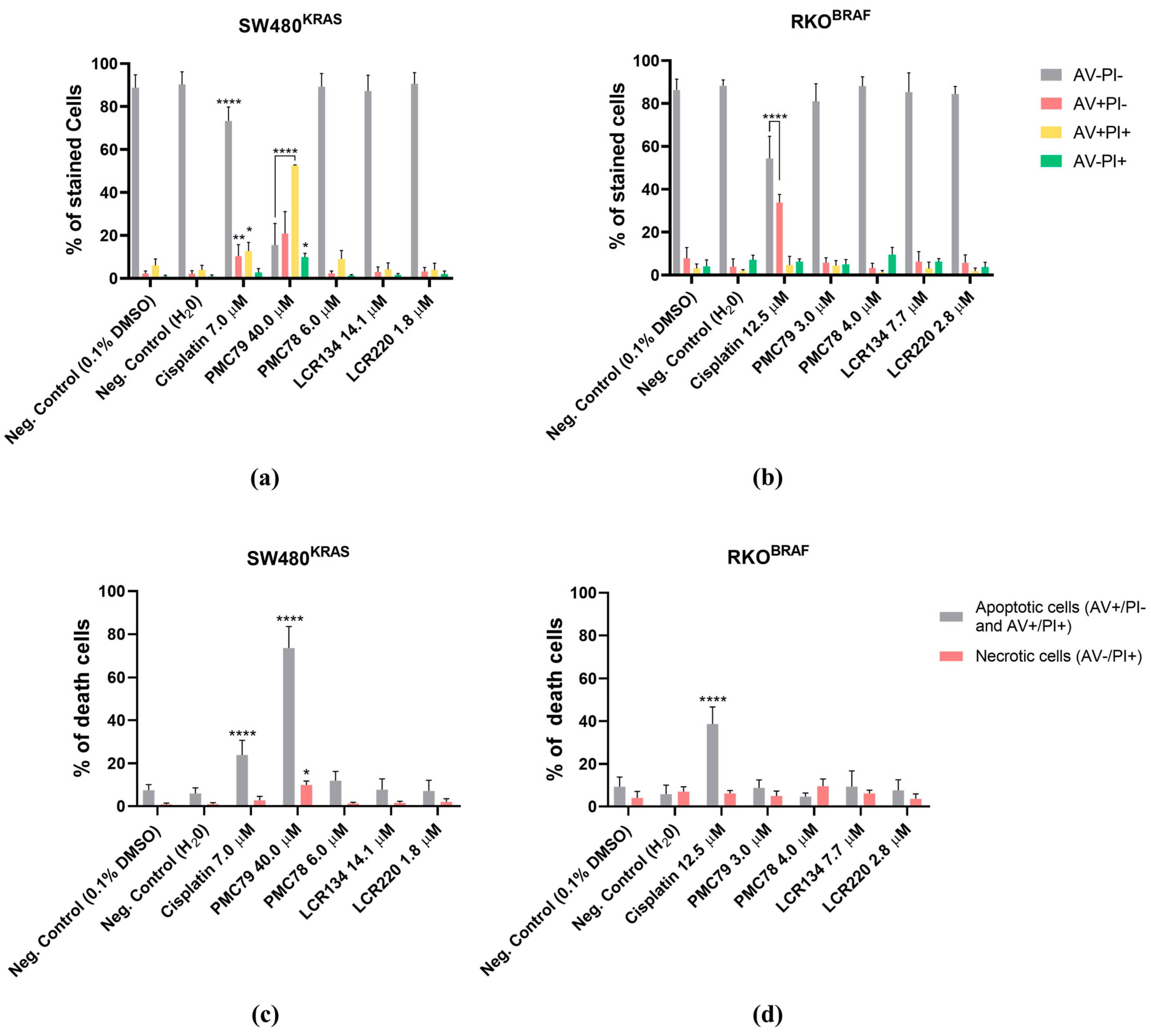
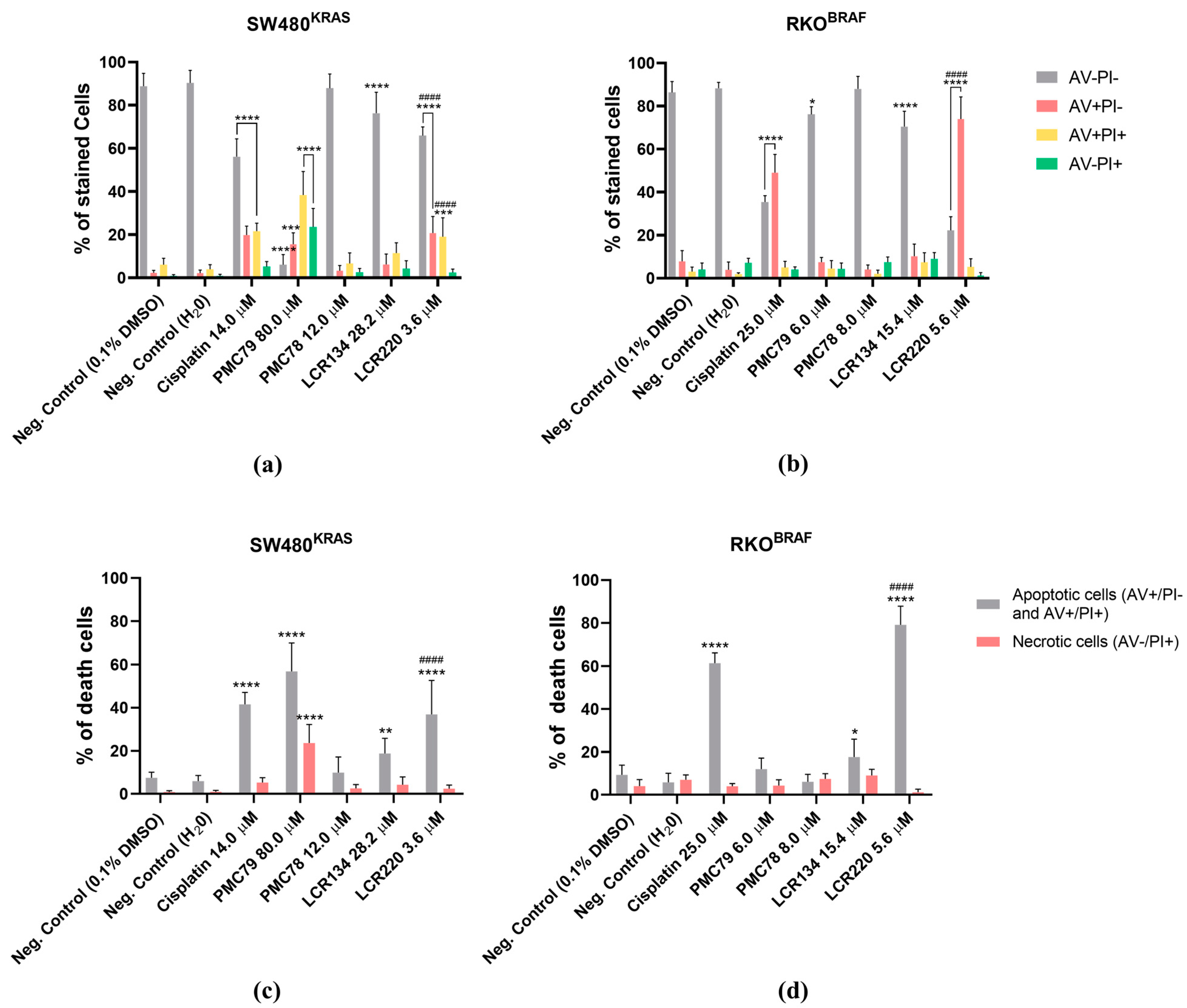
3.7. Ru Compounds Induce Apoptosis in CRC Cells
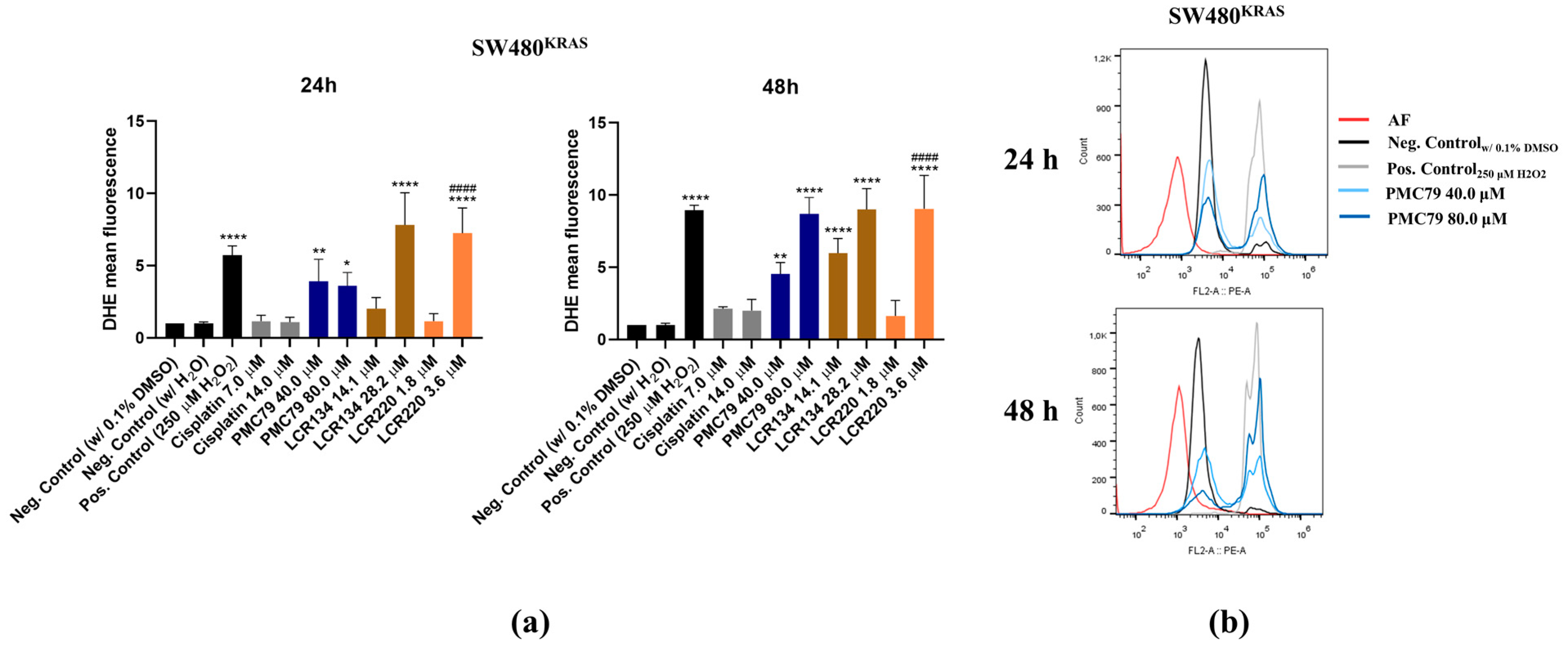
3.8. Ru Compounds Increase Reactive Oxygen Species Production in CRC Cells
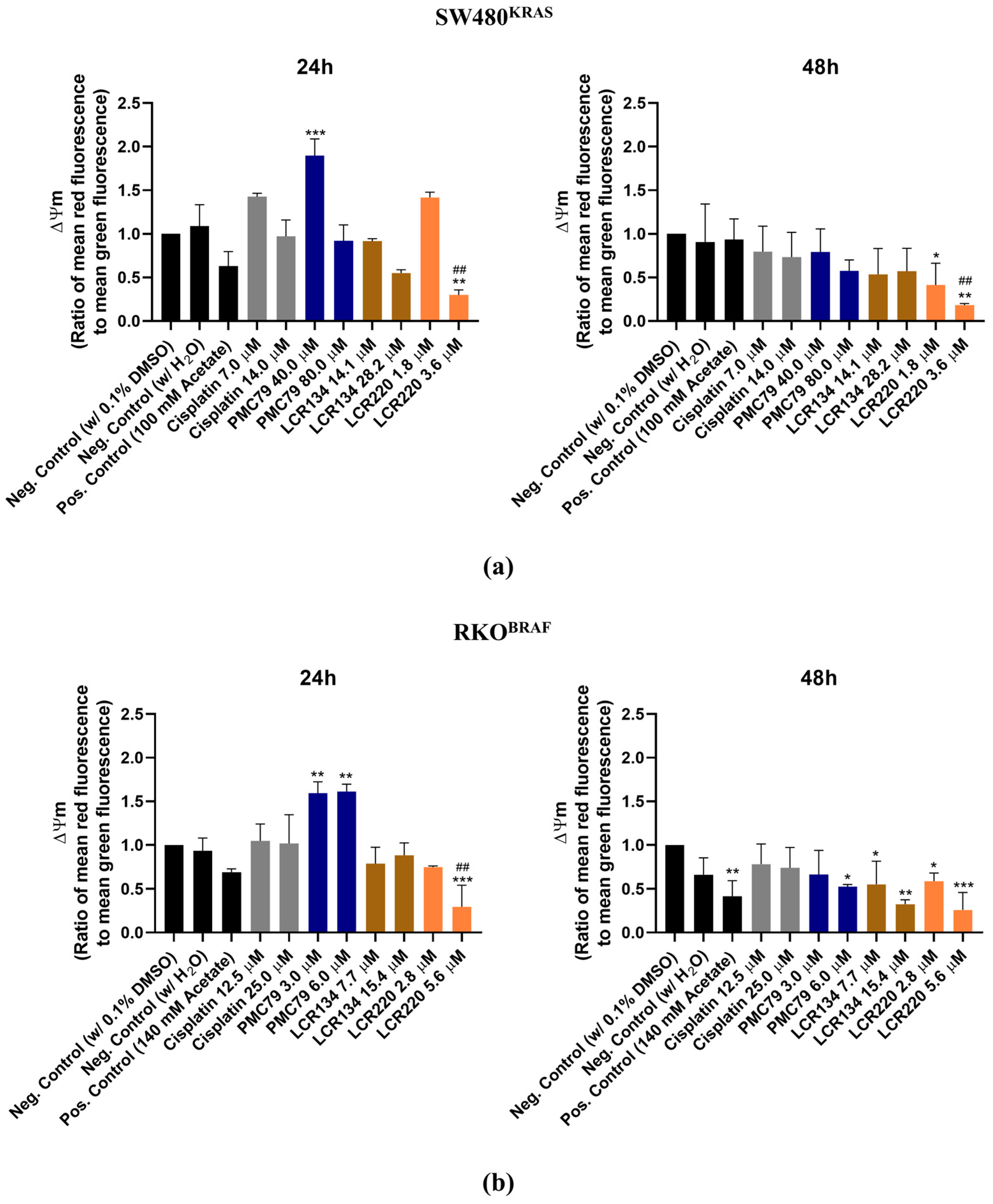
3.9. Ru Compounds Increase Mitochondrial Mass and Induce Changes in Mitochondrial Membrane Potential in CRC Cells
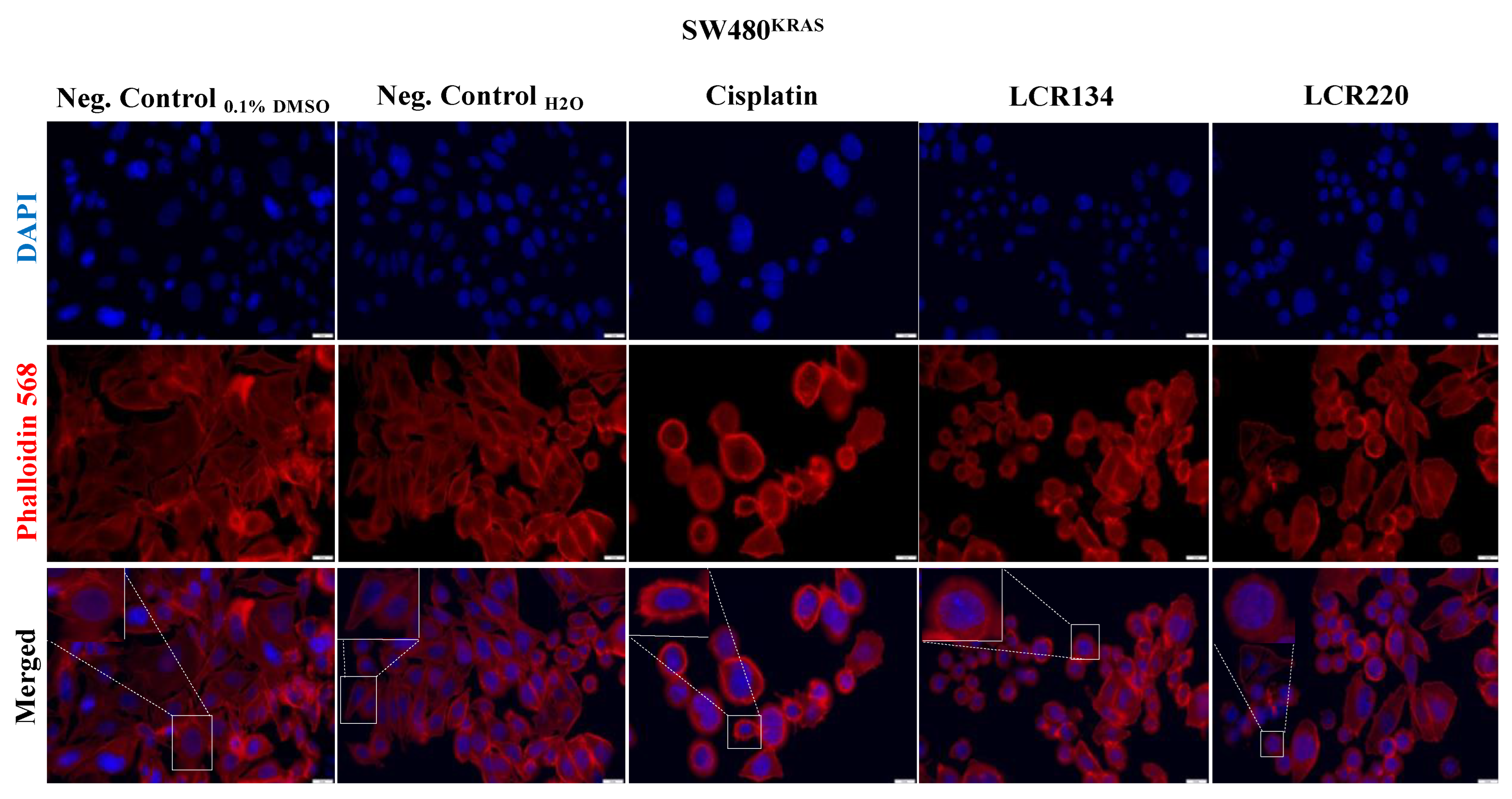
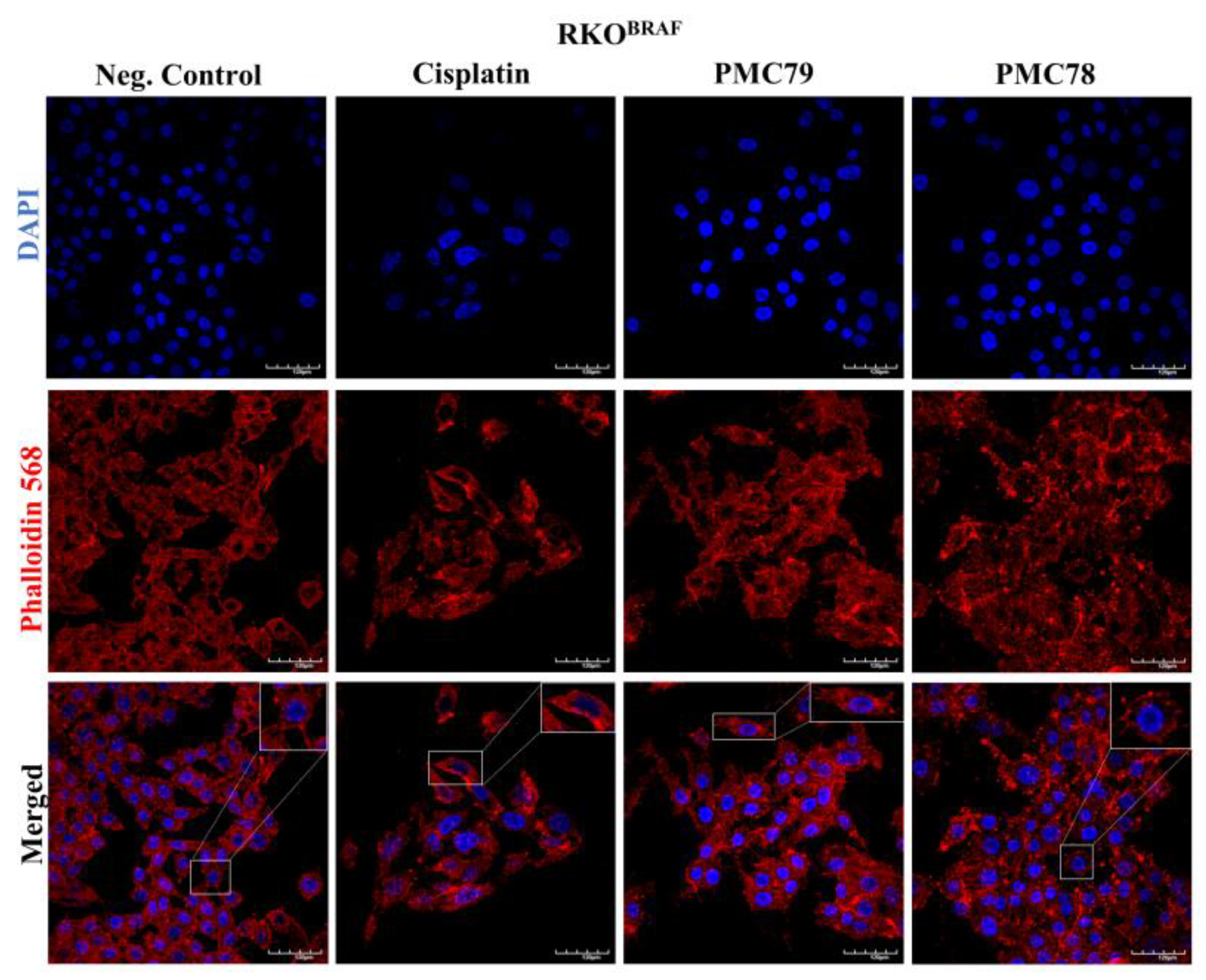
3.10. Ru Compounds Induce Alteration in the Actin Cytoskeleton of CRC Cells
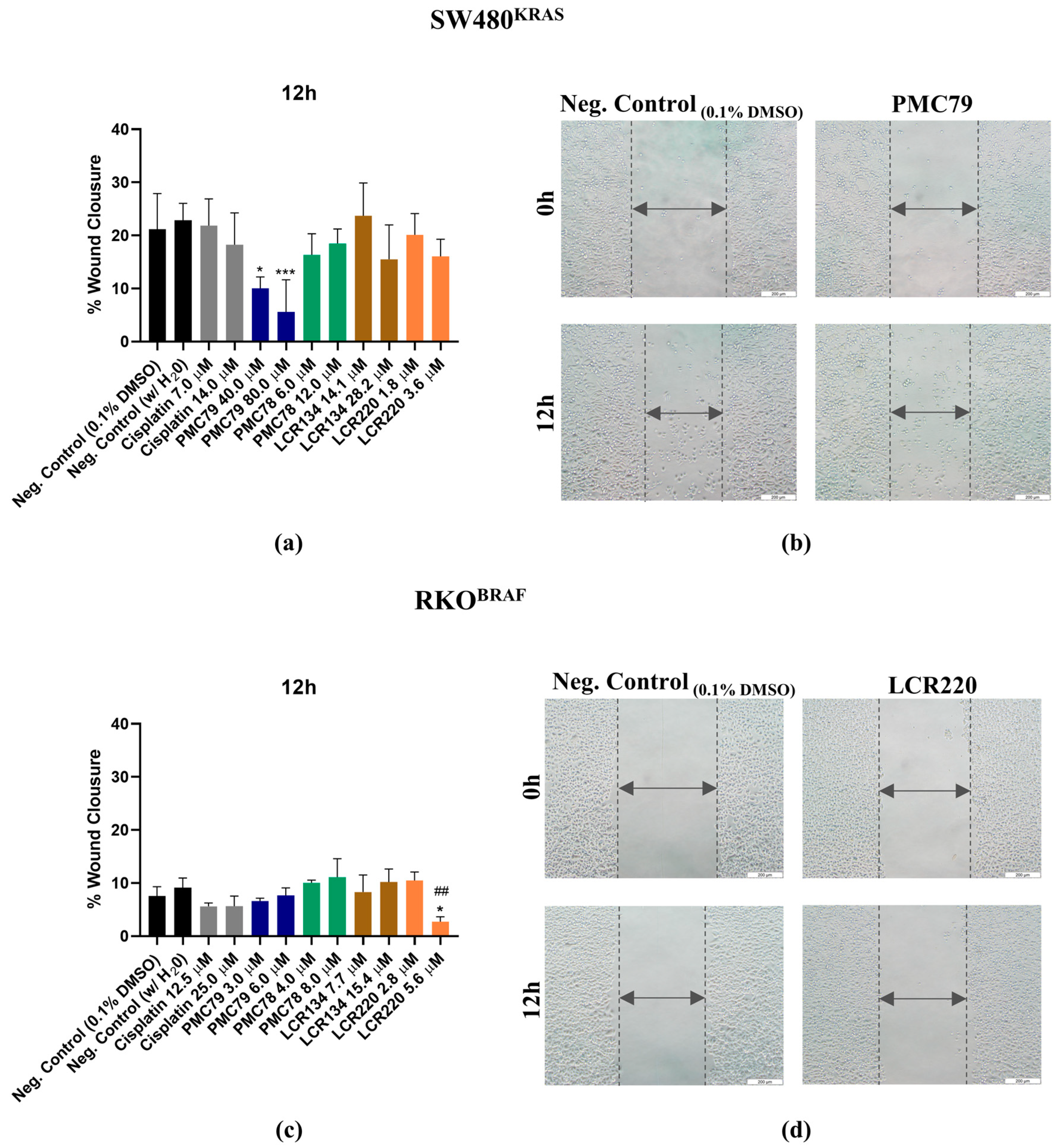
3.11. Ru Compounds Inhibit Cellular Motility in CRC Cells
3.12. Ru Compounds Lead to Alteration of CRC Cellular Proteome
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A





References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, M.; Sierra, M.S.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global patterns and trends in colorectal cancer incidence and mortality. Gut 2017, 66, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Cutsem, E.; Cervantes, A.; Adam, R.; Sobrero, A.; van Krieken, J.H.; Aderka, D.; Aguilar, E.A.; Bardelli, A.; Benson, A.; Bodoky, G.; et al. ESMO consensus guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 1386–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardini, B.; Kumar, R.; Naccarati, A.; Novotny, J.; Prasad, R.B.; Forsti, A.; Hemminki, K.; Vodicka, P.; Bermejo, J.L. 5-Fluorouracil-based chemotherapy for colorectal cancer and MTHFR/MTRR genotypes. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 72, 162–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cazzanelli, G.; Moreira, T.; Ferro, S.; Azevedo-Silva, J.; Nogueira, E.; Preto, A. Colorectal Cancer Therapeutic Approaches: From Classical Drugs to New Nanoparticles. In Frontiers in Anti-Cancer Drug Discovery; Bentham Books: Sharjah, UAE, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kelland, L. The resurgence of platinum-based cancer chemotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, T.S.; Valente, A.; Tomaz, A.I.; Marques, F.; Garcia, M.H. Tracking antitumor metallodrugs: Promising agents with the Ru(II)- and Fe(II)-cyclopentadienyl scaffolds. Future Med. Chem. 2016, 8, 527–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.J.; Yan, Y.K.; Lee, P.P.F.; Lim, K.H. Copper, gold and silver compounds as potential new anti-tumor metallodrugs. Future Sci. 2010, 2, 1591–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnard, C. Platinum Group Metal Compounds in Cancer Chemotherapy. Johnson Matthey Technol. Rev. 2017, 61, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamo, A.; Gaiddon, C.; Schellens, J.H.M.; Beijnen, J.H.; Sava, G. Approaching tumour therapy beyond platinum drugs: Status of the art and perspectives of ruthenium drug candidates. