Forecasting Fetal Buprenorphine Exposure through Maternal–Fetal Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
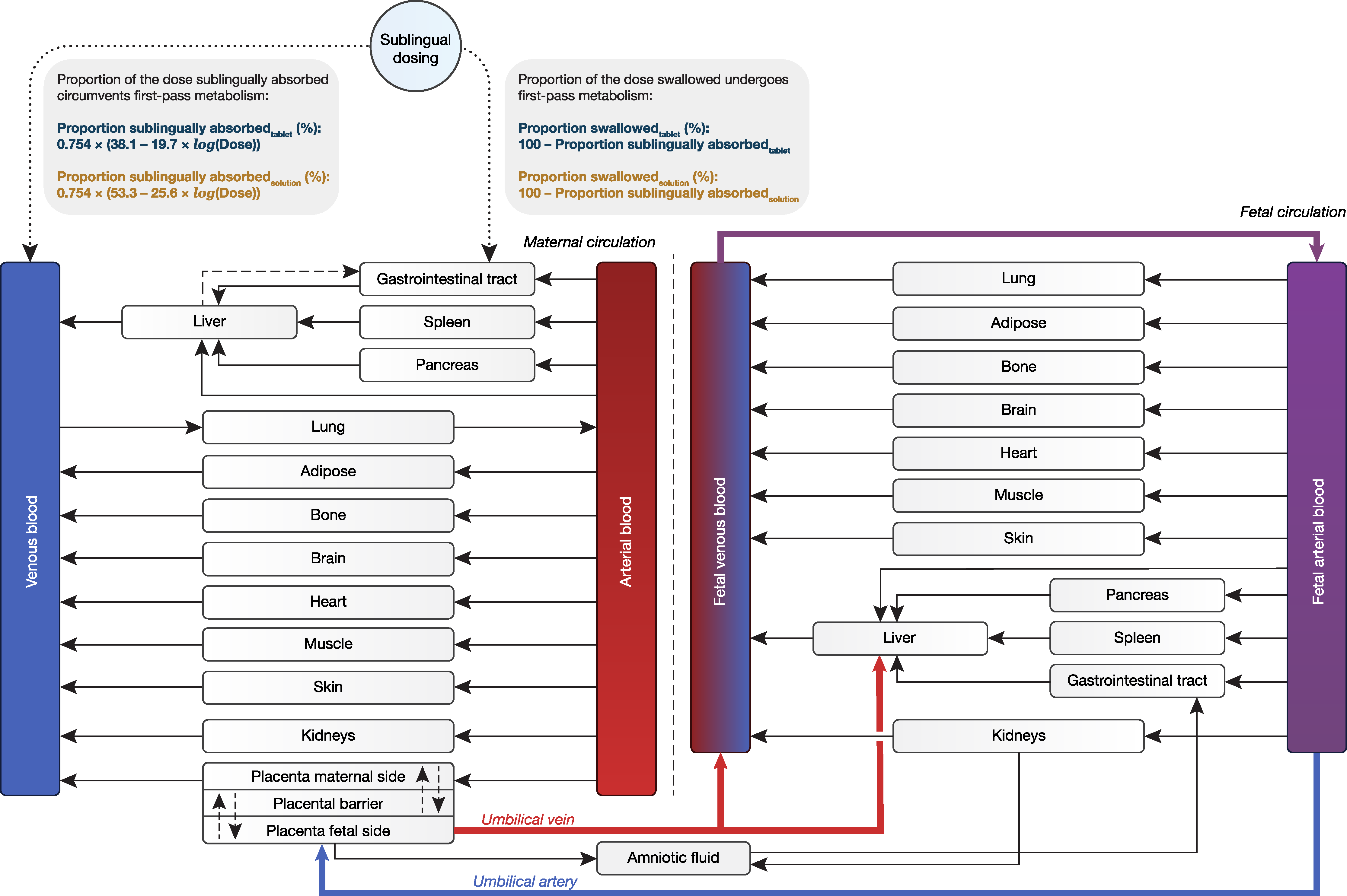
2.1. Maternal–Fetal PBPK Model Structure
2.2. Effect of Salivary pH on Sublingual Absorption of Buprenorphine
2.3. Buprenorphine Tissue Partitioning throughout Gestation
2.4. Pregnancy-Induced Changes in Enzyme Expression
2.5. Placental Transfer of Buprenorphine
2.6. Verifying the Prediction of Maternal Pharmacokinetics (PK) during Pregnancy
2.7. Verifying the Prediction of Fetal PK during Pregnancy
2.8. Statistical Analysis and Evaluation of Potential Bias
3. Results
3.1. Reduced Sublingual Absorption of Buprenorphine Due to Lower Salivary pH during Pregnancy
3.2. Maternal PBPK Model Prediction during Pregnancy
3.3. Maternal–Fetal PBPK Model Prediction at Delivery
3.4. Evaluation of Bias in the Maternal–Fetal PBPK Model Prediction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Syme, M.R.; Paxton, J.W.; Keelan, J.A. Drug transfer and metabolism by the human placenta. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2004, 43, 487–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacifici, G.M.; Nottoli, R. Placental transfer of drugs administered to the mother. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1995, 28, 235–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Mao, Q. ATP-binding cassette efflux transporters in human placenta. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2011, 12, 674–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speirs, A.L. Thalidomide and congenital abnormalities. Lancet 1962, 1, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, A.H.; Ko, J.Y.; Owens, P.L.; Stocks, C.; Patrick, S.W. Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome and Maternal Opioid-Related Diagnoses in the US, 2010-2017. JAMA 2021, 325, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraft, W.K.; Adeniyi-Jones, S.C.; Chervoneva, I.; Greenspan, J.S.; Abatemarco, D.; Kaltenbach, K.; Ehrlich, M.E. Buprenorphine for the Treatment of the Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 2341–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disher, T.; Gullickson, C.; Singh, B.; Cameron, C.; Boulos, L.; Beaubien, L.; Campbell-Yeo, M. Pharmacological Treatments for Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. JAMA Pediatr. 2019, 173, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krans, E.E.; Kim, J.Y.; James, A.E., 3rd; Kelley, D.; Jarlenski, M.P. Medication-Assisted Treatment Use Among Pregnant Women with Opioid Use Disorder. Obstet. Gynecol. 2019, 133, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, A.E.; Freund, M.P.; Archer, S.W.; Bremer, A.A. Toward the use of buprenorphine in infants for neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome: Summary of an NIH workshop. J. Perinatol. 2021, 41, 1213–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraft, W.K. Buprenorphine in Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 103, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, T.; McPhail, B.T.; Kamatkar, S.; Wexelblatt, S.; Ward, L.; Christians, U.; Akinbi, H.T.; Vinks, A.A. Physiologic Indirect Response Modeling to Describe Buprenorphine Pharmacodynamics in Newborns Treated for Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2021, 60, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Hoogdalem, M.W.; Johnson, T.N.; McPhail, B.T.; Kamatkar, S.; Wexelblatt, S.L.; Ward, L.P.; Christians, U.; Akinbi, H.T.; Vinks, A.A.; Mizuno, T. Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling to Investigate the Effect of Maturation on Buprenorphine Pharmacokinetics in Newborns with Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 111, 496–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, J.N.; Gastonguay, M.R.; Ng, C.M.; Adeniyi-Jones, S.C.; Moody, D.E.; Fang, W.B.; Ehrlich, M.E.; Kraft, W.K. The Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Buprenorphine in Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 103, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrick, S.W.; Barfield, W.D.; Poindexter, B.B. Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome. Pediatrics 2020, 146, e2020029074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Hoogdalem, M.W.; Wexelblatt, S.L.; Akinbi, H.T.; Vinks, A.A.; Mizuno, T. A review of pregnancy-induced changes in opioid pharmacokinetics, placental transfer, and fetal exposure: Towards fetomaternal physiologically-based pharmacokinetic modeling to improve the treatment of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 234, 108045. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Donohue, J.M.; Jarlenski, M.P.; Kim, J.Y.; Tang, L.; Ahrens, K.; Allen, L.; Austin, A.; Barnes, A.J.; Burns, M.; Chang, C.H.; et al. Use of Medications for Treatment of Opioid Use Disorder Among US Medicaid Enrollees in 11 States, 2014–2018. JAMA 2021, 326, 154–164. [Google Scholar]
