New MoS2/Tegafur-Containing Pharmaceutical Formulations for Selective LED-Based Skin Cancer Photo-Chemotherapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. MoS2 Nanosheet Production
2.2. MoS2 Nanosheets Characterization
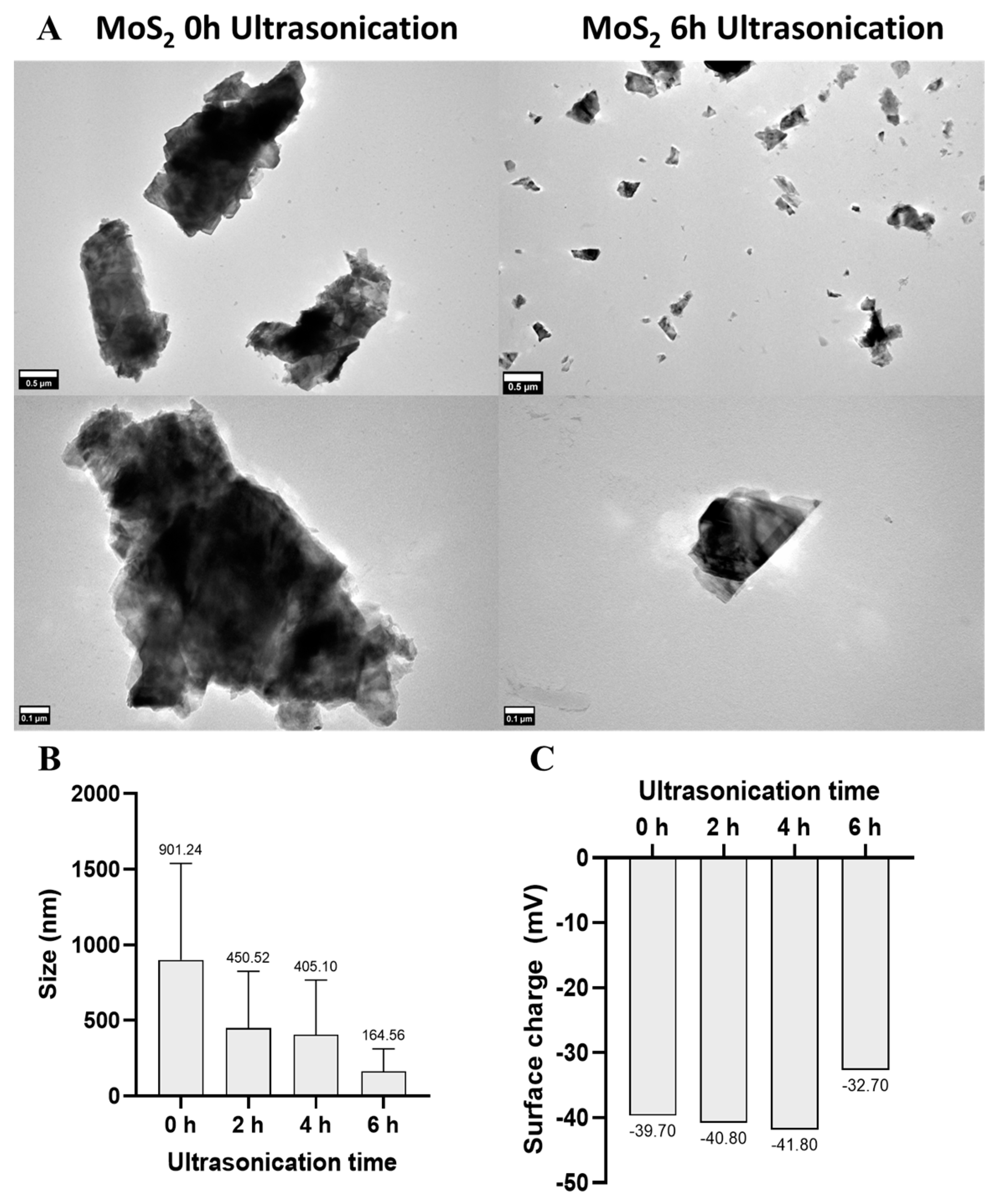
2.2.1. Transmission Electron Microscopy
2.2.2. Zeta Potential Measurements
2.2.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis
2.2.4. Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectrometry
2.2.5. UV–Visible Spectroscopy
2.2.6. Photothermal Properties
2.3. Hydrogel Production
2.4. In Vitro Studies
2.4.1. Cell Culture
2.4.2. Cytotoxicity Assays of Tegafur and MoS2 Nanosheets
2.4.3. Cytocompatibility of MoS2/Tegafur Hydrogels and Photothermal Therapy
Live/Dead Assays
2.4.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. MoS2 Dispersions’ Physico-Chemical Characterization
3.2. MoS2 Cytocompatibility Optimization
3.3. MoS2 Cytotoxicity under NIR Irradiation
3.4. Tegafur Cytotoxicity/Cytocompatibility Optimization
4. Hydrogels’ Characterization
4.1. MoS2/Tegafur Hydrogels’ Cytocompatibility
4.2. MoS2/Tegafur Hydrogels’ Selective PTT Effect Optimization
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pacheco, A.G.; Krohling, R.A. The impact of patient clinical information on automated skin cancer detection. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 116, 103545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehiniya, H.; Soltani, S.; Enayatrad, M.; Fathali-Loy-Dizaji, M.; Razi, S.; Mohammadian-Hafshejani, A. The epidemiology of skin cancer and its trend in Iran. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2015, 6, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics. Ca Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, A.I.; Chen, E.H.; Ratner, D. Basal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 2262–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauvar, A.N.; Cronin, T., Jr.; Roenigk, R.; Hruza, G.; Bennett, R. Consensus for nonmelanoma skin cancer treatment: Basal cell carcinoma, including a cost analysis of treatment methods. Dermatol. Surg. 2015, 41, 550–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermertcan, A.T.; Hellings, P.W.; Cingi, C. Nonmelanoma Skin Cancer of the Head and Neck Nonsurgical Treatment. Facial Plast. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 20, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newlands, C.; Currie, R.; Memon, A.; Whitaker, S.; Woolford, T. Non-melanoma skin cancer: United Kingdom National Multidisciplinary Guidelines. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2016, 130, S125–S132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, M.C.F.; Sousa, J.J.S.; Pais, A.A.C.C. Skin cancer and new treatment perspectives: A review. Cancer Lett. 2015, 357, 8–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tohme, S.; Simmons, R.L.; Tsung, A. Surgery for cancer: A trigger for metastases. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 1548–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grewal, S.; Oosterling, S.J.; van Egmond, M. Surgery for Colorectal Cancer: A Trigger for Liver Metastases Development? New Insights into the Underlying Mechanisms. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, A.; Schmalbach, C.E. Surgery in the Era of Immunotherapy for Advanced Head and Neck Non-melanoma Skin Cancer. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2023, 25, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kansara, S.; Bell, D.; Weber, R. Surgical management of non melanoma skin cancer of the head and neck. Oral Oncol. 2020, 100, 104485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabir, F.; Barani, M.; Rahdar, A.; Bilal, M.; Nadeem, M. How to face skin cancer with nanomaterials: A review. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2021, 11, 11931–11955. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, N.; Nadaf, A.; Imran, M.; Jiba, U.; Sheikh, A.; Almalki, W.H.; Almujri, S.S.; Mohammed, Y.H.; Kesharwani, P.; Ahmad, F.J. Skin cancer: Understanding the journey of transformation from conventional to advanced treatment approaches. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caro, C.; Gámez, F.; Quaresma, P.; Páez-Muñoz, J.; Domínguez, A.; Pearson, J.; Leal, M.P.; Beltrán, A.; Fernandez-Afonso, Y.; De la Fuente, J.; et al. Fe3O4-Au Core-Shell Nanoparticles as a Multimodal Platform for In Vivo Imaging and Focused Photothermal Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Li, D.; Lee, C.; Xie, J. Nanoparticle Phototherapy in the Era of Cancer Immunotherapy. Trends Chem. 2020, 2, 1082–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, F.; Sarmento, B. Targeted Photodynamic Immunotherapy, in Systemic Drug Delivery Strategies; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 463–481. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, X.; Shao, Z.; Zhao, Y. Solutions to the Drawbacks of Photothermal and Photodynamic Cancer Therapy. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2002504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Wang, H.; He, B.; Zeng, L.; Tan, T.; Cao, H.; He, X.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, S.; Li, Y. Current Approaches of Photothermal Therapy in Treating Cancer Metastasis with Nanotherapeutics. Theranostics 2016, 6, 762–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattani, V.P.; Shah, J.; Atalis, A.; Sharma, A.; Tunnell, J.W. Role of apoptosis and necrosis in cell death induced by nanoparticle-mediated photothermal therapy. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2015, 17, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhan, X.; Xiong, J.; Peng, S.; Huang, W.; Joshi, R.; Cai, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, R.; Yuan, K.; et al. Temperature-dependent cell death patterns induced by functionalized gold nanoparticle photothermal therapy in melanoma cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lv, Q.; Ma, G.; Gao, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, C.; Li, C.; Sun, X.; et al. A Polyoxometalate-Encapsulated Metal–Organic Framework Nanoplatform for Synergistic Photothermal–Chemotherapy and Anti-Inflammation of Ovarian Cancer. Molecules 2022, 27, 8350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Liang, X.; He, T.; Li, X.; Huang, X.; Wang, N.; Shen, M.; Shu, Y.; Wu, R.; Zhang, M.; et al. Multifunctional light-activatable nanocomplex conducting temperate-heat photothermal therapy to avert excessive inflammation and trigger augmented immunotherapy. Biomaterials 2022, 290, 121815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, F.A.L.S.; Chang, H.; Incorvia, J.A.C.; Oliveira, M.J.; Sarmento, B.; Santos, S.G.; Magalhães, F.D.; Pinto, A.M. 2D Nanomaterials and Their Drug Conjugates for Phototherapy and Magnetic Hyperthermia Therapy of Cancer and Infections. Small 2023, 20, e2306137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, R.K.; Prabhakar, P.; Bisht, N.; Patel, M.; Mishra, S.; Yadav, A.K.; Venu, D.V.; Gupta, G.K.; Solanki, P.R.; Ramakrishnan, S.; et al. 2D Materials-Based Aptamer Biosensors: Present Status and Way Forward. Curr. Med. Chem. 2022, 29, 5815–5849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Li, A.; Zhao, W.; Liu, J. Recent Advances in Functional Polymer Decorated Two-Dimensional Transition-Metal Dichalcogenides Nanomaterials for Chemo-Photothermal Therapy. Chem.—A Eur. J. 2018, 24, 4215–4227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, S.; Gu, Z.; Zhao, Y. A bibliometric analysis: Research progress and prospects on transition metal dichalcogenides in the biomedical field. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 3762–3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Kumar, P.; Late, D.; Kumar, A.; Patel, S.; Singh, J. 2D layered transition metal dichalcogenides (MoS2): Synthesis, applications and theoretical aspects. Appl. Mater. Today 2018, 13, 242–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolobov, A.V.; Tominaga, J. Two-Dimensional Transition-Metal Dichalcogenides; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; Volume 239. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Sun, H.; Bai, X. Two-Dimensional Transition Metal Dichalcogenides: Synthesis, Biomedical Applications and Biosafety Evaluation. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Liu, Z. 2D MoS2 Nanostructures for Biomedical Applications. Adv. Health Mater. 2017, 7, e1701158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.; Roy, S.; Singh, P.; Khan, Z.; Jaiswal, A. 2D MoS2-based nanomaterials for therapeutic, bioimaging, and biosensing applications. Small 2019, 15, 1803706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazaka, K.; Levchenko, I.; Lim, J.W.M.; Baranov, O.; Corbella, C.; Xu, S.; Keidar, M. MoS2-based nanostructures: Synthesis and applications in medicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2019, 52, 183001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, C.Y. Recent advances in MoS2-based photothermal therapy for cancer and infectious disease treatment. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 5793–5807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Pan, J.; Fang, Y.; Che, X.; Wang, D.; Bu, K.; Huang, F. Metastable MoS2: Crystal structure, electronic band structure, synthetic approach and intriguing physical properties. Chem.—A Eur. J. 2018, 24, 15942–15954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Zhu, H.; Wang, Y.; Sevencan, C.; Li, B.L. Functionalized MoS2-Based Nanomaterials for Cancer Phototherapy and Other Biomedical Applications. ACS Mater. Lett. 2021, 3, 462–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radisavljevic, B.; Radenovic, A.; Brivio, J.; Giacometti, V.; Kis, A. Single-layer MoS2 transistors. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Liu, C.; Hu, D.; Wang, F.; Wu, H.; Gong, X.; Liu, X.; Song, L.; Sheng, Z.; Zheng, H. Single-Layer MoS2 Nanosheets with Amplified Photoacoustic Effect for Highly Sensitive Photoacoustic Imaging of Orthotopic Brain Tumors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 8715–8725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, S.; Tripathi, S.; Singh, K. Recent progress in MoS2 nanostructures for biomedical applications: Experimental and computational approach. Anal. Biochem. 2023, 685, 115404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Lu, J.; Zheng, X.; Chen, B.; Luo, Y.; Tahir, M.N.; Huang, B.; Xia, X.; Pan, X. A critical review on the applications and potential risks of emerging MoS2 nanomaterials. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 399, 123057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caro, C.; Avasthi, A.; Paez-Muñoz, J.M.; Pernia Leal, M.; García-Martín, M.L. Passive targeting of high-grade gliomas via the EPR effect: A closed path for metallic nanoparticles? Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 7984–7995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, J.W.; Bae, Y.H. EPR: Evidence and fallacy. J. Control. Release 2014, 190, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.A.L.S.; Costa-Almeida, R.; Timochenco, L.; Amaral, S.I.; Pinto, S.; Gonçalves, I.C.; Fernandes, J.R.; Magalhães, F.D.; Sarmento, B.; Pinto, A.M. Graphene Oxide Topical Administration: Skin Permeability Studies. Materials 2021, 14, 2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wang, C.; Gu, X.; Gong, H.; Cheng, L.; Shi, X.; Feng, L.; Sun, B.; Liu, Z. Drug Delivery with PEGylated MoS2 Nano-sheets for Combined Photothermal and Chemotherapy of Cancer. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 3433–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ji, X.; Liu, J.; Tong, W.W.L.; Askhatova, D.; Shi, J. Tantalum Sulfide Nanosheets as a Theranostic Nanoplatform for Computed Tomography Imaging-Guided Combinatorial Chemo-Photothermal Therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1703261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Liu, Z.; Cao, Y.; Dai, W.; Zhang, K.; Dong, H.; Feng, X.; Zhang, X. Fabricating Aptamer-Conjugated PEGylated-MoS2/Cu1. 8S Theranostic Nanoplatform for Multiplexed Imaging Diagnosis and Chemo-Photothermal Therapy of Cancer. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1605592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, J.; Bremner, D.H.; Niu, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xie, X.; Zhu, L.-M. A multifunctional nanoplatform based on MoS2-nanosheets for targeted drug delivery and chemo-photothermal therapy. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2020, 185, 110585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, J.; Williams, G.R.; Niu, S.; Qian, Q.; Zhu, L.-M. Functionalized MoS2-nanosheets for targeted drug delivery and chemo-photothermal therapy. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2019, 173, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Yan, L.; Yu, J.; Tian, G.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, X.; Yong, Y.; Li, J.; Gu, Z.; et al. High-Throughput Synthesis of Single-Layer MoS2 Nanosheets as a Near-Infrared Photothermal-Triggered Drug Delivery for Effective Cancer Therapy. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 6922–6933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zheng, J.; Nie, H.; Chen, H.; Li, B.; Jia, L. Co-delivery of erlotinib and doxorubicin by MoS2 nanosheets for synergetic photothermal chemotherapy of cancer. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 381, 122541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Yang, N.; Cheng, J.; Yang, M.; Deng, T.; Li, Y.; Feng, C. Layered MoS2 nanosheets modified by biomimetic phospholipids: Enhanced stability and its synergistic treatment of cancer with chemo-photothermal therapy. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2020, 187, 110631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, N.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Feng, J.; Zhang, X. NIR Light-Triggered Degradable MoTe2 Nanosheets for Combined Photothermal and Chemotherapy of Cancer. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1801139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, K.; Zhang, Y. Multifunctional MoS2 nanosheets with Au NPs grown in situ for synergistic chemo-photothermal therapy. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2019, 184, 110551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, S.; Kan, S.; Sun, R.; Zhou, R.; Sun, Y.; Chen, W.; Yu, B. Fabricating polydopamine-coated MoSe2-wrapped hollow mesoporous silica nanoplatform for controlled drug release and chemo-photothermal therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 7607–7621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Q.; Yang, P.; Lin, H.; Qu, F. Hierarchical MoSe2 nanoflowers as novel nanocarriers for NIR-light-mediated synergistic photo-thermal/dynamic and chemo-therapy. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 14534–14545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Bai, J.; Liu, Y.; Jia, X.; Jiang, X. Polydopamine Coated Selenide Molybdenum: A New Photothermal Nanocarrier for Highly Effective Chemo-Photothermal Synergistic Therapy. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2, 2011–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Lin, H.; Qu, F. Biodegradable hollow MoSe2/Fe3O4 nanospheres as the photodynamic therapy-enhanced agent for multimode CT/MR/IR imaging and synergistic antitumor therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 43964–43975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Ye, P.; Zhao, R.; Yang, M. Magnetic WS2 nanosheets functionalized by biomimetic lipids with enhanced dispersibility for combined photothermal and chemotherapy therapy. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 86, 104744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Wu, X.; Li, Z.; Fan, J.; Hu, X.; Liu, B. PEGylated WS2 nanodrug system with erythrocyte membrane coating for chemo/photothermal therapy of cervical cancer. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 5088–5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qi, X.; Ye, P.; Yang, M.; Xie, M. Construction of WS2/Au-lipid drug delivery system for multiple combined therapy of tumor. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 76, 103747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.; Yi, H.; Fan, F.; Fu, L.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ji, S.; Su, Y. Facile exfoliation of MoS2 nanosheets by protein as a photothermal-triggered drug delivery system for synergistic tumor therapy. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 77083–77092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronson, J.K. Meyler’s Side Effects of Drugs 15E The International Encyclopedia of Adverse Drug Reactions and Interactions; Newnes: Waltham, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- E Ward, S.; Kaltenthaler, E.; Cowan, J.; Marples, M.; Orr, B.; Seymour, M.T. The clinical and economic benefits of capecitabine and tegafur with uracil in metastatic colorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 95, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayakawa, M.; Kojima, Y. Tegafur/gimeracil/oteracil (S-1) approved for the treatment of advanced gastric cancer in adults when given in combination with cisplatin: A review comparing it with other fluoropyrimidine-based therapies. OncoTargets Ther. 2011, 4, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saif, M.W.; Elfiky, A.A. Identifying and treating fluoropyrimidine-associated hand-and-foot syndrome in white and non-white patients. J. Support. Oncol. 2007, 5, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rifai, N.; Horvath, A.R.; Wittwer, C.T. Principles and Applications of Molecular Diagnostics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto, Y.; Yoshida, Y.; Yamada, T.; Aisu, N.; Yoshimatsu, G.; Yoshimura, F.; Hasegawa, S. Current Status of Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of 5-Fluorouracil Prodrugs. Anticancer. Res. 2020, 40, 4655–4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taveira, S.F.; Lopez, R.V. Topical Administration of Anticancer Drugs for Skin Cancer Treatment. In Skin Cancers-Risk Factors, Prevention and Therapy; Porta, C.A.L., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; pp. 247–272. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Mooney, D.J. Designing hydrogels for controlled drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Song, C.; Wang, C.; Hu, Y.; Wu, J. Hydrogel-Based Controlled Drug Delivery for Cancer Treatment: A Review. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 17, 373–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safitri, F.I.; Nawangsari, D.; Febrina, D. Overview: Application of carbopol 940 in gel. In International Conference on Health and Medical Sciences (AHMS 2020); Atlantis Press: Paris, France, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhu, D.; Shen, X.; Yang, B. Preparation and pharmaceutical/pharmacodynamic evaluation of topical brucine-loaded liposomal hydrogel. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2009, 20, 2075–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Wang, E. Ultrafine transition metal dichalcogenide nanodots prepared by polyvinylpyrrolidone-assisted liquid phase exfoliation. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 2609–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timochenco, L.; Costa-Almeida, R.; Bogas, D.; Silva, F.A.L.S.; Silva, J.; Pereira, A.; Magalhães, F.D.; Pinto, A.M. High-Yield Production of Nano-Lateral Size Graphene Oxide by High-Power Ultrasonication. Materials 2021, 14, 1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.A.; Timochenco, L.; Costa-Almeida, R.; Fernandes, J.R.; Santos, S.G.; Magalhães, F.D.; Pinto, A.M. UV-C driven reduction of nanographene oxide opens path for new applications in phototherapy. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2024, 233, 113594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Das, M.K. Production and Physicochemical Characterization of Nanocosmeceuticals, in Nanocosmeceuticals; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 95–138. [Google Scholar]
- Thangappan, R.; Kalaiselvam, S.; Elayaperumal, A.; Jayavel, R.; Arivanandhan, M.; Karthikeyan, R.; Hayakawa, Y. Graphene decorated with MoS2 nanosheets: A synergetic energy storage composite electrode for supercapacitor applications. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 2637–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Y. Preparation of high-performance natural rubber/carbon black/molybdenum disulfide composite by using the premixture of epoxidized natural rubber and cysteine-modified molybdenum disulfide. Polym. Bull. 2021, 78, 1213–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-H.; Tsai, C.-H.; Tseng, F.-G.; Yu, Y.-Y.; Wu, H.-C.; Hsieh, C.-K. Low-Temperature Thermally Reduced Molybdenum Disulfide as a Pt-Free Counter Electrode for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Song, P.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Q. Facile synthesis, characterization and gas sensing performance of ZnO nanoparticles-coated MoS2 nanosheets. J. Alloy. Compd. 2016, 662, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tsuzuki, T.; Tang, B.; Cizek, P.; Sun, L.; Wang, X. Synthesis of silica-coated ZnO nanocomposite: The resonance structure of polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP) as a coupling agent. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2010, 288, 1705–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, D.; Li, Z.; Wang, J. Enhanced Exfoliation Effect of Solid Auxiliary Agent On the Synthesis of Biofunctionalized MoS2 Using Grindstone Chemistry. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2016, 33, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.T.; Tabakman, S.M.; Liang, Y.; Wang, H.; Casalongue, H.S.; Vinh, D.; Dai, H. Ultrasmall Reduced Graphene Oxide with High Near-Infrared Absorbance for Photothermal Therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 6825–6831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumcenco, D.; Ovchinnikov, D.; Marinov, K.; Lazic, P.; Gibertini, M.; Marzari, N.; Sanchez, O.L.; Kung, Y.C.; Krasnozhon, D.; Chen, M.W. Large-area epitaxial monolayer MoS2. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 4611–4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramana, L.N.; Mudakavi, R.J.; Raichur, A.M. Self-assembled albumin decorated MoS2 aggregates and photo-stimuli induced geometrical switching for enhanced theranostics applications. Mater. Adv. 2020, 1, 3000–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 10993-5:2009; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices. Part 5: Tests for In Vitro Cytotoxicity. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- Hu, Q.-D.; Fan, H.; Lou, W.-J.; Wang, Q.-Q.; Tang, G.-P. Polyethylenimine-cyclodextrin-tegafur conjugate shows anti-cancer activity and a potential for gene delivery. J. Zhejiang Univ. B 2011, 12, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badea, I.; Moja, D.; Tudose, A.; Stoicescu, D. Determination of the 5-fluorouracil and N1(2’-furanidyl)uracil in the presence of tegafur by zero-crossing first derivative spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2002, 30, 1371–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avendaäno, C.; Menâendez, J.C. Medicinal Chemistry of Anticancer Drugs; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhai, G. Recent Developments of Phototherapy Based on Graphene Family Nanomaterials. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 268–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, S.I.; Silva, F.A.L.S.; Costa-Almeida, R.; Timochenco, L.; Fernandes, J.R.; Sarmento, B.; Gonçalves, I.C.; Magalhães, F.D.; Pinto, A.M. Pharmaceutical Formulations Containing Graphene and 5-Fluorouracil for Light-Emitting Diode-Based Photochemotherapy of Skin Cancer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 4333–4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Cui, H.; Yan, S.; Jing, X.; Wang, D.; Meng, L. Gold nanostars decorated MnO2 nanosheets for magnetic resonance imaging and photothermal erasion of lung cancer cell. Mater. Today Commun. 2018, 16, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, A.; Choi, W.I.; Lee, J.H.; Tae, G. Graphene oxide mediated delivery of methylene blue for combined photodynamic and photothermal therapy. Biomater. 2013, 34, 6239–6248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, D.; Nudelman, A.; Tarasenko, N.; Levovich, I.; Makarovsky, I.; Sochotnikov, S.; Tarasenko, I.; Rephaeli, A. Novel Prodrugs of Tegafur that Display Improved Anticancer Activity and Antiangiogenic Properties. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa-Almeida, R.; Bogas, D.; Fernandes, J.R.; Timochenco, L.; Silva, F.A.L.S.; Meneses, J.; Gonçalves, I.C.; Magalhães, F.D.; Pinto, A.M. Near-Infrared Radiation-Based Mild Photohyperthermia Therapy of Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer with PEGylated Reduced Nanographene Oxide. Polymers 2020, 12, 1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadis, M.A.; Cooper, P.R.; Milward, M.R.; Gorecki, P.C.; Tarte, E.; Churm, J.; Palin, W.M. Development and application of LED arrays for use in phototherapy research. J. Biophotonics 2017, 10, 1514–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, N.G.; Wu, C.-H.; Cheng, T.C. Light-emitting diodes—Their potential in biomedical applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 2161–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Element Number | Element Symbol | Element Name | Atomic % | Weight % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | C | Carbon | 24.7 | 8.5 |
| 12 | Mg | Magnesium | 1.3 | 0.9 |
| 13 | Al | Aluminum | 32.1 | 24.8 |
| 16 | S | Sulfur | 27.0 | 24.8 |
| 42 | Mo | Molybdenum | 14.9 | 41.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Campos, M.T.; Silva, F.A.L.S.; Fernandes, J.R.; Santos, S.G.; Magalhães, F.D.; Oliveira, M.J.; Pinto, A.M. New MoS2/Tegafur-Containing Pharmaceutical Formulations for Selective LED-Based Skin Cancer Photo-Chemotherapy. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16030360
Campos MT, Silva FALS, Fernandes JR, Santos SG, Magalhães FD, Oliveira MJ, Pinto AM. New MoS2/Tegafur-Containing Pharmaceutical Formulations for Selective LED-Based Skin Cancer Photo-Chemotherapy. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(3):360. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16030360
Chicago/Turabian StyleCampos, Miguel T., Filipa A. L. S. Silva, José Ramiro Fernandes, Susana G. Santos, Fernão D. Magalhães, Maria J. Oliveira, and Artur M. Pinto. 2024. "New MoS2/Tegafur-Containing Pharmaceutical Formulations for Selective LED-Based Skin Cancer Photo-Chemotherapy" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 3: 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16030360
APA StyleCampos, M. T., Silva, F. A. L. S., Fernandes, J. R., Santos, S. G., Magalhães, F. D., Oliveira, M. J., & Pinto, A. M. (2024). New MoS2/Tegafur-Containing Pharmaceutical Formulations for Selective LED-Based Skin Cancer Photo-Chemotherapy. Pharmaceutics, 16(3), 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16030360