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2012, 106, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, T.; Francisco, R.; Comsa, E.; Duban-Deweer, S.; Labas, V.; Teixeira-Gomes, A.-P.; Combes-Soia, L.; Marques, F.; Matos, A.; Favrelle-Huret, A.; et al. Polymer ‘ruthenium-cyclopentadienyl’ conjugates—New emerging anti-cancer drugs. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 168, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thota, S.; Rodrigues, D.A.; Crans, D.C.; Barreiro, E.J. Ru(II) Compounds: Next-Generation Anticancer Metallotherapeutics? J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 5805–5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaab, H.O.; Alghamdi, M.S.; Alotaibi, A.S.; Alzhrani, R.; Alwuthaynani, F.; Althobaiti, Y.S.; Almalki, A.H.; Sau, S.; Iyer, A.K. Progress in clinical trials of photodynamic therapy for solid tumors and the role of nanomedicine. Cancers 2020, 12, 2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monro, S.; Colón, K.L.; Yin, H.; Roque, J., III; Konda, P.; Gujar, S.; Thummel, R.P.; Lilge, L.; Cameron, C.G.; McFarland, S.A. Transition Metal Complexes and Photodynamic Therapy from a Tumor-Centered Approach: Challenges, Opportunities, and Highlights from the Development of TLD1433. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 797–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougan, S.J.; Sadler, P.J. The design of organometallic ruthenium arene anticancer agents. Chimia 2007, 61, 704–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, B.S.; Babak, M.V.; Hartinger, C.G.; Dyson, P.J. The development of RAPTA compounds for the treatment of tumors. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 306, 86–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motswainyana, W.M.; Ajibade, P.A. Anticancer Activities of Mononuclear Ruthenium(II) Coordination Complexes. Adv. Chem. 2015, 2015, 859730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valente, A.; Garcia, M.H.; Marques, F.; Miao, Y.; Rousseau, C.; Zinck, P. First polymer ‘ruthenium-cyclopentadienyl’ complex as potential anticancer agent. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2013, 127, 79–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaz, A.I.; Jakusch, T.; Morais, T.S.; Marques, F.; de Almeida, R.F.; Mendes, F.; Enyedy, A.; Santos, F.; Pessoa, J.; Kiss, T.; et al. [RuII(η5-C5H5)(bipy)(PPh3)]+, a promising large spectrum antitumor agent: Cytotoxic activity and interaction with human serum albumin. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2012, 117, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, V.; Font-Bardia, M.; Calvet, T.; Lorenzo, J.; Avilés, F.X.; Garcia, M.H.; Morais, T.S.; Valente, A.; Robalo, M.P. DNA interaction and cytotoxicity studies of new ruthenium(II) cyclopentadienyl derivative complexes containing heteroaromatic ligands. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2011, 105, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, B.; Gullotti, D.; Mangraviti, A.; Utsuki, T.; Brem, H. Polylactic acid (PLA) controlled delivery carriers for biomedical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, H.; Wu, J.; Sawa, T.; Matsumura, Y.; Hori, K. Tumor vascular permeability and the EPR effect in macromolecular therapeutics: A review. J. Control. Release 2000, 65, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Côrte-real, L.; Brás, A.R.; Pilon, A.; Mendes, N.; Ribeiro, A.S.; Martins, T.D.; Farinha, J.P.S.; Oliveira, M.C.; Gärtner, F.; Garcia, M.H.; et al. Biotinylated Polymer-Ruthenium Conjugates: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies in a Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Model. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Côrte-Real, L.; Karas, B.; Gírio, P.; Moreno, A.; Avecilla, F.; Marques, F.; Buckley, B.T.; Cooper, K.R.; Doherty, C.; Falson, P.; et al. Unprecedented inhibition of P-gp activity by a novel ruthenium-cyclopentadienyl compound bearing a bipyridine-biotin ligand. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 163, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Côrte-Real, L.; Karas, B.; Brás, A.R.; Pilon, A.; Avecilla, F.; Marques, F.; Preto, A.; Buckley, B.T.; Cooper, K.R.; Doherty, C.; et al. Ruthenium–Cyclopentadienyl Bipyridine–Biotin Based Compounds: Synthesis and Biological Effect. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 9135–9149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zempleni, J.; Wijeratne, S.S.K.; Hassan, Y.I. Biotin. Biofactors 2009, 35, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tripodo, G.; Mandracchia, D.; Collina, S.; Rui, M.; Rossi, D. New Perspectives in Cancer Therapy: The Biotin-Antitumor Molecule Conjugates. Med. Chem. 2014, 8, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, W.X.; Han, J.; Uhm, S.; Jang, Y.J.; Kang, C.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, J.S. Recent development of biotin conjugation in biological imaging, sensing, and target delivery. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 10403–10418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.H.; Valente, A.; Morais, T.S.F.; Tomaz, A.I. Macromolecular Transition Metal Complexes for Treatment of Cancer and Process for Their Preparation. Patent Application WO/2016/087932, 9 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Moyer, M.P.; Manzano, L.A.; Merriman, R.L.; Stauffer, J.S.; Tanzer, L.R. NCM460, a normal human colon mucosal epithelial cell line. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 1996, 32, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Morán, O.; Villarreal, M.; Álvarez-Berber, L.; Meneses-Acosta, A.; Rodríguez-López, V. Cytotoxicity, Post-Treatment Recovery, and Selectivity Analysis of Naturally Occurring Podophyllotoxins from Bursera fagaroides var. fagaroides on Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Molecules 2016, 21, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Côrte-Real, L.; Matos, A.P.; Alho, I.; Morais, T.S.; Tomaz, A.I.; Garcia, M.H.; Santos, I.; Bicho, M.P.; Marques, F. Cellular uptake mechanisms of an antitumor ruthenium compound: The endosomal/lysosomal system as a target for anticancer metal-based drugs. Microsc. Microanal. 2013, 19, 1122–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.C.C.; Granja, S.; Almeida, A.F.; Baltazar, F.; Gonçalves, M.S.T.; Preto, A.; Sousa, M.J. Targeting Lysosomes in Colorectal Cancer: Exploring the Anticancer Activity of a New Benzo[a]phenoxazine Derivative. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, R.G.; Brás, A.R.; Côrte-Real, L.; Tatikonda, R.; Sanches, A.; Robalo, M.P.; Avecilla, F.; Moreira, T.; Garcia, M.H.; Haukka, M.; et al. Novel ruthenium methylcyclopentadienyl complex bearing a bipyridine perfluorinated ligand showing strong activity towards colorectal cancer cell lines. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 143, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, C.S.F.; Pereira, H.; Alves, S.; Castro, L.; Baltazar, F.; Chaves, S.R.; Preto, A.; Côrte-Real, M. Cathepsin D protects colorectal cancer cells from acetate-induced apoptosis through autophagy-independent degradation of damaged mitochondria. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pilon, A.; Brás, A.R.; Côrte-Real, L.; Avecilla, F.; Costa, P.J.; Preto, A.; Garcia, M.H.; Valente, A. A new family of iron(II)-cyclopentadienyl compounds shows strong activity against colorectal and triple negative breast cancer cells. Molecules 2020, 25, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teixeira-Guedes, C.; Brás, A.R.; Teixeira, R.G.; Valente, A.; Preto, A. Ruthenium(II)–Cyclopentadienyl-Derived Complexes as New Emerging Anti-Colorectal Cancer Drugs. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiva, C.; Olivella, R.; Borràs, E.; Espadas, G.; Pastor, O.; Solé, A.; Sabidó, E. QCloud: A cloud-based quality control system for mass spectrometry-based proteomics laboratories. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0189209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olivella, R.; Chiva, C.; Serret, M.; Mancera, D.; Cozzuto, L.; Hermoso, A.; Borràs, E.; Espadas, G.; Morales, J.; Pastor, O.; et al. QCloud2: An Improved Cloud-based Quality-Control System for Mass-Spectrometry-based Proteomics Laboratories. J. Proteome Res. 2021, 20, 2010–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, D.N.; Pappin, D.J.C.; Creasy, D.M.; Cottrell, J.S. Probability-based protein identification by searching sequence databases using mass spectrometry data. Electrophoresis 1999, 20, 3551–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, L.A.; Liu, P.; Ky, B.; Barnhart, K.T.; Speicher, D.W. Efficient quantitative comparisons of plasma proteomes using label-free analysis with MaxQuant. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1619, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perez-Riverol, Y.; Bai, J.; Bandla, C.; García-Seisdedos, D.; Hewapathirana, S.; Kamatchinathan, S.; Kundu, D.J.; Prakash, A.; Frericks-Zipper, A.; Eisenacher, M.; et al. The PRIDE database resources in 2022: A hub for mass spectrometry-based proteomics evidences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D543–D552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.; Assunção, L.S.; Silva, A.H.; Filippin-Monteiro, F.B.; Creczynski-Pasa, T.B.; Sá, M.M. Allylic isothiouronium salts: The discovery of a novel class of thiourea analogues with antitumor activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 129, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaloam, D.; Tchounwou, P.B. Cisplatin in cancer therapy: Molecular mechanisms of action. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 740, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Colucci, G.; Gebbia, V.; Paoletti, G.; Giuliani, F.; Caruso, M.; Gebbia, N.; Cartenì, G.; Agostara, B.; Pezzella, G.; Manzione, L.; et al. Phase III randomized trial of FOLFIRI versus FOLFOX4 in the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer: A Multicenter Study of the Gruppo Oncologico Dell’Italia Meridionale. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 4866–4875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jing, C.; Li, H.; Du, Y.; Cao, H.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Ma, R.; Feng, J.; Wu, J. MEK inhibitor enhanced the antitumor effect of oxaliplatin and 5-fluorouracil in MEK1 Q56P-mutant colorectal cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 1092–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, J.; Li, Z.; Zhou, J.; Sun, Z.; Bai, C. Response prediction to oxaliplatin plus 5-fluorouracil chemotherapy in patients with colorectal cancer using a four-protein immunohistochemical model. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 2091–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vodenkova, S.; Buchler, T.; Cervena, K.; Veskrnova, V.; Vodicka, P.; Vymetalkova, V. 5-fluorouracil and other fluoropyrimidines in colorectal cancer: Past, present and future. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 206, 107447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oun, R.; Moussa, Y.E.; Wheate, N.J. The side effects of platinum-based chemotherapy drugs: A review for chemists. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 6645–6653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callacondo-Riva, D.; Quispe-Mauricio, A.; Lindo-Gamarra, S.; Vaisberg, A.J. Actividad citotóxica del extracto etanólico de gnaphalium spicatum ‘keto keto’ en cultivos de líneas celulares tumorales humanas. Rev. Peru. Med. Exp. Salud Publica 2008, 25, 380–385. [Google Scholar]
- Mousavi, E.; Tavakolfar, S.; Almasirad, A.; Kooshafar, Z.; Dehghani, S.; Afsharinasab, A.; Amanzadeh, A.; Shafiee, S.; Salimi, M. In vitro and in vivo assessments of two novel hydrazide compounds against breast cancer as well as mammary tumor cells. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2017, 79, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karas, B.F.; Hotz, J.M.; Gural, B.M.; Terez, K.R.; DiBona, V.L.; Côrte-Real, L.; Valente, A.; Buckley, B.T.; Cooper, K.R. Anticancer Activity and in Vitro to in Vivo Mechanistic Recapitulation of Novel Ruthenium-Based Metallodrugs in the Zebrafish Model. Toxicol. Sci. 2021, 182, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, K.M.; Niloy, M.S.; Shakil, S. Ruthenium Complexes: An Alternative to Platinum Drugs in Colorectal Cancer Treatment. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudhindra, P.; Ajay Sharma, S.; Roy, N.; Moharana, P.; Paira, P. Recent advances in cytotoxicity, cellular uptake and mechanism of action of ruthenium metallodrugs: A review. Polyhedron 2020, 192, 114827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierroz, V.; Joshi, T.; Leonidova, A.; Mari, C.; Schur, J.; Ott, I.; Spiccia, L.; Ferrari, S.; Gasser, G. Molecular and Cellular Characterization of the Biological Effects of Ruthenium(II) Complexes Incorporating 2-Pyridyl-2-pyrimidine-4-carboxylic Acid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 20376–20387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yugandhar, D.; Nayak, V.L.; Archana, S.; Shekar, K.C.; Srivastava, A.K. Design, synthesis and anticancer properties of novel oxa/azaspiro[4,5]trienones as potent apoptosis inducers through mitochondrial disruption. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 101, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wong, Y.-S.; Chen, T.; Fan, C.; Zheng, W. Ruthenium complexes containing bis-benzimidazole derivatives as a new class of apoptosis inducers. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 1138–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, D.; Tang, B.; Wang, Y.-J.; Guo, B.-H.; Yin, H.; Yi, Q.-Y.; Liu, Y.-J. Synthesis and anticancer properties of ruthenium (II) complexes as potent apoptosis inducers through mitochondrial disruption. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 139, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Q.; Zhang, P.Y.; Qian, C.; Hou, X.J.; Ji, L.N.; Chao, H. Mitochondria are the primary target in the induction of apoptosis by chiral ruthenium(II) polypyridyl complexes in cancer cells. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 19, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.C.; Lai, S.-H.; Yao, J.-H.; Zhang, C.; Yin, H.; Li, W.; Han, B.-J.; Liu, Y.-J. The induction of apoptosis in HepG-2 cells by ruthenium(II) complexes through an intrinsic ROS-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction pathway. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 122, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapitza, S.; Jakupec, M.A.; Uhl, M.; Keppler, B.K.; Marian, B. The heterocyclic ruthenium(III) complex KP1019 (FFC14A) causes DNA damage and oxidative stress in colorectal tumor cells. Cancer Lett. 2005, 226, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łomzik, M.; Mazuryk, O.; Rutkowska-Zbik, D.; Stochel, G.; Gros, P.C.; Brindell, M. New ruthenium compounds bearing semicarbazone 2-formylopyridine moiety: Playing with auxiliary ligands for tuning the mechanism of biological activity. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2017, 175, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- FractionPREPTM Cell Fractionation Kit. Available online: https://www.biovision.com/fractionpreptm-cell-fractionation-kit.html (accessed on 29 December 2022).