- Dallmann, A.; van den Anker, J.N. Editorial: Exploring Maternal-Fetal Pharmacology Through PBPK Modeling Approaches. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 880402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abduljalil, K.; Ning, J.; Pansari, A.; Pan, X.; Jamei, M. Prediction of Maternal and Fetoplacental Concentrations of Cefazolin, Cefuroxime, and Amoxicillin during Pregnancy Using Bottom-Up Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Models. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2022, 50, 386–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hoogdalem, M.W.; Johnson, T.N.; Vinks, A.A.; Mizuno, T. Development and validation of a full physiologically-based pharmacokinetic model for sublingual buprenorphine that accounts for nonlinear bioavailability. Authorea 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abduljalil, K.; Furness, P.; Johnson, T.N.; Rostami-Hodjegan, A.; Soltani, H. Anatomical, physiological and metabolic changes with gestational age during normal pregnancy: A database for parameters required in physiologically based pharmacokinetic modelling. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2012, 51, 365–396. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Avdeef, A.; Barrett, D.A.; Shaw, P.N.; Knaggs, R.D.; Davis, S.S. Octanol-, chloroform-, and propylene glycol dipelargonat-water partitioning of morphine-6-glucuronide and other related opiates. J. Med. Chem. 1996, 39, 4377–4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migliario, M.; Bindi, M.; Surico, D.; De Pedrini, A.; Minsenti, S.; Pezzotti, F.; Mele, B.; Foglio Bonda, P.L. Changes in salivary flow rate and pH in pregnancy. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 1804–1810. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mendelson, J.; Upton, R.A.; Everhart, E.T.; Jacob, P., 3rd; Jones, R.T. Bioavailability of sublingual buprenorphine. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1997, 37, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodgers, T.; Rowland, M. Mechanistic approaches to volume of distribution predictions: Understanding the processes. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 918–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, T.; Rowland, M. Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modelling 2: Predicting the tissue distribution of acids, very weak bases, neutrals and zwitterions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 95, 1238–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abduljalil, K.; Pansari, A.; Jamei, M. Prediction of maternal pharmacokinetics using physiologically based pharmacokinetic models: Assessing the impact of the longitudinal changes in the activity of CYP1A2, CYP2D6 and CYP3A4 enzymes during pregnancy. J. Pharmacokinet. Pharmacodyn. 2020, 47, 361–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Jamei, M.; Yeo, K.R.; Tucker, G.T.; Rostami-Hodjegan, A. Prediction of intestinal first-pass drug metabolism. Curr. Drug Metab. 2007, 8, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NCBI. National Center for Biotechnology Information: PubChem Compound Summary for CID 644073, Buprenorphine. 2022. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/644073 (accessed on 20 April 2022).
