Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Puerarin: Characterization, Antimicrobial Potential, Angiogenesis, and In Ovo Safety Profile Assessment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Microbial Strains
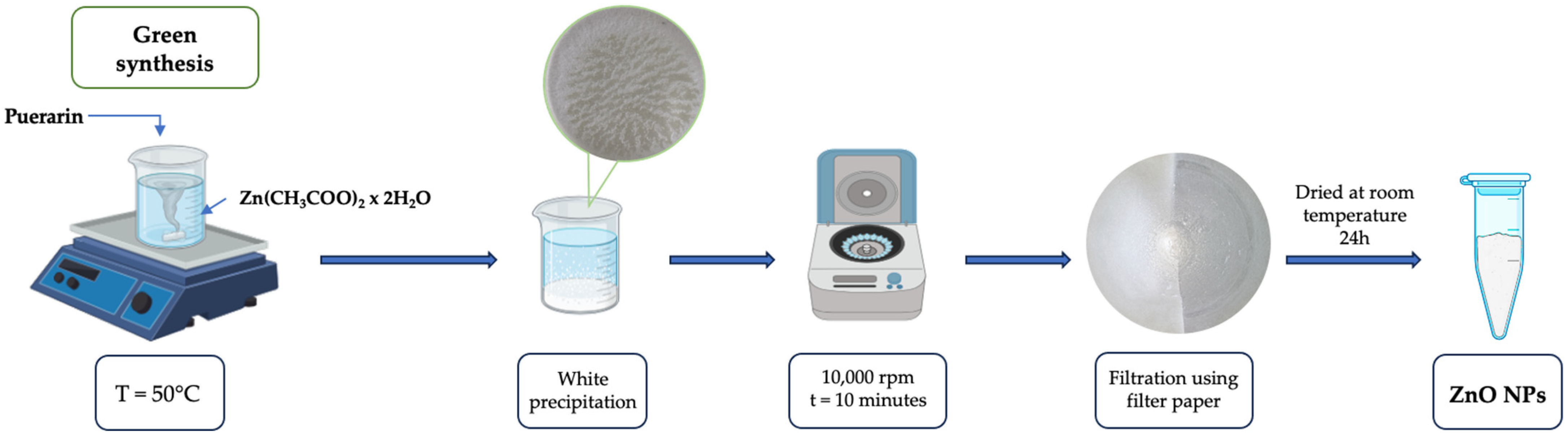
2.2. Green Synthesis and Characterization of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Puerarin (PUE-ZnO NPs)
2.3. Characterization of Green Synthesized PUE-ZnO NPs
2.4. In Vitro Evaluation of the Antibacterial Activity
Determination of the Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations by Dilution Method
2.5. In Ovo CAM Assay
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physicochemical Characterization of ZnO NPs Synthesized by a Green Chemistry Pathway
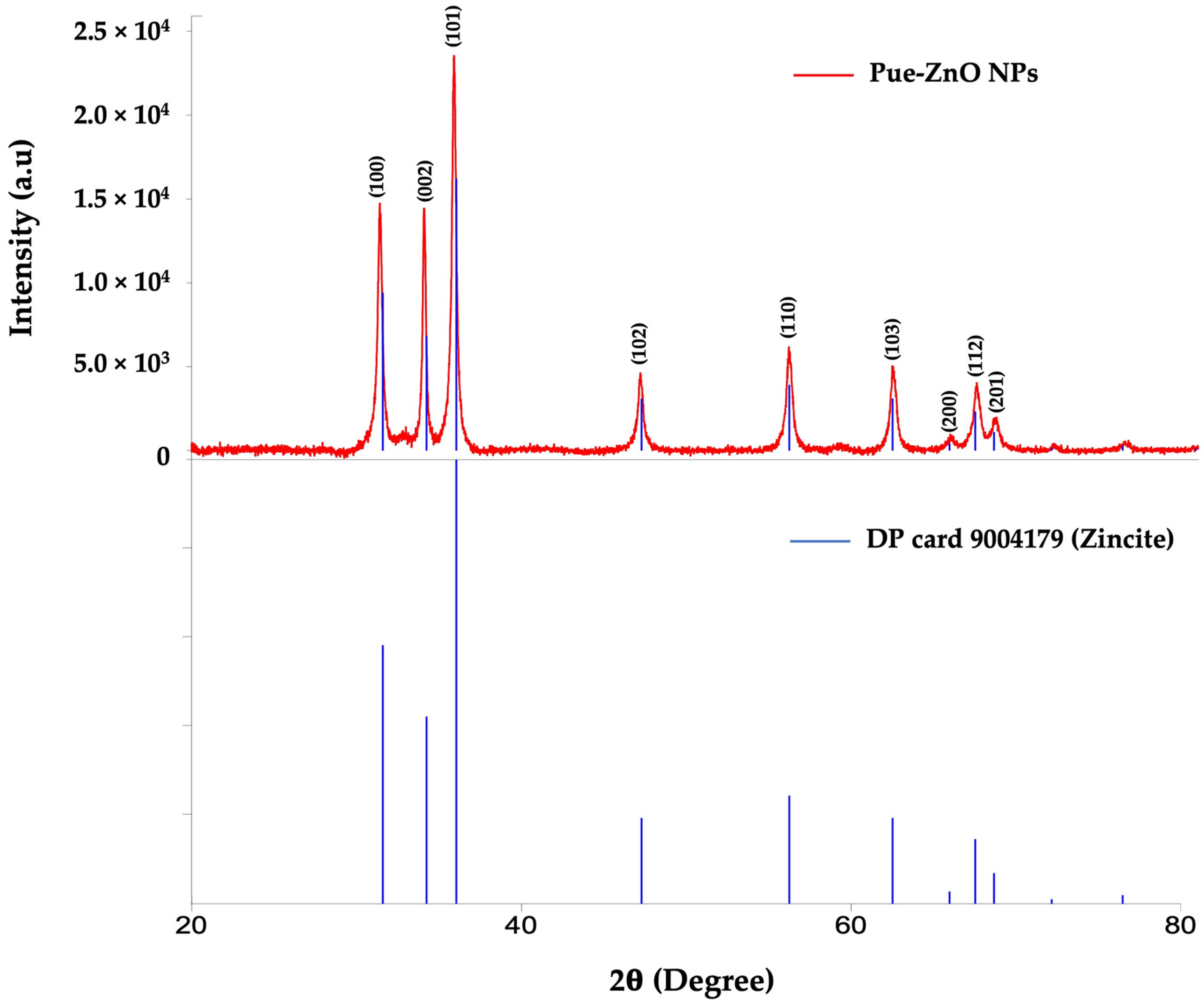
3.1.1. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
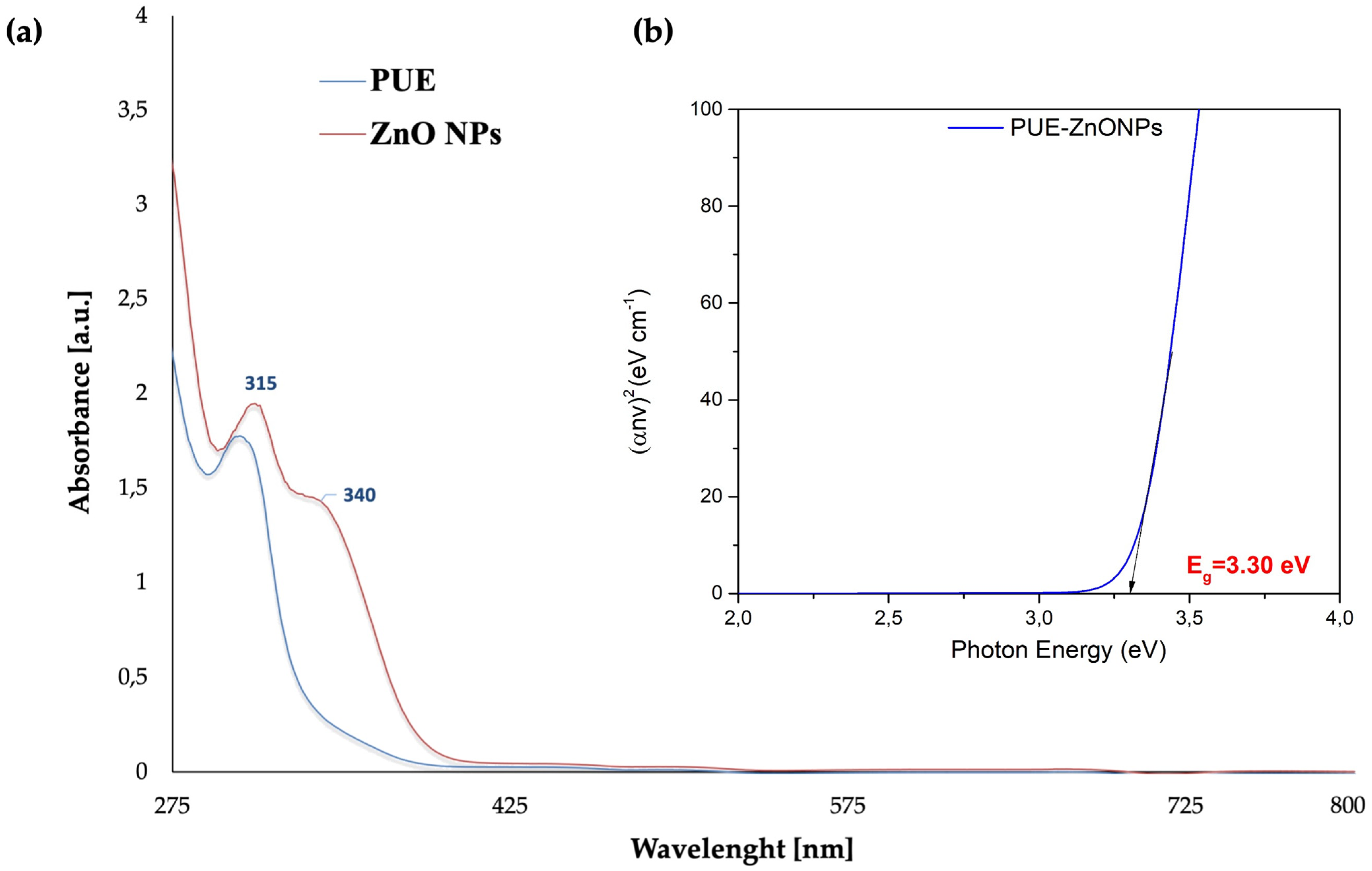
3.1.2. UV-Visible Spectroscopy
3.1.3. Fourier Transform Infrared (ATR-FT-IR) Spectroscopy
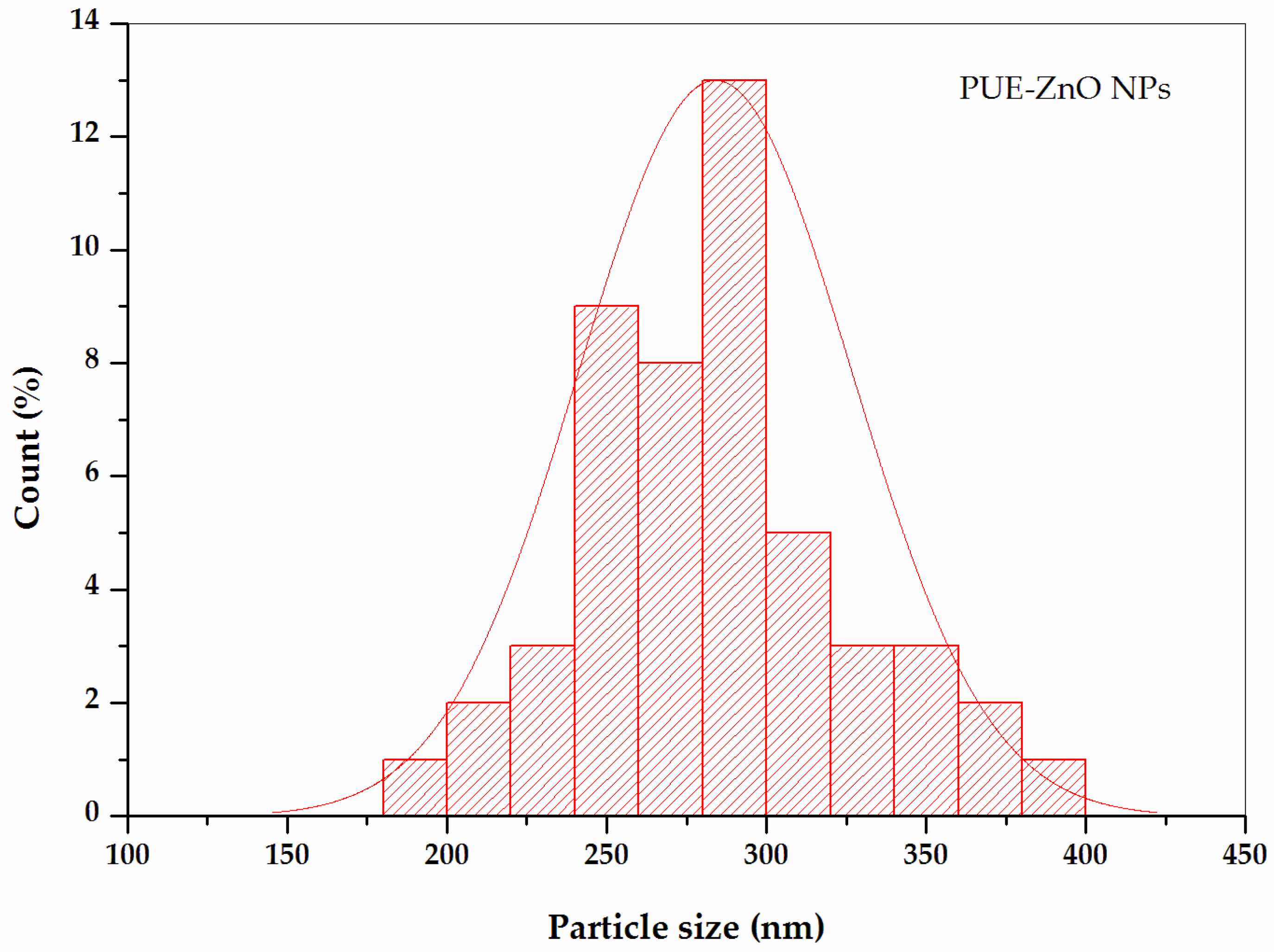
3.1.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and EDX Analysis
3.1.5. Atomic Force Microscopy Analysis (AFM) of PUE-ZnO NPs
3.2. Antimicrobial Potential of Green-Synthesized PUE-ZnO NPs
3.3. In Ovo Assay
3.3.1. The Anti-Irritant Effect by PUE-ZnO NPs Using the HET-CAM Method
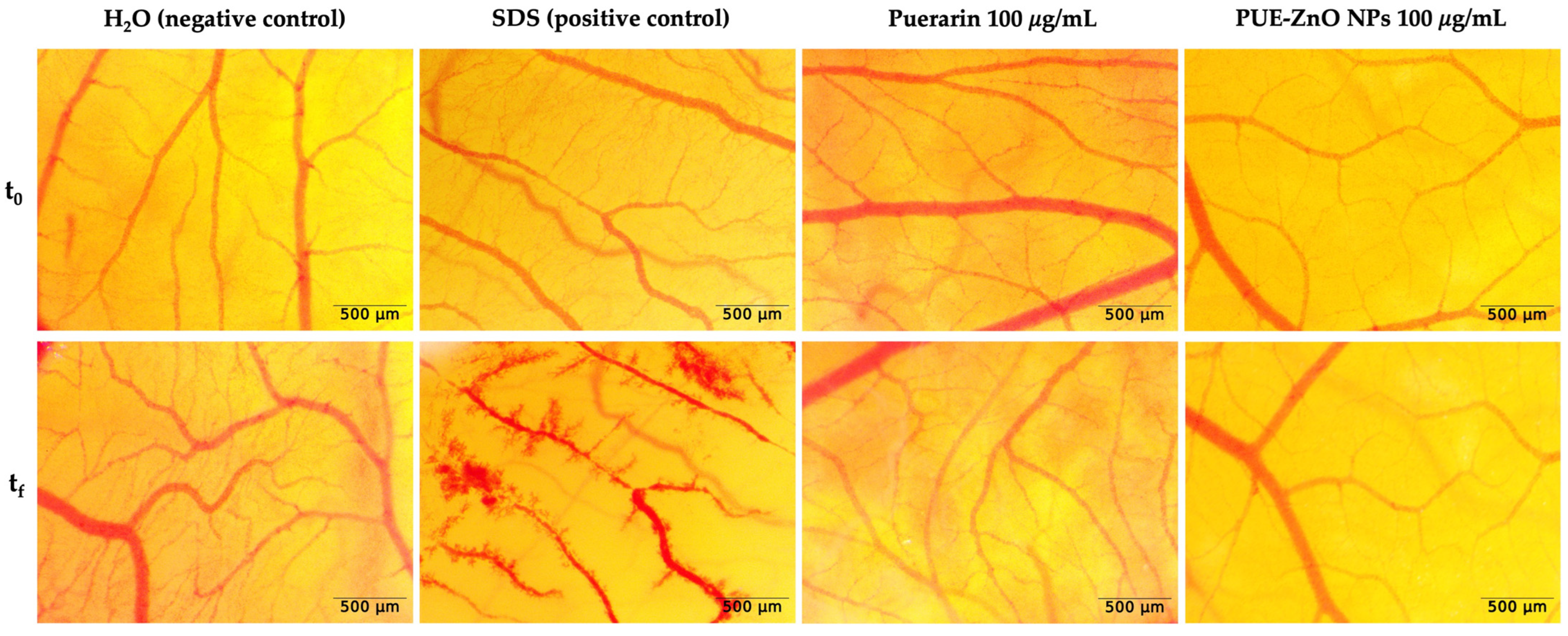
3.3.2. Modulation of Angiogenesis by PUE-ZnO NPs Using CAM Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khan, S.; Mansoor, S.; Rafi, Z.; Kumari, B.; Shoaib, A.; Saeed, M.; Alshehri, S.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Rahamathulla, M.; Hani, U.; et al. A Review on Nanotechnology: Properties, Applications, and Mechanistic Insights of Cellular Uptake Mechanisms. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 348, 118008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.; Muhammad, K.; Waheed, Y. Nanotechnology: A Revolution in Modern Industry. Molecules 2023, 28, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gubala, V.; Johnston, L.J.; Liu, Z.; Krug, H.; Moore, C.J.; Ober, C.K.; Schwenk, M.; Vert, M. Engineered Nanomaterials and Human Health: Part 1. Preparation, Functionalization and