- Dugina, V.B.; Shagieva, G.S.; Kopnin, P.B. Biological Role of Actin Isoforms in Mammalian Cells. Biochemistry 2019, 84, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominguez, R.; Holmes, K.C. Actin structure and function. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2011, 40, 169–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Taieb, J.; Lapeyre-Prost, A.; Puig, P.L.; Zaanan, A. Exploring the best treatment options for BRAF-mutant metastatic colon cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| IC50 (μM) | SI | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compounds | SW480KRAS | RKOBRAF | NCM460 | SW480 | RKO |
| PMC79 | 40.0 ± 2.0 | 3.0 ± 0.5 | 44.0 ± 6.9 | 1.1 | 14.7 |
| PMC78 | 6.0 ± 0.2 | 4.0 ± 0.2 | 14.3 ± 0.6 | 2.4 | 3.6 |
| LCR134 | 14.1 ± 0.7 | 7.7 ± 0.4 | 57.2 ± 6.0 | 4.1 | 7.4 |
| LCR220 | 1.8 ± 0.1 | 2.8 ± 0.1 | 4.3 ± 0.1 | 2.4 | 1.5 |
| Cisplatin | 7.0 ± 0.1 [33] | 12.5 ± 1.2 [33] | 6.3 ± 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brás, A.R.; Fernandes, P.; Moreira, T.; Morales-Sanfrutos, J.; Sabidó, E.; Antunes, A.M.M.; Valente, A.; Preto, A. New Ruthenium-Cyclopentadienyl Complexes Affect Colorectal Cancer Hallmarks Showing High Therapeutic Potential. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1731. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061731
Brás AR, Fernandes P, Moreira T, Morales-Sanfrutos J, Sabidó E, Antunes AMM, Valente A, Preto A. New Ruthenium-Cyclopentadienyl Complexes Affect Colorectal Cancer Hallmarks Showing High Therapeutic Potential. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(6):1731. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061731
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrás, Ana Rita, Pedro Fernandes, Tiago Moreira, Julia Morales-Sanfrutos, Eduard Sabidó, Alexandra M. M. Antunes, Andreia Valente, and Ana Preto. 2023. "New Ruthenium-Cyclopentadienyl Complexes Affect Colorectal Cancer Hallmarks Showing High Therapeutic Potential" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 6: 1731. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061731
APA StyleBrás, A. R., Fernandes, P., Moreira, T., Morales-Sanfrutos, J., Sabidó, E., Antunes, A. M. M., Valente, A., & Preto, A. (2023). New Ruthenium-Cyclopentadienyl Complexes Affect Colorectal Cancer Hallmarks Showing High Therapeutic Potential. Pharmaceutics, 15(6), 1731. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15061731