- Zhang, H.; Kalluri, H.V.; Bastian, J.R.; Chen, H.; Alshabi, A.; Caritis, S.N.; Venkataramanan, R. Gestational changes in buprenorphine exposure: A physiologically-based pharmacokinetic analysis. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 84, 2075–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastian, J.R.; Chen, H.; Zhang, H.; Rothenberger, S.; Tarter, R.; English, D.; Venkataramanan, R.; Caritis, S.N. Dose-adjusted plasma concentrations of sublingual buprenorphine are lower during than after pregnancy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 216, 64.e1–64.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartu, A.E.; Ilett, K.F.; Hackett, L.P.; Doherty, D.A.; Hamilton, D. Buprenorphine exposure in infants of opioid-dependent mothers at birth. Aust. N. Z. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2012, 52, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegand, S.L.; Swortwood, M.J.; Huestis, M.A.; Thorp, J.; Jones, H.E.; Vora, N.L. Naloxone and Metabolites Quantification in Cord Blood of Prenatally Exposed Newborns and Correlations with Maternal Concentrations. AJP Rep. 2016, 6, e385–e390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullingham, R.E.; McQuay, H.J.; Porter, E.J.; Allen, M.C.; Moore, R.A. Sublingual buprenorphine used postoperatively: Ten hour plasma drug concentration analysis. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1982, 13, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAleer, S.D.; Mills, R.J.; Polack, T.; Hussain, T.; Rolan, P.E.; Gibbs, A.D.; Mullins, F.G.; Hussein, Z. Pharmacokinetics of high-dose buprenorphine following single administration of sublingual tablet formulations in opioid naïve healthy male volunteers under a naltrexone block. Drug Alcohol. Depend. 2003, 72, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanovskaya, T.N.; Bowen, R.S.; Patrikeeva, S.L.; Hankins, G.D.; Ahmed, M.S. Effect of plasma proteins on buprenorphine transfer across dually perfused placental lobule. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2009, 22, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanovskaya, T.; Deshmukh, S.; Brooks, M.; Ahmed, M.S. Transplacental transfer and metabolism of buprenorphine. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 300, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tournier, N.; Chevillard, L.; Megarbane, B.; Pirnay, S.; Scherrmann, J.M.; Declèves, X. Interaction of drugs of abuse and maintenance treatments with human P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) and breast cancer resistance protein (ABCG2). Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010, 13, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.Y.; Koh, K.H.; Jeong, H. Isoform-specific regulation of cytochromes P450 expression by estradiol and progesterone. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2013, 41, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerdin, E.; Salmonson, T.; Lindberg, B.; Rane, A. Maternal kinetics of morphine during labour. J. Perinat. Med. 1990, 18, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, D.H.; Brown, Z.A.; Tartaglione, T.; Burchett, S.K.; Opheim, K.; Coombs, R.; Corey, L. Pharmacokinetic disposition of zidovudine during pregnancy. J. Infect. Dis. 1991, 163, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanski, D.R.; Greenblatt, D.J.; Lowenstein, E. Kinetics of intravenous and intramuscular morphine. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1978, 24, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naritomi, Y.; Terashita, S.; Kagayama, A.; Sugiyama, Y. Utility of hepatocytes in predicting drug metabolism: Comparison of hepatic intrinsic clearance in rats and humans in vivo and in vitro. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2003, 31, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, A.; Sekiya, I.; Oya, A.; Koshino, T.; Araki, T. Assessment of the hepatic arterial and portal venous blood flows during pregnancy with Doppler ultrasonography. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2002, 266, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, X.; Wang, H.; Mikheev, A.M.; Mao, Q.; Unadkat, J.D. Effect of pregnancy on cytochrome P450 3a and P-glycoprotein expression and activity in the mouse: Mechanisms, tissue specificity, and time course. Mol. Pharmacol. 