Characterization (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2018, 90, 1283–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, N.H.; Luong, N.H. Nanoparticles: Synthesis and Applications. In Materials for Biomedical Engineering: Inorganic Micro- and Nanostructures; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 211–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission; Directorate General for Health & Consumers. Scientific Basis for the Definition of the Term “Nanomaterial”; SCENIHR, Ed.; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramasivam, G.; Palem, V.V.; Sundaram, T.; Sundaram, V.; Kishore, S.C.; Bellucci, S. Nanomaterials: Synthesis and Applications in Theranostics. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekuye, B.; Abera, B. Nanomaterials: An Overview of Synthesis, Classification, Characterization, and Applications. Nano Sel. 2023, 4, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kady, M.M.; Ansari, I.; Arora, C.; Rai, N.; Soni, S.; Verma, D.K.; Singh, P.; Mahmoud, A.E.D. Nanomaterials: A Comprehensive Review of Applications, Toxicity, Impact, and Fate to Environment. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 370, 121046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liga, S.; Paul, C.; Moacă, E.-A.; Péter, F. Niosomes: Composition, Formulation Techniques, and Recent Progress as Delivery Systems in Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.; Truong, P.L.; Lee, D.; Ko, S.H. Metal-Oxide Nanomaterials Synthesis and Applications in Flexible and Wearable Sensors. ACS Nanosci. Au 2022, 2, 64–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolova, M.P.; Chavali, M.S. Metal Oxide Nanoparticles as Biomedical Materials. Biomimetics 2020, 5, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, N.; Pandey, D.K.; Mistry, B.G.; Singh, D.K. Metal Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Properties, Characterization, and Applications. In Nanomaterials: Advances and Applications; Singh, D.K., Singh, S., Singh, P., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 103–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhalili, Z. Metal Oxides Nanoparticles: General Structural