2008, 74, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, B.A.; Caperton, C.O.; Russell, L.N.; Cabanlong, C.V.; Wilson, C.D.; Urquhart, K.R.; Martins, B.S.; Zita, M.D.; Patton, A.L.; Alund, A.W.; et al. In Utero Exposure to Norbuprenorphine, a Major Metabolite of Buprenorphine, Induces Fetal Opioid Dependence and Leads to Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2019, 370, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laine, M.; Tenovuo, J.; Lehtonen, O.P.; Ojanotko-Harri, A.; Vilja, P.; Tuohimaa, P. Pregnancy-related changes in human whole saliva. Arch. Oral. Biol. 1988, 33, 913–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullingham, R.E.; McQuay, H.J.; Moore, A.; Bennett, M.R. Buprenorphine kinetics. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1980, 28, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkader, A.; Sproule, B. Buprenorphine: Clinical pharmacokinetics in the treatment of opioid dependence. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2005, 44, 661–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Ishii, S.; Arizono, H.; Nishimura, S.; Tsuruda, K.; Saito, N.; Nemoto, H.; Jin, Y.; Esumi, Y. Pharmacokinetics of buprenorphine hydrochloride (BN•HCl) (1): Absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion after percutaneous (TSN-09: BN·HCl containing tape application) or subcutaneous administration of BN·HCl in rats. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2001, 16, 569–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.E.; Myers, A.L.; Coop, A.; Eddington, N.D. Differential involvement of P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) in permeability, tissue distribution, and antinociceptive activity of methadone, buprenorphine, and diprenorphine: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 98, 4928–4940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, M.J.; Carr, K.D.; Simon, E.J. Pharmacokinetics of [3H]-buprenorphine in the rat. Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol. 1989, 64, 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Picard, N.; Cresteil, T.; Djebli, N.; Marquet, P. In vitro metabolism study of buprenorphine: Evidence for new metabolic pathways. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2005, 33, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.; Moody, D.E. Glucuronidation of buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine by human liver microsomes and UDP-glucuronosyltransferases. Drug Metab. Lett. 2009, 3, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cubitt, H.E.; Houston, J.B.; Galetin, A. Relative importance of intestinal and hepatic glucuronidation-impact on the prediction of drug clearance. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, T.N.; Jamei, M.; Rowland-Yeo, K. How Does In Vivo Biliary Elimination of Drugs Change with Age? Evidence from In Vitro and Clinical Data Using a Systems Pharmacology Approach. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2016, 44, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reckitt & Colman Pharmaceuticals, Inc. NDA: 20-733 Suboxone® Sublingual Tablets—Clinical Pharmacology/Biopharmaceutics Review; Reckitt & Colman Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Richmond, VA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
van Hoogdalem, M.W.; Tanaka, R.; Abduljalil, K.; Johnson, T.N.; Wexelblatt, S.L.; Akinbi, H.T.; Vinks, A.A.; Mizuno, T. Forecasting Fetal Buprenorphine Exposure through Maternal–Fetal Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16030375
van Hoogdalem MW, Tanaka R, Abduljalil K, Johnson TN, Wexelblatt SL, Akinbi HT, Vinks AA, Mizuno T. Forecasting Fetal Buprenorphine Exposure through Maternal–Fetal Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling. Pharmaceutics. 2024; 16(3):375. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16030375
Chicago/Turabian Stylevan Hoogdalem, Matthijs W., Ryota Tanaka, Khaled Abduljalil, Trevor N. Johnson, Scott L. Wexelblatt, Henry T. Akinbi, Alexander A. Vinks, and Tomoyuki Mizuno. 2024. "Forecasting Fetal Buprenorphine Exposure through Maternal–Fetal Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling" Pharmaceutics 16, no. 3: 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16030375
APA Stylevan Hoogdalem, M. W., Tanaka, R., Abduljalil, K., Johnson, T. N., Wexelblatt, S. L., Akinbi, H. T., Vinks, A. A., & Mizuno, T. (2024). Forecasting Fetal Buprenorphine Exposure through Maternal–Fetal Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling. Pharmaceutics, 16(3), 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics16030375