Description, Chemical, Physical, and Biological Synthesis Methods, Role in Pesticides and Heavy Metal Removal through Wastewater Treatment. Molecules 2023, 28, 3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseem, T.; Durrani, T. The Role of Some Important Metal Oxide Nanoparticles for Wastewater and Antibacterial Applications: A Review. J. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2021, 3, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrescu, A.M.; Killian, M.S.; Raghu, S.N.V.; Schmuki, P.; Mazare, A.; Cimpean, A. Metal Oxide Nanoparticles: Review of Synthesis, Characterization and Biological Effects. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 13, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaur, J.; Kumar, S.; Pal, M.; Kaur, H.; Batoo, K.M.; Momoh, J.O.; Supreet. Current Trends: Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Preparation via Chemical and Green Method for the Photocatalytic Degradation of Various Organic Dyes. Hybrid. Adv. 2024, 5, 100128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.A.; Das, J.; Sil, P.C. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: A Comprehensive Review on Its Synthesis, Anticancer and Drug Delivery Applications as Well as Health Risks. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 286, 102317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, R.; Kumar, A.; Tripathi, R.; Kumar, A. Advancing of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for Cosmetic Applications. In Handbook of Consumer Nanoproducts; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 1057–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Mohanty, D.L.; Divya, N.; Bakshi, V.; Mohanty, A.; Rath, D.; Das, S.; Mondal, A.; Roy, S.; Sabui, R. A Critical Review on Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Properties and Biomedical Applications. Intell. Pharm. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.S.; Bawiskar, D.; Wagh, V. Nanocosmetics and Skin Health: A Comprehensive Review of Nanomaterials in Cosmetic Formulations. Cureus 2024, 16, e52754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahdal, F.A.M.; Qashqoosh, M.T.A.; Manea, Y.K.; Salem, M.A.S.; Khan, A.M.T.; Naqvi, S. Eco-Friendly Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles as Nanosensor, Nanocatalyst and Antioxidant Agent Using Leaf Extract of P. Austroarabica. OpenNano 2022, 8, 100067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamkhande, P.G.; Ghule, N.W.; Bamer, A.H.; Kalaskar, M.G. Metal Nanoparticles Synthesis: An Overview on Methods of Preparation, Advantages and Disadvantages, and Applications. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 101174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatou, M.-A.; Lagopati, N.; Vagena, I.-A.; Gazouli, M.; Pavlatou, E.A. ZnO Nanoparticles from Different Precursors and Their Photocatalytic Potential for Biomedical Use. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleemi, M.A.; Alallam, B.; Yong, Y.K.; Lim, V. Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles with Bioflavonoid Rutin: Characterisation, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities and In Vivo Cytotoxic Effects on Artemia Nauplii. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, V.; Muthukumar Sathya, P.; Srivalli, T.; Mohan, H. Synthesis of Quercetin Functionalized Wurtzite Type Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles and Their Potential to Regulate Intrinsic Apoptosis Signaling Pathway in Human Metastatic Ovarian Cancer. Life Sci. 2022, 309, 121022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halevas, E.; Mavroidi, B.; Pelecanou, M.; Hatzidimitriou, A.G. Structurally Characterized Zinc Complexes of Flavonoids Chrysin and Quercetin with Antioxidant Potential. Inorganica Chim. Acta. 2021, 523, 120407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Desimone, M.F.; Pandya, S.; Jasani, S.; George, N.; Adnan, M.; Aldarhami, A.; Bazaid, A.S.; Alderhami, S.A. Revisiting the Green Synthesis of Nanoparticles: Uncovering Influences of Plant Extracts as Reducing Agents for Enhanced Synthesis Efficiency and Its Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 4727–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrzynska, M.; Napierala, M.; Florek, E. Flavonoid Nanoparticles: A Promising Approach for Cancer Therapy. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terenteva, E.A.; Apyari, V.V.; Dmitrienko, S.G.; Zolotov, Y.A. Formation of Plasmonic Silver Nanoparticles by Flavonoid Reduction: A Comparative Study and Application for Determination of These Substances. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 151, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sysak, S.; Czarczynska-Goslinska, B.; Szyk, P.; Koczorowski, T.; Mlynarczyk, D.T.; Szczolko, W.; Lesyk, R.; Goslinski, T. Metal Nanoparticle-Flavonoid Connections: Synthesis, Physicochemical and Biological Properties, as Well as Potential Applications in Medicine. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirotkin, A.V.; Harrath, A.H. Phytoestrogens and Their Effects. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 741, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Křížová, L.; Dadáková, K.; Kašparovská, J.; Kašparovský, T. Isoflavones. Molecules 2019, 24, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Zorita, S.; González-Arceo, M.; Fernández-Quintela, A.; Eseberri, I.; Trepiana, J.; Portillo, M.P. Scientific Evidence Supporting the Beneficial Effects of Isoflavones on Human Health. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liga, S.; Paul, C. Puerarin-A Promising Flavonoid: Biosynthesis, Extraction Methods, Analytical Techniques, and Biological Effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.-X.; Zhang, H.; Peng, C. Puerarin: A Review of Pharmacological Effects. Phytother. Res. 2014, 28, 961–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Guan, Z.-Y.; Zhu, W.-F.; Zhong, L.-Y.; Qiu, Z.-Q.; Yue, P.-F.; Wu, W.-T.; Liu, J.; Huang, X. Preparation of Puerarin Chitosan Oral Nanoparticles by Ionic Gelation Method and Its Related Kinetics. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Q.; Chen, K.; Su, C.; Liu, X.; Luo, X. Puerarin Loaded PLGA Nanoparticles: Optimization Processes of Preparation and Anti-Alcohol Intoxication Effects in Mice. AAPS PharmSciTech 2021, 22, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, S.; Gu, L.; Kuang, Y.; Zhao, M.; You, Y.; Han, Q. Changes in the Content of Puerarin-PLGA Nanoparticles in Mice under the Influence of Alcohol and Analysis of Their Antialcoholism. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2023, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehra, T.; Ahsan, F.; Versiani, M.A.; Wahid, S.; Jahangir, S.; Shah, M.R. Puerarin-Coated Gold Nanoparticles (PUE-AuNPs) Synthesized via Green Synthetic Route: A New Colorimetric Probe for the Detection of Ciprofloxacin. Turk. J. Chem. 2021, 45, 1814–1827. [Google Scholar]
- Arendrup, M.C.; Cuenca-Estrella, M.; Lass-Flörl, C.; Hope, W. EUCAST Technical Note on the EUCAST Definitive Document EDef 7.2: Method for the Determination of Broth Dilution Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations of Antifungal Agents for Yeasts EDef 7.2 (EUCAST-AFST)*. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, E246–E247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically, 11th ed.; M07Ed11; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2018; Available online: www.clsi.org (accessed on 11 July 2024).
- Andrews, J.M. Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2001, 48 (Suppl. S1), 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buda, V.; Brezoiu, A.-M.; Berger, D.; Pavel, I.Z.; Muntean, D.; Minda, D.; Dehelean, C.A.; Soica, C.; Diaconeasa, Z.; Folescu, R.; et al. Biological Evaluation of Black Chokeberry Extract Free and Embedded in Two Mesoporous Silica-Type Matrices. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribatti, D. The Chick Embryo Chorioallantoic Membrane in the Study of Tumor Angiogenesis. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2008, 49, 131–135. [Google Scholar]
- Interagency Coordinating Committee on the Validation of Alternative Methods (ICCVAM). ICCVAM Test Method Evaluation Report: Current Validation Status of In Vitro Test Methods Proposed for Identifying Eye Injury Hazard Potential of Chemicals and Products Interagency Coordinating Committee on the Validation of Alternative Methods National Toxicology Program Interagency Center for the Evaluation of Alternative Toxicological Methods; NICEATM: Research Triangle Park, NC, USA, 2010. Available online: https://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/sites/default/files/iccvam/docs/ocutox_docs/invitro-2010/tmer-vol1.pdf (accessed on 6 July 2024).
- Luepke, N.P. Hen’s Egg Chorioallantoic Membrane Test for Irritation Potential. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1985, 23, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista-Duharte, A.; Murillo, G.J.; Pérez, U.M.; Tur, E.N.; Portuondo, D.F.; Martínez, B.T.; Téllez-Martínez, D.; Betancourt, J.E.; Pérez, O. The Hen’s Egg Test on Chorioallantoic Membrane: An Alternative Assay for the Assessment of the Irritating Effect of Vaccine Adjuvants. Int. J. Toxicol. 2016, 35, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvaraj, S.; Krishnaswamy, S.; Devashya, V.; Sethuraman, S.; Krishnan, U.M. Flavonoid–Metal Ion Complexes: A Novel Class of Therapeutic Agents. Med. Res. Rev. 2014, 34, 677–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, H.; Zhong, Q.-Z.; Li, J.; Lin, Z.; Cui, J.; Caruso, F.; Hao, J. Metal Ion-Directed Functional Metal–Phenolic Materials. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 11432–11473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walencik, P.K.; Choińska, R.; Gołębiewska, E.; Kalinowska, M. Metal–Flavonoid Interactions—From Simple Complexes to Advanced Systems. Molecules 2024, 29, 2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveenkumar, S.; Chandramohan, S.; Muthukumaran, A. A Novel Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Various Carbohydrate Sources and Its Antimicrobial Effects. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 36, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbrolesy, A.; Elhussiny, F.A.; Abdou, Y.; Morsy, R. Facile Synthesis and Biophysical Characterization of Novel Zinc Oxide/Fe3O4 Hybrid Nanocomposite as a Potentially Active Agent in Sunscreens. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2024, 49, 1083–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekar, M.; Mary, J.; Sivakumar, M.; Selvam, M. Recent Developments in Sunscreens Based on Chromophore Compounds and Nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 2529–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharathi, D.; Bhuvaneshwari, V. Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) Using Pure Bioflavonoid Rutin and Their Biomedical Applications: Antibacterial, Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Activities. Res. Chem. Interm. 2019, 45, 2065–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauc, J.; Menth, A. States in the Gap. J. Non Cryst. Solids 1972, 8–10, 569–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viezbicke, B.D.; Patel, S.; Davis, B.E.; Birnie, D.P., III. Evaluation of the Tauc Method for Optical Absorption Edge Determination: ZnO Thin Films as a Model System. Phys. Status Solidi (B) 2015, 252, 1700–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, E.P.I.I. Investigating Bandgap Energies, Materials, and Design of Light-Emitting Diodes. J. Chem. Educ. 2016, 93, 1289–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.; Yarbrough, R.; Froeschle, M.; White, J.; Rathnayake, H. Band Gap Engineered Zinc Oxide Nanostructures: Via a Sol-Gel Synthesis of Solvent Driven Shape-Controlled Crystal Growth. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 14638–14648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faisal, S.; Jan, H.; Shah, S.A.; Shah, S.; Khan, A.; Akbar, M.T.; Rizwan, M.; Jan, F.; Wajidullah; Akhtar, N.; et al. Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide (ZnO) Nanoparticles Using Aqueous Fruit Extracts of Myristica Fragrans: Their Characterizations and Biological and Environmental Applications. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 9709–9722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu Boppudi, H.; Subba Rao, Y.; Kuchi, C.; Ramesh Babu, A.; Govinda, V.; Jagadeesh, M.; Lavanya, M. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles as an Efficient Antioxidant, Photocatalyst, and Heterogeneous Catalyst in C–P Bond Synthesis. Results Chem. 2023, 6, 101227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczesny, R.; Scigala, A.; Derkowska-Zielinska, B.; Skowronski, L.; Cassagne, C.; Boudebs, G.; Viter, R.; Szłyk, E. Synthesis, Optical, and Morphological Studies of ZnO Powders and Thin Films Fabricated by Wet Chemical Methods. Materials 2020, 13, 2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A. A Review on the Factors Affecting the Photocatalytic Degradation of Hazardous Materials. Mater. Sci. Eng. Int. J. 2017, 1, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modwi, A.; Ghanem, M.A.; Al-Mayouf, A.M.; Houas, A. Lowering Energy Band Gap and Enhancing Photocatalytic Properties of Cu/ZnO Composite Decorated by Transition Metals. J. Mol. Struct. 2018, 1173, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyaleela, G.D.; Vimala, J.R.; Sheela, S.M.; Agila, A.R.; Bharathy, M.S.; Divya, M. Biofabrication of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using the Isolated Flavonoid from Combretum Ovalifolium and Its Anti-Oxidative Ability and Catalytic Degradation of Methylene Blue Dye. Orient. J. Chem. 2020, 36, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handore, K.; Bhavsar, S.; Horne, A.; Chhattise, P.; Mohite, K.; Ambekar, J.; Pande, N.; Chabukswar, V. Novel Green Route of Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles by Using Natural Biodegradable Polymer and Its Application as a Catalyst for Oxidation of Aldehydes. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A 2014, 51, 941–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sypniewska, M.; Szczesny, R.; Popielarski, P.; Strzalkowski, K.; Derkowska-Zielinska, B. Structural, Morphological and Photoluminescent Properties of Annealed ZnO Thin Layers Obtained by the Rapid Sol-Gel Spin-Coating Method. Opto-Electron. Rev. 2020, 28, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, T.-T.; Dang, C.-H.; Doan, V.-D.; Dang, V.-S.; Nguyen, T.-D. Biogenic Synthesis of Silver and Gold Nanoparticles from Lactuca Indica Leaf Extract and Their Application in Catalytic Degradation of Toxic Compounds. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020, 30, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.; Schoenenberger, M.; Gnecco, E.; Glatzel, T.; Meyer, E.; Brändlin, D.; Scandella, L. Characterization of Nanoparticles Using Atomic Force Microscopy. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2007, 61, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellotti, R.; Picotto, G.B.; Ribotta, L. AFM Measurements and Tip Characterization of Nanoparticles with Different Shapes. Nanomater. Metrol. 2022, 5, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamkouri, N.; Jomehzadeh, N.; Naserzadeh, N. Rapid Biosynthesis and Antibacterial Activity of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Fruit Peel of Punica Granatum L as Cellulose. Curr. Res. Green Sustain. Chem. 2023, 6, 100366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzakar, S.; Skali Senhaji, N.; Saidi, M.Z.; El Hadri, M.; El Baaboua, A.; El Harsal, A.; Abrini, J. Antibacterial and Antifungal Activity of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Produced by Phaeodactylum Tricornutum Culture Supernatants and Their Potential Application to Extend the Shelf Life of Sweet Cherry (Prunus avium L.). Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2023, 49, 102666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudley, A.C.; Griffioen, A.W. Pathological Angiogenesis: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies. Angiogenesis 2023, 26, 313–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-L.; Chen, H.-H.; Zheng, L.-L.; Sun, L.-P.; Shi, L. Angiogenic Signaling Pathways and Anti-Angiogenic Therapy for Cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace Intasa-ard, S.; Birault, A. Nanoparticles Characterization Using the CAM Assay. Enzymes 2019, 46, 129–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhr, C.R.; Wiesmann, N.; Tanner, R.C.; Brieger, J.; Eckrich, J. The Chorioallantoic Membrane Assay in Nanotoxicological Research—An Alternative for In Vivo Experimentation. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Possible Assignment for Compound Class | Absorption Peaks in PUE-ZnO NPs (cm−1) | Absorption Peaks in Puerarin (cm−1) |
|---|---|---|
| O-H stretching vibrations | 3363 | 3324 |
| - | 3224 | |
| - | 3118 | |
| - | 2899 | |
| C-C bond stretching of the aromatic rings | 1550 | 1564 |
| C=O stretching vibrations of the aryl ketone group | 1506 | 1514 |
| O-H bending in-plane vibrations of the phenolic groups | 1390 | 1396 |
| C-O-C stretching vibrations | 1043 | 1057 |
| C-H aromatic bending vibrations with substituted arrays | 831 | 835 |
| Zn-O symmetric vibrations | 543 | - |
| 451 | - |
| Bacterial and Yeast Strains | MIC Value (mg/mL) |
|---|---|
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 | 25 |
| Streptococcus pyogenes ATCC 19615 | 25 |
| Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 | 25 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 27853 | NA |
| Candida parapsilosis ATCC 22019 | 50 |
| Test Compound and Controls | Irritation Score (IS) | * Irritation Category/Type of Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Negative control H2O | 0 | Non-irritant |
| Positive control SDS 0.5% | 17.29 | Strongly irritant |
| Puerarin, 100 μg/mL | 0 | Non-irritant |
| PUE-ZnO NPs, 100 μg/mL | 0 | Non-irritant |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liga, S.; Vodă, R.; Lupa, L.; Paul, C.; Nemeş, N.S.; Muntean, D.; Avram, Ș.; Gherban, M.; Péter, F. Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Puerarin: Characterization, Antimicrobial Potential, Angiogenesis, and In Ovo Safety Profile Assessment. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1464. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16111464
Liga S, Vodă R, Lupa L, Paul C, Nemeş NS, Muntean D, Avram Ș, Gherban M, Péter F. Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Puerarin: Characterization, Antimicrobial Potential, Angiogenesis, and In Ovo Safety Profile Assessment. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(11):1464. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16111464
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiga, Sergio, Raluca Vodă, Lavinia Lupa, Cristina Paul, Nicoleta Sorina Nemeş, Delia Muntean, Ștefana Avram, Mihaela Gherban, and Francisc Péter. 2024. "Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Puerarin: Characterization, Antimicrobial Potential, Angiogenesis, and In Ovo Safety Profile Assessment" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 11: 1464. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16111464
APA StyleLiga, S., Vodă, R., Lupa, L., Paul, C., Nemeş, N. S., Muntean, D., Avram, Ș., Gherban, M., & Péter, F. (2024). Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Puerarin: Characterization, Antimicrobial Potential, Angiogenesis, and In Ovo Safety Profile Assessment. Pharmaceutics, 16(11), 1464. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16111464











